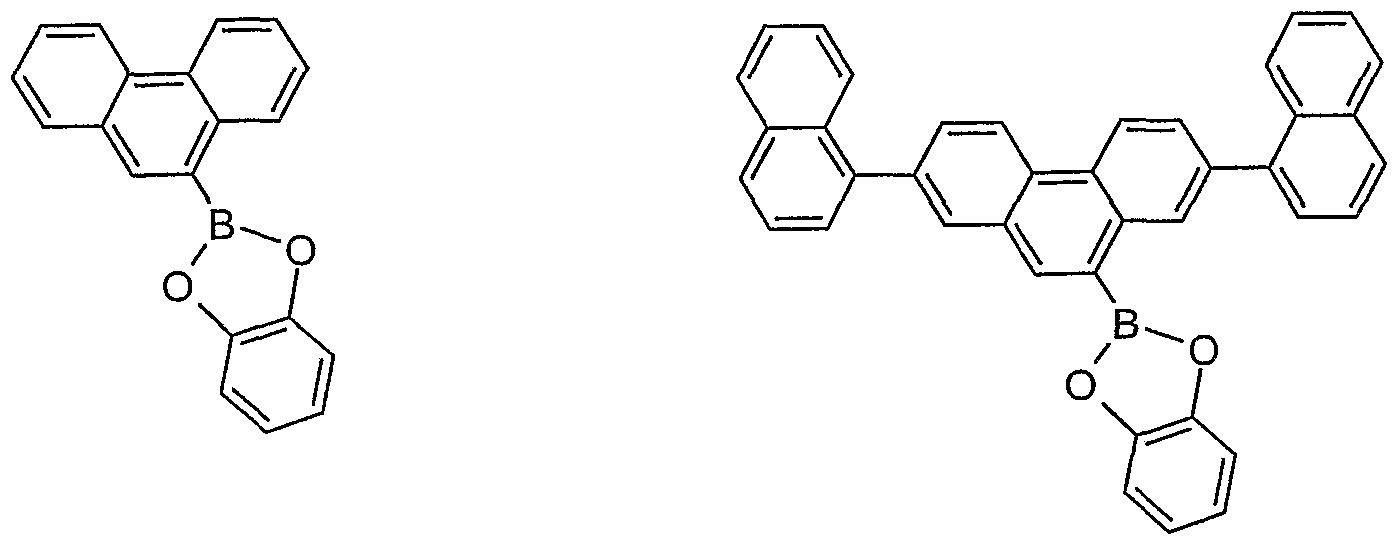
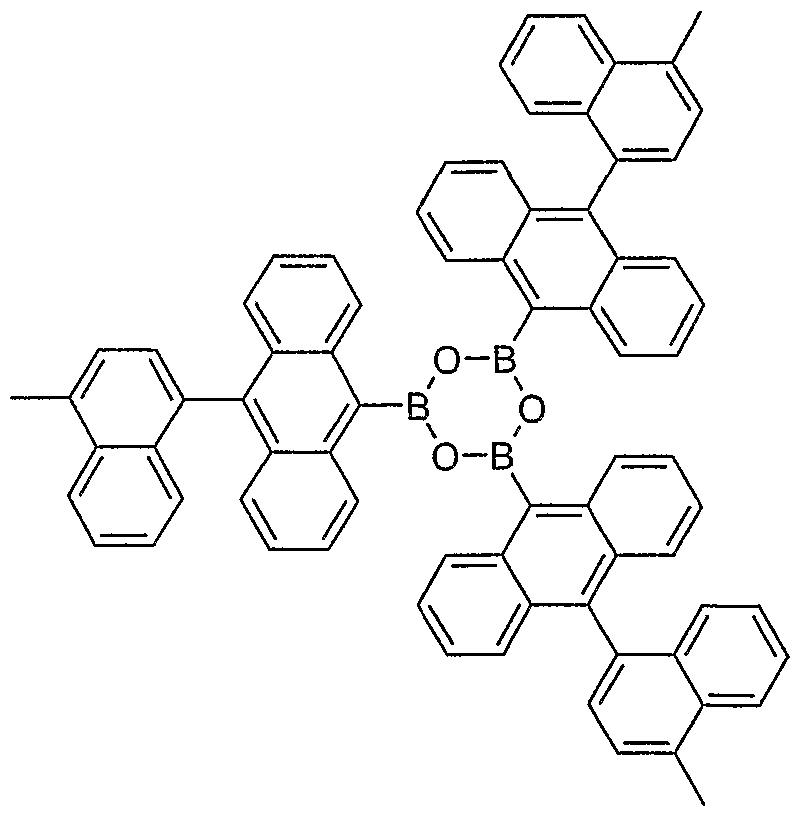
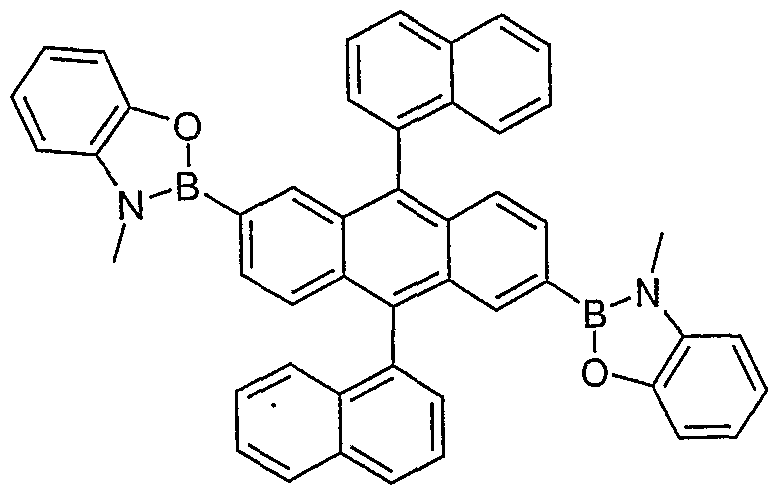
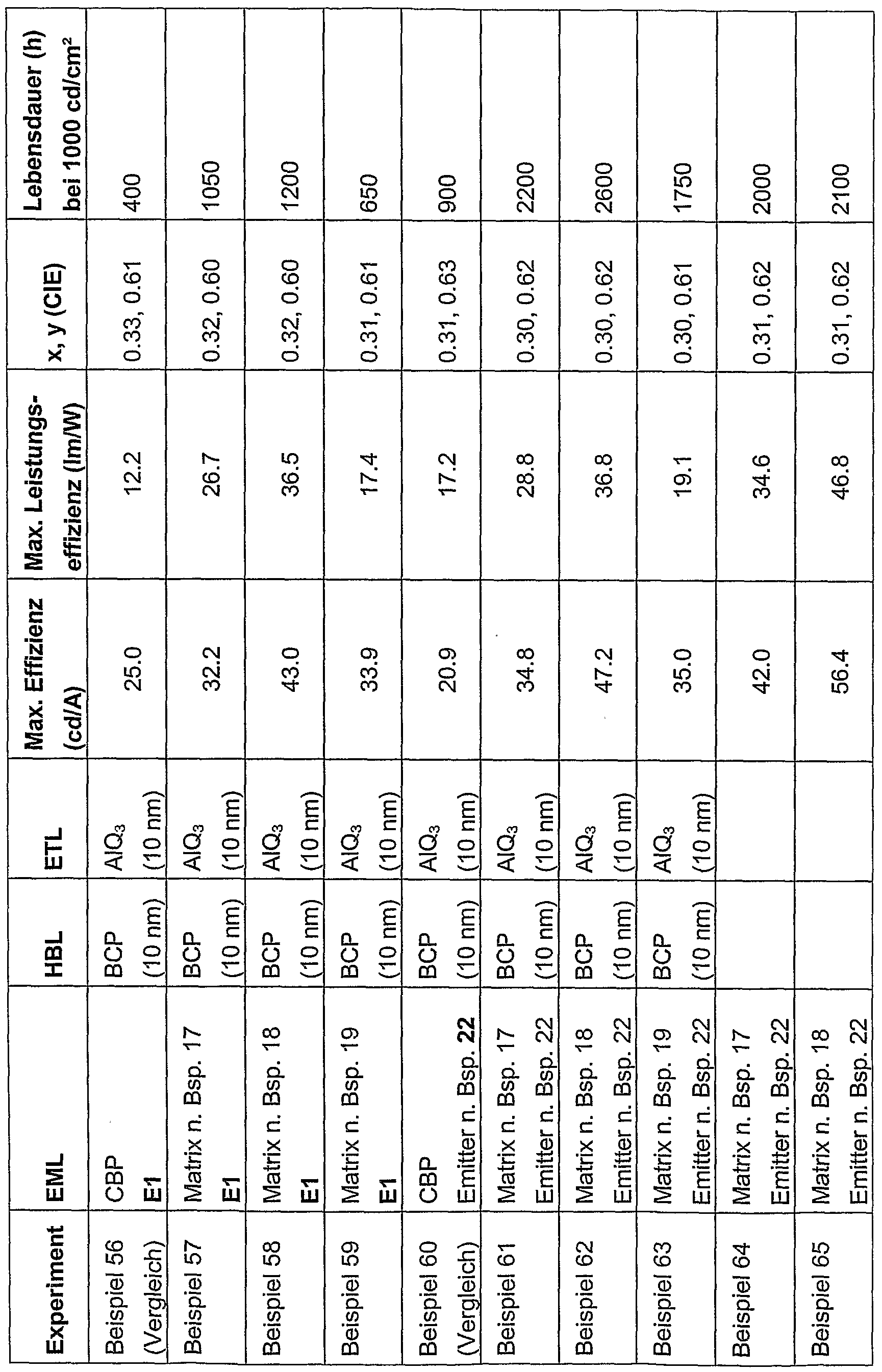
WO2006117052A1 - Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate - Google Patents
Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2006117052A1 WO2006117052A1 PCT/EP2006/003150 EP2006003150W WO2006117052A1 WO 2006117052 A1 WO2006117052 A1 WO 2006117052A1 EP 2006003150 W EP2006003150 W EP 2006003150W WO 2006117052 A1 WO2006117052 A1 WO 2006117052A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- occurrence
- boronic acid
- different
- same
- Prior art date
Links
- UYANAUSDHIFLFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N borinic acid Chemical class OB UYANAUSDHIFLFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 107
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title abstract description 3
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 title abstract description 3
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims abstract description 147
- ZADPBFCGQRWHPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N boronic acid Chemical compound OBO ZADPBFCGQRWHPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 110
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 100
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 93
- -1 cyclic boronic acid imide Chemical class 0.000 claims description 91
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 89
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 51
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 43
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 42
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 41
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 40
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 39
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 29
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 27
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 27
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- IVDFJHOHABJVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pinacol Chemical compound CC(C)(O)C(C)(C)O IVDFJHOHABJVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 26
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 25
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 claims description 25
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 24
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical group [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 18
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 claims description 17
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000002950 monocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000005620 boronic acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 150000001642 boronic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000003367 polycyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- ICPSWZFVWAPUKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-spirobi[fluorene] Chemical class C1=CC=C2C=C3C4(C=5C(C6=CC=CC=C6C=5)=CC=C4)C=CC=C3C2=C1 ICPSWZFVWAPUKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000412 dendrimer Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229920000736 dendritic polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N stilbene Chemical group C=1C=CC=CC=1C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PJANXHGTPQOBST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005259 triarylamine group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- LISGWWQJIMNQTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N boranyloxyborane Chemical compound BOB LISGWWQJIMNQTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- RMBPEFMHABBEKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=C[CH]C=CC3=CC2=C1 RMBPEFMHABBEKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 5
- NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-biphenylenemethane Natural products C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000003573 thiols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- 229930192474 thiophene Natural products 0.000 claims description 5
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001491 aromatic compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000006165 cyclic alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000004985 diamines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002009 diols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxyacetaldehyde Natural products OCC=O WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005309 thioalkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000003577 thiophenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N (2s)-2-[[4-[2-(2,4-diaminoquinazolin-6-yl)ethyl]benzoyl]amino]-4-methylidenepentanedioic acid Chemical compound C1=CC2=NC(N)=NC(N)=C2C=C1CCC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=C)C(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 NAWXUBYGYWOOIX-SFHVURJKSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UWRZIZXBOLBCON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylethenamine Chemical class NC=CC1=CC=CC=C1 UWRZIZXBOLBCON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JRXXLCKWQFKACW-UHFFFAOYSA-N biphenylacetylene Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1C#CC1=CC=CC=C1 JRXXLCKWQFKACW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000001716 carbazoles Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910002091 carbon monoxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004662 dithiols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- PJULCNAVAGQLAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N indeno[2,1-a]fluorene Chemical class C1=CC=C2C=C3C4=CC5=CC=CC=C5C4=CC=C3C2=C1 PJULCNAVAGQLAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000002987 phenanthrenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000006068 polycondensation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N (+)-propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-propanediol Substances OCCCO YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940035437 1,3-propanediol Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001338 aliphatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000008365 aromatic ketones Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- KKAXNAVSOBXHTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N boranamine Chemical compound NB KKAXNAVSOBXHTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OWBTYPJTUOEWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N butane-2,3-diol Chemical compound CC(O)C(C)O OWBTYPJTUOEWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000539 dimer Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002220 fluorenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004356 hydroxy functional group Chemical group O* 0.000 claims description 2
- SLCVBVWXLSEKPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N neopentyl glycol Chemical compound OCC(C)(C)CO SLCVBVWXLSEKPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000843 phenylene group Chemical group C1(=C(C=CC=C1)*)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 108091008695 photoreceptors Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000166 polytrimethylene carbonate Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000013638 trimer Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- HXNZTJULPKRNPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N borinine Chemical compound B1=CC=CC=C1 HXNZTJULPKRNPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 125000000962 organic group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 68
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 48
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 45
- MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C21 MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 39
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 38
- 238000000859 sublimation Methods 0.000 description 31
- 230000008022 sublimation Effects 0.000 description 31
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 26
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 25
- BBEAQIROQSPTKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C=CC3=CC=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 BBEAQIROQSPTKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 19
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- PCLIMKBDDGJMGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-bromosuccinimide Chemical compound BrN1C(=O)CCC1=O PCLIMKBDDGJMGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- YNPNZTXNASCQKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenanthrene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC2=C1 YNPNZTXNASCQKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 18
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 16
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 15
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 15
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Quinoline Chemical compound N1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 SMWDFEZZVXVKRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- AWJUIBRHMBBTKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoquinoline Chemical compound C1=NC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 AWJUIBRHMBBTKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 14
- NEJQCQFYOYURPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-bis(2-bromophenyl)anthracene Chemical compound BrC1=CC=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=CC=C1Br NEJQCQFYOYURPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- GVEPBJHOBDJJJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluoranthrene Natural products C1=CC(C2=CC=CC=C22)=C3C2=CC=CC3=C1 GVEPBJHOBDJJJI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 238000007429 general method Methods 0.000 description 13
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 0 C1O*(c2c(cccc3)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3c2cccc3)OCC11CON(c2c(cccc3)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3c2cccc3)OC1 Chemical compound C1O*(c2c(cccc3)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3c2cccc3)OCC11CON(c2c(cccc3)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3c2cccc3)OC1 0.000 description 12
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 12
- 229910052741 iridium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- VFUDMQLBKNMONU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[4-(4-carbazol-9-ylphenyl)phenyl]carbazole Chemical group C12=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C2N1C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)N2C3=CC=CC=C3C3=CC=CC=C32)C=C1 VFUDMQLBKNMONU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 229920000547 conjugated polymer Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 11
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium atom Chemical compound [Ir] GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butyllithium Chemical compound [Li]CCCC MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- OXCIGGOKELWQSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N NBO Chemical compound NBO OXCIGGOKELWQSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- KYQCOXFCLRTKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrazine Chemical compound C1=CN=CC=N1 KYQCOXFCLRTKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 8
- MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1 MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 8
- 125000002080 perylenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=C2C=CC=C3C4=CC=CC5=CC=CC(C1=C23)=C45)* 0.000 description 8
- CSHWQDPOILHKBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N peryrene Natural products C1=CC(C2=CC=CC=3C2=C2C=CC=3)=C3C2=CC=CC3=C1 CSHWQDPOILHKBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 8
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- XSCHRSMBECNVNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinoxaline Chemical compound N1=CC=NC2=CC=CC=C21 XSCHRSMBECNVNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229910000085 borane Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- MPQXHAGKBWFSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxidophosphanium Chemical class [PH3]=O MPQXHAGKBWFSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- FCEHBMOGCRZNNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzothiophene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SC=CC2=C1 FCEHBMOGCRZNNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Indole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC=CC2=C1 SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229920001609 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Polymers 0.000 description 6
- KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrrole Chemical compound C=1C=CNC=1 KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YTPLMLYBLZKORZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Thiophene Chemical compound C=1C=CSC=1 YTPLMLYBLZKORZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- DZBUGLKDJFMEHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N acridine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3N=C21 DZBUGLKDJFMEHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- REDXJYDRNCIFBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium(3+) Chemical compound [Al+3] REDXJYDRNCIFBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000004305 biphenyl Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000001194 electroluminescence spectrum Methods 0.000 description 6
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-dihydroxy-benzene Natural products OC1=CC=CC=C1O YCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 125000005504 styryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- HDGCGHBEIGZDSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dibromo-9,10-dinaphthalen-1-ylanthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C3=C4C=CC(Br)=CC4=C(C=4C5=CC=CC=C5C=CC=4)C4=CC=C(C=C43)Br)=CC=CC2=C1 HDGCGHBEIGZDSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- MTUBTKOZCCGPSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-n-naphthalen-1-yl-1-n,1-n,2-n-triphenylbenzene-1,2-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C(=CC=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 MTUBTKOZCCGPSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- SNFCXVRWFNAHQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,9'-spirobi[fluorene] Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C2C21C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C21 SNFCXVRWFNAHQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- PCNDJXKNXGMECE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenazine Natural products C1=CC=CC2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N=C21 PCNDJXKNXGMECE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- UORVGPXVDQYIDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N borane Chemical class B UORVGPXVDQYIDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000000543 intermediate Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 150000003462 sulfoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- WRECIMRULFAWHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethyl borate Chemical compound COB(OC)OC WRECIMRULFAWHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 5
- WQONPSCCEXUXTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dibromobenzene Chemical compound BrC1=CC=CC=C1Br WQONPSCCEXUXTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VOIVTTPPKHORBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-naphthalen-1-ylanthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C=3C4=CC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4C=CC=3)=CC=CC2=C1 VOIVTTPPKHORBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IGTQPXMEWQTTBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,7-dibromopyrene Chemical compound C1=C(Br)C=C2C=CC3=CC(Br)=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 IGTQPXMEWQTTBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline Chemical compound C=12C=CC3=C(C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=C(C)N=C3C2=NC(C)=CC=1C1=CC=CC=C1 STTGYIUESPWXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BMIBJCFFZPYJHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methoxy-5-methyl-3-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyridine Chemical compound COC1=NC=C(C)C=C1B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 BMIBJCFFZPYJHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LZPWAYBEOJRFAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2$l^{2}-dioxaborolane Chemical compound CC1(C)O[B]OC1(C)C LZPWAYBEOJRFAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VAJLGRHMEFMPPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(2,2-diphenylethenyl)-n,n-bis[4-(2,2-diphenylethenyl)phenyl]aniline Chemical compound C=1C=C(N(C=2C=CC(C=C(C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=3C=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)C=2C=CC(C=C(C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=3C=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)C=CC=1C=C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 VAJLGRHMEFMPPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 125000004800 4-bromophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C1Br 0.000 description 4
- YSSVQYFOHYQSHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-bis(4-bromonaphthalen-1-yl)anthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(Br)=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=C(Br)C2=CC=CC=C12 YSSVQYFOHYQSHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Furan Chemical compound C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CZPWVGJYEJSRLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrimidine Chemical compound C1=CN=CN=C1 CZPWVGJYEJSRLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 150000001721 carbon Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- WDECIBYCCFPHNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N chrysene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=C3C4=CC=CC=C4C=CC3=C21 WDECIBYCCFPHNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PBMFSQRYOILNGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridazine Chemical compound C1=CC=NN=C1 PBMFSQRYOILNGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 4
- 125000003003 spiro group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 4
- IFLREYGFSNHWGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC4=CC=CC=C4C=C3C=C21 IFLREYGFSNHWGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K tripotassium phosphate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 4
- JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3-triazine Chemical compound C1=CN=NN=C1 JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- IBGUDZMIAZLJNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-dibromonaphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(Br)=CC=C(Br)C2=C1 IBGUDZMIAZLJNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MVGJIMIVNAKXMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,6-bis(2,5-dimethylphenyl)pyrene Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C)C(C=2C3=CC=C4C=CC(=C5C=CC(C3=C54)=CC=2)C=2C(=CC=C(C)C=2)C)=C1 MVGJIMIVNAKXMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000001637 1-naphthyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C2C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C2=C1[H] 0.000 description 3
- PSQJKSUGRXMJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[9,10-dinaphthalen-1-yl-6-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)anthracen-2-yl]-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Chemical compound O1C(C)(C)C(C)(C)OB1C1=CC=C(C(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)=C2C(C=CC(=C2)B2OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O2)=C2C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C=CC=3)C2=C1 PSQJKSUGRXMJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- AEBGSJKDFZNJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[2-[4-[2-[4-(4-bromo-n-(4-bromophenyl)anilino)phenyl]ethenyl]phenyl]ethenyl]-n,n-bis(4-bromophenyl)aniline Chemical compound C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC(C=CC=2C=CC(C=CC=3C=CC(=CC=3)N(C=3C=CC(Br)=CC=3)C=3C=CC(Br)=CC=3)=CC=2)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 AEBGSJKDFZNJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- BRUOAURMAFDGLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-dibromoanthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(Br)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C(Br)C2=C1 BRUOAURMAFDGLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- GWNJZSGBZMLRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-dinaphthalen-1-ylanthracene Chemical class C12=CC=CC=C2C(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12 GWNJZSGBZMLRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OSDONTNFJISHKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-(2-anthracen-9-ylphenyl)anthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C3=CC=CC=C3C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C=C4C=CC=CC4=3)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=CC2=C1 OSDONTNFJISHKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LMKPXUCLBVQWIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-bromo-10-[4-(10-bromoanthracen-9-yl)naphthalen-1-yl]anthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(Br)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=CC=C1C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C(Br)C2=CC=CC=C12 LMKPXUCLBVQWIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DGEZNRSVGBDHLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N [1,10]phenanthroline Chemical compound C1=CN=C2C3=NC=CC=C3C=CC2=C1 DGEZNRSVGBDHLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- TZHYBRCGYCPGBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [B].[N] Chemical class [B].[N] TZHYBRCGYCPGBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000000862 absorption spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000001638 boron Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 3
- 238000006555 catalytic reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000011097 chromatography purification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003480 eluent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 3
- PZOUSPYUWWUPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N indole Natural products CC1=CC=CC2=C1C=CN2 PZOUSPYUWWUPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RKJUIXBNRJVNHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N indolenine Natural products C1=CC=C2CC=NC2=C1 RKJUIXBNRJVNHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- DKTXXUNXVCHYDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenoxyborinic acid Chemical class OBOC1=CC=CC=C1 DKTXXUNXVCHYDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphine group Chemical group P XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- JHVQEUGNYSVSDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl)boronic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C(B(O)O)C2=C1 JHVQEUGNYSVSDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GKDCWKGUOZVDFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)butane-2,3-diol Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C(C(F)(F)F)(O)C(O)(C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F GKDCWKGUOZVDFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HQDYNFWTFJFEPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,3a-tetrahydropyrene Chemical compound C1=C2CCCC(C=C3)C2=C2C3=CC=CC2=C1 HQDYNFWTFJFEPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-Diphenylbenzene Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 YJTKZCDBKVTVBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QUTBMZURZNTQON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,6-dibromo-3,8-bis(2,5-dimethylphenyl)pyrene Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C)C(C=2C3=CC=C4C(Br)=CC(=C5C=CC(C3=C54)=C(Br)C=2)C=2C(=CC=C(C)C=2)C)=C1 QUTBMZURZNTQON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UHXOHPVVEHBKKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(2,2-diphenylethenyl)-4-[4-(2,2-diphenylethenyl)phenyl]benzene Chemical compound C=1C=C(C=2C=CC(C=C(C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=3C=CC=CC=3)=CC=2)C=CC=1C=C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 UHXOHPVVEHBKKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UGJKKUZKHLDZRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-N,6-N-bis(4-methylphenyl)-3,8-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyrene-1,6-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1NC(C1=CC=C2C(B3OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O3)=C3)=CC(B4OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O4)=C(C=C4)C1=C2C4=C3NC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 UGJKKUZKHLDZRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FSRNAMDNZVDOAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-[4-[4,4-bis(1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)carbazol-1-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-4,4-bis(1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)carbazole Chemical group O1CCOB1C1(B2OCCO2)C2=C3C=CC=CC3=NC2=C(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)C=2C=CC(=CC=2)C=2C=CC(C3=C4C=CC=CC4=NC3=2)(B2OCCO2)B2OCCO2)C=C1 FSRNAMDNZVDOAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QJVXYPMHBUUJMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-n,6-n-bis(4-methylphenyl)pyrene-1,6-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1NC(C1=CC=C2C=C3)=CC=C(C=C4)C1=C2C4=C3NC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 QJVXYPMHBUUJMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LPCWDYWZIWDTCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-phenylisoquinoline Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=NC=CC2=CC=CC=C12 LPCWDYWZIWDTCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WJFKNYWRSNBZNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10H-phenothiazine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC3=CC=CC=C3SC2=C1 WJFKNYWRSNBZNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- TZMSYXZUNZXBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10H-phenoxazine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 TZMSYXZUNZXBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JUFYHUWBLXKCJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dibromoanthracene-9,10-dione Chemical compound BrC1=CC=C2C(=O)C3=CC(Br)=CC=C3C(=O)C2=C1 JUFYHUWBLXKCJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VQGHOUODWALEFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylpyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=N1 VQGHOUODWALEFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FSEXLNMNADBYJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylquinoline Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=C(C=CC=C2)C2=N1 FSEXLNMNADBYJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NCPUXHNPVZMXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4-dibromo-1-[4-[4-(4,4-dibromocarbazol-1-yl)phenyl]phenyl]carbazole Chemical group N1=C2C=CC=CC2=C(C(Br)(Br)C=C2)C1=C2C(C=C1)=CC=C1C(C=C1)=CC=C1C(C=CC1(Br)Br)=C2C1=C1C=CC=CC1=N2 NCPUXHNPVZMXMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IDCRGMNEAOWPRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(4-bromo-n-(4-bromophenyl)anilino)benzaldehyde Chemical compound C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC(C=O)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 IDCRGMNEAOWPRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CRGHMHFRUWWRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-(4-bromo-n-(4-bromophenyl)anilino)phenyl]-n,n-bis(4-bromophenyl)aniline Chemical compound C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC(Br)=CC=1)C=1C=CC(Br)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 CRGHMHFRUWWRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RHPVVNRNAHRJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-n-(4-methylphenyl)aniline Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1NC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 RHPVVNRNAHRJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KDCGOANMDULRCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7H-purine Chemical compound N1=CNC2=NC=NC2=C1 KDCGOANMDULRCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HAOKDDFIDHVSCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-(4-anthracen-9-ylnaphthalen-1-yl)anthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C=4C5=CC=CC=C5C=C5C=CC=CC5=4)=CC=3)=C21 HAOKDDFIDHVSCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IBFNLCZFNABMHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-(4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl)anthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=CC2=CC=CC=C12 IBFNLCZFNABMHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QXAIDADUIMVTPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-(9h-fluoren-9-yl)-9h-fluorene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C2C1C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C21 QXAIDADUIMVTPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DHZAOIUIXWGTHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-bromo-10-(4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl)anthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C(Br)C2=CC=CC=C12 DHZAOIUIXWGTHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BOKBJQGIHDNSEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-bromo-10-[2-(10-bromoanthracen-9-yl)phenyl]anthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(Br)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=CC=C1C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C(Br)C2=CC=CC=C12 BOKBJQGIHDNSEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZIRVQSRSPDUEOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-bromoanthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(Br)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=CC2=C1 ZIRVQSRSPDUEOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RZGMFRRDBNHLJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-n,9-n,10-n,10-n-tetraphenylanthracene-9,10-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C(N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C2C=CC=CC2=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RZGMFRRDBNHLJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PANUKMYENAQJTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCOP(=O)OCC.CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 Chemical compound CCOP(=O)OCC.CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 PANUKMYENAQJTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000007818 Grignard reagent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101000801643 Homo sapiens Retinal-specific phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA4 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- WTKZEGDFNFYCGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrazole Chemical compound C=1C=NNC=1 WTKZEGDFNFYCGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100033617 Retinal-specific phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA4 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 238000006069 Suzuki reaction reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910021626 Tin(II) chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- VOYBYJOEGZUTHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N [2'-(4-bromobenzoyl)-9,9'-spirobi[fluorene]-2-yl]-(4-bromophenyl)methanone Chemical compound C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1C(=O)C1=CC=C(C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C23C4=CC(=CC=C4C4=CC=CC=C43)C(=O)C=3C=CC(Br)=CC=3)C2=C1 VOYBYJOEGZUTHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000009102 absorption Effects 0.000 description 2
- VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium trichloride Chemical compound Cl[Al](Cl)Cl VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- VHHDLIWHHXBLBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthracen-9-ylboronic acid Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(B(O)O)=C(C=CC=C3)C3=CC2=C1 VHHDLIWHHXBLBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- VERMEZLHWFHDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,2,3,4-tetrol Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1O VERMEZLHWFHDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IOJUPLGTWVMSFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzothiazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SC=NC2=C1 IOJUPLGTWVMSFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000001639 boron compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000018044 dehydration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006297 dehydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- TXCDCPKCNAJMEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzofuran Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 TXCDCPKCNAJMEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IYYZUPMFVPLQIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzothiophene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3SC2=C1 IYYZUPMFVPLQIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XXPBFNVKTVJZKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dihydrophenanthrene Natural products C1=CC=C2CCC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 XXPBFNVKTVJZKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl ether Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1OC1=CC=CC=C1 USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DMBHHRLKUKUOEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenylamine Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1NC1=CC=CC=C1 DMBHHRLKUKUOEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000000295 emission spectrum Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000002534 ethynyl group Chemical group [H]C#C* 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000004795 grignard reagents Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007641 inkjet printing Methods 0.000 description 2
- DLEDOFVPSDKWEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N lithium butane Chemical compound [Li+].CCC[CH2-] DLEDOFVPSDKWEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000007040 multi-step synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- DCZNSJVFOQPSRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N n,n-diphenyl-4-[4-(n-phenylanilino)phenyl]aniline Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC(=CC=1)C=1C=CC(=CC=1)N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 DCZNSJVFOQPSRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ADUFDSSCDCLUFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(4-aminophenyl)phenyl]-n-phenylnaphthalen-1-amine Chemical group C1=CC(N)=CC=C1C1=CC=C(N(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)C=C1 ADUFDSSCDCLUFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000002900 organolithium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- WCPAKWJPBJAGKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxadiazole Chemical compound C1=CON=N1 WCPAKWJPBJAGKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- AUONHKJOIZSQGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxophosphane Chemical compound P=O AUONHKJOIZSQGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LXNAVEXFUKBNMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium(II) acetate Substances [Pd].CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O LXNAVEXFUKBNMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YJVFFLUZDVXJQI-UHFFFAOYSA-L palladium(ii) acetate Chemical compound [Pd+2].CC([O-])=O.CC([O-])=O YJVFFLUZDVXJQI-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- SLIUAWYAILUBJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentacene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC4=CC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4C=C3C=C21 SLIUAWYAILUBJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RDOWQLZANAYVLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenanthridine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C=NC2=C1 RDOWQLZANAYVLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229950000688 phenothiazine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 2
- 229960005235 piperonyl butoxide Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- NROKBHXJSPEDAR-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium fluoride Chemical compound [F-].[K+] NROKBHXJSPEDAR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000003220 pyrenes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- JWVCLYRUEFBMGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinazoline Chemical compound N1=CN=CC2=CC=CC=C21 JWVCLYRUEFBMGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000011150 stannous chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 235000021286 stilbenes Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 238000005092 sublimation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000005846 sugar alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000003457 sulfones Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- AXZWODMDQAVCJE-UHFFFAOYSA-L tin(II) chloride (anhydrous) Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Sn+2] AXZWODMDQAVCJE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 description 2
- ODHXBMXNKOYIBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylamine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 ODHXBMXNKOYIBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- COIOYMYWGDAQPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris(2-methylphenyl)phosphane Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C(=CC=CC=1)C)C1=CC=CC=C1C COIOYMYWGDAQPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005019 vapor deposition process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010792 warming Methods 0.000 description 2
- OOMZKLJLVGQZGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dimethylphenyl)boronic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C)C(B(O)O)=C1 OOMZKLJLVGQZGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N (R)-(-)-Propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KQFYWHQMZPLKLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-spirobi[fluorene]-2',3',6',7'-tetrol Chemical compound C12=CC3=CC(O)=C(O)C=C3C2=CC(O)=C(O)C11C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=CC=C1 KQFYWHQMZPLKLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZFXBERJDEUDDMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,5-tetrazine Chemical compound C1=NC=NN=N1 ZFXBERJDEUDDMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FNQJDLTXOVEEFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3-benzothiadiazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SN=NC2=C1 FNQJDLTXOVEEFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UGUHFDPGDQDVGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3-thiadiazole Chemical compound C1=CSN=N1 UGUHFDPGDQDVGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HTJMXYRLEDBSLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,4,5-tetrazine Chemical compound C1=NN=CN=N1 HTJMXYRLEDBSLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BBVIDBNAYOIXOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,4-oxadiazole Chemical compound C=1N=CON=1 BBVIDBNAYOIXOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YGTAZGSLCXNBQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,4-thiadiazole Chemical compound C=1N=CSN=1 YGTAZGSLCXNBQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYADHXFMURLYQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,4-triazine Chemical compound C1=CN=NC=N1 FYADHXFMURLYQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UDGKZGLPXCRRAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,5-thiadiazole Chemical compound C=1C=NSN=1 UDGKZGLPXCRRAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UUSUFQUCLACDTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dihydropyrene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C=CC3=CCCC4=CC=C1C2=C43 UUSUFQUCLACDTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000000180 1,2-diols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002030 1,2-phenylene group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([*:1])=C([*:2])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- FKASFBLJDCHBNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,4-oxadiazole Chemical compound C1=NN=CO1 FKASFBLJDCHBNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MBIZXFATKUQOOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,4-thiadiazole Chemical compound C1=NN=CS1 MBIZXFATKUQOOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JIHQDMXYYFUGFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,5-triazine Chemical compound C1=NC=NC=N1 JIHQDMXYYFUGFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-benzoxazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC=NC2=C1 BCMCBBGGLRIHSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000000185 1,3-diols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- FLBAYUMRQUHISI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,8-naphthyridine Chemical compound N1=CC=CC2=CC=CN=C21 FLBAYUMRQUHISI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WYECURVXVYPVAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanone Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 WYECURVXVYPVAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BATKIZWNRQGSKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl]ethanone Chemical compound C1=CC(C(=O)C)=CC=C1B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 BATKIZWNRQGSKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWNXKZVIZARMME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[[5-[2-[(2-chloropyridin-4-yl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-4-(cyclopropylmethyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]-2-methylpropan-2-ol Chemical compound N=1C(NCC(C)(O)C)=NC=C(C=2N=C(NC=3C=C(Cl)N=CC=3)N=CC=2)C=1CC1CC1 AWNXKZVIZARMME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BSIIGUGKOPPTPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-bromo-4-(chloromethyl)benzene Chemical compound ClCC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 BSIIGUGKOPPTPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DLKQHBOKULLWDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-bromonaphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(Br)=CC=CC2=C1 DLKQHBOKULLWDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QWENRTYMTSOGBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-1,2,3-Triazole Chemical compound C=1C=NNN=1 QWENRTYMTSOGBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HYZJCKYKOHLVJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-benzimidazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC=NC2=C1 HYZJCKYKOHLVJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BAXOFTOLAUCFNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-indazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C=NNC2=C1 BAXOFTOLAUCFNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- USYCQABRSUEURP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1h-benzo[f]benzimidazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C=C(NC=N3)C3=CC2=C1 USYCQABRSUEURP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JUUZQMUWOVDZSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1h-imidazole;pyrazine Chemical compound C1=CNC=N1.C1=CN=CC=N1 JUUZQMUWOVDZSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PLJDGKPRGUMSAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2',7,7'-tetraphenyl-1,1'-spirobi[fluorene] Chemical compound C12=CC=C(C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=C2C=C(C23C(=CC=C4C5=CC=C(C=C5C=C43)C=3C=CC=CC=3)C=3C=CC=CC=3)C1=CC=C2C1=CC=CC=C1 PLJDGKPRGUMSAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004206 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])(*)C(F)(F)F 0.000 description 1
- NIBFJPXGNVPNHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxole-4-carbaldehyde Chemical group C1=CC(C=O)=C2OC(F)(F)OC2=C1 NIBFJPXGNVPNHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PFRPMHBYYJIARU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-diazatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(14),2,4,6,8(16),9,11(15),12-octaene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N=NC3=CC=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 PFRPMHBYYJIARU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VEPOHXYIFQMVHW-XOZOLZJESA-N 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid (2S,3S)-3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine Chemical compound OC(C(O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O.C[C@H]1[C@@H](OCCN1C)c1ccccc1 VEPOHXYIFQMVHW-XOZOLZJESA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFTHTJAPODJVSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1-benzothiophen-5-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Chemical compound O1C(C)(C)C(C)(C)OB1C1=CC=C(SC=C2)C2=C1 YFTHTJAPODJVSL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BIEFDNUEROKZRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-phenylethenyl)aniline Chemical class NC1=CC=CC=C1C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 BIEFDNUEROKZRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JHKKTXXMAQLGJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(methylamino)phenol Chemical compound CNC1=CC=CC=C1O JHKKTXXMAQLGJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABZBLTKQJXUGNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-N',2-N',3-N',3-N',4-N',4-N',5-N',5-N'-octakis-phenyl-1,1'-spirobi[fluorene]-2',3',4',5'-tetramine Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C=C2C1=CC=CC2(C(=C(N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C(N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)=C1C2=3)N(C=4C=CC=CC=4)C=4C=CC=CC=4)C1=CC2=CC=CC=3N(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 ABZBLTKQJXUGNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UXGVMFHEKMGWMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzofuran Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=COC=C21 UXGVMFHEKMGWMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LYTMVABTDYMBQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzothiophene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CSC=C21 LYTMVABTDYMBQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AZYGEWXDKHFOKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-1,3,2-benzodioxaborole Chemical class C1=CC=C2OB(Cl)OC2=C1 AZYGEWXDKHFOKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004493 2-methylbut-1-yl group Chemical group CC(C*)CC 0.000 description 1
- VHMICKWLTGFITH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2H-isoindole Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CNC=C21 VHMICKWLTGFITH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- REDNJKONEFITKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,8-dibromo-1-n,6-n-bis(4-methylphenyl)pyrene-1,6-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC(C)=CC=C1NC(C1=CC=C2C(Br)=C3)=CC(Br)=C(C=C4)C1=C2C4=C3NC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 REDNJKONEFITKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GLXOHSHPIMRJFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methyl-n-[4-[2-[4-[2-[4-(3-methyl-n-(3-methylphenyl)anilino)phenyl]ethenyl]phenyl]ethenyl]phenyl]-n-(3-methylphenyl)aniline Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(N(C=2C=CC(C=CC=3C=CC(C=CC=4C=CC(=CC=4)N(C=4C=C(C)C=CC=4)C=4C=C(C)C=CC=4)=CC=3)=CC=2)C=2C=C(C)C=CC=2)=C1 GLXOHSHPIMRJFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NHBVMVFOELWZQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-[10-(4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl)anthracen-9-yl]-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C2C=CC=CC2=C1B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 NHBVMVFOELWZQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LATPBRSZRSCCLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-2-[6-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)pyren-1-yl]-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Chemical compound O1C(C)(C)C(C)(C)OB1C1=CC=C(C=C2)C3=C4C2=C(B2OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O2)C=CC4=CC=C13 LATPBRSZRSCCLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DENKGPBHLYFNGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromobenzoyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 DENKGPBHLYFNGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PDVGPRKWYIVXGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-phenylcyclohexa-2,4-diene-1,1-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC(N)(N)CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 PDVGPRKWYIVXGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NSPMIYGKQJPBQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4H-1,2,4-triazole Chemical compound C=1N=CNN=1 NSPMIYGKQJPBQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUKNPBPXZUWMNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,12-diazatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(15),2,4,6,8(16),9,11,13-octaene Chemical compound N1=CC=C2C=CC3=NC=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 IUKNPBPXZUWMNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NHWJSCHQRMCCAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,14-diazatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(14),2,4,6,8(16),9,11(15),12-octaene Chemical compound C1=CN=C2C=CC3=NC=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 NHWJSCHQRMCCAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PODJSIAAYWCBDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,6-diazatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(14),2,4(16),5,7,9,11(15),12-octaene Chemical compound C1=NN=C2C=CC3=CC=CC4=CC=C1C2=C43 PODJSIAAYWCBDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KJCRNHQXMXUTEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 69637-93-0 Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N=C(N=C3NC=4C(=CC=CC=4)NC3=N3)C3=NC2=C1 KJCRNHQXMXUTEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VIZUPBYFLORCRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-dinaphthalen-2-ylanthracene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C2)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C1=CC=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1 VIZUPBYFLORCRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NVMYRXGXUBZAIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-fluoren-9-ylidenefluorene Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C2C1=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C21 NVMYRXGXUBZAIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DEJGCXGGTKKUEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-n,9-n,10-n,10-n-tetrakis(4-bromophenyl)anthracene-9,10-diamine Chemical compound C1=CC(Br)=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C(N(C=2C=CC(Br)=CC=2)C=2C=CC(Br)=CC=2)=C2C=CC=CC2=1)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 DEJGCXGGTKKUEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BPMFPOGUJAAYHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9H-Pyrido[2,3-b]indole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=N1 BPMFPOGUJAAYHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000005964 Acibenzolar-S-methyl Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000945 Amylopectin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000856 Amylose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- UTSQJHKMBJQFEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N B(S)(O)O.BN Chemical compound B(S)(O)O.BN UTSQJHKMBJQFEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIGMDKJJXMFPRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N B1CCCCO1 Chemical compound B1CCCCO1 PIGMDKJJXMFPRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODXMMDJMDRNJRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N B1NCCN1 Chemical compound B1NCCN1 ODXMMDJMDRNJRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FMMWHPNWAFZXNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benz[a]pyrene Chemical compound C1=C2C3=CC=CC=C3C=C(C=C3)C2=C2C3=CC=CC2=C1 FMMWHPNWAFZXNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Borate Chemical compound [O-]B([O-])[O-] BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PTPMMPXEQFDTQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1B1OB(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C)=CC=3)=C3C=CC=CC3=2)OB(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C)=CC=3)=C3C=CC=CC3=2)O1 Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C(C1=CC=CC=C11)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1B1OB(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C)=CC=3)=C3C=CC=CC3=2)OB(C=2C3=CC=CC=C3C(C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C)=CC=3)=C3C=CC=CC3=2)O1 PTPMMPXEQFDTQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZPIPUFJBRZFYKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1=NC=C2C=CC3=CN=CC4=CC=C1C2=C34 Chemical compound C1=NC=C2C=CC3=CN=CC4=CC=C1C2=C34 ZPIPUFJBRZFYKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ICEASUYZXPCLJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1OB(c(cc2)ccc2N(c2ccc(B3OCCO3)cc2)c(cc2)ccc2-c(cc2)ccc2N(c2ccc(B3OCCO3)cc2)c(cc2)ccc2S2OCCO2)OC1 Chemical compound C1OB(c(cc2)ccc2N(c2ccc(B3OCCO3)cc2)c(cc2)ccc2-c(cc2)ccc2N(c2ccc(B3OCCO3)cc2)c(cc2)ccc2S2OCCO2)OC1 ICEASUYZXPCLJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NQDKXZJGIDNRSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1OB(c2c(ccc3ccccc33)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3ccccc23)OC1 Chemical compound C1OB(c2c(ccc3ccccc33)c3c(-c3ccccc3)c3ccccc23)OC1 NQDKXZJGIDNRSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MMOPGGKIALEXPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1OB(c2c3nccnc3c(B3OCCO3)c3c2nccn3)OC1 Chemical compound C1OB(c2c3nccnc3c(B3OCCO3)c3c2nccn3)OC1 MMOPGGKIALEXPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MPGINABSKXRAKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C)C1=C(C(C)(C)C)OB(C2=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C(c3ccccc3)C3=CCCC=C23)O1 Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C(C(C)(C)C)OB(C2=C(C=CC=C3)C3=C(c3ccccc3)C3=CCCC=C23)O1 MPGINABSKXRAKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZKLAOHRNXHUYFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1(C)OB(c(cc2)ccc2P(c(cc2C34c5ccccc5-c5c3cccc5)ccc2-c2c4cccc2)(c(cc2)cc(C34c5ccccc5-c5ccccc35)c2-c2c4cccc2)=O)OC1(C)C Chemical compound CC1(C)OB(c(cc2)ccc2P(c(cc2C34c5ccccc5-c5c3cccc5)ccc2-c2c4cccc2)(c(cc2)cc(C34c5ccccc5-c5ccccc35)c2-c2c4cccc2)=O)OC1(C)C ZKLAOHRNXHUYFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JDXOOJGRKUUEQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C)C1=CC(=C2C=CC3=CC=C(C4=CC=C1C2=C34)B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1)B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 Chemical compound CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C)C1=CC(=C2C=CC3=CC=C(C4=CC=C1C2=C34)B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1)B1OC(C)(C)C(C)(C)O1 JDXOOJGRKUUEQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RDHLGLPMYKSJPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1C(c2c(cc(cccc3)c3c3)c3c(B3OCCO3)c3c2cc(cccc2)c2c3)=CC=CC1 Chemical compound CC1C(c2c(cc(cccc3)c3c3)c3c(B3OCCO3)c3c2cc(cccc2)c2c3)=CC=CC1 RDHLGLPMYKSJPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTRRQKZAYDQDJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cc(cc1)cc2c1c(B1OC(c3cccc4c3cccc4)=C(c3c(cccc4)c4ccc3)O1)c(cccc1)c1c2-c1ccccc1 Chemical compound Cc(cc1)cc2c1c(B1OC(c3cccc4c3cccc4)=C(c3c(cccc4)c4ccc3)O1)c(cccc1)c1c2-c1ccccc1 MTRRQKZAYDQDJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001432959 Chernes Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000858 Cyclodextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052693 Europium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SMKBUBQVBQXOML-UHFFFAOYSA-N OCCOBc1c2nccnc2c(B2OCCO2)c2c1cccc2 Chemical compound OCCOBc1c2nccnc2c(B2OCCO2)c2c1cccc2 SMKBUBQVBQXOML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZCQWOFVYLHDMMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxazole Chemical compound C1=COC=N1 ZCQWOFVYLHDMMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ruthenium Chemical compound [Ru] KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PJANXHGTPQOBST-VAWYXSNFSA-N Stilbene Natural products C=1C=CC=CC=1/C=C/C1=CC=CC=C1 PJANXHGTPQOBST-VAWYXSNFSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZWLAAWBMGSTSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Thiazole Chemical compound C1=CSC=N1 FZWLAAWBMGSTSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KTCDMUNJNVKKOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N [10-(4-methylnaphthalen-1-yl)anthracen-9-yl]boronic acid Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(C)=CC=C1C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C(B(O)O)C2=CC=CC=C12 KTCDMUNJNVKKOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000641 acridinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000002015 acyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003158 alcohol group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000007824 aliphatic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-acetylene Natural products C#C HSFWRNGVRCDJHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UNKKIEMUNUHYPD-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminum 2-carboxy-5-hydroxy-4-oxo-1H-quinolin-3-olate Chemical compound [Al+3].[O-]C(=O)C1=C(O)C(O)=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=N1.[O-]C(=O)C1=C(O)C(O)=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=N1.[O-]C(=O)C1=C(O)C(O)=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=N1 UNKKIEMUNUHYPD-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005365 aminothiol group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005577 anthracene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001454 anthracenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PYKYMHQGRFAEBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthraquinone Natural products CCC(=O)c1c(O)c2C(=O)C3C(C=CC=C3O)C(=O)c2cc1CC(=O)OC PYKYMHQGRFAEBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004056 anthraquinones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004984 aromatic diamines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001543 aryl boronic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001499 aryl bromides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005801 aryl-aryl coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000732 arylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- LPXYDHFBXZNQRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N azaborinane Chemical compound B1CCCCN1 LPXYDHFBXZNQRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RFRXIWQYSOIBDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzarone Chemical compound CCC=1OC2=CC=CC=C2C=1C(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 RFRXIWQYSOIBDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UYQMSQMCIYSXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,2,4,5-tetrol Chemical compound OC1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1O UYQMSQMCIYSXOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWPUAXALDFFXJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenehexol Chemical compound OC1=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1O VWPUAXALDFFXJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WMUIZUWOEIQJEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzo[e][1,3]benzoxazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(N=CO3)=C3C=CC2=C1 WMUIZUWOEIQJEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N[N][N]C2=C1 QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012964 benzotriazole Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002619 bicyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ZDZHCHYQNPQSGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N binaphthyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12 ZDZHCHYQNPQSGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AIEZFWSIZQLXEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N biphenyl-2,2',3,3'-tetraol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC(C=2C(=C(O)C=CC=2)O)=C1O AIEZFWSIZQLXEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006269 biphenyl-2-yl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C1=C(*)C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000006268 biphenyl-3-yl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000000319 biphenyl-4-yl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1C1=C([H])C([H])=C([*])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002529 biphenylenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- UORVGPXVDQYIDP-BJUDXGSMSA-N borane Chemical group [10BH3] UORVGPXVDQYIDP-BJUDXGSMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000031709 bromination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005893 bromination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 244000309464 bull Species 0.000 description 1
- 125000004369 butenyl group Chemical group C(=CCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000480 butynyl group Chemical group [*]C#CC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- PQJFBTRAVPCDHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N c(cc1)ccc1-c(cc1)c2OB(c(cc3cc4)ccc3c3c4cc(B4Oc(c(-c5ccccc5)ccc5-c6ccccc6)c5O4)cc3)Oc2c1-c1ccccc1 Chemical compound c(cc1)ccc1-c(cc1)c2OB(c(cc3cc4)ccc3c3c4cc(B4Oc(c(-c5ccccc5)ccc5-c6ccccc6)c5O4)cc3)Oc2c1-c1ccccc1 PQJFBTRAVPCDHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CLUPIJXPLHSOCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N c1ccc2OB(c(cc3)cc4c3c3ccc(B5Oc(cccc6)c6O5)cc3cc4)Oc2c1 Chemical compound c1ccc2OB(c(cc3)cc4c3c3ccc(B5Oc(cccc6)c6O5)cc3cc4)Oc2c1 CLUPIJXPLHSOCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012159 carrier gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002800 charge carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001311 chemical methods and process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001846 chrysenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- WCZVZNOTHYJIEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N cinnoline Chemical compound N1=NC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 WCZVZNOTHYJIEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004696 coordination complex Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000001162 cycloheptenyl group Chemical group C1(=CCCCCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000582 cycloheptyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000000596 cyclohexenyl group Chemical group C1(=CCCCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000113 cyclohexyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000000522 cyclooctenyl group Chemical group C1(=CCCCCCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000640 cyclooctyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002433 cyclopentenyl group Chemical group C1(=CCCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001511 cyclopentyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010511 deprotection reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001987 diarylethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- JVPXMLWTXLVEDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibromo-(4-bromophenyl)phosphane Chemical compound BrP(Br)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 JVPXMLWTXLVEDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IMDXZWRLUZPMDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichlorophenylphosphine Chemical compound ClP(Cl)C1=CC=CC=C1 IMDXZWRLUZPMDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003670 easy-to-clean Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004185 ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- RLODKUVHHRFYRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethynylborane Chemical class BC#C RLODKUVHHRFYRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OGPBJKLSAFTDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N europium atom Chemical compound [Eu] OGPBJKLSAFTDLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 1
- JKFAIQOWCVVSKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N furazan Chemical compound C=1C=NON=1 JKFAIQOWCVVSKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVZRCNQLWOELDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N gamma-Phenylpyridine Natural products C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=NC=C1 JVZRCNQLWOELDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007496 glass forming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004676 glycans Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006038 hexenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005980 hexynyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003949 imides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002466 imines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HOBCFUWDNJPFHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N indolizine Chemical compound C1=CC=CN2C=CC=C21 HOBCFUWDNJPFHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002503 iridium Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- MILUBEOXRNEUHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium(3+) Chemical compound [Ir+3] MILUBEOXRNEUHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960004592 isopropanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- ZLTPDFXIESTBQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N isothiazole Chemical compound C=1C=NSC=1 ZLTPDFXIESTBQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTAPFRYPJLPFDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoxazole Chemical compound C=1C=NOC=1 CTAPFRYPJLPFDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000468 ketone group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005647 linker group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000006138 lithiation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008204 material by function Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002772 monosaccharides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012452 mother liquor Substances 0.000 description 1
- FGGAOQTXQHKQOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N n,n-diphenylnaphthalen-1-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1N(C=1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 FGGAOQTXQHKQOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YKZHNHRLNBPFBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(4-aminophenyl)phenyl]benzo[a]anthracen-1-amine Chemical compound C1=CC(N)=CC=C1C(C=C1)=CC=C1NC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(C=C3C(C=CC=C3)=C3)C3=C12 YKZHNHRLNBPFBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- OVALYCIUDYJCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetrol Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=C2C(O)=CC=C(O)C2=C1O OVALYCIUDYJCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002825 nitriles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004365 octenyl group Chemical group C(=CCCCCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005069 octynyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C#C* 0.000 description 1
- 238000007645 offset printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001542 oligosaccharide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000002482 oligosaccharides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005580 one pot reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052762 osmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N osmium atom Chemical compound [Os] SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 description 1
- 125000006340 pentafluoro ethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)C(F)(F)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000002255 pentenyl group Chemical group C(=CCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005981 pentynyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000005359 phenylpyridines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003003 phosphines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910000073 phosphorus hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005424 photoluminescence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000103 photoluminescence spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001282 polysaccharide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005017 polysaccharide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000003270 potassium fluoride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011698 potassium fluoride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000160 potassium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011009 potassium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004368 propenyl group Chemical group C(=CC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002568 propynyl group Chemical group [*]C#CC([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- CPNGPNLZQNNVQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N pteridine Chemical compound N1=CN=CC2=NC=CN=C21 CPNGPNLZQNNVQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005581 pyrene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- GDISDVBCNPLSDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrido[2,3-g]quinoline Chemical compound C1=CC=NC2=CC3=CC=CN=C3C=C21 GDISDVBCNPLSDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001567 quinoxalinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=NC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000009103 reabsorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009257 reactivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052702 rhenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhenium atom Chemical compound [Re] WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052703 rhodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010948 rhodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhodium atom Chemical compound [Rh] MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006413 ring segment Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001629 stilbenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003463 sulfur Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003464 sulfur compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010189 synthetic method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001911 terphenyls Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003536 tetrazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001931 thermography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004149 thio group Chemical group *S* 0.000 description 1
- 150000003568 thioethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 231100000331 toxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000002588 toxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010023 transfer printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007832 transition metal-catalyzed coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003852 triazoles Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910000404 tripotassium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019798 tripotassium phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001771 vacuum deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002061 vacuum sublimation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001947 vapour-phase growth Methods 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/30—Coordination compounds
- H10K85/321—Metal complexes comprising a group IIIA element, e.g. Tris (8-hydroxyquinoline) gallium [Gaq3]
- H10K85/322—Metal complexes comprising a group IIIA element, e.g. Tris (8-hydroxyquinoline) gallium [Gaq3] comprising boron
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F15/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 8, 9, 10 or 18 of the Periodic Table
- C07F15/0006—Compounds containing elements of Groups 8, 9, 10 or 18 of the Periodic Table compounds of the platinum group
- C07F15/0033—Iridium compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F15/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 8, 9, 10 or 18 of the Periodic Table
- C07F15/0006—Compounds containing elements of Groups 8, 9, 10 or 18 of the Periodic Table compounds of the platinum group
- C07F15/0086—Platinum compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F5/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 3 or 13 of the Periodic Table
- C07F5/02—Boron compounds
- C07F5/025—Boronic and borinic acid compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F5/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 3 or 13 of the Periodic Table
- C07F5/02—Boron compounds
- C07F5/04—Esters of boric acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F5/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 3 or 13 of the Periodic Table
- C07F5/02—Boron compounds
- C07F5/05—Cyclic compounds having at least one ring containing boron but no carbon in the ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic Table
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/28—Phosphorus compounds with one or more P—C bonds
- C07F9/46—Phosphinous acids [R2POH], [R2P(= O)H]: Thiophosphinous acids including[R2PSH]; [R2P(=S)H]; Aminophosphines [R2PNH2]; Derivatives thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic Table
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/28—Phosphorus compounds with one or more P—C bonds
- C07F9/50—Organo-phosphines
- C07F9/53—Organo-phosphine oxides; Organo-phosphine thioxides
- C07F9/5325—Aromatic phosphine oxides or thioxides (P-C aromatic linkage)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G79/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing atoms other than silicon, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon with or without the latter elements in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G79/08—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing atoms other than silicon, sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon with or without the latter elements in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing boron
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B1/00—Dyes with anthracene nucleus not condensed with any other ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B1/00—Dyes with anthracene nucleus not condensed with any other ring
- C09B1/02—Hydroxy-anthraquinones; Ethers or esters thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B23/00—Methine or polymethine dyes, e.g. cyanine dyes
- C09B23/14—Styryl dyes
- C09B23/141—Bis styryl dyes containing two radicals C6H5-CH=CH-
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B23/00—Methine or polymethine dyes, e.g. cyanine dyes
- C09B23/14—Styryl dyes
- C09B23/148—Stilbene dyes containing the moiety -C6H5-CH=CH-C6H5
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B3/00—Dyes with an anthracene nucleus condensed with one or more carbocyclic rings
- C09B3/02—Benzathrones
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B3/00—Dyes with an anthracene nucleus condensed with one or more carbocyclic rings
- C09B3/78—Other dyes in which the anthracene nucleus is condensed with one or more carbocyclic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B57/00—Other synthetic dyes of known constitution
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B57/00—Other synthetic dyes of known constitution
- C09B57/001—Pyrene dyes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B57/00—Other synthetic dyes of known constitution
- C09B57/008—Triarylamine dyes containing no other chromophores
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B57/00—Other synthetic dyes of known constitution
- C09B57/10—Metal complexes of organic compounds not being dyes in uncomplexed form
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/02—Use of particular materials as binders, particle coatings or suspension media therefor
- C09K11/025—Use of particular materials as binders, particle coatings or suspension media therefor non-luminescent particle coatings or suspension media
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K11/00—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials
- C09K11/06—Luminescent, e.g. electroluminescent, chemiluminescent materials containing organic luminescent materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B33/00—Electroluminescent light sources
- H05B33/12—Light sources with substantially two-dimensional radiating surfaces
- H05B33/14—Light sources with substantially two-dimensional radiating surfaces characterised by the chemical or physical composition or the arrangement of the electroluminescent material, or by the simultaneous addition of the electroluminescent material in or onto the light source
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/10—Organic polymers or oligomers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/10—Organic polymers or oligomers
- H10K85/111—Organic polymers or oligomers comprising aromatic, heteroaromatic, or aryl chains, e.g. polyaniline, polyphenylene or polyphenylene vinylene
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/30—Coordination compounds
- H10K85/341—Transition metal complexes, e.g. Ru(II)polypyridine complexes
- H10K85/342—Transition metal complexes, e.g. Ru(II)polypyridine complexes comprising iridium
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/30—Coordination compounds
- H10K85/361—Polynuclear complexes, i.e. complexes comprising two or more metal centers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/658—Organoboranes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1003—Carbocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1007—Non-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1003—Carbocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1011—Condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1003—Carbocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1014—Carbocyclic compounds bridged by heteroatoms, e.g. N, P, Si or B
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1022—Heterocyclic compounds bridged by heteroatoms, e.g. N, P, Si or B
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1029—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing one nitrogen atom as the heteroatom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1029—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing one nitrogen atom as the heteroatom
- C09K2211/104—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing one nitrogen atom as the heteroatom with other heteroatoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1044—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing two nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms
- C09K2211/1055—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing two nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms with other heteroatoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1059—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing three nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms
- C09K2211/1062—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing three nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms with oxygen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1059—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing three nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms
- C09K2211/107—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing three nitrogen atoms as heteroatoms with other heteroatoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/10—Non-macromolecular compounds
- C09K2211/1018—Heterocyclic compounds
- C09K2211/1025—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands
- C09K2211/1096—Heterocyclic compounds characterised by ligands containing other heteroatoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2211/00—Chemical nature of organic luminescent or tenebrescent compounds
- C09K2211/18—Metal complexes
- C09K2211/185—Metal complexes of the platinum group, i.e. Os, Ir, Pt, Ru, Rh or Pd
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K2101/00—Properties of the organic materials covered by group H10K85/00
- H10K2101/10—Triplet emission
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/11—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED] characterised by the electroluminescent [EL] layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/14—Carrier transporting layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K50/00—Organic light-emitting devices
- H10K50/10—OLEDs or polymer light-emitting diodes [PLED]
- H10K50/14—Carrier transporting layers
- H10K50/16—Electron transporting layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/615—Polycyclic condensed aromatic hydrocarbons, e.g. anthracene
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K85/00—Organic materials used in the body or electrodes of devices covered by this subclass
- H10K85/60—Organic compounds having low molecular weight
- H10K85/631—Amine compounds having at least two aryl rest on at least one amine-nitrogen atom, e.g. triphenylamine
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/549—Organic PV cells
Definitions
- anthracene derivatives which are suitable as host materials are described in WO 01/076323, in WO 01/021729, in WO 04/013073, in WO 04/018588, in WO 03/087023 or in WO 04/018587 , Host materials based on aryl-substituted pyrenes and chrysenes are described in WO 04/016575 0, which in principle also includes corresponding anthracene and phenanthrene derivatives. Although good results have been achieved with these compounds, it is necessary for high quality applications to have improved host materials available. Moreover, some of these compounds are only accessible in a complex manner in 5 multistep syntheses.
- CBP 4,4'-bis (N-carbazolyl) biphenyl
- the drawbacks include short lifetimes of the devices manufactured with them and often high operating voltages, which lead to low power efficiencies. Furthermore, it has been found that, for energetic reasons, CBP is unsuitable for blue-emitting electroluminescent devices, resulting in poor efficiency.
- the structure of the devices is complex when CBP is used as the matrix material, since in addition a 5-hole blocking layer and an electron-transport layer must be used.
- Improved triplet matrix materials based on Keto compounds of spirobifluorene are described in WO 04/093207. For the best of the matrix materials described therein, however, toxic inorganic cyanides are needed in the synthesis, so that the production of these materials is ecologically questionable.
- AlQ 3 aluminum tris-hydroxyquinolinate
- US 4539507 As an electron transport compound in organic Eiektrolumineszenz- devices mostly AlQ 3 (aluminum tris-hydroxyquinolinate) is used (US 4539507).
- This has several disadvantages: it can not be vapor-deposited without residue, since it partially decomposes at the sublimation temperature, which represents a major problem, in particular for production plants.
- a decisive practical disadvantage is the strong hygroscopicity of AIQ 3 .
- AIQ 3 therefore has to be laboriously cleaned in complex, multi-stage sublimation processes and then stored and handled in a protective gas atmosphere with exclusion of water.
- AIQ 3 also has low electron mobility, resulting in higher voltages and lower power efficiency.
- boron-nitrogen compounds with tetrabasubstituted boron have been described in the literature (eg US 2005/0048311). These compounds carry a negative charge on the boron and a positive charge on the nitrogen and thus have completely different electronic properties than boron-nitrogen compounds in which the boron atom is only trisubstituted.
- boron-nitrogen compounds fertilize with three-substituted boron, especially those that still have a boron-carbon bond is not apparent from the description.
- WO 02/052661 and WO 02/051850 describe the use of aromatic boranes, ie boron compounds which have three boron-aryl bonds, in OLEDs.
- JP 2003/031368 describes bisboranes in which two substituted borane groups are bridged by an aromatic group, with further aromatic or aliphatic groups attached to the boron. These materials are described as electron transport and hole blocking materials and as host materials.
- boranes generally have the problem of high chemical reactivity. In particular, these compounds are highly susceptible to oxidation, which makes their synthesis and handling significantly more difficult. Thus, sterically less hindered boranes already decompose in air within a short time (A. Schulz, W. Kaim, Chem.
- Arylboronic acid or arylborinic acid derivatives do not have the abovementioned disadvantages of the boranes or to a significantly reduced extent.
- Such boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives are key intermediates for coupling reactions according to Suzuki and have hitherto been frequently used as starting materials or intermediates for the synthesis of organic semiconductors. Their use as an active component in OLEDs, however, is unknown.
- the invention relates to the use of aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives in organic electronic devices.
- the invention furthermore relates to organic electronic devices comprising at least one organic layer which contains at least one aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivative.
- an aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is meant a compound in which the boron atom is bonded directly to an aromatic or heteroaromatic unit.
- the boron atom is bonded to a carbon atom of the aromatic or heteroaromatic unit and not to an optionally present heteroatom.
- an aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid Derivatives in the context of this invention are not understood to mean polymers or oligomers which contain the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative bound only at the chain ends.
- boron atom is trisubstituted.
- Compounds with four-substituted boron do not fall under the name boronic acid or borinic acid derivative.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is preferably a cyclic boronic anhydride, a cyclic boronic acid imide, a boronic acid ester, a boronic acid amide, a boronic acid amido ester, a boronic acid nitride, a borinic anhydride, a borinic acid imide, a borinic acid ester, a borinic acid amide or a borinic acid nitride , Also preferred are the corresponding sulfur analogs.
- Oligomeric or polymeric boronic anhydrides, boronic imides, boronic esters or corresponding sulfur compounds are also suitable if they are applied from solution; however, they are less suitable if they are to be applied by sublimation.
- the use of free boronic acids or borinic acids in organic electronic devices is unsuitable because they are thermally prone to dehydration to form boronic or borinic anhydrides with liberation of water.
- the term boronic acid or borinic acid derivative thus does not include the free boronic acid or the free borinic acid.
- free boronic acids or borinic acids can be used as starting materials, from which the corresponding boronic acid or borinic anhydrides are vapor-deposited in a vapor-deposition process.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative forms glassy films having a glass transition temperature T 9 of greater than 70 0 C, more preferably greater than 100 0 C, most preferably greater than 130 0 C.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative has a molecular weight of at least 250 g / mol, more preferably at least 300 g / mol, most preferably at least 400 g / mol.
- the molecular weight of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative if it is to be applied by a vapor deposition process, is preferably less than 5000 g / mol, more preferably less than 2000 g / moi, most preferably less than 1500 g / mol. This is preferably a defined compound.
- the organic electronic device is preferably selected from the group consisting of organic or polymeric light-emitting diodes
- OLEDs organic field-effect transistors
- O-FETs organic thin-film transistors
- O-TFTs organic light-emitting transistors
- O-ICs organic integrated circuits
- O-SCs organic solar cells
- O-FQDs organic field quench devices
- LECs light-emitting electrochemical cells
- O-lasers organic laser diodes
- the organic electronic device usually contains an anode, a cathode and at least one organic layer containing at least one aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivative.
- at least one of the organic layers is an emission layer.
- the emission can be fluorescence or phosphorescence, or several different emitters can also be present in one or more layers, with one part of the emitter showing fluorescence and another part of the emitter showing phosphorescence.
- the organic electronic device contains other layers besides the anode, cathode and the emission layer. These can be, for example: hole injection layer, hole transport layer, hole blocking layer, electron transport layer and / or electron injection layer. However, it should be noted at this point that not necessarily each of these layers must be present.
- the organic electroluminescent device does not contain a separate electron transport layer and / or a separate hole blocking layer and the emitting layer directly to the electron injection layer or adjacent to the cathode. It may also be preferred if the organic electroluminescent device is not separate Contains hole transport layer and the emitting layer directly adjacent to the hole injection layer or to the anode.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used in an emission layer. It can be used as a pure substance, but is preferably used as a host material in combination with a fluorescent or phosphorescent dopant.
- a fluorescent or phosphorescent dopant for this purpose, in principle, all fluorescent or phosphorescent dopants come into question, as described in the literature and explained in more detail below.
- the dopant is preferably selected from the class of monostyrylamines, distyrylamines, tristyrylamines, tetrastyrylamines and arylamines.
- a monostyrylamine is meant a compound having a styryl group and at least one
- Contains amine which is preferably aromatic.
- a distyrylamine is meant a compound containing two styryl groups and at least one amine, which is preferably aromatic.
- a tristyrylamine is understood as meaning a compound which contains three styryl groups and at least one amine, which is preferably aromatic.
- Tetrastyrylamine is understood to mean a compound containing four styryl groups and at least one amine, which is preferably aromatic.
- An arylamine or an aromatic amine in the context of this invention is understood as meaning a compound which contains three aromatic or heteroaromatic ring systems bonded directly to the nitrogen.
- a styryl group is understood as meaning a substituted or unsubstituted vinyl group which is bonded directly to an aryl or heteroaryl group.
- the styryl groups are particularly preferably stilbenes, which may also be further substituted on the double bond or on the aromatic. Suitable substituents are, in particular, the groups R 1 listed below.
- the proportion of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative as host in the fluorescent mixture of the emission layer is usually between 1 and 99.9% by weight, preferably between 50 and 99.5% by weight, particularly preferably between 80 and 99% by weight, in particular between 90 and 99% by weight. Accordingly, the proportion of the fluorescent
- Dotands between 0.1 and 99 wt.% Preferably between 0.5 and 50 wt.%, Particularly preferably between 1 and 20 wt.%, In particular between 1 and 10 wt.%.
- the dopant is preferably selected from the class of the metal complexes containing at least one element of atomic number greater than 20, preferably greater than 38 and less than 84, more preferably greater than 56 and less than 80.
- the phosphorescence emitter used is metal complexes comprising molybdenum, tungsten, Rhenium, ruthenium, osmium, rhodium, iridium, palladium, platinum, silver, gold or europium, in particular iridium or platinum.
- the ligands on the metal are preferably monoanionic, bidentate chelating ligands. Particularly suitable for this purpose are ligands which form a metal-carbon bond and furthermore a coordinative bond of a donor atom, in particular nitrogen, oxygen or phosphorus, to the metal.
- the metal complex preferably contains at least one such ligand, more preferably at least two such ligands. The formation of a metal-carbon and a metal-nitrogen bond is preferred.
- Both coordinating groups can be cyclic, for example phenylpyridine, phenylisoquinoline or derivatives thereof, or they can also be acyclic, for example ligands which bind via pyridine and a vinyl C atom. It is also possible for further ligands to be present, for example ⁇ -diketonates, etc.
- the complex contains only bidentate chelating ligands which form a metal-carbon bond.
- Preferred mixtures comprise, as phosphorescent emitters, at least one compound of the formula (A) to (D) 03150
- DCy is the same or different at each occurrence as a cyclic one
- CCy is the same or different at each occurrence and is a cyclic group containing a carbon atom through which the cyclic group is bonded to the metal and which in turn may carry one or more substituents R 1 ;
- A is the same or different at each occurrence as a monoanionic, bidentate chelating ligand, preferably a diketonate ligand;
- R 1 has the same meaning as explained below.
- the cyclic groups CCy and DCy can be monocyclic or polycyclic and are preferably aromatic or heteroaromatic.
- the groups CCy and DCy are preferably monocyclic or bicyclic, the individual cycles preferably having 5 or 6 ring atoms, for example, benzene, pyridine, naphthalene, quinoline or isoquinoline.
- several of the ligands can be linked via one or more substituents R 1 as a bridging unit to a larger polypodal ligand and / or there may be a bridge, in particular with 1, 2 or 3 bridge atoms between CCy and DCy in addition to the direct covalent bond.
- Examples of phosphorescent emitters can be found in applications WO 00/70655, WO 01/41512, WO 02/02714, WO 02/15645, EP 1191613, EP 1191612, EP 1191614, WO 04/081017, WO 05/033244 and those not disclosed Applications EP 04029182.5 and EP 05002237.5 are taken.
- the proportion of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative as host in the phosphorescent mixture is usually between 1 and 99.9% by weight, preferably between 50 and 99.5% by weight, more preferably between 70 and 99% by weight, in particular between 80 and 95 wt.%. Accordingly, the proportion of the phosphorescent dopant is between 0.1 and 99% by weight, preferably between 0.5 and 50% by weight, more preferably between 1 and 30% by weight, in particular between 5 and 20% by weight.
- organic electroluminescent devices characterized in that a plurality of emitting compounds are used in the same layer or a plurality of emitting layers are present, wherein at least one of the emitting layers contains at least one boronic acid or borinic acid derivative.
- This device particularly preferably has a plurality of emission maxima between 380 nm and 750 nm, so that overall white emission results.
- the emitting compounds both those that show fluorescence, as well as those that show phosphorescence can be used.
- An alternative to generating white emission is the use of broadband emitters.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used as the electron transport material as pure substance or in a mixture, preferably as pure substance, in an electron transport layer in an organic electronic device, in particular in a fluorescent or phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative may also be doped, for example with alkali metals.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used as hole-blocking material as pure substance or in a mixture, preferably as pure substance, in a hole-blocking layer, in particular in a phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used as hole transport material as pure substance or in a mixture, preferably as pure substance, in a hole transport layer or in a hole injection layer in an organic electronic device, in particular in a fluorescent or phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device used.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative contains one or more triarylamine groups.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative can also be doped, as described, for example, in WO 03/070822.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used as a fluorescent dopant, preferably in combination with a host material, in an emission layer in a fluorescent organic electroluminescent device.
- a host material preferably in combination with one or more stilbene groups, in particular in combination with one or more triarylamine groups.
- Suitable host materials are also boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives, as already described above.
- oligo-arylenes for example 2,2 ', 7,7'-tetraphenyl-spirobifluorene according to EP 676461 or dinaphthyl anthracene
- the oligo arylenes containing fused aromatic groups e.g DPVBi or spiro
- DPVBi according to EP 676461
- the polypodal metal complexes eg according to WO 04/081017)
- the hole-conducting compounds eg according to WO 04/058911
- the electron-conducting compounds in particular ketones, phosphine oxides, sulfoxides, etc. (for example according to WO 05/084081 or WO 05/084082) or the atropisomers (eg according to the unpublished application EP 04026402.0).
- Particularly preferred host materials are selected from the classes of oligoarylenes containing naphthalene, anthracene and / or pyrene or atropisomers of these compounds, the oligo-arylenevinylenes, the ketones, the phosphine oxides and the sulfoxides.
- Very particularly preferred host materials are selected from the classes of oligoarylenes containing anthracene and / or pyrene or atropisomers of these compounds, the phosphine oxides and the sulfoxides.
- the proportion of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative as dopant in the mixture is preferably as described above for dopants in fluorescent organic electroluminescent devices.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used as a phosphorescent dopant, preferably in combination with a host material, in an emission layer in a phosphorescent organic electroluminescent device.
- host materials come here as boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives in question, as already described above.
- other compounds commonly used as host materials come into question, preferably selected from the classes of
- Carbazole derivatives e.g. 4,4'-bis (N-carbazolyl) biphenyl (CBP), the ketones and imines (eg according to WO 04/093207), the phosphine oxides, sulfoxides and sulfones (eg according to WO 05 / 003253), the phosphines and sulfides (eg according to WO 05/053051), the tetraarylsilanes (eg according to WO 04/095598) or the oligoarylene derivatives.
- CBP 4,4'-bis (N-carbazolyl) biphenyl
- ketones and imines eg according to WO 04/093207
- the phosphine oxides, sulfoxides and sulfones eg according to WO 05 / 003253
- the phosphines and sulfides eg according to WO 05/
- the phosphorescent dopant according to the invention containing boronic acid or boric acid Derivatives, preferably the elements and a structure, as described above for phosphorescent emitter, wherein at least one ligand is bound at least one boronic acid or borinic acid derivative.
- the ligand is a derivative of phenylpyridine, phenylquinoline or phenylisoquinoline and the boronic acid
- Derivative is a boronic acid ester, this preferably has a cyclic structure.
- the boronic acid derivative is a boronic ester, it generally has a cyclic structure.
- Further preferred phosphorescent dopants which carry boronic acid or borinic acid derivative groups are metal-carbene complexes. Simple metal-carbene complexes, as known for use in OLEDs, are described, for example, in WO 05/019373.
- a boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is used in several layers and / or functions simultaneously.
- it can be used simultaneously in one or more emission layers as well as in one or more electron transport layers and / or hole blocking layers and / or hole transport layers.
- These may be the same or different boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives in the different layers.
- an organic electronic device characterized in that one or more layers are coated with a sublimation process.
- the materials are vacuum deposited in vacuum sublimation at a pressure less than 10 "5 mbar, preferably less than 10 " 6 mbar, more preferably less than 10 "7 mbar.
- an organic electronic device characterized in that one or more layers are coated with the OVPD (Organic Vapor Phase Deposition) method or with the aid of a carrier gas sublimation. The materials are usually applied at a pressure between 10 '5 mbar and 1 bar.
- an organic electronic device characterized in that one or more layers of solution, such. B. by spin coating, or with any printing process, such. As screen printing, flexographic printing or offset printing, but particularly preferably LITI (Light Induced Thermal Imaging, thermal transfer printing) or inkjet printing
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative contains at least one partial structure of the formula (1),
- B 1 in each occurrence represents a boron atom which is triply substituted
- Ar is the same or different at each occurrence, an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system having 5 to 40 aromatic ring atoms, which may be substituted by one or more radicals R 1 ;
- E is the same or different at each occurrence as an oxygen
- R 3 is identical or different at each occurrence, H or an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon radical having 1 to 20 C-atoms.
- the partial structure according to formula (1) comprises both compounds which have bound exactly one boronic acid or borinic acid derivative to the aromatic ring system, as well as two or more. Also included are compounds in which several partial structures Ar-B 'are bridged by a plurality of groups E, for example by oligo alcohols, oligothiols or oligoamines. In addition, defined low molecular weight compounds are included as well as oligomeric, dendritic or polymeric. Furthermore, metal complexes are included in which the group Ar binds to one or more metal atoms.
- Preferred boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives are selected from the group of the compounds of the formulas (2) to (8), which are explained in more detail below.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative preferably has a structure of the formula (2), formula (3) or formula (4),
- B is a boron atom at each occurrence
- X is identically or differently a group OR 2 at each occurrence
- Y is the same or different at each occurrence and is a group Ar or X;
- Z is the same or different O, S, NR 2 or NH at each occurrence;
- Atoms which also by a or a plurality of R 3 may be substituted, or a combination of two, three or four of these systems; two or more radicals R 2 together may also form a mono- or polycyclic, aliphatic or aromatic ring system;
- n is the same or different at each occurrence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6;
- n is the same or different at each occurrence 1, 2 or 3;
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative has a structure according to formula (5), formula (6), formula (7) or formula (8),
- CCy is the same or different at each occurrence and is a cyclic group containing a carbon atom through which the cyclic group is bonded to the metal and which in turn may carry one or more substituents R 1 ;
- A is, identically or differently, a monoanionic, bidentate chelating ligand on each occurrence, preferably one
- z is the same or different at each occurrence 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or
- the cyclic groups CCy and DCy can be monocyclic or polycyclic and are preferably aromatic or heteroaromatic. Furthermore, several of the ligands can be linked via one or more substituents R 1 as a bridging unit to a larger polypodal ligand, and / or there can be a bridge, in particular with 1, 2 or 3 direct bridge atoms, between CCy and DCy present.
- radicals R 1 can form a ring system with one another and / or that several radicals R 2 can form a ring system with one another.
- aromatic ring system should also include heteroaromatic ring systems It is preferred if several radicals R 2 together form an aliphatic or aromatic ring system.
- An aromatic ring system in the sense of this invention contains 6 to 60 carbon atoms in the ring system.
- a heteroaromatic ring system in the context of this invention contains 2 to 60 C atoms and at least one heteroatom in the ring system, with the proviso that the sum of the C atoms and Heteroatoms gives at least 5.
- the heteroatoms are preferably selected from N, O and / or S. These ring systems can be substituted with R 1 .
- an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system is to be understood as meaning a system which does not necessarily contain only aryl or heteroaryl groups but in which several aryl or heteroaryl groups are also replaced by a short, nonaromatic moiety (preferably less than 10% of the total) atoms other than H, more preferably less than 5% of the atoms other than H), such as.
- a short, nonaromatic moiety preferably less than 10% of the total
- atoms other than H preferably less than 5% of the atoms other than H
- an sp 3 -hybridized C, N or O atom may be interrupted.
- several aryl or heteroaryl groups may be interrupted by vinyl groups or acetylene groups.
- several aryl or heteroaryl groups can be interrupted by carbonyl groups, phosphine oxide groups, etc.
- systems such as 9,9'-spirobifluorene, 9,9-diarylfluorene, triarylamine, diaryl ether, stilbene, tolane, etc. are also to be understood as aromatic ring systems in the context of this invention.
- aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system or a part thereof may also be a condensed group as defined below.
- a fused aryl or heteroaryl group is understood as meaning a ring system having 9 to 40 aromatic ring atoms in which at least two aromatic or heteroaromatic rings are "fused together", ie fused together by annealing, ie at least one common edge and one common one - having Sames aromatic ⁇ -electron system
- These ring systems may be substituted, or R 1 may be unsubstituted
- fused aromatic or heteroaromatic ring systems are naphthalene, quinoline, isoquinoline, quinoxaline, anthracene, acridine, phenanthrene, anthrolin phen-, pyrene, naphthacene, perylene,.
- biphenyl does not represent a fused aryl group since there is no common edge between the two ring systems, nor does fluorene or spiro bifluorene represent a fused aromatic ring system because the phenyl moieties are not a common aromatic electron train ystem.
- a C 1 - to C 4 -alkyl group in which also individual H atoms or CH 2 groups can be substituted by the abovementioned groups particularly preferably the radicals methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, i Propyl, n-butyl, i -butyl, s -butyl, t -butyl, 2-Methylbutyl, n -pentyl, s -pentyl, cyclopentyl, n -hexyl, cyclohexyl, n -heptyl, cycloheptyl, n -octyl , Cyclooctyl, 2-ethylhexyl, trifluoromethyl, pentafluoroethyl, 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl, ethenyl, propenyl, butenyl, pentenyl
- C r -C 40 -alkoxy group is particularly preferably methoxy, ethoxy, n-propoxy, i-propoxy, n-butoxy, i-butoxy, s-butoxy, t-butoxy or 2-methylbutoxy understood.
- the symbol X stands for OR 2 or OBAr 2 .
- the compounds of the formulas (2) and (5) to (8) are therefore preferably a boronic acid ester or a borinic acid ester or a borinic anhydride.
- the symbol X stands for OR 2 .
- the symbol X stands for OR 2 and the symbol Y simultaneously for OR 2 .
- the compounds of the formula (2) and (5) to (8) are therefore very particularly preferably a boronic acid ester. In this case, it is very particularly preferred if the two radicals R 2 of the groups OR 2 together form an aliphatic or aromatic ring system.
- the boronic acid ester is formed by an aliphatic or aromatic diol.
- the resulting cyclic system is preferably a five-membered ring ([1,2,2-dioxaborolane) or a six-membered ring ([1,2,2] dioxaborinane), ie the cyclic boronic acid ester is preferably derived from a 1,2-diol or formed by a 1, 3-diol.
- the symbols X and Y are identical or different at each occurrence for NHR 2 or N (R 2 ) 2), particularly preferably for N (R 2 ) 2 .
- the compounds of the formula (2) and (5) to (8) are therefore preferably a boronic acid amide.
- R 2 of the groups N (R 2 ) 2 it is very particularly preferred for two radicals R 2 of the groups N (R 2 ) 2 to form an aliphatic or aromatic ring system with different N atoms. This means that the boronic ester is formed by an aliphatic or aromatic diamine.
- the resulting cyclic system is preferably a five-membered ring ([1, 3,2] -diazaborolane) or a six-membered ring ([1,2,2] -diazaborinane), ie the cyclic boronic acid amide is preferably derived from a 1,2-diamine or formed by a 1, 3-diamine.
- the symbol Z in formula (3) stands for O.
- the symbol Z in formula (4) is identical or different at each occurrence for O or for NR 2 , particularly preferably all Z stands for O or for NR 2 .
- the compound of the formula (4) is therefore particularly preferably an oligoboronic acid ester in which a plurality of boronic acid esters are linked via the group L, or for an oligoboronic acid amide in which several boronic acid amides are linked via the group L.
- Suitable linking group L are both straight-chain, branched or cyclic aliphatic compounds and also aromatic compounds.
- all aliphatic oligo alcohols and oligoamines are suitable for the synthesis. Preference is given to those which are synthetically easily accessible or which are naturally available.
- a preferred aliphatic alcohol is pentaerythrol.
- Further preferred aliphatic compounds are sugar alcohols which are reacted with the corresponding free boronic acids to give the oligoboronic acid esters. These may be straight-chain (for example mannitol) or cyclic (for example cis-, epi-, allo-, myo-, neo-, muco-, chiro- or scyllo-1-nositol). In principle, all naturally occurring sugar alcohols are preferred.
- monosaccharides oligosaccharides or polysaccharides
- cyclic sugars such as ⁇ -, ß- or ⁇ -cyclodextrins.
- aromatic compounds in principle all aromatics which have four or more hydroxyl groups and / or are suitable
- Amino groups are substituted.
- the hydroxy groups may be bound to one or more aryl groups linked together.
- Preferred units here are 1, 2,3,4-tetrahydroxybenzene, 1, 2,4,5-tetra-hydroxybenzene, 1, 2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroxybenzene, 4,5,9,10-tetrahydroxybenzene tetrahydropyrene, 1, 4,5,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene, 2,2 ', 3,3'-tetrahydroxy-1, 1'-biphenyl, 3,3 ⁇ 4,4'-tetrahydroxy-1, 1'-biphenyl, 2 , 3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-spirobifluorene, etc.
- radicals R 2 together can also form a mono- or polycyclic, aliphatic or aromatic ring system.
- two radicals R 2 together with B, X and Y form a ring system, the formation of a five-, six- or seven-membered ring, in particular a five-membered ring. or six-membered ring is particularly preferred.
- R 2 are in the formation of ring systems 1, 2-EthyIen, 1, 3-propylene, 1, 2-phenylene and 1, 8-naphthylene, which may each be substituted by one or more radicals R 3 . It is furthermore preferred if the radicals R 2 form a ring system with R 1 .
- the preferred groups Ar of formulas (2) to (4) depend on the particular intended use of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives in the organic electronic device. In particular, they differ depending on whether the compound is used as a host for fluorescent or for phosphorescent emitters. As electron transport materials, the preferred host materials are equally suitable. Likewise, different groups Ar are preferred if the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative is to be used as a hole transport compound or as a fluorescent or phosphorescent dopant.
- the aromatic ring system Ar contains at least one fused aryl or heteroaryl group.
- the boron atom is preferably bonded directly to this condensed aryl or heteroaryl group. It may be preferred if further aromatic radicals are bonded to the fused aryl or heteroaryl group. It may likewise be preferred if more than one boron atom is bonded to the fused aryl or heteroaryl group or if a plurality of fused aryl or heteroaryl groups are bonded to one another, to which one or more boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives are bound. Furthermore, it is preferred, in particular for blue-emitting devices, if the host material contains no double bonds, ie no stilbene structures, etc.
- the fused aryl or heteroaryl group contains two, three, four or five aromatic or heteroaromatic units which are each fused to one another via one or more common edges and thereby form a common aromatic system.
- the fused aryl or heteroaryl group contains three or four aromatic or heteroaromatic units which are each fused to each other via one or more common edges and thereby form a common aromatic system and which may be substituted by R 1 or unsubstituted.
- the fused aromatic and heteroaromatic moieties are selected from benzene, pyridine, pyrimidine, pyrazine and pyridazine, which may be substituted or unsubstituted by R 1 , especially benzene and pyridine, each of which may be substituted by R 1 or unsubstituted ,
- the condensed aryl or heteroaryl groups are particularly preferably selected from the group consisting of anthracene, acridine, phenanthrene, phenanthroline, pyrene, naphthacene, chrysene, pentacene and perylene, which may optionally be substituted by R 1 .
- the condensed aromatic ring systems are particularly preferably selected from the group consisting of anthracene, phenanthrene, pyrene or naphthacene, in particular, anthracene, phenanthrene or pyrene, which may be optionally substituted by R.
- R 2 is a bridging group between X and Y selected from 1, 2-phenylene, 1, 8-naphthylene, 1, 2-ethylene and 1,3-propylene. Further preferably, a plurality of R 2 groups on different boronic acid derivatives in the same compound can also form a ring system and thus produce, for example, an ansa compound.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative on the anthracene preferably takes place via the 2- or the 9-position, if only one such group is present, in particular via the 9-position. With particular preference, the 10-position is then further substituted by an aromatic substituent.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives on the anthracene is preferably carried out via the 2,9-position, the 2,10-position, the 9,10-position or the 2,6-position, if two such groups are present, more preferably via the 9,10-position.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative on the pyrene is preferably carried out via the 1- or the 2-position, if only one such group is present.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives to the pyrene is preferably carried out via the 1, 6, 1, 8, 1, 3 or 2,7-position, if two such groups are present, particularly preferably via the 1, 6 or the 2,7-position.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives on the pyrene is preferably carried out via the 1, 3, 6, 8-position, if four such groups are present.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative to the phenanthrene preferably takes place via the 2-, 3- or 9-position, if only one such group is present.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives on phenanthrene preferably takes place via the 2,7-, 3,6-, 2,9-, 2,10- or 9,10-position, if two such groups are present, more preferably via the 2,7- or via the 3,6-position.
- the linkage of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative to the perylene is preferably via the 3-position, if only one such group is present.
- the linking of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives to the perylene is preferably effected via the 3,4, the 3,9 or the 3,10-position, when two such groups are present, more preferably via the 3,9 or 3,10 position.
- the linkage of the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives to the perylene is preferably via the 3,4,9,10-position, if four such groups are present.
- the aromatic ring system Ar contains only aryl or heteroaryl groups having 5 to 14 aromatic ring atoms, but none having more than 14 aromatic ring atoms. This does not exclude that several such
- Groups may be present in the aromatic ring system Ar, but excludes condensed aryl or heteroaryl groups with more than 14 aromatic ring atoms. It may be preferred if more than one boron atom is bound to the aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system. Furthermore, it is preferred if the host material contains no double bonds, ie no stilbene structures, etc. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the aromatic ring system Ar contains only aryl or heteroaryl groups which contain not more than 10 aromatic ring atoms, in particular selected from benzene, naphthalene, pyridine, pyrimidine, pyrazine, pyridazine, quinoline, isoquinoline, quinoxaline,
- a plurality of aryl groups are interrupted by a non-conjugated unit, more preferably a carbonyl group, an aromatic phosphine group, an aromatic phosphine oxide group, a thio group, a sulfoxide , a sulfone or a C (R 1 ) 2 group, in particular a carbonyl or an aromatic phosphine oxide group.
- Ar groups include benzene, 2-biphenyl, 3-biphenyl, 4-biphenyl, fluorene, dihydrophenanthrene, spirobifluorene, terphenyl, naphthyl or binaphthyl. These may each be substituted by R 1 or unsubstituted and may have one or more boronic or borinic acid derivatives attached.
- the group Ar contains at least one triarylamine unit and / or at least one thiophene derivative.
- the group particularly preferably contains at least one triarylamine unit. These may be structures with exactly one or more nitrogen atoms, for example triphenylamine, naphthyldiphenylamine, TAD, NPB, naphDATA, etc.
- the group Ar contains at least one stilbene unit and / or at least one tolan unit, more preferably at least one stilbene unit. Most preferably, the group Ar contains, in addition to the stilbene unit, at least one triarylamine unit.
- boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives which are suitable as host materials for fluorescent or phosphorescent devices, as electron transport materials, as hole transport materials or as emitter are the structures (1) to (198) shown below. Which of the depicted compounds is particularly suitable for fluorescent devices and which is suitable for phosphorescent devices, or which is also suitable for other uses, can be taken from the above description.
- Aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives and their synthesis are known above all as intermediates for coupling reactions according to Suzuki. They are readily synthesized by standard methods of organic chemistry: Typically, the synthesis is from an aromatic halide which is converted to an organolithium compound or a Grignard compound, followed by reaction with a trialkyl borate, usually trimethyl borate. The preparation can also be carried out by a one-pot process in which the aromatic halide is reacted in the presence of the alkyl borate with a reactive metal (Li, Mg, etc.) or an organolithium compound (K.-T. Wong et al., J. Org Chern 2002, 67, 1041-1044).
- a reactive metal Li, Mg, etc.
- organolithium compound K.-T. Wong et al., J. Org Chern 2002, 67, 1041-1044.
- the boronic acid obtained by hydrolysis can either be converted by dehydration to boronic anhydride, by reaction with an alcohol with water separation to the corresponding boronic acid ester or by reaction with an amine to the corresponding boronic acid amide.
- the reaction with a diol gives a cyclic boronic acid ester, while the reaction with a diamine leads to cyclic boronic acid amides (G. Kaupp et al., Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 4156-4160).
- the alcohols, thiols and amines may be aromatic or aliphatic.
- the reaction with aromatic or aliphatic amino alcohols is possible and leads to cyclic Boronkladreamidoestern, as well as with aminothiols.
- aromatic boronic acid derivatives can also be obtained by reacting an aromatic halide with a compound containing a boron-boron bond (for example, bis-pinacolato-diborane) under palladium catalysis (JP 2004/189705, T. Ishiyama et al. , Special Publication - Royal Society of Chemistry 1997, 201 (Advances in Boron Chemistry), 92-95).
- the compounds are already in the synthesis in high purity and can be further purified by standard methods of organic chemistry, in particular by recrystallization. Due to their high thermal stability, they can also be easily cleaned by sublimation. This is of great importance for use in OLEDs, since sublimated compounds are usually used for this purpose and the compounds are often applied by vapor deposition.
- the aromatic halide used as the starting compound may be either a commercially available halide, for example an aryl bromide or aryl dibromide. It is also possible to build only more complex aromatic systems containing, for example, several aryl groups. A standard reaction for this is the aryl-aryl coupling according to Suzuki under palladium catalysis, the aryl-N-coupling according to Hartwig-Buchwald under palladium catalysis or other transition-metal-catalyzed coupling reactions. In a next step, one of the Aromatics are halogenated, for example by bromination with bromine or NBS.
- Another object is the use of oligomers, polymers or dendrimers containing aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives, in organic electronic devices, in particular in organic electroluminescent devices, with the proviso that the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative in oligomers or Polymer is not bound or not only as an end group to the chain ends of the oligomer or polymer.
- Yet another object of the invention are organic electronic devices, in particular organic Elektrolumineszenzvor- directions containing at least one oligomer, polymer or dendrimer containing at least one boronic acid or borinic acid derivative, with the proviso that the Boronklare- or borinic Derivative is bound in oligomers or polymers at least one point within the main chain and / or the side chain and is not bound or not only as an end group to the chain ends of the oligomer or polymer.
- the polymers may be conjugated, partially conjugated or non-conjugated polymers.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives may be bound in the main chain and / or in the side chain of the polymer.
- Polymers used in organic electronic devices are usually conjugated or partially conjugated polymers containing aromatic repeating units. In general, these polymers are synthesized by palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions, in particular Suzuki coupling between an aromatic halide and an aromatic boronic acid or an aromatic boronic acid derivative. If the reaction has not gone to completion or no end capping has been carried out, it is possible that boronic acids or boronic acid derivatives remain as end groups in the polymer and these are also present in the organic electronic device.
- polymeric and oligomeric boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives do not include those polymers which contain the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative only as an end group at the chain ends of the Contain polymer or oligomer bound, since there remain these groups only as an impurity of an incomplete reaction.
- polymers according to the invention are those which do not contain the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative bound, or not only as an end group, to one chain end of the polymer but at least to a further point in the polymer which does not represent an end group. This also applies to oligomers.
- the minimum content of boron in the polymer is preferably at least 5 ppm, more preferably at least 10 ppm, most preferably at least 100 ppm.
- conjugated or partially conjugated polymers containing the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative bound in a side chain of the polymer.
- non-conjugated polymers containing bound to the boronic acid or borinic acid derivative in a side chain of the polymer.
- the non-conjugated polymer backbone is derivatives of oligomeric or polymeric sugars, for example amylose or amylopectin.
- Preferred repeat units of the conjugated, partially conjugated or non-conjugated polymer or oligomer are selected from fluorenes (eg according to EP 842208 or WO 00/22026), spirobifluorenes (eg according to EP 707020, EP 894107 or EP 04028865.6), phenylenes (for example, according to WO 92/18552), carbazoles (for example according to WO 04/070772 and WO 04/113468), thiophenes (for example according to EP 1028136), dihydrophenanthrenes (for example according to US Pat WO 05/014689), indenofluorenes (for example according to WO 04/041901 and WO 04/113412), phenanthrenes (for example according to WO 05/104264), aromatic ketones (eg according to WO 05/040302) or from several of these units.
- Phosphorescent metal complexes may also represent repeat units of the polymer (
- Complexes may represent repeat units of the polymer (for example according to WO 02/068435 or WO 06/003000.
- the commonly used Suzuki coupling or occasionally used Yamamoto coupling is not suitable as a synthesis method, if the polymer should contain aromatic boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives and if these units are already present in the monomers because these groups react under the usual polycondensation conditions. Thus, the synthesis of such polymers can not be performed under the standard conditions commonly used commonly for conjugated or partially conjugated polymers.
- standard syntheses can be used, for example the polymerization of vinylic double bonds which contain the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives in the side group.
- Another possibility for synthesis is the synthesis of a conjugated or partially conjugated polymer according to standard methods which contains unprotected or preferably protected alcohol, thiol or amino groups in the side chain. It preferably contains protected alcohol groups, more preferably protected diols. These can be reacted after deprotection with a boronic acid to the corresponding boronic acid derivative in a polymer-analogous reaction.
- Yet another synthetic method that results in the production of unconjugated or partially conjugated polymers is the reaction of an aliphatic or aromatic bis (diol), bis (dithiol), or bis (diamines) with an aromatic bisboronic acid in a polycondensation reaction, as shown in Scheme 1a. or the reaction of an aromatic compound containing both hydroxy, thiol or amino groups as well as a boronic acid group, as shown in Scheme 1b: Scheme 1a
- B, Ar, L and Z have the same meaning as described above, and o may be the same or different in each occurrence, an integer between 3 and 10,000, preferably between 10 and 1000.
- a corresponding reaction is possible using oligoboronic acids and / or oligoalcohols or oligoamines and leads to dendrimers or to branched polymer structures.
- the invention therefore relates to compounds of the formula (9) and (9a),
- anthracene or acridine backbone can also be substituted by substituents R 1 and wherein B, X, Y and R 1 have the same meaning as described above, and furthermore:
- G is the same or different CH, CR 1 , C-BXY or N at each occurrence;
- v is 0 or 1 at each occurrence
- G is C-BXY or CR 1 .
- G is particularly preferably CR 1 , where R 1 is an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system.
- R 1 is an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system.
- the anthracene backbone is unsubstituted except in the 9 and 10 positions.
- G is CR 1 .
- R 1 is particularly preferably an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring system.
- Another object of the invention are compounds of the formula (10) and (11),
- pyrene skeleton may also be substituted by substituents R 1 and wherein B, X, Y and R 1 have the same meaning as described above, and furthermore:
- J is the same or different CH, CR 1 or C-BXY at each occurrence;
- the invention further relates to compounds of the formulas (12) to (17)
- phenanthrene or phenanthroline backbone may also be substituted by substituents R 1 and wherein B, X, Y, J and R 1 have the same meaning as described above;
- Another object of the invention are compounds of the formula
- perylene backbone may also be substituted by substituents R 1 and B, X, Y, J and R 1 have the same meaning as described above.
- the invention further relates to compounds of the formulas (19) to (23),
- naphthalene, quinoline, isoquinoline or quinoxaline backbone may also be substituted by substituents R 1 and B, X, Y, J and R 1 have the same meaning as described above, and Ar 1 represents an aryl or heteroaryl group having 5 to 40 aromatic ring atoms, which may also be substituted by R 1 .
- Another object of the invention are compounds of the formula (24) and (25),
- the compound according to formula (24) is substituted in the 9,9-position with two substituents R 1 and otherwise unsubstituted.
- the compound according to formula (25) is unsubstituted or it carries substituents only in one or more of the positions 2, 7, 2 'and T.
- Another object of the invention are compounds according to formula (26),
- Another object of the invention are compounds according to formula (27) and (27a),
- Ar 2 is the same or different at each occurrence, a fused aryl or heteroaryl group having 9 to 20 aromatic ring atoms, which may be substituted with R 1 ;
- Ar 3 is the same or different at each instance and is a fluoro or spiro bifluorene group which may be substituted with R 1 ;
- the same or different Q is a bivalent at each occurrence
- p is the same or different at each occurrence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6;
- Ar 2 is preferably the same or different at each occurrence and is a fused aryl or heteroaryl group having 9 to 20 C atoms, particularly preferably a fused aryl group having 10 to 16 C atoms.
- Another object of the invention are compounds of formula (28),
- v is the same or different at each occurrence 0 or 1;
- w is the same or different at each occurrence 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6; with the proviso that boronic acid esters formed with pinacol, 1, 2-ethanediol, 2,2-dimethyl-1, 3-propanediol, 2,3-butanediol and iso-propanol are excluded from the invention.
- Another object of the invention are compounds according to formula (29),
- B, X, Y, Ar, R 1 , R 2 and v have the same meaning as described above, and wherein a is the same or different at each occurrence for 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that it is for structures of the formula (29) is not Boronklareester of pinacol, glycol and / or 1, 3-propanediol.
- Ar or Ar 1 preferably represents a group which is derived from benzene, biphenyl or naphthalene, which may each be substituted by R 1 or unsubstituted.
- the invention further relates to compounds of the formula (30), formula (31), formula (32) or formula (33),
- DCy is the same or different at each occurrence as a cyclic one
- CCy is the same or different at each occurrence and is a cyclic group containing a carbon atom through which the cyclic group is bonded to the metal and which in turn may carry one or more substituents R 1 ;
- A is the same or different at each occurrence as a monoanionic, bidentate chelating ligand, preferably a diketonate ligand;
- z is the same or different at each occurrence 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or
- the group DCy is a monocyclic group having 5 or 6 aromatic ring atoms or a condensed group having 9 or 10 aromatic ring atoms, more preferably selected from pyridine, pyrimidine, pyridazine, pyrazine, triazine, quinoline, isoquinoline, quinoxaline or Benzpyrimidin; more preferably DCy is pyridine, quinoline or isoquinoline.
- These groups may each be substituted by R 1 .
- the group CCy is a monocyclic group having 5 or 6 aromatic ring atoms or a fused group having 9 or 10 aromatic ring atoms, more preferably also selected benzene, naphthalene, anthracene, thiophene, benzothiophene, pyrrole or indole; CCy is particularly preferably benzene or naphthalene. These groups may each be substituted by R 1 .
- radicals R 1 can form a ring system with one another.
- radicals R 1 on the groups CCy and DCy can also connect these two cycles through another bridge.
- Boronic acid or borinic acid derivative which is used as a host, with the absorption spectrum of the dopant, a large overlap.
- the overlap of emission and absorption spectrum is the prerequisite for a good transfer of energy to the dopant and thus for a high efficiency.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives are readily soluble and therefore easier to clean or easier to process from solution.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives used can be easily synthesized according to standard methods of organic chemistry and are easy to purify. This is an advantage over compounds used in the prior art. 5.
- the boronic acid and borinic acid derivatives have a lower evaporation temperature than comparable compounds which do not carry these substituents. This is of great advantage for the production of OLEDs by vacuum deposition, since it puts less stress on thermally sensitive parts of the apparatus, such as, for example, the shadow masks.
- the boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives, in particular of triplet emitters have a higher thermal stability than corresponding compounds, in particular triplet emitters, according to the prior art, which are unsubstituted or, according to the prior art, only with alkyl or aryl groups, halogens, etc. are substituted. Due to the higher sublimation stability, they are easier to process, especially by sublimation in the
- boronic acid or borinic acid derivatives are significantly more stable to oxidation than boranes, as according to the prior art
- fac-tris [2- (2-pyridinyl- ⁇ N) (5-bromo-phenyl) - ⁇ C] -iridium (III), fac-tris [2- (2-pyridinyl- ⁇ N) (4-fluoro-5-bromo -phenyl) - ⁇ C] - iridium (III) and / ac-tris [2- (1-isoquinolinyl- ⁇ N) (5-bromo-phenyl) -KC] -hydroidium (III) are prepared according to / analogously to WO 02/068435 (Example 4) are shown.
- a suspension of 19.5 g (40 mmol) of 9,10-bis (2-bromophenyl) anthracene in 1000 ml of diethyl ether is mixed with 40.0 ml of n-BuLi (2.5 M in hexane) and stirred at room temperature for 6 h. Subsequently, the reaction mixture is cooled to -78 0 C and quickly added with vigorous stirring to 26.8 ml (240 mmol) of trimethyl borate.
- Representation analog 8b instead of 25.8 g (63 mmol) of 1,6-bis (2,5-dimethylphenyl) -pyrene, 29.6 g (50 mmol) of 1,6-bis ((4-methylphenyl) -amino) pyrene, instead of 24, 8 g (139 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide are used 19.6 g (110 mmol) of N-bromosuccinimide. Yield: 27.4 g (36.5 mmol), 73.0% of theory. Th .; Purity 99% n. 1 H-NMR.
- Example 20a Representation analogous to Example 20a. Instead of 76.0 g (211 mmol) dibromopyrene (mixture of isomers) and 94.7 g (480 mmol) of bis (4-methylphenyl) amine, 70.9 g (211 mmol) of 9,10-dibromoanthracene and 81.2 g (480 mmol) of diphenylamine are used. Yield: 86.2 g (168 mmol), 79.7% of theory. Th .; Purity 99% n. 1 H-NMR.
- OLEDs takes place according to a general method according to WO 04/058911, which in individual cases is adapted to the respective circumstances (eg layer thickness variation in order to achieve optimum efficiency or color).
- HIL Hole Injection Layer
- HTM Hole Transport Layer 30 nm 4,4 ', 4 "-tris (N-1-naphthyl-N-phenylamino) -triphenylamine (abbreviated as
- NaphDATA purchased from SynTec
- Hole Transport Layer (HTM) 30 nm NPB (N-Naphthyl-N-phenyl-4,4 1 -diaminobiphenyl)
- Dotand (abbreviated D1, evaporated, synthesized according to WO 06/000388)
- OLEDs are characterized by default; For this purpose, the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (IUL characteristics) are determined.
- Table 1 summarizes the results of some OLEDs (Examples 26-39).
- the host material for the comparative example is 9,10-bis (1-naphthyl) anthracene; as dopant D1 is used in all examples. Both are shown below:
- Example 40 Production of OLEDs Using the Host Materials According to Examples 5 to 8 or Host H and the Emitters According to Examples 14 and 15
- HIL Hole Injection Layer 20 nm PEDOT (spun from water; from H. C. Starck, Goslar, Germany;
- HTM hole transport layer 30 mn 4,4 ', 4 "-tris (N-1-naphthyl-N-phenylamino) -triphenylamine (abbreviated as
- NaphDATA purchased from SynTec
- OLEDs are characterized by default; For this purpose, the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (IUL characteristics) are determined.
- Table 2 summarizes the results of some OLEDs (Examples 41 to 51).
- the host material for the comparative examples is 9,10-bis (1-naphthyl) anthracene (see above), as dopants for the comparative examples D1 (see above) and D2 are used.
- OLEDs containing the host materials according to the invention show markedly improved efficiencies with comparable color coordinates and improved lifetimes.
- Example 52 Production of OLEDs with the Hole Transport Material According to Example 16
- HIL Hole Injection Layer 20 nm PEDOT (spun from water; from H. C. Starck, Goslar, Germany;
- HTM hole transport layer
- TAD N.N.N'.N'-tetraphenylti.r-biphenyl] ⁇ , diamine
- HTM Hole transport layer
- NPB N-naphthyl-N-phenyl-4,4'-diaminobiphenyl emission layer
- EML emission layer
- Example 8 (see table), doped with 5%
- OLEDs are characterized by default; for this the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the Power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (IUL characteristics).
- Table 3 shows the results of two OLEDs (Examples 53 and 54). As can be seen from the examples in Table 3, OLEDs containing the hole transport material according to the invention of Example 16 show markedly improved efficiencies with comparable color coordinates and improved lifetimes.
- Example 55 Production of OLEDs with matrix materials according to
- OLEDs takes place according to a general method according to WO 04/093207, which in individual cases is adapted to the respective conditions (eg layer thickness variation in order to achieve optimum efficiency or color).
- the results of different OLEDs are compared.
- the basic structure, such as the materials used, degree of doping and their layer thicknesses are identical for the example experiments for better comparability. Only the host material in the emitter layer is exchanged, and the examples are carried out with different triplet emitters.
- the first example describes a comparative standard according to the prior art, in which the emitter layer consists of the matrix material CBP. Furthermore, OLEDs with an emitter layer consisting of the matrix materials of Examples 17, 18 and 19 according to the invention are described.
- PEDOT 60 nm spun from water, supplied by H. C. Starck, poly (3,4-ethylenedioxy-2,5-thiophene)
- NaphDATA 20 nm (evaporated, NaphDATA purchased from SynTec; 4,4 ', 4 "-tris (N-1-naphthyl-N-phenyl-amino) -triphenylamine
- Emitter layer 20 nm of the matrix material according to Example 17,
- BCP Bathocuproine 10 nm (evaporated, BCP purchased from ABCR, used as received; 2,9-dimethyl-4,7-diphenyl-1, 10-phenanthroline); not used in all examples
- AlQ 3 10 nm (evaporated, AlQ 3 purchased from SynTec; Tris (quinolinolato) aluminum (III)), not used in all examples
- OLEDs are characterized by default; For this purpose, the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (LUL characteristic curves), and the service life are determined.
- the lifetime is defined as the time after which the initial brightness of 1000 cd / m 2 has fallen to half.
- the triplet emitters used and the host materials used are shown below:
- the OLEDs, both of the comparative examples and the OLEDs containing the matrices and emitters according to the invention show comparable color coordinates, with the emitters according to the invention of Examples 22, 23 and 24 containing 4,4,5,5-tetramethyl- [1, 3,2] carrying dioxaborolan-2-yl groups, having somewhat hypsochromic shifted emission.
- OLEDs prepared with the inventive matrix materials after 0 example 17, 18 or 19 and comprising the emitter of Example 22, 23 and 24 show both significantly better photometric efficiency and improved power efficiencies, compared to the matrix material according to the prior art. This applies in particular to the power efficiency which is decisive in terms of application technology, owing to the lower operating voltages when using the matrix materials according to the invention.
- the emitters according to Examples 22, 23 and 24 have a significantly higher thermal stability compared to the structurally analogous but not substituted by Boronklareester phenomenon compounds. This improved stability, particularly in the technical application 5 fertil of crucial importance, as dopants in industrial use Must have lifetimes of several days to weeks at high temperatures.
- Example 76 Preparation of the OLEDs with the Electron Transport Materials According to Examples 17, 18 and 19
- OLEDs takes place according to a general method according to WO 04/058911, which in individual cases is adapted to the respective circumstances (eg layer thickness variation in order to achieve optimum efficiency or color).
- HIL Hole Injection Layer 20 nm PEDOT (spun from water; from H. C. Starck, Goslar, Germany; poly (3,4-ethylenedioxy-2,5-thiophene))
- HTM Hole Transport Layer 30 nm 4,4 ', 4 "-tris (N-1-naphthyl-N-phenylamino) -triphenylamine (abbreviated as NaphDATA purchased from SynTec)
- HTM Hole transport layer 30 nm NPB (N-naphthyl-N-phenyl-4,4'-diaminobiphenyl)
- Emission layer 30 nm, doped layer of 9,10-bis (1-naphthylanthracene) as a host material (abbreviated H), doped with 5% tris [4- (2,2-diphenyl-vinyl) -phenyl] amine as a dopant (abbreviated D1, evaporated)
- These OLEDs are characterized by default; For this purpose, the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (ILJL characteristics) are determined.
- Table 5 summarizes the results of some OLEDs (Examples 79, 80) in which the electron transport layer (ETM) consists of compounds 17 and 18 according to the invention.
- ETM electron transport layer
- Examples 77 to 79 in Table 5 show OLED devices containing the inventive electron transport materials according to Example 17 and 18, a significantly lower operating voltage at 1000 cd / m 2 , which manifests itself in better shoveeffizien.
- OLEDs takes place according to a general method according to WO 04/058911, which in individual cases is adapted to the respective circumstances (eg layer thickness variation in order to achieve optimum efficiency or color).
- WO 04/058911 a general method according to WO 04/058911
- the results of different OLEDs are presented.
- the basic structure and the materials used (except for the electron transport layer) are identical in the examples for better comparability.
- OLEDs are produced with the following structure:
- HIL Hole Injection Layer
- PEDOT spun from water; from HC Starck, Goslar, Germany; poly (3,4-ethylenedioxy-2,5-thiophene)) hole transport layer (HTM) 30 nm 4,4 ', 4 "tris (N-1-naphthyl-N-phenyl-amino) -triphenylamine (abbreviated as NaphDATA purchased from SynTec)
- HTM Hole transport layer
- NPB N-naphthyl-N-phenyl-4,4 1 -diaminobiphenyl
- EML emission layer
- OLEDs are characterized by default; For this purpose, the electroluminescence spectra, the efficiency (measured in cd / A), the power efficiency (measured in Im / W) as a function of the brightness, calculated from current-voltage-brightness characteristics (IUL characteristics) are determined.
- Table 6 summarizes the results of some OLEDs (Examples 81 and 82, respectively) in which the emitter materials consist of compounds 20 and 21 of the invention.
- the sublimation temperatures (at a pressure of 1 ⁇ 10 -5 mbar) of some compounds described in the preceding examples are compared with the sublimation temperatures of compounds which have the same basic structure but are not substituted with boronic acid esters
- the sublimation temperature of the corresponding boronic esters is consistently lower than that of the unsubstituted compounds, which is a considerable technical advantage since it exposes temperature-sensitive parts of the vapor deposition apparatus, such as shadow masks, only to a lower thermal load.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Polymers With Sulfur, Phosphorus Or Metals In The Main Chain (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP06724095.2A EP1888706B1 (de) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate |
| US11/912,939 US8674141B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | Organic electroluminescent device and boric acid and borinic acid derivatives used therein |
| KR1020077028263A KR101289923B1 (ko) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | 유기 전계발광 장치 및 그에 사용되는 붕산 및 보린산유도체 |
| JP2008509318A JP5242380B2 (ja) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | 有機エレクトロルミネッセンス素子 |
| CN2006800154018A CN101171320B (zh) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | 有机电致发光器件 |
| US14/154,323 US9403849B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2014-01-14 | Organic electroluminescent device and boric acid and borinic acid derivatives used therein |
| US15/186,723 US9871213B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2016-06-20 | Organic electroluminescent device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05009643 | 2005-05-03 | ||
| EP05009643.7 | 2005-05-03 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US11/912,939 A-371-Of-International US8674141B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | Organic electroluminescent device and boric acid and borinic acid derivatives used therein |
| US14/154,323 Division US9403849B2 (en) | 2005-05-03 | 2014-01-14 | Organic electroluminescent device and boric acid and borinic acid derivatives used therein |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2006117052A1 true WO2006117052A1 (de) | 2006-11-09 |
Family
ID=34936062
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2006/003150 WO2006117052A1 (de) | 2005-05-03 | 2006-04-06 | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8674141B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1888706B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP5242380B2 (de) |
| KR (1) | KR101289923B1 (de) |
| CN (2) | CN103204996B (de) |
| TW (1) | TW200710198A (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2006117052A1 (de) |
Cited By (467)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007065678A1 (de) * | 2005-12-08 | 2007-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektroluminieszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2007108457A1 (ja) * | 2006-03-20 | 2007-09-27 | Pioneer Corporation | ピレン系有機化合物、トランジスタ材料及び発光トランジスタ素子 |
| WO2008006449A1 (de) | 2006-07-11 | 2008-01-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2008022633A2 (de) * | 2006-08-23 | 2008-02-28 | Johannes Werner | Halbleitende polyaddukte mit kolumnarer struktur |
| WO2008136492A1 (ja) * | 2007-04-27 | 2008-11-13 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | ピレン系高分子化合物及びそれを用いてなる発光素子 |
| DE102007024850A1 (de) | 2007-05-29 | 2008-12-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102008018670A1 (de) | 2008-04-14 | 2009-10-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102008027005A1 (de) | 2008-06-05 | 2009-12-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| DE102008035413A1 (de) | 2008-07-29 | 2010-02-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102008036982A1 (de) | 2008-08-08 | 2010-02-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102008036247A1 (de) | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtungen enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| WO2010049050A1 (de) | 2008-10-31 | 2010-05-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102008063490A1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2010-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102008063470A1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2010-07-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009005288A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009005289A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009005290A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009005746A1 (de) | 2009-01-23 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009007038A1 (de) | 2009-02-02 | 2010-08-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009009277A1 (de) | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung |
| WO2010099852A1 (de) | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe mit azaborol-liganden und elektronische vorrichtung damit |
| DE102009013041A1 (de) | 2009-03-13 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009012346A1 (de) | 2009-03-09 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009017064A1 (de) | 2009-04-09 | 2010-10-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009023155A1 (de) | 2009-05-29 | 2010-12-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2010149258A1 (de) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polymere enthaltend substituierte anthracenyleinheiten, blends enthaltend diese polymere sowie vorrichtungen enthaltend diese polymere oder blends |
| WO2010149259A2 (en) | 2009-06-22 | 2010-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Conducting formulation |
| DE102009031021A1 (de) | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009032922A1 (de) | 2009-07-14 | 2011-01-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011012212A1 (de) | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011015265A2 (en) | 2009-08-04 | 2011-02-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices comprising multi cyclic hydrocarbons |
| DE102009041414A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009041289A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009042693A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009042680A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011032686A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen zur herstellung von elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| DE102009048791A1 (de) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009049587A1 (de) | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009033371A1 (de) | 2009-07-16 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009052428A1 (de) | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindung für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011054442A2 (de) | 2009-11-06 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102009053644A1 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009053382A1 (de) | 2009-11-14 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009053645A1 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009053836A1 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2011-05-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009057167A1 (de) | 2009-12-05 | 2011-06-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtung enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009023154A1 (de) | 2009-05-29 | 2011-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung, enthaltend mindestens eine Emitterverbindung und mindestens ein Polymer mit konjugationsunterbrechenden Einheiten |
| WO2011076380A1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition for the preparation of organic electronic (oe) devices |
| WO2011076324A1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions comprising organic semiconducting compounds |
| WO2011076314A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electroluminescent formulations |
| WO2011076326A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electroluminescent functional surfactants |
| WO2011076323A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations comprising phase-separated functional materials |
| DE102010004803A1 (de) | 2010-01-16 | 2011-07-21 | Merck Patent GmbH, 64293 | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011088877A1 (de) | 2010-01-25 | 2011-07-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010009193A1 (de) | 2010-02-24 | 2011-08-25 | Merck Patent GmbH, 64293 | Fluor-Fluor Assoziate |
| DE102010010481A1 (de) | 2010-03-06 | 2011-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010009903A1 (de) | 2010-03-02 | 2011-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010010631A1 (de) | 2010-03-09 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011110275A2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Radiative fibers |
| WO2011110277A1 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Fibers in therapy and cosmetics |
| WO2011116869A1 (de) | 2010-03-26 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2011116865A1 (de) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011116857A1 (en) | 2010-03-23 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2011128034A1 (en) | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition having improved performance |
| WO2011128035A1 (en) | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition and method for preparation of organic electronic devices |
| DE102010014933A1 (de) | 2010-04-14 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010018321A1 (de) | 2010-04-27 | 2011-10-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010019306A1 (de) | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011137922A1 (de) | 2010-05-03 | 2011-11-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2011141120A1 (de) | 2010-05-14 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2011141109A1 (de) | 2010-05-11 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011147522A1 (en) | 2010-05-27 | 2011-12-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions comprising quantum dots |
| WO2011147523A1 (en) | 2010-05-27 | 2011-12-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation and method for preparation of organic electronic devices |
| DE102009022858A1 (de) | 2009-05-27 | 2011-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010024542A1 (de) | 2010-06-22 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010024335A1 (de) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011157339A1 (de) | 2010-06-15 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010024897A1 (de) | 2010-06-24 | 2011-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010027316A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012007103A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe mit organischen liganden und deren verwendung in oleds |
| DE102010027317A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012007088A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012013271A1 (de) | 2010-07-30 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012013270A1 (en) | 2010-07-26 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Nanocrystals in devices |
| WO2012013272A1 (en) | 2010-07-26 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Quantum dots and hosts |
| DE102010033548A1 (de) | 2010-08-05 | 2012-02-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010045405A1 (de) | 2010-09-15 | 2012-03-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012038029A1 (de) | 2010-09-24 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phosphorhaltige metallkomplexe |
| DE102010046412A1 (de) | 2010-09-23 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metall-Ligand Koordinationsverbindungen |
| WO2012045384A1 (de) | 2010-10-09 | 2012-04-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010048608A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010048607A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010054525A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-04-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012069121A1 (de) | 2010-11-24 | 2012-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010054316A1 (de) | 2010-12-13 | 2012-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte Tetraarylbenzole |
| WO2012079741A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010055901A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012084115A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012095143A1 (de) | 2011-01-13 | 2012-07-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102012000064A1 (de) | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP2482159A2 (de) | 2011-01-28 | 2012-08-01 | Honeywell International, Inc. | Verfahren und umkonfigurierbare System zur Optimierung der Leistung eines zustandsabhängigen Wartungssystems |
| DE102011010841A1 (de) | 2011-02-10 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | (1,3)-Dioxan-5-on-Verbindungen |
| DE102011011104A1 (de) | 2011-02-12 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte Dibenzonaphtacene |
| DE102011011539A1 (de) | 2011-02-17 | 2012-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2012110178A1 (en) | 2011-02-14 | 2012-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Device and method for treatment of cells and cell tissue |
| WO2012126566A1 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2012-09-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic ionic functional materials |
| WO2012136296A1 (de) | 2011-04-04 | 2012-10-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012136295A1 (de) | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012139693A1 (de) | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012139692A1 (de) | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012143079A1 (de) | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012143080A2 (de) | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012150001A1 (de) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012149992A1 (de) | 2011-05-04 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur aufbewahrung von frischwaren |
| WO2012149999A1 (de) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012152366A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 | 2012-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic ionic compounds, compositions and electronic devices |
| DE102012007810A1 (de) | 2011-05-16 | 2012-11-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102011102586A1 (de) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-11-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung |
| WO2012163465A1 (de) | 2011-06-03 | 2012-12-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012163471A1 (de) | 2011-06-03 | 2012-12-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2013000531A1 (de) | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2013013754A1 (en) | 2011-07-25 | 2013-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Copolymers with functionalized side chains |
| WO2013017189A1 (de) | 2011-07-29 | 2013-02-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013017192A1 (de) | 2011-08-03 | 2013-02-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013020631A1 (de) | 2011-08-10 | 2013-02-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102012016192A1 (de) | 2011-08-19 | 2013-02-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013026515A1 (de) | 2011-08-22 | 2013-02-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2013041176A1 (de) | 2011-09-21 | 2013-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazolderivate für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013050101A1 (de) | 2011-10-06 | 2013-04-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102011116165A1 (de) | 2011-10-14 | 2013-04-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Benzodioxepin-3-on-Verbindungen |
| WO2013056776A1 (de) | 2011-10-20 | 2013-04-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013060418A1 (en) | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2013060411A1 (de) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hyperverzweigte polymere, verfahren zu deren herstellung sowie deren verwendung in elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2013064206A1 (de) | 2011-11-01 | 2013-05-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2013083216A1 (de) | 2011-11-17 | 2013-06-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Spiro -dihydroacridinderivate und ihre verwendung als materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013087142A1 (de) | 2011-12-12 | 2013-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102012022880A1 (de) | 2011-12-22 | 2013-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtungen enthaltend organische Schichten |
| WO2013097920A1 (en) | 2011-12-27 | 2013-07-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes comprising 1,2,3-triazoles |
| WO2013107487A1 (en) | 2012-01-16 | 2013-07-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic metal complexes |
| WO2013113349A1 (en) | 2012-01-30 | 2013-08-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Nanocrystals on fibers |
| WO2013120577A1 (en) | 2012-02-14 | 2013-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Spirobifluorene compounds for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2013135352A1 (de) | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013139431A1 (de) | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | 9,9'-spirobixanthenderivate für elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013174471A1 (en) | 2012-05-24 | 2013-11-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes comprising condensed heteroaromatic rings |
| US8597798B2 (en) | 2008-11-13 | 2013-12-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102012011335A1 (de) | 2012-06-06 | 2013-12-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für Organische Elekronische Vorrichtungen |
| US8610110B2 (en) | 2008-03-11 | 2013-12-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Optoelectronic component comprising neutral transition metal complexes |
| WO2013185871A1 (en) | 2012-06-12 | 2013-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| US8618317B2 (en) | 2008-07-17 | 2013-12-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescence device |
| WO2014008967A2 (de) | 2012-07-10 | 2014-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2014008982A1 (de) | 2012-07-13 | 2014-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| US8637168B2 (en) | 2008-10-08 | 2014-01-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescence devices |
| WO2014015937A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen und organische elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| WO2014015935A2 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014015931A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2014015938A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Derivate von 2-diarylaminofluoren und diese enthaltnde organische elektronische verbindungen |
| WO2014023377A2 (de) | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014023388A1 (de) | 2012-08-10 | 2014-02-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US8658832B2 (en) | 2007-07-05 | 2014-02-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Luminescent metal complexes for organic electronic devices |
| EP2712000A1 (de) | 2008-09-22 | 2014-03-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2014044347A1 (de) | 2012-09-20 | 2014-03-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014044344A1 (de) | 2012-09-18 | 2014-03-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014056567A1 (de) | 2012-10-11 | 2014-04-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102012020167A1 (de) | 2012-10-13 | 2014-04-17 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014067614A1 (de) | 2012-10-31 | 2014-05-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| DE102012021650A1 (de) | 2012-11-03 | 2014-05-08 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014079532A1 (de) | 2012-11-20 | 2014-05-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierung in hochreinem l?sungsmittel zur herstellung elektronischer vorrichtungen |
| WO2014082705A1 (de) | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2014106523A1 (de) * | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2014106522A1 (de) | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014106524A2 (de) | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| US8865321B2 (en) | 2008-11-11 | 2014-10-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102013008189A1 (de) | 2013-05-14 | 2014-12-04 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2015014427A1 (de) | 2013-07-29 | 2015-02-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrooptische vorrichtung und deren verwendung |
| US8999521B2 (en) | 2006-03-24 | 2015-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2015082037A1 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2015-06-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions containing a polymeric binder which comprises acrylic and/or methacrylic acid ester units |
| WO2015082046A2 (de) | 2013-12-06 | 2015-06-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte oxepine |
| WO2015086108A1 (de) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2015090504A2 (de) | 2013-12-19 | 2015-06-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische spiroverbindungen |
| EP2927221A1 (de) | 2014-03-31 | 2015-10-07 | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | Diaminverbindungen für phosphoreszierende diazaborolmetallkomplexe und elektrolumineszente vorrichtungen |
| EP2927300A1 (de) | 2014-03-31 | 2015-10-07 | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | Phenylenediaminverbindungen für phosphoreszierende diazaborolmetallkomplexe |
| WO2015165563A1 (de) | 2014-04-30 | 2015-11-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| JP2015199740A (ja) * | 2008-09-03 | 2015-11-12 | ユニバーサル ディスプレイ コーポレイション | リン光性材料 |
| WO2015169412A1 (de) | 2014-05-05 | 2015-11-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102015006708A1 (de) | 2014-06-12 | 2015-12-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2015192941A1 (de) | 2014-06-18 | 2015-12-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP2960315A1 (de) | 2014-06-27 | 2015-12-30 | cynora GmbH | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2015197156A1 (de) | 2014-06-25 | 2015-12-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP2963044A1 (de) | 2014-06-30 | 2016-01-06 | cynora GmbH | Zweikernige Metall(I)-Komplexe mit tetradentaten Liganden für optoelektronische Anwendungen |
| DE102014012818A1 (de) | 2014-08-28 | 2016-03-03 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2016034262A1 (de) | 2014-09-05 | 2016-03-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2016055557A1 (de) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Cynora Gmbh | Metall-komplexe mit tridentaten liganden für optoelektronische anwendungen |
| WO2016074755A1 (de) | 2014-11-11 | 2016-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2016079097A1 (de) | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-26 | Cynora Gmbh | Kupfer(i)komplexe für optoelektronische anwendungen |
| WO2016091353A1 (de) | 2014-12-12 | 2016-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische verbindungen mit löslichen gruppen |
| WO2016107663A1 (de) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2016119992A1 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2016120007A1 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations with a low particle content |
| WO2016124304A1 (de) | 2015-02-03 | 2016-08-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2016155866A1 (en) | 2015-03-30 | 2016-10-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material comprising a siloxane solvent |
| WO2016198141A1 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2016-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Esters containing non-aromatic cycles as solvents for oled formulations |
| WO2016198144A1 (en) | 2015-06-10 | 2016-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017008883A1 (en) | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition comprising organic semiconducting compounds |
| WO2017012694A1 (en) | 2015-07-23 | 2017-01-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phenyl derivatives substituted with at least two electron acceptors and at least two electron donors for use in organic electronic devices |
| WO2017012687A1 (en) | 2015-07-22 | 2017-01-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| US9559311B2 (en) | 2013-02-22 | 2017-01-31 | Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. | Anthracene derivative, organic-electroluminescence-device material, organic electroluminescence device, and electronic equipment |
| WO2017016630A1 (en) | 2015-07-30 | 2017-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017025166A1 (en) | 2015-08-13 | 2017-02-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hexamethylindanes |
| WO2017028940A1 (en) | 2015-08-14 | 2017-02-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phenoxazine derivatives for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017036572A1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material comprising an epoxy group containing solvent |
| WO2017036573A1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| DE102015013381A1 (de) | 2015-10-14 | 2017-04-20 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2017071791A1 (en) | 2015-10-27 | 2017-05-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102015016016A1 (de) | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-14 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2017097391A1 (en) | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing ketones comprising non-aromatic cycles |
| WO2017102048A1 (en) | 2015-12-15 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Esters containing aromatic groups as solvents for organic electronic formulations |
| WO2017102049A1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing a mixture of at least two different solvents |
| WO2017102052A1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing a solid solvent |
| WO2017133829A1 (de) | 2016-02-05 | 2017-08-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2017140404A1 (en) | 2016-02-17 | 2017-08-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2017148564A1 (de) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2017157783A1 (de) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Behälter umfassend eine formulierung enthaltend mindestens einen organischen halbleiter |
| WO2017157983A1 (de) | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit spirobifluoren-strukturen |
| WO2017178311A1 (de) | 2016-04-11 | 2017-10-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen mit dibenzofuran- und/oder dibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| WO2017186760A1 (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-11-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017194435A1 (de) | 2016-05-11 | 2017-11-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektrochemische zellen |
| WO2017207596A1 (en) | 2016-06-03 | 2017-12-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017216128A1 (en) | 2016-06-17 | 2017-12-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2017216129A1 (en) | 2016-06-16 | 2017-12-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018001990A1 (de) | 2016-06-30 | 2018-01-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur auftrennung von enantiomerenmischungen von metallkomplexen |
| WO2018001928A1 (en) | 2016-06-28 | 2018-01-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018007421A1 (en) | 2016-07-08 | 2018-01-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018011186A1 (de) | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018019688A1 (de) | 2016-07-25 | 2018-02-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe für den einsatz als emitter in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018019687A1 (de) | 2016-07-25 | 2018-02-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Di- und oligonukleare metallkomplexe mit tripodalen bidentaten teilliganden sowie deren verwendung in elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2018024719A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 | 2018-02-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018041769A1 (de) | 2016-08-30 | 2018-03-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bl- und trinukleare metallkomplexe aufgebaut aus zwei miteinander verknüpften tripodalen hexadentaten liganden zur verwendung in elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018050583A1 (de) | 2016-09-14 | 2018-03-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit carbazol-strukturen |
| WO2018050584A1 (de) | 2016-09-14 | 2018-03-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit spirobifluoren-strukturen |
| WO2018054798A1 (de) | 2016-09-21 | 2018-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Binukleare metallkomplexe für den einsatz als emitter in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018060218A1 (de) | 2016-09-30 | 2018-04-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazole mit diazadibenzofuran- oder diazadibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| WO2018060307A1 (de) | 2016-09-30 | 2018-04-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit diazadibenzofuran- oder diazadibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| WO2018069197A1 (de) | 2016-10-12 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018069167A1 (de) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2018069196A1 (de) | 2016-10-12 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Binukleare metallkomplexe sowie elektronische vorrichtungen, insbesondere organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen, enthaltend diese metallkomplexe |
| WO2018069273A1 (de) | 2016-10-13 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102017008794A1 (de) | 2016-10-17 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien zur Verwendung in elektronischen Vorrichtungen |
| WO2018077662A1 (en) | 2016-10-31 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018077769A1 (de) | 2016-10-25 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018077660A1 (en) | 2016-10-31 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018083053A1 (de) | 2016-11-02 | 2018-05-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018087022A1 (de) | 2016-11-09 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018087346A1 (de) | 2016-11-14 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit einer akzeptor- und einer donorgruppe |
| WO2018087020A1 (en) | 2016-11-08 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| WO2018091435A1 (en) | 2016-11-17 | 2018-05-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018095888A1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bisbenzofuran-fused 2,8-diaminoindeno[1,2-b]fluorene derivatives and related compounds as materials for organic electroluminescent devices (oled) |
| WO2018095839A1 (de) | 2016-11-22 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbrückte triarylamine für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018095940A1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bisbenzofuran-fused indeno[1,2-b]fluorene derivatives and related compounds as materials for organic electroluminescent devices (oled) |
| WO2018099846A1 (de) | 2016-11-30 | 2018-06-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit valerolaktam-strukturen |
| WO2018104193A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018104202A1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Preparation process for an electronic device |
| WO2018104194A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018104195A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2018108760A1 (en) | 2016-12-13 | 2018-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018114744A1 (en) | 2016-12-20 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | A white light emitting solid state light source |
| WO2018114883A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mischungen umfassend mindestens zwei organisch funktionelle verbindungen |
| WO2018114882A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3345984A1 (de) | 2013-12-06 | 2018-07-11 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018127465A1 (de) | 2017-01-04 | 2018-07-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018138319A1 (en) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic electroluminescence (el) element |
| WO2018138306A1 (de) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018138039A1 (de) | 2017-01-25 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazolderivate |
| WO2018138318A1 (en) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2018141706A1 (de) | 2017-02-02 | 2018-08-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018149769A1 (de) | 2017-02-14 | 2018-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018157981A1 (de) | 2017-03-02 | 2018-09-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018158232A1 (en) | 2017-03-01 | 2018-09-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescent device |
| WO2018166932A1 (de) | 2017-03-13 | 2018-09-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit arylamin-strukturen |
| WO2018166934A1 (de) | 2017-03-15 | 2018-09-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP3378857A1 (de) | 2012-11-12 | 2018-09-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018177981A1 (de) | 2017-03-29 | 2018-10-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische verbindungen |
| WO2018178136A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2018-10-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Printing method for an organic light emitting diode (oled) |
| WO2018189134A1 (de) | 2017-04-13 | 2018-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018189050A1 (en) | 2017-04-10 | 2018-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018197447A1 (de) | 2017-04-25 | 2018-11-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018202603A1 (en) | 2017-05-03 | 2018-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018206526A1 (en) | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organoboron complexes for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018206537A1 (en) | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazole-based bodipys for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018215318A1 (de) | 2017-05-22 | 2018-11-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hexazyklische heteroaromatische verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018234346A1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2018-12-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2018234220A1 (de) | 2017-06-21 | 2018-12-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019002190A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2019-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ELECTRONIC DEVICES |
| WO2019002198A1 (en) | 2017-06-26 | 2019-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURES |
| WO2019007867A1 (de) | 2017-07-05 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019007823A1 (en) | 2017-07-03 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | LOW-PHENOL IMPURITY FORMULATIONS |
| WO2019007866A1 (de) | 2017-07-05 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019007825A1 (en) | 2017-07-03 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENCE DEVICE |
| WO2019016184A1 (en) | 2017-07-18 | 2019-01-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | FORMULATION OF AN ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL MATERIAL |
| WO2019020538A1 (de) | 2017-07-25 | 2019-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019020654A1 (en) | 2017-07-28 | 2019-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | SPIROBIFLUORENE DERIVATIVES FOR USE IN ELECTRONIC DEVICES |
| WO2019048443A1 (de) | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019052933A1 (de) | 2017-09-12 | 2019-03-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019068679A1 (en) | 2017-10-06 | 2019-04-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2019076789A1 (en) | 2017-10-17 | 2019-04-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2019081391A1 (de) | 2017-10-24 | 2019-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019096717A2 (de) | 2017-11-14 | 2019-05-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019101833A1 (en) | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019101719A1 (de) | 2017-11-23 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019101835A1 (en) | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019115573A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2019115577A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituted aromatic amines for use in organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019115423A1 (de) | 2017-12-13 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019121458A1 (de) | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindung zur verwendung in electronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2019121483A1 (en) | 2017-12-20 | 2019-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatic compounds |
| WO2019145316A1 (de) | 2018-01-25 | 2019-08-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019158453A1 (de) | 2018-02-13 | 2019-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019162483A1 (en) | 2018-02-26 | 2019-08-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2019170572A1 (en) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019170578A1 (en) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019175149A1 (en) | 2018-03-16 | 2019-09-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019179909A1 (de) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019229011A1 (de) | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019233904A1 (de) | 2018-06-07 | 2019-12-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019238782A1 (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2020011686A1 (de) | 2018-07-09 | 2020-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020016264A1 (en) | 2018-07-20 | 2020-01-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043657A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043646A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043640A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102018122708A1 (de) * | 2018-09-17 | 2020-03-19 | Novaled Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung, organisches halbleitendes Material und eine Boranverbindung |
| WO2020053150A1 (en) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020053314A1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| WO2020053315A1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| WO2020064582A1 (de) | 2018-09-24 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von granulat |
| WO2020064666A1 (de) | 2018-09-27 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen, die in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung als aktive verbindungen einsetzbar sind |
| WO2020064662A2 (de) | 2018-09-27 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von sterisch gehinderten stickstoffhaltigen heteroaromatischen verbindungen |
| EP3647393A1 (de) | 2013-07-30 | 2020-05-06 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2020089138A1 (en) | 2018-10-31 | 2020-05-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020094542A1 (de) | 2018-11-06 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | 5,6-diphenyl-5,6-dihydro-dibenz[c,e][1,2]azaphosphorin- und 6-phenyl-6h-dibenzo[c,e][1,2]thiazin-5,5-dioxid-derivate und ähnliche verbindungen als organische elektrolumineszenzmaterialien für oleds |
| WO2020094539A1 (de) | 2018-11-05 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | In einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2020094538A1 (en) | 2018-11-06 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2020099349A1 (de) | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zur herstellung einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2020099307A1 (de) | 2018-11-15 | 2020-05-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020127165A1 (de) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020148243A1 (en) | 2019-01-16 | 2020-07-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020165064A1 (de) | 2019-02-11 | 2020-08-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mononukleare iridiumkomplexe mit drei ortho-metallierten bidentaten liganden und optischer orientierungsanisotropie |
| WO2020169241A1 (de) | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2020178230A1 (en) | 2019-03-04 | 2020-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Ligands for nano-sized materials |
| WO2020182779A1 (de) | 2019-03-12 | 2020-09-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP3712229A1 (de) | 2013-07-30 | 2020-09-23 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2020187865A1 (de) | 2019-03-20 | 2020-09-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020193447A1 (de) | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020208051A1 (en) | 2019-04-11 | 2020-10-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020212296A1 (de) | 2019-04-15 | 2020-10-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2021037401A1 (de) | 2019-08-26 | 2021-03-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021043755A1 (de) | 2019-09-03 | 2021-03-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021043703A1 (de) | 2019-09-02 | 2021-03-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021052921A1 (de) | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mischung von zwei hostmaterialien und organische elektrolumineszierende vorrichtung damit |
| WO2021053046A1 (de) | 2019-09-20 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Peri-kondensierte heterozyklische verbindungen als materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2021052924A1 (en) | 2019-09-16 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021078831A1 (de) | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | In einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2021078710A1 (en) | 2019-10-22 | 2021-04-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021089450A1 (en) | 2019-11-04 | 2021-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021094269A1 (en) | 2019-11-12 | 2021-05-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021110741A1 (en) | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021110720A1 (de) | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2021122538A1 (de) | 2019-12-18 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021122740A1 (de) | 2019-12-19 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polycyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021122535A1 (de) | 2019-12-17 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021151922A1 (de) | 2020-01-29 | 2021-08-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Benzimidazol-derivate |
| WO2021160898A2 (de) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-08-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2021170522A1 (de) | 2020-02-25 | 2021-09-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verwendung von heterocyclischen verbindungen in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung |
| WO2021175706A1 (de) | 2020-03-02 | 2021-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verwendung von sulfonverbindungen in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung |
| WO2021180950A1 (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2021-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021185829A1 (de) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-09-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021185712A1 (de) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-09-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021191183A1 (de) | 2020-03-26 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021191058A1 (en) | 2020-03-23 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021191117A1 (de) | 2020-03-24 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2021198213A1 (de) | 2020-04-02 | 2021-10-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021204646A1 (de) | 2020-04-06 | 2021-10-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polycyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021213918A1 (en) | 2020-04-21 | 2021-10-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2021213917A1 (en) | 2020-04-21 | 2021-10-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Emulsions comprising organic functional materials |
| EP3904361A2 (de) | 2013-10-02 | 2021-11-03 | Merck Patent GmbH | Borenthaltende verbindungen |
| DE102020108402B4 (de) | 2020-03-26 | 2021-11-11 | Novaled Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung, organisches halbleitendes Material, eine Trioxatriborinanverbindung und deren Verwendung |
| WO2021254984A1 (de) | 2020-06-18 | 2021-12-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Indenoazanaphthaline |
| WO2021259824A1 (de) | 2020-06-23 | 2021-12-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung einer mischung |
| WO2022002772A1 (de) | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022002771A1 (de) | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022017998A1 (en) | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022017997A1 (en) | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022029096A1 (de) | 2020-08-06 | 2022-02-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022034046A1 (de) | 2020-08-13 | 2022-02-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2022038066A1 (de) | 2020-08-19 | 2022-02-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022038065A1 (de) | 2020-08-18 | 2022-02-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022069380A1 (de) | 2020-09-29 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mononukleare tripodale hexadentate iridium komplexe zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2022069421A1 (de) | 2020-09-30 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zur strukturierung von funktionalen schichten organischer elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2022069422A1 (de) | 2020-09-30 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen zur strukturierung von funktionalen schichten organischer elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022079067A1 (de) | 2020-10-16 | 2022-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit heteroatomen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022079068A1 (de) | 2020-10-16 | 2022-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022101171A1 (de) | 2020-11-10 | 2022-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Schwefelhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022117473A1 (de) | 2020-12-02 | 2022-06-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022122607A1 (en) | 2020-12-08 | 2022-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | An ink system and a method for inkjet printing |
| WO2022122682A2 (de) | 2020-12-10 | 2022-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022129113A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heteroaromaten für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022129114A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022129116A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Indolo[3.2.1-jk]carbazole-6-carbonitril-derivate als blau fluoreszierende emitter zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2022148717A1 (de) | 2021-01-05 | 2022-07-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022157343A1 (de) | 2021-01-25 | 2022-07-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4037000A1 (de) | 2014-07-21 | 2022-08-03 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2022184601A1 (de) | 2021-03-02 | 2022-09-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022194799A1 (de) | 2021-03-18 | 2022-09-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022200638A1 (de) | 2021-07-06 | 2022-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022214507A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022214506A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022214566A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| EP4079742A1 (de) | 2021-04-14 | 2022-10-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2022223675A1 (en) | 2021-04-23 | 2022-10-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2022229234A1 (de) | 2021-04-30 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022229298A1 (de) | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022229126A1 (de) | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022243403A1 (de) | 2021-05-21 | 2022-11-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur kontinuierlichen aufreinigung von mindestens einem funktionalen material und vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen aufreinigung von mindestens einem funktionalen material |
| WO2023012084A1 (en) | 2021-08-02 | 2023-02-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | A printing method by combining inks |
| WO2023041454A1 (de) | 2021-09-14 | 2023-03-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Borhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023052272A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052313A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052275A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052314A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023057327A1 (en) | 2021-10-05 | 2023-04-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2023072799A1 (de) | 2021-10-27 | 2023-05-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bor- und stickstoffhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023094412A1 (de) | 2021-11-25 | 2023-06-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023099543A1 (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2023-06-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds having fluorene structures |
| WO2023110742A1 (de) | 2021-12-13 | 2023-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023117836A1 (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices |
| WO2023117835A1 (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices |
| WO2023117837A1 (de) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von deuterierten organischen verbindungen |
| WO2023152346A1 (de) | 2022-02-14 | 2023-08-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023152063A1 (de) | 2022-02-09 | 2023-08-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4236652A2 (de) | 2015-07-29 | 2023-08-30 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023161167A1 (de) | 2022-02-23 | 2023-08-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023161168A1 (de) | 2022-02-23 | 2023-08-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023213837A1 (de) | 2022-05-06 | 2023-11-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023222559A1 (de) | 2022-05-18 | 2023-11-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von deuterierten organischen verbindungen |
| WO2023237458A1 (en) | 2022-06-07 | 2023-12-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method of printing a functional layer of an electronic device by combining inks |
| WO2023247345A1 (de) | 2022-06-20 | 2023-12-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023247338A1 (de) | 2022-06-20 | 2023-12-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024013004A1 (de) | 2022-07-11 | 2024-01-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP4311849A1 (de) | 2022-07-27 | 2024-01-31 | UDC Ireland Limited | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2024061948A1 (de) | 2022-09-22 | 2024-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffenthaltende heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024061942A1 (de) | 2022-09-22 | 2024-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffenthaltende verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024094592A2 (de) | 2022-11-01 | 2024-05-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024105066A1 (en) | 2022-11-17 | 2024-05-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2024126635A1 (en) | 2022-12-16 | 2024-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2024133048A1 (en) | 2022-12-20 | 2024-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for preparing deuterated aromatic compounds |
| WO2024132993A1 (de) | 2022-12-19 | 2024-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024149694A1 (de) | 2023-01-10 | 2024-07-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024153568A1 (de) | 2023-01-17 | 2024-07-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024170605A1 (en) | 2023-02-17 | 2024-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2024184050A1 (de) | 2023-03-07 | 2024-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische stickstoffverbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024194264A1 (de) | 2023-03-20 | 2024-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024218109A1 (de) | 2023-04-20 | 2024-10-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024240725A1 (de) | 2023-05-25 | 2024-11-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Tris[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a:1',5'-c:1'',5''-e][1,3,5]triazin-derivate zur verwendung in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024256357A1 (de) | 2023-06-12 | 2024-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| EP4486099A1 (de) | 2023-06-30 | 2025-01-01 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2025003084A1 (de) | 2023-06-28 | 2025-01-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Dicyanoarylverbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2025012253A1 (en) | 2023-07-12 | 2025-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2025021855A1 (de) | 2023-07-27 | 2025-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische lichtemittierende vorrichtungen und organische sensoren |
Families Citing this family (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2006117052A1 (de) * | 2005-05-03 | 2006-11-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate |
| EP2239259B1 (de) | 2007-12-28 | 2016-04-13 | Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. | Aromatisches aminderivat und dessen verwendung in einem organischen elektrolumineszenzelement |
| EP2423206B1 (de) | 2009-04-24 | 2014-01-08 | Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. | Aromatische aminderivate und deren verwendung in organischen elektrolumineszenzelementen |
| US8586203B2 (en) * | 2009-05-20 | 2013-11-19 | Universal Display Corporation | Metal complexes with boron-nitrogen heterocycle containing ligands |
| KR101314383B1 (ko) * | 2009-07-15 | 2013-10-04 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 신규한 화합물 및 이를 이용한 유기 전자 소자 |
| JPWO2011099232A1 (ja) * | 2010-02-12 | 2013-06-13 | 嶋田 豊司 | ハロゲノ芳香族化合物の製造方法 |
| US9287514B2 (en) | 2010-09-15 | 2016-03-15 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Metal complex and device using the metal complex |
| CN102464794B (zh) * | 2010-11-16 | 2014-05-07 | 海洋王照明科技股份有限公司 | 含苯并三唑基共聚物、其制备方法和应用 |
| US9353085B2 (en) * | 2011-08-26 | 2016-05-31 | E-Ray Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. | Compound for organic electroluminescent device and organic electroluminescent devices using the same |
| US9859517B2 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2018-01-02 | Nitto Denko Corporation | White organic light-emitting diode |
| KR102240991B1 (ko) | 2012-09-12 | 2021-04-16 | 이데미쓰 고산 가부시키가이샤 | 신규 화합물, 유기 일렉트로 루미네선스 소자용 재료, 유기 일렉트로 루미네선스 소자 및 전자 기기 |
| US9287513B2 (en) * | 2012-09-24 | 2016-03-15 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| CN103554444B (zh) * | 2013-10-21 | 2016-02-24 | 南京邮电大学 | 一种白光聚合物材料及其制备方法与应用 |
| KR101559428B1 (ko) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-10-13 | 주식회사 엠비케이 | 신규한 유기화합물, 이를 포함하는 유기전계발광소자 및 전자 기기 |
| WO2015068987A1 (ko) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-05-14 | (주)씨에스엘쏠라 | 신규한 유기화합물, 이를 포함하는 유기전계발광소자 및 전자 기기 |
| JP6252170B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-26 | 2017-12-27 | 東ソー株式会社 | アリールボロン酸アルキレンジオールエステル結晶の製造方法 |
| KR102277659B1 (ko) | 2014-07-03 | 2021-07-15 | 덕산네오룩스 주식회사 | 유기전기 소자용 화합물, 이를 이용한 유기전기소자 및 그 전자 장치 |
| KR102314735B1 (ko) * | 2014-07-24 | 2021-10-21 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 유기 발광 소자 및 이를 포함하는 표시 장치 |
| KR102287341B1 (ko) * | 2014-08-19 | 2021-08-06 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 유기 발광 소자 및 이를 포함하는 유기 발광 표시 장치 |
| CN104447358B (zh) * | 2014-10-28 | 2016-04-13 | 常州大学 | 一种合成n,n′,n″,n″′-四(3-溴苯基)-联苯胺方法 |
| US9882151B2 (en) * | 2014-11-14 | 2018-01-30 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| JP6925982B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-16 | 2021-08-25 | メルク パテント ゲーエムベーハー | 電子素子のための材料 |
| US10600966B2 (en) * | 2015-02-27 | 2020-03-24 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| CN104725378A (zh) * | 2015-04-01 | 2015-06-24 | 吉林奥来德光电材料股份有限公司 | 有机电致发光材料、其合成方法及其制成的器件 |
| US10147893B2 (en) * | 2015-04-10 | 2018-12-04 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Organometallic compound and organic light-emitting device including the same |
| CN106146810B (zh) * | 2016-07-13 | 2018-04-24 | 山西大学 | 一种发射红光的聚合物及其制备方法 |
| CN107868018A (zh) * | 2017-11-22 | 2018-04-03 | 遵义医学院 | N,n,n′,n′‑四[4‑(4′‑羧基)联苯基)]‑ 9,10‑蒽二胺合成法 |
| EP3503241B1 (de) * | 2017-12-22 | 2022-08-24 | Novaled GmbH | Elektronische vorrichtung und verfahren zur herstellung davon |
| CN110372863B (zh) * | 2019-08-31 | 2022-11-01 | 湘潭大学 | 一种具有聚集诱导发光性质的聚酰亚胺及其制备方法 |
| KR20210047392A (ko) | 2019-10-21 | 2021-04-30 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 유기 전계 발광 소자 및 유기 전계 발광 소자용 유기 금속 화합물 |
| CN111019098B (zh) * | 2019-12-23 | 2023-05-16 | 黑龙江大学 | 含联苯结构的三苯胺类苯并噻二唑聚合物及其制备方法和应用 |
| CN110951054A (zh) * | 2019-12-23 | 2020-04-03 | 黑龙江大学 | 含联苯结构的三苯胺类异靛蓝聚合物及其制备方法和应用 |
| US11917900B2 (en) * | 2020-01-28 | 2024-02-27 | Universal Display Corporation | Organic electroluminescent materials and devices |
| US20230340185A1 (en) | 2020-09-02 | 2023-10-26 | Lg Chem, Ltd | Polymer, Coating Composition Comprising Same, and Organic Light-Emitting Element Using Same |
| JP7512522B2 (ja) | 2020-09-18 | 2024-07-08 | 三星ディスプレイ株式會社 | 有機エレクトロルミネッセンス素子および光発生方法 |
| CN115449085B (zh) * | 2022-09-12 | 2023-08-08 | 西北工业大学 | 核壳型超支化聚硼硅氧烷红色延迟荧光材料及制备方法 |
| CN116574131A (zh) * | 2022-12-08 | 2023-08-11 | 四川阿格瑞新材料有限公司 | 一种电子传输材料及其在电致发光器件中的应用 |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1142895A1 (de) * | 1999-01-08 | 2001-10-10 | Chisso Corporation | Borderivate und organische elektrolumineszierende verbindungen |
| US20020019527A1 (en) * | 2000-04-27 | 2002-02-14 | Wei-Bo Wang | Substituted phenyl farnesyltransferase inhibitors |
| WO2002052661A1 (de) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-04 | Covion Organic Semiconductors Gmbh | Verwendung von bor- und aluminium-verbindungen in elektronik-bauteilen |
| WO2002051850A1 (de) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-04 | Covion Organic Semiconductors Gmbh | Bor- oder aluminium-spiroverbindungen, deren verwendung in electronikindustrie |
| JP2003031368A (ja) * | 2001-07-11 | 2003-01-31 | Konica Corp | 有機エレクトロルミネッセンス素子及び表示装置 |
| WO2003033617A1 (en) * | 2001-10-17 | 2003-04-24 | Universal Display Corporation | Phosphorescent compounds and devices comprising the same |
| WO2003095445A1 (en) * | 2002-05-07 | 2003-11-20 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | New organic compounds for electroluminescence and organic electroluminescent devices using the same |
| US20030229096A1 (en) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-12-11 | Bernd Buettelmann | Substituted imidazol-pyridazine derivatives |
| JP2004189705A (ja) * | 2002-12-13 | 2004-07-08 | Koei Chem Co Ltd | アリールボラン化合物の製造法 |
| US20040147742A1 (en) * | 2003-01-21 | 2004-07-29 | Wong Ken Tsung | Pyrimidine spirobifluorene oligomer for organic light-emitting device |
| US20040260090A1 (en) * | 2001-12-06 | 2004-12-23 | Kevin Treacher | Process for producing aryl-aryl coupled compounds |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19829947A1 (de) * | 1998-07-04 | 2000-01-05 | Bayer Ag | Elektrolumineszierende Anordnungen mit Bor-Chelaten |
| DE19858594A1 (de) * | 1998-12-18 | 2000-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Cyanbenzolboronsäuren |
| JP3759925B2 (ja) * | 2001-11-27 | 2006-03-29 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 発光素子 |
| US6734457B2 (en) * | 2001-11-27 | 2004-05-11 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Light emitting device |
| GB0226010D0 (en) * | 2002-11-08 | 2002-12-18 | Cambridge Display Tech Ltd | Polymers for use in organic electroluminescent devices |
| KR20050085622A (ko) * | 2002-12-13 | 2005-08-29 | 코닌클리케 필립스 일렉트로닉스 엔.브이. | 전자발광 디바이스 |
| WO2006117052A1 (de) * | 2005-05-03 | 2006-11-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate |
-
2006
- 2006-04-06 WO PCT/EP2006/003150 patent/WO2006117052A1/de not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2006-04-06 JP JP2008509318A patent/JP5242380B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2006-04-06 CN CN201310075065.8A patent/CN103204996B/zh active Active
- 2006-04-06 EP EP06724095.2A patent/EP1888706B1/de not_active Not-in-force
- 2006-04-06 KR KR1020077028263A patent/KR101289923B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2006-04-06 CN CN2006800154018A patent/CN101171320B/zh active Active
- 2006-04-06 US US11/912,939 patent/US8674141B2/en active Active
- 2006-04-28 TW TW095115339A patent/TW200710198A/zh unknown
-
2014
- 2014-01-14 US US14/154,323 patent/US9403849B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2016
- 2016-06-20 US US15/186,723 patent/US9871213B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1142895A1 (de) * | 1999-01-08 | 2001-10-10 | Chisso Corporation | Borderivate und organische elektrolumineszierende verbindungen |
| US20020019527A1 (en) * | 2000-04-27 | 2002-02-14 | Wei-Bo Wang | Substituted phenyl farnesyltransferase inhibitors |
| WO2002052661A1 (de) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-04 | Covion Organic Semiconductors Gmbh | Verwendung von bor- und aluminium-verbindungen in elektronik-bauteilen |
| WO2002051850A1 (de) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-04 | Covion Organic Semiconductors Gmbh | Bor- oder aluminium-spiroverbindungen, deren verwendung in electronikindustrie |
| JP2003031368A (ja) * | 2001-07-11 | 2003-01-31 | Konica Corp | 有機エレクトロルミネッセンス素子及び表示装置 |
| WO2003033617A1 (en) * | 2001-10-17 | 2003-04-24 | Universal Display Corporation | Phosphorescent compounds and devices comprising the same |
| US20040260090A1 (en) * | 2001-12-06 | 2004-12-23 | Kevin Treacher | Process for producing aryl-aryl coupled compounds |
| WO2003095445A1 (en) * | 2002-05-07 | 2003-11-20 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | New organic compounds for electroluminescence and organic electroluminescent devices using the same |
| US20030229096A1 (en) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-12-11 | Bernd Buettelmann | Substituted imidazol-pyridazine derivatives |
| JP2004189705A (ja) * | 2002-12-13 | 2004-07-08 | Koei Chem Co Ltd | アリールボラン化合物の製造法 |
| US20040147742A1 (en) * | 2003-01-21 | 2004-07-29 | Wong Ken Tsung | Pyrimidine spirobifluorene oligomer for organic light-emitting device |
Non-Patent Citations (21)
| Title |
|---|
| AMANN N ET AL: "Electron injection into DNA: synthesis and spectroscopic properties of pyrenyl-modified oligonucleotides", CHEMISTRY, A EUROPEAN JOURNAL, vol. 8, no. 21, 4 November 2002 (2002-11-04), pages 4877 - 4883, XP009060440, ISSN: 0947-6539 * |
| AMANN N ET AL: "Preparation of pyrenyl-modified nucleosides via Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions", SYNLETT, no. 5, May 2002 (2002-05-01), pages 687 - 691, XP009060442, ISSN: 0936-5214 * |
| BAUMGARTEN M ET AL: "Electronic decoupling in ground and excited states of asymmetric biaryls", JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY A, vol. 104, no. 6, 17 February 2000 (2000-02-17), pages 1130 - 1140, XP009060435, ISSN: 1089-5639 * |
| BEINHOFF M ET AL: "Synthesis and spectroscopic properties of arene-substituted pyrene derivatives as moel compounds for fluorescent polarity probes", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, no. 20, October 2001 (2001-10-01), pages 3819 - 3829, XP009060439, ISSN: 1434-193X * |
| CHOW H F ET AL: "Atropisomerism of the C-1-C'-1 axis of 2,2',8,8'-unsubstituted 1,1'-binaphthyl derivatives.", JOURNAL OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, vol. 66, no. 15, 27 July 2001 (2001-07-27), pages 5042 - 5047, XP001206512, ISSN: 0022-3263 * |
| CHOW H-F ET AL: "Multicenter homogeneous dendritic catalysts: The higher the generation, the better the reactivity and selectivity? - A comparative study of the catalytic efficiency of dendrimeric [1,1'-binaphthalene]-2,2'-diol-derived catalysts", HELVETICA CHIMICA ACTA, vol. 85, no. 10, October 2002 (2002-10-01), pages 3444 - 3454, XP009060464, ISSN: 0018-019X * |
| FINOCCHIARO P ET AL: "Conformational dynamics of alkoxydiarylboranes", JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY USA, vol. 95, no. 21, 17 October 1973 (1973-10-17), pages 7029 - 7036, XP009060436, ISSN: 0002-7863 * |
| GOSWAMI A ET AL: "Cobalt-mediated cyclooligomerisation reactions of borylacetylenes", EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF INORGANIC CHEMISTRY, no. 13, July 2004 (2004-07-01), pages 2635 - 2645, XP009060530 * |
| ISHIKURA M ET AL: "A simple and regioselective preparation of 2 or 3 substituted quinoline derivatives via dialkylquinolylboranes", HETEROCYCLES, vol. 23, no. 9, 1985, pages 2375 - 2386, XP009060474, ISSN: 0385-5414 * |
| ISHIYAMA T ET AL: "Synthesis of arylboronates via palladium-catalysed cross-coupling reaction of alkoxydiboron with aryl halides or triflates", SPECIAL PUBLICATION - ROYAL SOCIETY OF CHEMISTRY, vol. 201, 1997, pages 92 - 95, XP009060529 * |
| KAUPP GERD ET AL: "Waste-free and facile solid-state protection of diamines, anthranilic acid, diols, and polyols with phenylboronic acid.", CHEMISTRY, A EUROPEAN JOURNAL, vol. 9, no. 17, 5 September 2003 (2003-09-05), pages 4156 - 4161, XP009060528, ISSN: 0947-6539 * |
| KOCH K-H ET AL: "Polyarylenes and poly(arylenevinylene)s, V. Synthesis of tetraalkyl-substituted oligo(1,4-naphthylene)s and cyclisation to soluble oligo(peri-naphthylene)s", CHEMISCHE BERICHTE, vol. 124, no. 9, 1991, pages 2091 - 2100, XP009060533, ISSN: 0009-2940 * |
| MICHELS J J ET AL: "Synthesis of Conjugated Polyrotaxanes", CHEMISTRY, A EUROPEAN JOURNAL, vol. 9, no. 24, 15 December 2003 (2003-12-15), pages 6167 - 6176, XP009060485, ISSN: 0947-6539 * |
| MODRAKOWSKI C ET AL: "Synthesis of pyrene containing building blocks for dendrimer synthesis", SYNTHESIS, no. 14, 2001, pages 2143 - 2155, XP002970491, ISSN: 0039-7881 * |
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN vol. 2003, no. 05 12 May 2003 (2003-05-12) * |
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN vol. 2003, no. 12 5 December 2003 (2003-12-05) * |
| RAMSEY B G ET AL: "A laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry investigation of triarylboranes and tri-9-anthrylborane photolysis products", JOURNAL OF ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY, vol. 690, no. 4, 14 February 2005 (2005-02-14), pages 962 - 971, XP004736553, ISSN: 0022-328X * |
| TIRAPATTUR S ET AL: "Spectroscopic study of intermolecular interactions in various oligofluorenes: precursors of light-emitting polymers", JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY B, vol. 106, no. 25, 5 September 2002 (2002-09-05), pages 8959 - 8966, XP009060470, ISSN: 1089-5647 * |
| WONG KEN-TSUNG ET AL: "Efficient and convenient nonaqueous workup procedure for the preparation of arylboronic esters.", JOURNAL OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, vol. 67, no. 3, 8 February 2002 (2002-02-08), pages 1041 - 1044, XP009060532, ISSN: 0022-3263 * |
| WONG K-T ET AL: "Ter(9,9-diarylfluorene)s: Highly efficient blue emitter with promising electrochemical and thermal stability", JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, vol. 124, no. 39, 2 October 2002 (2002-10-02), pages 11576 - 11577, XP009060461, ISSN: 0002-7863 * |
| YAMASHITA M ET AL: "Synthesis of a versatile tridentate anthracene ligand and its application for the synthesis of hypervalent pentacoordinate boron compounds (10-B-5)", ANGEWANDTE CHEMIE INTERNATIONAL EDITION, vol. 39, no. 22, 17 November 2000 (2000-11-17), pages 4055 - 4058, XP009060434, ISSN: 1433-7851 * |
Cited By (601)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007065678A1 (de) * | 2005-12-08 | 2007-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektroluminieszenzvorrichtungen |
| US9017825B2 (en) | 2005-12-08 | 2015-04-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Anthracene derivatives and their use in organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2007108457A1 (ja) * | 2006-03-20 | 2007-09-27 | Pioneer Corporation | ピレン系有機化合物、トランジスタ材料及び発光トランジスタ素子 |
| JP2008101182A (ja) * | 2006-03-20 | 2008-05-01 | Kyoto Univ | ピレン系有機化合物、トランジスタ材料及び発光トランジスタ素子 |
| US8999521B2 (en) | 2006-03-24 | 2015-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2008006449A1 (de) | 2006-07-11 | 2008-01-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2008022633A2 (de) * | 2006-08-23 | 2008-02-28 | Johannes Werner | Halbleitende polyaddukte mit kolumnarer struktur |
| WO2008022633A3 (de) * | 2006-08-23 | 2009-03-19 | Johannes Werner | Halbleitende polyaddukte mit kolumnarer struktur |
| WO2008136492A1 (ja) * | 2007-04-27 | 2008-11-13 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | ピレン系高分子化合物及びそれを用いてなる発光素子 |
| JP2009096983A (ja) * | 2007-04-27 | 2009-05-07 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | ピレン系高分子化合物及びそれを用いてなる発光素子 |
| DE102007024850A1 (de) | 2007-05-29 | 2008-12-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US8658832B2 (en) | 2007-07-05 | 2014-02-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Luminescent metal complexes for organic electronic devices |
| US8610110B2 (en) | 2008-03-11 | 2013-12-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Optoelectronic component comprising neutral transition metal complexes |
| DE102008018670A1 (de) | 2008-04-14 | 2009-10-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US10538698B2 (en) | 2008-06-05 | 2020-01-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic device comprising metal complexes |
| DE102008027005A1 (de) | 2008-06-05 | 2009-12-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| US9481826B2 (en) | 2008-06-05 | 2016-11-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic device comprising metal complexes |
| US8618317B2 (en) | 2008-07-17 | 2013-12-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescence device |
| DE102008035413A1 (de) | 2008-07-29 | 2010-02-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102008036247A1 (de) | 2008-08-04 | 2010-02-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtungen enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| US8691400B2 (en) | 2008-08-04 | 2014-04-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices comprising metal complexes having isonitrile ligands |
| DE102008036982A1 (de) | 2008-08-08 | 2010-02-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| JP2015199740A (ja) * | 2008-09-03 | 2015-11-12 | ユニバーサル ディスプレイ コーポレイション | リン光性材料 |
| US8835021B2 (en) | 2008-09-22 | 2014-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescence devices |
| EP2712000A1 (de) | 2008-09-22 | 2014-03-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP2712001A1 (de) | 2008-09-22 | 2014-03-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US8637168B2 (en) | 2008-10-08 | 2014-01-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescence devices |
| DE102008050841B4 (de) | 2008-10-08 | 2019-08-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102008054141A1 (de) | 2008-10-31 | 2010-05-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2010049050A1 (de) | 2008-10-31 | 2010-05-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US8865321B2 (en) | 2008-11-11 | 2014-10-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescent devices |
| US8597798B2 (en) | 2008-11-13 | 2013-12-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102008063490A1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2010-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102008063490B4 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2023-06-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und Verfahren zum Einstellen des Farbortes einer weiß emittierenden Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102008063470A1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2010-07-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2010083871A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102009005290A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2010083872A2 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009005289B4 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2023-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und elektronische Vorrichtungen, enthaltend diese |
| DE102009005289A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2010083873A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009005288A1 (de) | 2009-01-20 | 2010-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US9034485B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2015-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| US9475792B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2016-10-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescence devices |
| DE102009005746A1 (de) | 2009-01-23 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US9006503B2 (en) | 2009-01-23 | 2015-04-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescence devices containing substituted benzo[C]phenanthrenes |
| US8710284B2 (en) | 2009-01-23 | 2014-04-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices containing substituted 10-benzo[c]phenanthrenes |
| WO2010083869A2 (de) | 2009-01-23 | 2010-07-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US9169282B2 (en) | 2009-02-02 | 2015-10-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes |
| WO2010086089A1 (de) | 2009-02-02 | 2010-08-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009007038A1 (de) | 2009-02-02 | 2010-08-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2010094378A1 (de) | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische vorrichtung |
| DE102009009277B4 (de) | 2009-02-17 | 2023-12-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und Verwendung von Verbindungen |
| US9066410B2 (en) | 2009-02-17 | 2015-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electronic device |
| DE102009009277A1 (de) | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung |
| US9074128B2 (en) | 2009-03-02 | 2015-07-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes having azaborol ligands and electronic device having the same |
| CN102317407A (zh) * | 2009-03-02 | 2012-01-11 | 默克专利有限公司 | 含有氮杂硼杂环戊烯配体的金属络合物和含有该金属络合物的电子器件 |
| WO2010099852A1 (de) | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe mit azaborol-liganden und elektronische vorrichtung damit |
| CN102317407B (zh) * | 2009-03-02 | 2014-12-31 | 默克专利有限公司 | 含有氮杂硼杂环戊烯配体的金属络合物和含有该金属络合物的电子器件 |
| DE102009011223A1 (de) | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2010102706A1 (de) | 2009-03-09 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009012346B4 (de) | 2009-03-09 | 2024-02-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung |
| DE102009012346A1 (de) | 2009-03-09 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2010102709A1 (de) | 2009-03-13 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US9085579B2 (en) | 2009-03-13 | 2015-07-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102009013041A1 (de) | 2009-03-13 | 2010-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009017064A1 (de) | 2009-04-09 | 2010-10-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2010115498A1 (de) | 2009-04-09 | 2010-10-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009022858A1 (de) | 2009-05-27 | 2011-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009023154A1 (de) | 2009-05-29 | 2011-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung, enthaltend mindestens eine Emitterverbindung und mindestens ein Polymer mit konjugationsunterbrechenden Einheiten |
| DE102009023155A1 (de) | 2009-05-29 | 2010-12-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2010149259A2 (en) | 2009-06-22 | 2010-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Conducting formulation |
| WO2010149258A1 (de) * | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polymere enthaltend substituierte anthracenyleinheiten, blends enthaltend diese polymere sowie vorrichtungen enthaltend diese polymere oder blends |
| US8557953B2 (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2013-10-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polymers comprising substituted anthracenyl units, blends comprising these polymers, and devices comprising these polymers or blends |
| DE102009031021A1 (de) | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011000455A1 (de) | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011006574A1 (de) | 2009-07-14 | 2011-01-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009032922A1 (de) | 2009-07-14 | 2011-01-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009032922B4 (de) | 2009-07-14 | 2024-04-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung, deren Verwendung sowie elektronische Vorrichtung |
| DE102009033371A1 (de) | 2009-07-16 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011012212A1 (de) | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009034625A1 (de) | 2009-07-27 | 2011-02-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011015265A2 (en) | 2009-08-04 | 2011-02-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices comprising multi cyclic hydrocarbons |
| WO2011032624A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011032686A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen zur herstellung von elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2011032626A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009041289A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102009041414A1 (de) | 2009-09-16 | 2011-03-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009042693A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009042680A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011035835A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011035836A1 (de) | 2009-09-23 | 2011-03-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102009048791A1 (de) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011042107A2 (de) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011044988A1 (de) | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102009049587A1 (de) | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2011054442A2 (de) | 2009-11-06 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102009053191A1 (de) | 2009-11-06 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102009052428A1 (de) | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindung für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011057701A1 (de) | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische verbindungen für elektroluminiszenz vorrichtungen |
| DE102009053382A1 (de) | 2009-11-14 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011057706A2 (de) | 2009-11-14 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102009053645A1 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011060877A2 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011060859A1 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009053644A1 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009053644B4 (de) | 2009-11-17 | 2019-07-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011060867A1 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2011-05-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige kondensierte heterozyklen für oleds |
| DE102009053836A1 (de) | 2009-11-18 | 2011-05-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102009057167A1 (de) | 2009-12-05 | 2011-06-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtung enthaltend Metallkomplexe |
| WO2011066898A1 (de) | 2009-12-05 | 2011-06-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung enthaltend metallkomplexe |
| WO2011076314A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electroluminescent formulations |
| WO2011076323A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations comprising phase-separated functional materials |
| WO2011076326A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electroluminescent functional surfactants |
| EP2725632A1 (de) | 2009-12-23 | 2014-04-30 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verwendung von zusammensetzungen mit inerten polymerbindern zur herstellung einer lichtmittierenden diode |
| WO2011076325A1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions comprising polymeric binders |
| WO2011076324A1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions comprising organic semiconducting compounds |
| WO2011076380A1 (en) | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition for the preparation of organic electronic (oe) devices |
| DE102010004803A1 (de) | 2010-01-16 | 2011-07-21 | Merck Patent GmbH, 64293 | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011085781A1 (de) | 2010-01-16 | 2011-07-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011088877A1 (de) | 2010-01-25 | 2011-07-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010005697A1 (de) | 2010-01-25 | 2011-07-28 | Merck Patent GmbH, 64293 | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010009193B4 (de) | 2010-02-24 | 2022-05-19 | MERCK Patent Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Zusammensetzung enthaltend Fluor-Fluor Assoziate, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung, deren Verwendung sowie organische elektronische Vorrichtung diese enthaltend |
| DE102010009193A1 (de) | 2010-02-24 | 2011-08-25 | Merck Patent GmbH, 64293 | Fluor-Fluor Assoziate |
| WO2011103953A1 (de) | 2010-02-24 | 2011-09-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Fluor-fluor assoziate |
| DE102010009903A1 (de) | 2010-03-02 | 2011-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011107186A2 (de) | 2010-03-02 | 2011-09-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2011110262A1 (de) | 2010-03-06 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010010481A1 (de) | 2010-03-06 | 2011-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010010631A1 (de) | 2010-03-09 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011110276A1 (de) | 2010-03-09 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2011110277A1 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Fibers in therapy and cosmetics |
| WO2011110275A2 (en) | 2010-03-11 | 2011-09-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Radiative fibers |
| WO2011116857A1 (en) | 2010-03-23 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2011116865A1 (de) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010012738A1 (de) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010013068A1 (de) | 2010-03-26 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011116869A1 (de) | 2010-03-26 | 2011-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2011128034A1 (en) | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition having improved performance |
| WO2011128035A1 (en) | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition and method for preparation of organic electronic devices |
| WO2011128017A1 (de) | 2010-04-14 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Überbrückte triarylamine und -phosphine als materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010014933A1 (de) | 2010-04-14 | 2011-10-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011134577A1 (de) | 2010-04-27 | 2011-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010018321A1 (de) | 2010-04-27 | 2011-10-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011137922A1 (de) | 2010-05-03 | 2011-11-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010019306A1 (de) | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011137951A1 (de) | 2010-05-04 | 2011-11-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011141109A1 (de) | 2010-05-11 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010020044A1 (de) | 2010-05-11 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2011141120A1 (de) | 2010-05-14 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010020567A1 (de) | 2010-05-14 | 2011-11-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| EP3309236A1 (de) | 2010-05-27 | 2018-04-18 | Merck Patent GmbH | Zusammensetzungen mit quantenpunkten |
| WO2011147523A1 (en) | 2010-05-27 | 2011-12-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation and method for preparation of organic electronic devices |
| WO2011147522A1 (en) | 2010-05-27 | 2011-12-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions comprising quantum dots |
| WO2011157339A1 (de) | 2010-06-15 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2011157346A1 (de) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010024335A1 (de) | 2010-06-18 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010024542A1 (de) | 2010-06-22 | 2011-12-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2011160757A1 (de) | 2010-06-22 | 2011-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010024897A1 (de) | 2010-06-24 | 2011-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2011160758A1 (de) | 2010-06-24 | 2011-12-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012007103A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe mit organischen liganden und deren verwendung in oleds |
| EP3121183A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2017-01-25 | Merck Patent GmbH | Organische komplexe enthaltend metalle |
| DE102010027218A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Komplexe enthaltend Metalle |
| EP2896627A1 (de) | 2010-07-15 | 2015-07-22 | Merck Patent GmbH | Organische Komplexe enthaltend Metalle |
| WO2012007086A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010027317A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012007087A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012007088A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010027316A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010027319A1 (de) | 2010-07-16 | 2012-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012013270A1 (en) | 2010-07-26 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Nanocrystals in devices |
| WO2012013272A1 (en) | 2010-07-26 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Quantum dots and hosts |
| WO2012013271A1 (de) | 2010-07-30 | 2012-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010033548A1 (de) | 2010-08-05 | 2012-02-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2012016630A1 (de) | 2010-08-05 | 2012-02-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012034627A1 (de) | 2010-09-15 | 2012-03-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010045405A1 (de) | 2010-09-15 | 2012-03-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010046412B4 (de) | 2010-09-23 | 2022-01-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metall-Ligand Koordinationsverbindungen |
| DE102010046412A1 (de) | 2010-09-23 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metall-Ligand Koordinationsverbindungen |
| DE102010046512A1 (de) | 2010-09-24 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phosphorhaltige Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012038029A1 (de) | 2010-09-24 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phosphorhaltige metallkomplexe |
| WO2012045384A1 (de) | 2010-10-09 | 2012-04-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102010048074A1 (de) | 2010-10-09 | 2012-04-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102010048608A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102010048607A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2012048781A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien auf basis von triphenylen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012048780A1 (de) | 2010-10-15 | 2012-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012069121A1 (de) | 2010-11-24 | 2012-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012079678A1 (de) | 2010-12-13 | 2012-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte tetraarylbenzole |
| DE102010054316A1 (de) | 2010-12-13 | 2012-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte Tetraarylbenzole |
| WO2012079673A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012079741A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102010054525A1 (de) | 2010-12-15 | 2012-04-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010055902A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102010055901A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012084115A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012084114A1 (de) | 2010-12-23 | 2012-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012095143A1 (de) | 2011-01-13 | 2012-07-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102012000064A1 (de) | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP2482159A2 (de) | 2011-01-28 | 2012-08-01 | Honeywell International, Inc. | Verfahren und umkonfigurierbare System zur Optimierung der Leistung eines zustandsabhängigen Wartungssystems |
| DE102011010841A1 (de) | 2011-02-10 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | (1,3)-Dioxan-5-on-Verbindungen |
| WO2012107158A1 (de) | 2011-02-10 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | 1,3 - dioxan-5-on-verbindungen |
| DE102011011104A1 (de) | 2011-02-12 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte Dibenzonaphtacene |
| WO2012107163A1 (de) | 2011-02-12 | 2012-08-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte dibenzonaphtacene |
| WO2012110178A1 (en) | 2011-02-14 | 2012-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Device and method for treatment of cells and cell tissue |
| DE102011011539A1 (de) | 2011-02-17 | 2012-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2012110182A1 (de) | 2011-02-17 | 2012-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012126566A1 (en) | 2011-03-24 | 2012-09-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic ionic functional materials |
| WO2012136296A1 (de) | 2011-04-04 | 2012-10-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2012136295A1 (de) | 2011-04-05 | 2012-10-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012139692A1 (de) | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012139693A1 (de) | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012143079A1 (de) | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012143080A2 (de) | 2011-04-18 | 2012-10-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2012149992A1 (de) | 2011-05-04 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur aufbewahrung von frischwaren |
| WO2012150001A1 (de) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012149999A1 (de) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2012152366A1 (en) | 2011-05-12 | 2012-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic ionic compounds, compositions and electronic devices |
| DE102012007810A1 (de) | 2011-05-16 | 2012-11-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012163480A1 (de) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-12-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische vorrichtung |
| DE102011102586A1 (de) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-11-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung |
| WO2012163465A1 (de) | 2011-06-03 | 2012-12-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2012163471A1 (de) | 2011-06-03 | 2012-12-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2013000531A1 (de) | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2013013754A1 (en) | 2011-07-25 | 2013-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Copolymers with functionalized side chains |
| WO2013017189A1 (de) | 2011-07-29 | 2013-02-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3439065A1 (de) | 2011-08-03 | 2019-02-06 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013017192A1 (de) | 2011-08-03 | 2013-02-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013020631A1 (de) | 2011-08-10 | 2013-02-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102012016192A1 (de) | 2011-08-19 | 2013-02-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013026515A1 (de) | 2011-08-22 | 2013-02-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2013041176A1 (de) | 2011-09-21 | 2013-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazolderivate für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013050101A1 (de) | 2011-10-06 | 2013-04-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| DE102011116165A1 (de) | 2011-10-14 | 2013-04-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Benzodioxepin-3-on-Verbindungen |
| WO2013056776A1 (de) | 2011-10-20 | 2013-04-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013060418A1 (en) | 2011-10-27 | 2013-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2013060411A1 (de) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hyperverzweigte polymere, verfahren zu deren herstellung sowie deren verwendung in elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2013064206A1 (de) | 2011-11-01 | 2013-05-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| WO2013083216A1 (de) | 2011-11-17 | 2013-06-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Spiro -dihydroacridinderivate und ihre verwendung als materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013087142A1 (de) | 2011-12-12 | 2013-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102012022880A1 (de) | 2011-12-22 | 2013-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische Vorrichtungen enthaltend organische Schichten |
| WO2013097920A1 (en) | 2011-12-27 | 2013-07-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes comprising 1,2,3-triazoles |
| WO2013107487A1 (en) | 2012-01-16 | 2013-07-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic metal complexes |
| WO2013113349A1 (en) | 2012-01-30 | 2013-08-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Nanocrystals on fibers |
| EP3101088A1 (de) | 2012-02-14 | 2016-12-07 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013120577A1 (en) | 2012-02-14 | 2013-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Spirobifluorene compounds for organic electroluminescent devices |
| EP3235892A1 (de) | 2012-02-14 | 2017-10-25 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4369378A2 (de) | 2012-03-15 | 2024-05-15 | Merck Patent GmbH | Elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3460864A1 (de) | 2012-03-15 | 2019-03-27 | Merck Patent GmbH | Elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013135352A1 (de) | 2012-03-15 | 2013-09-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2013139431A1 (de) | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | 9,9'-spirobixanthenderivate für elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2013174471A1 (en) | 2012-05-24 | 2013-11-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metal complexes comprising condensed heteroaromatic rings |
| WO2013182263A1 (de) | 2012-06-06 | 2013-12-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phenanthrenverbindungen für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102012011335A1 (de) | 2012-06-06 | 2013-12-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für Organische Elekronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2013185871A1 (en) | 2012-06-12 | 2013-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| WO2014008967A2 (de) | 2012-07-10 | 2014-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2014008982A1 (de) | 2012-07-13 | 2014-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014015938A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Derivate von 2-diarylaminofluoren und diese enthaltnde organische elektronische verbindungen |
| WO2014015937A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen und organische elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| WO2014015935A2 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014015931A1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2014-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP3424907A2 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2019-01-09 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE202013012401U1 (de) | 2012-07-23 | 2016-10-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen und Organische Elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| WO2014023377A2 (de) | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| EP3424936A1 (de) | 2012-08-07 | 2019-01-09 | Merck Patent GmbH | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014023388A1 (de) | 2012-08-10 | 2014-02-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2014044344A1 (de) | 2012-09-18 | 2014-03-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014044347A1 (de) | 2012-09-20 | 2014-03-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2014056567A1 (de) | 2012-10-11 | 2014-04-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102012020167A1 (de) | 2012-10-13 | 2014-04-17 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| EP3806176A1 (de) | 2012-10-31 | 2021-04-14 | Merck Patent GmbH | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2014067614A1 (de) | 2012-10-31 | 2014-05-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| DE102012021650A1 (de) | 2012-11-03 | 2014-05-08 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| EP3378857A1 (de) | 2012-11-12 | 2018-09-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014079532A1 (de) | 2012-11-20 | 2014-05-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierung in hochreinem l?sungsmittel zur herstellung elektronischer vorrichtungen |
| WO2014082705A1 (de) | 2012-11-30 | 2014-06-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2014106524A2 (de) | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014106522A1 (de) | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2014106523A1 (de) * | 2013-01-03 | 2014-07-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| US11631816B2 (en) | 2013-01-03 | 2023-04-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic device |
| US9559311B2 (en) | 2013-02-22 | 2017-01-31 | Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. | Anthracene derivative, organic-electroluminescence-device material, organic electroluminescence device, and electronic equipment |
| DE102013008189A1 (de) | 2013-05-14 | 2014-12-04 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2015014427A1 (de) | 2013-07-29 | 2015-02-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrooptische vorrichtung und deren verwendung |
| EP3647393A1 (de) | 2013-07-30 | 2020-05-06 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3712229A1 (de) | 2013-07-30 | 2020-09-23 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3904361A2 (de) | 2013-10-02 | 2021-11-03 | Merck Patent GmbH | Borenthaltende verbindungen |
| EP3693437A1 (de) | 2013-12-06 | 2020-08-12 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3345984A1 (de) | 2013-12-06 | 2018-07-11 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen und organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2015082037A1 (en) | 2013-12-06 | 2015-06-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compositions containing a polymeric binder which comprises acrylic and/or methacrylic acid ester units |
| WO2015082046A2 (de) | 2013-12-06 | 2015-06-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituierte oxepine |
| WO2015086108A1 (de) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP3708634A1 (de) | 2013-12-19 | 2020-09-16 | Merck Patent GmbH | Heterocyclische spiroverbindungen |
| EP4438693A2 (de) | 2013-12-19 | 2024-10-02 | Merck Patent GmbH | Heterocyclische spiroverbindungen |
| WO2015090504A2 (de) | 2013-12-19 | 2015-06-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische spiroverbindungen |
| EP2927221A1 (de) | 2014-03-31 | 2015-10-07 | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | Diaminverbindungen für phosphoreszierende diazaborolmetallkomplexe und elektrolumineszente vorrichtungen |
| EP2927300A1 (de) | 2014-03-31 | 2015-10-07 | Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation | Phenylenediaminverbindungen für phosphoreszierende diazaborolmetallkomplexe |
| EP3533794A2 (de) | 2014-04-30 | 2019-09-04 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2015165563A1 (de) | 2014-04-30 | 2015-11-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2015169412A1 (de) | 2014-05-05 | 2015-11-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102015006708A1 (de) | 2014-06-12 | 2015-12-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102014008722A1 (de) | 2014-06-18 | 2015-12-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen |
| DE102014008722B4 (de) | 2014-06-18 | 2024-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektronische Vorrichtungen, Formulierung diese enthaltend, Verwendung der Zusammensetzung, Verwendung der Formulierung sowie organische elektronische Vorrichtung enthaltend die Zusammensetzung |
| WO2015192941A1 (de) | 2014-06-18 | 2015-12-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2015197156A1 (de) | 2014-06-25 | 2015-12-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP2960315A1 (de) | 2014-06-27 | 2015-12-30 | cynora GmbH | Organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung |
| EP2963044A1 (de) | 2014-06-30 | 2016-01-06 | cynora GmbH | Zweikernige Metall(I)-Komplexe mit tetradentaten Liganden für optoelektronische Anwendungen |
| WO2016001064A1 (de) | 2014-06-30 | 2016-01-07 | Cynora Gmbh | Zweikernige metall(i)-komplexe mit tetradentaten liganden für optoelektronische anwendungen |
| EP4037000A1 (de) | 2014-07-21 | 2022-08-03 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102014012818A1 (de) | 2014-08-28 | 2016-03-03 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2016034262A1 (de) | 2014-09-05 | 2016-03-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2016055557A1 (de) | 2014-10-08 | 2016-04-14 | Cynora Gmbh | Metall-komplexe mit tridentaten liganden für optoelektronische anwendungen |
| WO2016074755A1 (de) | 2014-11-11 | 2016-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2016079097A1 (de) | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-26 | Cynora Gmbh | Kupfer(i)komplexe für optoelektronische anwendungen |
| WO2016091353A1 (de) | 2014-12-12 | 2016-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische verbindungen mit löslichen gruppen |
| WO2016107663A1 (de) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulierungen und elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2016120007A1 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations with a low particle content |
| WO2016119992A1 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2016-08-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2016124304A1 (de) | 2015-02-03 | 2016-08-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2016155866A1 (en) | 2015-03-30 | 2016-10-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material comprising a siloxane solvent |
| WO2016198144A1 (en) | 2015-06-10 | 2016-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2016198141A1 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2016-12-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Esters containing non-aromatic cycles as solvents for oled formulations |
| EP3581633A1 (de) | 2015-06-12 | 2019-12-18 | Merck Patent GmbH | Ester mit nichtaromatischen zyklen als lösungsmittel für oled-formulierungen |
| WO2017008883A1 (en) | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Composition comprising organic semiconducting compounds |
| WO2017012687A1 (en) | 2015-07-22 | 2017-01-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017012694A1 (en) | 2015-07-23 | 2017-01-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phenyl derivatives substituted with at least two electron acceptors and at least two electron donors for use in organic electronic devices |
| EP4236652A2 (de) | 2015-07-29 | 2023-08-30 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4301110A2 (de) | 2015-07-30 | 2024-01-03 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2017016630A1 (en) | 2015-07-30 | 2017-02-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017025166A1 (en) | 2015-08-13 | 2017-02-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hexamethylindanes |
| WO2017028940A1 (en) | 2015-08-14 | 2017-02-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Phenoxazine derivatives for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017036572A1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material comprising an epoxy group containing solvent |
| WO2017036573A1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| DE102015013381A1 (de) | 2015-10-14 | 2017-04-20 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2017071791A1 (en) | 2015-10-27 | 2017-05-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE102015016016A1 (de) | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-14 | Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2017097397A1 (de) | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2017097391A1 (en) | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing ketones comprising non-aromatic cycles |
| WO2017102048A1 (en) | 2015-12-15 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Esters containing aromatic groups as solvents for organic electronic formulations |
| EP4084109A1 (de) | 2015-12-15 | 2022-11-02 | Merck Patent GmbH | Ester mit aromatischen gruppen als lösungsmittel für organische elektronische formulierungen |
| WO2017102052A1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing a solid solvent |
| WO2017102049A1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulations containing a mixture of at least two different solvents |
| WO2017133829A1 (de) | 2016-02-05 | 2017-08-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2017140404A1 (en) | 2016-02-17 | 2017-08-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2017148565A1 (de) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2017148564A1 (de) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-09-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| DE102016003104A1 (de) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Behälter umfassend eine Formulierung enthaltend mindestens einen organischen Halbleiter |
| WO2017157783A1 (de) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Behälter umfassend eine formulierung enthaltend mindestens einen organischen halbleiter |
| WO2017157983A1 (de) | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit spirobifluoren-strukturen |
| WO2017178311A1 (de) | 2016-04-11 | 2017-10-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen mit dibenzofuran- und/oder dibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| WO2017186760A1 (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-11-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017194435A1 (de) | 2016-05-11 | 2017-11-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzungen für elektrochemische zellen |
| EP3978477A2 (de) | 2016-06-03 | 2022-04-06 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszente vorrichtungen |
| WO2017207596A1 (en) | 2016-06-03 | 2017-12-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2017216129A1 (en) | 2016-06-16 | 2017-12-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2017216128A1 (en) | 2016-06-17 | 2017-12-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018001928A1 (en) | 2016-06-28 | 2018-01-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018001990A1 (de) | 2016-06-30 | 2018-01-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur auftrennung von enantiomerenmischungen von metallkomplexen |
| EP3792235A1 (de) | 2016-07-08 | 2021-03-17 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszente vorrichtungen |
| WO2018007421A1 (en) | 2016-07-08 | 2018-01-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018011186A1 (de) | 2016-07-14 | 2018-01-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018019688A1 (de) | 2016-07-25 | 2018-02-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe für den einsatz als emitter in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018019687A1 (de) | 2016-07-25 | 2018-02-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Di- und oligonukleare metallkomplexe mit tripodalen bidentaten teilliganden sowie deren verwendung in elektronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2018024719A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 | 2018-02-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018041769A1 (de) | 2016-08-30 | 2018-03-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bl- und trinukleare metallkomplexe aufgebaut aus zwei miteinander verknüpften tripodalen hexadentaten liganden zur verwendung in elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018050583A1 (de) | 2016-09-14 | 2018-03-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit carbazol-strukturen |
| WO2018050584A1 (de) | 2016-09-14 | 2018-03-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit spirobifluoren-strukturen |
| WO2018054798A1 (de) | 2016-09-21 | 2018-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Binukleare metallkomplexe für den einsatz als emitter in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018060307A1 (de) | 2016-09-30 | 2018-04-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit diazadibenzofuran- oder diazadibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| WO2018060218A1 (de) | 2016-09-30 | 2018-04-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazole mit diazadibenzofuran- oder diazadibenzothiophen-strukturen |
| EP4255151A2 (de) | 2016-10-10 | 2023-10-04 | Merck Patent GmbH | Spiro[fluoren-9,9'-(thio)xanthen] verbindungen |
| WO2018069167A1 (de) | 2016-10-10 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| EP4113643A1 (de) | 2016-10-10 | 2023-01-04 | Merck Patent GmbH | Elektronische vorrichtung |
| WO2018069197A1 (de) | 2016-10-12 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018069196A1 (de) | 2016-10-12 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Binukleare metallkomplexe sowie elektronische vorrichtungen, insbesondere organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen, enthaltend diese metallkomplexe |
| WO2018069273A1 (de) | 2016-10-13 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| DE102017008794A1 (de) | 2016-10-17 | 2018-04-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien zur Verwendung in elektronischen Vorrichtungen |
| WO2018077769A1 (de) | 2016-10-25 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2018077662A1 (en) | 2016-10-31 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018077660A1 (en) | 2016-10-31 | 2018-05-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018083053A1 (de) | 2016-11-02 | 2018-05-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018087020A1 (en) | 2016-11-08 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds for electronic devices |
| WO2018087022A1 (de) | 2016-11-09 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4271163A2 (de) | 2016-11-14 | 2023-11-01 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen mit einer akzeptor- und einer donorgruppe |
| WO2018087346A1 (de) | 2016-11-14 | 2018-05-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit einer akzeptor- und einer donorgruppe |
| WO2018091435A1 (en) | 2016-11-17 | 2018-05-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018095839A1 (de) | 2016-11-22 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbrückte triarylamine für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018095940A1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bisbenzofuran-fused indeno[1,2-b]fluorene derivatives and related compounds as materials for organic electroluminescent devices (oled) |
| WO2018095888A1 (en) | 2016-11-25 | 2018-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bisbenzofuran-fused 2,8-diaminoindeno[1,2-b]fluorene derivatives and related compounds as materials for organic electroluminescent devices (oled) |
| WO2018099846A1 (de) | 2016-11-30 | 2018-06-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit valerolaktam-strukturen |
| WO2018104193A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018104194A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018104195A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen zur verwendung in oleds |
| EP3978491A1 (de) | 2016-12-05 | 2022-04-06 | Merck Patent GmbH | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2018104202A1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2018-06-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Preparation process for an electronic device |
| WO2018108760A1 (en) | 2016-12-13 | 2018-06-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018114744A1 (en) | 2016-12-20 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | A white light emitting solid state light source |
| WO2018114883A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mischungen umfassend mindestens zwei organisch funktionelle verbindungen |
| WO2018114882A1 (de) | 2016-12-22 | 2018-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018127465A1 (de) | 2017-01-04 | 2018-07-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018138039A1 (de) | 2017-01-25 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazolderivate |
| WO2018138319A1 (en) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic electroluminescence (el) element |
| WO2018138306A1 (de) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018138318A1 (en) | 2017-01-30 | 2018-08-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2018141706A1 (de) | 2017-02-02 | 2018-08-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018149769A1 (de) | 2017-02-14 | 2018-08-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018158232A1 (en) | 2017-03-01 | 2018-09-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organic electroluminescent device |
| WO2018157981A1 (de) | 2017-03-02 | 2018-09-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018166932A1 (de) | 2017-03-13 | 2018-09-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit arylamin-strukturen |
| WO2018166934A1 (de) | 2017-03-15 | 2018-09-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2018177981A1 (de) | 2017-03-29 | 2018-10-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische verbindungen |
| WO2018178136A1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2018-10-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Printing method for an organic light emitting diode (oled) |
| WO2018189050A1 (en) | 2017-04-10 | 2018-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018189134A1 (de) | 2017-04-13 | 2018-10-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018197447A1 (de) | 2017-04-25 | 2018-11-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018202603A1 (en) | 2017-05-03 | 2018-11-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2018206526A1 (en) | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organoboron complexes for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018206537A1 (en) | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Carbazole-based bodipys for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2018215318A1 (de) | 2017-05-22 | 2018-11-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Hexazyklische heteroaromatische verbindungen für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018234220A1 (de) | 2017-06-21 | 2018-12-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2018234346A1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2018-12-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2019002198A1 (en) | 2017-06-26 | 2019-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | HOMOGENEOUS MIXTURES |
| WO2019002190A1 (en) | 2017-06-28 | 2019-01-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ELECTRONIC DEVICES |
| WO2019007823A1 (en) | 2017-07-03 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | LOW-PHENOL IMPURITY FORMULATIONS |
| WO2019007825A1 (en) | 2017-07-03 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENCE DEVICE |
| WO2019007867A1 (de) | 2017-07-05 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019007866A1 (de) | 2017-07-05 | 2019-01-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP4186898A1 (de) | 2017-07-05 | 2023-05-31 | Merck Patent GmbH | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische verbindungen |
| WO2019016184A1 (en) | 2017-07-18 | 2019-01-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | FORMULATION OF AN ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL MATERIAL |
| WO2019020538A1 (de) | 2017-07-25 | 2019-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019020654A1 (en) | 2017-07-28 | 2019-01-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | SPIROBIFLUORENE DERIVATIVES FOR USE IN ELECTRONIC DEVICES |
| WO2019048443A1 (de) | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019052933A1 (de) | 2017-09-12 | 2019-03-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| US11370965B2 (en) | 2017-09-12 | 2022-06-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| CN111065640B (zh) * | 2017-09-12 | 2023-04-18 | 默克专利有限公司 | 用于有机电致发光器件的材料 |
| CN111065640A (zh) * | 2017-09-12 | 2020-04-24 | 默克专利有限公司 | 用于有机电致发光器件的材料 |
| WO2019068679A1 (en) | 2017-10-06 | 2019-04-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2019076789A1 (en) | 2017-10-17 | 2019-04-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | MATERIALS FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DEVICES |
| WO2019081391A1 (de) | 2017-10-24 | 2019-05-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019096717A2 (de) | 2017-11-14 | 2019-05-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019101719A1 (de) | 2017-11-23 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP4242286A2 (de) | 2017-11-23 | 2023-09-13 | Merck Patent GmbH | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019101835A1 (en) | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019101833A1 (en) | 2017-11-24 | 2019-05-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019115423A1 (de) | 2017-12-13 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019115573A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2019115577A1 (en) | 2017-12-15 | 2019-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Substituted aromatic amines for use in organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019121458A1 (de) | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindung zur verwendung in electronischen vorrichtungen |
| WO2019121483A1 (en) | 2017-12-20 | 2019-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatic compounds |
| EP4451832A2 (de) | 2017-12-20 | 2024-10-23 | Merck Patent GmbH | Heteroaromatische verbindungen |
| WO2019145316A1 (de) | 2018-01-25 | 2019-08-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019158453A1 (de) | 2018-02-13 | 2019-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019162483A1 (en) | 2018-02-26 | 2019-08-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2019170572A1 (en) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019170578A1 (en) | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019175149A1 (en) | 2018-03-16 | 2019-09-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2019179909A1 (de) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2019229011A1 (de) | 2018-05-30 | 2019-12-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2019233904A1 (de) | 2018-06-07 | 2019-12-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2019238782A1 (en) | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2020011686A1 (de) | 2018-07-09 | 2020-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020016264A1 (en) | 2018-07-20 | 2020-01-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043640A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043657A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020043646A1 (en) | 2018-08-28 | 2020-03-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| DE202019005924U1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2023-05-10 | MERCK Patent Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Elektrolumineszierende Vorrichtungen |
| WO2020053150A1 (en) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020053314A1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| WO2020053315A1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2020-03-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Elektrolumineszierende vorrichtungen |
| DE202019005923U1 (de) | 2018-09-12 | 2023-06-27 | MERCK Patent Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Elektrolumineszierende Vorrichtungen |
| DE102018122708A1 (de) * | 2018-09-17 | 2020-03-19 | Novaled Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung, organisches halbleitendes Material und eine Boranverbindung |
| WO2020064582A1 (de) | 2018-09-24 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von granulat |
| WO2020064666A1 (de) | 2018-09-27 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen, die in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung als aktive verbindungen einsetzbar sind |
| WO2020064662A2 (de) | 2018-09-27 | 2020-04-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von sterisch gehinderten stickstoffhaltigen heteroaromatischen verbindungen |
| EP4190880A1 (de) | 2018-09-27 | 2023-06-07 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen, die in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung als aktive verbindungen einsetzbar sind |
| WO2020089138A1 (en) | 2018-10-31 | 2020-05-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020094539A1 (de) | 2018-11-05 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | In einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2020094542A1 (de) | 2018-11-06 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | 5,6-diphenyl-5,6-dihydro-dibenz[c,e][1,2]azaphosphorin- und 6-phenyl-6h-dibenzo[c,e][1,2]thiazin-5,5-dioxid-derivate und ähnliche verbindungen als organische elektrolumineszenzmaterialien für oleds |
| WO2020094538A1 (en) | 2018-11-06 | 2020-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2020099349A1 (de) | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zur herstellung einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2020099307A1 (de) | 2018-11-15 | 2020-05-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020127165A1 (de) | 2018-12-19 | 2020-06-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020148243A1 (en) | 2019-01-16 | 2020-07-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020165064A1 (de) | 2019-02-11 | 2020-08-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mononukleare iridiumkomplexe mit drei ortho-metallierten bidentaten liganden und optischer orientierungsanisotropie |
| WO2020169241A1 (de) | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zusammensetzung für organische elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2020178230A1 (en) | 2019-03-04 | 2020-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Ligands for nano-sized materials |
| WO2020182779A1 (de) | 2019-03-12 | 2020-09-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020187865A1 (de) | 2019-03-20 | 2020-09-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020193447A1 (de) | 2019-03-25 | 2020-10-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2020208051A1 (en) | 2019-04-11 | 2020-10-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2020212296A1 (de) | 2019-04-15 | 2020-10-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2021037401A1 (de) | 2019-08-26 | 2021-03-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021043703A1 (de) | 2019-09-02 | 2021-03-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021043755A1 (de) | 2019-09-03 | 2021-03-11 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021052924A1 (en) | 2019-09-16 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021052921A1 (de) | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mischung von zwei hostmaterialien und organische elektrolumineszierende vorrichtung damit |
| WO2021053046A1 (de) | 2019-09-20 | 2021-03-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Peri-kondensierte heterozyklische verbindungen als materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2021078710A1 (en) | 2019-10-22 | 2021-04-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021078831A1 (de) | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | In einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2021089450A1 (en) | 2019-11-04 | 2021-05-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021094269A1 (en) | 2019-11-12 | 2021-05-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021110741A1 (en) | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021110720A1 (de) | 2019-12-04 | 2021-06-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2021122535A1 (de) | 2019-12-17 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021122538A1 (de) | 2019-12-18 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021122740A1 (de) | 2019-12-19 | 2021-06-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polycyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021151922A1 (de) | 2020-01-29 | 2021-08-05 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Benzimidazol-derivate |
| WO2021170522A1 (de) | 2020-02-25 | 2021-09-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verwendung von heterocyclischen verbindungen in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung |
| WO2021175706A1 (de) | 2020-03-02 | 2021-09-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verwendung von sulfonverbindungen in einer organischen elektronischen vorrichtung |
| WO2021180950A1 (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2021-09-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021185829A1 (de) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-09-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021185712A1 (de) | 2020-03-17 | 2021-09-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021191058A1 (en) | 2020-03-23 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2021191117A1 (de) | 2020-03-24 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| DE102020108402B4 (de) | 2020-03-26 | 2021-11-11 | Novaled Gmbh | Organische elektronische Vorrichtung, organisches halbleitendes Material, eine Trioxatriborinanverbindung und deren Verwendung |
| WO2021191183A1 (de) | 2020-03-26 | 2021-09-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021198213A1 (de) | 2020-04-02 | 2021-10-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021204646A1 (de) | 2020-04-06 | 2021-10-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Polycyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2021213918A1 (en) | 2020-04-21 | 2021-10-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2021213917A1 (en) | 2020-04-21 | 2021-10-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Emulsions comprising organic functional materials |
| WO2021160898A2 (de) | 2020-05-27 | 2021-08-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2021254984A1 (de) | 2020-06-18 | 2021-12-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Indenoazanaphthaline |
| WO2021259824A1 (de) | 2020-06-23 | 2021-12-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung einer mischung |
| WO2022002772A1 (de) | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022002771A1 (de) | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022017998A1 (en) | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022017997A1 (en) | 2020-07-22 | 2022-01-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022029096A1 (de) | 2020-08-06 | 2022-02-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022034046A1 (de) | 2020-08-13 | 2022-02-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2022038065A1 (de) | 2020-08-18 | 2022-02-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022038066A1 (de) | 2020-08-19 | 2022-02-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022069380A1 (de) | 2020-09-29 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Mononukleare tripodale hexadentate iridium komplexe zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2022069421A1 (de) | 2020-09-30 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Zur strukturierung von funktionalen schichten organischer elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen einsetzbare verbindungen |
| WO2022069422A1 (de) | 2020-09-30 | 2022-04-07 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen zur strukturierung von funktionalen schichten organischer elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022079067A1 (de) | 2020-10-16 | 2022-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen mit heteroatomen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022079068A1 (de) | 2020-10-16 | 2022-04-21 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022101171A1 (de) | 2020-11-10 | 2022-05-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Schwefelhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022117473A1 (de) | 2020-12-02 | 2022-06-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022122607A1 (en) | 2020-12-08 | 2022-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | An ink system and a method for inkjet printing |
| WO2022122682A2 (de) | 2020-12-10 | 2022-06-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022129116A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Indolo[3.2.1-jk]carbazole-6-carbonitril-derivate als blau fluoreszierende emitter zur verwendung in oleds |
| WO2022129113A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heteroaromaten für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022129114A1 (de) | 2020-12-18 | 2022-06-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022148717A1 (de) | 2021-01-05 | 2022-07-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022157343A1 (de) | 2021-01-25 | 2022-07-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022184601A1 (de) | 2021-03-02 | 2022-09-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022194799A1 (de) | 2021-03-18 | 2022-09-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heteroaromatische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022214566A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022214506A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2022214507A1 (en) | 2021-04-09 | 2022-10-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| EP4079742A1 (de) | 2021-04-14 | 2022-10-26 | Merck Patent GmbH | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2022223675A1 (en) | 2021-04-23 | 2022-10-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2022229298A1 (de) | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022229126A1 (de) | 2021-04-29 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022229234A1 (de) | 2021-04-30 | 2022-11-03 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2022243403A1 (de) | 2021-05-21 | 2022-11-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur kontinuierlichen aufreinigung von mindestens einem funktionalen material und vorrichtung zur kontinuierlichen aufreinigung von mindestens einem funktionalen material |
| WO2022200638A1 (de) | 2021-07-06 | 2022-09-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023012084A1 (en) | 2021-08-02 | 2023-02-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | A printing method by combining inks |
| WO2023041454A1 (de) | 2021-09-14 | 2023-03-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Borhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023052272A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052313A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052275A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023052314A1 (de) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023057327A1 (en) | 2021-10-05 | 2023-04-13 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for forming an organic element of an electronic device |
| WO2023072799A1 (de) | 2021-10-27 | 2023-05-04 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Bor- und stickstoffhaltige, heterocyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023094412A1 (de) | 2021-11-25 | 2023-06-01 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023099543A1 (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2023-06-08 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Compounds having fluorene structures |
| WO2023110742A1 (de) | 2021-12-13 | 2023-06-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023117837A1 (de) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von deuterierten organischen verbindungen |
| WO2023117835A1 (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices |
| WO2023117836A1 (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2023-06-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Electronic devices |
| WO2023152063A1 (de) | 2022-02-09 | 2023-08-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023152346A1 (de) | 2022-02-14 | 2023-08-17 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023161168A1 (de) | 2022-02-23 | 2023-08-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Aromatische heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023161167A1 (de) | 2022-02-23 | 2023-08-31 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023213837A1 (de) | 2022-05-06 | 2023-11-09 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2023222559A1 (de) | 2022-05-18 | 2023-11-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Verfahren zur herstellung von deuterierten organischen verbindungen |
| WO2023237458A1 (en) | 2022-06-07 | 2023-12-14 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method of printing a functional layer of an electronic device by combining inks |
| WO2023247345A1 (de) | 2022-06-20 | 2023-12-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| WO2023247338A1 (de) | 2022-06-20 | 2023-12-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024013004A1 (de) | 2022-07-11 | 2024-01-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| EP4311849A1 (de) | 2022-07-27 | 2024-01-31 | UDC Ireland Limited | Metallkomplexe |
| WO2024061948A1 (de) | 2022-09-22 | 2024-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffenthaltende heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024061942A1 (de) | 2022-09-22 | 2024-03-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffenthaltende verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024094592A2 (de) | 2022-11-01 | 2024-05-10 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024105066A1 (en) | 2022-11-17 | 2024-05-23 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2024126635A1 (en) | 2022-12-16 | 2024-06-20 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Formulation of an organic functional material |
| WO2024132993A1 (de) | 2022-12-19 | 2024-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024133048A1 (en) | 2022-12-20 | 2024-06-27 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Method for preparing deuterated aromatic compounds |
| WO2024149694A1 (de) | 2023-01-10 | 2024-07-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Stickstoffhaltige heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024153568A1 (de) | 2023-01-17 | 2024-07-25 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Heterocyclen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024170605A1 (en) | 2023-02-17 | 2024-08-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for organic electroluminescent devices |
| WO2024184050A1 (de) | 2023-03-07 | 2024-09-12 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Cyclische stickstoffverbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024194264A1 (de) | 2023-03-20 | 2024-09-26 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024218109A1 (de) | 2023-04-20 | 2024-10-24 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für elektronische vorrichtungen |
| WO2024240725A1 (de) | 2023-05-25 | 2024-11-28 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Tris[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a:1',5'-c:1'',5''-e][1,3,5]triazin-derivate zur verwendung in organischen elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2024256357A1 (de) | 2023-06-12 | 2024-12-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Organische heterocyclen für photoelektrische vorrichtungen |
| WO2025003084A1 (de) | 2023-06-28 | 2025-01-02 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Dicyanoarylverbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| EP4486099A1 (de) | 2023-06-30 | 2025-01-01 | Merck Patent GmbH | Verbindungen für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
| WO2025012253A1 (en) | 2023-07-12 | 2025-01-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materials for electronic devices |
| WO2025021855A1 (de) | 2023-07-27 | 2025-01-30 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Materialien für organische lichtemittierende vorrichtungen und organische sensoren |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20080012337A (ko) | 2008-02-11 |
| KR101289923B1 (ko) | 2013-07-25 |
| CN103204996A (zh) | 2013-07-17 |
| EP1888706B1 (de) | 2017-03-01 |
| CN103204996B (zh) | 2015-12-09 |
| US20160322570A1 (en) | 2016-11-03 |
| JP5242380B2 (ja) | 2013-07-24 |
| EP1888706A1 (de) | 2008-02-20 |
| CN101171320A (zh) | 2008-04-30 |
| US9871213B2 (en) | 2018-01-16 |
| US20090134384A1 (en) | 2009-05-28 |
| US8674141B2 (en) | 2014-03-18 |
| US9403849B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 |
| JP2008541417A (ja) | 2008-11-20 |
| CN101171320B (zh) | 2013-04-10 |
| TW200710198A (en) | 2007-03-16 |
| US20150322091A1 (en) | 2015-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1888706B1 (de) | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung und in deren herstellung verwendete boronsäure- und borinsäure-derivate | |
| EP1957604B1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP2046915B1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP1888707B1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP1999226B1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP1924670B1 (de) | Verbindungen für organische elektronische vorrichtungen | |
| EP1765750A2 (de) | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtung | |
| EP1917323A1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP2038370A1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| WO2007140847A1 (de) | Materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| WO2008145239A2 (de) | Benzanthracen-derivate für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP1957606A1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektroluminieszenzvorrichtungen | |
| DE102009034625A1 (de) | Neue Materialien für organische Elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| WO2010049050A1 (de) | Neue materialien für organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen | |
| EP1871856A1 (de) | Organische elektrolumineszenzvorrichtungen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2006724095 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2006724095 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 11912939 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2008509318 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200680015401.8 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: DE |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: RU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1020077028263 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: RU |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2006724095 Country of ref document: EP |