JP6380652B2 - R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 - Google Patents
R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6380652B2 JP6380652B2 JP2017509070A JP2017509070A JP6380652B2 JP 6380652 B2 JP6380652 B2 JP 6380652B2 JP 2017509070 A JP2017509070 A JP 2017509070A JP 2017509070 A JP2017509070 A JP 2017509070A JP 6380652 B2 JP6380652 B2 JP 6380652B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sintered magnet
- rtb
- mass
- alloy
- based sintered
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 27
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 86
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 85
- 229910000807 Ga alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 72
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 35
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 34
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 55
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 21
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 20
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 20
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron Substances [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 19
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 17
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 229910052777 Praseodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000010298 pulverizing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052692 Dysprosium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000002354 inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 4
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052771 Terbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002612 dispersion medium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 3
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052779 Neodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- -1 T 17 transition metal Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003302 ferromagnetic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007429 general method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005324 grain boundary diffusion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002074 melt spinning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011802 pulverized particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002910 rare earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc stearate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical group [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052684 Cerium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000722 Didymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 241000224487 Didymium Species 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052772 Samarium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001299 aldehydes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012300 argon atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000005347 demagnetization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000280 densification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004512 die casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007561 laser diffraction method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004570 mortar (masonry) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001172 neodymium magnet Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010408 sweeping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F41/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties
- H01F41/02—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets
- H01F41/0253—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets for manufacturing permanent magnets
- H01F41/0293—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets for manufacturing permanent magnets diffusion of rare earth elements, e.g. Tb, Dy or Ho, into permanent magnets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F3/00—Manufacture of workpieces or articles from metallic powder characterised by the manner of compacting or sintering; Apparatus specially adapted therefor ; Presses and furnaces
- B22F3/10—Sintering only
- B22F3/1003—Use of special medium during sintering, e.g. sintering aid
- B22F3/1007—Atmosphere
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F3/00—Manufacture of workpieces or articles from metallic powder characterised by the manner of compacting or sintering; Apparatus specially adapted therefor ; Presses and furnaces
- B22F3/24—After-treatment of workpieces or articles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C21—METALLURGY OF IRON
- C21D—MODIFYING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF FERROUS METALS; GENERAL DEVICES FOR HEAT TREATMENT OF FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS METALS OR ALLOYS; MAKING METAL MALLEABLE, e.g. BY DECARBURISATION OR TEMPERING
- C21D6/00—Heat treatment of ferrous alloys
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C1/00—Making non-ferrous alloys
- C22C1/04—Making non-ferrous alloys by powder metallurgy
- C22C1/0433—Nickel- or cobalt-based alloys
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C28/00—Alloys based on a metal not provided for in groups C22C5/00 - C22C27/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C33/00—Making ferrous alloys
- C22C33/02—Making ferrous alloys by powder metallurgy
- C22C33/0257—Making ferrous alloys by powder metallurgy characterised by the range of the alloying elements
- C22C33/0278—Making ferrous alloys by powder metallurgy characterised by the range of the alloying elements with at least one alloying element having a minimum content above 5%
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/005—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing rare earths, i.e. Sc, Y, Lanthanides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/06—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing aluminium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/10—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing cobalt
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/12—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing tungsten, tantalum, molybdenum, vanadium, or niobium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/14—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing titanium or zirconium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/16—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing copper
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22F—CHANGING THE PHYSICAL STRUCTURE OF NON-FERROUS METALS AND NON-FERROUS ALLOYS
- C22F1/00—Changing the physical structure of non-ferrous metals or alloys by heat treatment or by hot or cold working
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
- H01F1/032—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials
- H01F1/04—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys
- H01F1/047—Alloys characterised by their composition
- H01F1/053—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals
- H01F1/055—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5
- H01F1/057—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
- H01F1/032—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials
- H01F1/04—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys
- H01F1/047—Alloys characterised by their composition
- H01F1/053—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals
- H01F1/055—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5
- H01F1/057—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B
- H01F1/0571—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes
- H01F1/0575—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes pressed, sintered or bonded together
- H01F1/0577—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes pressed, sintered or bonded together sintered
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
- H01F1/032—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials
- H01F1/04—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys
- H01F1/06—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys in the form of particles, e.g. powder
- H01F1/08—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys in the form of particles, e.g. powder pressed, sintered, or bound together
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F41/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties
- H01F41/02—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F41/00—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties
- H01F41/02—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets
- H01F41/0253—Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing or assembling magnets, inductances or transformers; Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing materials characterised by their magnetic properties for manufacturing cores, coils, or magnets for manufacturing permanent magnets
- H01F41/0266—Moulding; Pressing
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F3/00—Manufacture of workpieces or articles from metallic powder characterised by the manner of compacting or sintering; Apparatus specially adapted therefor ; Presses and furnaces
- B22F3/24—After-treatment of workpieces or articles
- B22F2003/248—Thermal after-treatment
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F2201/00—Treatment under specific atmosphere
- B22F2201/20—Use of vacuum
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F2202/00—Treatment under specific physical conditions
- B22F2202/05—Use of magnetic field
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F2301/00—Metallic composition of the powder or its coating
- B22F2301/35—Iron
- B22F2301/355—Rare Earth - Fe intermetallic alloys
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B22—CASTING; POWDER METALLURGY
- B22F—WORKING METALLIC POWDER; MANUFACTURE OF ARTICLES FROM METALLIC POWDER; MAKING METALLIC POWDER; APPARATUS OR DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR METALLIC POWDER
- B22F2999/00—Aspects linked to processes or compositions used in powder metallurgy
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C2202/00—Physical properties
- C22C2202/02—Magnetic
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Hard Magnetic Materials (AREA)
- Powder Metallurgy (AREA)
- Manufacturing Cores, Coils, And Magnets (AREA)
Description
B:0.80〜0.99質量%、
Ga:0〜0.8質量%、
M:0〜2質量%(MはCu、Al、Nb、Zrの少なくとも一種)、
を含有し、
残部T(TはFe又はFeとCo)及び不可避的不純物からなり、且つ、下記不等式(1)を満足する組成を有するR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を準備する工程と、
[T]/55.85>14[B]/10.8 (1)
([T]は質量%で示すTの含有量であり、[B]は質量%で示すBの含有量である)
Pr−Ga(PrがPr−Ga合金全体の65〜97質量%であり、Prの20質量%以下をNdで置換することができ、Prの30質量%以下をDy及び/又はTbで置換することができる。GaはPr−Ga合金全体の3質量%〜35質量%であり、Gaの50質量%以下をCuで置換することができる。不可避的不純物を含むんでいても良い。)合金を準備する工程と、
前記R−T−B系焼結磁石素材表面の少なくとも一部に、前記Pr−Ga合金の少なくとも一部を接触させ、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、600℃超950℃以下の温度で第一の熱処理を実施する工程と、
前記第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に対して、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、前記第一の熱処理を実施する工程で実施した温度よりも低い温度で且つ、450℃以上750℃以下の温度で第二の熱処理を実施する工程と、
を含む、R−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。
R:27.5〜35.0質量%(Rは希土類元素うちの少なくとも一種であり、Ndを必ず含む)、
B:0.80〜0.99質量%、
Ga:0〜0.8質量%、
M:0〜2質量%(MはCu、Al、Nb、Zrの少なくとも一種)、
を含有し、
残部T(TはFe又はFeとCo)、及び
不可避的不純物からなる。
このR−T−B系焼結磁石素材は、Tの含有量(質量%)を[T]、Bの含有量(質量%)を[B]とするとき、下記の不等式(1)を満足する。
[T]/55.85>14[B]/10.8 (1)
R−T−B系焼結磁石は、原料合金の粉末粒子が焼結によって結合した構造を有しており、主としてR2T14B化合物からなる主相と、この主相の粒界部分に位置する粒界相とから構成されている。
(R−T−B系焼結磁石素材とR−T−B系焼結磁石)
本発明において、第一の熱処理前及び第一の熱処理中のR−T−B系焼結磁石を「R−T−B系焼結磁石素材」と称し、第一の熱処理後、第二の熱処理前及び第二の熱処理中のR−T−B系焼結磁石を「第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材」と称し、第二の熱処理後のR−T−B系焼結磁石を単に「R−T−B系焼結磁石」と称する。
R−T−Ga相とは、R、T、及びGaを含む化合物であり、その典型例は、R6T13Ga化合物である。また、R6T13Ga化合物は、La6Co11Ga3型結晶構造を有する。R6T13Ga化合物は、R6T13-δGa1+δ化合物の状態にある場合があり得る。R−T−B系焼結磁石中にCu、Al及びSiが含有される場合、R−T−Ga相はR6T13-δ(Ga1-x-y-zCuxAlySiz )1+δであり得る。
(R)
Rの含有量は27.5〜35.0質量%である。Rは希土類元素うちの少なくとも一種であり、Ndを必ず含む。Rが27.5質量%未満では焼結過程で液相が十分に生成せず、焼結体を充分に緻密化することが困難になる。一方、Rが35.0質量%を超えても本発明の効果を得ることができるが、焼結体の製造工程中における合金粉末が非常に活性になり、合金粉末の著しい酸化や発火などが生じる可能性があるため、35質量%以下が好ましい。Rは28質量%〜33質量%以下であることがより好ましく、29質量%〜33質量%以下であることがさらに好ましい。RHの含有量は、R−T−B系焼結磁石全体の5質量%以下が好ましい。本発明はRHを使用しなくても高いBrと高いHcJを得ることができるため、より高いHcJを求められる場合でもRHの添加量を削減できる。
Bの含有量は、0.80〜0.99質量%である。不等式(1)を満たした上で、Bの含有量を0.80〜0.99質量%含有させたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に対して、後述するPr−Ga合金を拡散させることにより、R−T−Ga相を生成させることができる。Bの含有量が0.80質量%未満であるとBrが低下する可能性があり、0.99質量%を超えるとR−T−Ga相の生成量が少なすぎてHcJが低下する可能性がある。また、Bの一部はCで置換できる。
Pr−Ga合金からGaを拡散する前のR−T−B系焼結磁石素材におけるGaの含有量は、0〜0.8質量%である。本発明は、Pr−Ga合金をR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に拡散させることによりGaを導入するため、R−T−B系焼結磁石素材のGa量は比較的少ない量(又はGaを含有しない)にする。Gaの含有量が0.8質量%を超えると、上述したように主相中にGaが含有することで主相の磁化が低下し、高いBrを得ることができない可能性がある。好ましくはGaの含有量は、0.5質量%以下である。より高いBrを得ることができる。
Mの含有量は、0〜2質量%である。MはCu、Al、Nb、Zrの少なくとも一種であり、0質量%であっても本発明の効果を奏することができるが、Cu、Al、Nb、Zrの合計で2質量%以下含有することができる。Cu、Alを含有することによりHcJを向上させることができる。Cu、Alは積極的に添加してもよいし、使用原料や合金粉末の製造過程において不可避的に導入されるものを活用してもよい(不純物としてCu、Alを含有する原料を使用してもよい)。また、Nb、Zrを含有することにより焼結時における結晶粒の異常粒成長を抑制することができる。Mは好ましくは、Cuを必ず含み、Cuを0.05〜0.30質量%含有する。Cuを0.05〜0.30質量%含有することにより、よりHcJを向上させることができるからである。
残部はT(TはFe又はFeとCo)であり、Tは、不等式(1)を満足する。質量比でTの90%以上がFeであることが好ましい。Feの一部をCoで置換することができる。但し、Coの置換量が、質量比でT全体の10%を超えるとBrが低下するため好ましくない。さらに、本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石素材は、ジジム合金(Nd−Pr)、電解鉄、フェロボロンなどの合金中及び製造工程中に通常含有される不可避的不純物並びに少量の上記以外の元素(上記R、B、Ga、M、T以外の元素)を含有してもよい。例えば、Ti、V、Cr、Mn、Ni、Si、La、Ce、Sm、Ca、Mg、O(酸素)、N(炭素)、C(窒素)、Mo、Hf、Ta、Wなどをそれぞれ含有してもよい。
不等式(1)を満足することにより、Bの含有量が一般的なR−T−B系焼結磁石よりも少なくなる。一般的なR−T−B系焼結磁石は、主相であるR2T14B相以外にFe相やR2T17相が生成しないよう[T]/55.85(Feの原子量)が14[B]/10.8(Bの原子量)よりも少ない組成となっている([T]は質量%で示すTの含有量であり、[B]は質量%で示すBの含有量である)。本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石は、一般的なR−T−B系焼結磁石と異なり、[T]/55.85(Feの原子量)が14[B]/10.8(Bの原子量)よりも多くなるように不等式(1)で規定する。なお、本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石におけるTはFeが主成分であるためFeの原子量を用いた。
Pr−Ga合金は、PrがPr−Ga合金全体の65〜97質量%であり、Prの20質量%以下をNdで置換することができ、Prの30質量%以下をDy及び/又はTbで置換することができる。GaはPr−Ga合金全体の3質量%〜35質量%であり、Gaの50質量%以下をCuで置換することができる。不可避的不純物を含んでいても良い。なお、本発明における「Prの20%以下をNdで置換することができ」とは、Pr−Ga合金中のPrの含有量(質量%)を100%とし、そのうち20%をNdで置換できることを意味する。例えば、Pr−Ga合金中のPrが65質量%(Gaが35質量%)であれば、Ndを13質量%まで置換することができる。すなわち、Prが52質量%、Ndが13質量%となる。Dy、Tb、Cuの場合も同様である。Pr及びGaを上記範囲内としたPr−Ga合金を本発明の組成範囲のR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に対して後述する第一の熱処理を行うことにより、Gaを、粒界を通じて磁石内部の奥深くまで拡散させることができる。本発明は、Prを主成分とするGaを含む合金を用いることを特徴とする。Prは、Nd、Dy及び/又はTbと置換することができるが、それぞれの置換量が上記範囲を超えるとPrが少なすぎるため、高いBrと高いHcJを得ることができない。好ましくは、前記Pr−Ga合金のNd含有量は不可避的不純物含有量以下(およそ1質量%以下)である。Gaは、50%以下をCuで置換することができるが、Cuの置換量が50%を超えるとHcJが低下する可能性がある。
(R−T−B系焼結磁石素材を準備する工程)
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材は、Nd−Fe−B系焼結磁石に代表される一般的なR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法を用いて準備することができる。一例を挙げると、ストリップキャスト法等で作製された原料合金を、ジェットミルなどを用いて1μm以上10μm以下に粉砕した後、磁界中で成形し、900℃以上1100℃以下の温度で焼結することにより準備することができる。
Pr−Ga合金は、一般的なR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法において採用されている原料合金の作製方法、例えば、金型鋳造法やストリップキャスト法や単ロール超急冷法(メルトスピニング法)やアトマイズ法などを用いて準備することができる。また、Pr−Ga合金は、前記によって得られた合金をピンミルなどの公知の粉砕手段によって粉砕されたものであってもよい。
(第一の熱処理を実施する工程)
前記によって準備したR−T−B系焼結磁石素材表面の少なくとも一部に、前記Pr−Ga合金の少なくとも一部を接触させ、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、600℃超950℃以下の温度で熱処理をする。本発明においてこの熱処理を第一の熱処理という。これにより、Pr−Ga合金からPrやGaを含む液相が生成し、その液相がR−T−B系焼結磁石素材中の粒界を経由して焼結素材表面から内部に拡散導入される。これにより、Prと共にGaを、粒界を通じてR−T−B系焼結磁石素材の奥深くまで拡散させることができる。第一の熱処理温度が600℃以下であると、PrやGaを含む液相量が少なすぎて高いHcJを得ることが出来ない可能性があり、950℃を超えるとHcJが低下する可能性がある。また、好ましくは、第一の熱処理(600℃超940℃以下)が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を前記第一の熱処理を実施した温度から5℃/分以上の冷却速度で300℃まで冷却した方が好ましい。より高いHcJを得ることができる。さらに好ましくは、300℃までの冷却速度は15℃/分以上である。
第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に対して、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、前記第一の熱処理を実施する工程で実施した温度よりも低い温度で且つ、450℃以上750℃以下の温度で熱処理を行う。本発明においてこの熱処理を第二の熱処理という。第二の熱処理を行うことにより、R−T−Ga相が生成され、高いHcJを得ることができる。第二の熱処理が第一の熱処理よりも高い温度であったり、第二の熱処理の温度が450℃未満及び750℃を超える場合は、R−T−Ga相の生成量が少なすぎて高いHcJを得ることができない。
[R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の準備]
表1のNo.A−1及びA−2に示す合金組成となるように各元素の原料を秤量し、ストリップキャスティング法により合金を作製した。得られた各合金を水素粉砕法により粗粉砕し粗粉砕粉を得た。次に、得られた粗粉砕粉に、潤滑剤としてステアリン酸亜鉛を粗粉砕粉100質量%に対して0.04質量%添加、混合した後、気流式粉砕機(ジェットミル装置)を用いて、窒素気流中で乾式粉砕し、粒径D50が4μmの微粉砕粉(合金粉末)を得た。前記微粉砕粉に、潤滑剤としてステアリン酸亜鉛を微粉砕粉100質量%に対して0.05質量%添加、混合した後磁界中で成形し成形体を得た。なお、成形装置には、磁界印加方向と加圧方向とが直交するいわゆる直角磁界成形装置(横磁界成形装置)を用いた。得られた成形体を、真空中、1060℃以上1090℃以下(サンプル毎に焼結による緻密化が十分起こる温度を選定)で4時間焼結し、R−T−B系焼結磁石素材を得た。得られたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材の密度は7.5Mg/m3 以上であった。得られたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材の成分の結果を表1に示す。なお、表1における各成分は、高周波誘導結合プラズマ発光分光分析法(ICP−OES)を使用して測定した。また、本発明の不等式(1)を満足する場合は「○」と、満足しない場合は「×」と記載した。以下、表5、9、13、17も同様である。尚、表1の各組成を合計しても100質量%にはならない。これは、表1に挙げた成分以外の成分(例えばO(酸素)やN(窒素)など)が存在するためである。以下、表5、9、13、17も同様である。
表2のNo.a―1に示す合金組成となるように各元素の原料を秤量しそれらの原料を溶解して、単ロール超急冷法(メルトスピニング法)によりリボンまたはフレーク状の合金を得た。得られた合金を、乳鉢を用いてアルゴン雰囲気中で粉砕した後、目開き425μmの篩を通過させ、Pr−Ga合金を準備した。得られたPr−Ga合金の組成を表2に示す。
表1のNo.A−1及びA−2のR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を切断、研削加工し、7.4mm×7.4mm×7.4mmの立方体とした。次に、No.A−1のR−T−B系焼結磁石素材において、配向方向に垂直な面(二面)にR−T−B系焼結磁石素材の100質量部に対してPr−Ga合金(No.a−1)を0.25質量部(一面あたり0.125質量部)散布した。その後、50Paに制御した減圧アルゴン中で、表3に示す温度で第一の熱処理を行った後室温まで冷却を行い、第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を得た。更に、当該第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材及びNo.A−2(第一の熱処理を行わなかったR−T−B系焼結磁石素材)に対して、50Paに制御した減圧アルゴン中で、表3に示す温度で第二の熱処理を行いR−T−B系焼結磁石(No.1及び2)を作製した。尚、前記冷却(前記第一の熱処理を行った後室温まで冷却)は、炉内にアルゴンガスを導入することにより、熱処理した温度(900℃)から300℃までの平均冷却速度を25℃/分の冷却速度で行った。平均冷却速度(25℃/分)における冷却速度ばらつき(冷却速度の最高値と最低値の差)は、3℃/分以内であった。また、No.1のR−T−B系焼結磁石(Pr−Ga合金を用いてPrやGaを拡散させたサンプル)の組成を、高周波誘導結合プラズマ発光分光分析法(ICP−OES)を使用して測定したところ、No.2(No.2は、Pr−Ga合金を用いていないため、No.A−2と同じ組成)の組成と同等であった。No.1及びNo.2に対して、表面研削盤を用いて各サンプルの全面を0.2mmずつ切削加工し、7.0mm×7.0mm×7.0mmの立方体状のサンプルを得た。
得られたサンプルを、超伝導コイルを備えた振動試料型磁力計(VSM:東英工業製VSM−5SC−10HF)にセットし、4MA/mまで磁界を付与した後、−4MA/mまで磁界を掃引しながら、焼結体の配向方向の磁気ヒステリシス曲線を測定した。得られたヒステリシス曲線から求めたBr及びHcJの値を表4に示す。
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の組成が表5のNo.B−1に示す組成となるように配合する以外は実施例1と同様の方法でR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を作製した。
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の組成が表9のNo.C−1〜C−4に示す組成となるように配合する以外は実施例1と同様の方法でR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を作製した。
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の組成が表13のNo.D−1〜D−16に示す組成となるように配合する以外は実施例1と同様の方法でR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を作製した。
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の組成が表17のNo.E−1に示す組成となるように配合する以外は実施例1と同様の方法でR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を作製した。
R−T−B系焼結磁石素材の組成が表21のNo.F−1及びF−2に示す組成となるように配合する以外は実施例1と同様の方法でR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を作製した。
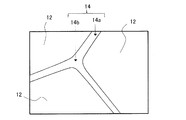
14 粒界相
14a 二粒子粒界相
14b 粒界三重点
Claims (5)
- R:27.5〜35.0質量%(Rは希土類元素うちの少なくとも一種であり、Ndを必ず含む)、
B:0.80〜0.99質量%、
Ga:0〜0.8質量%、
M:0〜2質量%(MはCu、Al、Nb、Zrの少なくとも一種)、
を含有し、
残部T(TはFe又はFeとCo)及び不可避的不純物からなり、且つ、下記不等式(1)を満足する組成を有するR−T−B系焼結磁石素材を準備する工程と、
[T]/55.85>14[B]/10.8 (1)
([T]は質量%で示すTの含有量であり、[B]は質量%で示すBの含有量である)
Pr−Ga(PrがPr−Ga合金全体の65〜97質量%であり、Prの20質量%以下をNdで置換することができ、Prの30質量%以下をDy及び/又はTbで置換することができる。GaはPr−Ga合金全体の3質量%〜35質量%であり、Gaの50質量%以下をCuで置換することができる。不可避的不純物を含むんでいても良い。)合金を準備する工程と、
前記R−T−B系焼結磁石素材表面の少なくとも一部に、前記Pr−Ga合金の少なくとも一部を接触させ、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、600℃超950℃以下の温度で第一の熱処理を実施する工程と、
前記第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石素材に対して、真空又は不活性ガス雰囲気中、前記第一の熱処理を実施する工程で実施した温度よりも低い温度で且つ、450℃以上750℃以下の温度で第二の熱処理を実施する工程と、
を含む、R−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。 - 前記R−T−B系焼結磁石素材のGa量が0〜0.5質量%である請求項1に記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。
- 前記Pr−Ga合金のNd含有量は不可避的不純物含有量以下である、請求項1又は2に記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。
- 前記第一の熱処理が実施されたR−T−B系焼結磁石を前記第一の熱処理を実施した温度から5℃/分以上の冷却速度で300℃まで冷却する、請求項1〜3のいずれかに記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。
- 前記冷却速度が15℃/分以上である、請求項4に記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石の製造方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015150585 | 2015-07-30 | ||
| JP2015150585 | 2015-07-30 | ||
| JP2016026583 | 2016-02-16 | ||
| JP2016026583 | 2016-02-16 | ||
| PCT/JP2016/071244 WO2017018291A1 (ja) | 2015-07-30 | 2016-07-20 | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2017018291A1 JPWO2017018291A1 (ja) | 2017-07-27 |
| JP6380652B2 true JP6380652B2 (ja) | 2018-08-29 |
Family
ID=57885533
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017509070A Active JP6380652B2 (ja) | 2015-07-30 | 2016-07-20 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11177069B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3330984B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6380652B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN107077965B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017018291A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6780646B2 (ja) | 2015-08-24 | 2020-11-04 | 日立金属株式会社 | 拡散処理装置およびそれを用いたr−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| JP6501038B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-17 | 2019-04-17 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| US10658107B2 (en) | 2016-10-12 | 2020-05-19 | Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. | Method of manufacturing permanent magnet |
| JP6939337B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-09-22 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| US10984930B2 (en) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-04-20 | Hitachi Metals, Ltd. | Method for producing sintered R—T—B based magnet and diffusion source |
| US11062843B2 (en) | 2017-09-28 | 2021-07-13 | Hitachi Metals, Ltd. | Method for producing sintered R-T-B based magnet and diffusion source |
| CN109585151B (zh) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-06-29 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁体的制造方法和扩散源 |
| CN109585108B (zh) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-05-14 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁体的制造方法和扩散源 |
| JP6939339B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-09-22 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| JP6939338B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-28 | 2021-09-22 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| CN110106334B (zh) * | 2018-02-01 | 2021-06-22 | 福建省长汀金龙稀土有限公司 | 一种连续进行晶界扩散和热处理的装置以及方法 |
| JP7180089B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-22 | 2022-11-30 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| JP7155813B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-22 | 2022-10-19 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| JP7020224B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-22 | 2022-02-16 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系焼結磁石及びその製造方法 |
| JP7110662B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-28 | 2022-08-02 | Tdk株式会社 | R‐t‐b系焼結磁石 |
| CN111937102A (zh) * | 2018-03-29 | 2020-11-13 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁体的制造方法 |
| JP7248016B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-29 | 2023-03-29 | 株式会社プロテリアル | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| CN111489874A (zh) * | 2019-01-28 | 2020-08-04 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁体的制造方法 |
| JP7228096B2 (ja) | 2019-03-22 | 2023-02-24 | 株式会社プロテリアル | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| JP7059995B2 (ja) * | 2019-03-25 | 2022-04-26 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系焼結磁石 |
| US11239011B2 (en) * | 2019-03-25 | 2022-02-01 | Hitachi Metals, Ltd. | Sintered R-T-B based magnet |
| CN110993233B (zh) * | 2019-12-09 | 2021-08-27 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种r-t-b系永磁材料、原料组合物、制备方法、应用 |
| WO2022181808A1 (ja) * | 2021-02-26 | 2022-09-01 | 日本電産株式会社 | モータ、駆動システム、掃除機、無人飛行体、電動航空機 |
| JP2022132088A (ja) * | 2021-02-26 | 2022-09-07 | 日本電産株式会社 | モータ、駆動システム、掃除機、無人飛行体、電動航空機 |
| EP4105951A4 (en) * | 2021-04-30 | 2024-02-28 | JL Mag Rare-Earth Co., Ltd. | SINTERED NEODYMUM IRON BORON MAGNET AND PRODUCTION METHOD THEREOF |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09129424A (ja) * | 1995-10-30 | 1997-05-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | 永久磁石用磁性粉末、永久磁石およびその製造方法 |
| CN101641750B (zh) * | 2007-05-01 | 2012-07-11 | 因太金属株式会社 | NdFeB系烧结磁体制造方法 |
| JP5057111B2 (ja) * | 2009-07-01 | 2012-10-24 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 希土類磁石の製造方法 |
| CN103098155B (zh) * | 2010-09-15 | 2016-01-06 | 丰田自动车株式会社 | 稀土类磁铁的制造方法 |
| JP5088596B2 (ja) | 2010-09-30 | 2012-12-05 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| EP2667385A4 (en) * | 2011-01-19 | 2018-04-04 | Hitachi Metals, Ltd. | R-t-b sintered magnet |
| US9177705B2 (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2015-11-03 | Tdk Corporation | Sintered rare earth magnet, method of producing the same, and rotating machine |
| JP5572673B2 (ja) | 2011-07-08 | 2014-08-13 | 昭和電工株式会社 | R−t−b系希土類焼結磁石用合金、r−t−b系希土類焼結磁石用合金の製造方法、r−t−b系希土類焼結磁石用合金材料、r−t−b系希土類焼結磁石、r−t−b系希土類焼結磁石の製造方法およびモーター |
| JP2014086529A (ja) | 2012-10-23 | 2014-05-12 | Toyota Motor Corp | 希土類焼結磁石とその製造方法 |
| JP6303480B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-28 | 2018-04-04 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類磁石 |
| CN105453196B (zh) | 2013-08-09 | 2017-12-22 | Tdk株式会社 | R‑t‑b系烧结磁铁以及电动机 |
| US10109403B2 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2018-10-23 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B based sintered magnet and motor |
| DE112014003678T5 (de) * | 2013-08-09 | 2016-04-21 | Tdk Corporation | Sintermagnet auf R-T-B Basis und Motor |
| CN107251175B (zh) * | 2015-02-18 | 2019-04-09 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁体的制造方法 |
| WO2016133080A1 (ja) * | 2015-02-18 | 2016-08-25 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
-
2016
- 2016-07-20 CN CN201680003212.2A patent/CN107077965B/zh active Active
- 2016-07-20 WO PCT/JP2016/071244 patent/WO2017018291A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2016-07-20 EP EP16830396.4A patent/EP3330984B1/en active Active
- 2016-07-20 JP JP2017509070A patent/JP6380652B2/ja active Active
- 2016-07-20 US US15/548,466 patent/US11177069B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3330984A4 (en) | 2019-03-13 |
| JPWO2017018291A1 (ja) | 2017-07-27 |
| EP3330984B1 (en) | 2020-03-18 |
| WO2017018291A1 (ja) | 2017-02-02 |
| US11177069B2 (en) | 2021-11-16 |
| CN107077965A (zh) | 2017-08-18 |
| US20180240590A1 (en) | 2018-08-23 |
| CN107077965B (zh) | 2018-12-28 |
| EP3330984A1 (en) | 2018-06-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6380652B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6361813B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6501038B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| JP6414653B1 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6414654B1 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6489201B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6860808B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2018160642A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| JP2019169542A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP7537536B2 (ja) | R-t-b系焼結磁石 | |
| JP6624455B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| WO2017110680A1 (ja) | R-t-b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2019075426A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石及びその製造方法 | |
| JP6474043B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| JP6508447B1 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2020161789A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| JP6623998B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP6610957B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2019169697A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2019169560A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2019169506A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2021057564A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2021153148A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法及び拡散用合金 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180403 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180703 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180716 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6380652 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |