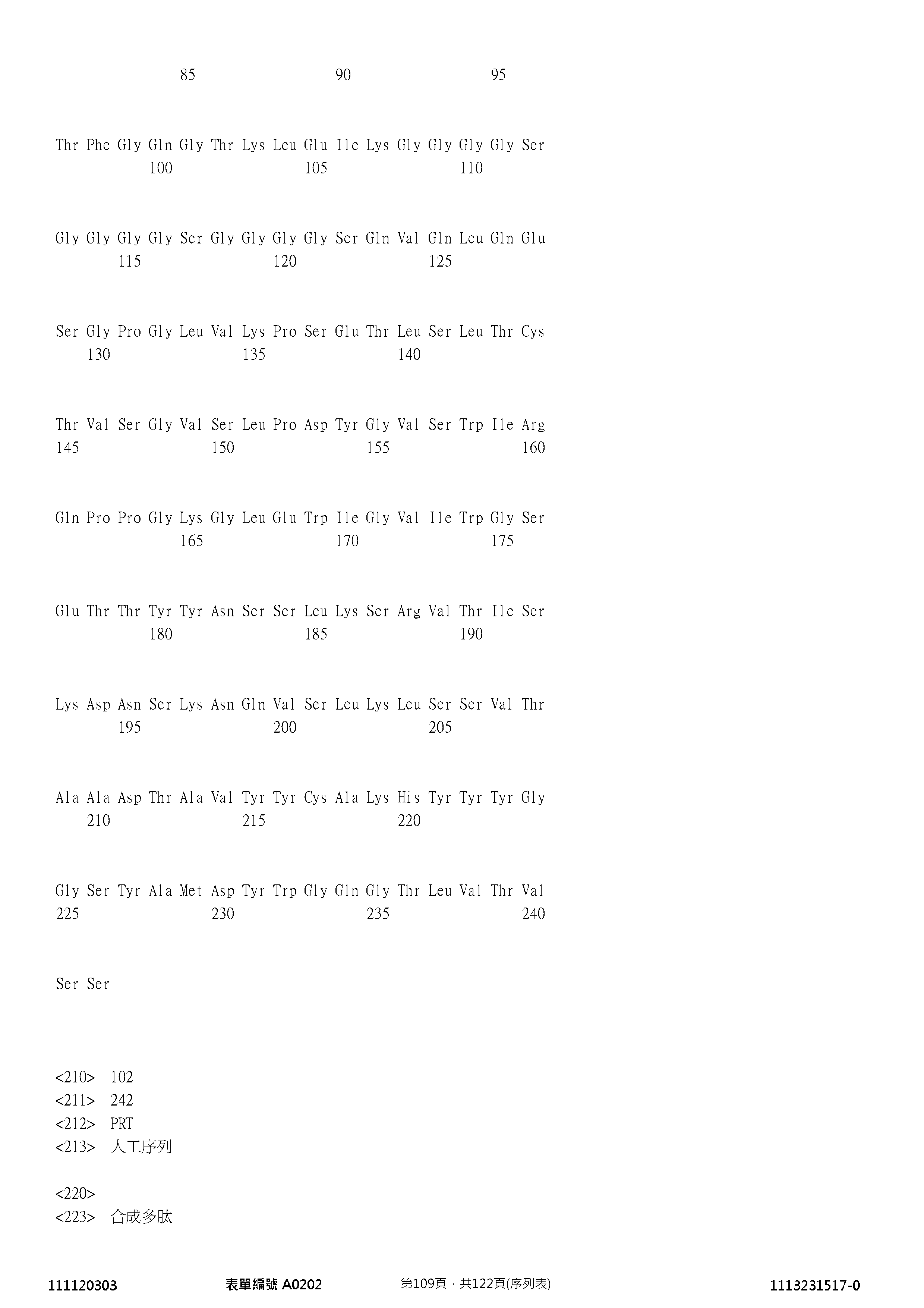TW202307210A - Cd19 and cd22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof - Google Patents
Cd19 and cd22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- TW202307210A TW202307210A TW111120303A TW111120303A TW202307210A TW 202307210 A TW202307210 A TW 202307210A TW 111120303 A TW111120303 A TW 111120303A TW 111120303 A TW111120303 A TW 111120303A TW 202307210 A TW202307210 A TW 202307210A
- Authority
- TW
- Taiwan
- Prior art keywords
- cells
- domain
- car
- body weight
- amino acid
- Prior art date
Links
- 108010019670 Chimeric Antigen Receptors Proteins 0.000 title claims description 461
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 493
- 102100024222 B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Human genes 0.000 claims abstract description 174
- 101000980825 Homo sapiens B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 174
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 137
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 86
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 56
- 102100038080 B-cell receptor CD22 Human genes 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 101000884305 Homo sapiens B-cell receptor CD22 Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 claims description 409
- 150000007523 nucleic acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 328
- 239000000427 antigen Substances 0.000 claims description 304
- 108091007433 antigens Proteins 0.000 claims description 304
- 102000036639 antigens Human genes 0.000 claims description 304
- 102000039446 nucleic acids Human genes 0.000 claims description 279
- 108020004707 nucleic acids Proteins 0.000 claims description 279
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 claims description 242
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 240
- 239000002773 nucleotide Substances 0.000 claims description 238
- 125000003275 alpha amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 196
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 89
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 claims description 77
- 230000000139 costimulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 58
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 54
- 108010047041 Complementarity Determining Regions Proteins 0.000 claims description 51
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 claims description 38
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 31
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- 201000003793 Myelodysplastic syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims description 22
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000005303 weighing Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000036210 malignancy Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 208000024893 Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 11
- 208000014697 Acute lymphocytic leukaemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 11
- 208000006664 Precursor Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000002062 proliferating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 208000025324 B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 10
- 208000010839 B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 10
- 208000031422 Lymphocytic Chronic B-Cell Leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 10
- 208000015914 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 10
- 208000025205 Mantle-Cell Lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 208000007541 Preleukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 201000003444 follicular lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- 208000032791 BCR-ABL1 positive chronic myelogenous leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- 208000031671 Large B-Cell Diffuse Lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- 206010012818 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- 206010025323 Lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000010833 Chronic myeloid leukaemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000017604 Hodgkin disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000021519 Hodgkin lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000010747 Hodgkins lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000033761 Myelogenous Chronic BCR-ABL Positive Leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 201000009277 hairy cell leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 210000005134 plasmacytoid dendritic cell Anatomy 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000031261 Acute myeloid leukaemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000036170 B-Cell Marginal Zone Lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000032568 B-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000011691 Burkitt lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 206010061850 Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (MALT type) Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 201000003791 MALT lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000034578 Multiple myelomas Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 206010035226 Plasma cell myeloma Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000035416 Prolymphocytic B-Cell Leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000033559 Waldenström macroglobulinemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000035269 cancer or benign tumor Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 201000007224 Myeloproliferative neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 210000004443 dendritic cell Anatomy 0.000 claims description 3
- 210000004698 lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 claims description 3
- 201000007924 marginal zone B-cell lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000021937 marginal zone lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000007525 plasmablastic lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000016025 Waldenstroem macroglobulinemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 abstract description 63
- 210000001744 T-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 abstract description 52
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 97
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 68
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 description 59
- 102100035360 Cerebellar degeneration-related antigen 1 Human genes 0.000 description 56
- 102000053602 DNA Human genes 0.000 description 54
- 108020004414 DNA Proteins 0.000 description 54
- 108091028043 Nucleic acid sequence Proteins 0.000 description 54
- 229920001184 polypeptide Polymers 0.000 description 46
- 239000012642 immune effector Substances 0.000 description 43
- 229940121354 immunomodulator Drugs 0.000 description 43
- 229920002477 rna polymer Polymers 0.000 description 41
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 40
- 108020004999 messenger RNA Proteins 0.000 description 36
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 36
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 34
- 229940024606 amino acid Drugs 0.000 description 31
- 102000008394 Immunoglobulin Fragments Human genes 0.000 description 30
- 230000004068 intracellular signaling Effects 0.000 description 30
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 30
- 108010021625 Immunoglobulin Fragments Proteins 0.000 description 29
- 108010029157 Sialic Acid Binding Ig-like Lectin 2 Proteins 0.000 description 29
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 28
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 26
- 210000000822 natural killer cell Anatomy 0.000 description 24
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 23
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 23
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 23
- 210000002706 plastid Anatomy 0.000 description 22
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 21
- 238000013518 transcription Methods 0.000 description 21
- 230000035897 transcription Effects 0.000 description 21
- 238000003752 polymerase chain reaction Methods 0.000 description 20
- -1 CD22 Proteins 0.000 description 19
- 101000851370 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 Proteins 0.000 description 19
- 102100036856 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 Human genes 0.000 description 19
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 19
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 18
- 102000040430 polynucleotide Human genes 0.000 description 18
- 108091033319 polynucleotide Proteins 0.000 description 18
- 239000002157 polynucleotide Substances 0.000 description 18
- 102100035932 Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript protein Human genes 0.000 description 17
- 101000715592 Homo sapiens Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript protein Proteins 0.000 description 17
- 125000000539 amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 17
- 108060003951 Immunoglobulin Proteins 0.000 description 16
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 16
- 102000018358 immunoglobulin Human genes 0.000 description 16
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 16
- 108020003589 5' Untranslated Regions Proteins 0.000 description 15
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 15
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 15
- 102100024952 Protein CBFA2T1 Human genes 0.000 description 14
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 14
- 102100034922 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain Human genes 0.000 description 13
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 13
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000004936 stimulating effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 230000014616 translation Effects 0.000 description 13
- NFGXHKASABOEEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylethyl 11-methoxy-3,7,11-trimethyl-2,4-dodecadienoate Chemical compound COC(C)(C)CCCC(C)CC=CC(C)=CC(=O)OC(C)C NFGXHKASABOEEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 108020005345 3' Untranslated Regions Proteins 0.000 description 12
- 108010005327 CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor Proteins 0.000 description 12
- 230000001086 cytosolic effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000006471 dimerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 108020001507 fusion proteins Proteins 0.000 description 12
- 102000037865 fusion proteins Human genes 0.000 description 12
- 230000002489 hematologic effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 12
- 238000013519 translation Methods 0.000 description 12
- 101000914514 Homo sapiens T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein CD28 Proteins 0.000 description 11
- 108091008874 T cell receptors Proteins 0.000 description 11
- 102000016266 T-Cell Antigen Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 11
- 102100027213 T-cell-specific surface glycoprotein CD28 Human genes 0.000 description 11
- 210000004899 c-terminal region Anatomy 0.000 description 11
- 239000013604 expression vector Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000003612 virological effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 102100027207 CD27 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 10
- 101000914511 Homo sapiens CD27 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 10
- 102000035195 Peptidases Human genes 0.000 description 10
- 108091005804 Peptidases Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 239000004365 Protease Substances 0.000 description 10
- 108700019146 Transgenes Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 102100022153 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 4 Human genes 0.000 description 10
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 10
- 108091036407 Polyadenylation Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 210000003719 b-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 9
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229940124302 mTOR inhibitor Drugs 0.000 description 9
- 239000003628 mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 9
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 9
- 238000001890 transfection Methods 0.000 description 9
- 101000716102 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 108010064548 Lymphocyte Function-Associated Antigen-1 Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 102100040678 Programmed cell death protein 1 Human genes 0.000 description 8
- 101710089372 Programmed cell death protein 1 Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 108700008625 Reporter Genes Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 102100036011 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4 Human genes 0.000 description 8
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 description 8
- 239000000306 component Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000028993 immune response Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 8
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 8
- 102000017420 CD3 protein, epsilon/gamma/delta subunit Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108050005493 CD3 protein, epsilon/gamma/delta subunit Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 101000935040 Homo sapiens Integrin beta-2 Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102100025390 Integrin beta-2 Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108010064593 Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 102100037877 Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 108020004684 Internal Ribosome Entry Sites Proteins 0.000 description 7
- 241000713666 Lentivirus Species 0.000 description 7
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 7
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 7
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 7
- 241000282693 Cercopithecidae Species 0.000 description 6
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 108090000626 DNA-directed RNA polymerases Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 102000004163 DNA-directed RNA polymerases Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 101000946860 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain Proteins 0.000 description 6
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 241001529936 Murinae Species 0.000 description 6
- 208000006994 Precancerous Conditions Diseases 0.000 description 6
- 241000283984 Rodentia Species 0.000 description 6
- 102100025237 T-cell surface antigen CD2 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 102100035794 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 101710165473 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 4 Proteins 0.000 description 6
- 239000002299 complementary DNA Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 210000003071 memory t lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 230000008488 polyadenylation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000013603 viral vector Substances 0.000 description 6
- FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N 4-amino-1-[(2r)-6-amino-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]piperidine-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N1CCC(N)(CC1)C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](N)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N 0.000 description 5
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycine Chemical compound NCC(O)=O DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 101000934346 Homo sapiens T-cell surface antigen CD2 Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 108700026244 Open Reading Frames Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 238000001994 activation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000735 allogeneic effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000001476 gene delivery Methods 0.000 description 5
- 210000004962 mammalian cell Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 230000035772 mutation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000035755 proliferation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000001177 retroviral effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000019491 signal transduction Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 241001430294 unidentified retrovirus Species 0.000 description 5
- 108010013238 70-kDa Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102100037904 CD9 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108091026890 Coding region Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 108091033380 Coding strand Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 241000701022 Cytomegalovirus Species 0.000 description 4
- HKVAMNSJSFKALM-GKUWKFKPSA-N Everolimus Chemical compound C1C[C@@H](OCCO)[C@H](OC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@@H]2CCCCN2C(=O)C(=O)[C@](O)(O2)[C@H](C)CC[C@H]2C[C@H](OC)/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](OC)[C@H](O)/C(C)=C/[C@@H](C)C(=O)C1 HKVAMNSJSFKALM-GKUWKFKPSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102100026122 High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 101000738354 Homo sapiens CD9 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000913074 Homo sapiens High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000777628 Homo sapiens Leukocyte antigen CD37 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000917858 Homo sapiens Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000917839 Homo sapiens Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000934338 Homo sapiens Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000738771 Homo sapiens Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000934341 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD5 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000946843 Homo sapiens T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 101000914484 Homo sapiens T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD80 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-tyrosine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102100031586 Leukocyte antigen CD37 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 102100029185 Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 4
- 102100025243 Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 102100037422 Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase C Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010074687 Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family Member 1 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102100029215 Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010003723 Single-Domain Antibodies Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102100025244 T-cell surface glycoprotein CD5 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 102100027222 T-lymphocyte activation antigen CD80 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000005809 anti-tumor immunity Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004520 electroporation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229960005167 everolimus Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 230000003463 hyperproliferative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000002766 immunoenhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003211 malignant effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000693 micelle Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000009126 molecular therapy Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 208000016691 refractory malignant neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 4
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyrosine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N (2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropansäure Chemical compound OC[C@H](N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102100024263 CD160 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108020004705 Codon Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 241000702421 Dependoparvovirus Species 0.000 description 3
- 241000206602 Eukaryota Species 0.000 description 3
- 101000761938 Homo sapiens CD160 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101000994375 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-4 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101000971538 Homo sapiens Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily F member 1 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101000633786 Homo sapiens SLAM family member 6 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 241000725303 Human immunodeficiency virus Species 0.000 description 3
- 102100032818 Integrin alpha-4 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 102100032816 Integrin alpha-6 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108091092195 Intron Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102100021458 Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily F member 1 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 239000000232 Lipid Bilayer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 208000030289 Lymphoproliferative disease Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 101710124239 Poly(A) polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 108091034057 RNA (poly(A)) Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 3
- 108020004511 Recombinant DNA Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 206010070308 Refractory cancer Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 102100029197 SLAM family member 6 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108060008683 Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 102100028785 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010017070 Zinc Finger Nucleases Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N adenosine Chemical compound C1=NC=2C(N)=NC=NC=2N1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O OIRDTQYFTABQOQ-KQYNXXCUSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000000170 cell membrane Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010367 cloning Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001900 immune effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 208000032839 leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 238000001638 lipofection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002521 macromolecule Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010369 molecular cloning Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002777 nucleoside Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 3
- 231100000628 reference dose Toxicity 0.000 description 3
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012174 single-cell RNA sequencing Methods 0.000 description 3
- QFJCIRLUMZQUOT-HPLJOQBZSA-N sirolimus Chemical compound C1C[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC)C[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@@H]2CCCCN2C(=O)C(=O)[C@](O)(O2)[C@H](C)CC[C@H]2C[C@H](OC)/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](OC)[C@H](O)/C(C)=C/[C@@H](C)C(=O)C1 QFJCIRLUMZQUOT-HPLJOQBZSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 3
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 210000004881 tumor cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 102000003298 tumor necrosis factor receptor Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 241000701161 unidentified adenovirus Species 0.000 description 3
- 239000003981 vehicle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 108091032973 (ribonucleotides)n+m Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000040650 (ribonucleotides)n+m Human genes 0.000 description 2
- GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Adenine Chemical compound NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2 GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100021569 Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 208000025321 B-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 108091012583 BCL2 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000026310 Breast neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 102100038077 CD226 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100038078 CD276 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 101710185679 CD276 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 208000016778 CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 101150013553 CD40 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100035793 CD83 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 206010008342 Cervix carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000017815 Dendritic cell tumor Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 108700035208 EC 7.-.-.- Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100031780 Endonuclease Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010042407 Endonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108060002716 Exonuclease Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108010021468 Fc gamma receptor IIA Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000004471 Glycine Substances 0.000 description 2
- NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N Guanosine Chemical compound C1=NC=2C(=O)NC(N)=NC=2N1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100029360 Hematopoietic cell signal transducer Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100022132 High affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor subunit gamma Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 101100383038 Homo sapiens CD19 gene Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000884298 Homo sapiens CD226 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000946856 Homo sapiens CD83 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000990188 Homo sapiens Hematopoietic cell signal transducer Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000824104 Homo sapiens High affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor subunit gamma Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001078158 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000994365 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-6 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001035237 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-D Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001046687 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-E Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000935043 Homo sapiens Integrin beta-1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000971533 Homo sapiens Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001018097 Homo sapiens L-selectin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001109503 Homo sapiens NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101001109501 Homo sapiens NKG2-D type II integral membrane protein Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000589305 Homo sapiens Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000633784 Homo sapiens SLAM family member 7 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000633780 Homo sapiens Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000809875 Homo sapiens TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000795169 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000801234 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 101000851376 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 8 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100025323 Integrin alpha-1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100039904 Integrin alpha-D Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100022341 Integrin alpha-E Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100022338 Integrin alpha-M Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100022297 Integrin alpha-X Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100025304 Integrin beta-1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 208000008839 Kidney Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 102100021457 Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-histidine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-WHFBIAKZSA-N L-isoleucine Chemical compound CC[C@H](C)[C@H](N)C(O)=O AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-WHFBIAKZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100033467 L-selectin Human genes 0.000 description 2
- AYFVYJQAPQTCCC-GBXIJSLDSA-N L-threonine Chemical compound C[C@@H](O)[C@H](N)C(O)=O AYFVYJQAPQTCCC-GBXIJSLDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N L-tryptophane Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 2
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-valine Chemical compound CC(C)[C@H](N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100029204 Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor II-a Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 206010058467 Lung neoplasm malignant Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 241000829100 Macaca mulatta polyomavirus 1 Species 0.000 description 2
- 108010061593 Member 14 Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000027581 NK cell receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108091008877 NK cell receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100022683 NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100022680 NKG2-D type II integral membrane protein Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010004217 Natural Cytotoxicity Triggering Receptor 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108010004222 Natural Cytotoxicity Triggering Receptor 3 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100032870 Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100032851 Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 2 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100032852 Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100038082 Natural killer cell receptor 2B4 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102000015636 Oligopeptides Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010038807 Oligopeptides Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 206010033128 Ovarian cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010061535 Ovarian neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 240000007019 Oxalis corniculata Species 0.000 description 2
- 206010061902 Pancreatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 108010077524 Peptide Elongation Factor 1 Proteins 0.000 description 2
- RJKFOVLPORLFTN-LEKSSAKUSA-N Progesterone Chemical compound C1CC2=CC(=O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H](C(=O)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 RJKFOVLPORLFTN-LEKSSAKUSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010060862 Prostate cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000000236 Prostatic Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 102000014128 RANK Ligand Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010025832 RANK Ligand Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 238000003559 RNA-seq method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 206010038389 Renal cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000007660 Residual Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 102100029198 SLAM family member 7 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 2
- 102100027744 Semaphorin-4D Human genes 0.000 description 2
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Serine Natural products OCC(N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000008115 Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family Member 1 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100027208 T-cell antigen CD7 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 238000010459 TALEN Methods 0.000 description 2
- 102000013530 TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010065917 TOR Serine-Threonine Kinases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102100038717 TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein Human genes 0.000 description 2
- AYFVYJQAPQTCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Threonine Natural products CC(O)C(N)C(O)=O AYFVYJQAPQTCCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004473 Threonine Substances 0.000 description 2
- IQFYYKKMVGJFEH-XLPZGREQSA-N Thymidine Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)C1 IQFYYKKMVGJFEH-XLPZGREQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108010043645 Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tryptophan Natural products C1=CC=C2C(CC(N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 QIVBCDIJIAJPQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100029690 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100033728 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100040245 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 102100036857 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 8 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108091023045 Untranslated Region Proteins 0.000 description 2
- DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-XVFCMESISA-N Uridine Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1 DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-XVFCMESISA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000006105 Uterine Cervical Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Valine Natural products CC(C)C(N)C(O)=O KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003838 adenosines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001093 anti-cancer Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000259 anti-tumor effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000000612 antigen-presenting cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000000890 antigenic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012736 aqueous medium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001580 bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012472 biological sample Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000001772 blood platelet Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000001185 bone marrow Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000001506 calcium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000389 calcium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000011010 calcium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000004663 cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 201000010881 cervical cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000032852 chronic lymphocytic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000000805 cytoplasm Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- OPTASPLRGRRNAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N cytosine Chemical compound NC=1C=CNC(=O)N=1 OPTASPLRGRRNAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002716 delivery method Methods 0.000 description 2
- RNPXCFINMKSQPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dicetyl hydrogen phosphate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOP(O)(=O)OCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC RNPXCFINMKSQPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940088598 enzyme Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 102000013165 exonuclease Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001415 gene therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000014951 hematologic disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N histidine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000044389 human CD22 Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 210000005260 human cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000008004 immune attack Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000002865 immune cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000002163 immunogen Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005847 immunogenicity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940072221 immunoglobulins Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 102000006495 integrins Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010044426 integrins Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 108010093036 interleukin receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000002467 interleukin receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoleucine Natural products CCC(C)C(N)C(O)=O AGPKZVBTJJNPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960000310 isoleucine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 201000010982 kidney cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 201000007270 liver cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000014018 liver neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000004807 localization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 2
- 201000005202 lung cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000020816 lung neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 201000001268 lymphoproliferative syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000015486 malignant pancreatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000000440 neutrophil Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 150000003833 nucleoside derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 210000004940 nucleus Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- JMANVNJQNLATNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxalonitrile Chemical compound N#CC#N JMANVNJQNLATNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 201000002528 pancreatic cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000008443 pancreatic carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000037361 pathway Effects 0.000 description 2
- 108010079892 phosphoglycerol kinase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 150000003904 phospholipids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000013612 plasmid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 208000017426 precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- ZAHRKKWIAAJSAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N rapamycin Natural products COCC(O)C(=C/C(C)C(=O)CC(OC(=O)C1CCCCN1C(=O)C(=O)C2(O)OC(CC(OC)C(=CC=CC=CC(C)CC(C)C(=O)C)C)CCC2C)C(C)CC3CCC(O)C(C3)OC)C ZAHRKKWIAAJSAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003362 replicative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000028327 secretion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229960002930 sirolimus Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000011580 syndromic disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002103 transcriptional effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002463 transducing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005945 translocation Effects 0.000 description 2
- QORWJWZARLRLPR-UHFFFAOYSA-H tricalcium bis(phosphate) Chemical compound [Ca+2].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O QORWJWZARLRLPR-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 2
- 239000004474 valine Substances 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001262 western blot Methods 0.000 description 2
- DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N (2R)-6-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R,3S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[(2-amino-1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-3-carboxy-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1,5-dihydroxy-5-iminopentylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]hexanoic acid Chemical compound C[C@@H]([C@@H](C(=N[C@@H](CS)C(=N[C@@H](C)C(=N[C@@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@@H](CCC(=N)O)C(=NC(CS)C(=N[C@H]([C@H](C)O)C(=N[C@H](CS)C(=N[C@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CS)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](C)N=C(CN=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C(CN=C(C(CS)N=C(C(CC(=O)O)N=C(CN)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N 0.000 description 1
- KWTSXDURSIMDCE-QMMMGPOBSA-N (S)-amphetamine Chemical compound C[C@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 KWTSXDURSIMDCE-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FGRBYDKOBBBPOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10,10-dioxo-2-[4-(N-phenylanilino)phenyl]thioxanthen-9-one Chemical group O=C1c2ccccc2S(=O)(=O)c2ccc(cc12)-c1ccc(cc1)N(c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1 FGRBYDKOBBBPOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGONTNSXDCQUGY-RRKCRQDMSA-N 2'-deoxyinosine Chemical group C1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C(N=CNC2=O)=C2N=C1 VGONTNSXDCQUGY-RRKCRQDMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108020005029 5' Flanking Region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- TVEXGJYMHHTVKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-oxabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-en-7-one Chemical group C1C2C(=O)OC1C=CC2 TVEXGJYMHHTVKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OGHAROSJZRTIOK-KQYNXXCUSA-O 7-methylguanosine Chemical compound C1=2N=C(N)NC(=O)C=2[N+](C)=CN1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O OGHAROSJZRTIOK-KQYNXXCUSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 108020005176 AU Rich Elements Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000007469 Actins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010085238 Actins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010000830 Acute leukaemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229930024421 Adenine Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 102000002260 Alkaline Phosphatase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004774 Alkaline Phosphatase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108700028369 Alleles Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000006306 Antigen Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010083359 Antigen Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091023037 Aptamer Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Asparagine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC(N)=O DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000023275 Autoimmune disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000713826 Avian leukosis virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100029822 B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229940123121 B-cell inhibitor Drugs 0.000 description 1
- DWRXFEITVBNRMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Beta-D-1-Arabinofuranosylthymine Natural products O=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1C1C(O)C(O)C(CO)O1 DWRXFEITVBNRMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100026189 Beta-galactosidase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 206010005003 Bladder cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000003174 Brain Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000002126 C01EB10 - Adenosine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010056102 CD100 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010017009 CD11b Antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010062802 CD66 antigens Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 210000001266 CD8-positive T-lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 102100027217 CD82 antigen Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710139831 CD82 antigen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091033409 CRISPR Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000010453 CRISPR/Cas method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102100024533 Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000000844 Cell Surface Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010001857 Cell Surface Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010035563 Chloramphenicol O-acetyltransferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010038061 Chymotrypsinogen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108020004638 Circular DNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091062157 Cis-regulatory element Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010009944 Colon cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000001333 Colorectal Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108091028732 Concatemer Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004420 Creatine Kinase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010042126 Creatine kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- MIKUYHXYGGJMLM-GIMIYPNGSA-N Crotonoside Natural products C1=NC2=C(N)NC(=O)N=C2N1[C@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O MIKUYHXYGGJMLM-GIMIYPNGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000004127 Cytokines Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000695 Cytokines Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100027816 Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule Human genes 0.000 description 1
- NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N D-guanosine Natural products C1=2NC(N)=NC(=O)C=2N=CN1C1OC(CO)C(O)C1O NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000016928 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010014303 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydrogen disulfide Chemical compound SS BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GZDFHIJNHHMENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethyl dicarbonate Chemical compound COC(=O)OC(=O)OC GZDFHIJNHHMENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010061818 Disease progression Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010058314 Dysplasia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000002965 ELISA Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102100025137 Early activation antigen CD69 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101000585551 Equus caballus Pregnancy-associated glycoprotein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000588724 Escherichia coli Species 0.000 description 1
- 101000686777 Escherichia phage T7 T7 RNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108700024394 Exon Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010008177 Fd immunoglobulins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000002090 Fibronectin type III Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108050009401 Fibronectin type III Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000016359 Fibronectins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010067306 Fibronectins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100022086 GRB2-related adapter protein 2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108700028146 Genetic Enhancer Elements Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108700039691 Genetic Promoter Regions Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glutamic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010043121 Green Fluorescent Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000238631 Hexapoda Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000008949 Histocompatibility Antigens Class I Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 1
- 101000864344 Homo sapiens B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000934374 Homo sapiens Early activation antigen CD69 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000900690 Homo sapiens GRB2-related adapter protein 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001046683 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-L Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001046686 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-M Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001046668 Homo sapiens Integrin alpha-X Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001015037 Homo sapiens Integrin beta-7 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001047640 Homo sapiens Linker for activation of T-cells family member 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001090688 Homo sapiens Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000873418 Homo sapiens P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001124867 Homo sapiens Peroxiredoxin-1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000692259 Homo sapiens Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000702132 Homo sapiens Protein spinster homolog 1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000633778 Homo sapiens SLAM family member 5 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000914496 Homo sapiens T-cell antigen CD7 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000596234 Homo sapiens T-cell surface protein tactile Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000848014 Homo sapiens Trypsin-2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000648507 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000679857 Homo sapiens Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091006905 Human Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000008100 Human Serum Albumin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000701044 Human gammaherpesvirus 4 Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010020751 Hypersensitivity Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010021143 Hypoxia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101150102264 IE gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010009817 Immunoglobulin Constant Regions Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000009786 Immunoglobulin Constant Regions Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010054477 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000001706 Immunoglobulin Fab Fragments Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010079585 Immunoglobulin Subunits Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000012745 Immunoglobulin Subunits Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010067060 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000017727 Immunoglobulin Variable Region Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 206010062016 Immunosuppression Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102100022339 Integrin alpha-L Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010041100 Integrin alpha6 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010030465 Integrin alpha6beta1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100033016 Integrin beta-7 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010002350 Interleukin-2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000000588 Interleukin-2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N L-Cysteine Chemical compound SC[C@H](N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-Proline Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCN1 ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N L-alanine Chemical compound C[C@H](N)C(O)=O QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P L-argininium(2+) Chemical compound NC(=[NH2+])NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P 0.000 description 1
- DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-REOHCLBHSA-N L-asparagine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(N)=O DCXYFEDJOCDNAF-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(N)=O ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-leucine Chemical compound CC(C)C[C@H](N)C(O)=O ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-lysine Chemical compound NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N L-methionine Chemical compound CSCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O FFEARJCKVFRZRR-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- COLNVLDHVKWLRT-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-phenylalanine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 COLNVLDHVKWLRT-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108091026898 Leader sequence (mRNA) Proteins 0.000 description 1
- ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Leucine Natural products CC(C)CC(N)C(O)=O ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010062489 Leukaemia recurrent Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102100024032 Linker for activation of T-cells family member 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108060001084 Luciferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000005089 Luciferase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000008771 Lymphadenopathy Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102100034709 Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091054437 MHC class I family Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000003792 Metallothionein Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000157 Metallothionein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010027476 Metastases Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010027480 Metastatic malignant melanoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000713333 Mouse mammary tumor virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 101150097381 Mtor gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000714177 Murine leukemia virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 101100341510 Mus musculus Itgal gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100236305 Mus musculus Ly9 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000033776 Myeloid Acute Leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010028561 Myeloid metaplasia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000003505 Myosin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108060008487 Myosin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710141230 Natural killer cell receptor 2B4 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000000636 Northern blotting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 101710163270 Nuclease Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091005461 Nucleic proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091034117 Oligonucleotide Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100034925 P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000010292 Peptide Elongation Factor 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102100026066 Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains 1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010039918 Polylysine Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000015623 Polynucleotide Adenylyltransferase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010024055 Polynucleotide adenylyltransferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100037935 Polyubiquitin-C Human genes 0.000 description 1
- ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Proline Natural products OC(=O)C1CCCN1 ONIBWKKTOPOVIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000033766 Prolymphocytic Leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010029485 Protein Isoforms Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000001708 Protein Isoforms Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010076504 Protein Sorting Signals Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108020005161 RNA Caps Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010065868 RNA polymerase SP6 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000006819 RNA synthesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010008281 Recombinant Fusion Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000007056 Recombinant Fusion Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000712907 Retroviridae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000714474 Rous sarcoma virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102100029216 SLAM family member 5 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 206010039491 Sarcoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000700584 Simplexvirus Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000000453 Skin Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000002105 Southern blotting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 206010041660 Splenomegaly Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006044 T cell activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005867 T cell response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 102100035268 T-cell surface protein tactile Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102000018679 Tacrolimus Binding Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010027179 Tacrolimus Binding Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010058901 Testicular mass Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004098 Tetracycline Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091036066 Three prime untranslated region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000006601 Thymidine Kinase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004440 Thymidine kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100037116 Transcription elongation factor 1 homolog Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004566 Transfer RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000008579 Transposases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010020764 Transposases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100033733 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 101710187830 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100022156 Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010056354 Ubiquitin C Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000007097 Urinary Bladder Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000002495 Uterine Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101001038499 Yarrowia lipolytica (strain CLIB 122 / E 150) Lysine acetyltransferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012190 activator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960000643 adenine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 208000009956 adenocarcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229960005305 adenosine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002671 adjuvant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000004279 alanine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001299 aldehydes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001338 aliphatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 208000026935 allergic disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000007815 allergy Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003281 allosteric effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001414 amino alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940025084 amphetamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000823 artificial membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 235000009582 asparagine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960001230 asparagine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000003704 aspartic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 208000006673 asthma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000004900 autophagic degradation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010028263 bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010005774 beta-Galactosidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- IQFYYKKMVGJFEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-L-thymidine Natural products O=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1C1OC(CO)C(O)C1 IQFYYKKMVGJFEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-PSQAKQOGSA-N beta-L-uridine Natural products O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O[C@@H]1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1 DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-PSQAKQOGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-carboxyaspartic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)C(C(O)=O)C(O)=O OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003012 bilayer membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005842 biochemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003115 biocidal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010170 biological method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000031018 biological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000601 blood cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009395 breeding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001488 breeding effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009702 cancer cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002619 cancer immunotherapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000029499 cancer-related condition Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000010261 cell growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000022534 cell killing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002659 cell therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008668 cellular reprogramming Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005754 cellular signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003169 central nervous system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 125000003636 chemical group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000018805 childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000002759 chromosomal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000349 chromosome Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000024207 chronic leukemia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010072917 class-I restricted T cell-associated molecule Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000013599 cloning vector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011260 co-administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012761 co-transfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001246 colloidal dispersion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000084 colloidal system Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000018417 cysteine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cysteine Natural products SCC(N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001461 cytolytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940104302 cytosine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001687 destabilization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940093541 dicetylphosphate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000000447 dimerizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- BPHQZTVXXXJVHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimyristoyl phosphatidylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COP(O)(=O)OCC(O)CO)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCC BPHQZTVXXXJVHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005750 disease progression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 241001493065 dsRNA viruses Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000012636 effector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003162 effector t lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003527 eukaryotic cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000000684 flow cytometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002825 functional assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012215 gene cloning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010362 genome editing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003862 glucocorticoid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013922 glutamic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004220 glutamic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N glutamine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCC(N)=O ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003630 glycyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 230000012010 growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N guanine Chemical class O=C1NC(N)=NC2=C1N=CN2 UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940029575 guanosine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003278 haem Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002443 helper t lymphocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000011132 hemopoiesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003494 hepatocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000005734 heterodimerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003630 histaminocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000006801 homologous recombination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002744 homologous recombination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102000043864 human PRSS2 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007954 hypoxia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005931 immune cell recruitment Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000987 immune system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003053 immunization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002649 immunization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000016784 immunoglobulin production Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001506 immunosuppresive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000099 in vitro assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005462 in vivo assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000411 inducer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000027866 inflammatory disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940090044 injection Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007918 intramuscular administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002601 intratumoral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007794 irritation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002147 killing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002045 lasting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010025135 lupus erythematosus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 210000004324 lymphatic system Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000018555 lymphatic system disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000021039 metastatic melanoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229930182817 methionine Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 238000000520 microinjection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004005 microsphere Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002703 mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000350 mutagenesis Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 125000001421 myristyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000002088 nanocapsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003835 nucleoside group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001539 phagocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- COLNVLDHVKWLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylalanine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 COLNVLDHVKWLRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000053 physical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004962 physiological condition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003720 plasmablast Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000004180 plasmocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229920000656 polylysine Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000020004 porter Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012794 pre-harvesting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000186 progesterone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960003387 progesterone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000000069 prophylactic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001243 protein synthesis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006337 proteolytic cleavage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005180 public health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010188 recombinant method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000022532 regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108091008146 restriction endonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000010839 reverse transcription Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003757 reverse transcription PCR Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012552 review Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003705 ribosome Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 102220058139 rs372082751 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 102220080600 rs797046116 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012163 sequencing technique Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000012201 sexual and gender identity disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000015891 sexual disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000002741 site-directed mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003491 skin Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 201000000849 skin cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009295 sperm incapacitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011301 standard therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000130 stem cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000011550 stock solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010189 synthetic method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960002180 tetracycline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229930101283 tetracycline Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 235000019364 tetracycline Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003522 tetracyclines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940104230 thymidine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 208000008732 thymoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108010078373 tisagenlecleucel Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000001988 toxicity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000419 toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000005026 transcription initiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005030 transcription termination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001052 transient effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010474 transient expression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003146 transient transfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000014621 translational initiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002054 transplantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011269 treatment regimen Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004614 tumor growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004222 uncontrolled growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 241001529453 unidentified herpesvirus Species 0.000 description 1
- DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N uracil arabinoside Natural products OC1C(O)C(CO)OC1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1 DRTQHJPVMGBUCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940045145 uridine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 201000005112 urinary bladder cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010046766 uterine cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000035899 viability Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- A61P35/02—Antineoplastic agents specific for leukemia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/10—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the cell type used
- A61K40/11—T-cells, e.g. tumour infiltrating lymphocytes [TIL] or regulatory T [Treg] cells; Lymphokine-activated killer [LAK] cells
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/30—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the recombinant expression of specific molecules in the cells of the immune system
- A61K40/31—Chimeric antigen receptors [CAR]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/40—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by antigens that are targeted or presented by cells of the immune system
- A61K40/41—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K40/42—Cancer antigens
- A61K40/4202—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K40/421—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- A61K40/4211—CD19 or B4
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/40—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by antigens that are targeted or presented by cells of the immune system
- A61K40/41—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K40/42—Cancer antigens
- A61K40/4202—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K40/421—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- A61K40/4212—CD22, BL-CAM, siglec-2 or sialic acid binding Ig-related lectin 2
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/545—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/80—Vaccine for a specifically defined cancer
- A61K2039/804—Blood cells [leukemia, lymphoma]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00
- A61K2239/31—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00 characterized by the route of administration
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00
- A61K2239/38—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00 characterised by the dose, timing or administration schedule
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00
- A61K2239/46—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00 characterised by the cancer treated
- A61K2239/48—Blood cells, e.g. leukemia or lymphoma
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
Abstract
Description
許多患有B細胞惡性腫瘤患者無法用標準療法治療。此外,傳統的治療選擇通常會產生嚴重的副作用。在癌症免疫療法方面已經進行了嘗試,然而,若干障礙使得這難以達到臨床上的有效性目標。雖然已經鑒定了數百種所謂的腫瘤抗原,但該等抗原通常衍生自自身,並且因此免疫原性差。此外,腫瘤利用若干種機制使其自身抵制免疫攻擊的啟動和傳播。Many patients with B-cell malignancies are refractory to standard therapies. Additionally, traditional treatment options often have serious side effects. Attempts have been made in cancer immunotherapy, however, several obstacles make it difficult to achieve clinical effectiveness goals. Although hundreds of so-called tumor antigens have been identified, these antigens are usually self-derived and are therefore poorly immunogenic. In addition, tumors employ several mechanisms to make themselves resistant to the initiation and propagation of immune attack.
使用嵌合抗原受體(CAR)修飾的自體T細胞(CART)療法的最新發展依賴於將T細胞重定向至癌細胞如B細胞惡性腫瘤上的合適細胞表面分子,該最新發展在利用免疫系統治療B細胞惡性腫瘤和其他癌症的能力方面顯示出有希望的結果(參見例如,Sadelain等人, Cancer Discovery [癌症發現] 3:388-398 (2013))。鼠來源的CART19(即「CTL019」)的臨床結果已顯示出在患有CLL以及兒童ALL的患者中建立完全緩解的希望(參見例如,Kalos等人, Sci Transl Med [科學轉化醫學] 3:95ra73 (2011);Porter等人, NEJM [新英格蘭醫學雜誌] 365:725-733 (2011);Grupp等人, NEJM [新英格蘭醫學雜誌] 368:1509-1518 (2013))。除了遺傳修飾的T細胞上的嵌合抗原受體識別和破壞靶細胞的能力之外,成功的治療性T細胞療法需要具有隨時間增殖和持續的能力,以為了監測白血病復發。T細胞的可變品質(失能、抑制或耗竭的結果)都會對CAR轉化的T細胞的性能產生影響,對於熟練的從業者來說,此時對該性能的控制有限。為了使其有效,CAR轉化的患者T細胞需要持續並維持響應於同源抗原而增殖的能力。Recent developments in therapy using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified autologous T cells (CART), which rely on redirecting T cells to appropriate cell surface molecules on cancer cells such as B-cell malignancies, are Promising results have been shown in the ability of the system to treat B-cell malignancies and other cancers (see eg, Sadelain et al., Cancer Discovery 3:388-398 (2013)). Clinical results with murine-derived CART19 (ie, "CTL019") have shown promise in establishing complete remissions in patients with CLL as well as pediatric ALL (see, eg, Kalos et al., Sci Transl Med 3:95ra73 (2011); Porter et al, NEJM 365:725-733 (2011); Grupp et al, NEJM 368:1509-1518 (2013)). In addition to the ability of chimeric antigen receptors on genetically modified T cells to recognize and destroy target cells, successful therapeutic T cell therapy requires the ability to proliferate and persist over time in order to monitor leukemia relapse. The variable qualities of T cells (as a result of incapacitation, suppression, or exhaustion) all have an impact on the performance of CAR-transformed T cells, and for the skilled practitioner there is limited control over this performance at this time. To be effective, CAR-transformed patient T cells need to persist and maintain the ability to proliferate in response to cognate antigens.
本揭露的特徵尤其在於治療疾病之方法,該等方法包括以基於細胞/kg體重和/或患者的年齡的劑量,向該有需要的患者投與包含細胞群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22結合的嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子。在一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約3 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 > 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約1.5 × 10 6個細胞。在另一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約10 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 > 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約5 × 10 6個細胞。在另一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 > 50 kg的患者,該劑量為約15 × 10 6個細胞。 雙重CAR The disclosure features, inter alia, methods of treating disease comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a pharmaceutical composition comprising a cell population comprising A nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecule that binds to CD19 and CD22. In one embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, the dose is about 3 x 104 cells/kg body weight for patients weighing ≤ 50 kg, or the dose for patients weighing > 50 kg It is about 1.5 × 10 6 cells. In another embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, the dose is about 10 x 104 cells/kg body weight for patients weighing ≤ 50 kg, or the dose for patients weighing > 50 kg The dose is about 5 x 106 cells. In another embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, the dose is about 30 x 104 cells/kg body weight for patients weighing ≤ 50 kg, or the dose is about 30 x 10 cells/kg body weight for patients weighing > 50 kg. The dose is about 15 x 106 cells. double CAR
在一個方面,本揭露提供了一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子包含: (a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及 (b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域, 其中: (i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同; (ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含如SEQ ID NO: 70中任一項該的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或 (iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。 In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecule, wherein the CAR molecule comprises: (a) a first CAR comprising a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22; a first transmembrane domain; a first co-stimulatory signaling domain; and/or a first primary signaling domain; and (b) a second CAR comprising a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19; a second transmembrane domain; a second co-stimulatory signaling domain; and/or a second primary signaling domain, in: (i) the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 65 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the first The nucleotide sequence of the transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule; (ii) the first co-stimulatory signaling domain and the second co-stimulatory signaling domain comprise an amino acid sequence as described in any one of SEQ ID NO: 70 or an amino acid sequence having at least 90% identity therewith , optionally wherein the nucleotide sequence encoding the first costimulatory signaling domain and comprised in the nucleic acid molecule differs from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second costimulatory signaling domain comprised in the nucleic acid molecule; and /or (iii) the first primary signaling domain and the second primary signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 75 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the primary signaling The nucleotide sequence of the structural domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule.
在實施方式中,第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、和第一共刺激傳訊結構域。在實施方式中,第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域。在實施方式中,第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、第一共刺激傳訊結構域、和第一初級傳訊結構域。In an embodiment, the first CAR comprises a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22, a first transmembrane domain, and a first co-stimulatory signaling domain. In an embodiment, the first CAR comprises a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22, a first transmembrane domain; and a first primary signaling domain. In an embodiment, the first CAR comprises a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22, a first transmembrane domain, a first co-stimulatory signaling domain, and a first primary signaling domain.
在實施方式中,第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二共刺激傳訊結構域。在實施方式中,第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域。在實施方式中,第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域。In an embodiment, the second CAR comprises a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19; a second transmembrane domain; and a second co-stimulatory signaling domain. In an embodiment, the second CAR comprises a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19; a second transmembrane domain; and a second primary signaling domain. In an embodiment, the second CAR comprises a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19; a second transmembrane domain; a second co-stimulatory signaling domain; and a second primary signaling domain.
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3);和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3)。在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含分別含有如下的HC CDR1、HC CDR2、HC CDR3、LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3:(i) SEQ ID NO: 20、21、22、28、29、和30的胺基酸序列;(ii) SEQ ID NO: 23、24、22、31、32和33的胺基酸序列;或 (iii) SEQ ID NO: 25、26、27、34、32和30的胺基酸序列。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises one or more (eg, all three) of the light chain complementarity determining region 1 (LC) of a CD22 binding domain described herein (eg, in Table 1A, 2A or 3A). CDR1), light chain complementarity determining region 2 (LC CDR2), and light chain complementarity determining region 3 (LC CDR3); and/or one or A plurality (eg, all three) of heavy chain complementarity determining region 1 (HC CDR1 ), heavy chain complementarity determining region 2 (HC CDR2), and heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 (HC CDR3). In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises HC CDR1, HC CDR2, HC CDR3, LC CDR1, LC CDR2, and LC CDR3 comprising, respectively: (i) SEQ ID NOs: 20, 21, 22, 28, 29, and The amino acid sequence of 30; (ii) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 23, 24, 22, 31, 32 and 33; or (iii) SEQ ID NO: 25, 26, 27, 34, 32 and 30 amino acid sequence.
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50、53、或55)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50、53、或55)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50、53、或55)的胺基酸序列。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising at least one, two or three of the CD22 scFv sequences provided in Table 1A or 3A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 50, 53, or 55). Modified (eg, substituted) but not more than 30, 20 or 10 modified (eg, substituted) amino acid sequences. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising an amine group at least 95% identical to a CD22 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 50, 53, or 55) acid sequence. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD22 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 50, 53, or 55).
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv由與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 49、51、52、54、56、或57)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv consisting of at least 95% of the CD22 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 49, 51, 52, 54, 56, or 57). %, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, or 100% identical nucleotide sequence codes.
在實施方式中,該CD19抗原結合結構域包含本文(例如在表1A、2A、3A、或5A中)所述之CD19抗原結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3);和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A、3A、或5A中)所述之CD19抗原結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3)。在實施方式中,CD19結合結構域包含分別含有如下的HC CDR1、HC CDR2、HC CDR3、LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3:(i) SEQ ID NO: 35、36、39、40、41、和42的胺基酸序列;(ii) SEQ ID NO: 35、37、39、40、41和42的胺基酸序列;或 (iii) SEQ ID NO: 35、38、39、40、41和42的胺基酸序列。In an embodiment, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises one or more (eg, all three) light chain complements of a CD19 antigen binding domain described herein (eg, in Table 1A, 2A, 3A, or 5A). Light chain complementarity determining region 1 (LC CDR1), light chain complementarity determining region 2 (LC CDR2), and light chain complementarity determining region 3 (LC CDR3); and/or described herein (e.g., in Table 1A, 2A, 3A, or 5A) One or more (eg, all three) of the heavy chain complementarity determining region 1 (HC CDR1), heavy chain complementarity determining region 2 (HC CDR2) and heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 (HC CDR3) of the CD19 antigen binding domain . In an embodiment, the CD19 binding domain comprises HC CDR1, HC CDR2, HC CDR3, LC CDR1, LC CDR2, and LC CDR3 comprising, respectively: (i) SEQ ID NOs: 35, 36, 39, 40, 41, and The amino acid sequence of 42; (ii) the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 35, 37, 39, 40, 41 and 42; or (iii) SEQ ID NO: 35, 38, 39, 40, 41 and 42 amino acid sequence.
在實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含具有表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44或47)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含與表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44或47)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44或47)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv由與表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 43、45、46、或48)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。In an embodiment, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising at least one, two or three of the CD19 scFv sequences provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 44 or 47) Modified (eg, substituted) but not more than 30, 20 or 10 modified (eg, substituted) amino acid sequences. In an embodiment, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising an amine group at least 95% identical to a CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 44 or 47) acid sequence. In an embodiment, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 44 or 47). In an embodiment, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv that is at least 95% identical to the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 43, 45, 46, or 48) , 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, or 100% identical nucleotide sequence codes.
在本文揭露的編碼CAR分子的核酸的實施方式中,編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列。在實施方式中,編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、150個核苷酸、200個核苷酸或全部核苷酸。In the embodiment of the nucleic acid encoding the CAR molecule disclosed herein, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first transmembrane domain is at least 1%, 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60% %, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, or 100% different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain. In an embodiment, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first transmembrane domain differs from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain by at least 1 nucleotide, 10 nucleotides, or 20 nucleosides acid, 30 nucleotides, 40 nucleotides, 50 nucleotides, 60 nucleotides, 70 nucleotides, 80 nucleotides, 90 nucleotides, 100 nucleotides, 150 nucleotides, 200 nucleotides or all nucleotides.
在本文揭露的編碼CAR分子的核酸的實施方式中,編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。在實施方式中,編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、150個核苷酸、200個核苷酸或全部核苷酸。In the embodiment of the nucleic acid encoding the CAR molecule disclosed herein, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first co-stimulatory signaling domain is at least 1%, 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, or 100% differ from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second co-stimulatory signaling domain. In an embodiment, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first co-stimulatory signaling domain differs from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second co-stimulatory signaling domain by at least 1 nucleotide, 10 nucleotides, 20 nucleotides Nucleotides, 30 nucleotides, 40 nucleotides, 50 nucleotides, 60 nucleotides, 70 nucleotides, 80 nucleotides, 90 nucleotides, 100 nucleotides acid, 150 nucleotides, 200 nucleotides, or all nucleotides.
在本文揭露的編碼CAR分子的核酸的實施方式中,編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。在實施方式中,編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、150個核苷酸、200個核苷酸或全部核苷酸。In the embodiment of the nucleic acid encoding the CAR molecule disclosed herein, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first primary signaling domain is at least 1%, 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, 60% %, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, or 100% different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain. In an embodiment, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first primary signaling domain differs from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain by at least 1 nucleotide, 10 nucleotides, or 20 nucleotides acid, 30 nucleotides, 40 nucleotides, 50 nucleotides, 60 nucleotides, 70 nucleotides, 80 nucleotides, 90 nucleotides, 100 nucleotides, 150 nucleotides, 200 nucleotides or all nucleotides.
在本文揭露的編碼CAR分子的核酸序列的一個方面中,CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 11、15或19的核苷酸序列或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%或99%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。In one aspect of the nucleic acid sequence encoding the CAR molecule disclosed herein, the CAR molecule consists of the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 11, 15 or 19 or has at least 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 96% , 97%, 98% or 99% identical nucleotide sequence codes.
在一個方面,本文揭露的CAR分子包含SEQ ID NO: 12或16的胺基酸序列,與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列。In one aspect, a CAR molecule disclosed herein comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 12 or 16, an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto.
在一個方面,本揭露提供了一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸序列,其中所述CAR分子包含: (a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及 (b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域, 其中: (i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同; (ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或 (iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。 In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a cell (eg, an immune effector cell) comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecule, wherein the CAR molecule comprises: (a) a first CAR comprising a first antigen binding domain and a first transmembrane domain that bind CD22; a first costimulatory signaling domain; and/or a first primary signaling domain; and (b) a second CAR comprising a second antigen binding domain and a second transmembrane domain that bind CD19; a second costimulatory signaling domain; and/or a second primary signaling domain, in: (i) the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 65 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the first The nucleotide sequence of the transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule; (ii) the first costimulatory signaling domain and the second costimulatory signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 70 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the The nucleotide sequence of the first co-stimulatory signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second co-stimulatory signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule; and/or (iii) the first primary signaling domain and the second primary signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 75 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the first The nucleotide sequence of the primary signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule.
在一方面,該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 108的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。In one aspect, the first primary signaling domain and the second primary signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 108 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the second primary signaling domain. A primary signaling domain comprised in the nucleic acid molecule differs in nucleotide sequence from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain comprised in the nucleic acid molecule.
在另一方面,本文提供了一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子,其中所述CAR分子包含: (a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及 (b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域, 其中: (i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同; (ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或 (iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。 In another aspect, provided herein is a cell (e.g., an immune effector cell) comprising a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecule, wherein the CAR molecule comprises: (a) a first CAR comprising a first antigen binding domain and a first transmembrane domain that bind CD22; a first costimulatory signaling domain; and/or a first primary signaling domain; and (b) a second CAR comprising a second antigen binding domain and a second transmembrane domain that bind CD19; a second costimulatory signaling domain; and/or a second primary signaling domain, in: (i) the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 65 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the first The nucleotide sequence of the transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain and contained in the nucleic acid molecule; (ii) the first costimulatory signaling domain and the second costimulatory signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 70 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the The nucleotide sequence of the first co-stimulatory signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule is different from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second co-stimulatory signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule; and/or (iii) the first primary signaling domain and the second primary signaling domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 75 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto, optionally encoding the first The nucleotide sequence of the primary signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule differs from the nucleotide sequence encoding the second primary signaling domain contained in the nucleic acid molecule.
在實施方式中,細胞係免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞(例如CD3+、CD4+或CD8+ T細胞)、或NK細胞。在實施方式中,細胞係人細胞。In an embodiment, the cell line is an immune effector cell, such as a T cell (eg, a CD3+, CD4+ or CD8+ T cell), or an NK cell. In an embodiment, the cell is a human cell.
在一個方面,本文提供了一種提供抗腫瘤免疫之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞群體),該細胞包含,例如,表現本文揭露的CAR分子,例如本文揭露的雙重CAR分子。In one aspect, provided herein is a method of providing anti-tumor immunity comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of cells (e.g., a population of immune effector cells) comprising, e.g., expressing the CAR molecules, such as the dual CAR molecules disclosed herein.
在另一方面,本揭露提供了治療患有與抗原(例如,CD19和/或CD22)相關的疾病的受試者之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞群體),該細胞包含,例如,表現本文揭露的CAR分子,例如本文揭露的雙重CAR分子。 串聯CAR In another aspect, the present disclosure provides a method of treating a subject with a disease associated with an antigen (eg, CD19 and/or CD22), the method comprising administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of cells ( For example, a population of immune effector cells) comprising, for example, expressing a CAR molecule disclosed herein, such as a dual CAR molecule disclosed herein. Tandem CAR
在一個方面,本揭露提供了雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域。In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a bispecific antigen binding domain comprising a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22 and a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19.
在另一方面,本文提供嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該嵌合抗原受體包含本文所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域。In another aspect, provided herein are chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) comprising a bispecific antigen binding domain described herein.
在又另一個方面,本揭露提供了編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)的核酸,該嵌合抗原受體包含本文所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域。In yet another aspect, the present disclosure provides a nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) comprising a bispecific antigen binding domain described herein.
在本文所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域的一些實施方式中,例如,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR,或編碼包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR的核酸,第一抗原結合結構域可位於第二抗原結合結構域的上游(例如,在N-末端方向),或第一抗原結合結構域可位於第二抗原結合結構域的下游(例如,在C-末端方向)。In some embodiments of the bispecific antigen binding domains described herein, e.g., a CAR comprising a bispecific antigen binding domain, or a nucleic acid encoding a CAR comprising a bispecific antigen binding domain, the first antigen binds The domain can be located upstream (eg, in the N-terminal direction) of the second antigen binding domain, or the first antigen binding domain can be located downstream (eg, in the C-terminal direction) of the second antigen binding domain.
在一些實施方式中,第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域中的每一個包含scFv,例如,輕鏈可變(VL)結構域和重鏈可變(VH)結構域。在一些實施方式中,第一抗原結合結構域包含含有第一VH(VH1)和第一VL(VL1)的scFv。在一些實施方式中,第二抗原結合結構域包含含有第二VH(VH2)和第二VL(VL2)的scFv。In some embodiments, each of the first antigen binding domain and the second antigen binding domain comprises a scFv, eg, a light chain variable (VL) domain and a heavy chain variable (VH) domain. In some embodiments, the first antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising a first VH (VH1) and a first VL (VL1). In some embodiments, the second antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising a second VH (VH2) and a second VL (VL2).
在一些實施方式中,雙特異性抗原結合結構域具有以下N末端到C末端組態中的任一個:VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2;VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2;VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2;VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2、VH2-VL2-VL1-VH1;VL2-VH2-VL1-VH1;VH2-VL2-VH1-VL1;或VL2-VH2-VH1-VL1。In some embodiments, the bispecific antigen binding domain has any of the following N-terminal to C-terminal configurations: VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2; VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2; VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2 ; VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2, VH2-VL2-VL1-VH1; VL2-VH2-VL1-VH1; VH2-VL2-VH1-VL1; or VL2-VH2-VH1-VL1.
在一個方面,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 2的胺基酸序列並且由SEQ ID NO: 1的核酸序列編碼。在另一方面,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 4的胺基酸序列並且由SEQ ID NO: 3的核酸序列編碼。In one aspect, the CAR comprising the bispecific antigen binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 and is encoded by the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. In another aspect, the CAR comprising the bispecific antigen binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 4 and is encoded by the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3.
在另一方面,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 6的胺基酸序列並且由SEQ ID NO: 5的核酸序列編碼。In another aspect, the CAR comprising the bispecific antigen binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 6 and is encoded by the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 5.
在另一方面,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 8的胺基酸序列並且由SEQ ID NO: 7的核酸序列編碼。In another aspect, the CAR comprising the bispecific antigen binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 8 and is encoded by the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 7.
在另一方面,包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 10的胺基酸序列並且由SEQ ID NO: 9的核酸序列編碼。In another aspect, the CAR comprising the bispecific antigen binding domain comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 10 and is encoded by the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 9.
在一個方面,本揭露提供了載體,該載體包含編碼本文揭露的CAR分子的核酸分子、編碼本文揭露的雙特異性抗原結合結構域的核酸、或編碼包含本文揭露的雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR的核酸。In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR molecule disclosed herein, a nucleic acid encoding a bispecific antigen binding domain disclosed herein, or a nucleic acid encoding a nucleic acid molecule comprising a bispecific antigen binding domain disclosed herein. Nucleic acid of the CAR.
在另一方面,本文提供了藥物組成物,該藥物組成物包含編碼本文揭露的CAR分子的核酸或包含本文揭露的CAR分子的藥物組成物。在一些實施方式中,該藥物組成物包含賦形劑、載體、稀釋劑和/或穩定劑。In another aspect, provided herein are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a nucleic acid encoding a CAR molecule disclosed herein or a pharmaceutical composition comprising a CAR molecule disclosed herein. In some embodiments, the pharmaceutical composition comprises excipients, carriers, diluents and/or stabilizers.
在又另一個方面,本揭露提供了包含本文揭露的雙特異性抗原結合結構域的藥物組成物、包含本文揭露的雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR、或編碼本文揭露的雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR核酸。在一些實施方式中,該藥物組成物包含賦形劑、載體、稀釋劑和/或穩定劑。In yet another aspect, the present disclosure provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the bispecific antigen binding domains disclosed herein, CARs comprising the bispecific antigen binding domains disclosed herein, or encoding the bispecific antigen binding domains disclosed herein. domain CAR nucleic acid. In some embodiments, the pharmaceutical composition comprises excipients, carriers, diluents and/or stabilizers.
在一個方面,本文提供了一種提供抗腫瘤免疫之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞群體),該細胞包含,例如,表現本文揭露的CAR,例如本文揭露的串聯CAR。In one aspect, provided herein is a method of providing anti-tumor immunity comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of cells (e.g., a population of immune effector cells) comprising, e.g., expressing the CARs, such as the tandem CARs disclosed herein.
在另一方面,本揭露提供了治療患有與抗原(例如,CD19和/或CD22)相關的疾病的受試者之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞群體),該細胞包含,例如,表現本文揭露的CAR,例如本文揭露的串聯CAR。In another aspect, the present disclosure provides a method of treating a subject with a disease associated with an antigen (eg, CD19 and/or CD22), the method comprising administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of cells ( For example, a population of immune effector cells) comprising, for example, expressing a CAR disclosed herein, such as a tandem CAR disclosed herein.
本領域的技術者僅使用常規實驗就將認識到或能夠確定本文所述之本發明該等具體實施方式的許多等效形式。這種等同物旨在由以下列舉的實施方式涵蓋。
列舉的實施方式
1. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中:
(i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;
(ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或
(iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。
2. 如實施方式1所述之核酸分子,其中該第一CAR包含:
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、和第一共刺激傳訊結構域;
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;或
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、第一共刺激傳訊結構域、和第一初級傳訊結構域。
3. 如實施方式1或2所述之核酸分子,其中該第二CAR包含:
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二共刺激傳訊結構域;
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域;或
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域。
4. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含:
本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3);和/或
本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3)。
5. 如實施方式4所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3;和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的HC CDR1、HC CDR2和HC CDR3。
6. 如實施方式4或5所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含:編碼SEQ ID NO: 28、31、或34的LC CDR1的核苷酸序列、編碼SEQ ID NO: 29或32的LC CDR2的核苷酸序列;編碼SEQ ID NO: 30或33的LC CDR3的核苷酸序列;和/或編碼SEQ ID NO: 20、23、或25的HC CDR1的核苷酸序列、編碼SEQ ID NO: 21、24、或26的HC CDR2的核苷酸序列;編碼SEQ ID NO: 22或27的HC CDR3的核苷酸序列。
7. 如實施方式4至6中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域(例如,scFv)包含本文(例如在表1A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的輕鏈可變(VL)區;和/或本文(例如在表1A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的重鏈可變(VH)區。
8. 如實施方式7所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含VL區:
該VL區包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VL區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
該VL區包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VL區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;或
該VL區由編碼表1A或3A中提供的CD22VL 區序列的胺基酸序列的核苷酸序列編碼。
9. 如實施方式7或8所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含VH區:
該VH區包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
該VH區包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;或
該VH區由編碼表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列的胺基酸序列的核苷酸序列編碼。
10. 如實施方式7至9中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域的VH和VL區藉由連接子(例如,與本文所述之連接子具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的連接子,例如表4A中揭露的連接子)連接。
11. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD22抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv:
包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 50)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 50)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;
包含表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 50)的胺基酸序列;或
由與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 49或51)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。
12. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含:
本文(例如在表1A、2A、3A或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3);和/或
本文(例如在表1A、2A、3A或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3)。
13. 如實施方式12所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含本文(例如在表1A或2A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3;和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的HC CDR1、HC CDR2和HC CDR3。
14. 如實施方式12或13所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 40的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 41的LC CDR2;和SEQ ID NO: 42的LC CDR3;和/或SEQ ID NO: 35的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 36-38的HC CDR2;和SEQ ID NO: 39的HC CDR3。
15. 如實施方式12至14中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域(例如,scFv)包含本文(例如在表1A、3A、或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的輕鏈可變(VL)區;和/或本文(例如在表1A、3A、或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的重鏈可變(VH)區。
16. 如實施方式15所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含:
具有表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;或
表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列的胺基酸序列。
17. 如實施方式15或16所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含:
具有表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;或
表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列的胺基酸序列。
18. 如實施方式15至17中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域的VH和VL區用連接子(例如,與本文所述之連接子具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的連接子,例如表4A中揭露的連接子)連接。
19. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv:
包含具有表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 44)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列;
包含與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 44)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列;
包含表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如SEQ ID NO: 44)的胺基酸序列;或
由與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 43或48)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。
20. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含與SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。
21. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含與SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列具有一個、兩個、三個、四個、五個、六個或七個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。
22. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列。
23. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列。
24. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、150個核苷酸、200個核苷酸或全部核苷酸。
25. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 64或66具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
26. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 67或68具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
27. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。
28. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 70中任一項所述之胺基酸序列具有一個、兩個、三個、四個或五個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。
29. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含如SEQ ID NO: 70中任一項所述之胺基酸序列。
30. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。
31. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、120個核苷酸或全部核苷酸。
32. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一共刺激結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 69或72具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
33. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第二共刺激結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 71或73具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
34. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。
35. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一初級傳訊結構域和所述第二初級傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列具有一個、兩個、三個、四個、五個、六個、七個、八個、九個、十個、十一個或十二個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。
36. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列。
37. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。
38. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列相差至少1個核苷酸、10個核苷酸、20個核苷酸、30個核苷酸、40個核苷酸、50個核苷酸、60個核苷酸、70個核苷酸、80個核苷酸、90個核苷酸、100個核苷酸、150個核苷酸、200個核苷酸、250個核苷酸、300個苷酸或全部核苷酸。
39. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 74或77具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
40. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列選自與SEQ ID NO: 76或78具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的序列。
41. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該第一CAR和/或第二CAR包含訊息肽,例如,包含一段疏水性胺基酸(例如,5-16個殘基)的肽。
42. 如實施方式41所述之核酸分子,其中該訊息肽選自CD8 α訊息肽、介白素2訊息肽、人白蛋白訊息肽、人胰凝乳蛋白酶原訊息肽、人胰蛋白酶原-2訊息肽或在Stern B.等人 「Improving mammalian cell factories: The selection of signal peptide has a major impact on recombinant protein synthesis and secretion in mammalian cells.[改進哺乳動物細胞工廠:在哺乳動物細胞中,訊息肽的選擇對重組蛋白的合成和分泌產生重大影響]」 (2007)中揭露的其他類似的訊息肽。
43. 如實施方式41或42所述之核酸分子,其中該訊息肽:
包含表4A中提供的訊息肽;
包含SEQ ID NO: 59的胺基酸或
由SEQ ID NO: 58、60、61、62、或63中任一項所述之核酸、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核酸編碼。
44. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該核酸分子在5’至3’方向上包含第一CAR,隨後第二CAR。
45. 如實施方式1至43中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中該核酸分子在5’至3’方向上包含第二CAR,隨後第一CAR。
46. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,該核酸分子進一步包含蛋白酶切割位點(例如,T2A、P2A、E2A、或F2A切割位點)或內部核糖體進入位點。
47. 如實施方式46所述之核酸分子,其中該蛋白酶切割位點係P2A位點。
48. 如實施方式46或47所述之核酸分子,其中P2A位點包含:編碼SEQ ID NO: 86的胺基酸序列的核苷酸序列;或SEQ ID NO: 85或87的核苷酸序列。
49. 如實施方式46至48中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中蛋白酶切割位點或內部核糖體進入位點位於第一CAR和第二CAR之間。
50. 如實施方式46至49中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中蛋白酶切割位點位於使得細胞可以表現包含第一CAR和第二CAR的融合蛋白,視需要其中該融合蛋白藉由蛋白水解切割被加工成兩個肽。
51. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含SEQ ID NO: 11的核苷酸序列,或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核苷酸序列。
52. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含:第一CAR,該第一CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 13的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸,和第二CAR,該第二CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 14的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
53. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
54. 如實施方式1至50中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 15的核苷酸序列,或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。
55. 如實施方式1至50或54中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含:第一CAR,該第一CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 17的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸,和第二CAR,該第二CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 18的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
56. 如實施方式1至50、或54或55中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子由編碼SEQ ID NO: 16的胺基酸序列或編碼與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸的核酸編碼。
57. 如實施方式1至50中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 19的核苷酸序列,或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。
58. 如實施方式1至50或57中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含:第一CAR,該第一CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 13的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸,和第二CAR,該第二CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 14的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
59. 如實施方式1至50、或57或58中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中CAR分子包含SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
60. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子在5’至3’方向上包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;
(b) P2A蛋白酶切割位點;
(c) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 11的核苷酸序列編碼;或編碼SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列的核酸。
61. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子在5’至3’方向上包含:
(a) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域;
(b) P2A蛋白酶切割位點;
(c) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 15的核苷酸序列編碼;或編碼SEQ ID NO: 16的胺基酸序列的核酸。
62. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子在5’至3’方向上包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;
(b) P2A蛋白酶切割位點;
(c) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 19的核苷酸序列編碼;或編碼SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列的核酸。
63. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,該核酸分子進一步包含啟動子序列,例如,EF1啟動子。
64. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一CAR的核苷酸序列和編碼該第二CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於單個核酸構建體上。
65. 如實施方式64所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一CAR的核苷酸序列和編碼該第二CAR的核酸被佈置於相同的載體上。
66. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一CAR的核苷酸序列和編碼該第二CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於不同的核酸構建體上,例如,編碼該第一CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於第一核酸構建體上,並且編碼該第二CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於第二核酸構建體上。
67. 如實施方式66所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第一CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於第一載體上。
68. 如實施方式66所述之核酸分子,其中編碼該第二CAR的核苷酸序列被佈置於第二載體上。
69. 該核酸分子包含病毒元件,例如,病毒包裝元件。
70. 一種載體,該載體包含如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之核酸分子。
71. 如實施方式70所述之載體,其中該載體選自DNA、RNA、質體、慢病毒載體、腺病毒載體、或反轉錄病毒載體。
72. 一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含如實施方式70或71所述之載體,或如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之核酸分子。
73. 一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子,其中所述CAR分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中:
(i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;
(ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或
(iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含如SEQ ID NO: 75中任一項該的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。
74. 一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子,其中所述CAR分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中:
(i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;
(ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或
(iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,視需要其中編碼初級傳訊結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。
75. 如實施方式74所述之細胞,其中該細胞包含編碼CAR分子的核酸。
76. 如實施方式73或75所述之細胞,該細胞包含如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之核酸分子或如實施方式70或71所述之載體。
77. 一種包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的細胞,該嵌合抗原受體分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 11的核苷酸序列編碼;或包含SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列。
78. 一種包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的細胞,該嵌合抗原受體分子包含:
(a) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域;
(b) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 15的核苷酸序列編碼;或包含SEQ ID NO: 16的胺基酸序列。
79. 一種包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的細胞,該嵌合抗原受體分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含:第一訊息肽;結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含:第二訊息肽;結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域,
其中CAR分子由SEQ ID NO: 19的核苷酸序列編碼;或包含SEQ ID NO: 12的胺基酸序列。
80. 如實施方式72至79中任一項所述之細胞,其中該細胞係免疫效應細胞,例如,T細胞(例如,CD3+、CD4+或CD8+ T細胞),或NK細胞。
81. 如實施方式72至80中任一實施方式所述之細胞,其中該細胞係人細胞。
82. 一種製備細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞)之方法,該方法包括用如實施方式70或71所述之載體轉導免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)。
83. 一種製備細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞)之方法,該方法包括將如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之核酸分子引入免疫效應細胞,例如,T細胞或NK細胞。
84. 一種產生RNA工程化細胞群體之方法,該方法包括將體外轉錄的RNA或合成RNA引入到細胞中,其中該RNA包含如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之核酸分子。
85. 一種雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域。
86. 在實施方式85所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第一抗原結合結構域可位於第二抗原結合結構域的上游(例如,在N-末端方向),或第一抗原結合結構域可位於第二抗原結合結構域的下游(例如,在C-末端方向)。
87. 如實施方式85或86所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域中的每一個包含scFv,例如,輕鏈可變(VL)結構域和重鏈可變(VH)結構域。
88. 如實施方式87所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中VH可位於VL的上游或下游。
89. 如實施方式87或88所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第一抗原結合結構域包含含有第一VH(VH1)和第一VL(VL1)的scFv。
90. 如實施方式87至89中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第二抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含第二VH(VH2)和第二VL(VL2)。
91. 如實施方式87至90中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第一抗原結合結構域排列為VH1在VL1的上游。
92. 如實施方式87至90中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第一抗原結合結構域排列為VL1在VH1的上游。
93. 如實施方式87至92中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第二抗原結合結構域排列為VH2在VL2的上游。
94. 如實施方式87至92中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中第二抗原結合結構域排列為VL2在VH2的上游。
95. 如實施方式87至90、或92至93中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該抗原結合結構域具有以下N末端至C末端組態:VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2。
96. 如實施方式87至90、91或93中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該抗原結合結構域具有以下N末端至C末端組態:VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2。
97. 如實施方式87至90、92、或94中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該抗原結合結構域具有以下N末端至C末端組態:VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2。
98. 如實施方式87至90、91、或94中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該抗原結合結構域具有以下N末端至C末端組態:VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2。
99. 如實施方式85至98中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子。
100. 如實施方式99所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中在第一抗原結合結構域的scFv和第二抗原結合結構域的scFv之間佈置連接子。
101. 如實施方式100所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該連接子佈置在:
VH1和VH2之間,如果構建體具有組態:VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2;
VL1和VH2之間,如果構建體具有組態:VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2;
VH1和VL2之間,如果構建體具有組態:VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2;或
VL1和VL2之間,如果構建體具有組態:VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2。
102. 如實施方式99至101中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該連接子足夠長以避免兩個scFv的結構域之間的錯配。
103. 如實施方式99至102中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該連接子係本文所述之連接子,例如,表1A或4A中提供的連接子。
104. 如實施方式99至103中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n連接子,其中n係1、2、3、4、5、或6。
105. 如實施方式104所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中n = 1,例如,該連接子具有Gly4-Ser的胺基酸序列。
106. 如實施方式104所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中n = 3,例如,SEQ ID NO: 82。
107. 如實施方式99至103中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中該連接子包含胺基酸序列:LAEAAAK,例如,SEQ ID NO: 80。
108. 如實施方式99至107中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中在第一抗原結合結構域的scFv的VL和VH之間佈置連接子,例如,本文所述之連接子。
109. 如實施方式99至108中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,其中在第二抗原結合結構域的scFv的VL和VH之間佈置連接子,例如,本文所述之連接子。
110. 如實施方式99至109中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含表1A或4A中提供的抗原結合結構域的胺基酸序列,例如,SEQ ID NO: 2、4、6、8、10、44、47、53、或55中任一項,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。
112. 如實施方式99至109中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域由表1A或4a中提供的抗原結合結構域的核苷酸序列編碼,例如,SEQ ID NO: 1、3、5、7、9、43、45、46、52、54、56或57中任一項或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核苷酸序列。
113. 一種雙特異性嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性嵌合抗原受體包含如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域。
114. 一種編碼雙特異性嵌合抗原受體(CAR)的核酸構建體,其中該核酸構建體編碼如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域。
115. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含:
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和/或初級傳訊結構域。
116. 如實施方式115所述之CAR,該CAR包含如實施方式86至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域。
117. 如實施方式115或116所述之CAR,該CAR包含:
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;和共刺激傳訊結構域;
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;和初級傳訊結構域;或
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域。
118. 如實施方式115至117中任一項所述之CAR,其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域,其中該跨膜結構域選自T細胞受體的α、β或ζ鏈,CD28,CD3ε,CD45,CD4,CD5,CD8,CD9,CD16,CD22,CD33,CD37,CD64,CD80,CD86,CD123,CD134,CD137或CD154。
119. 如實施方式118所述之CAR,其中該雙特異性抗原結合結構域藉由鉸鏈區(例如本文所述之鉸鏈區)與跨膜結構域連接。
120. 如實施方式115至119中任一項所述之CAR,其中該CAR包含共刺激結構域,其中該共刺激結構域包含OX40、CD2、CD27、CD28、CDS、ICAM-1、LFA-1(CD11a/CD18)、ICOS(CD278)或4-1BB(CD137)的傳訊結構域。
121. 如實施方式115至120中任一項所述之CAR,其中該共刺激結構域包含4-1BB傳訊結構域。
122. 如實施方式115至121中任一項所述之CAR,其中該CAR包含含有CD3 ζ的傳訊結構域的初級傳訊結構域。
123. 如實施方式115至122中任一項所述之CAR,其中該CAR包含表4A中提供的胺基酸序列,例如,SEQ ID NO: 2、4、6、8、10中任一項,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。
124. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第二抗原結合結構域定向在第一抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 2的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
125. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 4的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
126. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 6的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
127. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 8的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
128. 一種包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的嵌合抗原受體(CAR),該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 10的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
129. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含:
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和/或初級傳訊結構域。
130. 如實施方式129所述之CAR核酸,該CAR核酸包含編碼如實施方式86至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域的核酸。
131. 如實施方式129或130所述之CAR核酸,其中該CAR包含:
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;和共刺激傳訊結構域;
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;和初級傳訊結構域;或
特異性抗原結合結構域;跨膜結構域;共刺激傳訊結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域。
132. 如實施方式129至131中任一項所述之CAR核酸,其中該CAR核酸包含跨膜結構域,其中該跨膜結構域選自T細胞受體的α、β或ζ鏈,CD28,CD3ε,CD45,CD4,CD5,CD8,CD9,CD16,CD22,CD33,CD37,CD64,CD80,CD86,CD123,CD134,CD137或CD154。
133. 如實施方式132所述之CAR核酸,其中該雙特異性抗原結合結構域藉由鉸鏈區(例如,本文所述之鉸鏈區)與跨膜結構域連接。
134. 如實施方式129至133中任一項所述之CAR核酸,其中該CAR包含共刺激結構域,其中該共刺激結構域包含OX40、CD2、CD27、CD28、CDS、ICAM-1、LFA-1(CD11a/CD18)、ICOS(CD278)或4-1BB(CD137)的傳訊結構域。
135. 如實施方式134所述之CAR核酸,其中該共刺激結構域包含4-1BB傳訊結構域。
136. 如實施方式129至135中任一項所述之CAR核酸,其中該CAR包含含有CD3 ζ的傳訊結構域的初級傳訊結構域。
137. 如實施方式129至136中任一項所述之CAR核酸,該CAR核酸包含表4A中提供的核苷酸序列,例如,SEQ ID NO: 1、3、5、7、或9中任一項或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的核苷酸序列。
138. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第二抗原結合結構域定向在第一抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 2的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
139. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 4的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少80%、85%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
140. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 6的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
141. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 8的胺基酸序列、或與其具有至少80%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
142. 一種編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR核酸)的核酸,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,其中:
(i) 第一和第二抗原結合結構域各自是scFv;
(ii) 第一抗原結合結構域定向在第二抗原結合結構域的上游;並且
(iii) 在第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域之間佈置連接子,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和初級傳訊結構域,並且
其中該CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 10的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的序列。
143. 一種載體,該載體包含如實施方式85-112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115-128中任一項所述之CAR、或如實施方式114或129-142中任一項所述之CAR核酸。
144. 一種細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含如實施方式85-112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115-128中任一項所述之CAR、如實施方式114或129-142中任一項所述之CAR核酸、或如實施方式143所述之載體。
145. 一種包含嵌合抗原受體(CAR)的細胞,其中該CAR包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域,該雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含:
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域,
其中該CAR包含跨膜結構域、共刺激結構域、和/或初級傳訊結構域。
146. 如實施方式145所述之細胞,該細胞包含如實施方式116至123中任一項所述之CAR。
147. 一種製備細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞)之方法,該方法包括:
用如實施方式143所述之載體轉導免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞);或
將如實施方式129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸分子引入免疫效應細胞,例如,T細胞或NK細胞。
148. 一種藥物組成物,該藥物組成物包含如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之編碼CAR分子的核酸、如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115至128中任一項所述之CAR、或如實施方式114或129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸,視需要其中該藥物組成物包含賦形劑、載體、稀釋劑和/或穩定劑。
149. 一種提供抗腫瘤免疫之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞,例如免疫效應細胞群體,該細胞包含,例如,表現如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之編碼CAR分子的核酸、如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115至128中任一項所述之CAR,或如實施方式114或129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸。
150. 一種細胞,例如免疫效應細胞群體,該細胞包含,例如,表現如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之編碼CAR分子的核酸、如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115至128中任一項所述之CAR,或如實施方式114或129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸,用於在向受試者提供抗腫瘤免疫之方法中使用。
151. 如實施方式149所述之方法或如實施方式150所述之用途,其中該細胞係T細胞或NK細胞。
152. 如實施方式149或151所述之方法或如實施方式150或151所述之用途,其中該細胞係自體細胞或同種異體細胞。
153. 如實施方式149所述之方法或如實施方式150所述之用途,其中該受試者係人。
154. 一種治療患有與抗原(例如,CD19和/或CD22)相關的疾病的受試者之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的細胞,例如免疫效應細胞群體,該細胞包含,例如,表現如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之編碼CAR分子的核酸、如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115至128中任一項所述之CAR,或如實施方式114或129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸。
155. 一種細胞,例如免疫效應細胞群體,該細胞包含,例如,表現如實施方式1至69中任一項所述之編碼CAR分子的核酸、如實施方式85至112中任一項所述之雙特異性抗原結合結構域、如實施方式113或115至128中任一項所述之CAR,或如實施方式114或129至142中任一項所述之CAR核酸,用於在治療患有與抗原(例如,CD19和/或CD22)相關疾病的受試者之方法中使用。
156. 如實施方式154所述之方法或如實施方式155所述之用途,其中該細胞係T細胞或NK細胞。
157. 如實施方式154或155所述之方法或如實施方式154或155所述之用途,其中該細胞係自體細胞或同種異體細胞。
158. 如實施方式154所述之方法或如實施方式155所述之用途,其中該受試者係人。
159. 如實施方式154或155至158中任一項所述之方法,或如實施方式155至158中任一項所述之用途,其中與CD19和/或CD22相關的疾病選自增生性疾病(例如癌症或惡性腫瘤)、癌前病症(例如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病),或者與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症。
160. 如實施方式159所述之方法或用途,其中該疾病係癌症,例如,血液學癌症。
161. 如實施方式154或155至160中任一項所述之方法,或如實施方式155至160中任一項所述之用途,其中該疾病係B細胞惡性腫瘤。
162. 如實施方式160或161所述之方法或用途,其中該血液學癌症選自急性髓系白血病(AML)、B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)、慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)、慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL)、套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞淋巴瘤、大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、多發性骨髓瘤、骨髓化生不良或骨髓化生不良綜合症、骨髓增殖性腫瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症、前白血病、或其組合。
163. 如實施方式154或155至162中任一項所述之方法,或如實施方式155至162中任一項所述之用途,該方法或用途進一步包括向受試者投與:
增加表現CAR分子的細胞的功效的藥劑;
改善與投與表現CAR分子的細胞相關的一或多種副作用的藥劑;或
治療與CD19和/或CD22相關的疾病的藥劑。
進一步列舉的實施方式
1. 一種治療疾病之方法,該方法包括以基於細胞/kg體重和/或患者的年齡的劑量,向該有需要的患者投與包含細胞群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22結合的嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子。
2. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重小於或等於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約3 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重。
3. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重大於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約1.5 × 10
6個細胞。
4. 如實施方式2所述之方法,其中該患者在1和30歲之間。
5. 如實施方式2所述之方法,其中該劑量為約3.0 × 10
5至1.5 × 10
6個細胞。
6. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重小於或等於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約10 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重。
7. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重大於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約5 × 10
6個細胞。
8. 如實施方式6所述之方法,其中該患者在1和30歲之間。
9. 如實施方式6所述之方法,其中該劑量為約1 × 10
6至5 × 10
6個細胞。
10. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重小於或等於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約30 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重。
11. 如實施方式1所述之方法,其中基於該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞,對於體重大於50 kg的患者,該劑量為約15 × 10
6個細胞。
12. 如實施方式10所述之方法,其中該患者在1和30歲之間。
13. 如實施方式10所述之方法,其中該劑量為約3 × 10
6至15 × 10
6個細胞。
14. 如實施方式1至13中任一項所述之方法,其中該劑量為約1 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、2 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、3 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、4 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、5 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、6 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、7 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、8 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、9 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、10 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、11 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、12 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、13 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、14 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、15 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、16 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、17 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、18 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、19 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、20 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、21 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、22 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、23 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、24 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、25 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、26 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、27 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、28 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、29 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、30 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、40 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、50 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、60 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、70 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、80 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重、或90 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重。
15. 如實施方式1至13中任一項所述之方法,其中該劑量為約0.5 × 10
6個細胞、1 × 10
6個細胞、1.5 × 10
6個細胞、2 × 10
6個細胞、2.5 × 10
6個細胞、3 × 10
6個細胞、3.5 × 10
6個細胞、4 × 10
6個細胞、4.5 × 10
6個細胞、5 × 10
6個細胞、5.5 × 10
6個細胞、6 × 10
6個細胞、6.5 × 10
6個細胞、7 × 10
6個細胞、7.5 × 10
6個細胞、8 × 10
6個細胞、8.5 × 10
6個細胞、9 × 10
6個細胞、9.5 × 10
6個細胞、10 × 10
6個細胞、10.5 × 10
6個細胞、11 × 10
6個細胞、11.5 × 10
6個細胞、12 × 10
6個細胞、12.5 × 10
6個細胞、13 × 10
6個細胞、13.5 × 10
6個細胞、14 × 10
6個細胞、14.5 × 10
6個細胞、15 × 10
6個細胞、16 × 10
6個細胞、17 × 10
6個細胞、18 × 10
6個細胞、19 × 10
6個細胞、20 × 10
6個細胞、21 × 10
6個細胞、22 × 10
6個細胞、23 × 10
6個細胞、24 × 10
6個細胞、25 × 10
6個細胞、26 × 10
6個細胞、27 × 10
6個細胞、28 × 10
6個細胞、29 × 10
6個細胞、30 × 10
6個細胞、31 × 10
6個細胞、32 × 10
6個細胞、33 × 10
6個細胞、34 × 10
6個細胞、35 × 10
6個細胞、36 × 10
6個細胞、37 × 10
6個細胞、38 × 10
6個細胞、39 × 10
6個細胞、40 × 10
6個細胞、41 × 10
6個細胞、42 × 10
6個細胞、43 × 10
6個細胞、44 × 10
6個細胞、或45 × 10
6個細胞。
16. 如實施方式1至15中任一項所述之方法,其中該CAR分子包含:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;以及
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域,其中:
(i) 該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,並且其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二跨膜結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;
(ii) 該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,並且其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同;和/或
(iii) 該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列,並且其中編碼該初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列與編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域並包含在該核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同。
17. 如實施方式16所述之方法,其中該第一CAR包含:
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、和第一共刺激傳訊結構域;
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域;和第一初級傳訊結構域;或
結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域、第一跨膜結構域、第一共刺激傳訊結構域、和第一初級傳訊結構域。
18. 如實施方式16或17所述之方法,其中該第二CAR包含:
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二共刺激傳訊結構域;
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域;或
結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和第二初級傳訊結構域。
19. 如前述請求項中任一項所述之方法,其中:
(a) 第一CAR,該第一CAR包含結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域;並且其中該CD22結合結構域包含重鏈可變區(VH)和輕鏈可變區(VL),該重鏈可變區包含重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3),並且該輕鏈可變區包含輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3),其中該HC CDR1、HC CDR2、HC CDR3、LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3分別包含:
(i) SEQ ID NO: 20、21、22、28、29和30的胺基酸序列;
(ii) SEQ ID NO: 23、24、22、31、32和33的胺基酸序列;或
(iii) SEQ ID NO: 25、26、27、34、32和30的胺基酸序列;以及
(b) 第二CAR,該第二CAR包含結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域;第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域,其中該CD19結合結構域包含含有HC CDR1、HC CDR2、和HC CDR3的VH,和含有LC CDR1、LC CDR2、和LC CDR3的VL,其中該HC CDR1、HC CDR2、HC CDR3、LC CDR1、LC CDR2、和LC CDR3分別包含:
(i) SEQ ID NO: 35、36、39、40、41和42的胺基酸序列;
(ii) SEQ ID NO: 35、37、39、40、41和42的胺基酸序列;或
(iii) SEQ ID NO: 35、38、39、40、41和42的胺基酸序列。
20. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中
(i) 該第一CAR的CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 50的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少約85%、90%、95%或99%的序列同一性的胺基酸序列;和/或
(ii) 該第二CAR的CD19結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 44的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少約85%、90%、95%或99%的序列同一性的胺基酸序列。
21. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該第一跨膜結構域和該第二跨膜結構域包含與SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的胺基酸序列。
22. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中編碼該第一跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二跨膜結構域的核苷酸序列。
23. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該第一共刺激傳訊結構域和該第二共刺激傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 70的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的胺基酸序列。
24. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中編碼該第一共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二共刺激傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。
25. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該第一初級傳訊結構域和該第二初級傳訊結構域包含與該SEQ ID NO: 75的胺基酸序列具有至少90%、95%、96%、97%、98%、99%或100%同一性的胺基酸序列。
26. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中編碼該第一初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列至少1%、5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或100%不同於編碼該第二初級傳訊結構域的核苷酸序列。
27. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中
(i) 該第一CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 13或18的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的胺基酸;和/或
(ii) 該第二CAR包含SEQ ID NO: 14或17的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%的同一性的胺基酸。
28. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該CAR分子包含SEQ ID NO: 12或16的胺基酸序列,或與其具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、或99%同一性的胺基酸。
29. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該藥物組成物進一步包含賦形劑、載體、稀釋劑和/或穩定劑。
30. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該細胞群體係T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞或CD8+ T細胞)或NK細胞。
31. 如前述實施方式中任一項所述之方法,其中該疾病與CD19和/或CD22相關,並且選自增生性疾病(例如癌症或惡性腫瘤)、癌前病症(例如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病)、或與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症。
32. 如實施方式31所述之方法,其中該疾病係癌症,例如,血液學癌症。
33. 如實施方式32所述之方法,其中該血液學癌症選自由以下組成之群組:急性髓系白血病(AML)、B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)、慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)、慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL)、套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞淋巴瘤、大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、多發性骨髓瘤、骨髓化生不良或骨髓化生不良綜合症、骨髓增殖性腫瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤(NHL)、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症、前白血病、或其組合。
34. 如實施方式32所述之方法,其中該血液學癌症係小兒BALL。
35. 如實施方式32所述之方法,其中該血液學癌症係成人BALL。
36. 如實施方式32所述之方法,其中該血液學癌症係NHL。
Those skilled in the art will recognize, or be able to ascertain using no more than routine experimentation, many equivalents to the specific embodiments of the invention described herein. Such equivalents are intended to be covered by the embodiments listed below.
相關申請的交叉引用Cross References to Related Applications
本申請根據35 U.S.C. §119(e)要求2021年6月1日提交的美國臨時申請案號63/195,573的權益,藉由引用以其全文併入本文。 序列表的併入 This application claims the benefit under 35 USC §119(e) of US Provisional Application Serial No. 63/195,573, filed June 1, 2021, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. Incorporation of Sequence Listings
隨此提交了包含在名為「PAT059124-US-PSP SQL_ST25」的文檔中的序列表並藉由引用併入本文,該序列表係182,837位元組(在作業系統MS-Windows中測量)並且於2021年5月31日創建。 定義 The sequence listing contained in the document entitled "PAT059124-US-PSP SQL_ST25", which is 182,837 bytes (measured in the operating system MS-Windows) and is incorporated herein by reference, is hereby submitted and incorporated herein by reference Created May 31, 2021. definition
除非另外定義,否則本文使用的所有技術和科學術語具有本發明所屬領域的普通技術者通常所理解的相同的含義。Unless defined otherwise, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs.
術語「一個/種(a/an)」係指一個/種或多於一個/種(即,至少一個/種)該冠詞的語法賓語。藉由舉例,「一個元件」意指一個元件或多於一個元件。The term "a/an" refers to one or more than one (ie at least one) of the grammatical object of the article. By way of example, "an element" means one element or more than one element.
當指可測量的值如量、時距等時,術語「約」意在涵蓋與規定值 ± 20%或在一些情況下 ± 10%、或在一些情況下 ± 5%、或在一些情況下 ± 1%、或在一些情況下 ± 0.1%的變化,因為此類變化適於執行所揭露的方法。When referring to a measurable value such as an amount, time interval, etc., the term "about" is intended to cover ± 20%, or in some cases ± 10%, or in some cases ± 5%, or in some cases, the stated value Variations of ± 1%, or in some cases ± 0.1%, as such variations are suitable for performing the disclosed methods.
如本文所用,術語「藥學上可接受的鹽」係指在合理的醫學判斷的範圍內適合用於與受試者的組織接觸,而沒有不適當的毒性、刺激、過敏響應等,並且與合理的益處/風險比相稱的那些鹽。藥學上可接受的鹽在本領域中係熟知的。例如,Berge等人在 J. Pharmaceutical Sciences[藥物科學雜誌] (1977) 66:1-19中詳細地描述了藥學上可接受的鹽。 As used herein, the term "pharmaceutically acceptable salt" means, within the scope of sound medical judgment, suitable for use in contact with the tissues of a subject without undue toxicity, irritation, allergic response, etc., and with reasonable The benefit/risk ratios are commensurate with those of salt. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts are well known in the art. For example, Berge et al. describe pharmaceutically acceptable salts in detail in J. Pharmaceutical Sciences (1977) 66:1-19.
術語「嵌合抗原受體」、「CAR」或「CAR分子」係指一組多肽,在最簡單的實施方式中典型地是兩種多肽,當在免疫效應細胞中時,它為該細胞提供針對靶細胞(典型地針對癌細胞)的特異性,並且提供細胞內訊息生成。在一些實施方式中,CAR至少包含細胞外抗原結合結構域、跨膜結構域和細胞質傳訊結構域(本文中也稱為「細胞內傳訊結構域」),該細胞質傳訊結構域包含衍生自如下定義的刺激分子和/或共刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域。在一些方面,該組多肽彼此連續,例如在相同的多肽鏈中,例如,包含嵌合融合蛋白。在一些實施方式中,該組多肽彼此不連續,例如在不同的多肽鏈中。在一些實施方式中,該組多肽包括二聚化開關,該二聚化開關在存在二聚化分子時可以將多肽彼此偶合,例如,可以將抗原結合結構域偶合至細胞內傳訊結構域。在一方面,刺激分子係與T細胞受體複合物相關的ζ鏈。在一方面,胞質傳訊結構域進一步包含源自如下定義的至少一種共刺激分子的一或多個功能性傳訊結構域。在一方面,共刺激分子選自本文描述的共刺激分子,例如4-1BB(即CD137)、CD27和/或CD28。在一方面,CAR包括嵌合融合蛋白,該嵌合融合蛋白包含細胞外抗原結合結構域、跨膜結構域和細胞內傳訊結構域,該細胞內傳訊結構域包含衍生自刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域。在一方面,CAR包括嵌合融合蛋白,該嵌合融合蛋白包含細胞外抗原結合結構域、跨膜結構域和細胞內傳訊結構域,該細胞內傳訊結構域包含衍生自共刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域和衍生自刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域。在一方面,CAR包括嵌合融合蛋白,該嵌合融合蛋白包含細胞外抗原結合結構域、跨膜結構域和細胞內傳訊結構域,該細胞內傳訊結構域包含衍生自一或多種共刺激分子的兩個功能性傳訊結構域和衍生自刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域。在一方面,CAR包括嵌合融合蛋白,該嵌合融合蛋白包含細胞外抗原結合結構域、跨膜結構域和細胞內傳訊結構域,該細胞內傳訊結構域包含衍生自一或多種共刺激分子的至少兩個功能性傳訊結構域和衍生自刺激分子的功能性傳訊結構域。在一方面,CAR包含CAR融合蛋白的胺基末端(N-ter)處的視需要的前導序列。在一方面,CAR在細胞外抗原結合結構域的N-末端進一步包含前導序列,其中前導序列視需要在細胞加工和CAR定位至細胞膜期間從抗原結合結構域(例如,scFv)裂解。The term "chimeric antigen receptor", "CAR" or "CAR molecule" refers to a group of polypeptides, typically two polypeptides in the simplest embodiment, which, when in an immune effector cell, provides the cell with Specific for target cells (typically cancer cells) and provide intracellular message generation. In some embodiments, the CAR comprises at least an extracellular antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic signaling domain (also referred to herein as an "intracellular signaling domain"), the cytoplasmic signaling domain comprising A functional signaling domain of a stimulatory molecule and/or a co-stimulatory molecule. In some aspects, the set of polypeptides is contiguous to each other, eg, in the same polypeptide chain, eg, comprising a chimeric fusion protein. In some embodiments, the set of polypeptides is discontinuous with each other, eg, in different polypeptide chains. In some embodiments, the set of polypeptides includes a dimerization switch that, in the presence of a dimerization molecule, can couple polypeptides to each other, eg, can couple an antigen binding domain to an intracellular signaling domain. In one aspect, the stimulatory molecule is the zeta chain associated with the T cell receptor complex. In one aspect, the cytoplasmic signaling domain further comprises one or more functional signaling domains derived from at least one co-stimulatory molecule as defined below. In one aspect, the co-stimulatory molecule is selected from the co-stimulatory molecules described herein, eg 4-1BB (ie CD137), CD27 and/or CD28. In one aspect, the CAR comprises a chimeric fusion protein comprising an extracellular antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signaling domain comprising a functional signaling domain derived from a stimulatory molecule. domain. In one aspect, the CAR comprises a chimeric fusion protein comprising an extracellular antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular signaling domain comprising a functional co-stimulatory molecule derived Signaling domains and functional signaling domains derived from stimulatory molecules. In one aspect, the CAR comprises a chimeric fusion protein comprising an extracellular antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain comprising molecules derived from one or more costimulatory molecules. Two functional signaling domains of and a functional signaling domain derived from a stimulatory molecule. In one aspect, the CAR comprises a chimeric fusion protein comprising an extracellular antigen-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain comprising molecules derived from one or more costimulatory molecules. and a functional signaling domain derived from a stimulatory molecule. In one aspect, the CAR comprises an optional leader sequence at the amino terminus (N-ter) of the CAR fusion protein. In one aspect, the CAR further comprises a leader sequence at the N-terminus of the extracellular antigen binding domain, wherein the leader sequence is optionally cleaved from the antigen binding domain (eg, scFv) during cellular processing and localization of the CAR to the cell membrane.
術語「傳訊結構域」係指蛋白質的功能性部分,其藉由在細胞內傳遞資訊以藉由產生第二信使或藉由回應於此類信使而用作效應子,經由定義的傳訊途徑調控細胞活性起作用。The term "signalling domain" refers to a functional portion of a protein that regulates a cell via a defined signaling pathway by transmitting information within the cell to serve as an effector by producing a second messenger or by responding to such a messenger Activity works.
如本文所用,術語「CD19」係指分化簇19蛋白,它係在白血病先質細胞上可檢測的抗原決定簇。人和鼠胺基酸和核酸序列可以在公共數據庫中找到,例如GenBank、UniProt和Swiss-Prot。例如,人CD19的胺基酸序列可以作為UniProt/Swiss-Prot登錄號P15391找到,並且編碼人CD19的核酸序列可以登錄號NM_001178098找到。CD19在大多數B譜系癌症上表現,該等B譜系癌症包括例如急性淋巴母細胞白血病、慢性淋巴球白血病和非何杰金氏淋巴瘤。表現CD19的其他細胞在下文「與CD19表現相關的疾病」的定義中提供。它也是B細胞先驅細胞的早期標記物。參見例如,Nicholson等人 Mol. Immun.[分子免疫學] 34 (16-17): 1157-1165 (1997)。在一方面,CART的抗原結合部分識別並結合CD19蛋白的細胞外結構域內的抗原。在一方面,CD19蛋白在癌細胞上表現。如本文所用,「CD19」包括含有突變的蛋白質,例如全長野生型CD19的點突變、片段、插入、缺失和剪接變體。As used herein, the term "CD19" refers to the cluster of
如本文所用,術語「CD22」係指已知在白血病先質細胞上可檢測的抗原決定簇。人和鼠胺基酸和核酸序列可以在公共數據庫中找到,例如GenBank、UniProt和Swiss-Prot。例如,同種型1-5人CD22的胺基酸序列可分別以登錄號NP 001762.2、NP 001172028.1、NP 001172029.1、NP 001172030.1和NP 001265346.1找到,並且編碼人CD22的變體1-5的核酸序列可分別以登錄號NM 001771.3、NM 001185099.1、NM 001185100.1、NM 001185101.1、和NM 001278417.1找到。在一方面,CAR的抗原結合部分識別並結合CD22蛋白的細胞外結構域內的抗原。在一方面,CD22蛋白在癌細胞上表現。如本文所用,「CD22」包括含有突變的蛋白質,例如全長野生型CD22的點突變、片段、插入、缺失和剪接變體。As used herein, the term "CD22" refers to an antigenic determinant known to be detectable on leukemic precursor cells. Human and murine amino acid and nucleic acid sequences can be found in public databases such as GenBank, UniProt and Swiss-Prot. For example, the amino acid sequences of isoforms 1-5 human CD22 can be found at accession numbers NP 001762.2, NP 001172028.1, NP 001172029.1, NP 001172030.1, and NP 001265346.1, respectively, and the nucleic acid sequences encoding variants 1-5 of human CD22 can be found in Found under accession numbers NM 001771.3, NM 001185099.1, NM 001185100.1, NM 001185101.1, and NM 001278417.1. In one aspect, the antigen binding portion of the CAR recognizes and binds an antigen within the extracellular domain of the CD22 protein. In one aspect, the CD22 protein is expressed on cancer cells. As used herein, "CD22" includes proteins containing mutations, such as point mutations, fragments, insertions, deletions, and splice variants of full-length wild-type CD22.
如本文所用,術語「結合結構域」(例如「CD22結合結構域」)係指包含至少一個免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列的蛋白質,例如免疫球蛋白鏈或其片段。術語「結合結構域」(在本文中也稱為「抗體分子」)涵蓋抗體和抗體片段。在實施方式中,抗體分子係多特異性抗體分子,例如它包含多個免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列,其中該多個中的第一免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列對第一表位具有結合特異性並且該多個中的第二免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列對第二表位具有結合特異性。在實施方式中,多特異性抗體分子係雙特異性抗體分子。雙特異性抗體對不多於兩種抗原具有特異性。雙特異性抗體分子的特徵在於具有對第一表位的結合特異性的第一免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列、和具有對第二表位的結合特異性的第二免疫球蛋白可變結構域序列。As used herein, the term "binding domain" (eg, "CD22 binding domain") refers to a protein, such as an immunoglobulin chain or fragment thereof, comprising at least one immunoglobulin variable domain sequence. The term "binding domain" (also referred to herein as "antibody molecule") encompasses antibodies and antibody fragments. In an embodiment, the antibody molecule is a multispecific antibody molecule, e.g., it comprises a plurality of immunoglobulin variable domain sequences, wherein a first immunoglobulin variable domain sequence of the plurality has an affinity for a first epitope binding specificity and the second immunoglobulin variable domain sequence in the plurality has binding specificity for a second epitope. In an embodiment, the multispecific antibody molecule is a bispecific antibody molecule. Bispecific antibodies are specific for no more than two antigens. The bispecific antibody molecule is characterized by a first immunoglobulin variable domain sequence having binding specificity for a first epitope, and a second immunoglobulin variable structure having binding specificity for a second epitope domain sequence.
術語「抗體片段」係指抗體的至少一部分,該至少一部分保留與抗原表位特異性地相互作用(例如,藉由結合、立體阻礙、穩定/去穩定、空間分佈)的能力。抗體片段之實例包括但不限於Fab、Fab'、F(ab') 2、Fv片段、scFv抗體片段、二硫鍵連接的Fv(sdFv)、由VH和CH1結構域組成的Fd片段、線性抗體、單結構域抗體如sdAb(VL或VH)、駱駝科VHH結構域、由抗體片段(例如包含在鉸鏈區藉由二硫鍵連接的兩個Fab片段的二價片段)形成的多特異性抗體、和分離的CDR、或抗體的其他表位結合片段。抗原結合片段還可以併入到單結構域抗體、大型抗體(maxibody)、微型抗體(minibody)、奈米抗體、胞內抗體、雙體抗體、三體抗體、四體抗體、v-NAR和bis-scFv中(參見例如,Hollinger和Hudson, Nature Biotechnology [自然生物技術] 23:1126-1136, 2005)。還可以將抗原結合片段移植到基於多肽如纖網蛋白III型(Fn3)的支架中(參見美國專利案號6,703,199,該文獻描述了纖網蛋白多肽微型抗體)。術語「scFv」係指融合蛋白,該融合蛋白包含至少一個包含輕鏈可變區的抗體片段和至少一個包含重鏈可變區的抗體片段,其中輕鏈可變區和重鏈可變區例如經由合成連接子(例如短柔性多肽連接子)係連續連接的並且能夠表現為單鏈多肽,並且其中scFv保留了衍生出它的完整抗體的特異性。除非另有說明,否則如本文所用,scFv可以例如相對於多肽的N末端和C末端以任何順序具有VL和VH可變區,該scFv可以包含VL-連接子-VH或者可以包含VH-連接子-VL。 The term "antibody fragment" refers to at least a portion of an antibody that retains the ability to specifically interact (eg, by binding, steric hindrance, stabilization/destabilization, spatial distribution) with an antigenic epitope. Examples of antibody fragments include, but are not limited to, Fab, Fab', F(ab') 2 , Fv fragments, scFv antibody fragments, disulfide-linked Fv (sdFv), Fd fragments consisting of VH and CH1 domains, linear antibody , single domain antibodies such as sdAb (VL or VH), camelid VHH domains, multispecific antibodies formed from antibody fragments (e.g. bivalent fragments comprising two Fab fragments linked by disulfide bonds at the hinge region) , and isolated CDRs, or other epitope-binding fragments of antibodies. Antigen-binding fragments can also be incorporated into single domain antibodies, maxibodies, minibodies, nanobodies, intrabodies, diabodies, triabodies, tetrabodies, v-NAR and bis - in scFv (see eg, Hollinger and Hudson, Nature Biotechnology 23:1126-1136, 2005). Antigen-binding fragments can also be grafted into scaffolds based on polypeptides such as fibronectin type III (Fn3) (see US Pat. No. 6,703,199, which describes fibronectin polypeptide minibodies). The term "scFv" refers to a fusion protein comprising at least one antibody fragment comprising a light chain variable region and at least one antibody fragment comprising a heavy chain variable region, wherein the light chain variable region and the heavy chain variable region are e.g. It is contiguously linked via a synthetic linker (eg, a short flexible polypeptide linker) and is capable of appearing as a single-chain polypeptide, and wherein the scFv retains the specificity of the intact antibody from which it was derived. Unless otherwise stated, as used herein, a scFv may, for example, have VL and VH variable regions in any order relative to the N-terminus and C-terminus of a polypeptide, the scFv may comprise a VL-linker-VH or may comprise a VH-linker -VL.
如本文所用,術語「互補決定區」或「CDR」係指賦予抗原特異性和結合親和力的抗體可變區內的胺基酸序列。給定CDR的精確胺基酸序列邊界可以使用許多眾所周知的方案中的任一種來確定,該等方案包括由以下文獻描述的那些:Kabat等人 (1991), 「Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest」[具有免疫學重要性的蛋白序列],第5版,美國國立衛生研究院,公共衛生事業部,馬里蘭州貝塞斯達市(「卡巴特(Kabat)」編號方案);Al-Lazikani等人, (1997) JMB 273, 927-948(「喬西亞(Chothia)」編號方案),和ImMunoGenTics(IMGT)編號(Lefranc, M.-P., The Immunologist [免疫學者], 7, 132-136 (1999);Lefranc, M.-P.等人, Dev. Comp.Immunol. [發育免疫學與比較免疫學], 27, 55-77 (2003)(「IMGT」編號方案)。例如,對於經典形式,根據卡巴特,將重鏈可變結構域(VH)中的CDR胺基酸殘基編號為31-35(HCDR1)、50-65(HCDR2)和95-102(HCDR3);並將輕鏈可變結構域(VL)中的CDR胺基酸殘基編號為24-34(LCDR1)、50-56(LCDR2)和89-97(LCDR3)。根據喬西亞,將VH中的CDR胺基酸編號為26-32(HCDR1)、52-56(HCDR2)和95-102(HCDR3);並且將VL中的胺基酸殘基編號為26-32(LCDR1)、50-52(LCDR2)和91-96(LCDR3)。藉由結合卡巴特和喬西亞的CDR定義,CDR由人VH中的胺基酸殘基26-35(HCDR1)、50-65(HCDR2)和95-102(HCDR3)和人VL中的胺基酸殘基24-34(LCDR1)、50-56(LCDR2)和89-97(LCDR3)組成。根據IMGT,VH中的CDR胺基酸殘基編號為大約26-35(CDR1)、51-57(CDR2)和93-102(CDR3),並且VL中的CDR胺基酸殘基編號為大約27-32(CDR1)、50-52(CDR2)和89-97(CDR3)(根據「IMGT」編號)。根據IMGT,抗體的CDR區可以使用程式IMGT/DomainGap Align測定。As used herein, the term "complementarity determining region" or "CDR" refers to the amino acid sequences within the variable region of an antibody that confer antigen specificity and binding affinity. The precise amino acid sequence boundaries for a given CDR can be determined using any of a number of well-known protocols, including those described by Kabat et al. (1991), "Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest" [ Protein Sequences of Immunological Importance], 5th ed., National Institutes of Health, Division of Public Health, Bethesda, MD ("Kabat" numbering scheme); Al-Lazikani et al., (1997) JMB 273, 927-948 ("Chothia" numbering scheme), and ImMunoGenTics (IMGT) numbering (Lefranc, M.-P., The Immunologist, 7, 132-136 (1999 ); Lefranc, M.-P. et al., Dev. Comp. Immunol. [Developmental and Comparative Immunology], 27, 55-77 (2003) (“IMGT” numbering scheme). For example, for the classical form, According to Kabat, the CDR amino acid residues in the heavy chain variable domain (VH) are numbered 31-35 (HCDR1), 50-65 (HCDR2), and 95-102 (HCDR3); The CDR amino acid residues in the variable domain (VL) are numbered 24-34 (LCDR1), 50-56 (LCDR2) and 89-97 (LCDR3). According to Josiah, the CDR amino acid residues in VH are numbered are 26-32 (HCDR1), 52-56 (HCDR2) and 95-102 (HCDR3); and the amino acid residues in VL are numbered 26-32 (LCDR1), 50-52 (LCDR2) and 91- 96 (LCDR3). Defined by combining the CDRs of Kabat and Josiah, the CDR consists of amino acid residues 26-35 (HCDR1), 50-65 (HCDR2) and 95-102 (HCDR3) in human VH and human Amino acid residues 24-34 (LCDR1), 50-56 (LCDR2) and 89-97 (LCDR3) in VL are composed. According to IMGT, CDR amino acid residues in VH are numbered approximately 26-35 (CDR1 ), 51-57 (CDR2) and 93-102 (CDR3), and the CDR amino acid residues in VL are numbered approximately 27-32 (CDR1), 50-52 (CDR2) and 89-97 (CDR3) ( Numbering according to "IMGT"). According to IMGT, the CDR regions of an antibody can be determined using the program IMGT/DomainGap Align.
包含抗體或其抗體片段的本發明CAR部分可以按多種形式存在,其中抗原結合結構域表現為連續多肽鏈的一部分,該連續多肽鏈包括例如單結構域抗體片段(sdAb)、單鏈抗體(scFv)、人源化抗體、或雙特異性抗體(Harlow等人, 1999: Using Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual [使用抗體:實驗室手冊], Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press [冷泉港實驗室出版社], 紐約;Harlow等人, 1989: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual [抗體:實驗室手冊], Cold Spring Harbor [冷泉港], 紐約;Houston等人, 1988, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA [美國國家科學院院刊] 85:5879-5883;Bird等人, 1988, Science [科學] 242:423-426)。在一方面,本發明之CAR組成物的抗原結合結構域包含抗體片段。在另一方面,CAR包含含有scFv的抗體片段。The CAR portion of the invention comprising an antibody or antibody fragment thereof may exist in a variety of forms wherein the antigen binding domain appears as part of a continuous polypeptide chain including, for example, single domain antibody fragments (sdAbs), single chain antibodies (scFv ), humanized antibodies, or bispecific antibodies (Harlow et al., 1999: Using Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual [Using Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual], Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press [Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press], New York; Harlow et al., 1989: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor, New York; Houston et al., 1988, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA [Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America] ] 85:5879-5883; Bird et al., 1988, Science 242:423-426). In one aspect, the antigen binding domain of the CAR composition of the invention comprises an antibody fragment. In another aspect, the CAR comprises an antibody fragment comprising a scFv.
術語「抗體重鏈」係指抗體分子中天然存在的構象中存在的兩種類型多肽鏈中較大的一種,並且通常決定抗體所屬的類別。The term "antibody heavy chain" refers to the larger of the two types of polypeptide chains found in the naturally occurring conformation of an antibody molecule and usually determines the class to which the antibody belongs.
術語「抗體輕鏈」係指抗體分子中天然存在的構象中存在的兩種類型多肽鏈中較小的一種。Kappa(κ)和lambda(λ)輕鏈係指兩種主要的抗體輕鏈同種型。The term "antibody light chain" refers to the smaller of the two types of polypeptide chains found in the naturally occurring conformation of an antibody molecule. Kappa (κ) and lambda (λ) light chains refer to the two major antibody light chain isotypes.
術語「重組抗體」係指使用重組DNA技術產生的抗體,例如像由噬菌體或酵母表現系統表現的抗體。該術語還應解釋為意指藉由合成編碼抗體的DNA分子和表現抗體蛋白的DNA分子或指定抗體的胺基酸序列產生的抗體,其中該DNA或胺基酸序列已經使用本領域可得和熟知的重組DNA或胺基酸序列技術獲得。The term "recombinant antibody" refers to antibodies produced using recombinant DNA techniques, such as antibodies expressed by phage or yeast expression systems, for example. The term should also be interpreted to mean an antibody produced by synthesizing DNA molecules encoding the antibody and DNA molecules expressing the antibody protein, or specifying the amino acid sequence of the antibody, wherein the DNA or amino acid sequence has been obtained using and Obtained by well-known recombinant DNA or amino acid sequence techniques.
術語「抗原」或「Ag」係指引起免疫反應的分子。免疫反應可以涉及抗體產生或特定免疫活性細胞的活化或兩者。技術者將理解實際上包括所有蛋白質或肽的任何大分子都可以充當抗原。此外,抗原可以源自重組或基因組DNA。熟悉該項技術者將理解包含編碼引發免疫反應的蛋白質的核酸序列或部分核酸序列的任何DNA都因此編碼「抗原」(當該術語在本文中使用時)。此外,熟悉該項技術者將理解抗原不需要僅由基因的全長核酸序列編碼。顯而易見的是,本發明包括但不限於使用多於一種基因的部分核酸序列,並且該等核酸序列以各種組合排列以編碼引發所希望免疫反應的多肽。另外,技術者將理解抗原根本不需要由「基因」編碼。顯而易見的是,抗原可以合成產生或可以衍生自生物樣本,或者可為除多肽外的大分子。這種生物樣本可以包括但不限於組織樣本、腫瘤樣本、細胞或具有其他生物組分的流體。The term "antigen" or "Ag" refers to a molecule that elicits an immune response. The immune response may involve antibody production or activation of specific immunocompetent cells or both. The skilled person will understand that any macromolecule, including virtually all proteins or peptides, can serve as an antigen. In addition, antigens can be derived from recombinant or genomic DNA. Those skilled in the art will understand that any DNA comprising a nucleic acid sequence or partial nucleic acid sequence encoding a protein that elicits an immune response thus encodes an "antigen" (as the term is used herein). Furthermore, those skilled in the art will understand that an antigen need not be encoded solely by the full-length nucleic acid sequence of a gene. It will be apparent that the present invention includes, but is not limited to, the use of partial nucleic acid sequences of more than one gene, arranged in various combinations to encode polypeptides that elicit a desired immune response. Additionally, the skilled artisan will understand that an antigen need not be encoded by a "gene" at all. It will be apparent that the antigen may be produced synthetically or may be derived from a biological sample, or may be a macromolecule other than a polypeptide. Such biological samples may include, but are not limited to, tissue samples, tumor samples, cells, or fluids with other biological components.
術語「抗癌作用」係指可以藉由各種手段顯現的生物學作用,包括但不限於例如腫瘤體積減少、癌細胞數量減少、轉移數量減少、預期壽命延長、癌細胞增殖減少、癌細胞存活率降低、或改善與癌症相關的各種生理症狀。「抗癌作用」也可以藉由本發明之肽、多核苷酸、細胞和抗體首先預防癌症發生的能力來表現。術語「抗腫瘤作用」係指可以藉由各種手段顯現的生物學作用,包括但不限於例如腫瘤體積減少、腫瘤細胞數量減少、腫瘤細胞增殖減少、或腫瘤細胞存活率降低。術語「自體的」係指源自與後來將其重新引入個體中的同一個體的任何材料。The term "anticancer effect" refers to a biological effect that can be manifested by various means, including but not limited to, for example, reduction in tumor volume, reduction in number of cancer cells, reduction in number of metastases, extension of life expectancy, reduction in cancer cell proliferation, cancer cell survival rate Reduce or improve various physiological symptoms related to cancer. "Anticancer effect" can also be manifested by the ability of the peptides, polynucleotides, cells and antibodies of the invention to prevent cancer from occurring in the first place. The term "anti-tumor effect" refers to a biological effect that can be manifested by various means, including but not limited to, for example, reduction in tumor volume, reduction in tumor cell number, reduction in tumor cell proliferation, or reduction in tumor cell survival rate. The term "autologous" refers to any material derived from the same individual into which it is later reintroduced.
術語「同種異體的」係指源自與引入材料的個體相同的物種的不同動物的任何材料。當一或多個基因座處的基因不相同時,稱兩個或更多個個體彼此是同種異體的。在一些方面,來自相同物種的個體的同種異體材料可以在遺傳上充分不同以抗原性地相互作用。The term "allogeneic" refers to any material derived from a different animal of the same species as the individual into whom the material is introduced. Two or more individuals are said to be allogeneic to each other when the genes at one or more loci are not identical. In some aspects, allogeneic material from individuals of the same species may be sufficiently different genetically to interact antigenically.
術語「異種的」係指源自不同物種的動物的移植物。The term "xenogeneic" refers to a graft derived from an animal of a different species.
術語「組合」係指呈一個劑量單位形式的固定組合;或組合投與,其中本發明之化合物與組合配偶物(partner)(例如下文所解釋的另一種藥物,也稱為「治療劑」或「共藥劑(co-agent)」)可以在同一時間獨立地投與或在時間間隔內分開地投與,特別是在該等時間間隔允許組合配偶物顯示協作(例如協同)效應的情況下。單個組分可以包裝在一個套組(kit)中或分開包裝。可在投與之前將一種或兩種組分(例如粉末或液體)重構或稀釋至所希望的劑量。如本文所用,術語「共同投與」或「組合投與」等意在涵蓋將所選擇的組合配偶體投與至對其有需要的單個受試者(例如患者),並且旨在包括其中藥劑不一定藉由相同的投與途徑投與或同時投與的治療方案。如本文所用,術語「藥物組合」意指由多於一種治療劑的混合或組合所產生的產品,並且包括治療劑的固定和非固定組合兩者。術語「固定組合」意指治療劑(例如,本發明之化合物和組合配偶體)以單一實體或劑量的形式同時地投與至患者。術語「非固定組合」意指治療劑(例如,本發明之化合物和組合配偶體)作為分開的實體同時地、並行地或依序地投與至患者(沒有特定的時間限制),其中這種投與在患者體內提供治療有效水平的兩種化合物。後者也適用於雞尾酒療法,例如三種或更多種治療劑的投與。The term "combination" refers to a fixed combination in the form of one dosage unit; or combined administration, wherein a compound of the invention is combined with a partner (such as another drug as explained below, also referred to as a "therapeutic agent" or "Co-agents") can be administered independently at the same time or separately within time intervals, particularly where such time intervals allow the combination partners to exhibit synergistic (eg, synergistic) effects. Individual components can be packaged in a kit or separately. One or both components (eg powders or liquids) may be reconstituted or diluted to the desired dosage prior to administration. As used herein, the terms "co-administration" or "combination administration" and the like are intended to encompass the administration of selected combination partners to a single subject (e.g., patient) in need thereof, and are intended to include agents thereof. Treatment regimens that are not necessarily administered by the same route of administration or administered at the same time. As used herein, the term "pharmaceutical combination" means a product resulting from the admixture or combination of more than one therapeutic agent, and includes both fixed and non-fixed combinations of therapeutic agents. The term "fixed combination" means that the therapeutic agents (eg, a compound of the invention and a combination partner) are administered to a patient simultaneously in the form of a single entity or dosage. The term "non-fixed combination" means that the therapeutic agents (e.g., a compound of the invention and a combination partner) are administered to a patient as separate entities simultaneously, concurrently, or sequentially (without specific time constraints), wherein such Administration provides therapeutically effective levels of both compounds in the patient. The latter also applies to cocktail therapy, eg, the administration of three or more therapeutic agents.
術語「癌症」係指以異常細胞的快速和不受控制的生長為特徵的疾病。癌細胞可以局部或通過血流和淋巴系統擴散到身體的其他部位。本文描述了各種癌症之實例,並且包括但不限於乳癌、前列腺癌、卵巢癌、子宮頸癌、皮膚癌、胰臟癌、結腸直腸癌、腎癌、肝癌、腦癌、淋巴瘤、白血病、肺癌等。術語「腫瘤」和「癌症」在本文中可互換使用,例如,這兩個術語涵蓋實性和液體腫瘤。如本文所用,術語「癌症」或「腫瘤」包括惡化前以及惡性癌症和腫瘤。The term "cancer" refers to a disease characterized by the rapid and uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body locally or through the bloodstream and lymphatic system. Examples of various cancers are described herein and include but are not limited to breast cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, skin cancer, pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, brain cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, lung cancer wait. The terms "tumor" and "cancer" are used interchangeably herein, eg, both terms encompass solid and liquid tumors. As used herein, the term "cancer" or "tumor" includes premalignant as well as malignant cancers and tumors.
如本文所用,短語「與CD22表現相關的疾病」包括但不限於與CD22(例如,野生型或突變型CD22)表現相關的疾病或與表現或在任何時間表現CD22(例如,野生型或突變型CD22)的細胞相關的病症,包括例如增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症(如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病);或與表現CD22(例如,野生型或突變型CD22)的細胞相關的非癌症相關適應症。為避免疑義,與CD22表現相關的疾病可以包括與目前不表現CD22但曾經有一段時間表現CD22的細胞相關的病狀,例如因為例如由於用靶向CD22的分子(例如CD22 CAR)處理已下調CD22表現。在一方面,與CD22表現相關的癌症係血液學癌症。在一方面,血液學癌症包括但不限於AML、骨髓化生不良綜合症、ALL、毛細胞白血病、前淋巴球白血病、慢性髓性白血病、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤等。此外,與CD22表現相關的疾病包括但不限於例如與CD22表現相關的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病。還可以包括與CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症。在一些實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞表現或在曾在任何時間表現CD22 Mrna。在實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞產生CD22蛋白(例如,野生型或突變型),並且CD22蛋白可以以正常水平或降低的水平存在。在實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞在一個時間點產生可檢測水平的CD22蛋白,並且隨後基本上不產生可檢測的CD22蛋白。As used herein, the phrase "a disease associated with CD22 expression" includes, but is not limited to, a disease associated with expression of CD22 (e.g., wild-type or mutant CD22) or a disease associated with expression or expression of CD22 (e.g., wild-type or mutant CD22-type cell-associated disorders, including, for example, proliferative disorders (such as cancer or malignancy) or precancerous conditions (such as myelodysplasia, myelodysplasia syndrome, or preleukemia); or disorders associated with expressing CD22 (such as, Wild-type or mutant CD22) cell-related non-cancer-related indications. For the avoidance of doubt, diseases associated with CD22 expression may include conditions associated with cells that do not presently express CD22 but have at one time expressed CD22, e.g. because CD22 has been down-regulated e.g. Performance. In one aspect, the cancer associated with CD22 expression is a hematological cancer. In one aspect, hematological cancers include, but are not limited to, AML, myelodysplastic syndrome, ALL, hairy cell leukemia, prolymphocytic leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell tumors, etc. Furthermore, diseases associated with CD22 expression include, but are not limited to, for example, atypical and/or atypical cancers, malignancies, precancerous conditions, or proliferative diseases associated with CD22 expression. Non-cancer related indications related to CD22 expression may also be included. In some embodiments, the CD22 expressing cell expresses or has expressed the CD22 mRNA at any time. In embodiments, cells expressing CD22 produce CD22 protein (eg, wild-type or mutant), and CD22 protein may be present at normal or reduced levels. In an embodiment, a cell expressing CD22 produces a detectable level of CD22 protein at one time point, and subsequently produces substantially no detectable CD22 protein.
短語「與CD19表現相關的疾病」包括但不限於與CD19(例如,野生型或突變型CD19)表現相關的疾病或與表現或在任何時間表現CD19(例如,野生型或突變型CD19)的細胞相關的病症,包括例如增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症(如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病);或與表現CD19的細胞相關的非癌症相關適應症。為避免疑義,與CD19表現相關的疾病可以包括與目前不表現CD19(例如,因為例如由於用靶向CD19的分子例如CD19 CAR進行治療導致CD19表現已被下調)但曾經表現CD19的細胞相關的病症。在一方面,與CD19表現相關的癌症係血液學癌症。在一方面,血液學癌症係白血病或淋巴瘤。在一方面,與CD19表現相關的癌症包括癌症和惡性腫瘤,該等癌症和惡性腫瘤包括但不限於:例如一或多種急性白血病,包括但不限於例如B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)、T細胞急性淋巴球白血病(TALL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL);一或多種慢性白血病,包括但不限於例如慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)、慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL)。與CD19表現相關的其他癌症或血液學病症包含但不限於例如B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞或大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、緣帶淋巴瘤、多發性骨髓瘤、骨髓化生不良和骨髓化生不良綜合症、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症、和「前白血病」(這係由髓系血細胞的無效產生(或發育不良)聯合的血液學病症的多樣化集合)等。此外,與CD19表現相關的疾病包括但不限於例如與CD19表現相關的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病。與CD19表現相關的非癌症相關適應症包括但不限於例如自體免疫疾病(例如,狼瘡)、炎性障礙(過敏和氣喘)和移植。在一些實施方式中,表現CD19的細胞表現或在曾在任何時間表現CD19 Mrna。在實施方式中,表現CD19的細胞產生CD19蛋白(例如,野生型或突變型),並且CD19蛋白可以以正常水平或降低的水平存在。在實施方式中,表現CD19的細胞在一個時間點產生可檢測水平的CD19蛋白,並且隨後基本上不產生可檢測的CD19蛋白。The phrase "a disease associated with CD19 expression" includes, but is not limited to, a disease associated with the expression of CD19 (e.g., wild-type or mutant CD19) or a disease associated with expression of CD19 (e.g., wild-type or mutant CD19) Cell-associated disorders including, for example, proliferative disorders (such as cancer or malignancy) or precancerous conditions (such as myelodysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, or preleukemia); or non-cancer-related conditions associated with CD19-expressing cells indications. For the avoidance of doubt, a disease associated with CD19 expression may include a disorder associated with cells that do not currently express CD19 (e.g. because CD19 expression has been downregulated, e.g., as a result of treatment with a CD19-targeting molecule, such as a CD19 CAR), but once expressed CD19 . In one aspect, the cancer associated with CD19 expression is a hematological cancer. In one aspect, the hematological cancer is leukemia or lymphoma. In one aspect, cancers associated with CD19 expression include cancers and malignancies including, but not limited to, for example, one or more acute leukemias, including but not limited to, for example, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BALL), T Cellular acute lymphocytic leukemia (TALL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); one or more chronic leukemias, including but not limited to, eg, chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Other cancers or hematological disorders associated with CD19 expression include, but are not limited to, e.g., B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Burkitt's lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, small cell or large cell follicular lymphoma, malignant lymphoproliferative disorder, MALT lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), marginal zone lymphoma, multiple myeloma, myeloid metaplasia Dysplastic and Myelometaplastic Syndrome, Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Plasmablastic Lymphoma, Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Tumor, Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia, and "preleukemias" (a diverse collection of hematological disorders associated with ineffective production (or dysplasia) of myeloid blood cells), among others. Furthermore, diseases associated with CD19 expression include, but are not limited to, for example, atypical and/or atypical cancers, malignancies, precancerous conditions, or proliferative diseases associated with CD19 expression. Non-cancer-related indications associated with CD19 expression include, but are not limited to, eg, autoimmune diseases (eg, lupus), inflammatory disorders (allergies and asthma), and transplantation. In some embodiments, the CD19 expressing cell expresses or has expressed the CD19 mRNA at any time. In embodiments, cells expressing CD19 produce CD19 protein (eg, wild-type or mutant), and CD19 protein may be present at normal or reduced levels. In an embodiment, a cell expressing CD19 produces a detectable level of CD19 protein at one time point and subsequently produces substantially no detectable CD19 protein.
如本文所用,除非另外說明,術語「預防(prevent、preventing、prevention)」係指在受試者開始患該病症或病症的復發之前發生的作用。預防無需導致完全預防該病症;本術語涵蓋部分預防或減輕病症或病症的症狀,或降低病症發展的風險。As used herein, unless otherwise stated, the terms "prevent, preventing, prevention" refer to an effect that occurs before a subject begins to suffer from the disorder or a recurrence of the disorder. Prevention need not result in complete prevention of the condition; the term encompasses partial prevention or alleviation of a condition or symptoms of a condition, or reducing the risk of developing a condition.
如本文所用,「組合」投與意指在受試者患有障礙的過程期間將兩種(或更多種)不同的治療遞送至受試者,例如在受試者被診斷患有障礙後並且在該障礙被治癒或消除或者在由於其他原因終止治療之前遞送兩種或更多種治療。在一些實施方式中,當第二治療的遞送開始時,第一治療的遞送仍在進行,所以就投與而言存在重疊。這在本文中有時被稱為「同時遞送」或「並行遞送」。在其他實施方式中,一種治療的遞送在另一種治療的遞送開始前結束。在每一種情況的一些實施方式中,由於是組合投與,該治療更有效。例如,與不存在第一治療的條件下投與第二治療所觀察到的結果相比,第二治療更有效,例如使用更少的第二治療觀察到等效的作用,或者第二治療將症狀減少更大的程度,或者觀察到對第一治療而言類似的情況。在一些實施方式中,與不存在另一種治療的條件下遞送一種治療所觀察到的結果相比,遞送使得症狀或與該障礙相關的其他參數減少更多。兩種治療的作用可以部分累加、完全累加、或大於累加。該遞送可以使得當遞送第二治療時,遞送的第一治療的作用仍然是可檢測的。在一個實施方式中,表現CAR的細胞以本文所述之劑量和/或給藥方案投與,並且B細胞抑制劑,或增強表現CD19 CAR的細胞的活性的藥劑以本文所述之劑量和/或給藥方案投與。As used herein, "combination" administration means the delivery of two (or more) different treatments to a subject during the course of the subject's suffering from the disorder, for example after the subject has been diagnosed with the disorder And two or more treatments are delivered until the disorder is cured or eliminated or before treatment is discontinued for other reasons. In some embodiments, when the delivery of the second therapy begins, the delivery of the first therapy is still in progress, so there is an overlap in terms of administration. This is sometimes referred to herein as "simultaneous delivery" or "parallel delivery." In other embodiments, delivery of one treatment ends before delivery of another treatment begins. In some embodiments in each case, the treatment is more effective due to the combined administration. For example, the second treatment is more effective than that observed when the second treatment is administered in the absence of the first treatment, e.g., an equivalent effect is observed with less of the second treatment, or the second treatment will Symptoms were reduced to a greater extent, or a similar situation was observed for the first treatment. In some embodiments, delivery results in a greater reduction in symptoms or other parameters associated with the disorder than is observed with delivery of one treatment in the absence of the other treatment. The effects of the two treatments can be partially additive, fully additive, or more than additive. The delivery may be such that the effect of the first therapy delivered is still detectable when the second therapy is delivered. In one embodiment, the CAR-expressing cells are administered at the doses and/or dosing regimens described herein, and the B cell inhibitor, or agent that enhances the activity of CD19 CAR-expressing cells, is administered at the doses and/or regimens described herein or dosing regimen administration.
「源自」(當該術語在本文中使用時)表示第一分子和第二分子之間的關係。它通常係指第一分子和第二分子之間的結構相似性,並不暗示或包括對衍生自第二分子的第一分子的過程或來源的限制。例如,在衍生自CD3ζ分子的細胞內傳訊結構域的情況下,細胞內傳訊結構域保留足夠的CD3ζ結構,使得其具有所需的功能,即在適當條件下產生訊息的能力。它沒有暗示或包括對產生細胞內傳訊結構域的特定過程的限制,例如,它並不意指為了提供細胞內傳訊結構域,必須從CD3ζ序列開始並刪除不需要的序列,或強加突變,以到達細胞內傳訊結構域。"Derived from" as the term is used herein means the relationship between a first molecule and a second molecule. It generally refers to a structural similarity between a first molecule and a second molecule, and does not imply or include a limitation as to the process or source of the first molecule derived from the second molecule. For example, in the case of an intracellular signaling domain derived from a CD3ζ molecule, the intracellular signaling domain retains sufficient CD3ζ structure such that it has the desired function, namely the ability to generate a message under appropriate conditions. It does not imply or include limitations on the particular process by which intracellular signaling domains are produced, for example, it does not imply that in order to provide intracellular signaling domains one must start with the CD3ζ sequence and delete undesired sequences, or impose mutations, to reach Intracellular signaling domain.
術語「保守序列修飾」係指不顯著影響或改變含有胺基酸序列的抗體或抗體片段的結合特徵的胺基酸修飾。此類保守修飾包括胺基酸取代、添加和缺失。可以藉由本領域已知的標準技術(如定點誘變和PCR介導的誘變)將修飾引入本發明之抗體或抗體片段中。保守胺基酸取代係其中胺基酸殘基被具有相似側鏈的胺基酸殘基替代的胺基酸取代。本領域中已經定義了具有相似側鏈的胺基酸殘基家族。該等家族包括具有鹼性側鏈(例如離胺酸、精胺酸、組胺酸)、酸性側鏈(例如天冬胺酸、麩胺酸)、不帶電荷的極性側鏈(例如甘胺酸、天冬醯胺、麩醯胺酸、絲胺酸、蘇胺酸、酪胺酸、半胱胺酸、色胺酸)、非極性側鏈(例如丙胺酸、纈胺酸、白胺酸、異白胺酸、脯胺酸、苯丙胺酸、甲硫胺酸)、β分支側鏈(例如蘇胺酸、纈胺酸、異白胺酸)以及芳香族側鏈(例如酪胺酸、苯丙胺酸、色胺酸、組胺酸)的胺基酸。因此,本發明之CAR內的一或多個胺基酸殘基可以被來自相同側鏈家族的其他胺基酸殘基替代,並且可以使用本文描述的功能測定法測試改變的CAR。The term "conservative sequence modification" refers to an amino acid modification that does not significantly affect or alter the binding characteristics of an antibody or antibody fragment containing the amino acid sequence. Such conservative modifications include amino acid substitutions, additions and deletions. Modifications can be introduced into antibodies or antibody fragments of the invention by standard techniques known in the art, such as site-directed mutagenesis and PCR-mediated mutagenesis. Conservative amino acid substitutions are amino acid substitutions in which the amino acid residue is replaced by an amino acid residue having a similar side chain. Families of amino acid residues having similar side chains have been defined in the art. These families include those with basic side chains (e.g. lysine, arginine, histidine), acidic side chains (e.g. aspartic acid, glutamic acid), uncharged polar side chains (e.g. glycine acid, asparagine, glutamine, serine, threonine, tyrosine, cysteine, tryptophan), nonpolar side chains (e.g. alanine, valine, leucine , isoleucine, proline, phenylalanine, methionine), beta branched side chains (e.g. threonine, valine, isoleucine) and aromatic side chains (e.g. tyrosine, amphetamine acid, tryptophan, histidine). Accordingly, one or more amino acid residues within a CAR of the invention can be replaced with other amino acid residues from the same side chain family, and the altered CAR can be tested using the functional assays described herein.
術語「刺激」係指藉由刺激分子(例如,TCR/CD3複合物或CAR)與其同源配體(或CAR的情況下的腫瘤抗原)結合誘導的初級響應,從而介導訊息轉導事件,如但不限於,藉由TCR/CD3複合物的訊息轉導或藉由CAR的適當NK受體或傳訊結構域的訊息轉導。刺激可以介導某些分子的改變的表現。The term "stimulation" refers to the primary response induced by the binding of a stimulatory molecule (e.g., TCR/CD3 complex or CAR) to its cognate ligand (or tumor antigen in the case of CAR), thereby mediating a signal transduction event, For example, but not limited to, signal transduction by the TCR/CD3 complex or by the appropriate NK receptor or signaling domain of the CAR. Stimulation can mediate altered expression of certain molecules.
術語「刺激分子」係指由免疫細胞(例如,T細胞、NK細胞或B細胞)表現的分子,該分子提供以針對免疫細胞傳訊途徑的至少一些方面的刺激方式調節免疫細胞激活的一或多個細胞質傳訊序列。在一方面,訊息係初級訊息,該初級訊息藉由例如TCR/CD3複合物與載有肽的MHC分子的結合而激活,並且導致了介導T細胞響應,包括但不限於增殖、激活、分化等。以刺激方式起作用的初級胞質傳訊序列(也稱為「初級傳訊結構域」)可以含有被稱為基於免疫受體酪胺酸的活化模體或ITAM的傳訊模體。在本發明中特別有用的含有ITAM的細胞質傳訊序列之實例包括但不限於衍生自CD3ζ、常見FcRγ(FCER1G)、Fcγ RIIa、FcRβ(Fcε R1b)、CD3γ、CD3δ、CD3ε、CD79a、CD79b、DAP10和DAP12的那些。在本發明之特定CAR中,本發明之任何一或多種CAR中的細胞內傳訊結構域包含細胞內傳訊序列,例如CD3-ζ的初級傳訊序列。在本發明之特定CAR中,CD3-ζ的初級傳訊序列係提供為SEQ ID NO: 96的序列,或來自非人物種的等同殘基,例如小鼠、齧齒動物、猴子、猿等。The term "stimulatory molecule" refers to a molecule expressed by an immune cell (e.g., a T cell, NK cell, or B cell) that provides one or more molecules that modulate immune cell activation in a stimulating manner directed at at least some aspects of immune cell signaling pathways. a cytoplasmic signaling sequence. In one aspect, the message is a primary message that is activated by, for example, the binding of a TCR/CD3 complex to a peptide-loaded MHC molecule and results in the mediation of a T cell response, including but not limited to proliferation, activation, differentiation wait. Primary cytoplasmic signaling sequences (also referred to as "primary signaling domains") that act in a stimulatory manner may contain signaling motifs known as immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs or ITAMs. Examples of ITAM-containing cytoplasmic signaling sequences that are particularly useful in the present invention include, but are not limited to, those derived from CD3ζ, common FcRγ (FCER1G), FcγRIIa, FcRβ (FcεR1b), CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ε, CD79a, CD79b, DAP10, and Those of DAP12. In certain CARs of the invention, the intracellular signaling domain in any one or more CARs of the invention comprises an intracellular signaling sequence, such as the primary signaling sequence of CD3-ζ. In certain CARs of the present invention, the primary signaling sequence of CD3-ζ is provided as the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 96, or equivalent residues from non-human species, such as mouse, rodent, monkey, ape, etc.
術語「抗原呈遞細胞」或「APC」係指免疫系統細胞如輔助細胞(例如,B細胞、樹突細胞等),該免疫系統細胞在其表面上展示與主要組織相容性複合物(MHC)複合的外來抗原。T細胞可以使用它們的T細胞受體(TCR)識別該等複合物。APC處理抗原並將它們呈遞給T細胞。The term "antigen presenting cell" or "APC" refers to an immune system cell such as a helper cell (e.g., B cell, dendritic cell, etc.) Complex foreign antigens. T cells can recognize these complexes using their T cell receptor (TCR). APCs process antigens and present them to T cells.
如本文所用,術語「免疫效應細胞」係指參與免疫反應例如促進免疫效應子響應的細胞。免疫效應細胞之實例包括T細胞,例如α/β T細胞和γ/δ T細胞、B細胞、自然殺手(NK)細胞、自然殺手T(NK-T)細胞、肥大細胞和骨髓衍生的吞噬細胞。As used herein, the term "immune effector cell" refers to a cell that participates in an immune response, eg, promotes an immune effector response. Examples of immune effector cells include T cells, such as α/β T cells and γ/δ T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, natural killer T (NK-T) cells, mast cells, and bone marrow-derived phagocytes .
當該術語在本文中使用時,「免疫效應子功能或免疫效應子響應」係指例如免疫效應細胞的增強或促進靶細胞的免疫攻擊的功能或響應。例如,免疫效應子功能或響應係指促進靶細胞的殺傷或抑制生長或增殖的T或NK細胞的特性。在T細胞的情況下,初級刺激和共刺激係免疫效應子功能或響應之實例。As the term is used herein, "immune effector function or immune effector response" refers to, for example, the function or response of immune effector cells to enhance or facilitate immune attack of target cells. For example, immune effector function or response refers to properties of T or NK cells that promote killing of target cells or inhibit growth or proliferation. In the case of T cells, primary stimulation and co-stimulation are examples of immune effector functions or responses.
如本文所用的術語「細胞內傳訊結構域」係指分子的細胞內部分。細胞內傳訊結構域產生促進含有CAR的細胞(例如,CART細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的免疫效應子功能的訊息。免疫效應子功能之實例(例如,在CART細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞中)包括細胞溶解活性和輔助活性,包括細胞介素的分泌。The term "intracellular signaling domain" as used herein refers to the intracellular portion of a molecule. The intracellular signaling domain generates messages that facilitate immune effector function of CAR-containing cells (eg, CART cells or CAR-expressing NK cells). Examples of immune effector functions (eg, in CART cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) include cytolytic activity and adjuvant activities, including secretion of cytokines.
在實施方式中,細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含初級細胞內傳訊結構域。示例性初級細胞內傳訊結構域包括源自負責初級刺激、或抗原依賴性模擬的分子的那些。在實施方式中,細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含共刺激細胞內結構域。示例性共刺激細胞內傳訊結構域包括源自負責共刺激訊息、或抗原非依賴性刺激的分子的那些。例如,在CART的情況下,初級細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含T細胞受體的胞質序列,並且共刺激細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含來自共受體或共刺激分子的胞質序列。In embodiments, the intracellular signaling domain may comprise a primary intracellular signaling domain. Exemplary primary intracellular signaling domains include those derived from molecules responsible for primary stimuli, or antigen-dependent mimicry. In embodiments, the intracellular signaling domain may comprise a co-stimulatory intracellular domain. Exemplary costimulatory intracellular signaling domains include those derived from molecules responsible for costimulatory messages, or antigen-independent stimulation. For example, in the case of a CART, the primary intracellular signaling domain may comprise the cytoplasmic sequence of the T cell receptor, and the co-stimulatory intracellular signaling domain may comprise the cytoplasmic sequence from a co-receptor or co-stimulatory molecule.
初級細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含被稱為基於免疫受體酪胺酸的活化模體或ITAM的傳訊模體。含有ITAM的初級細胞質傳訊序列之實例包括但不限於衍生自CD3ζ、常見FcRγ(FCER1G)、Fcγ RIIa、FcRβ(Fcε R1b)、CD3γ、CD3δ、CD3ε、CD79a、CD79b、DAP10和DAP12的那些。Primary intracellular signaling domains may comprise signaling motifs known as immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs or ITAMs. Examples of ITAM-containing primary cytoplasmic signaling sequences include, but are not limited to, those derived from CD3ζ, common FcRγ (FCER1G), FcγRIIa, FcRβ (FcεR1b), CD3γ, CD3δ, CD3ε, CD79a, CD79b, DAP10, and DAP12.
術語「ζ」或可替代地「ζ鏈」、「CD3-ζ」或「TCR-ζ」被定義為以GenBan登錄號BAG36664.1提供的蛋白質或來自非人物種例如小鼠、齧齒動物、猴子、猿等的等同殘基,並且「ζ刺激結構域」或可替代地「CD3-ζ刺激結構域」或「TCR-ζ刺激結構域」被定義為來自ζ鏈的細胞質結構域的胺基酸殘基或其功能衍生物,該等胺基酸殘基或其功能衍生物足以在功能上傳遞T細胞激活所必需的初始訊息。在一方面,ζ的細胞質結構域包含GenBank登錄號BAG36664.1的殘基52至164或來自非人物種例如小鼠、齧齒動物、猴子、猿等的等同殘基,它們係其功能性直系同源物。在一方面,「ζ刺激結構域」或「CD3-ζ刺激結構域」係提供為SEQ ID NO: 96的序列。The term "ζ" or alternatively "ζ chain", "CD3-ζ" or "TCR-ζ" is defined as a protein provided under GenBan Accession No. BAG36664.1 or from a non-human species such as mouse, rodent, monkey , simian, etc., and "ζ-stimulatory domain" or alternatively "CD3-ζ-stimulatory domain" or "TCR-ζ-stimulatory domain" is defined as an amino acid from the cytoplasmic domain of the zeta chain Residues or functional derivatives thereof, these amino acid residues or functional derivatives thereof are sufficient to functionally transmit the initial information necessary for T cell activation. In one aspect, the cytoplasmic domain of ζ comprises residues 52 to 164 of GenBank Accession No. BAG36664.1 or the equivalent residues from a non-human species such as mouse, rodent, monkey, ape, etc., which are functional orthologs thereof Source material. In one aspect, the "zeta stimulating domain" or "CD3-zeta stimulating domain" is provided as the sequence of SEQ ID NO:96.
術語「共刺激分子」係指T細胞上的同源結合配偶體,該同源結合配偶體與共刺激配體特異性地結合,從而介導T細胞的共刺激響應,如但不限於增殖。共刺激分子係除抗原受體或其配體之外的有助於高效的免疫反應的細胞表面分子。共刺激分子包括但不限於MHC I類分子、TNF受體蛋白、免疫球蛋白樣蛋白、細胞介素受體、整聯蛋白、傳訊淋巴球激活分子(SLAM蛋白)、激活型NK細胞受體、BTLA、Toll配體受體、OX40、CD2、CD7、CD27、CD28、CD30、CD40、CDS、ICAM-1、LFA-1(CD11a/CD18)、4-1BB(CD137)、B7-H3、CDS、ICAM-1、ICOS 5(CD278)、GITR、BAFFR、LIGHT、HVEM(LIGHTR)、KIRDS2、SLAMF7、NKp80(KLRF1)、NKp44、NKp30、NKp46、CD19、CD4、CD8α、CD8β、IL2Rβ、IL2Rγ、IL7Rα、ITGA4、VLA1、CD49a、ITGA4、IA4、CD49D、ITGA6、VLA-6、CD49f、ITGAD、CD11d、ITGAE、CD103、ITGAL、CD11a、LFA-1、ITGAM、CD11b、ITGAX、CD11c、ITGB1、CD29、ITGB2、CD18、LFA-1、ITGB7、NKG2D、NKG2C、TNFR2、TRANCE/RANKL、DNAM1(CD226)、SLAMF4(CD244、2B4)、CD84、CD96(Tactile)、CEACAM1、CRTAM、Ly9(CD229)、CD160(BY55)、PSGL1、CD100(SEMA4D)、CD69、SLAMF6(NTB-A、Ly108)、SLAM(SLAMF1、CD150、IPO-3)、BLAME(SLAMF8)、SELPLG(CD162)、LTBR、LAT、GADS、SLP-76、PAG/Cbp、CD19a和與CD83特異性結合的配體。The term "costimulatory molecule" refers to a cognate binding partner on a T cell that specifically binds to a costimulatory ligand, thereby mediating a costimulatory response of the T cell, such as but not limited to proliferation. Costimulatory molecules are cell surface molecules other than antigen receptors or their ligands that contribute to an efficient immune response. Costimulatory molecules include but are not limited to MHC class I molecules, TNF receptor proteins, immunoglobulin-like proteins, interleukin receptors, integrins, signaling lymphocyte activating molecules (SLAM proteins), activating NK cell receptors, BTLA, Toll ligand receptor, OX40, CD2, CD7, CD27, CD28, CD30, CD40, CDS, ICAM-1, LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18), 4-1BB (CD137), B7-H3, CDS, ICAM-1, ICOS 5 (CD278), GITR, BAFFR, LIGHT, HVEM (LIGHTR), KIRDS2, SLAMF7, NKp80 (KLRF1), NKp44, NKp30, NKp46, CD19, CD4, CD8α, CD8β, IL2Rβ, IL2Rγ, IL7Rα, ITGA4, VLA1, CD49a, ITGA4, IA4, CD49D, ITGA6, VLA-6, CD49f, ITGAD, CD11d, ITGAE, CD103, ITGAL, CD11a, LFA-1, ITGAM, CD11b, ITGAX, CD11c, ITGB1, CD29, ITGB2, CD18, LFA-1, ITGB7, NKG2D, NKG2C, TNFR2, TRANCE/RANKL, DNAM1 (CD226), SLAMF4 (CD244, 2B4), CD84, CD96 (Tactile), CEACAM1, CRTAM, Ly9 (CD229), CD160 (BY55) , PSGL1, CD100 (SEMA4D), CD69, SLAMF6 (NTB-A, Ly108), SLAM (SLAMF1, CD150, IPO-3), BLAME (SLAMF8), SELPLG (CD162), LTBR, LAT, GADS, SLP-76, PAG/Cbp, CD19a, and ligands that specifically bind to CD83.
共刺激細胞內傳訊結構域可為共刺激分子的細胞內部分。共刺激分子可以表現在以下蛋白質家族中:TNF受體蛋白、免疫球蛋白樣蛋白、細胞介素受體、整聯蛋白、傳訊淋巴球激活分子(SLAM蛋白)和激活型NK細胞受體。此類分子之實例包括CD27、CD28、4-1BB(CD137)、OX40、GITR、CD30、CD40、ICOS、BAFFR、HVEM、ICAM-1、淋巴球功能相關抗原-1(LFA-1)、CD2、CSD、CD7、CD287、LIGHT、NKG2C、NKG2D、SLAMF7、NKp80、NKp30、NKp44、NKp46、CD160、B7-H3、和與CD83特異性地結合的配體等。A costimulatory intracellular signaling domain can be the intracellular portion of a costimulatory molecule. Costimulatory molecules can be expressed in the following protein families: TNF receptor proteins, immunoglobulin-like proteins, interleukin receptors, integrins, signaling lymphocyte activating molecules (SLAM proteins), and activating NK cell receptors. Examples of such molecules include CD27, CD28, 4-1BB (CD137), OX40, GITR, CD30, CD40, ICOS, BAFFR, HVEM, ICAM-1, lymphocyte function associated antigen-1 (LFA-1), CD2, CSD, CD7, CD287, LIGHT, NKG2C, NKG2D, SLAMF7, NKp80, NKp30, NKp44, NKp46, CD160, B7-H3, and ligands that specifically bind to CD83, etc.
細胞內傳訊結構域可以包含衍生出它的分子的整個細胞內部分或整個天然細胞內傳訊結構域,或其功能片段或衍生物。The intracellular signaling domain may comprise the entire intracellular portion of the molecule from which it is derived or the entire native intracellular signaling domain, or a functional fragment or derivative thereof.
術語「4-1BB」係指TNFR超家族的成員,具有以GenBank登錄號AAA62478.2提供的胺基酸序列,或來自非人物種例如小鼠、齧齒動物、猴子、猿等的等同殘基;並且「4-1BB共刺激結構域」定義為GenBank登錄號AAA62478.2的胺基酸殘基214-255,或來自非人物種(例如,小鼠、齧齒動物、猴、猿等)的等同殘基。在一方面,「4-1BB共刺激結構域」係提供為SEQ ID NO: 70的序列,或來自非人物種例如小鼠、齧齒動物、猴子、猿等的等同殘基。The term "4-1BB" refers to a member of the TNFR superfamily having the amino acid sequence provided in GenBank Accession No. AAA62478.2, or equivalent residues from non-human species such as mouse, rodent, monkey, ape, etc.; And "4-1BB co-stimulatory domain" is defined as amino acid residues 214-255 of GenBank accession number AAA62478.2, or equivalent residues from non-human species (e.g., mouse, rodent, monkey, ape, etc.) base. In one aspect, a "4-1BB costimulatory domain" is provided as the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 70, or equivalent residues from a non-human species such as mouse, rodent, monkey, ape, and the like.
術語「編碼」係指多核苷酸(如基因、cDNA或mRNA)中特定核苷酸序列用作在生物過程中用於合成具有確定核苷酸序列(例如,rRNA、tRNA和mRNA)或確定胺基酸序列的其他聚合物和大分子的模板的固有特性,以及由此產生的生物學特性。因此,如果與基因對應的mRNA的轉錄和翻譯在細胞或其他生物系統中產生蛋白質,則該基因、cDNA或RNA編碼該蛋白質。編碼股(其核酸序列與mRNA序列相同並且通常在序列表中提供)和非編碼股(用作基因或cDNA轉錄的模板)都可以稱為編碼蛋白質或者該基因或cDNA的其他產物。The term "encoding" refers to a specific sequence of nucleotides in a polynucleotide (such as a gene, cDNA or mRNA) used in a biological process to synthesize Intrinsic properties of amino acid sequences as templates for other polymers and macromolecules, and the resulting biological properties. Thus, a gene, cDNA or RNA encodes a protein if transcription and translation of the mRNA corresponding to the gene produces the protein in a cell or other biological system. Both the coding strand (whose nucleic acid sequence is identical to the mRNA sequence and is usually provided in the sequence listing) and the non-coding strand (used as a template for transcription of a gene or cDNA) can both be referred to as encoding a protein or other product of that gene or cDNA.
除非另外說明,否則「編碼胺基酸序列的核酸序列」包括彼此呈簡併形式且編碼相同胺基酸序列的所有核酸序列。短語編碼蛋白質或RNA的核酸序列還可以包括內含子,其程度為編碼該蛋白質的核酸序列可以在某些形式中含有一或多個內含子。Unless otherwise stated, a "nucleic acid sequence encoding an amino acid sequence" includes all nucleic acid sequences that are degenerate forms of each other and encode the same amino acid sequence. The phrase nucleic acid sequence encoding a protein or RNA may also include introns to the extent that the nucleic acid sequence encoding the protein may, in some forms, contain one or more introns.
術語「有效量」或「治療有效量」在本文中可互換使用,並且係指如本文描述的化合物、配製物、材料或組成物的有效於實現特定的生物學結果的量。The terms "effective amount" or "therapeutically effective amount" are used interchangeably herein and refer to an amount of a compound, formulation, material or composition as described herein effective to achieve a particular biological result.
術語「內源的」係指來自生物體、細胞、組織或系統或在其內部產生的任何材料。The term "endogenous" refers to any material derived from or produced within an organism, cell, tissue or system.
術語「外源的」係指從生物體、細胞、組織或系統引入或在其外部產生的任何材料。The term "exogenous" refers to any material introduced from or produced externally to an organism, cell, tissue or system.
術語「表現」係指由啟動子驅動的特定核酸序列的翻譯和/或轉錄。The term "expression" refers to the translation and/or transcription of a particular nucleic acid sequence driven by a promoter.
術語「轉移載體」係指包含分離的核酸並且可以用於向細胞內部遞送該分離的核酸的物質組成物。許多載體在本領域中係已知的,包括但不限於線性多核苷酸、與離子化合物或兩親化合物相關的多核苷酸、質體、以及病毒。因此,術語「轉移載體」包括自主複製的質體或病毒。該術語還應當解釋為進一步包括促進將核酸轉移到細胞中的非質體和非病毒化合物,例如像聚離胺酸化合物、脂質體等。病毒轉移載體之實例包括但不限於腺病毒載體、腺相關病毒載體、反轉錄病毒載體、慢病毒載體等。The term "transfer vector" refers to a composition of matter comprising an isolated nucleic acid and which can be used to deliver the isolated nucleic acid inside a cell. Many vectors are known in the art, including but not limited to linear polynucleotides, polynucleotides associated with ionic or amphiphilic compounds, plastids, and viruses. Thus, the term "transfer vector" includes autonomously replicating plasmids or viruses. The term should also be interpreted to further include aplastids and non-viral compounds that facilitate the transfer of nucleic acids into cells, such as, for example, polylysine compounds, liposomes, and the like. Examples of viral transfer vectors include, but are not limited to, adenoviral vectors, adeno-associated viral vectors, retroviral vectors, lentiviral vectors, and the like.
術語「表現載體」係指包含重組多核苷酸的載體,該重組多核苷酸包含與待表現的核酸序列有效地連接的表現控制序列。表現載體包含足夠的用於表現的順式作用元件;用於表現的其他元件可以由宿主細胞提供或在體外表現系統中提供。表現載體包括本領域已知的所有表現載體,包括摻入重組多核苷酸的黏粒、質體(例如,裸露的或包含在脂質體中)和病毒(例如,慢病毒、反轉錄病毒、腺病毒和腺相關病毒)。The term "expression vector" refers to a vector comprising a recombinant polynucleotide comprising expression control sequences operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence to be expressed. Expression vectors contain sufficient cis-acting elements for expression; other elements for expression may be provided by the host cell or in an in vitro expression system. Expression vectors include all expression vectors known in the art, including cosmids, plastids (e.g., naked or contained in liposomes) and viruses (e.g., lentiviruses, retroviruses, adenoviruses) incorporating recombinant polynucleotides. virus and adeno-associated virus).
術語「慢病毒」係指反轉錄病毒科的一個屬。慢病毒在反轉錄病毒中係獨特的,能夠感染非分裂細胞;它們可以將顯著量的遺傳信息遞送到宿主細胞的DNA中,因此它們係基因遞送載體的最有效方法中的一種。HIV、SIV、和FIV都是慢病毒之實例。The term "lentivirus" refers to a genus of the Retroviridae family. Lentiviruses are unique among retroviruses in their ability to infect non-dividing cells; they can deliver significant amounts of genetic information into the host cell's DNA, making them one of the most efficient methods of gene delivery vectors. HIV, SIV, and FIV are examples of lentiviruses.
術語「慢病毒載體」係指源自慢病毒基因組的至少一部分的載體,尤其包括如下提供的自滅活慢病毒載體:Milone等人, Mol. Ther.[分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。可以在臨床中使用的慢病毒載體的其他實例包括但不限於例如來自牛津生物醫藥公司(Oxford BioMedica)的LENTIVECTOR®基因遞送技術、來自Lentigen公司的LENTIMAX™載體系統等。非臨床類型的慢病毒載體也是可得的並且係熟悉該項技術者已知的。The term "lentiviral vector" refers to a vector derived from at least a portion of the lentiviral genome, including inter alia the self-inactivating lentiviral vectors provided in: Milone et al., Mol. Ther. 17(8): 1453-1464 ( 2009). Other examples of lentiviral vectors that can be used in the clinic include, but are not limited to, for example, LENTIVECTOR® gene delivery technology from Oxford BioMedica, LENTIMAX™ vector system from Lentigen, etc. Non-clinical types of lentiviral vectors are also available and known to those skilled in the art.
術語「同源的」或「同一性」係指兩個聚合分子之間(例如,兩個核酸分子(如兩個DNA分子或兩個RNA分子)之間、或兩個多肽分子之間)的亞基序列同一性。當這兩個分子中的亞基位置被相同的單體亞基佔據時;例如,如果兩個DNA分子中的每一個中的位置被腺嘌呤佔據,則它們在該位置係同源的或相同的。兩個序列之間的同源性係匹配位置或同源位置的數量的直接函數;例如,如果兩個序列中一半的位置(例如,長度為十個亞基的聚合物中的五個位置)係同源的,則這兩個序列係50%同源的;如果90%的位置(例如,10個中的9個)係匹配的或同源的,則這兩個序列係90%同源的。The terms "homologous" or "identity" refer to the relationship between two polymeric molecules (e.g., between two nucleic acid molecules (such as two DNA molecules or two RNA molecules), or between two polypeptide molecules). Subunit sequence identity. When a subunit position in both molecules is occupied by the same monomeric subunit; for example, if a position in each of two DNA molecules is occupied by an adenine, they are homologous or identical at that position of. Homology between two sequences is a direct function of the number of matching positions or homologous positions; for example, if half the positions in the two sequences (for example, five positions in a polymer ten subunits in length) If 90% of the positions (for example, 9 out of 10) are matched or homologous, then the two sequences are 90% homologous of.
非人(例如鼠)抗體的「人源化」形式係嵌合免疫球蛋白、免疫球蛋白鏈或其片段(如Fv、Fab、Fab'、F(ab')2或抗體的其他抗原結合子序列),其含有來自非人免疫球蛋白的最小序列。在大多數情況下,人源化抗體及其抗體片段係人免疫球蛋白(接受者抗體或抗體片段),其中來自接受者的互補決定區(CDR)的殘基被來自非人物種(如小鼠、大鼠或兔)(供體抗體)的具有所希望特異性、親和力和能力的CDR的殘基替代。在一些情況下,人免疫球蛋白的Fv框架區(FR)殘基由對應的非人殘基置換。此外,人源化抗體/抗體片段可以包含既不在接受者抗體中也不在導入的CDR或框架序列中發現的殘基。該等修飾可以進一步改進和優化抗體或抗體片段性能。通常,人源化抗體或其抗體片段將包含基本上所有如下項:至少一個(典型地兩個)可變結構域,其中所有或基本上所有CDR區對應於非人免疫球蛋白的那些CDR區,且FR區的所有或顯著一部分係人免疫球蛋白序列的那些。人源化抗體或抗體片段還可以包含免疫球蛋白恒定區(Fc)的至少一部分,典型地是人免疫球蛋白的恒定區的至少一部分。有關進一步的細節,參見Jones等人, Nature [自然], 321: 522-525, 1986;Reichmann等人, Nature [自然], 332: 323-329, 1988;Presta, Curr. Op. Struct. Biol.[結構生物學現狀], 2: 593-596, 1992。"Humanized" forms of non-human (e.g., murine) antibodies are chimeric immunoglobulins, immunoglobulin chains or fragments thereof (such as Fv, Fab, Fab', F(ab')2, or other antigen-binding partners of antibodies sequence) containing minimal sequence from a non-human immunoglobulin. In most cases, humanized antibodies and antibody fragments thereof are human immunoglobulins (recipient antibodies or antibody fragments) in which residues from the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) of the recipient are replaced by mouse, rat or rabbit) (donor antibody) for residue substitutions in CDRs with the desired specificity, affinity and capacity. In some instances, Fv framework region (FR) residues of the human immunoglobulin are replaced by corresponding non-human residues. Furthermore, humanized antibodies/antibody fragments may comprise residues which are found neither in the recipient antibody nor in the imported CDR or framework sequences. Such modifications can further improve and optimize antibody or antibody fragment performance. Typically, a humanized antibody or antibody fragment thereof will comprise substantially all of the following: at least one (typically two) variable domains in which all or substantially all of the CDR regions correspond to those of a non-human immunoglobulin , and all or a substantial portion of the FR regions are those of human immunoglobulin sequences. The humanized antibody or antibody fragment can also comprise at least a portion of an immunoglobulin constant region (Fc), typically that of a human immunoglobulin. For further details see Jones et al., Nature, 321: 522-525, 1986; Reichmann et al., Nature, 332: 323-329, 1988; Presta, Curr. Op. Struct. Biol. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2: 593-596, 1992.
「完全人」係指如下免疫球蛋白,如抗體或抗體片段,其中整個分子係人起源或由與抗體或免疫球蛋白的人形式相同的胺基酸序列組成。"Fully human" refers to an immunoglobulin, such as an antibody or antibody fragment, in which the entire molecule is of human origin or consists of the same amino acid sequence as the human form of the antibody or immunoglobulin.
「鼠」係指小鼠或大鼠。例如,鼠抗體或其片段含有從鼠動物(例如,小鼠或大鼠)分離的抗體或其片段的序列。"Mouse" means a mouse or a rat. For example, a murine antibody or fragment thereof comprises the sequence of an antibody or fragment thereof isolated from a murine animal (eg, mouse or rat).
術語「分離的」意指從天然狀態改變的或去除的。例如,天然存在於活體動物中的核酸或肽不是「分離的」,但是與其天然狀態的共存材料部分或完全分開的相同核酸或肽係「分離的」。分離的核酸或蛋白質能以基本上純化的形式存在,或者可以存在於非天然環境(例如像,宿主細胞)中。The term "isolated" means altered or removed from the natural state. For example, a nucleic acid or peptide naturally present in a living animal is not "isolated", but the same nucleic acid or peptide partially or completely separated from the coexisting materials of its natural state is "isolated". An isolated nucleic acid or protein can exist in substantially purified form, or it can exist in a non-native environment such as, for example, a host cell.
在本發明之上下文中,使用以下對常見核酸鹼基的縮寫。「A」係指腺苷,「C」係指胞嘧啶,「G」係指鳥苷,「T」係指胸苷,並且「U」係指尿苷。In the context of the present invention, the following abbreviations for common nucleic acid bases are used. "A" refers to adenosine, "C" refers to cytosine, "G" refers to guanosine, "T" refers to thymidine, and "U" refers to uridine.
術語「可操作地連接」或「轉錄控制」係指調控序列和異源核酸序列之間的導致後者的表現的功能性連接。例如,當第一核酸序列被放置成與第二核酸序列有功能關係時,該第一核酸序列與該第二核酸序列可操作地連接。例如,如果啟動子影響編碼序列的轉錄或表現,則該啟動子與該編碼序列可操作地連接。可操作地連接的DNA序列可以彼此鄰接,並且例如在需要連接兩個蛋白質編碼區的情況下,它們處於同一閱讀框中。The term "operably linked" or "transcriptional control" refers to a functional linkage between a regulatory sequence and a heterologous nucleic acid sequence resulting in the expression of the latter. For example, a first nucleic acid sequence is operably linked to a second nucleic acid sequence when the first nucleic acid sequence is placed into a functional relationship with the second nucleic acid sequence. For example, a promoter is operably linked to a coding sequence if the promoter affects the transcription or expression of the coding sequence. Operably linked DNA sequences may be contiguous to each other and, for example, where necessary to join two protein coding regions, be in the same reading frame.
術語「腸胃外」投與免疫原性組成物包括例如皮下(s.c.)、靜脈內(i.v.)、肌肉內(i.m.)、或胸骨內注射、腫瘤內或輸注技術。The term "parenteral" administration of an immunogenic composition includes, for example, subcutaneous (s.c.), intravenous (i.v.), intramuscular (i.m.), or intrasternal injection, intratumoral or infusion techniques.
術語「核酸」或「多核苷酸」係指單股或雙股形式的去氧核糖核酸(DNA)或核糖核酸(RNA)及其聚合物。除非特別限定,否則該術語涵蓋含有已知的天然核苷酸類似物的核酸,該等核酸具有與參考核酸類似的結合特性並且以與天然存在的核苷酸類似的方式進行代謝。除非另外指出,否則特定的核酸序列還隱含地涵蓋其保守修飾的變體(例如,簡併密碼子取代)、等位基因、直向同源物、SNP和互補序列以及明確指明的序列。具體地,簡併密碼子取代可以藉由產生如下序列而獲得,在該等序列中,一或多個所選的(或全部)密碼子的第三位被混合鹼基和/或去氧肌苷殘基取代(Batzer等人, Nucleic Acid Res. [核酸研究] 19:5081 (1991);Ohtsuka等人, J. Biol. Chem. [生物化學雜誌] 260:2605-2608 (1985);和Rossolini等人, Mol. Cell. Probes [分子與細胞探針] 8:91-98 (1994))。The term "nucleic acid" or "polynucleotide" refers to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA) and polymers thereof in single- or double-stranded form. Unless specifically limited, the term encompasses nucleic acids that contain known analogs of natural nucleotides that have similar binding properties to the reference nucleic acid and are metabolized in a manner similar to naturally occurring nucleotides. Unless otherwise indicated, a particular nucleic acid sequence also implicitly encompasses conservatively modified variants thereof (eg, degenerate codon substitutions), alleles, orthologs, SNPs, and complementary sequences, as well as explicitly indicated sequences. Specifically, degenerate codon substitutions can be obtained by generating sequences in which the third position of one or more selected (or all) codons is replaced by mixed bases and/or deoxyinosine Residue substitution (Batzer et al., Nucleic Acid Res. 19:5081 (1991); Ohtsuka et al., J. Biol. Chem. 260:2605-2608 (1985); and Rossolini et al. Al, Mol. Cell. Probes 8:91-98 (1994)).
術語「肽」、「多肽」和「蛋白質」可互換地使用,並且係指包含由肽鍵共價連接的胺基酸殘基的化合物。蛋白質或肽必須含有至少兩個胺基酸,並且對可構成蛋白質或肽序列的胺基酸的最大數量沒有限制。多肽包括包含由肽鍵彼此相連的兩個或更多個胺基酸的任何肽或蛋白質。如本文所用,該術語係指短鏈,例如其在本領域中通常也稱為肽、寡肽和寡聚體;並且還係指較長的鏈,其在本領域中通常稱為蛋白質,存在有很多類型的蛋白質。「多肽」包括例如生物活性片段、基本上同源的多肽、寡肽、同源二聚體、異源二聚體、多肽的變體、經修飾的多肽、衍生物、類似物、融合蛋白等。多肽包括天然肽、重組肽、或其組合。The terms "peptide", "polypeptide" and "protein" are used interchangeably and refer to a compound comprising amino acid residues covalently linked by peptide bonds. A protein or peptide must contain at least two amino acids, and there is no limit to the maximum number of amino acids that can make up a protein or peptide sequence. Polypeptides include any peptide or protein comprising two or more amino acids joined to each other by peptide bonds. As used herein, the term refers to short chains, such as are also commonly referred to in the art as peptides, oligopeptides, and oligomers; and also to longer chains, commonly referred to in the art as proteins, in the presence of There are many types of protein. "Polypeptide" includes, for example, biologically active fragments, substantially homologous polypeptides, oligopeptides, homodimers, heterodimers, variants of polypeptides, modified polypeptides, derivatives, analogs, fusion proteins, etc. . Polypeptides include natural peptides, recombinant peptides, or combinations thereof.
術語「啟動子」係指啟動多核苷酸序列的特異性轉錄所需的由細胞合成機器或引入的合成機器所識別的DNA序列。The term "promoter" refers to a DNA sequence recognized by the cellular synthetic machinery or introduced synthetic machinery required to initiate the specific transcription of a polynucleotide sequence.
術語「啟動子/調節序列」係指表現與啟動子/調節序列可操作地連接的基因產物所需的核酸序列。在一些情況下,該序列可為核心啟動子序列,並且在其他情況下,該序列還可以包括強化子序列和表現基因產物所需的其他調控元件。啟動子/調節序列可為例如以組織特異性方式表現基因產物的啟動子/調節序列。The term "promoter/regulatory sequence" refers to a nucleic acid sequence required for expression of a gene product to which a promoter/regulatory sequence is operably linked. In some cases, this sequence may be a core promoter sequence, and in other cases, this sequence may also include enhancer sequences and other regulatory elements required for expression of the gene product. The promoter/regulatory sequence may be, for example, a promoter/regulatory sequence that expresses the gene product in a tissue-specific manner.
術語「組成型」啟動子係指當與編碼或指定基因產物的多核苷酸可操作地連接時,在細胞的大多數或全部生理條件下致使基因產物在細胞中產生的核酸序列。The term "constitutive" promoter refers to a nucleic acid sequence that, when operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding or specifying a gene product, causes the gene product to be produced in a cell under most or all physiological conditions of the cell.
術語「誘導型」啟動子係指當與編碼或指定基因產物的多核苷酸可操作地連接時,基本上僅在對應於啟動子的誘導物存在於細胞中時才致使基因產物在細胞中產生的核酸序列。The term "inducible" promoter refers to a promoter which, when operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding or specifying a gene product, causes the gene product to be produced in the cell substantially only when an inducer corresponding to the promoter is present in the cell. nucleic acid sequence.
術語「組織特異性」啟動子係指當與編碼或指定基因產物的多核苷酸可操作地連接時,基本上僅在細胞係對應於啟動子的組織類型的細胞時才致使基因產物在細胞中產生的核酸序列。The term "tissue-specific" promoter means that, when operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding or specifying a gene product, it causes the gene product to be present in the cell substantially only when the cell line corresponds to the promoter's tissue-type cell. Nucleic acid sequence generated.
如在scFv的上下文中使用的術語「柔性多肽連接子」或「連接子」係指由單獨或組合使用的胺基酸如甘胺酸和/或絲胺酸殘基組成的肽連接子,以將可變重鏈區和可變輕鏈區連接在一起。在一個實施方式中,柔性多肽連接子係Gly/Ser連接子並且包含重複n次的胺基酸序列(Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser)(SEQ ID NO: 89),其中n係等於或大於1的正整數。例如,n = 1,n = 2,n = 3。N = 4,n = 5和n = 6,n = 7,n = 8,n = 9和n = 10。在一個實施方式中,柔性多肽連接子係(Gly 4Ser) 3(SEQ ID NO: 82)。在另一個實施方式中,連接子包括(Gly 2Ser)和(GlySer)的多個重複。在另一個實施方式中,多肽不包括連接子,例如(n = 0)。WO 2012/138475中描述的連接子也被包括在本發明之範圍內,將該文獻藉由引用併入本文。 The term "flexible polypeptide linker" or "linker" as used in the context of scFv refers to a peptide linker consisting of amino acid residues such as glycine and/or serine, alone or in combination, to The variable heavy chain region and the variable light chain region are linked together. In one embodiment, the flexible polypeptide linker is a Gly/Ser linker and comprises an amino acid sequence (Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser) (SEQ ID NO: 89) repeated n times, wherein n is equal to or greater than 1 positive integer of . For example, n=1, n=2, n=3. N=4, n=5 and n=6, n=7, n=8, n=9 and n=10. In one embodiment, the flexible polypeptide linker is (Gly 4 Ser) 3 (SEQ ID NO: 82). In another embodiment, the linker comprises multiple repeats of ( Gly2Ser ) and (GlySer). In another embodiment, the polypeptide does not include a linker, eg (n=0). Also included within the scope of the present invention are linkers described in WO 2012/138475, which is incorporated herein by reference.
如本文所用,5’帽(也稱為RNA帽、RNA 7-甲基鳥苷帽或RNA m 7G帽)係已經在轉錄開始後不久添加到真核傳訊RNA的「前」端或5'端的經修飾的鳥嘌呤核苷酸。5’帽由與第一轉錄核苷酸連接的末端基團組成。它的存在對於被核糖體識別和被保護免於RNA酶至關重要。帽添加與轉錄偶合,並且共轉錄地發生,使得每個都影響另一個。在轉錄開始後不久,合成的mRNA的5’端被與RNA聚合酶相關的帽合成複合物結合。這種酶複合物催化mRNA加帽所需的化學反應。合成作為多步生物化學反應進行。可以修飾加帽部分以調製mRNA的功能,如其穩定性或翻譯效率。 As used herein, a 5' cap (also known as an RNA cap, RNA 7-methylguanosine cap, or RNA m 7 G cap) has been added to the "front" or 5' end of a eukaryotic messenger RNA shortly after transcription begins. modified guanine nucleotides. The 5' cap consists of a terminal group attached to the first transcribed nucleotide. Its presence is essential for being recognized by ribosomes and being protected from RNases. Cap addition is coupled to transcription and occurs co-transcriptionally such that each affects the other. Shortly after initiation of transcription, the 5' end of the synthesized mRNA is bound by the cap synthesis complex associated with RNA polymerase. This enzyme complex catalyzes the chemical reactions required for mRNA capping. Synthesis proceeds as a multistep biochemical reaction. The capping moiety can be modified to modulate the function of the mRNA, such as its stability or translation efficiency.
如本文所用,「體外轉錄的RNA」係指已在體外合成的RNA,較佳的是mRNA。通常,體外轉錄的RNA由體外轉錄載體產生。體外轉錄載體包含用於產生體外轉錄的RNA的模板。As used herein, "in vitro transcribed RNA" refers to RNA, preferably mRNA, that has been synthesized in vitro. Typically, in vitro transcribed RNA is produced from an in vitro transcription vector. In vitro transcription vectors contain templates for the production of RNA for in vitro transcription.
如本文所用,「聚(A)」係藉由聚腺苷酸化與mRNA附接的一系列腺苷。在用於瞬時表現的構建體的較佳的實施方式中,聚A在50個與5000個之間,較佳的是大於64個、更較佳的是大於100個、最較佳的是大於300個或400個。聚(A)序列可以經化學修飾或酶促修飾以調節mRNA功能,如定位、穩定性或翻譯效率。As used herein, "poly(A)" is a series of adenosines attached to mRNA by polyadenylation. In a preferred embodiment of the construct for transient expression, the poly A is between 50 and 5000, preferably greater than 64, more preferably greater than 100, most preferably greater than 300 or 400. Poly(A) sequences can be modified chemically or enzymatically to modulate mRNA function, such as localization, stability or translation efficiency.
如本文所用,「聚腺苷酸化」係指聚腺苷醯基部分或其經修飾的變體與傳訊RNA分子的共價連接。在真核生物中,大多數傳訊RNA(mRNA)分子在3’端被聚腺苷酸化。3’聚(A)尾係通過酶(聚腺苷酸聚合酶)的作用添加到前mRNA上的腺嘌呤核苷酸(通常數百個)的長序列。在高等真核生物中,將聚(A)尾添加到含有特定序列(聚腺苷酸化訊息)的轉錄物上。聚(A)尾和與其結合的蛋白質有助於保護mRNA免於被外切核酸酶降解。聚腺苷酸化對於轉錄終止、從細胞核輸出mRNA以及翻譯也是重要的。聚腺苷酸化在DNA轉錄成RNA後立即在細胞核中發生,但另外也可稍後在胞質中發生。在轉錄已經終止後,通過與RNA聚合酶締合的內切核酸酶複合物的作用切割mRNA鏈。切割位點通常被表徵為切割位點附近存在鹼基序列AAUAAA。在mRNA被切割後,腺苷殘基被添加到切割位點處的游離3’端上。As used herein, "polyadenylation" refers to the covalent attachment of a polyadenylation moiety, or modified variant thereof, to a messenger RNA molecule. In eukaryotes, most messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules are polyadenylated at the 3' end. The 3' poly(A) tail is a long sequence of adenine nucleotides (usually several hundred) added to pre-mRNA by the action of an enzyme (polyadenylate polymerase). In higher eukaryotes, poly(A) tails are added to transcripts containing specific sequences (polyadenylation messages). The poly(A) tail and the proteins associated with it help protect the mRNA from degradation by exonucleases. Polyadenylation is also important for transcription termination, mRNA export from the nucleus, and translation. Polyadenylation occurs in the nucleus immediately after the transcription of DNA into RNA, but can alternatively occur later in the cytoplasm. After transcription has terminated, the mRNA strand is cleaved by the action of an endonuclease complex associated with RNA polymerase. The cleavage site is usually characterized by the presence of the base sequence AAUAAA near the cleavage site. After the mRNA is cleaved, an adenosine residue is added to the free 3' end at the cleavage site.
如本文所用,「瞬時」係指非整合轉基因的持續數小時、數天或數週的表現,其中表現的時間段小於在整合到基因組中或包含在宿主細胞中的穩定質體複製子內的情況下基因的表現的時間段。As used herein, "transient" refers to the expression of a non-integrated transgene lasting hours, days or weeks, wherein the time period of expression is shorter than that of a stable plastid replicon integrated into the genome or contained in the host cell. The time period of expression of the gene in the case.
如本文所用,術語「治療(treat、treatment和treating)」係指減少或改善增殖性障礙的進展、嚴重程度和/或持續時間,或者改善增殖性障礙的一或多種症狀(較佳的是,一或多種可辨別的症狀),這由投與一或多種療法(例如一或多種治療劑,如本發明之CAR)引起。在具體的實施方式中,術語「治療(treat、treatment和treating)」係指改善增殖性障礙的至少一種可測量的物理參數,如腫瘤的生長,這不一定是患者可辨別的。在一些實施方式中,術語「治療(treat、treatment和treating)」係指藉由例如穩定可辨別的症狀來物理地,或藉由例如穩定物理參數來生理地,或藉由兩者,抑制增生性障礙的進展。在一些實施方式中,術語「治療(treat、treatment和treating)」係指減少或穩定腫瘤大小或癌細胞計數。As used herein, the terms "treat, treatment and treating" refer to reducing or ameliorating the progression, severity and/or duration of a proliferative disorder, or ameliorating one or more symptoms of a proliferative disorder (preferably, One or more identifiable symptoms), which result from the administration of one or more therapies (eg, one or more therapeutic agents, such as the CAR of the invention). In a specific embodiment, the terms "treat, treatment and treating" refer to the improvement of at least one measurable physical parameter of a proliferative disorder, such as tumor growth, which is not necessarily discernible by the patient. In some embodiments, the terms "treat, treatment, and treating" refer to inhibiting proliferation, either physically, such as by stabilizing discernible symptoms, or physiologically, such as by stabilizing a physical parameter, or both. Progression of sexual disorders. In some embodiments, the terms "treat, treatment and treating" refer to reducing or stabilizing tumor size or cancer cell count.
術語「訊息轉導途徑」係指在多種訊息轉導分子之間的生物化學關係,該等訊息轉導分子在訊息從細胞的部分傳遞至細胞的另一部分中發揮作用。短語「細胞表面受體」包括能夠接收信號並且傳遞訊息跨過細胞膜的分子以及分子複合物。The term "signal transduction pathway" refers to the biochemical relationship between the various signal transduction molecules that play a role in the transmission of a message from one part of a cell to another part of the cell. The phrase "cell surface receptor" includes molecules and molecular complexes capable of receiving signals and transmitting messages across cell membranes.
術語「受試者」旨在包括可以在其中引發免疫反應的活生物體(例如,哺乳動物、人)。The term "subject" is intended to include living organisms (eg, mammals, humans) in which an immune response can be elicited.
術語「基本上純化的」細胞係指本質上不含其他細胞類型的細胞。基本上純化的細胞還指已經與其天然存在狀態下正常相關的其他細胞類型分離的細胞。在一些情況下,基本上純化的細胞群體係指同質的細胞群體。在其他情況下,該術語僅指已經與其天然狀態下天然相關的細胞分離的細胞。在一些方面,在體外培養細胞。在其他方面,不在體外培養細胞。The term "substantially purified" cells refers to cells that are essentially free of other cell types. A substantially purified cell also refers to a cell that has been separated from other cell types with which it is normally associated in its naturally occurring state. In some instances, a substantially purified cell population refers to a homogeneous cell population. In other instances, the term simply refers to cells that have been separated from cells with which they are naturally associated in their natural state. In some aspects, cells are cultured in vitro. In other aspects, the cells are not cultured in vitro.
如本文所用的術語「治療劑」意指治療。藉由減少、抑制、緩解或根除疾病狀態來獲得治療效果。The term "therapeutic agent" as used herein means treatment. A therapeutic effect is achieved by reducing, inhibiting, relieving or eradicating a disease state.
如本文所用的術語「預防」意指對疾病或疾病狀態的預防或保護性治療。The term "prevention" as used herein means prophylactic or protective treatment of a disease or condition.
在本發明之上下文中,「腫瘤抗原」或「過度增殖性障礙抗原」或「與過度增殖性障礙相關的抗原」係指特異性過度增殖性障礙常見的抗原。在某些方面,本發明之過度增生性障礙抗原衍生自:癌症,包括但不限於原發性或轉移性黑色素瘤、胸腺瘤、淋巴瘤、肉瘤、肺癌、肝癌、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、白血病、子宮癌、子宮頸癌、膀胱癌、腎癌和腺癌(如乳癌、前列腺癌、卵巢癌、胰臟癌等)。In the context of the present invention, "tumor antigen" or "hyperproliferative disorder antigen" or "antigen associated with a hyperproliferative disorder" refers to an antigen common to a specific hyperproliferative disorder. In certain aspects, the hyperproliferative disorder antigens of the invention are derived from: cancer, including but not limited to primary or metastatic melanoma, thymoma, lymphoma, sarcoma, lung cancer, liver cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma , Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, leukemia, uterine cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer and adenocarcinoma (such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, etc.).
術語「轉染的」或「轉化的」或「轉導的」係指將外源核酸轉移或引入宿主細胞中的過程。「轉染的」或「轉化的」或「轉導的」細胞係已用外源核酸轉染、轉化或轉導的細胞。細胞包括原代主體細胞及其子代。The term "transfected" or "transformed" or "transduced" refers to the process of transferring or introducing exogenous nucleic acid into a host cell. "Transfected" or "transformed" or "transduced" cell line A cell that has been transfected, transformed or transduced with an exogenous nucleic acid. Cells include primary host cells and their progeny.
術語「特異性地結合」係指抗體或配體識別樣本中存在的結合配偶體(例如刺激性腫瘤抗原)蛋白並與之結合,但該抗體或配體基本上不識別或結合樣本中的其他分子。The term "specifically binds" means that the antibody or ligand recognizes and binds to a binding partner (e.g. stimulatory tumor antigen) protein present in the sample, but the antibody or ligand does not substantially recognize or bind to other proteins in the sample. molecular.
如本文所用的「難治性」係指對治療無響應的疾病,例如癌症。在實施方式中,難治性癌症可以在治療開始之前或治療開始時對治療具有抗性。在一些實施方式中,難治性癌症可在治療期間產生抗性。難治性癌症也稱為抗性癌症。"Refractory" as used herein refers to a disease that does not respond to treatment, such as cancer. In an embodiment, the refractory cancer may be resistant to therapy before or when therapy is initiated. In some embodiments, a refractory cancer can develop resistance during treatment. Refractory cancer is also called resistant cancer.
如果受試者中的癌症參數(例如,血液學癌症,例如癌細胞生長、增殖和/或存活)被延緩或減少可檢測的量,例如約5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%、90%或更多(如藉由任何適當的量度,例如質量、細胞計數或體積所測定),則受試者對治療作出「響應」。在一個實例中,如果受試者經歷的預期壽命比不投與治療情況下的預期壽命延長約5%、10%、20%、30%、40%、50%或更多,則受試者對治療作出響應。在另一個實例中,如果受試者具有增加的無病存活期、總體存活期或增加的進展時間,則受試者對治療作出響應。可以使用若干種方法來確定患者是否對治療作出響應,包括例如NCCN腫瘤學臨床實踐指南(NCCN Guidelines®)提供的標準。例如,在B-ALL的上下文中,完全響應或完全響應者可能涉及以下中的一或多種:< 5% BM幼稚細胞,> 1000個嗜中性球/ANC(/µL)。> 100,000個血小板(/µL)其中無循環幼稚細胞或髓外疾病(無淋巴結腫大、脾腫大、皮膚/牙齦浸潤/睪丸團塊/CNS受累),三譜系造血,並且4週無復發。部分響應者可能涉及以下中的一或多個:BM幼稚細胞減少 > 50%,> 1000個嗜中性球/ANC(/µL)。> 100,000血小板(/µL)。非響應者可以顯示疾病進展,例如BM母細胞 > 25%。在實施方式中,完全響應者被定義為在CD8+ 群體中具有7%或更多的CD27+ CD45RO-細胞。在實施方式中,收穫前水平的CAR+ 細胞百分比區分了響應者(例如,完全響應者和部分響應者)與非響應者(NR)。If a parameter of cancer (e.g., hematological cancer, e.g., cancer cell growth, proliferation, and/or survival) in the subject is delayed or reduced by a detectable amount, e.g., about 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% %, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90% or more (as determined by any suitable measure, such as mass, cell count, or volume), the subject then "responds" to the treatment. In one example, if the subject experiences an increase in life expectancy of about 5%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50% or more compared to life expectancy without administration of the treatment, the subject Respond to treatment. In another example, a subject responds to treatment if the subject has increased disease-free survival, overall survival, or increased time to progression. Several methods can be used to determine whether a patient is responding to therapy, including, for example, the criteria provided by the NCCN Oncology Clinical Practice Guidelines (NCCN Guidelines®). For example, in the context of B-ALL, a complete response or complete responder may involve one or more of the following: <5% BM naive cells, >1000 neutrophils/ANC (/µL). >100,000 platelets (/µL) without circulating immature cells or extramedullary disease (no lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, skin/gingival infiltration/testicular mass/CNS involvement), tri-lineage hematopoiesis, and 4 weeks without recurrence. Partial responders may involve one or more of the following: >50% reduction in BM naive cells, >1000 neutrophils/ANC (/µL). >100,000 platelets (/µL). Non-responders can show disease progression, such as >25% BM blasts. In an embodiment, a complete responder is defined as having 7% or more CD27+CD45RO- cells in the CD8+ population. In embodiments, the percentage of CAR+ cells at the pre-harvest level differentiates responders (eg, complete responders and partial responders) from non-responders (NR).
如本文所用,術語「復發」係指在初始響應期(例如,完全響應或部分響應)後癌症的再現。響應初始期可能涉及癌細胞水平降低至低於某一閾值,例如低於20%、1%、10%、5%、4%、3%、2%、或1%。再現可能涉及癌細胞水平升高超過某一閾值,例如高於20%、1%、10%、5%、4%、3%、2%、或1%。例如,如在B-ALL的上下文中,再現可能涉及例如在完全響應之後血液、骨髓(> 5%)或任何髓外位點中的母細胞再現。在本上下文中,完全響應可能涉及 < 5% BM母細胞。更通常地,在實施方式中,響應(例如,完全響應或部分響應)可能涉及不存在可檢測的MRD(微量殘存疾病)。在實施方式中,初始響應期持續至少1、2、3、4、5、或6天;至少1、2、3、或4週;至少1、2、3、4、6、8、10、或12個月;或至少1、2、3、4、或5年。As used herein, the term "relapse" refers to the recurrence of cancer after an initial period of response (eg, a complete response or a partial response). The initial period of response may involve a reduction in the level of cancer cells below a certain threshold, such as below 20%, 1%, 10%, 5%, 4%, 3%, 2%, or 1%. Reappearance may involve elevated levels of cancer cells above a certain threshold, such as above 20%, 1%, 10%, 5%, 4%, 3%, 2%, or 1%. For example, as in the context of B-ALL, reappearance may involve reappearance of blasts in the blood, bone marrow (>5%), or any extramedullary site, for example, following a complete response. In this context, a complete response may involve <5% BM blasts. More generally, in embodiments, a response (eg, a complete response or a partial response) may involve the absence of detectable MRD (minimal residual disease). In an embodiment, the initial response period lasts at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 days; at least 1, 2, 3, or 4 weeks; at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, or 12 months; or at least 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 years.
如本文所用,術語「可調節的嵌合抗原受體(RCAR)」係指一組多肽,在最簡單的實施方式中典型地是兩個多肽,當在RCARX細胞中時,該等多肽為RCARX細胞提供針對靶細胞(典型地為癌細胞)的特異性以及可調節的細胞內訊息產生或增殖,這可以優化RCARX細胞的免疫效應子特性。RCARX細胞至少部分地依賴於抗原結合結構域以提供針對靶細胞的特異性,該靶細胞包含被抗原結合結構域結合的抗原。在實施方式中,RCAR包括二聚化開關,該二聚化開關在存在二聚化分子時可以將細胞內傳訊結構域偶合至抗原結合結構域。As used herein, the term "regulatory chimeric antigen receptor (RCAR)" refers to a set of polypeptides, typically two polypeptides in the simplest embodiment, which when in RCARX cells are RCARX The cells provide specificity for target cells (typically cancer cells) and regulated intracellular message production or proliferation, which can optimize the immune effector properties of RCARX cells. RCARX cells rely at least in part on an antigen-binding domain to provide specificity for a target cell comprising an antigen bound by the antigen-binding domain. In an embodiment, the RCAR comprises a dimerization switch that, in the presence of a dimerization molecule, can couple the intracellular signaling domain to the antigen binding domain.
當該術語在本文中使用時,「膜錨」或「膜系鏈結構域」係指足以將細胞外或細胞內結構域錨定到質膜的多肽或部分(例如肉豆蔻醯基)。"Membrane anchor" or "membrane tethering domain" as the term is used herein refers to a polypeptide or moiety (eg, myristyl) sufficient to anchor an extracellular or intracellular domain to the plasma membrane.
當該術語在本文中使用時(例如當提及RCAR時),「開關結構域」係指實體(典型地是基於多肽的實體),該實體在二聚化分子存在下與另一個開關結構域締合。該締合導致連接到(例如融合到)第一開關結構域的第一實體和連接到(例如融合到)第二開關結構域的第二實體的功能偶合。第一開關結構域和第二開關結構域統稱為二聚化開關。在實施方式中,第一開關結構域和第二開關結構域彼此相同,例如它們係具有相同初級胺基酸序列的多肽,並且統稱為同源二聚化開關。在實施方式中,第一開關結構域和第二開關結構域彼此不同,例如它們係具有不同初級胺基酸序列的多肽,並且統稱為異源二聚化開關。在實施方式中,該開關係細胞內的。在實施方式中,該開關係細胞外的。在實施方式中,開關結構域係基於多肽(例如基於FKBP或FRB)的實體,並且二聚化分子係小分子(例如雷帕黴素類似物(rapalogue))。在實施方式中,開關結構域係基於多肽的實體(例如結合myc肽的scFv),並且二聚化分子係多肽、其片段、或多肽的多聚體,例如結合一或多個myc scFv的myc配體或myc配體的多聚體。在實施方式中,開關結構域係基於多肽的實體(例如myc受體),並且二聚化分子係抗體或其片段,例如myc抗體。As the term is used herein (e.g. when referring to RCAR), "switch domain" refers to an entity (typically a polypeptide-based entity) that binds to another switch domain in the presence of a dimerization molecule. association. This association results in a functional coupling of a first entity linked to (eg fused to) the first switch domain and a second entity linked to (eg fused to) the second switch domain. The first switch domain and the second switch domain are collectively referred to as a dimerization switch. In an embodiment, the first switch domain and the second switch domain are identical to each other, eg, they are polypeptides having the same primary amino acid sequence, and are collectively referred to as a homodimerization switch. In an embodiment, the first switch domain and the second switch domain are different from each other, eg, they are polypeptides with different primary amino acid sequences, and are collectively referred to as a heterodimerization switch. In an embodiment, the switch is intracellular. In an embodiment, the switch is extracellular. In an embodiment, the switch domain is a polypeptide based (eg FKBP or FRB based) entity and the dimerization molecule is a small molecule (eg a rapalogue). In an embodiment, the switch domain is a polypeptide-based entity (such as a scFv that binds a myc peptide), and the dimerization molecule is a polypeptide, a fragment thereof, or a multimer of polypeptides, such as a myc that binds one or more myc scFv Ligands or multimers of myc ligands. In an embodiment, the switch domain is a polypeptide-based entity such as a myc receptor, and the dimerization molecule is an antibody or fragment thereof, such as a myc antibody.
當該術語在本文中使用時(例如當提及RCAR時),「二聚化分子」係指促進第一開關結構域與第二開關結構域締合的分子。在實施方式中,二聚化分子不在受試者中天然發生,或者不以導致顯著二聚化的濃度發生。在實施方式中,二聚化分子係小分子,例如雷帕黴素(Rapamycin)或雷帕黴素類似物,例如RAD001。A "dimerization molecule" as the term is used herein (eg, when referring to RCAR) refers to a molecule that facilitates the association of a first switch domain with a second switch domain. In an embodiment, the dimerizing molecule does not occur naturally in the subject, or does not occur at a concentration that results in significant dimerization. In an embodiment, the dimerization molecule is a small molecule, such as Rapamycin or a rapamycin analog, such as RAD001.
術語「生物等效的」係指產生與參考劑量或參考量的參考化合物(例如,RAD001)產生的效果等同的效果所需的除參考化合物(例如,RAD001)之外的藥劑的量。在實施方式中,效果係mTOR抑制水平,例如如藉由P70 S6激酶抑制測量的,例如如在體內或體外測定中評價的,例如如藉由本文所述之測定(例如Boulay測定)或藉由西方墨點法測量磷酸化的S6水平測量的。在實施方式中,效果想如藉由細胞分選測量的PD-1陽性/PD-1陰性T細胞比率的改變。在實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑的生物等效量或劑量想實現與參考化合物的參考劑量或參考量相同水平的P70 S6激酶抑制的量或劑量。在實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑的生物等效量或劑量想實現與參考化合物的參考劑量或參考量相同水平的PD-1陽性/PD-1陰性T細胞比率改變的量或劑量。The term "bioequivalent" refers to the amount of an agent other than a reference compound (eg, RAD001 ) required to produce an effect equivalent to that produced by a reference dose or amount of a reference compound (eg, RAD001 ). In an embodiment, the effect is the level of mTOR inhibition, e.g. as measured by P70 S6 kinase inhibition, e.g. as assessed in an in vivo or in vitro assay, e.g. as by an assay described herein (e.g. Boulay assay) or by Phosphorylated S6 levels were measured by Western blotting. In an embodiment, the effect is like a change in the ratio of PD-1 positive/PD-1 negative T cells measured by cell sorting. In an embodiment, a bioequivalent amount or dose of an mTOR inhibitor is an amount or dose that achieves the same level of P70 S6 kinase inhibition as a reference dose or amount of a reference compound. In an embodiment, a bioequivalent amount or dose of an mTOR inhibitor is an amount or dose that achieves the same level of change in the ratio of PD-1 positive/PD-1 negative T cells as a reference dose or reference amount of a reference compound.
當與mTOR抑制劑(例如變構mTOR抑制劑,例如RAD001或雷帕黴素,或催化性mTOR抑制劑)聯合使用時,術語「低免疫增強劑量」係指mTOR抑制劑部分但不是完全抑制mTOR活性的劑量,例如,如藉由P70 S6激酶活性的抑制測量的。本文討論了用於評價Mtor活性之方法,例如藉由抑制P70 S6激酶。劑量不足以導致完全免疫抑制,但足以增強免疫反應。在實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑的低免疫增強劑量導致PD-1陽性T細胞數目的減少和/或PD-1陰性T細胞數目的增加,或PD-1陰性T細胞/PD-1陽性T細胞的比率的增加。在實施方式中,低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑導致初始T細胞的數目增加。在實施方式中,低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑導致以下中的一或多個: 以下標記物中的一或多個例如在記憶T細胞(例如,記憶T細胞先質)上的表現增加:CD62L 高、CD127 高、CD27 +和BCL2; KLRG1在例如記憶T細胞(例如,記憶T細胞先質)上的表現減少;以及 記憶T細胞先質,例如具有以下特徵中的任一個或組合的細胞的數目增加:增加的CD62L 高、增加的CD127 高、增加的CD27 +、減少的KLRG1、和增加的BCL2; 其中,例如,與未治療的受試者相比,例如至少瞬時地發生上述任何變化。 When used in combination with an mTOR inhibitor (e.g., an allosteric mTOR inhibitor, such as RAD001 or rapamycin, or a catalytic mTOR inhibitor), the term "low immunoenhancing dose" refers to partial but not complete inhibition of mTOR by an mTOR inhibitor A dose of activity, eg, as measured by inhibition of P70 S6 kinase activity. Methods for assessing Mtor activity, such as by inhibition of P70 S6 kinase, are discussed herein. The dose was insufficient to cause complete immunosuppression, but sufficient to enhance the immune response. In an embodiment, the low immunoenhancing dose of the mTOR inhibitor results in a decrease in the number of PD-1 positive T cells and/or an increase in the number of PD-1 negative T cells, or PD-1 negative T cells/PD-1 positive T cells increase in the ratio. In an embodiment, a low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor results in an increase in the number of naive T cells. In an embodiment, the low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor results in one or more of: Increased expression of one or more of the following markers, e.g., on memory T cells (e.g., memory T cell precursors): CD62L high , CD127 high , CD27 + , and BCL2; reduced expression of KLRG1 on, for example, memory T cells (eg, memory T cell precursors); and memory T cell precursors, such as cells with any one or combination of the following characteristics Increased number of: increased CD62L high , increased CD127 high , increased CD27 + , decreased KLRG1, and increased BCL2; wherein, for example, any of the above changes occur at least transiently, for example, compared to an untreated subject .
範圍:貫穿本揭露內容,能以範圍形式呈現本發明之各個方面。應該理解的是,範圍形式的描述僅僅是為了方便以及簡潔,不應該被理解為對本發明範圍的不靈活的限制。因此,範圍的描述應當被認為是具有確切揭露的所有可能的子範圍以及該範圍內的單獨數值。例如,範圍如從1至6的描述應當被認為是具有確切揭露的子範圍,如從1至3、從1至4、從1至5、從2至4、從2至6、從3至6等,以及該範圍內的單獨數字,例如1、2、2.7、3、4、5、5.3、和6。作為另一個實例,範圍如95%-99%同一性包括具有95%、96%、97%、98%或99%同一性,並且包括如96%-99%、96%-98%、96%-97%、97%-99%、97%-98%和98%-99%同一性的子範圍。無論範圍的寬度如何,這都適用。 雙重CAR Ranges: Throughout this disclosure, various aspects of this invention can be presented in a range format. It should be understood that the description in range format is merely for convenience and brevity and should not be construed as an inflexible limitation on the scope of the invention. Accordingly, the description of a range should be considered to have specifically disclosed all the possible subranges as well as individual numerical values within that range. For example, the description of a range such as from 1 to 6 should be considered to have explicitly disclosed subranges such as from 1 to 3, from 1 to 4, from 1 to 5, from 2 to 4, from 2 to 6, from 3 to 6 etc., and individual numbers within the range, such as 1, 2, 2.7, 3, 4, 5, 5.3, and 6. As another example, a range such as 95%-99% identity includes having 95%, 96%, 97%, 98% or 99% identity, and includes such as 96%-99%, 96%-98%, 96% Subranges of -97%, 97%-99%, 97%-98% and 98%-99% identity. This works regardless of the width of the range. double CAR
本揭露的特徵至少部分是編碼嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的新核酸分子,該新核酸分子包含含有CD22 CAR的第一CAR和含有CD19 CAR的第二CAR,例如,如本文所述之雙重CAR。在一些實施方式中,CD22 CAR包含CD22抗原結合結構域和第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域。在一些實施方式中,該CD19 CAR包含CD19抗原結合結構域和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域。在本文揭露的CAR分子的一些實施方式中,CAR分子包含兩個相同的多肽序列,例如,第一和第二跨膜結構域;第一和第二共刺激結構域;和/或第一和第二初級傳訊結構域,其中多肽序列由不同的核苷酸序列編碼。本文還揭露了使用所述CAR分子的方法。The present disclosure features, at least in part, novel nucleic acid molecules encoding chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecules comprising a first CAR comprising a CD22 CAR and a second CAR comprising a CD19 CAR, e.g., as described herein Double CAR. In some embodiments, a CD22 CAR comprises a CD22 antigen binding domain and a first transmembrane domain; a first co-stimulatory signaling domain; and/or a first primary signaling domain. In some embodiments, the CD19 CAR comprises a CD19 antigen binding domain and a second transmembrane domain; a second co-stimulatory signaling domain; and/or a second primary signaling domain. In some embodiments of the CAR molecules disclosed herein, the CAR molecule comprises two identical polypeptide sequences, for example, first and second transmembrane domains; first and second co-stimulatory domains; and/or first and second co-stimulatory domains; The second primary signaling domain, wherein the polypeptide sequence is encoded by a different nucleotide sequence. Also disclosed herein are methods of using the CAR molecules.
不希望受理論的束縛,據信在一些實施方式中,編碼CAR分子(例如,雙重CAR分子)的核酸分子被優化(例如密碼子優化),以預防重組(例如同源重組)。在一些實施方式中,CAR分子(例如,雙重CAR分子)包含兩個結構域(例如第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域),每個結構域包含類似的胺基酸序列,但由不同的核苷酸序列編碼。Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that in some embodiments, nucleic acid molecules encoding CAR molecules (eg, dual CAR molecules) are optimized (eg, codon-optimized) to prevent recombination (eg, homologous recombination). In some embodiments, a CAR molecule (e.g., a dual CAR molecule) comprises two domains (e.g., a first transmembrane domain and a second transmembrane domain), each domain comprising a similar amino acid sequence, but encoded by different nucleotide sequences.
在一個方面,本文揭露的CAR分子包含含有結合CD22的第一抗原結合結構域的第一CAR;第一跨膜結構域;第一共刺激傳訊結構域;和/或第一初級傳訊結構域。In one aspect, a CAR molecule disclosed herein comprises a first CAR comprising a first antigen binding domain that binds CD22; a first transmembrane domain; a first co-stimulatory signaling domain; and/or a first primary signaling domain.
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含本文所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3),例如在表1A、2A或3A中;和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3)。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含本文所述之CD22結合結構域的LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3,例如在表1A、2A或3A中;和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的HC CDR1、HC CDR2和HC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises one or more (eg, all three) of the light chain complementarity determining region 1 (LC CDR1 ), light chain complementarity determining region 2 (LC CDR1 ) of a CD22 binding domain described herein. CDR2) and light chain complementarity determining region 3 (LC CDR3), for example in Table 1A, 2A or 3A; and/or one or more of the CD22 binding domains described herein (for example in Table 1A, 2A or 3A) one (eg, all three) of heavy chain complementarity determining region 1 (HC CDR1), heavy chain complementarity determining region 2 (HC CDR2), and heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 (HC CDR3). In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises the LC CDR1, LC CDR2 and LC CDR3 of a CD22 binding domain described herein, for example in Table 1A, 2A or 3A; and/or herein (for example in Table 1A, 2A or HC CDR1, HC CDR2 and HC CDR3 of the CD22 binding domain described in 3A).
在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 28的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 29的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 30的LC CDR3。在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 31的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 32的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 33的LC CDR3。在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 34的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 32的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 30的LC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 28, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 29, and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 30. In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 31, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 32, and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 33. In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO:34, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO:32 and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO:30.
在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 20的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 21的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 22的HC CDR3。在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 23的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 24的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 22的HC CDR3。在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 25的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 26的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 27的HC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 20, the HC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 21 and the HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 22. In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 23, the HC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 24, and the HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 22. In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 25, the HC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 26, and the HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 27.
在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 28的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 29的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 30的LC CDR3;和SEQ ID NO: 20的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 21的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 22的HC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 28, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 29, and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 30; and the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 20, the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO HC CDR2 of : 21 and HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 22.
在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 31的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 32的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 33的LC CDR3;和SEQ ID NO: 23的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 24的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 22的HC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 31, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 32, and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 33; and the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 23, the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO HC CDR2 of : 24 and HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 22.
在實施方式中,CD22結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 34的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 32的LC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 30的LC CDR3;和SEQ ID NO: 25的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 26的HC CDR2和SEQ ID NO: 27的HC CDR3。In an embodiment, the CD22 binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 34, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 32, and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 30; and the HC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO: 25, the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO HC CDR2 of : 26 and HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 27.
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域(例如,scFv)包含本文所述之CD22結合結構域的輕鏈可變(VL)區,例如在表1A或3A中;和/或本文(例如在表1A或3A中)所述之CD22結合結構域的重鏈可變(VH)區。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VL區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VL區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VL區序列的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含表1A或3A中提供的CD22 VH區序列的胺基酸序列。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain (e.g., scFv) comprises the light chain variable (VL) region of a CD22 binding domain described herein, e.g., in Table 1A or 3A; and/or herein (e.g., in Table The heavy chain variable (VH) region of the CD22 binding domain described in 1A or 3A). In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising at least one, two or three modifications (e.g., substitutions) but no more than 30, 20 or 10 modified (eg, substituted) amino acid sequences. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising an amino acid sequence at least 95% identical to the CD22 VL region sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD22 VL region sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising at least one, two or three modifications (e.g., substitutions) but no more than 30, 20 or 10 modified (eg, substituted) amino acid sequences. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising an amino acid sequence at least 95% identical to the CD22 VH region sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A. In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD22 VH region sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A.
在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合包含scFv,該scFv包含具有表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合包含scFv,該scFv包含與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合包含scFv,該scFv包含表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 50)的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,CD22抗原結合包含scFv,該scFv由與表1A或3A中提供的CD22 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 49或51)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding comprises a scFv comprising at least one, two or three modifications (e.g., substitutions) having the CD22 scFv sequence (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 50) provided in Table 1A or 3A but Amino acid sequences with no more than 30, 20 or 10 modifications (eg, substitutions). In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding comprises a scFv comprising an amino acid sequence at least 95% identical to the CD22 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 50). In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding comprises a scFv comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD22 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A or 3A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 50). In an embodiment, the CD22 antigen binding comprises a scFv composed of at least 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, 99%, or 100% identical nucleotide sequence codes.
在一個方面,本文揭露的CAR分子包含含有結合CD19的第二抗原結合結構域的第二CAR和第二跨膜結構域;第二共刺激結構域;和/或第二初級傳訊結構域。In one aspect, a CAR molecule disclosed herein comprises a second CAR comprising a second antigen binding domain that binds CD19 and a second transmembrane domain; a second co-stimulatory domain; and/or a second primary signaling domain.
在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含:本文(例如在表1A、2A、3A或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)輕鏈互補決定區1(LC CDR1)、輕鏈互補決定區2(LC CDR2)和輕鏈互補決定區3(LC CDR3);和/或本文所述之CD19結合結構域的一或多個(例如,全部三個)重鏈互補決定區1(HC CDR1)、重鏈互補決定區2(HC CDR2)和重鏈互補決定區3(HC CDR3),例如在表1A、2A、3A、或5A中。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含本文所述之CD19結合結構域的LC CDR1、LC CDR2和LC CDR3,例如,在表1A或2A中;和/或本文(例如在表1A、2A或3A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的HC CDR1、HC CDR2和HC CDR3。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 40的LC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 41的LC CDR2;和SEQ ID NO: 42的LC CDR3;和/或SEQ ID NO: 35的HC CDR1、SEQ ID NO: 36-38的HC CDR2;和SEQ ID NO: 39的HC CDR3。In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises: one or more (e.g., all three) light chain complementarity determining elements of a CD19 binding domain described herein (e.g., in Table 1A, 2A, 3A, or 5A). Region 1 (LC CDR1), Light Chain Complementarity Determining Region 2 (LC CDR2), and Light Chain Complementarity Determining Region 3 (LC CDR3); and/or one or more (eg, all three) of the CD19 binding domains described herein each) heavy chain complementarity determining region 1 (HC CDR1), heavy chain complementarity determining region 2 (HC CDR2), and heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 (HC CDR3), for example in Table 1A, 2A, 3A, or 5A. In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises the LC CDR1, LC CDR2, and LC CDR3 of a CD19 binding domain described herein, e.g., in Table 1A or 2A; and/or herein (e.g., in Table 1A, 2A or HC CDR1, HC CDR2 and HC CDR3 of the CD19 binding domain described in 3A). In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises the LC CDR1 of SEQ ID NO:40, the LC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO:41; and the LC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO:42; and/or the HC of SEQ ID NO:35 CDR1, HC CDR2 of SEQ ID NO: 36-38; and HC CDR3 of SEQ ID NO: 39.
在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域(例如,scFv)包含本文所述之CD19結合結構域的輕鏈可變(VL)區,例如在表1A、3A或5A中;和/或本文(例如在表1A、3A、或5A中)所述之CD19結合結構域的重鏈可變(VH)區。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含具有表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VL區,該VL區包含表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VL區序列的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含具有表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含VH區,該VH區包含表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 VH區序列的胺基酸序列。In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain (e.g., scFv) comprises the light chain variable (VL) region of a CD19 binding domain described herein, e.g., in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A; and/or herein ( For example, the heavy chain variable (VH) region of the CD19 binding domain described in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A). In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising at least one, two or three modifications (e.g., substitutions) of the CD19 VL region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A or 5A but not Amino acid sequences with more than 30, 20 or 10 modifications (eg, substitutions). In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising an amino acid sequence at least 95% identical to the CD19 VL region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A. In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VL region comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD19 VL region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A or 5A. In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising at least one, two or three modifications (e.g., substitutions) of the CD19 VH region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A or 5A but not Amino acid sequences with more than 30, 20 or 10 modifications (eg, substitutions). In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising an amino acid sequence at least 95% identical to the CD19 VH region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A. In some embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a VH region comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD19 VH region sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A.
在其他實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含具有表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44)的至少一個、兩個或三個修飾(例如,取代)但不超過30、20或10個修飾(例如,取代)的胺基酸序列。在其他實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含與表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44)具有至少95%同一性的胺基酸序列。在其他實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv包含表1A、3A、或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 44)的胺基酸序列。在其他實施方式中,CD19抗原結合結構域包含scFv,該scFv由與表1A、3A或5A中提供的CD19 scFv序列(例如,SEQ ID NO: 43或48)具有至少95%、96%、97%、98%、99%、或100%同一性的核苷酸序列編碼。In other embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising at least one, two or three modifications having the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 44) (eg, substitutions) but not more than 30, 20 or 10 modified (eg, substitutions) amino acid sequences. In other embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising amino acids at least 95% identical to the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 44) sequence. In other embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv comprising the amino acid sequence of the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (eg, SEQ ID NO: 44). In other embodiments, the CD19 antigen binding domain comprises a scFv that is at least 95%, 96%, 97% identical to the CD19 scFv sequence provided in Table 1A, 3A, or 5A (e.g., SEQ ID NO: 43 or 48). %, 98%, 99%, or 100% identical nucleotide sequence codes.
在一個方面,本文揭露的CAR分子包含含有第一跨膜結構域的第一CAR和含有第二跨膜結構域的第二CAR。在實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域包含,例如,如本文揭露的相同的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域分別藉由第一核苷酸序列和第二核苷酸序列編碼。在一些實施方式中,第一核苷酸序列和第二核苷酸序列相差至少一個核苷酸。In one aspect, a CAR molecule disclosed herein comprises a first CAR comprising a first transmembrane domain and a second CAR comprising a second transmembrane domain. In an embodiment, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise, eg, the same amino acid sequence as disclosed herein. In an embodiment, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain are encoded by a first nucleotide sequence and a second nucleotide sequence, respectively. In some embodiments, the first nucleotide sequence and the second nucleotide sequence differ by at least one nucleotide.
在一些實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域係相同的跨膜結構域,例如選自T細胞受體的α、β或ζ鏈,CD28,CD3ε,CD45,CD4,CD5,CD8,CD9,CD16,CD22,CD33,CD37,CD64,CD80,CD86,CD123,CD134,CD137或CD154。In some embodiments, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain are the same transmembrane domain, for example selected from the alpha, beta or zeta chain of a T cell receptor, CD28, CD3ε, CD45, CD4, CD5, CD8, CD9, CD16, CD22, CD33, CD37, CD64, CD80, CD86, CD123, CD134, CD137 or CD154.
在一些實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域係不同的跨膜結構域,例如選自T細胞受體的α、β或ζ鏈,CD28,CD3ε,CD45,CD4,CD5,CD8,CD9,CD16,CD22,CD33,CD37,CD64,CD80,CD86,CD123,CD134,CD137或CD154。In some embodiments, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain are different transmembrane domains, for example selected from the alpha, beta or zeta chains of T cell receptors, CD28, CD3ε, CD45, CD4, CD5, CD8, CD9, CD16, CD22, CD33, CD37, CD64, CD80, CD86, CD123, CD134, CD137 or CD154.
在一個方面,編碼本文所述之CAR分子的核酸分子包含含有第一跨膜結構域的第一CAR和含有第二跨膜結構域的第二CAR。在一些實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域包含CD8 α跨膜結構域。在一些實施方式中,第一跨膜結構域和第二跨膜結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列。In one aspect, a nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR molecule described herein comprises a first CAR comprising a first transmembrane domain and a second CAR comprising a second transmembrane domain. In some embodiments, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise a CD8 alpha transmembrane domain. In some embodiments, the first transmembrane domain and the second transmembrane domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 65 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto.
在一些實施方式中,編碼第一跨膜結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同於編碼第二跨膜結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列。In some embodiments, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first transmembrane domain and comprised in the nucleic acid molecule is different than the nucleotide sequence encoding the second transmembrane domain comprised in the nucleic acid molecule.
在一個方面,本文揭露的CAR分子包含含有第一共刺激結構域的第一CAR和含有第二共刺激結構域的第二CAR。在實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域包含,例如,如本文揭露的相同的胺基酸序列。在實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域分別藉由第一核苷酸序列和第二核苷酸序列編碼。在一些實施方式中,第一核苷酸序列和第二核苷酸序列相差至少一個核苷酸。In one aspect, a CAR molecule disclosed herein comprises a first CAR comprising a first costimulatory domain and a second CAR comprising a second costimulatory domain. In an embodiment, the first co-stimulatory domain and the second co-stimulatory domain comprise, eg, the same amino acid sequence as disclosed herein. In an embodiment, the first co-stimulatory domain and the second co-stimulatory domain are encoded by a first nucleotide sequence and a second nucleotide sequence, respectively. In some embodiments, the first nucleotide sequence and the second nucleotide sequence differ by at least one nucleotide.
在一些實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域係相同的共刺激結構域,例如,選自OX40、CD2、CD27、CD28、CDS、ICAM-1、LFA-1(CD11a/CD18)、ICOS(CD278)或4-1BB(CD137)的傳訊結構域。In some embodiments, the first costimulatory domain and the second costimulatory domain are the same costimulatory domain, e.g., selected from OX40, CD2, CD27, CD28, CDS, ICAM-1, LFA-1 (CD11a /CD18), ICOS (CD278), or the signaling domain of 4-1BB (CD137).
在一些實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域係不同的共刺激結構域,例如,選自OX40、CD2、CD27、CD28、CDS、ICAM-1、LFA-1(CD11a/CD18)、ICOS(CD278)或4-1BB(CD137)的傳訊結構域。In some embodiments, the first costimulatory domain and the second costimulatory domain are different costimulatory domains, e.g., selected from OX40, CD2, CD27, CD28, CDS, ICAM-1, LFA-1 (CD11a /CD18), ICOS (CD278), or the signaling domain of 4-1BB (CD137).
在一個方面,編碼本文所述之CAR分子的核酸分子包含含有第一共刺激結構域的第一CAR和含有第二共刺激結構域的第二CAR。在一些實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域包含4-1BB共刺激結構域。在一些實施方式中,第一共刺激結構域和第二共刺激結構域包含SEQ ID NO: 65的胺基酸序列或與其具有至少90%同一性的胺基酸序列。In one aspect, a nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR molecule described herein comprises a first CAR comprising a first costimulatory domain and a second CAR comprising a second costimulatory domain. In some embodiments, the first costimulatory domain and the second costimulatory domain comprise a 4-1BB costimulatory domain. In some embodiments, the first costimulatory domain and the second costimulatory domain comprise the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 65 or an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical thereto.
在一些實施方式中,編碼第一共刺激結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列不同於編碼第二共刺激結構域並包含在核酸分子中的核苷酸序列。In some embodiments, the nucleotide sequence encoding the first costimulatory domain and comprised in the nucleic acid molecule is different than the nucleotide sequence encoding the second costimulatory domain comprised in the nucleic acid molecule.
在一些方面,本揭露提供了編碼CAR分子的核酸分子,例如,包含 (i) 含有CD22抗原結合結構域的第一CAR和 (ii) 含有CD19抗原結合結構域的第二CAR。在實施方式中,該核酸包含RNA或DNA。在實施方式中,編碼 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸序列以相同的定向定位,例如,編碼 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸序列以相同的方向進行轉錄。在實施方式中,編碼 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸序列以不同的定向定位。在實施方式中,單個啟動子控制編碼 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸序列的表現。在實施方式中,編碼蛋白酶切割位點(例如,T2A、P2A、E2A或F2A切割位點)的核酸位於編碼 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸序列之間。在實施方式中,以如下方式放置蛋白酶切割位點,該方式使得細胞可以表現包含 (i) 和 (ii) 的融合蛋白,該蛋白隨後藉由蛋白水解切割而加工成兩個肽。在一些實施方式中,編碼 (i) 的核酸序列在編碼 (ii) 的核酸序列的上游,或編碼 (ii) 的核酸序列在編碼 (i) 的核酸序列的上游。在實施方式中,第一啟動子控制編碼 (i) 的核酸序列的表現,並且第二啟動子控制編碼 (ii) 的核酸序列的表現。在實施方式中,該核酸係質體。在實施方式中,該核酸包含病毒包裝元件。在一些方面,本揭露提供了細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞),該細胞包含本文所述之核酸,例如,包含以上所述之 (i) 和 (ii) 的核酸。該細胞可以包含切割T2A、P2A、E2A或F2A切割位點的蛋白酶(例如,內源或外源)。In some aspects, the present disclosure provides nucleic acid molecules encoding CAR molecules, e.g., comprising (i) a first CAR comprising a CD22 antigen binding domain and (ii) a second CAR comprising a CD19 antigen binding domain. In embodiments, the nucleic acid comprises RNA or DNA. In an embodiment, the nucleic acid sequences encoding (i) and (ii) are positioned in the same orientation, eg, the nucleic acid sequences encoding (i) and (ii) are transcribed in the same direction. In an embodiment, the nucleic acid sequences encoding (i) and (ii) are positioned in different orientations. In an embodiment, a single promoter controls the expression of the nucleic acid sequences encoding (i) and (ii). In an embodiment, a nucleic acid encoding a protease cleavage site (eg, a T2A, P2A, E2A or F2A cleavage site) is located between the nucleic acid sequences encoding (i) and (ii). In an embodiment, the protease cleavage site is placed in such a way that the cell can express a fusion protein comprising (i) and (ii), which is then processed into the two peptides by proteolytic cleavage. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid sequence encoding (i) is upstream of the nucleic acid sequence encoding (ii), or the nucleic acid sequence encoding (ii) is upstream of the nucleic acid sequence encoding (i). In an embodiment, the first promoter controls the expression of the nucleic acid sequence encoding (i), and the second promoter controls the expression of the nucleic acid sequence encoding (ii). In an embodiment, the nucleic acid is a plastid. In embodiments, the nucleic acid comprises viral packaging elements. In some aspects, the disclosure provides cells (eg, immune effector cells) comprising a nucleic acid described herein, eg, comprising (i) and (ii) described above. The cell may comprise a protease (eg, endogenous or exogenous) that cleaves the T2A, P2A, E2A, or F2A cleavage site.
示例性CAR分子的核苷酸和胺基酸序列,例如,本文揭露的雙重CAR分子在表1A中提供。
[
表 1A]
:雙重和串聯 CD19-CD22 CAR 序列
本揭露之雙重CAR或串聯CAR的CD22和CD19 CDR在表2A中提供。
[
表 2A]
: CD22 和 CD19 CDR 序列
表3A提供了本文揭露的雙重CAR或串聯CAR的CD19和CD22結合結構域的核苷酸和胺基酸序列。
[
表 3A]
: CD19 和 CD22 結合結構域
表4A提供了另外的CAR組分(例如,訊息肽、連接子和P2A位點)的核苷酸和胺基酸序列。
[
表 4A]
:另外的 CAR 組分
在一個方面,本文揭露了包含雙特異性抗原結合結構域的CAR,例如,串聯CAR。在一些實施方式中,雙特異性抗原結合結構域包含兩個抗原結合結構域,例如,第一抗原結合結構域和第二抗原結合結構域。在一些實施方式中,串聯CAR包含含有CD22抗原結合結構域和CD19抗原結合結構域的雙特異性抗原結合結構域。In one aspect, disclosed herein are CARs comprising bispecific antigen binding domains, eg, tandem CARs. In some embodiments, a bispecific antigen binding domain comprises two antigen binding domains, eg, a first antigen binding domain and a second antigen binding domain. In some embodiments, the tandem CAR comprises a bispecific antigen binding domain comprising a CD22 antigen binding domain and a CD19 antigen binding domain.
在雙特異性抗原結合結構域的一些實施方式中,第一抗原結合結構域係抗體分子,例如抗體結合結構域(例如,scFv)。在雙特異性抗原結合結構域的一些實施方式中,第二抗原結合結構域係抗體分子,例如抗體結合結構域(例如,scFv)。在雙特異性抗原結合結構域的每個抗體分子(例如,scFv)內,VH可以在VL的上游或下游。In some embodiments of the bispecific antigen binding domain, the first antigen binding domain is an antibody molecule, eg, an antibody binding domain (eg, scFv). In some embodiments of the bispecific antigen binding domain, the second antigen binding domain is an antibody molecule, such as an antibody binding domain (eg, scFv). Within each antibody molecule (eg, scFv) of the bispecific antigen-binding domain, the VH can be upstream or downstream of the VL.
在一些實施方式中,上游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VH(VH1)在其VL(VL1)上游,並且下游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VL(VL2)在其VH(VH2)上游,使得整個雙特異性抗體分子從N末端至C末端取向具有VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2的排列。In some embodiments, the upstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VH (VH1) upstream of its VL (VL1), and the downstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VL (VL2) upstream Its VH (VH2) upstream, so that the whole bispecific antibody molecule has the arrangement of VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2 from N-terminal to C-terminal orientation.
在一些實施方式中,上游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VL(VL1)在其VH(VH1)上游,並且下游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VH(VH2)在其VL(VL2)上游,使得整個雙特異性抗體分子從N末端至C末端取向具有VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2的排列。In some embodiments, the upstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VL (VL1) upstream of its VH (VH1), and the downstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VH (VH2) upstream Its VL (VL2) is upstream such that the entire bispecific antibody molecule has an arrangement of VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2 from the N-terminal to the C-terminal orientation.
在一些實施方式中,上游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VL(VL1)在其VH(VH1)上游,並且下游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VL(VL2)在其VH(VH2)上游,使得整個雙特異性抗體分子從N末端至C末端取向具有VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2的排列。In some embodiments, the upstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VL (VL1) upstream of its VH (VH1), and the downstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VL (VL2) upstream Its VH (VH2) upstream, so that the entire bispecific antibody molecule has an arrangement of VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2 from the N-terminal to the C-terminal orientation.
在又一些實施方式中,上游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VH(VH1)在其VL(VL1)上游,並且下游抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)排列為其VH(VH2)在其VL(VL2)上游,使得整個雙特異性抗體分子從N末端至C末端取向具有VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2的排列。In yet other embodiments, the upstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VH (VH1) upstream of its VL (VL1), and the downstream antibody or antibody fragment (e.g., scFv) is arranged with its VH (VH2) Upstream of its VL (VL2), such that the entire bispecific antibody molecule has an arrangement of VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2 from N-terminal to C-terminal orientation.
在前述組態中的任一種中,視需要,在這兩個抗體或抗體片段(例如,scFv)之間佈置連接子,例如如果該構建體排列為VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2,則在VL1和VL2之間佈置該連接子;如果該構建體排列為VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2,則在VH1和VH2之間佈置該連接子;如果該構建體排列為VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2,則在VH1和VL2之間佈置該連接子;或者如果該構建體排列為VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2,則在VL1和VH2之間佈置該連接子。一般來說,兩個scFv之間的連接子應足夠長以避免兩個scFv的結構域之間的錯配。連接子可為如本文所述之連接子。在一些實施方式中,連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n連接子,其中n係1、2、3、4、5、或6。在一些實施方式中,連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n,其中n = 1,例如,連接子具有胺基酸序列Gly4-Ser。在一些實施方式中,連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n,其中n = 4(SEQ ID NO: 82)。在一些實施方式中,連接子包含以下胺基酸序列,例如由以下胺基酸序列組成:LAEAAAK(例如,SEQ ID NO: 80)。In any of the preceding configurations, a linker is optionally placed between the two antibodies or antibody fragments (e.g., scFv), e.g. if the construct is arranged as VH1-VL1-VL2-VH2, then at The linker is arranged between VL1 and VL2; if the construct is arranged as VL1-VH1-VH2-VL2, the linker is arranged between VH1 and VH2; if the construct is arranged as VL1-VH1-VL2-VH2, then The linker is placed between VH1 and VL2; or if the construct is arranged as VH1-VL1-VH2-VL2, the linker is placed between VL1 and VH2. In general, the linker between two scFvs should be long enough to avoid mismatches between the domains of the two scFvs. A linker can be a linker as described herein. In some embodiments, the linker is a (Gly4-Ser)n linker, where n is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. In some embodiments, the linker is (Gly4-Ser)n, where n=1, for example, the linker has the amino acid sequence Gly4-Ser. In some embodiments, the linker is (Gly4-Ser)n, where n = 4 (SEQ ID NO: 82). In some embodiments, the linker comprises, eg, consists of, the amino acid sequence of LAEAAAK (eg, SEQ ID NO: 80).
在前述組態中的任一種中,視需要,在第一scFv的VL與VH之間佈置連接子。視需要,連接子設置在第二scFv的VL與VH之間。在具有多個連接子的構建體中,連接子中的任何兩個或更多個可以相同或不同。因此,在一些實施方式中,雙特異性CAR在如本文描述的佈置中包含VL、VH、和視需要的一或多個連接子。In any of the foregoing configurations, optionally, a linker is placed between the VL and VH of the first scFv. Optionally, a linker is placed between the VL and VH of the second scFv. In constructs with multiple linkers, any two or more of the linkers may be the same or different. Thus, in some embodiments, a bispecific CAR comprises a VL, a VH, and optionally one or more linkers in an arrangement as described herein.
在一些實施方式中,每個抗體分子,例如每個抗原結合結構域(例如,每個scFv)在VH區與VL區之間包含連接子。在一些實施方式中,在VH和VL區之間的連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n連接子,其中n係1、2、3、4、5或6。在一些實施方式中,連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n,其中n = 1,例如,連接子具有胺基酸序列Gly4-Ser。在一些實施方式中,連接子係(Gly4-Ser)n,其中n= 4(SEQ ID NO: 82)。在一些實施方式中,VH區和VL區在沒有連接子的情況下連接。 分離的CAR In some embodiments, each antibody molecule, eg, each antigen binding domain (eg, each scFv), comprises a linker between the VH region and the VL region. In some embodiments, the linker between the VH and VL regions is a (Gly4-Ser)n linker, where n is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6. In some embodiments, the linker is (Gly4-Ser)n, where n=1, for example, the linker has the amino acid sequence Gly4-Ser. In some embodiments, the linker is (Gly4-Ser)n, where n=4 (SEQ ID NO: 82). In some embodiments, the VH and VL regions are linked without a linker. isolated CAR
在一些實施方式中,表現CAR的細胞使用分離的CAR。分離的CAR途徑在藉由引用併入本文的PCT公開WO 2014/055442和WO 2014/055657中更詳細地描述。簡而言之,分離的CAR系統包含表現具有第一抗原結合結構域和共刺激結構域(例如,4-1BB)的第一CAR的細胞,並且該細胞還表現具有第二抗原結合結構域和細胞內傳訊結構域(例如,CD3ζ)的第二CAR。當該細胞遇到第一抗原時,共刺激結構域被活化,並且細胞增殖。當該細胞遇到第二抗原時,細胞內傳訊結構域被活化並開始細胞殺傷活性。因此,該表現CAR的細胞僅在兩種抗原都存在下完全活化。 RNA轉染 In some embodiments, the cells expressing the CAR use an isolated CAR. Isolated CAR pathways are described in more detail in PCT Publications WO 2014/055442 and WO 2014/055657, which are incorporated herein by reference. Briefly, the isolated CAR system comprises a cell expressing a first CAR with a first antigen-binding domain and a co-stimulatory domain (e.g., 4-1BB), and the cell also expresses a second antigen-binding domain and A second CAR for the intracellular signaling domain (eg, CD3ζ). When the cell encounters the first antigen, the co-stimulatory domain is activated and the cell proliferates. When the cell encounters the second antigen, the intracellular signaling domain is activated and begins cell killing activity. Thus, the CAR-expressing cells were only fully activated in the presence of both antigens. RNA transfection
本文揭露了用於產生體外轉錄的RNA CAR之方法。本發明還包括一種編碼CAR的RNA構建體,該RNA構建體可以直接轉染到細胞中。產生用於轉染的mRNA之方法可以涉及用特別設計的引物對模板進行體外轉錄(IVT)、然後添加聚A以產生含有3'和5'非翻譯序列(「UTR」)、5’帽和/或內部核糖體進入位點(IRES)、待表現的核酸、和聚A尾的構建體,典型地長度為50-2000個鹼基。這樣產生的RNA可以有效地轉染不同類型的細胞。在一方面,模板包括CAR的序列。Disclosed herein are methods for generating in vitro transcribed RNA CARs. The present invention also includes a CAR-encoding RNA construct, which can be directly transfected into cells. Methods for generating mRNA for transfection may involve in vitro transcription (IVT) of the template with specially designed primers, followed by the addition of polyA to generate mRNAs containing 3' and 5' untranslated sequences ("UTR"), a 5' cap and Constructs of/or internal ribosome entry sites (IRES), nucleic acids to be expressed, and poly A tails are typically 50-2000 bases in length. The RNA thus produced can efficiently transfect different types of cells. In one aspect, the template includes the sequence of the CAR.
在一方面,CAR(例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR)由傳訊RNA(mRNA)編碼。在一方面,將編碼CAR(例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR)的mRNA引入到免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞中,以產生表現CAR的細胞,例如CART細胞或CAR NK細胞。In one aspect, a CAR (eg, a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) is encoded by a messenger RNA (mRNA). In one aspect, mRNA encoding a CAR (eg, dual CAR or tandem CAR) is introduced into immune effector cells, such as T cells or NK cells, to generate CAR-expressing cells, such as CART cells or CAR NK cells.
在一個實施方式中,體外轉錄的CAR的RNA可以作為瞬時轉染的形式引入到細胞。使用聚合酶鏈反應(PCR)產生的模板藉由體外轉錄產生RNA。可以將來自任何來源的感興趣的DNA直接藉由PCR轉化為模板,以使用適當的引物和RNA聚合酶體外合成mRNA。DNA的來源可為例如基因組DNA、質體DNA、噬菌體DNA、cDNA、合成DNA序列或任何其他合適的DNA來源。用於體外轉錄的所希望模板係本發明之CAR。例如,RNA CAR的模板可以包含含有抗腫瘤抗體的單鏈可變結構域的細胞外區;鉸鏈區、跨膜結構域(例如,CD8a的跨膜結構域);以及胞質區,該胞質區包括細胞內傳訊結構域,例如包含CD3-ζ的傳訊結構域和4-1BB的傳訊結構域。In one embodiment, in vitro transcribed CAR RNA can be introduced into cells as a transient transfection. RNA is produced by in vitro transcription using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated templates. DNA of interest from any source can be directly converted by PCR into a template for in vitro mRNA synthesis using appropriate primers and RNA polymerase. The source of DNA can be, for example, genomic DNA, plastid DNA, phage DNA, cDNA, synthetic DNA sequences, or any other suitable source of DNA. The desired template for in vitro transcription is a CAR of the invention. For example, a template for an RNA CAR may comprise an extracellular region containing a single-chain variable domain of an anti-tumor antibody; a hinge region, a transmembrane domain (e.g., that of CD8a); and a cytoplasmic region, which Regions include intracellular signaling domains, such as those comprising CD3-ζ and 4-1BB.
在一個實施方式中,待用於PCR的DNA含有開讀框。DNA可以來自生物體基因組的天然存在的DNA序列。在一個實施方式中,核酸可以包括5'和/或3'非翻譯區(UTR)中的一些或全部。核酸可以包括外顯子和內含子。在一個實施方式中,用於PCR的DNA係人核酸序列。在另一個實施方式中,用於PCR的DNA係包括5'和3'UTR的人核酸序列。替代性地,DNA可為通常不在天然存在的生物體中表現的人工DNA序列。示例性人工DNA序列係含有基因部分的序列,該等基因部分連接在一起以形成編碼融合蛋白的開讀框。連接在一起的DNA部分可以來自單個生物體或來自多於一個的生物體。In one embodiment, the DNA to be used for PCR contains an open reading frame. DNA can be derived from naturally occurring DNA sequences in the genome of an organism. In one embodiment, a nucleic acid may include some or all of the 5' and/or 3' untranslated regions (UTRs). A nucleic acid can include exons and introns. In one embodiment, the DNA used for PCR is a human nucleic acid sequence. In another embodiment, the DNA line used for PCR includes human nucleic acid sequences of the 5' and 3' UTRs. Alternatively, the DNA may be an artificial DNA sequence not normally expressed in naturally occurring organisms. An exemplary artificial DNA sequence is one that contains portions of a gene joined together to form an open reading frame encoding a fusion protein. The DNA portions linked together can be from a single organism or from more than one organism.
使用PCR以產生用於體外轉錄mRNA的模板,該mRNA用於轉染。用於進行PCR的方法在本領域中係熟知的。用於PCR的引物被設計成具有與待用作PCR模板的DNA區基本上互補的區。如本文所用,「基本上互補」係指這樣的核苷酸序列,其中引物序列中的大多數或全部的鹼基係互補的,或一或多個鹼基係不互補的或錯配的。基本上互補的序列能夠在用於PCR的退火條件下與預期的DNA靶標退火或雜交。可以設計引物以基本上互補於DNA模板的任何部分。例如,可以將引物設計為擴增通常在細胞中轉錄的核酸的一部分(開讀框),包括5'和3’ UTR。還可以設計引物以擴增編碼特定感興趣的結構域的核酸的一部分。在一個實施方式中,設計引物以擴增人cDNA的編碼區,包括5'和3' UTR的全部或部分。可用於PCR的引物可以藉由本領域熟知的合成方法產生。「正向引物」係含有核苷酸區的引物,該等核苷酸與DNA模板上的位於待擴增DNA序列上游的核苷酸基本上互補。「上游」在本文中用於指相對於編碼股而言待擴增的DNA序列的5'位置。「反向引物」係含有核苷酸區的引物,該等核苷酸區與待擴增的DNA序列下游的雙股DNA模板基本上互補。「下游」在本文中用於指相對於編碼股而言待擴增的DNA序列的3'位置。PCR is used to generate templates for in vitro transcription of mRNA for transfection. Methods for performing PCR are well known in the art. Primers for PCR are designed to have a region substantially complementary to a region of DNA to be used as a template for PCR. As used herein, "substantially complementary" refers to a nucleotide sequence in which most or all of the bases in the primer sequence are complementary, or one or more bases are non-complementary or mismatched. Substantially complementary sequences are capable of annealing or hybridizing to the intended DNA target under the annealing conditions used in PCR. Primers can be designed to be substantially complementary to any portion of the DNA template. For example, primers can be designed to amplify a portion of a nucleic acid normally transcribed in a cell (open reading frame), including the 5' and 3' UTRs. Primers can also be designed to amplify a portion of nucleic acid encoding a particular domain of interest. In one embodiment, primers are designed to amplify the coding region of human cDNA, including all or part of the 5' and 3' UTRs. Primers useful for PCR can be produced by synthetic methods well known in the art. A "forward primer" is a primer that contains a region of nucleotides that is substantially complementary to nucleotides on a DNA template upstream of the DNA sequence to be amplified. "Upstream" is used herein to refer to the 5' position of the DNA sequence to be amplified relative to the coding strand. A "reverse primer" is a primer that contains a region of nucleotides that is substantially complementary to a double-stranded DNA template downstream of the DNA sequence to be amplified. "Downstream" is used herein to refer to a position 3' to the DNA sequence to be amplified relative to the coding strand.
可用於PCR的任何DNA聚合酶均可用於本文揭露的方法中。試劑和聚合酶可從許多來源商購獲得。Any DNA polymerase that can be used in PCR can be used in the methods disclosed herein. Reagents and polymerases are commercially available from a number of sources.
也可以使用能夠促進穩定性和/或翻譯效率的化學結構。RNA較佳的是具有5'和3’ UTR。在一個實施方式中,5'UTR的長度在1個與3000個核苷酸之間。待添加到編碼區的5'和3'UTR序列的長度可以藉由不同方法改變,該等方法包括但不限於設計與UTR的不同區退火的PCR引物。使用該途徑,熟悉該項技術者可以改變所需的5'和3'UTR長度,以在經轉錄RNA的轉染後實現最佳翻譯效率。Chemical structures that promote stability and/or translation efficiency can also be used. The RNA preferably has 5' and 3' UTRs. In one embodiment, the 5'UTR is between 1 and 3000 nucleotides in length. The length of the 5' and 3' UTR sequences to be added to the coding region can be varied by various methods including, but not limited to, designing PCR primers that anneal to different regions of the UTR. Using this approach, one skilled in the art can vary the desired 5' and 3' UTR lengths to achieve optimal translation efficiency following transfection of the transcribed RNA.
5'和3'UTR可為感興趣的核酸的天然存在的內源性5'和3'UTR。替代性地,可以藉由將對感興趣的核酸不是內源的UTR序列併入到正向和反向引物中或藉由模板的任何其他修飾來添加該等UTR序列。使用對感興趣的核酸係內源的UTR序列可用於改變RNA的穩定性和/或翻譯效率。例如,已知3'UTR序列中的富含AU的元件可以降低mRNA的穩定性。因此,可以選擇或設計3'UTR,以基於本領域熟知的UTR的特性來增加經轉錄的RNA的穩定性。The 5' and 3'UTRs can be the naturally occurring endogenous 5' and 3'UTRs of the nucleic acid of interest. Alternatively, UTR sequences that are not endogenous to the nucleic acid of interest can be added by incorporating them into the forward and reverse primers or by any other modification of the template. The use of UTR sequences endogenous to a nucleic acid of interest can be used to alter RNA stability and/or translation efficiency. For example, AU-rich elements in 3'UTR sequences are known to reduce mRNA stability. Accordingly, the 3'UTR can be selected or designed to increase the stability of the transcribed RNA based on the properties of UTRs well known in the art.
在一個實施方式中,5'UTR可以含有內源性核酸的Kozak序列。替代性地,當如上所述藉由PCR添加對感興趣的核酸不是內源的5'UTR時,可以藉由添加5'UTR序列重新設計共有科紮克序列。科紮克序列可以提高一些RNA轉錄物的翻譯效率,但似乎不是所有RNA實現高效翻譯所需要的。對許多mRNA的科紮克序列的要求在本領域中係已知的。在一些實施方式中,5'UTR可為RNA基因組在細胞中係穩定的RNA病毒的5'UTR。在一些實施方式中,可以在3'或5'UTR中使用各種核苷酸類似物來阻止mRNA的外切核酸酶降解。In one embodiment, the 5'UTR may contain the Kozak sequence of the endogenous nucleic acid. Alternatively, when a 5'UTR that is not endogenous to the nucleic acid of interest is added by PCR as described above, the consensus Kozak sequence can be redesigned by adding the 5'UTR sequence. Kozak sequences can enhance the translation efficiency of some RNA transcripts, but do not appear to be required for efficient translation of all RNAs. The requirement for Kozak sequences for many mRNAs is known in the art. In some embodiments, the 5'UTR can be the 5'UTR of an RNA virus whose RNA genome is stable in cells. In some embodiments, various nucleotide analogs can be used in the 3' or 5' UTR to prevent exonuclease degradation of mRNA.
為了在無需基因選殖的情況下實現從DNA模板合成RNA,轉錄啟動子應附接到待轉錄序列上游的DNA模板上。當將發揮RNA聚合酶啟動子功能的序列添加至正向引物的5'端時,該RNA聚合酶啟動子將併入到PCR產物中位於待轉錄的開讀框上游。在一個較佳的實施方式中,啟動子係T7聚合酶啟動子,如本文其他地方所述。其他可用的啟動子包括但不限於T3和SP6 RNA聚合酶啟動子。T7、T3和SP6啟動子的共有核苷酸序列在本領域中係已知的。In order to achieve RNA synthesis from a DNA template without gene cloning, a transcriptional promoter should be attached to the DNA template upstream of the sequence to be transcribed. When a sequence that functions as an RNA polymerase promoter is added to the 5' end of the forward primer, the RNA polymerase promoter will be incorporated into the PCR product upstream of the open reading frame to be transcribed. In a preferred embodiment, the promoter is a T7 polymerase promoter, as described elsewhere herein. Other useful promoters include, but are not limited to, the T3 and SP6 RNA polymerase promoters. Consensus nucleotide sequences for T7, T3 and SP6 promoters are known in the art.
在較佳的實施方式中,mRNA具有5'端帽和3'聚(A)尾,它們決定核糖體結合、翻譯起始和mRNA在細胞中的穩定性。在環狀DNA模板例如質體DNA上,RNA聚合酶產生長的多聯產物,該多聯產物不適於在真核細胞中表現。轉錄在3' UTR端線性化的質體DNA產生正常大小的mRNA,該mRNA即使在轉錄後進行了多腺苷酸化,在真核轉染中也是無效的。In a preferred embodiment, the mRNA has a 5' cap and a 3' poly(A) tail, which determine ribosome binding, translation initiation, and stability of the mRNA in the cell. On circular DNA templates such as plastid DNA, RNA polymerase produces long concatemers that are not suitable for expression in eukaryotic cells. Transcription of plastid DNA linearized at the 3' UTR end yields normal sized mRNA that is ineffective in eukaryotic transfection even if it is polyadenylated post-transcriptionally.
在線性DNA模板上,噬菌體T7 RNA聚合酶可以將轉錄物的3'末端延伸到模板的最後一個鹼基之外(Schenborn和Mierendorf, Nuc Acids Res. [核酸研究], 13:6223-36 (1985);Nacheva和Berzal-Herranz, Eur.J. Biochem. [歐洲生物化學雜誌], 270:1485-65 (2003)。On linear DNA templates, bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase can extend the 3' end of the transcript beyond the last base of the template (Schenborn and Mierendorf, Nuc Acids Res. [Nucleic Acids Research], 13:6223-36 (1985 ); Nacheva and Berzal-Herranz, Eur.J. Biochem. [European Journal of Biochemistry], 270:1485-65 (2003).
將聚A/T伸展段整合到DNA模板中的常規方法係分子選殖。然而,整合到質體DNA中的聚A/T序列可導致質體不穩定,這就是為什麼從細菌細胞獲得的質體DNA模板經常被缺失和其他畸變高度污染的原因。這使得選殖程序不僅費力且耗時,而且通常是不可靠的。這就是為什麼非常期望允許在不進行選殖的情況下構建具有聚A/T 3'伸展段的DNA模板之方法。A conventional method for incorporating poly A/T stretches into DNA templates is molecular cloning. However, poly A/T sequences integrated into plastid DNA can lead to plastid instability, which is why plastid DNA templates obtained from bacterial cells are often highly contaminated with deletions and other aberrations. This makes breeding procedures not only laborious and time-consuming, but often unreliable. This is why a method that allows the construction of DNA templates with polyA/T 3' stretches without cloning is highly desirable.
轉錄DNA模板的聚A/T區段可以在PCR期間藉由使用含有聚T尾(如100T尾)(大小可為50-5000T)的反向引物產生,或在PCR後藉由任何其他方法(包括但不限於DNA連接或體外重組)產生。聚(A)尾也為RNA提供穩定性並降低其降解。通常,聚(A)尾的長度與轉錄的RNA的穩定性呈正相關。在一個實施方式中,聚(A)尾係100至5000個腺苷。The poly A/T segment of the transcribed DNA template can be generated during PCR by using a reverse primer containing a poly T tail (e.g. 100T tail) (size can be 50-5000T), or after PCR by any other method ( including but not limited to DNA ligation or in vitro recombination). The poly(A) tail also provides stability to the RNA and reduces its degradation. In general, the length of the poly(A) tail is positively correlated with the stability of the transcribed RNA. In one embodiment, the poly(A) tail is 100 to 5000 adenosines.
在使用聚(A)聚合酶(如大腸桿菌聚A聚合酶(E-PAP))進行體外轉錄後,可以進一步延伸RNA的聚(A)尾。在一個實施方式中,將聚(A)尾的長度從100個核苷酸增加到300至400個核苷酸導致RNA的翻譯效率增加約兩倍。另外,不同化學基團與3'端的附接可以增加mRNA穩定性。這種附接可以含有經修飾的/人工的核苷酸、適配體和其他化合物。例如,可以使用聚(A)聚合酶將ATP類似物併入到聚(A)尾中。ATP類似物還可以增加RNA的穩定性。The poly(A) tail of the RNA can be further extended after in vitro transcription using a poly(A) polymerase such as Escherichia coli poly(A) polymerase (E-PAP). In one embodiment, increasing the length of the poly(A) tail from 100 nucleotides to 300 to 400 nucleotides results in an approximately two-fold increase in the translation efficiency of the RNA. Additionally, the attachment of different chemical groups to the 3' end can increase mRNA stability. Such attachments may contain modified/artificial nucleotides, aptamers and other compounds. For example, an ATP analog can be incorporated into a poly(A) tail using a poly(A) polymerase. ATP analogs can also increase RNA stability.
5'帽也為RNA分子提供穩定性。在較佳的實施方式中,藉由本文揭露的方法產生的RNA包括5'帽。使用本領域已知的和本文所述之技術獲得5'帽(Cougot等人, Trends in Biochem. Sci. [生物化學科學趨勢], 29:436-444 (2001);Stepinski等人, RNA, 7:1468-95 (2001);Elango等人, Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. [生物化學與生物物理學研究通訊], 330:958-966 (2005))。The 5' cap also provides stability to the RNA molecule. In preferred embodiments, the RNA produced by the methods disclosed herein includes a 5' cap. The 5' cap was obtained using techniques known in the art and described herein (Cougot et al., Trends in Biochem. Sci. [Biochemical Science Trends], 29:436-444 (2001); Stepinski et al., RNA, 7 :1468-95 (2001); Elango et al., Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. [Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications], 330:958-966 (2005)).
藉由本文揭露的方法產生的RNA還可以含有內部核糖體進入位點(IRES)序列。IRES序列可為任何病毒、染色體或人工設計的序列,該序列啟動與帽無關的核糖體與mRNA的結合並促進翻譯的起始。可以包括適用於細胞電穿孔的任何溶質,該等溶質可以含有促進細胞滲透性和活力的因子,如糖、肽、脂質、蛋白質、抗氧化劑和界面活性劑。RNA produced by the methods disclosed herein may also contain internal ribosome entry site (IRES) sequences. The IRES sequence can be any viral, chromosomal or artificially designed sequence that initiates cap-independent ribosome binding to mRNA and facilitates initiation of translation. Any solute suitable for cell electroporation, which may contain factors that promote cell permeability and viability, such as sugars, peptides, lipids, proteins, antioxidants, and surfactants, can be included.
可以使用許多不同方法中的任一種將RNA引入到靶細胞中,該等不同方法例如可商購的方法,包括但不限於:電穿孔(Amaxa Nucleofector-II(德國科隆的艾瑪科薩生物系統公司(Amaxa Biosystems, Cologne, Germany)),(ECM 830(BTX)(麻塞諸塞州波士頓的哈佛儀器公司(Harvard Instruments, Boston, Mass.))或Gene Pulser II(科羅拉多州丹佛的伯樂公司(BioRad, Denver, Colo.)),Multiporator(德國漢堡的艾本德公司(Eppendort, Hamburg Germany));陽離子脂質體介導的轉染(使用脂質轉染);聚合物封裝;肽介導的轉染;或生物射彈顆粒遞送系統如「基因槍」(參見,例如Nishikawa等人 Hum Gene Ther.[人類基因療法], 12(8):861-70 (2001))。 非病毒遞送方法 RNA can be introduced into target cells using any of a number of different methods, such as commercially available methods, including but not limited to: Electroporation (Amaxa Nucleofector-II (Amaxa Biosystems, Cologne, Germany) (Amaxa Biosystems, Cologne, Germany), (ECM 830 (BTX) (Harvard Instruments, Boston, Mass.) or Gene Pulser II (Bio-Rad, Denver, CO ( BioRad, Denver, Colo.), Multiporator (Eppendort, Hamburg Germany); cationic liposome-mediated transfection (using lipofection); polymer encapsulation; peptide-mediated transfection or biolistic particle delivery systems such as "gene guns" (see, eg, Nishikawa et al. Hum Gene Ther., 12(8):861-70 (2001)). Non-viral delivery methods
在一些方面,可以使用非病毒方法將編碼本文所述CAR的核酸遞送至細胞或組織或受試者中。In some aspects, a nucleic acid encoding a CAR described herein can be delivered to a cell or tissue or subject using non-viral methods.
在一些實施方式中,非病毒方法包括使用轉位子(也稱為轉位元件)。在一些實施方式中,轉位子係可以將自身插入基因組中一位置的一條DNA,例如,能夠自我複製並將其拷貝插入基因組的一條DNA,或者係可以從較長的核酸中剪接出並插入基因組中的另一個位置的一條DNA。例如,轉位子包含由側接基因的用於轉位的反向重複序列構成的DNA序列。In some embodiments, non-viral methods include the use of transposons (also known as translocation elements). In some embodiments, a transposon line can insert itself into a piece of DNA at a location in the genome, for example, a piece of DNA capable of replicating itself and inserting a copy of it into the genome, or a line can be spliced out of a longer nucleic acid and inserted into the genome A piece of DNA at another location in the . For example, a transposon comprises a DNA sequence consisting of inverted repeats flanking a gene for translocation.
使用轉位子的核酸遞送的示例性方法包括睡美人轉位子系統(SBTS)和piggyBac(PB)轉位子系統。參見例如,Aronovich等人 Hum.Mol. Genet. [人類分子遺傳學] 20.R1(2011): R14-20;Singh等人 Cancer Res.[癌症研究] 15(2008):2961-2971;Huang等人. Mol. Ther.[分子療法] 16(2008): 580-589;Grabundzija等人. Mol. Ther.[分子療法] 18(2010):1200-1209;Kebriaei等人 Blood. [血液學]. 122.21(2013):166;Williams. Molecular Therapy [分子療法], 16.9(2008):1515-16;Bell等人 Nat. Protoc. [自然實驗手冊] 2.12(2007):3153-65;和Ding等人 Cell [細胞].122.3(2005):473-83,所有該等文獻均藉由引用併入本文。Exemplary methods of nucleic acid delivery using transposons include the Sleeping Beauty Transposon System (SBTS) and the piggyBac (PB) Transposon System. See, eg, Aronovich et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. [Human Molecular Genetics] 20. R1 (2011): R14-20; Singh et al. Cancer Res. [Cancer Research] 15 (2008): 2961-2971; Huang et al [Molecular Therapy] 16(2008): 580-589; Grabundzija et al. Mol. Ther. [Molecular Therapy] 18(2010):1200-1209; Kebriaei et al Blood. [Hematology]. 122.21(2013):166; Williams. Molecular Therapy, 16.9(2008):1515-16; Bell et al. Nat. Protoc. 2.12(2007):3153-65; and Ding et al. Cell [cell]. 122.3 (2005): 473-83, all of which are incorporated herein by reference.
SBTS包括兩個組分:1) 含有轉基因的轉位子和2) 轉位酶的來源。轉位酶可以將轉位子從載體質體(或其他供體DNA)轉移到靶標DNA,如宿主細胞染色體/基因組。例如,轉位酶與載體質體/供體DNA結合,從質體中切出轉位子(包括一或多個轉基因),並將它插入到宿主細胞的基因組中。參見例如,Aronovich等人。SBTS consists of two components: 1) the transposon containing the transgene and 2) the source of the translocase. Translocases can transfer transposons from carrier plastids (or other donor DNA) to target DNA, such as the host cell chromosome/genome. For example, a translocase binds to the vector plastid/donor DNA, excises the transposon (including one or more transgenes) from the plastid, and inserts it into the genome of the host cell. See, eg, Aronovich et al.
示例性轉位子包括基於pT2的轉位子。參見例如,Grabundzija等人 Nucleic Acids Res.[核酸研究] 41.3(2013):1829-47;和Singh等人 Cancer Res. [癌症研究] 68.8(2008): 2961-2971,所有該等文獻均藉由引用併入本文。示例性的轉位酶包括Tc1/海員型轉位酶(mariner-type transposase),例如SB10轉位酶或SB11轉位酶(可以例如從巨細胞病毒啟動子表現的過度活躍的轉位酶)。參見例如,Aronovich等人;Kebriaei等人;和Grabundzija等人,所有該等文獻均藉由引用併入本文。Exemplary transposons include pT2-based transposons. See, eg, Grabundzija et al. Nucleic Acids Res. [Nucleic Acids Research] 41.3 (2013): 1829-47; and Singh et al. Cancer Res. [Cancer Research] 68.8 (2008): 2961-2971, all of which are accessed by Incorporated herein by reference. Exemplary translocases include Tcl/mariner-type transposases, such as SB10 translocase or SB11 translocase (a hyperactive translocase that can be expressed, for example, from a cytomegalovirus promoter). See, eg, Aronovich et al.; Kebriaei et al.; and Grabundzija et al., all of which are incorporated herein by reference.
SBTS的使用允許轉基因(例如,編碼本文所述CAR的核酸)的高效整合和表現。本文提供了產生細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)之方法,該細胞例如使用轉位子系統(如,SBTS)穩定地表現本文所述之CAR。The use of SBTS allows efficient integration and expression of transgenes (eg, nucleic acids encoding CARs described herein). Provided herein are methods of generating cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) that stably express a CAR described herein, eg, using a transposon system (eg, SBTS).
根據本文所述之方法,在一些實施方式中,將含有SBTS組分的一或多種核酸(例如質體)遞送至細胞(例如,T或NK細胞)。例如,藉由核酸(例如,質體DNA)遞送的標準方法遞送一或多種核酸,該等標準方法例如本文所述之方法,例如電穿孔、轉染或脂質轉染。在一些實施方式中,核酸含有包含轉基因(例如,編碼本文所述CAR的核酸)的轉位子。在一些實施方式中,核酸含有包含轉基因(例如,編碼本文所述CAR的核酸)以及編碼轉位酶的核酸序列的轉位子。在一些實施方式中,提供了具有兩種核酸的系統,例如雙質體系統,例如,其中第一質體含有包含轉基因的轉位子,而第二質體含有編碼轉位酶的核酸序列。例如,將第一核酸和第二核酸共同遞送至宿主細胞中。According to the methods described herein, in some embodiments, one or more nucleic acids (eg, plastids) containing SBTS components are delivered to cells (eg, T or NK cells). For example, one or more nucleic acids are delivered by standard methods of nucleic acid (eg, plastid DNA) delivery, such as those described herein, such as electroporation, transfection, or lipofection. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid contains a transposon comprising a transgene (eg, a nucleic acid encoding a CAR described herein). In some embodiments, the nucleic acid contains a transposon comprising a transgene (eg, a nucleic acid encoding a CAR described herein) and a nucleic acid sequence encoding a translocase. In some embodiments, a system with two nucleic acids is provided, such as a two-plasmid system, eg, wherein a first plastid contains a transposon comprising a transgene and a second plastid contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a translocase. For example, the first nucleic acid and the second nucleic acid are co-delivered into the host cell.
在一些實施方式中,藉由使用基因插入(使用SBTS)和基因編輯(使用核酸酶(例如,鋅指核酸酶(ZFN)、轉錄激活因子樣效應子核酸酶(TALEN)、CRISPR/Cas系統、或工程化大範圍核酸酶重新工程化的歸巢內切核酸酶))的組合產生表現本文所述CAR的細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞。In some embodiments, by using gene insertion (using SBTS) and gene editing (using nucleases (e.g., zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), CRISPR/Cas systems, or engineered meganuclease reengineered homing endonuclease)) to generate cells expressing CARs described herein, such as T cells or NK cells.
在一些實施方式中,使用非病毒遞送方法允許細胞例如T細胞或NK細胞的重程序設計,並且將該等細胞直接輸注到受試者體內。非病毒載體的優點包括但不限於容易且相對低成本地產生滿足患者群體所需的足夠量、儲存期間的穩定性和缺乏免疫原性。 編碼CAR的核酸構建體 In some embodiments, the use of non-viral delivery methods allows the reprogramming of cells, such as T cells or NK cells, and infusion of these cells directly into a subject. Advantages of non-viral vectors include, but are not limited to, the ease and relatively low cost of producing sufficient quantities to satisfy a patient population, stability during storage, and lack of immunogenicity. Nucleic acid construct encoding CAR
本發明還提供了編碼一或多種本文所述CAR構建體的核酸分子。在一方面,核酸分子以傳訊RNA轉錄物提供。在一方面,核酸分子以DNA構建體提供。The invention also provides nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more of the CAR constructs described herein. In one aspect, nucleic acid molecules are provided as messenger RNA transcripts. In one aspect, the nucleic acid molecule is provided as a DNA construct.
編碼所希望分子的核酸序列可以使用本領域已知的重組方法獲得,例如藉由從表現該基因的細胞中篩選文庫,藉由從已知包括該基因的載體中獲得基因,或藉由使用標準技術直接從含有該基因的細胞和組織分離。替代性地,感興趣的基因可以合成產生,而不是選殖。A nucleic acid sequence encoding a desired molecule can be obtained using recombinant methods known in the art, for example, by screening a library from cells expressing the gene, by obtaining the gene from a vector known to include the gene, or by using standard technology to isolate directly from cells and tissues that contain the gene. Alternatively, the gene of interest can be produced synthetically rather than cloned.
本發明還提供了其中插入本發明之DNA的載體。衍生自反轉錄病毒如慢病毒的載體係實現長期基因轉移的合適工具,因為它們允許轉基因的長期穩定整合及其在子細胞中的繁殖。慢病毒載體相對於衍生自腫瘤反轉錄病毒如鼠白血病病毒的載體具有附加優點,因為它們可以轉導非增殖性細胞,例如肝細胞。它們還具有低免疫原性的附加優點。The present invention also provides a vector into which the DNA of the present invention is inserted. Vectors derived from retroviruses such as lentiviruses are suitable tools for long-term gene transfer, as they allow long-term stable integration of the transgene and its propagation in daughter cells. Lentiviral vectors have the added advantage of vectors derived from oncoretroviruses such as murine leukemia virus, in that they can transduce non-proliferative cells, such as hepatocytes. They also have the added advantage of low immunogenicity.
在另一個實施方式中,包含編碼本發明所希望CAR的核酸的載體係腺病毒載體(A5/35)。在另一個實施方式中,編碼CAR的核酸的表現可以使用轉位子如睡美人系統、crisper、CAS9和鋅指核酸酶完成。見下文June等人 2009 Nature Reviews Immunology[自然免疫學綜述] 9.10: 704-716,該文獻藉由引用併入本文。 In another embodiment, the vector comprising the nucleic acid encoding the desired CAR of the present invention is an adenoviral vector (A5/35). In another embodiment, expression of a CAR-encoding nucleic acid can be accomplished using transposons such as the Sleeping Beauty system, crisper, CAS9, and zinc finger nucleases. See below June et al. 2009 Nature Reviews Immunology 9.10: 704-716, which is hereby incorporated by reference.
簡而言之,編碼CAR的天然或合成核酸的表現典型地是藉由將編碼CAR多肽或其部分的核酸與啟動子可操作地連接、並將構建體併入到表現載體中來實現。載體可以適用於複製和整合真核生物。典型的選殖載體含有轉錄和翻譯終止子、起始序列和可用於調節所希望核酸序列表現的啟動子。Briefly, expression of a natural or synthetic nucleic acid encoding a CAR is typically achieved by operably linking a nucleic acid encoding a CAR polypeptide, or a portion thereof, to a promoter, and incorporating the construct into an expression vector. Vectors can be suitable for replication and integration in eukaryotes. A typical cloning vector contains transcriptional and translational terminators, initiation sequences and promoters that can be used to regulate the expression of the desired nucleic acid sequence.
使用標準基因遞送方案,本發明之表現構建體也可用於核酸免疫和基因療法。用於基因遞送的方法在本領域中係已知的。參見例如美國專利No. 5,399,346、5,580,859、5,589,466,該等專利藉由援引以其全文併入本文。在另一個實施方式中,本發明提供了一種基因治療載體。The expression constructs of the invention can also be used in nucleic acid immunization and gene therapy using standard gene delivery protocols. Methods for gene delivery are known in the art. See, eg, US Patent Nos. 5,399,346, 5,580,859, 5,589,466, which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a gene therapy vector.
可以將核酸選殖至許多類型的載體中。例如,可以將核酸選殖到載體中,該載體包括但不限於質體、噬菌粒、噬菌體衍生物、動物病毒和黏粒。特別感興趣的載體包括表現載體、複製載體、探針生成載體和定序載體。Nucleic acids can be cloned into many types of vectors. For example, nucleic acids can be cloned into vectors including, but not limited to, plastids, phagemids, phage derivatives, animal viruses, and cosmids. Vectors of particular interest include expression vectors, replication vectors, probe generation vectors and sequencing vectors.
此外,可以將表現載體以病毒載體的形式提供至細胞。病毒載體技術在本領域中係熟知的,並且例如描述於Sambrook等人, 2012, MOLECULAR CLONING: A LABORATORY MANUAL [分子選殖:實驗室手冊], 第1-4卷, Cold Spring Harbor Press [冷泉港出版社], 紐約中,以及其他病毒學和分子生物學手冊中。可用作載體的病毒包括但不限於反轉錄病毒、腺病毒、腺相關病毒、皰疹病毒和慢病毒。通常,合適的載體含有在至少一種生物體中具有複製功能的起點、啟動子序列、便利的限制性內切核酸酶位點和一或多種選擇標記物(例如,WO 01/96584;WO 01/29058;和美國專利案號6,326,193)。In addition, expression vectors can be provided to cells in the form of viral vectors. Viral vector technology is well known in the art and is described, for example, in Sambrook et al., 2012, MOLECULAR CLONING: A LABORATORY MANUAL [Molecular Selection: A Laboratory Manual], Volumes 1-4, Cold Spring Harbor Press [冷泉港Press], New York, and in other Handbooks of Virology and Molecular Biology. Viruses that can be used as vectors include, but are not limited to, retroviruses, adenoviruses, adeno-associated viruses, herpesviruses, and lentiviruses. Generally, suitable vectors contain an origin of replication functional in at least one organism, a promoter sequence, convenient restriction endonuclease sites, and one or more selectable markers (e.g., WO 01/96584; WO 01/ 29058; and U.S. Patent No. 6,326,193).
已經開發了許多基於病毒的系統用於將基因轉移到哺乳動物細胞中。例如,反轉錄病毒為基因遞送系統提供了便利的平臺。可以使用本領域已知的技術將選擇的基因插入到載體中並且包裝在反轉錄病毒顆粒中。然後可以分離重組病毒並在體內或離體遞送至受試者的細胞中。許多反轉錄病毒系統在本領域中係已知的。在一些實施方式中,使用了腺病毒載體。許多腺病毒載體在本領域中係已知的。在一個實施方式中,使用慢病毒載體。A number of virus-based systems have been developed for gene transfer into mammalian cells. For example, retroviruses provide a convenient platform for gene delivery systems. The selected gene can be inserted into a vector and packaged in retroviral particles using techniques known in the art. The recombinant virus can then be isolated and delivered to cells of a subject, either in vivo or ex vivo. Many retroviral systems are known in the art. In some embodiments, adenoviral vectors are used. Many adenoviral vectors are known in the art. In one embodiment, lentiviral vectors are used.
另外的啟動子元件(例如強化子)調節轉錄起始的頻率。典型地,該等位於起始位點上游30-110 bp的區中,但是已經顯示許多啟動子也含有起始位點下游的功能元件。啟動子元件之間的間隔常常是靈活的,使得當元件彼此相對發生顛倒或移動時啟動子功能可以得以保留。在胸苷激酶(tk)啟動子中,啟動子元件之間的間隔可以在活性開始下降之前增加到相隔50 bp。取決於激活子,顯現單獨的元件可以協同或獨立地起作用以激活轉錄。示例性啟動子包括CMV IE基因、EF-1α、泛素C、或磷酸甘油激酶(PGK)啟動子。Additional promoter elements, such as enhancers, regulate the frequency of transcription initiation. Typically these are located in a region of 30-110 bp upstream of the initiation site, but it has been shown that many promoters also contain functional elements downstream of the initiation site. The spacing between promoter elements is often flexible so that promoter function is preserved when elements are inverted or moved relative to each other. In the thymidine kinase (tk) promoter, the spacing between promoter elements can be increased to 50 bp apart before activity begins to decline. Depending on the activator, it appears that individual elements can act cooperatively or independently to activate transcription. Exemplary promoters include the CMV IE gene, EF-la, ubiquitin C, or phosphoglycerol kinase (PGK) promoters.
能夠在哺乳動物T細胞中表現CAR轉基因的啟動子之實例係EF1α(EF1a)啟動子。天然EF1a啟動子驅動延伸因子-1複合物的α亞基的表現,該複合物負責將胺醯tRNA酶促遞送至核糖體。EF1a啟動子已經廣泛用於哺乳動物表現質體中,並且已經顯示出有效地驅動選殖到慢病毒載體中的轉基因的CAR表現。參見例如,Milone等人, Mol. Ther. [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。在一方面,該EF1a啟動子包含如本領域已知的序列。An example of a promoter capable of expressing a CAR transgene in mammalian T cells is the EF1 alpha (EF1a) promoter. The native EF1a promoter drives the expression of the alpha subunit of the elongation factor-1 complex responsible for the enzymatic delivery of amine tRNAs to the ribosome. The EF1a promoter has been widely used in mammalian expression plastids and has been shown to efficiently drive CAR expression of transgenes colonized into lentiviral vectors. See, eg, Milone et al., Mol. Ther. [Molecular Therapy] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). In one aspect, the EF1a promoter comprises a sequence as known in the art.
啟動子的另一個實例係即時早期巨細胞病毒(CMV)啟動子序列。該啟動子序列係強組成型啟動子序列,能夠驅動與其可操作地連接的任何多核苷酸序列的高水平表現。然而,還可以使用其他組成型啟動子序列,包括但不限於猿猴病毒40(SV40)早期啟動子、小鼠乳腺腫瘤病毒(MMTV)、人免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)長末端重複序列(LTR)啟動子、MoMuLV啟動子、禽白血病病毒啟動子、Epstein-Barr病毒即刻早期啟動子、Rous肉瘤病毒啟動子、以及人基因啟動子,如但不限於肌動蛋白啟動子、肌凝蛋白啟動子、延伸因子-1α啟動子、血紅素啟動子、和肌酸激酶啟動子。此外,本發明不應限於使用組成型啟動子。誘導型啟動子也被考慮作為本發明之一部分。誘導型啟動子的使用提供了分子開關,該分子開關能夠當需要該啟動子可操作地連接的多核苷酸序列的表現時啟動這種表現,或者當不需要表現時關閉表現。誘導型啟動子之實例包括但不限於金屬硫蛋白啟動子、糖皮質激素啟動子、孕酮啟動子和四環素啟動子。Another example of a promoter is the immediate early cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter sequence. The promoter sequence is a strong constitutive promoter sequence capable of driving high-level expression of any polynucleotide sequence operably linked thereto. However, other constitutive promoter sequences can also be used, including but not limited to Simian virus 40 (SV40) early promoter, mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) long terminal repeat (LTR) promoter promoter, MoMuLV promoter, avian leukosis virus promoter, Epstein-Barr virus immediate early promoter, Rous sarcoma virus promoter, and human gene promoters such as but not limited to actin promoter, myosin promoter, elongation Factor-1 alpha promoter, heme promoter, and creatine kinase promoter. Furthermore, the present invention should not be limited to the use of constitutive promoters. Inducible promoters are also contemplated as part of the invention. The use of an inducible promoter provides a molecular switch capable of turning on expression of a polynucleotide sequence to which the promoter is operably linked when such expression is desired, or turning off expression when such expression is not desired. Examples of inducible promoters include, but are not limited to, the metallothionein promoter, the glucocorticoid promoter, the progesterone promoter, and the tetracycline promoter.
為了評估CAR多肽或其部分的表現,待引入到細胞中的表現載體還可含有選擇標記基因或報告基因或兩者,以便於從旨在通過病毒載體經轉染或感染的細胞群體中鑒定和選擇表現細胞。在其他方面,選擇標記物可以在單獨的DNA片段上攜帶並用於共轉染程序。選擇標記物和報告基因二者都可以側接適當的調節序列以實現在宿主細胞中的表現。有用的選擇標記物包括例如抗生素抗性基因,如neo等。The expression vector to be introduced into the cell may also contain a selectable marker gene or a reporter gene or both for the purpose of assessing the expression of the CAR polypeptide or a portion thereof, to facilitate identification and Select Presentation Cell. In other aspects, selectable markers can be carried on separate DNA fragments and used in co-transfection procedures. Both selectable markers and reporter genes can be flanked by appropriate regulatory sequences to enable expression in the host cell. Useful selectable markers include, for example, antibiotic resistance genes such as neo and the like.
報告基因用於鑒定可能經轉染的細胞和用於評價調節序列的功能。通常,報告基因係如下基因,該基因不存在於受體生物體或組織中或由其表現並且編碼多肽,該多肽的表現藉由一些可易於檢測的特性(例如,酶活性)表現出來。在將DNA引入到受體細胞中後的適當時間測定報告基因的表現。合適的報告基因可包括編碼螢光素酶、β-半乳糖苷酶、氯黴素乙醯轉移酶、分泌型鹼性磷酸酶的基因或綠色螢光蛋白基因(例如,Ui-Tei等人, 2000 FEBS Letters [歐洲生化學會聯合會快報] 479: 79-82)。合適的表現系統係熟知的,並且可以使用已知技術製備或商業獲得。通常,顯示報告基因的最高表現水平的具有最小5'側翼區的構建體被鑒定為啟動子。此類啟動子區可以與報告基因連接,並用於評價藥劑調節啟動子驅動的轉錄的能力。Reporter genes are used to identify potentially transfected cells and to assess the function of regulatory sequences. Typically, a reporter gene is a gene that is absent from or expressed by a recipient organism or tissue and that encodes a polypeptide whose expression is manifested by some readily detectable property (eg, enzymatic activity). Expression of the reporter gene is determined at an appropriate time after introduction of the DNA into the recipient cells. Suitable reporter genes may include genes encoding luciferase, β-galactosidase, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, secreted alkaline phosphatase, or the green fluorescent protein gene (e.g., Ui-Tei et al., 2000 FEBS Letters [Federation of European Biochemical Societies Letters] 479: 79-82). Suitable expression systems are well known and can be prepared using known techniques or obtained commercially. Typically, the construct with the smallest 5' flanking region showing the highest expression level of the reporter gene was identified as the promoter. Such promoter regions can be linked to reporter genes and used to assess the ability of agents to modulate promoter-driven transcription.
將基因引入到細胞中並將其在細胞中表現之方法在本領域中係已知的。在表現載體的背景下,可以藉由本領域的任何方法將載體容易地引入到宿主細胞,例如哺乳動物、細菌、酵母或昆蟲細胞中。例如,表現載體可以藉由物理、化學或生物手段轉移到宿主細胞中。Methods of introducing genes into cells and expressing them in cells are known in the art. In the context of expression vectors, the vectors can be readily introduced into host cells, such as mammalian, bacterial, yeast or insect cells, by any method in the art. For example, expression vectors can be transferred into host cells by physical, chemical or biological means.
用於將多核苷酸引入到宿主細胞中的物理方法包括磷酸鈣沈澱、脂質轉染、粒子轟擊、顯微注射、電穿孔等。產生包含載體和/或外源性核酸的細胞之方法在本領域中係熟知的。參見例如,Sambrook等人, 2012, MOLECULAR CLONING: A LABORATORY MANUAL [分子選殖實用指南], 第1-4卷, Cold Spring Harbor Press [冷泉港實驗出版社], 紐約)。將多核苷酸引入到宿主細胞中的較佳的方法係磷酸鈣轉染。Physical methods for introducing polynucleotides into host cells include calcium phosphate precipitation, lipofection, particle bombardment, microinjection, electroporation, and the like. Methods of producing cells comprising vectors and/or exogenous nucleic acids are well known in the art. See, eg, Sambrook et al., 2012, MOLECULAR CLONING: A LABORATORY MANUAL, Volumes 1-4, Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York). A preferred method of introducing polynucleotides into host cells is calcium phosphate transfection.
用於將感興趣的多核苷酸引入到宿主細胞中的生物學方法包括使用DNA和RNA載體。病毒載體,並且尤其是反轉錄病毒載體,已成為將基因插入哺乳動物例如人細胞中的最廣泛使用的方法。其他病毒載體可以衍生自慢病毒、痘病毒、單純皰疹病毒I、腺病毒和腺相關病毒等。參見,例如美國專利案號5,350,674和5,585,362。Biological methods for introducing polynucleotides of interest into host cells include the use of DNA and RNA vectors. Viral vectors, and especially retroviral vectors, have become the most widely used method for inserting genes into mammalian, eg human, cells. Other viral vectors can be derived from lentiviruses, poxviruses, herpes simplex virus I, adenoviruses, and adeno-associated viruses, among others. See, eg, US Patent Nos. 5,350,674 and 5,585,362.
用於將多核苷酸引入到宿主細胞中的化學手段包括膠體分散系統,如大分子複合物、奈米膠囊、微球、珠、和基於脂質的系統(包括水包油乳劑、膠束、混合膠束和脂質體)。用作體外和體內遞送運載體的示例性膠體系統係脂質體(例如,人造膜囊)。可獲得先前技術的靶向遞送核酸(如用靶向奈米顆粒或其他合適的亞微米大小的遞送系統遞送多核苷酸)的其他方法。Chemical means for introducing polynucleotides into host cells include colloidal dispersion systems such as macromolecular complexes, nanocapsules, microspheres, beads, and lipid-based systems (including oil-in-water emulsions, micelles, mixed micelles and liposomes). An exemplary colloidal system useful as a delivery vehicle in vitro and in vivo is liposomes (eg, artificial membrane vesicles). Other methods of targeted delivery of nucleic acids, such as delivery of polynucleotides using targeting nanoparticles or other suitable submicron sized delivery systems, are available in the prior art.
在使用非病毒遞送系統的情況下,示例性遞送運載體係脂質體。考慮使用脂質製劑以將核酸引入到宿主細胞(體外、離體或體內)中。在另一方面,核酸可以與脂質締合。與脂質結合的核酸可以被封裝在脂質體的水性內部,散佈在脂質體的脂質雙層內,經由與脂質體和寡核苷酸二者相關的連接分子附接至脂質體,包埋在脂質體中,與脂質體複合,分散在含有脂質的溶液中,與脂質混合,與脂質組合,以懸浮液形式包含在脂質中、包含在膠束中或與膠束複合,或以其他方式與脂質締合。脂質、脂質/DNA或脂質/表現載體締合的組成物不限於溶液中的任何特定結構。例如,它們可以以雙層結構、膠束或「塌陷」結構存在。它們也可以簡單地散佈在溶液中,可能形成大小或形狀不均勻的聚集體。脂質係脂肪物質,該等脂肪物質可為天然存在的或合成的脂質。例如,脂質包括天然存在於細胞質中的脂肪滴以及含有長鏈脂族烴及其衍生物(如脂肪酸、醇、胺、胺基醇和醛)的化合物類。Where a non-viral delivery system is used, the delivery vehicle liposomes are exemplary. Consider the use of lipid formulations to introduce nucleic acids into host cells (in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo). In another aspect, nucleic acids can be associated with lipids. Lipid-bound nucleic acids can be encapsulated within the aqueous interior of the liposome, interspersed within the lipid bilayer of the liposome, attached to the liposome via linker molecules associated with both the liposome and the oligonucleotide, embedded in the lipid In a body, complexed with a liposome, dispersed in a lipid-containing solution, mixed with a lipid, combined with a lipid, contained in a lipid in suspension, contained in or complexed with a micelle, or otherwise associated with a lipid association. The composition of lipid, lipid/DNA or lipid/expression vector associations is not limited to any particular structure in solution. For example, they may exist as bilayer structures, micelles or "collapsed" structures. They can also simply disperse in solution, possibly forming aggregates of uneven size or shape. Lipids are fatty substances which may be naturally occurring or synthetic lipids. Lipids, for example, include fat droplets naturally present in the cytoplasm and classes of compounds containing long-chain aliphatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives, such as fatty acids, alcohols, amines, aminoalcohols, and aldehydes.
適用的脂質可以從商業來源獲得。例如,二肉豆蔻醯基磷脂醯膽鹼(「DMPC」)可以從密蘇里州聖路易斯的西格瑪公司(Sigma, St. Louis, MO)獲得;磷酸二鯨蠟脂(「DCP」)可以從K & K實驗室(K & K Laboratories)(普萊恩維爾(Plainview),紐約)獲得;膽固醇(「Choi」)可以從Calbiochem-Behring獲得;二肉豆蔻基磷脂醯甘油(「DMPG」)和其他脂質可以從阿凡提極地脂質公司(Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc.)(伯明罕(Birmingham),阿拉巴馬州)獲得。脂質在氯仿或氯仿/甲醇中的儲備溶液可以在約-20°C下儲存。氯仿用作唯一的溶劑,因為它比甲醇更容易蒸發。「脂質體」係通用術語,涵蓋藉由產生封閉的脂質雙層或聚集體形成的各種單層和多層脂質運載體。脂質體可以表徵為具有囊泡結構,該等囊泡結構具有磷脂雙層膜和內部水性介質。多層脂質體具有由水性介質分開的多個脂質層。它們係在磷脂懸浮在過量的水性溶液中時自發形成。脂質組分在形成封閉結構之前經歷自重排,並在脂質雙層之間捕獲水和溶解的溶質(Ghosh等人, 1991 Glycobiology [糖生物學] 5: 505-10)。然而,還涵蓋在溶液中具有與正常囊泡結構不同的結構的組成物。例如,脂質可以呈現膠束結構或僅作為脂質分子的不均勻聚集體存在。還考慮了lipofectamine-核酸複合物。Suitable lipids are available from commercial sources. For example, dimyristylphosphatidylcholine (“DMPC”) is available from Sigma, St. Louis, MO; dicetyl phosphate (“DCP”) is available from K & K K & K Laboratories (Plainview, NY); cholesterol ("Choi") can be obtained from Calbiochem-Behring; dimyristylphosphatidylglycerol ("DMPG") and other lipids can be obtained from Acquired from Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc. (Birmingham, AL). Stock solutions of lipids in chloroform or chloroform/methanol can be stored at approximately -20°C. Chloroform was used as the only solvent because it evaporates more easily than methanol. "Liposome" is a general term encompassing various unilamellar and multilamellar lipid vehicles formed by the generation of closed lipid bilayers or aggregates. Liposomes can be characterized as having a vesicular structure with a phospholipid bilayer membrane and an inner aqueous medium. Multilamellar liposomes have multiple lipid layers separated by an aqueous medium. They form spontaneously when phospholipids are suspended in an excess of aqueous solution. Lipid components undergo self-rearrangement before forming closed structures and trap water and dissolved solutes between lipid bilayers (Ghosh et al., 1991 Glycobiology 5: 505-10). However, compositions having structures in solution that differ from normal vesicular structures are also contemplated. For example, lipids can assume a micellar structure or exist only as heterogeneous aggregates of lipid molecules. Also contemplated are lipofectamine-nucleic acid complexes.
無論用於將外源性核酸引入對宿主細胞中之方法還是以其他方式將細胞暴露於本發明之抑制劑,為了證實重組DNA序列在宿主細胞中的存在,可以進行多種測定。此類測定包括例如熟悉該項技術者熟知的「分子生物學」測定,如DNA和RNA印跡、RT-PCR和PCR;「生物化學」測定,如檢測特定肽的存在或不存在,例如藉由免疫學手段(ELISA和西方墨點法)或藉由本文所述之測定以鑒定落入本發明範圍內的藥劑。Regardless of the method used to introduce exogenous nucleic acid into the host cell or otherwise expose the cell to the inhibitors of the invention, a variety of assays can be performed to confirm the presence of the recombinant DNA sequence in the host cell. Such assays include, for example, "molecular biological" assays, such as Southern and Northern blots, RT-PCR and PCR, which are well known to those skilled in the art; "biochemical" assays, such as detecting the presence or absence of specific peptides, e.g. by Agents falling within the scope of the invention are identified by immunological means (ELISA and Western blot) or by assays as described herein.
本發明進一步提供了包含編碼CAR的核酸分子的載體。在一方面,可以將CAR載體直接轉導到細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞中。在一方面,載體係選殖或表現載體,例如,包括但不限於以下的載體:一或多種質體(例如表現質體、選殖載體、微環、微型載體、雙微染色體)、反轉錄病毒和慢病毒載體構建體。在一方面,載體能夠在哺乳動物T細胞或NK細胞中表現CAR構建體。在一方面,哺乳動物T細胞係人T細胞。 製造/生產方法 The present invention further provides a vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR. In one aspect, the CAR vector can be directly transduced into cells, such as T cells or NK cells. In one aspect, vectors for cloning or expressing vectors, for example, include but are not limited to vectors of: one or more plastids (e.g., expressing plastids, cloning vectors, minicircles, minivectors, double minichromosomes), reverse transcription Viral and lentiviral vector constructs. In one aspect, the vector is capable of expressing the CAR construct in mammalian T cells or NK cells. In one aspect, the mammalian T cells are human T cells. Manufacturing/production method
本發明還提供了製備本文揭露的細胞之方法,例如,將T細胞或NK細胞工程化以表現編碼本文所述之一或多個CAR構建體的核酸分子之方法。在一些實施方式中,本文揭露的製造方法用於製造包含編碼本文揭露的兩個CAR的核酸分子的細胞(例如,本文揭露的CD19/CD22串聯和/或雙重CAR)。在一些實施方式中,本文揭露的製造方法用於製造包含編碼本文揭露的雙抗體CAR的核酸分子的細胞,例如,本文揭露的抗CD22/抗CD19雙抗體CAR。在一些實施方式中,本文揭露的製造方法用於製造包含兩個核酸分子的細胞,每一個核酸分子編碼本文揭露的CAR(例如,一個核酸分子編碼抗CD22 CAR並且一個核酸分子編碼抗CD19 CAR)。在一些實施方式中,本文提供的細胞群體係由本文所述之任何製造過程製備的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體。 活化過程 The invention also provides methods of making the cells disclosed herein, eg, methods of engineering T cells or NK cells to express a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more of the CAR constructs described herein. In some embodiments, the manufacturing methods disclosed herein are used to manufacture cells comprising nucleic acid molecules encoding two CARs disclosed herein (eg, CD19/CD22 tandem and/or dual CARs disclosed herein). In some embodiments, the manufacturing methods disclosed herein are used to manufacture cells comprising nucleic acid molecules encoding the diabody CAR disclosed herein, for example, the anti-CD22/anti-CD19 diabody CAR disclosed herein. In some embodiments, the manufacturing methods disclosed herein are used to manufacture cells comprising two nucleic acid molecules, each nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR disclosed herein (e.g., one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD22 CAR and one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD19 CAR) . In some embodiments, a cell population provided herein is a population of cells (eg, immune effector cells such as T cells or NK cells) produced by any of the manufacturing processes described herein. activation process
在一些實施方式中,本文揭露的方法可以在不到24小時內製造經工程化以表現一或多個CAR的免疫效應細胞。不希望受理論束縛,本文提供的方法在製造過程期間保留T細胞的未分化表型,例如初始T細胞。該等具有未分化表型的表現CAR的細胞在輸注後可在體內持續更長時間和/或更好地擴增。在一些實施方式中,與藉由傳統的製造過程(例如,如使用單細胞或批量RNA-seq或使用本領域已知標記物的流動式細胞測量術測量)產生的CART細胞相比,由本文提供的製造方法產生的CART細胞包含更高百分比的幹細胞記憶T細胞。在一些實施方式中,與藉由傳統的製造過程(例如,如使用單細胞RNA-seq測量)產生的CART細胞相比,由本文提供的製造方法產生的CART細胞包含更低百分比的效應T細胞。在一些實施方式中,與藉由傳統的製造過程(例如,如使用scRNA-seq測量)產生的CART細胞相比,由本文提供的製造方法產生的CART細胞更好地保存T細胞的幹細胞性。在一些實施方式中,與藉由傳統的製造過程(例如,如使用scRNA-seq測量)產生的CART細胞相比,由本文提供的製造方法產生的CART細胞顯示出較低的缺氧水平。在一些實施方式中,與藉由傳統的製造過程(例如,如使用scRNA-seq測量)產生的CART細胞相比,由本文提供的製造方法產生的CART細胞顯示出較低的自體吞噬水平。在一些實施方式中,免疫效應細胞經工程化以包含編碼本文揭露的串聯或雙重CAR的核酸分子(例如,本文揭露的CD19/CD22串聯或雙重CAR)。在一些實施方式中,免疫效應細胞經工程化以包含編碼本文揭露的串聯或雙重CAR的核酸分子(例如,本文揭露的抗CD22/抗CD19串聯或雙重CAR)。在一些實施方式中,免疫效應細胞經工程化以包含兩個核酸分子,每一個核酸分子編碼本文揭露的CAR(例如,一個核酸分子編碼抗CD22 CAR並且一個核酸分子編碼抗CD19 CAR)。在其他實施方式中,免疫效應細胞經工程化以包含一個核酸分子,該核酸分子編碼本文揭露的一個或兩個CAR(例如,編碼抗CD22/抗CD19串聯或抗CD22/抗CD19 CAR的一個核酸分子)。In some embodiments, the methods disclosed herein can produce immune effector cells engineered to express one or more CARs in less than 24 hours. Without wishing to be bound by theory, the methods provided herein preserve the undifferentiated phenotype of T cells, eg, naive T cells, during the manufacturing process. These CAR-expressing cells with an undifferentiated phenotype can persist longer and/or expand better in vivo after infusion. In some embodiments, compared to CART cells produced by traditional manufacturing processes (e.g., as measured using single-cell or bulk RNA-seq or flow cytometry using markers known in the art), the CART cells produced by the present invention The provided manufacturing methods produce CART cells comprising a higher percentage of stem cell memory T cells. In some embodiments, CART cells produced by the manufacturing methods provided herein comprise a lower percentage of effector T cells than CART cells produced by traditional manufacturing processes (e.g., as measured using single-cell RNA-seq) . In some embodiments, CART cells produced by the manufacturing methods provided herein better preserve T cell stemness than CART cells produced by traditional manufacturing processes (eg, as measured using scRNA-seq). In some embodiments, CART cells produced by the manufacturing methods provided herein exhibit lower levels of hypoxia compared to CART cells produced by traditional manufacturing processes (eg, as measured using scRNA-seq). In some embodiments, CART cells produced by the manufacturing methods provided herein exhibit lower levels of autophagy compared to CART cells produced by traditional manufacturing processes (eg, as measured using scRNA-seq). In some embodiments, immune effector cells are engineered to comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding a tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein (eg, a CD19/CD22 tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein). In some embodiments, immune effector cells are engineered to comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding a tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein (eg, an anti-CD22/anti-CD19 tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein). In some embodiments, the immune effector cells are engineered to comprise two nucleic acid molecules, each nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR disclosed herein (eg, one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD22 CAR and one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD19 CAR). In other embodiments, immune effector cells are engineered to comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or two CARs disclosed herein (e.g., a nucleic acid encoding an anti-CD22/anti-CD19 tandem or anti-CD22/anti-CD19 CAR molecular).
在一些實施方式中,本文揭露的方法不涉及使用珠,例如Dynabeads ®(例如,CD3/CD28 Dynabeads ®),並且不涉及去珠步驟。在一些實施方式中,藉由本文揭露的方法製造的CART細胞可以以最小的離體擴增投與於受試者,例如,小於2天、小於1天、小於12小時、小於8小時、小於6小時、小於4小時、小於3小時、小於2小時、小於1小時、或沒有離體擴張。因此,本文描述的方法提供了製備改進的表現CAR的細胞產物的快速製造過程,該等細胞產物用於治療受試者的疾病。 In some embodiments, the methods disclosed herein do not involve the use of beads, such as Dynabeads ® (eg, CD3/CD28 Dynabeads ® ), and do not involve a bead removal step. In some embodiments, CART cells produced by the methods disclosed herein can be administered to a subject with minimal ex vivo expansion, e.g., less than 2 days, less than 1 day, less than 12 hours, less than 8 hours, less than 6 hours, less than 4 hours, less than 3 hours, less than 2 hours, less than 1 hour, or no ex vivo expansion. Accordingly, the methods described herein provide a rapid manufacturing process for the preparation of improved CAR-expressing cell products for use in the treatment of a disease in a subject.
在一些實施方式中,本揭露提供了製備表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR)(例如,一或多個CAR,例如,兩個CAR)的細胞(例如,T細胞)群體之方法,該等方法包括:(i) 使細胞(例如T細胞,例如從冷凍或新鮮的白血球分離產物中分離的T細胞)群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或與刺激細胞表面上共刺激分子的藥劑接觸;(ii) 使細胞(例如T細胞)群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子(例如DNA或RNA分子)接觸,從而提供包含核酸分子的細胞(例如T細胞)群體,和 (iii) 收穫細胞(例如T細胞)群體用於儲存(例如在冷凍保存培養基中重新配製細胞群體)或投與,其中:(a) 步驟 (ii) 與步驟 (i) 一起進行,或在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於20小時(例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於12、13、14、15、16、17、或18小時,例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於18小時)進行,並且步驟 (iii) 在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於26小時(例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於22、23、或24小時,例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於24小時)進行;(b) 步驟 (ii) 與步驟 (i) 一起進行,或在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於20小時(例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於12、13、14、15、16、17、或18小時,例如在步驟 (i) 開始後不晚於18小時)進行,並且步驟 (iii) 在步驟 (ii) 開始後不晚於30小時(例如在步驟 (ii) 開始後不晚於22、23、24、25、26、27、28、29、或30小時)進行;和/或 (c) 如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在步驟 (i) 開始時的細胞群體相比,來自步驟 (iii) 的細胞群體不擴增,或擴增不超過5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%、35%、或40%,例如,不超過10%;或d) 例如如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在步驟 (i) 開始時的細胞群體相比,來自步驟 (iii) 的細胞群體擴增更少,或少於5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、60%、65%、或70%。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子係DNA分子。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子係RNA分子。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子在病毒載體(例如選自慢病毒載體、腺病毒載體、或反轉錄病毒載體的病毒載體)上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子在非病毒載體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子在質體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 中的核酸分子不在任何載體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (ii) 包括用包含編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子的一或多個病毒載體轉導細胞(例如,T細胞)群體。In some embodiments, the disclosure provides methods of making a population of cells (eg, T cells) expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) (eg, one or more CARs, eg, two CARs), the methods Including: (i) subjecting a population of cells (e.g., T cells, e.g., from frozen or fresh leukapheresis) to an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface contacting; (ii) contacting a population of cells (e.g., T cells) with one or more nucleic acid molecules (e.g., DNA or RNA molecules) encoding one or more CARs, thereby providing a population of cells (e.g., T cells) comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and (iii) harvesting the population of cells (e.g., T cells) for storage (e.g., reconstitution of the cell population in a cryopreservation medium) or administration, wherein: (a) step (ii) is performed together with step (i), or at No later than 20 hours after step (i) started (for example no later than 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 or 18 hours after step (i) started, for example no later than 18 hours), and step (iii) is carried out no later than 26 hours after the start of step (i) (for example, no later than 22, 23, or 24 hours after the start of step (i), such as after the start of step (i) not later than 24 hours); (b) step (ii) is carried out together with step (i), or not later than 20 hours after the start of step (i) (for example, not later than 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, or 18 hours, such as not later than 18 hours after the start of step (i), and step (iii) is carried out no later than 30 hours after the start of step (ii) (for example, at Step (ii) is carried out no later than 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, or 30 hours) after initiation; and/or (c) as assessed by the number of viable cells, and in step ( i) The cell population from step (iii) does not expand, or expands by no more than 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, or 40% compared to the starting cell population %, for example, not more than 10%; or d) the cell population from step (iii) is less expanded than the cell population at the beginning of step (i), as assessed, for example, by the number of viable cells, or Less than 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, or 70%. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is a DNA molecule. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is an RNA molecule. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is on a viral vector (eg, a viral vector selected from a lentiviral vector, an adenoviral vector, or a retroviral vector). In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is on a non-viral vector. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is on a plastid. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (ii) is not on any carrier. In some embodiments, step (ii) comprises transducing a population of cells (eg, T cells) with one or more viral vectors comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs.
在前述方法的一些實施方式中,該等方法進一步包括在細胞培養基中添加佐劑或轉導增強試劑以增強轉導效率。在一些實施方式中,佐劑或轉導增強試劑包含陽離子聚合物。在一些實施方式中,佐劑或轉導增強試劑選自:LentiBOOST TM(Sirion Biotech公司(Sirion Biotech))、vectofusin-1、F108(泊洛沙姆338或Pluronic® F-38)、海美溴銨(聚凝胺)、PEA、普朗尼克F68、普朗尼克F127(泊洛沙姆407或聚伸烷基二醇PE/F-127)、硫酸魚精蛋白、聚伸烷基二醇或LentiTrans™。在一些實施方式中,佐劑為LentiBOOST TM(Sirion Biotech公司)。在其他實施方式中,佐劑為F108(泊洛沙姆338或Pluronic®F-38)。在其他實施方式中,佐劑為普朗尼克F127(泊洛沙姆407或聚伸烷基二醇PE/F-127)。 In some embodiments of the foregoing methods, the methods further comprise adding an adjuvant or a transduction enhancing agent to the cell culture medium to enhance transduction efficiency. In some embodiments, the adjuvant or transduction enhancing agent comprises a cationic polymer. In some embodiments, the adjuvant or transduction enhancing agent is selected from: LentiBOOST TM (Sirion Biotech Company (Sirion Biotech)), vectofusin-1, F108 (poloxamer 338 or Pluronic® F-38), heme bromide Ammonium (polybrene), PEA, Pluronic F68, Pluronic F127 (poloxamer 407 or polyalkylene glycol PE/F-127), protamine sulfate, polyalkylene glycol or LentiTrans™. In some embodiments, the adjuvant is LentiBOOST ™ (Sirion Biotech). In other embodiments, the adjuvant is F108 (poloxamer 338 or Pluronic® F-38). In other embodiments, the adjuvant is Pluronic F127 (poloxamer 407 or polyalkylene glycol PE/F-127).
在一些實施方式中,從受試者的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)收集細胞(例如,T細胞)群體。In some embodiments, a population of cells (eg, T cells) is collected from a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) of a subject.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)並作為冷凍樣本(例如,冷凍保存的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。然後解凍冷凍的單採樣本,並從單採樣本中選擇T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞),例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後使用本文所述之活化過程接種所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)用於CART製造。在一些實施方式中,選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)在接種用於CART製造之前經歷一輪或多輪凍融。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject and shipped to a cell manufacturing facility as a frozen sample (eg, a cryopreserved sample). The frozen single-sample is then thawed, and T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are selected from the single-sample, for example, using a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). The selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then inoculated for CART manufacturing using the activation process described herein. In some embodiments, selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) undergo one or more rounds of freeze-thawing prior to seeding for CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)並作為新鮮產品(例如,不冷凍的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。從單採樣本中選擇T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞),例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後使用本文所述之活化過程接種所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)用於CART製造。在一些實施方式中,選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)在接種用於CART製造之前經歷一輪或多輪凍融。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject and shipped to a cell manufacturing facility as a fresh product (eg, a sample that is not frozen). Select T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) from a single sample, eg, using a cell sorter (eg, CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). The selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then inoculated for CART manufacturing using the activation process described herein. In some embodiments, selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) undergo one or more rounds of freeze-thawing prior to seeding for CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)。從單採樣本中選擇T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞),例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後將選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)作為冷凍樣本(例如,冷凍保存的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。隨後解凍所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)並使用本文所述之活化過程接種用於CART製造。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject. Select T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) from a single sample, eg, using a cell sorter (eg, CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). The selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then shipped to the cell manufacturing facility as frozen samples (eg, cryopreserved samples). Selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then thawed and seeded for CART manufacturing using the activation process described herein.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞(例如,T細胞)與抗CD3和抗CD28抗體,例如,立即接觸,然後用編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的載體(例如,慢病毒載體)(例如,一或多個載體)轉導。培養開始後24小時,洗滌細胞,並配製用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, cells (e.g., T cells) are contacted with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, e.g., immediately, and then treated with a vector (e.g., lentiviral vector) encoding a CAR (e.g., one or more CARs) ( For example, one or more vectors) transduction. Twenty-four hours after initiation of culture, cells were washed and formulated for storage or administration.
不希望受理論束縛,簡短的CD3和CD28刺激可以促進自我更新T細胞的有效轉導。與傳統的CART製造方法相比,本文提供的活化過程不涉及延長的離體擴增。與細胞介素過程類似,本文提供的活化過程還在CART製造期間保留未分化的T細胞。Without wishing to be bound by theory, brief CD3 and CD28 stimulation can promote efficient transduction of self-renewing T cells. In contrast to traditional CART manufacturing methods, the activation process presented here does not involve prolonged ex vivo expansion. Similar to the cytokine process, the activation process provided herein also preserves undifferentiated T cells during CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞(例如,T細胞)與抗CD3和抗CD28抗體接觸例如12小時,然後用編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的載體(例如,慢病毒載體)(例如,一或多個載體)轉導。培養開始後24小時,洗滌細胞,並配製用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, cells (e.g., T cells) are contacted with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, e.g., for 12 hours, and then treated with a vector (e.g., a lentiviral vector) encoding a CAR (e.g., one or more CARs) (e.g., , one or more vectors) transduction. Twenty-four hours after initiation of culture, cells were washed and formulated for storage or administration.
不希望受理論束縛,簡短的CD3和CD28刺激可以促進自我更新T細胞的有效轉導。與傳統的CART製造方法相比,本文提供的活化過程不涉及延長的離體擴增。與細胞介素過程類似,本文提供的活化過程還在CART製造期間保留未分化的T細胞。Without wishing to be bound by theory, brief CD3 and CD28 stimulation can promote efficient transduction of self-renewing T cells. In contrast to traditional CART manufacturing methods, the activation process presented here does not involve prolonged ex vivo expansion. Similar to the cytokine process, the activation process provided herein also preserves undifferentiated T cells during CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸。In some embodiments, a population of cells is contacted with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the surface of the cells.
在一些實施方式中,藉由陽性選擇使用抗CD4和抗CD8珠來選擇T細胞,使用例如細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。 In some embodiments, T cells are selected by positive selection using anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 beads, using, for example, a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS® Prodigy® device).
在一些實施方式中,藉由陽性選擇使用抗CD45RA和抗CCR7珠來選擇T細胞,使用例如細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。 In some embodiments, T cells are selected by positive selection using anti-CD45RA and anti-CCR7 beads, using, for example, a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS® Prodigy® device).
在一些實施方式中,藉由陽性選擇使用抗CD45RA和抗CD27珠來選擇T細胞,使用例如細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。 In some embodiments, T cells are selected by positive selection using anti-CD45RA and anti-CD27 beads, using, for example, a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS® Prodigy® device).
在一些實施方式中,藉由陽性選擇使用抗CD3和抗CD28珠來選擇T細胞,使用例如細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。 In some embodiments, T cells are selected by positive selection using anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 beads, using, for example, a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS® Prodigy® device).
在一些實施方式中,藉由陰性選擇使用抗譜系珠(除T細胞以外)來選擇T細胞,使用例如細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。 In some embodiments, T cells are selected by negative selection using anti-lineage beads (in addition to T cells), using, for example, a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS® Prodigy® device).
在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑係刺激CD3的藥劑。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑係刺激CD28、ICOS、CD27、HVEM、LIGHT、CD40、4-1BB、OX40、DR3、GITR、CD30、TIM1、CD2、CD226、或其任何組合的藥劑。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑係刺激CD28的藥劑。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑選自抗體(例如單結構域抗體(例如重鏈可變結構域抗體)、肽體、Fab片段、或scFv)、小分子、或配體(例如天然存在的配體、重組配體、或嵌合配體)。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑係抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑係抗-CD3抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑選自抗體(例如單結構域抗體(例如重鏈可變結構域抗體)、肽體、Fab片段、或scFv)、小分子、或配體(例如天然存在的配體、重組配體、或嵌合配體)。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑係抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑係抗CD28抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑或刺激共刺激分子的藥劑不包含珠。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑包含與膠體聚合物奈米基質共價附接的抗CD3抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激共刺激分子的藥劑包含與膠體聚合物奈米基質共價附接的抗CD28抗體。在一些實施方式中,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和刺激共刺激分子的藥劑包含T細胞TransAct TM。 In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex is an agent that stimulates CD3. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule is an agent that stimulates CD28, ICOS, CD27, HVEM, LIGHT, CD40, 4-1BB, OX40, DR3, GITR, CD30, TIM1, CD2, CD226, or any combination thereof . In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule is an agent that stimulates CD28. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex is selected from an antibody (e.g., a single domain antibody (e.g., a heavy chain variable domain antibody), a peptibody, a Fab fragment, or a scFv), a small molecule, or a ligand (eg naturally occurring ligands, recombinant ligands, or chimeric ligands). In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex is an antibody. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex is an anti-CD3 antibody. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule is selected from an antibody (e.g., a single domain antibody (e.g., a heavy chain variable domain antibody), a peptibody, a Fab fragment, or a scFv), a small molecule, or a ligand (e.g., naturally occurring ligands, recombinant ligands, or chimeric ligands). In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the co-stimulatory molecule is an antibody. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the co-stimulatory molecule is an anti-CD28 antibody. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex or the agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule does not comprise beads. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex comprises an anti-CD3 antibody covalently attached to the colloidal polymer nanomatrix. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the co-stimulatory molecule comprises an anti-CD28 antibody covalently attached to the colloidal polymer nanomatrix. In some embodiments, the agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and the agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule comprises T cell TransAct ™ .
在一些實施方式中,該基質包含聚合物或由其組成,例如,可生物降解或生物相容的惰性材料,例如,其對細胞無毒。在一些實施方式中,該基質由親水性聚合物鏈組成,由於鏈的水合作用,其在水溶液中獲得最大的移動性。在一些實施方式中,該移動基質可為膠原蛋白、純化的蛋白質、純化的肽、多糖、糖胺聚糖或細胞外基質組成物。多糖可包括例如纖維素醚、澱粉、阿拉伯樹膠、瓊脂糖、葡聚糖、殼聚糖、透明質酸、果膠、黃原膠、瓜爾膠或海藻酸鹽。其他聚合物可包括聚酯、聚醚、聚丙烯酸酯、聚丙烯醯胺、聚胺、聚乙烯亞胺、聚季銨鹽聚合物、聚磷腈、聚乙烯醇、聚乙酸乙烯酯、聚乙烯吡咯啶酮、嵌段共聚物或聚胺酯。在一些實施方式中,移動基質係葡聚糖的聚合物。In some embodiments, the matrix comprises or consists of a polymer, eg, a biodegradable or biocompatible inert material, eg, that is nontoxic to cells. In some embodiments, the matrix is composed of hydrophilic polymer chains that achieve maximum mobility in aqueous solutions due to hydration of the chains. In some embodiments, the mobile matrix can be collagen, purified proteins, purified peptides, polysaccharides, glycosaminoglycans, or extracellular matrix components. Polysaccharides may include, for example, cellulose ethers, starches, gum arabic, agarose, dextran, chitosan, hyaluronic acid, pectin, xanthan gum, guar gum or alginates. Other polymers may include polyesters, polyethers, polyacrylates, polyacrylamides, polyamines, polyethyleneimines, polyquaternium polymers, polyphosphazenes, polyvinyl alcohols, polyvinyl acetates, polyethylene Pyrrolidone, block copolymer or polyurethane. In some embodiments, the mobile matrix is a polymer of dextran.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的核酸分子(例如,一或多個核酸分子)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的DNA分子(例如,一或多個DNA分子)轉導細胞群體。In some embodiments, a population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule (eg, one or more nucleic acid molecules) encoding a CAR (eg, one or more CARs). In some embodiments, a DNA molecule (eg, one or more DNA molecules) encoding a CAR (eg, one or more CARs) is transduced into a population of cells.
在一些實施方式中,在兩種核酸分子(例如慢病毒載體)共轉導的情況下,該兩種核酸分子各自編碼本文揭露的CAR(例如如本文揭露的,一種核酸分子編碼抗CD22 CAR,並且一種核酸分子編碼抗CD19 CAR),可以例如以1 : 1比率,將含有編碼該CAR的核酸分子的每種載體添加至反應混合物(例如含有細胞群體)。In some embodiments, where two nucleic acid molecules (e.g., lentiviral vectors) are co-transduced, each of the two nucleic acid molecules encodes a CAR disclosed herein (e.g., one nucleic acid molecule encodes an anti-CD22 CAR as disclosed herein, and one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD19 CAR), each vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding the CAR can be added to a reaction mixture (eg, containing a population of cells), eg, in a 1:1 ratio.
不希望受理論束縛,據信在一些實施方式中,針對含有編碼不同CAR分子的核酸分子的載體,使用不同的MOI可能會影響細胞群體的最終組成。例如,在編碼抗CD22 CAR的慢病毒載體和編碼抗CD19 CAR的慢病毒載體共轉導的情況下,可以將不同的MOI用於使單CD22 CART細胞和CD22/CD19雙重CART細胞的百分比最大化,同時導致更少的單CD19 CART細胞和未經轉導的細胞。Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that in some embodiments, using different MOIs for vectors containing nucleic acid molecules encoding different CAR molecules may affect the final composition of the cell population. For example, in the case of co-transduction of a lentiviral vector encoding an anti-CD22 CAR and a lentiviral vector encoding an anti-CD19 CAR, different MOIs can be used to maximize the percentage of single CD22 CART cells and CD22/CD19 dual CART cells , resulting in fewer single CD19 CART cells and untransduced cells simultaneously.
在一些實施方式中,在編碼抗CD22 CAR的慢病毒載體和編碼抗CD19 CAR的慢病毒載體共轉導的情況下,使細胞群體與如下MOI的該第一病毒載體接觸,該MOI高於、等於或低於該細胞群體與該第二病毒載體接觸時的MOI。在一些實施方式中,使該細胞群體與如下MOI的該第一病毒載體接觸,該MOI高於該細胞群體與該第二病毒載體接觸時的MOI。In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with the first viral vector at an MOI of greater than, Equal to or lower than the MOI at which the cell population was contacted with the second viral vector. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with the first viral vector at an MOI that is higher than the MOI at which the population of cells is contacted with the second viral vector.
在一些實施方式中,使該細胞群體與第一MOI的該第一病毒載體接觸,並且與第二MOI的該第二病毒載體接觸,使得所得細胞群體包含第一細胞群體、第二細胞群體和第三細胞群體,該第一細胞群體包含抗CD22 CAR但不包含抗CD19 CAR,該第二細胞群體包含抗CD19 CAR但不包含抗CD22 CAR,該第三細胞群體包含抗CD22 CAR和抗CD19 CAR二者。共轉導方法如本領域所述,例如在WO 2021/108661中,將其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。In some embodiments, the cell population is contacted with the first viral vector at a first MOI, and with the second viral vector at a second MOI, such that the resulting cell population comprises the first cell population, the second cell population, and A third cell population, the first cell population comprising an anti-CD22 CAR but not an anti-CD19 CAR, the second cell population comprising an anti-CD19 CAR but not an anti-CD22 CAR, the third cell population comprising an anti-CD22 CAR and an anti-CD19 CAR both. Co-transduction methods are described in the art, for example in WO 2021/108661, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸同時使細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於30、29、28、27、26、25、24、23、22、21、20、19、18、17、16、15、14、13、12、11、10、9、8、7、6、5、4、3、2、1、或0.5小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於20小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於19小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於18小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於17小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於16小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於15小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於14小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於14小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於13小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於12小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於11小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於10小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於9小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於8小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於7小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於6小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於5小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於4小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於3小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於2小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於1小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於30分鐘,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子接觸。In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with one or more nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more CARs simultaneously with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or stimulates co-expression on the cell surface as described above. Stimulating molecule exposure to agents. In some embodiments, no later than 30, 29, 28, 27, 26 hours after initiation of contacting the population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates costimulatory molecules on the surface of cells as described above , 25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20, 19, 18, 17, 16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 , or 0.5 hour, contacting the population of cells with one or more nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more CARs. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a or multiple CAR nucleic acid molecules in contact. In some embodiments, the population of cells is exposed to an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with an agent encoding a One or more nucleic acid molecules of one or more CARs are contacted.
在一些實施方式中,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, a population of cells is harvested for storage or administration.
在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於72、60、48、36、32、31、30、29、28、27、26、25、24、23、22、21、20、19、或18小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於26小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於25小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於24小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於23小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸開始後不遲於22小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, no later than 72, 60, 48, 36, 32 hours after initiation of contacting the population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the surface of cells as described above , 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26, 25, 24, 23, 22, 21, 20, 19, or 18 hours, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage no later than 26 hours after initiation of contact of the cell population with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a costimulatory molecule on the surface of the cells as described above or cast. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage no later than 25 hours after initiation of contact of the cell population with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface as described above or cast. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage no later than 24 hours after initiation of contact of the cell population with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface as described above or cast. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage no later than 23 hours after initiation of contact of the cell population with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface as described above or cast. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage no later than 22 hours after initiation of contact of the cell population with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface as described above or cast.
在一些實施方式中,細胞群體不是離體擴增的。In some embodiments, the population of cells is not expanded ex vivo.
在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、或60%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過5%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過10%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過15%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過20%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過25%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過30%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過35%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激如上所述之細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過40%。In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population expansion does not exceed 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15%, 16%, 17%, compared to the cell population 18%, 19%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, or 60%. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population expanded by no more than 5% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 10% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 15% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 20% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 25% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 30% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 35% compared to the cell population. In some embodiments, e.g., as assessed by viable cell number, prior to contacting a population of cells with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or an agent that stimulates co-stimulatory molecules on the cell surface as described above, The cell population does not expand more than 40% compared to the cell population.
在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4、4.5、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、16、20、24、36、或48小時。In some embodiments, for example, the cell population expands by no more than 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 16, 20, 24, 36, or 48 hours.
在一些實施方式中,該活化過程在無血清細胞培養基中進行。在一些實施方式中,該活化過程在包含一或多種選自以下的細胞介素的細胞培養基中進行:IL-2、IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))、或IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)。在一些實施方式中,hetIL-15包含如下的胺基酸序列:NWVNVISDLKKIEDLIQSMHIDATLYTESDVHPSCKVTAMKCFLLELQVISLESGDASIHDTVENLIILANNSLSSNGNVTESGCKECEELEEKNIKEFLQSFVHIVQMFINTSITCPPPMSVEHADIWVKSYSLYSRERYICNSGFKRKAGTSSLTECVLNKATNVAHWTTPSLKCIRDPALVHQRPAPPSTVTTAGVTPQPESLSPSGKEPAASSPSSNNTAATTAAIVPGSQLMPSKSPSTGTTEISSHESSHGTPSQTTAKNWELTASASHQPPGVYPQG(SEQ ID NO: 109)。在一些實施方式中,hetIL-15包含與SEQ ID NO: 109具有至少約70%、75%、80%、85%、90%、95%、或99%同一性的胺基酸序列。在一些實施方式中,該活化過程在包含LSD1抑制劑的細胞培養基中進行。在一些實施方式中,該活化過程在包含MALT1抑制劑的細胞培養基中進行。在一些實施方式中,無血清細胞培養基包含血清替代物。在一些實施方式中,該血清替代物係CTS™ 免疫細胞血清替代物(ICSR)。在一些實施方式中,ICSR的水平可為,例如,高達5%,例如,約1%、2%、3%、4%或5%。不希望受理論束縛,使用細胞培養基,例如,包含ICSR(例如2% ICSR)的Raid培養基,可以改善本文所述製造過程期間的細胞活力。In some embodiments, the activation process is performed in serum-free cell culture medium. In some embodiments, the activation process is performed in a cell culture medium comprising one or more cytokines selected from IL-2, IL-15 (e.g., hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)), or IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra).在一些實施方式中,hetIL-15包含如下的胺基酸序列:NWVNVISDLKKIEDLIQSMHIDATLYTESDVHPSCKVTAMKCFLLELQVISLESGDASIHDTVENLIILANNSLSSNGNVTESGCKECEELEEKNIKEFLQSFVHIVQMFINTSITCPPPMSVEHADIWVKSYSLYSRERYICNSGFKRKAGTSSLTECVLNKATNVAHWTTPSLKCIRDPALVHQRPAPPSTVTTAGVTPQPESLSPSGKEPAASSPSSNNTAATTAAIVPGSQLMPSKSPSTGTTEISSHESSHGTPSQTTAKNWELTASASHQPPGVYPQG(SEQ ID NO: 109)。 In some embodiments, hetIL-15 comprises an amino acid sequence that is at least about 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, or 99% identical to SEQ ID NO: 109. In some embodiments, the activation process is performed in cell culture medium comprising an LSD1 inhibitor. In some embodiments, the activation process is performed in cell culture medium comprising a MALT1 inhibitor. In some embodiments, the serum-free cell culture medium comprises a serum replacement. In some embodiments, the serum replacement is CTS™ Immune Cell Serum Replacement (ICSR). In some embodiments, the level of ICSR can be, eg, up to 5%, eg, about 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, or 5%. Without wishing to be bound by theory, cell viability during the manufacturing process described herein can be improved using a cell culture medium, eg, Raid medium containing ICSR (eg, 2% ICSR).
在一些實施方式中,本揭露提供了製備表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR)的細胞(例如,T細胞)群體之方法,該方法包括:(a) 提供從受試者收集的單採樣本(例如,新鮮或冷凍保存的白血球去除術樣本);(b) 從單採樣本中選擇T細胞(例如,使用陰性選擇、陽性選擇或無珠選擇);(c) 將分離的T細胞接種,例如,1 x 10 6至1 x 10 7個細胞/mL;(d) 使T細胞與刺激T細胞的藥劑接觸,例如,刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑和/或刺激細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑(例如,使T細胞與抗CD3和/或抗CD28抗體接觸,例如,使T細胞與TransAct接觸);(e) 使T細胞與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子(例如,DNA或RNA分子)接觸(例如,使T細胞與包含編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子的病毒接觸)例如6-48小時,例如,20-28小時;以及 (f) 洗滌和收穫T細胞用於儲存(例如,在冷凍保存培養基中重新配製T細胞)或投與。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (f) 在步驟 (d) 或 (e) 開始後不遲於30小時進行,例如,在步驟 (d) 或 (e) 開始後不遲於22、23、24、25、26、27、28、29、或30小時。 In some embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method of preparing a population of cells (e.g., T cells) expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), the method comprising: (a) providing a single sample collected from a subject ( (e.g., fresh or cryopreserved leukapheresis samples); (b) select T cells from a single sample (e.g., using negative selection, positive selection, or bead-free selection); (c) plate isolated T cells, e.g. , 1 x 106 to 1 x 107 cells/mL; (d) contacting the T cells with an agent that stimulates T cells, for example, an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex and/or stimulates costimulatory molecules on the cell surface (e.g., contacting T cells with anti-CD3 and/or anti-CD28 antibodies, e.g., contacting T cells with TransAct); (e) contacting T cells with one or more nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more CARs ( e.g., a DNA or RNA molecule) (e.g., contacting a T cell with a virus comprising one or more nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more CARs) for e.g. 6-48 hours, e.g., 20-28 hours; and (f) T cells are washed and harvested for storage (eg, reconstitution of T cells in cryopreservation medium) or administration. In some embodiments, step (f) is performed no later than 30 hours after initiation of step (d) or (e), for example, no later than 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, or 30 hours.
在一些實施方式中,本文提供的細胞群體係由本文所述之任何製造過程(例如,本文所述之活化過程)製備的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體。In some embodiments, a cell population provided herein is a population of cells (eg, immune effector cells such as T cells or NK cells) prepared by any of the manufacturing processes described herein (eg, the activation process described herein).
在一些實施方式中,在製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)細胞群體中初始細胞(例如初始T細胞,例如CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ T細胞)的百分比,與製造過程開始時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程開始時)細胞群體中初始細胞(例如初始T細胞,例如CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+細胞)的百分比相比 (1) 相同,(2) 相差例如不超過4%、5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、或15%,或 (3) 增加例如至少5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、21%、22%、23%、24%、或25%。在一些實施方式中,與藉由其他類似方法製造的細胞相比,製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)的細胞群體顯示較高百分比的初始細胞,例如初始T細胞,例如CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ T細胞(例如,至少高5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、或50%),該其他類似方法持續例如,超過26小時(例如,持續超過5、6、7、8、9、10、11、或12天)或涉及在體外擴增細胞群體持續,例如超過3天(例如,在體外擴增細胞群體持續3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、或15天)。In some embodiments, the percentage of naive cells (e.g., naive T cells, e.g., CD45RA+CD45RO-CCR7+ T cells) in the cell population at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) , compared to the percentage of naive cells (e.g., naive T cells, e.g., CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ cells) in the cell population at the beginning of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the beginning of the cytokine process or the activation process described herein)(1) , (2) differ by, for example, not more than 4%, 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, or 15%, or (3) increase For example at least 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15%, 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 21%, 22%, 23%, 24%, or 25%. In some embodiments, the cell population at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) exhibits a higher percentage of initial cells than cells produced by other similar methods , such as naive T cells, such as CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ T cells (eg, at least 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15% higher , 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, or 50%), the other similar method lasts, for example, for more than 26 hours (for example, for more than 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12 days) or involve expanding a cell population in vitro for, for example, more than 3 days (e.g., expanding a cell population in vitro for 3, 4, 5, 6 , 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, or 15 days).
在一些實施方式中,在製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)細胞群體中初始細胞,例如初始T細胞,例如CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ T細胞)的百分比不少於20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、或60%。In some embodiments, the percentage of naive cells, e.g., naive T cells, e.g., CD45RA+ CD45RO- CCR7+ T cells) in the cell population at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) Not less than 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, or 60%.
在一些實施方式中,在製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)細胞群體中的中樞記憶細胞(例如中樞記憶T細胞,例如CD95+中樞記憶T細胞、CD45RO+中樞記憶T細胞、和/或CCR7+中樞記憶T細胞)的百分比,與製造過程開始時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程開始時)細胞群體中的中樞記憶細胞(例如中樞記憶T細胞,例如CD95+中樞記憶T細胞)的百分比相比 (1) 相同,(2) 相差例如不超過4%、5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、或15%,或 (3) 降低例如至少5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、21%、22%、23%、24%、或25%。在一些實施方式中,與藉由其他類似方法製造的細胞相比,製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)的細胞群體顯示較低百分比的中樞記憶細胞,例如中樞記憶T細胞,例如CD95+中樞記憶T細胞(例如,至少低5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、或50%),該其他類似方法持續例如,超過26小時(例如,持續超過5、6、7、8、9、10、11、或12天)或涉及在體外擴增細胞群體持續,例如超過3天(例如,在體外擴增細胞群體持續3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、或15天)。In some embodiments, central memory cells (e.g., central memory T cells, e.g., CD95+ central memory T cells, CD95+ central memory T cells, The percentage of CD45RO+ central memory T cells, and/or CCR7+ central memory T cells) in relation to the central memory cells (e.g. The percentage of central memory T cells, such as CD95+ central memory T cells) is (1) the same, (2) differs by no more than 4%, 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11 %, 12%, 13%, 14%, or 15%, or (3) a reduction such as at least 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14 %, 15%, 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 21%, 22%, 23%, 24%, or 25%. In some embodiments, the population of cells at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) exhibits a lower percentage of central memory compared to cells produced by other similar methods cells, such as central memory T cells, such as CD95+ central memory T cells (e.g., at least 5%, 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15% lower %, 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, or 50%), the other similar method lasts, e.g., for more than 26 hours (e.g., for more than 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12 days) or involve expanding a cell population in vitro for, for example, more than 3 days (e.g., expanding a cell population in vitro for 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, or 15 days).
在一些實施方式中,在製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)細胞群體中的中樞記憶細胞,例如中樞記憶T細胞,例如CD95+中樞記憶T細胞)的百分比不超過40%、45%、50%、55%、60%、65%、70%、75%、或80%。In some embodiments, central memory cells, such as central memory T cells, such as CD95+ central memory T cells, in the cell population at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) The percentage does not exceed 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, or 80%.
在一些實施方式中,與藉由其他類似方法製造的細胞相比,製造過程結束時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程結束時)的細胞群體在體內投與後體持續更長時間或在更高水平上擴增(例如,至少高20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、60%、65%、70%、75%、80%、85%、或90%更高),該其他類似方法持續例如,超過26小時(例如,持續超過5、6、7、8、9、10、11、或12天)或涉及在體外擴增細胞群體持續,例如超過3天(例如,在體外擴增細胞群體持續3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、或15天)。In some embodiments, the population of cells at the end of the manufacturing process (e.g., at the end of the cytokine process or activation process described herein) persists after in vivo administration compared to cells produced by other similar methods. Amplified for longer or at a higher level (e.g., at least 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75% higher %, 80%, 85%, or 90% higher), the other similar method lasts, for example, for more than 26 hours (for example, for more than 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12 days) or involves Expanding the cell population in vitro for, for example, more than 3 days (e.g., expanding the cell population in vitro for 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, or 15 days) .
在一些實施方式中,在製造過程開始前(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程開始前),已經富集了用於表現IL6R的細胞(例如,IL6Rα和/或IL6Rβ陽性的細胞)的細胞群體。在一些實施方式中,在製造過程開始時(例如,在細胞介素過程或本文所述之活化過程開始時),細胞群體包括,例如,不少於30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、60%、65%、70%、75%、或80%的表現IL6R的細胞(例如,IL6Rα和/或IL6Rβ陽性的細胞)。 細胞介素過程 In some embodiments, cells that express IL6R (e.g., IL6Rα and/or IL6Rβ positive) have been enriched for IL6R expression prior to the start of the manufacturing process (e.g., before the start of the cytokine process or the activation process described herein). cells) cell populations. In some embodiments, at the beginning of the manufacturing process (for example, at the beginning of the cytokine process or the activation process described herein), the cell population comprises, for example, not less than 30%, 35%, 40%, 45% , 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, or 80% of cells expressing IL6R (eg, cells positive for IL6Rα and/or IL6Rβ). Cytokines process
在一些實施方式中,本揭露提供了製備表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR)(例如,一或多個CAR,例如,兩個CAR)的細胞(例如,T細胞)群體之方法,該等方法包括:(1) 使細胞群體與細胞介素(選自IL-2、IL-7、IL-15、IL-21、IL-6,或其組合)接觸;(2) 使細胞(例如,T細胞)群體與編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子(例如,DNA或RNA分子)接觸,從而提供包含核酸分子的細胞(例如,T細胞)群體;和 (3) 收穫細胞(例如,T細胞)群體用於儲存(例如,在冷凍保存培養基中重新配製細胞群體)或投與,其中:(a) 步驟 (2) 與步驟 (1) 一起進行,或在步驟 (1) 開始後不晚於5小時(例如,在步驟 (1) 開始後不晚於1、2、3、4、或5小時)進行,並且步驟 (3) 在步驟 (1) 開始後不晚於26小時(例如,在步驟 (1) 開始後不晚於22、23、或24小時,例如,在步驟 (1) 開始後不晚於24小時)進行;或 (b) 例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在步驟 (1) 開始時的細胞群體相比,來自步驟 (3) 的細胞群體不擴增,或擴增不超過5%、10%、15%、20%、25%、30%、35%、或40%(例如,不超過10%)。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子係DNA分子。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子係RNA分子。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子在病毒載體(例如選自慢病毒載體、腺病毒載體、或反轉錄病毒載體的病毒載體)上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子在非病毒載體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子在質體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 中的核酸分子不在任何載體上。在一些實施方式中,步驟 (2) 包括用包含編碼一或多個CAR的一或多個核酸分子的病毒載體轉導細胞(例如T細胞)群體。在一些實施方式中,細胞經工程化以包含編碼本文揭露的串聯或雙重CAR的核酸分子(例如,本文揭露的CD19/CD22串聯或雙重CAR)。在一些實施方式中,細胞經工程化以包含編碼本文揭露的雙抗體CAR的核酸分子(例如,本文揭露的抗CD22/抗CD19雙抗體CAR)。在一些實施方式中,細胞經工程化以包含兩個核酸分子,每一個核酸分子編碼本文揭露的CAR(例如,一個核酸分子編碼抗CD22 CAR並且一個核酸分子編碼抗CD19 CAR)。In some embodiments, the disclosure provides methods of making a population of cells (eg, T cells) expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) (eg, one or more CARs, eg, two CARs), the methods Including: (1) contacting a population of cells with an interleukin (selected from IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, IL-21, IL-6, or combinations thereof); (2) contacting cells (e.g., T cell) population with one or more nucleic acid molecules (e.g., DNA or RNA molecules) encoding one or more CARs, thereby providing a population of cells (e.g., T cells) comprising the nucleic acid molecules; and (3) harvesting the cells (e.g., , T cells) population for storage (e.g., reconstitution of the cell population in cryopreservation medium) or administration, wherein: (a) step (2) is performed together with step (1), or after step (1) has started performed no later than 5 hours (e.g., no later than 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 hours after starting step (1)), and step (3) was performed no later than 26 hours after starting step (1) ( For example, not later than 22, 23, or 24 hours after the initiation of step (1), for example, no later than 24 hours after the initiation of step (1); or (b) for example, as performed by the number of viable cells Assess that the cell population from step (3) is not expanded, or not expanded by more than 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, compared to the cell population at the beginning of step (1) , 35%, or 40% (for example, no more than 10%). In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is a DNA molecule. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is an RNA molecule. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is on a viral vector (eg, a viral vector selected from a lentiviral vector, an adenoviral vector, or a retroviral vector). In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is on a non-viral vector. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is on a plastid. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid molecule in step (2) is not on any carrier. In some embodiments, step (2) comprises transducing a population of cells (eg, T cells) with a viral vector comprising one or more nucleic acid molecules encoding one or more CARs. In some embodiments, a cell is engineered to comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding a tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein (eg, a CD19/CD22 tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein). In some embodiments, cells are engineered to comprise a nucleic acid molecule encoding a diabody CAR disclosed herein (eg, an anti-CD22/anti-CD19 diabody CAR disclosed herein). In some embodiments, the cell is engineered to contain two nucleic acid molecules, each nucleic acid molecule encoding a CAR disclosed herein (eg, one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD22 CAR and one nucleic acid molecule encoding an anti-CD19 CAR).
在一些實施方式中,從受試者的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)收集細胞(例如,T細胞)群體。In some embodiments, a population of cells (eg, T cells) is collected from a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) of a subject.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)並作為冷凍樣本(例如,冷凍保存的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。然後解凍冷凍的單採樣本,並且T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)選自單採樣本,例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後使用本文所述之細胞介素過程接種所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)用於CART製造。在一些實施方式中,在細胞介素過程結束時,將CAR T細胞冷凍保存,然後解凍並投與受試者。在一些實施方式中,選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)在接種用於CART製造之前經歷一輪或多輪凍融。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject and shipped to a cell manufacturing facility as a frozen sample (eg, a cryopreserved sample). The frozen single-sample is then thawed, and T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are selected from the single-sample, for example, using a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). Selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then inoculated for CART manufacturing using the cytokine procedure described herein. In some embodiments, at the end of the cytokinesis process, the CAR T cells are cryopreserved and then thawed and administered to the subject. In some embodiments, selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) undergo one or more rounds of freeze-thawing prior to seeding for CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集的單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)並作為新鮮產品(例如,不冷凍的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)選自單採樣本,例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後使用本文所述之細胞介素過程接種所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)用於CART製造。在一些實施方式中,選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)在接種用於CART製造之前經歷一輪或多輪凍融。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject and shipped to a cell manufacturing facility as a fresh product (eg, a sample that is not frozen). T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are selected from a single sample, eg, using a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). The selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then inoculated for CART manufacturing using the cytokine procedure described herein. In some embodiments, selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) undergo one or more rounds of freeze-thawing prior to seeding for CART manufacturing.
在一些實施方式中,從受試者收集單採樣本(例如,白血球去除術樣本)。T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)選自單採樣本,例如,使用細胞分選機(例如,CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®裝置)。然後將選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)作為冷凍樣本(例如,冷凍保存的樣本)運輸至細胞製造設施。隨後解凍所選擇的T細胞(例如,CD4+ T細胞和/或CD8+ T細胞)並使用本文所述之細胞介素過程接種用於CART製造。 In some embodiments, a single sample (eg, a leukapheresis sample) is collected from a subject. T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are selected from a single sample, eg, using a cell sorter (eg, a CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® device). The selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then shipped to the cell manufacturing facility as frozen samples (eg, cryopreserved samples). Selected T cells (eg, CD4+ T cells and/or CD8+ T cells) are then thawed and seeded for CART manufacturing using the cytokine procedure described herein.
在一些實施方式中,在細胞(例如,T細胞)接種後,將一或多種細胞介素(例如選自IL-2、IL-7、IL-15(例如hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))、IL-21、或IL-6(例如IL-6/sIL-6R)中的一或多種的細胞介素)以及編碼CAR(例如一或多個CAR)的載體(例如慢病毒載體)(例如一或多個載體)添加至細胞中。孵育20-24小時後,洗滌細胞,並配製用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, following inoculation of cells (e.g., T cells), one or more cytokines (e.g., selected from IL-2, IL-7, IL-15 (e.g., hetIL-15 (IL15/sIL-15Ra )), IL-21, or one or more of IL-6 (such as IL-6/sIL-6R) and vectors (such as lentiviral vectors) encoding CAR (such as one or more CARs) (such as one or more vectors) are added to the cells. After 20-24 hours of incubation, cells are washed and prepared for storage or administration.
與傳統的CART製造方法不同,本文提供的細胞介素過程不涉及CD3和/或CD28刺激或離體T細胞擴增。與抗CD3和抗CD28抗體接觸並且在體外廣泛擴增的T細胞傾向於顯示向中樞記憶表型的分化。不希望受理論束縛,本文提供的細胞介素過程在CART製造期間保留或增加T細胞的未分化表型,產生可在輸注入至受試者後持續更長時間的CART產物。Unlike traditional CART manufacturing methods, the cytokine process presented here does not involve CD3 and/or CD28 stimulation or ex vivo T cell expansion. T cells exposed to anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies and extensively expanded in vitro tended to show differentiation towards a central memory phenotype. Without wishing to be bound by theory, the cytokine process provided herein preserves or increases the undifferentiated phenotype of T cells during CART manufacture, resulting in a CART product that can persist longer after infusion into a subject.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與一或多種細胞介素接觸(例如,一或多種選自IL-2、IL-7、IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))、IL-21、或IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)的細胞介素)。In some embodiments, the cell population is contacted with one or more cytokines (e.g., one or more cytokines selected from IL-2, IL-7, IL-15 (e.g., hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)) , IL-21, or IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra)).
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-2接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-7接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-21接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-2和IL-7接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-2和IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-2和IL-21接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-2和IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-7和IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-7和IL-21接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-7和IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))和IL-21接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))和IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-21和IL-6(例如,IL-6/sIL-6Ra)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與IL-7、IL-15(例如,hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra))、和IL-21接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體進一步與LSD1抑制劑接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體進一步與MALT1抑制劑接觸。In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-2. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-7. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-21. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-2 and IL-7. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-2 and IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-2 and IL-21. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-2 and IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-7 and IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-7 and IL-21. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-7 and IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)) and IL-21. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15 (IL15/sIL-15Ra)) and IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-21 and IL-6 (eg, IL-6/sIL-6Ra). In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with IL-7, IL-15 (eg, hetIL-15(IL15/sIL-15Ra)), and IL-21. In some embodiments, the population of cells is further contacted with an LSD1 inhibitor. In some embodiments, the population of cells is further contacted with a MALT1 inhibitor.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與20、30、40、50、60、70、80、90、100、110、120、130、140、150、160、170、180、190、200、210、220、230、240、250、260、270、280、290、或300 U/ml的IL-2接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、15、16、17、18、19、或20 ng/ml的IL-7接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、15、16、17、18、19、或20 ng/ml的IL-15接觸。In some embodiments, the population of cells is combined with 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, 210, 220, 230, 240, 250, 260, 270, 280, 290, or 300 U/ml of IL-2 exposure. In some embodiments, the cell population is combined with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, or 20 ng/ml IL-7 exposure. In some embodiments, the cell population is combined with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, or 20 ng/ml IL-15 exposure.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的核酸分子(例如,一或多個核酸分子)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的DNA分子(例如,一或多個DNA分子)轉導細胞群體。In some embodiments, a population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule (eg, one or more nucleic acid molecules) encoding a CAR (eg, one or more CARs). In some embodiments, a DNA molecule (eg, one or more DNA molecules) encoding a CAR (eg, one or more CARs) is transduced into a population of cells.
在一些實施方式中,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸同時使細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4、4.5、5、5.5、6、6.5、7、7.5、8、8.5、9、9.5或10小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於5小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於4小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於3小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於2小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於1小時,使細胞群體與編碼一或多個CAR的核酸分子接觸。In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs simultaneously with the population of cells with one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, no later than 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 6.5, 7, 7.5 days after initiation of contact of the cell population with one or more of the above-mentioned cytokines , 8, 8.5, 9, 9.5, or 10 hours, contacting the population of cells with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs no later than 5 hours after the initiation of contacting the population of cells with the one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs no later than 4 hours after the initiation of contacting the population of cells with the one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs no later than 3 hours after the initiation of contacting the population of cells with the one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs no later than 2 hours after the initiation of contacting the population of cells with the one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding one or more CARs no later than 1 hour after the initiation of contacting the population of cells with the one or more cytokines described above.
在一些實施方式中,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, a population of cells is harvested for storage or administration.
在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於72、60、48、36、32、31、30、29、28、27、26、25、24、23、22、21、20、19、或18小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於26小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於25小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於24小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於23小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。在一些實施方式中,在細胞群體與上述一或多種細胞介素接觸開始後不遲於22小時,收穫細胞群體用於儲存或投與。In some embodiments, no later than 72, 60, 48, 36, 32, 31, 30, 29, 28, 27, 26, 25, 24, 23 after initiation of contact of the cell population with one or more of the above-mentioned cytokines , 22, 21, 20, 19, or 18 hours, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration no later than 26 hours after initiation of contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration no later than 25 hours after initiation of contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration no later than 24 hours after initiation of contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration no later than 23 hours after initiation of contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is harvested for storage or administration no later than 22 hours after initiation of contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines described above.
在一些實施方式中,細胞群體不是離體擴增的。In some embodiments, the population of cells is not expanded ex vivo.
在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、或60%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過5%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過10%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過15%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過20%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過25%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過30%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過35%。在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過40%。In some embodiments, for example, the cell population expands by no more than 5%, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. %, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15%, 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, or 60%. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 5%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 10%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 15%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 20%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 25%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is not expanded by more than 30%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population expands by no more than 35%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above. In some embodiments, the cell population is not expanded by more than 40%, eg, as assessed by viable cell number, compared to the cell population prior to contacting the cell population with one or more cytokines as described above.
在一些實施方式中,例如,如藉由活細胞數目進行評估,與在細胞群體與一或多種如上所述之細胞介素接觸之前的細胞群體相比,細胞群體擴增不超過1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4、4.5、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、16、20、24、36、或48小時。In some embodiments, for example, the cell population expands by no more than 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 16, 20, 24, 36, or 48 hours.
在一些實施方式中,細胞群體在體外不與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑(例如抗CD3抗體)和/或刺激細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑(例如抗CD28抗體)接觸,或如果進行接觸,接觸步驟少於1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4、4.5、或5小時。In some embodiments, the cell population is not contacted in vitro with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex (e.g., an anti-CD3 antibody) and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface (e.g., an anti-CD28 antibody), or if the Contacting, the contacting step is less than 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, or 5 hours.
在一些實施方式中,細胞群體在體外與刺激CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑(例如抗CD3抗體)和/或刺激細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑(例如抗CD28抗體)接觸20、21、22、23、24、25、26、27、或28小時。In some embodiments, the population of cells is contacted in vitro with an agent that stimulates the CD3/TCR complex (eg, an anti-CD3 antibody) and/or an agent that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the cell surface (eg, an anti-CD28 antibody) 20, 21, 22 , 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, or 28 hours.
在一些實施方式中,與藉由其他類似方法製備的細胞相比,使用本文提供的細胞介素過程製造的細胞群體顯示在表現CAR的細胞中較高百分比的初始細胞(例如,至少高5%、6%、7%、8%、9%、10%、11%、12%、13%、14%、15%、16%、17%、18%、19%、20%、25%、30%、35%、40%、45%、50%、55%、或60%),該其他類似方法還包括使細胞群體與例如,結合CD3/TCR複合物的藥劑(例如,抗CD3抗體)和/或結合細胞表面上的共刺激分子的藥劑(例如,抗CD28抗體)接觸。In some embodiments, cell populations made using the cytokine processes provided herein exhibit a higher percentage of initial cells (e.g., at least 5% higher) among CAR-expressing cells compared to cells made by other similar methods , 6%, 7%, 8%, 9%, 10%, 11%, 12%, 13%, 14%, 15%, 16%, 17%, 18%, 19%, 20%, 25%, 30% %, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, or 60%), the other similar methods also include making the cell population with, for example, an agent that binds to the CD3/TCR complex (for example, an anti-CD3 antibody) and and/or agents (eg, anti-CD28 antibodies) that bind costimulatory molecules on the cell surface.
在一些實施方式中,本文提供的細胞介素過程在包含不超過0%、0.5%、1%、1.5%、2%、2.5%、3%、3.5%、4%、4.5%、5%、5.5%、6%、6.5%、7%、7.5%、或8%血清的細胞培養基中進行。在一些實施方式中,本文提供的細胞介素過程在包含LSD1抑制劑、MALT1抑制劑或其組合的細胞培養基中進行。 其他示例性製造方法 In some embodiments, the cytokine process provided herein comprises no more than 0%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, 2%, 2.5%, 3%, 3.5%, 4%, 4.5%, 5%, 5.5%, 6%, 6.5%, 7%, 7.5%, or 8% serum in cell culture medium. In some embodiments, the cytokine processes provided herein are performed in a cell culture medium comprising an LSD1 inhibitor, a MALT1 inhibitor, or a combination thereof. Other Exemplary Manufacturing Methods
在一些實施方式中,細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)被激活,例如,使用包被Dynabeads ®的抗CD3/抗CD28抗體與編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的一或多個核酸分子接觸,然後在體外擴增,例如7、8、9、10或11天。在一些實施方式中,細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)選自新鮮或冷凍保存的白血球去除術樣本,例如,使用陽性或陰性選擇。在一些實施方式中,使細胞與編碼CAR(例如,一或多個CAR)的核酸分子(例如,一或多個核酸分子)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞與編碼本文揭露的串聯或雙重CAR的核酸分子(例如,CD19/CD22串聯或雙重CAR)接觸。在一些實施方式中,使細胞與兩個核酸分子接觸,一個表現第一CAR(例如,抗CD22 CAR),另一個表現第二CAR(例如,抗CD19 CAR)。在一些實施方式中,使細胞與編碼雙抗體CAR的核酸分子(例如,本文揭露的抗CD22/抗CD19雙抗體CAR)接觸。 淘洗 In some embodiments, cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) are activated, e.g., using Dynabeads® coated anti-CD3/anti-CD28 antibodies with one or more CARs (e.g., one or more CARs) The nucleic acid molecules are contacted and then amplified in vitro, eg, for 7, 8, 9, 10 or 11 days. In some embodiments, cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) are selected from fresh or cryopreserved leukapheresis samples, eg, using positive or negative selection. In some embodiments, the cell is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule (eg, one or more nucleic acid molecules) encoding a CAR (eg, one or more CARs). In some embodiments, a cell is contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a tandem or dual CAR disclosed herein (eg, a CD19/CD22 tandem or dual CAR). In some embodiments, the cell is contacted with two nucleic acid molecules, one expressing a first CAR (eg, an anti-CD22 CAR) and the other expressing a second CAR (eg, an anti-CD19 CAR). In some embodiments, cells are contacted with a nucleic acid molecule encoding a diabody CAR (eg, an anti-CD22/anti-CD19 diabody CAR disclosed herein). panning
在一些實施方式中,本文描述的方法的特徵在於淘洗方法,其去除不需要的細胞,例如單核細胞和胚細胞,從而導致適合CAR表現的所需免疫效應細胞的富集改進。在一些實施方式中,本文所述之淘洗方法針對從先前冷凍的樣本(例如,解凍的樣本)富集適合CAR表現的所希望的免疫效應細胞進行了優化。在一些實施方式中,與從本領域已知的淘洗方案收集的細胞製劑相比,本文所述之淘洗方法提供了具有改進的純度的細胞製劑。在一些實施方式中,本文所述之淘洗方法包括使用起始樣本(例如,細胞樣本,例如,解凍的細胞樣本)優化的黏度,藉由用某些等滲溶液(例如,PBS)稀釋,並使用流速的優化組合並藉由淘洗裝置收集的每個級分的收集體積。可應用於本發明的示例性淘洗方法描述於WO 2017/117112的第48-51頁,其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。 密度梯度離心 In some embodiments, the methods described herein are characterized by a panning method that removes unwanted cells, such as monocytes and blast cells, resulting in improved enrichment of desired immune effector cells suitable for CAR expression. In some embodiments, the panning methods described herein are optimized for enrichment of desired immune effector cells suitable for CAR expression from previously frozen samples (eg, thawed samples). In some embodiments, the elutriation methods described herein provide cell preparations with improved purity compared to cell preparations collected from elutriation protocols known in the art. In some embodiments, the elutriation methods described herein comprise using an optimized viscosity of a starting sample (e.g., a cell sample, e.g., a thawed cell sample) by diluting with certain isotonic solutions (e.g., PBS), And the collection volume of each fraction collected by the elutriation device using an optimized combination of flow rates. Exemplary elutriation methods applicable to the present invention are described on pages 48-51 of WO 2017/117112, which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. density gradient centrifugation
過繼性細胞治療產品的製造需要使所希望的細胞(例如,免疫效應細胞)遠離周圍血單采血起始材料中存在的血細胞和血液成分的複雜混合物。通過Ficoll溶液使用密度梯度離心成功分離了周圍血衍生的淋巴球樣本。然而,Ficoll不是用於分離治療用細胞的較佳的試劑,因為Ficoll不適合臨床使用。此外,Ficoll含有乙二醇,它對細胞有潛在毒性。此外,冷凍保存後解凍的單采血產物的Ficoll密度梯度離心產生次優的T細胞產物,例如,如本文實例中所述。例如,在通過Ficoll溶液的密度梯度離心分離的細胞製劑中觀察到最終產物中T細胞的損失,伴隨非T細胞的相對增加,尤其是不希望的B細胞、胚細胞和單核細胞。The manufacture of adoptive cell therapy products requires that the desired cells (eg, immune effector cells) be kept away from the complex mixture of blood cells and blood components present in the starting material of the peripheral blood apheresis. Peripheral blood-derived lymphocyte samples were successfully isolated using density gradient centrifugation through Ficoll solution. However, Ficoll is not a preferred reagent for isolating cells for therapy because Ficoll is not suitable for clinical use. In addition, Ficoll contains ethylene glycol, which is potentially toxic to cells. Furthermore, Ficoll density gradient centrifugation of thawed apheresis products following cryopreservation yields suboptimal T cell products, eg, as described in the Examples herein. For example, in cell preparations separated by density gradient centrifugation of Ficoll solution, a loss of T cells in the final product was observed, accompanied by a relative increase in non-T cells, especially unwanted B cells, blasts and monocytes.
不希望受理論束縛,據信免疫效應細胞(例如T細胞)在冷凍保存期間脫水,變得比新鮮細胞更稠密。不希望受理論束縛,還據信免疫效應細胞(例如T細胞)比其他血細胞保持密集更久,因此與其他細胞相比,在Ficoll密度梯度分離期間更容易丟失。因此,不希望受理論束縛,與Ficoll或具有與Ficoll相同密度(例如,1.077 g/mL)的其他培養基相比,認為密度大於Ficoll的培養基提供了所希望的免疫效應細胞的改進的分離。Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that immune effector cells (eg T cells) dehydrate during cryopreservation and become denser than fresh cells. Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is also believed that immune effector cells, such as T cells, remain denser longer than other blood cells and thus are more easily lost during Ficoll density gradient separation than other cells. Therefore, without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that media with a density greater than Ficoll provide the desired improved isolation of immune effector cells compared to Ficoll or other media with the same density as Ficoll (eg, 1.077 g/mL).
在一些實施方式中,本文所述之密度梯度離心方法包括使用包含碘克沙醇的密度梯度培養基。在一些實施方式中,密度梯度培養基包含約60%的碘克沙醇於水中的溶液。In some embodiments, the density gradient centrifugation methods described herein comprise the use of a density gradient medium comprising iodixanol. In some embodiments, the density gradient medium comprises about 60% iodixanol in water.
在一些實施方式中,本文所述之密度梯度離心方法包括使用具有密度大於Ficoll的密度梯度培養基。在一些實施方式中,本文所述之密度梯度離心方法包括使用密度梯度培養基,該密度梯度培養基具有大於1.077 g/mL,例如,大於1.077 g/mL、大於1.1 g/mL、大於1.15 g/mL、大於1.2 g/mL、大於1.25 g/mL、大於1.3 g/mL、大於1.31 g/mL的密度。在一些實施方式中,該密度梯度培養基具有約1.32 g/mL的密度。In some embodiments, the density gradient centrifugation methods described herein comprise using a density gradient medium having a density greater than Ficoll. In some embodiments, the density gradient centrifugation methods described herein comprise using a density gradient medium having a density gradient medium having a density greater than 1.077 g/mL, e.g., greater than 1.077 g/mL, greater than 1.1 g/mL, greater than 1.15 g/mL , Density greater than 1.2 g/mL, greater than 1.25 g/mL, greater than 1.3 g/mL, greater than 1.31 g/mL. In some embodiments, the density gradient medium has a density of about 1.32 g/mL.
密度梯度離心的另外的實施方式描述於WO 2017/117112的第51-53頁,其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。 藉由選擇富集 Additional embodiments of density gradient centrifugation are described on pages 51-53 of WO 2017/117112, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. enrichment by selection
本文提供了選擇特定細胞以改進適合CAR表現的所希望的免疫效應細胞富集之方法。在一些實施方式中,選擇包含陽性選擇,例如,選擇所需的免疫效應細胞。在一些實施方式中,選擇包含陰性選擇,例如,選擇不需要的細胞,例如,去除不需要的細胞。在實施方式中,本文所述之陽性或陰性選擇方法在流動條件下進行,例如,藉由使用流通裝置,例如本文所述之流通裝置。示例性的陽性和陰性選擇描述於WO 2017/117112的第53-57頁,其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。選擇方法可以在流動條件下進行,例如,藉由使用流通裝置,也稱為細胞加工系統,以進一步富集所希望的免疫效應細胞(例如,適合用於CAR表現的T細胞)的細胞製劑。示例性的流通裝置描述於WO 2017/117112的第57-70頁,其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。示例性細胞分離和去珠方法描述於WO 2017/117112的第70-78頁,其藉由引用以其全文併入本文。Provided herein are methods of selecting specific cells to improve the enrichment of desired immune effector cells suitable for CAR expression. In some embodiments, selection comprises positive selection, eg, selection of desired immune effector cells. In some embodiments, selecting comprises negative selection, eg, selecting for unwanted cells, eg, removing unwanted cells. In embodiments, the positive or negative selection methods described herein are performed under flow conditions, eg, by using a flow-through device, such as a flow-through device described herein. Exemplary positive and negative selections are described on pages 53-57 of WO 2017/117112, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. Selection methods can be performed under flow conditions, for example, by using a flow-through device, also known as a cell processing system, to further enrich the cell preparation for desired immune effector cells (eg, T cells suitable for CAR expression). Exemplary flow-through devices are described on pages 57-70 of WO 2017/117112, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. Exemplary cell isolation and debeading methods are described on pages 70-78 of WO 2017/117112, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
選擇程序不限於WO 2017/117112的第57-70頁所述之程序。可以使用經由CD19、CD14和CD26 Miltenyi珠與柱技術(CliniMACS ®Plus或CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®)組合去除不需要的細胞進行陰性T細胞選擇,或可以使用CD4和CD8 Miltenyi珠與柱技術的組合進行陽性T細胞選擇(CliniMACS ®Plus或CliniMACS ®Prodigy ®)。可替代地,可以使用具有可釋放CD3珠的無柱技術(GE醫療集團(GE Healthcare))。 The selection procedure is not limited to the procedure described on pages 57-70 of WO 2017/117112. Negative T cell selection can be performed using a combination of CD19, CD14 and CD26 Miltenyi bead and column technology (CliniMACS ® Plus or CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® ) for negative T cell selection or can be positive using a combination of CD4 and CD8 Miltenyi bead and column technology T cell selection (CliniMACS ® Plus or CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® ). Alternatively, column-free technology with releasable CD3 beads (GE Healthcare) can be used.
此外,還可以使用諸如ThermoGenesis X系列裝置的無珠技術。Additionally, bead-free technology such as the ThermoGenesis X-Series devices can be used.
本文揭露的製備細胞之方法包括本領域已知的那些,例如,如CN 108103105、CN 108085342、CN 108018312、CN 107287164、WO 18052947、WO 17123956、WO 17114497、WO 17103596、WO 17068421、WO 17023803、WO 17015427、WO 16196388、WO 16168595、WO 14186469、WO 17165245、 WO 18106732、WO 17015490、WO 18075813、WO 18102761、WO 17127755、WO 17214333、WO 18059549、WO 17190100、WO 16180778、WO 18057823、和/或 CN 106957822中所述之,該等申請中的每個藉由引用以其全文併入本文。 細胞來源 Methods for preparing cells disclosed herein include those known in the art, for example, such as CN 108103105, CN 108085342, CN 108018312, CN 107287164, WO 18052947, WO 17123956, WO 17114497, WO 17103596, WO 170678421, WO 301, WO 1702 、WO 16196388、WO 16168595、WO 14186469、WO 17165245、 WO 18106732、WO 17015490、WO 18075813、WO 18102761、WO 17127755、WO 17214333、WO 18059549、WO 17190100、WO 16180778、WO 18057823、和/或CN 106957822中所As stated, each of these applications is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. cell source
在擴增和基因修飾或其他修飾之前,可以從受試者獲得細胞來源,例如T細胞或自然殺手(NK)細胞。術語「受試者」旨在包括可以在其中引發免疫反應的活生物體(例如,哺乳動物)。受試者之實例包括人、猴、黑猩猩、狗、貓、小鼠、大鼠及其轉基因物種。T細胞可以從許多來源獲得,包括周圍血單核細胞、骨髓、淋巴結組織、臍帶血、胸腺組織、來自感染部位的組織、腹水、胸膜積液、脾組織、和腫瘤。在本發明之揭露內容的某些方面,可以使用熟悉該項技術者已知的任意數目的技術,例如Ficoll™分離,從採集自受試者的血液單位獲得免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞。在一個較佳的方面,藉由單采血液成分術獲得來自個體的循環血液的細胞。單采血液成分術產物典型地含有淋巴球,包括T細胞、單核細胞、粒細胞、B細胞、其他有核白血球、紅血球、和血小板。在一方面,可以洗滌藉由單采血液成分術收集的細胞以除去血漿部分,並視需要將細胞置於合適的緩衝液或培養基中以用於後續處理步驟。在本發明之一個方面,用磷酸鹽緩衝鹽水(PBS)洗滌細胞。在可替代的方面,洗滌溶液缺乏鈣並且可缺乏鎂,或者可缺乏許多(如果不是全部)二價陽離子。在不存在鈣的情況下的初始活化步驟可以導致放大的活化。如熟悉該項技術者將容易理解的,洗滌步驟可以藉由熟悉該項技術者已知的方法完成,如藉由根據製造商的說明使用半自動「流通」離心機(例如,Cobe 2991細胞處理器、Baxter CytoMate、或Haemonetics Cell Saver 5)。在洗滌後,可以將細胞重懸於多種生物相容性緩衝液中,例如像無Ca、無Mg的PBS、PlasmaLyte A、或者含有或不含緩衝液的其他鹽溶液。替代性地,可以除去單采血液成分術樣本中不希望的組分,並將細胞直接重懸於培養基中。Cell sources, such as T cells or natural killer (NK) cells, may be obtained from the subject prior to expansion and genetic modification or other modification. The term "subject" is intended to include living organisms (eg, mammals) in which an immune response can be elicited. Examples of subjects include humans, monkeys, chimpanzees, dogs, cats, mice, rats, and transgenic species thereof. T cells can be obtained from a number of sources, including peripheral blood mononuclear cells, bone marrow, lymph node tissue, cord blood, thymus tissue, tissue from a site of infection, ascites, pleural effusion, spleen tissue, and tumors. In certain aspects of the present disclosure, immune effector cells, such as T cells, can be obtained from blood units collected from a subject using any number of techniques known to those skilled in the art, such as Ficoll™ isolation. In a preferred aspect, cells from the circulating blood of the individual are obtained by apheresis. Apheresis products typically contain lymphocytes, including T cells, monocytes, granulocytes, B cells, other nucleated white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. In one aspect, cells collected by apheresis can be washed to remove the plasma fraction and, if desired, placed in a suitable buffer or culture medium for subsequent processing steps. In one aspect of the invention, cells are washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). In alternative aspects, the wash solution is deficient in calcium and may be deficient in magnesium, or may be deficient in many, if not all, divalent cations. An initial activation step in the absence of calcium can result in an amplified activation. As will be readily understood by those skilled in the art, the washing steps can be accomplished by methods known to those skilled in the art, such as by using a semi-automatic "flow-through" centrifuge (e.g., a Cobe 2991 Cell Processor) according to the manufacturer's instructions. , Baxter CytoMate, or Haemonetics Cell Saver 5). After washing, the cells can be resuspended in a variety of biocompatible buffers like, for example, Ca-free, Mg-free PBS, PlasmaLyte A, or other saline solutions with or without buffer. Alternatively, an apheresis sample can be stripped of unwanted components and the cells resuspended directly in culture medium.
在一方面,藉由裂解紅血球和耗減單核細胞(例如,藉由PERCOLLTM梯度離心或藉由對流離心淘洗)從周圍血淋巴球分離T細胞。In one aspect, T cells are isolated from peripheral blood lymphocytes by lysing erythrocytes and depleting monocytes (eg, by PERCOLL™ gradient centrifugation or by convection centrifugation).
本文描述的方法可以包括,例如使用例如(例如本文描述的)陰性選擇技術選擇免疫效應細胞(例如T細胞)的特定亞群,該亞群係T調節細胞耗減的群體,CD25+耗減的細胞。較佳的是,T調節耗減的細胞群體含有少於30%、25%、20%、15%、10%、5%、4%、3%、2%、1%的CD25+細胞。The methods described herein may include, for example, using negative selection techniques such as described herein to select specific subpopulations of immune effector cells (e.g. T cells), the subpopulations being T regulatory cell depleted populations, CD25+ depleted cells . Preferably, the T regulatory depleted cell population contains less than 30%, 25%, 20%, 15%, 10%, 5%, 4%, 3%, 2%, 1% CD25+ cells.
在一個實施方式中,使用抗C25抗體或其片段或CD25結合配體IL-2從群體中除去T調節性細胞,例如CD25+ T細胞。在一個實施方式中,抗CD25抗體或其片段或CD25結合配體與底物(例如,珠)軛合,或者以其他方式包被在底物例如珠上。在一個實施方式中,抗CD25抗體或其片段與如本文所述之底物軛合。In one embodiment, T regulatory cells, eg, CD25+ T cells, are depleted from a population using an anti-C25 antibody or fragment thereof or the CD25 binding ligand IL-2. In one embodiment, an anti-CD25 antibody or fragment thereof or a CD25-binding ligand is conjugated to, or otherwise coated on, a substrate (eg, beads). In one embodiment, an anti-CD25 antibody or fragment thereof is conjugated to a substrate as described herein.
在一個實施方式中,使用來自Militenyi TM的CD25耗減試劑從群體中除去T調節性細胞,例如CD25+ T細胞。在一個實施方式中,細胞與CD25耗減藥劑的比率係1e7個細胞至20 uL、或1e7個細胞至15 uL、或1e7個細胞至10 uL、或1e7個細胞至5 uL、或1e7個細胞至2.5 uL、或1e7個細胞至1.25 uL。 In one embodiment, T regulatory cells, such as CD25+ T cells, are depleted from a population using CD25 depleting reagents from Militenyi ™ . In one embodiment, the ratio of cells to CD25 depleting agent is 1e7 cells to 20 uL, or 1e7 cells to 15 uL, or 1e7 cells to 10 uL, or 1e7 cells to 5 uL, or 1e7 cells to 2.5 uL, or 1e7 cells to 1.25 uL.
在一個實施方式中,待耗減的免疫效應細胞群體包括約6 × 10 9個CD25+ T細胞。在其他方面,待耗減的免疫效應細胞群體包括約1 × 10 9至1 × 10 10個CD25+ T細胞,以及其間的任何整數值。在一個實施方式中,所產生的T調節性耗減細胞群體具有2 × 10 9個T調節性細胞(例如,CD25+細胞)或更少(例如,1 × 10 9、5 × 10 8、1 × 10 8、5 × 10 7、1 × 10 7或更少的CD25+細胞)。 In one embodiment, the population of immune effector cells to be depleted comprises about 6 x 10 9 CD25+ T cells. In other aspects, the population of immune effector cells to be depleted comprises about 1 x 109 to 1 x 1010 CD25+ T cells, and any integer value therebetween. In one embodiment, the resulting population of T regulatory-depleted cells has 2 x 10 9 T regulatory cells (eg, CD25+ cells) or fewer (eg, 1 x 10 9 , 5 x 10 8 , 1 x 10 8 , 5 × 10 7 , 1 × 10 7 or less CD25+ cells).
在一個實施方式中,使用具有耗減管件組的CliniMAC系統(例如像管件162-01)從群體中去除T調節性細胞,例如CD25+細胞。在一個實施方式中,CliniMAC系統在耗減設置例如像DEPLETION2.1上運行。In one embodiment, T regulatory cells, such as CD25+ cells, are depleted from a population using a CliniMAC system with a depleting tubing set, such as tubing 162-01 for example. In one embodiment, the CliniMAC system is run on a depletion setting like DEPLETION 2.1, for example.
本文描述的方法可以包括多於一個的選擇步驟,例如多於一個的耗減步驟。可以例如用針對陰性選擇的細胞特有的表面標誌物的抗體組合來完成藉由陰性選擇富集T細胞群體。一種方法係通過負磁性免疫吸附或流動式細胞測量術進行細胞分選和/或選擇,該負磁性免疫吸附或流動式細胞測量術使用針對存在於陰性選擇的細胞上的細胞表面標誌物的單株抗體的混合物。例如,為了藉由陰性選擇富集CD4+細胞,單株抗體混合物可以包括針對CD14、CD20、CD11b、CD16、HLA-DR、和CD8的抗體。The methods described herein may comprise more than one selection step, eg more than one depletion step. Enrichment of a T cell population by negative selection can be accomplished, for example, with a combination of antibodies directed against surface markers specific to the negatively selected cells. One method is cell sorting and/or selection by negative magnetic immunoadsorption or flow cytometry using a single cell surface marker directed against a cell surface marker present on negatively selected cells. Antibody mixture. For example, to enrich for CD4+ cells by negative selection, the monoclonal antibody cocktail can include antibodies against CD14, CD20, CD11b, CD16, HLA-DR, and CD8.
還提供了包括以下的方法:從表現檢查點抑制劑(例如本文描述的檢查點抑制劑)的群體除去細胞(例如PD1+細胞、LAG3+細胞、和TIM3+細胞中的一或多種),從而提供T調節耗減的(例如CD25+耗減的)細胞和檢查點抑制劑耗減的細胞(例如PD1+、LAG3+和/或TIM3+耗減的細胞)群體。示例性檢查點抑制劑包括B7-H1、B&-1、CD160、P1H、2B4、PD1、TIM3、CEACAM(例如,CEACAM-1、CEACAM-3和/或CEACAM-5)、LAG3、TIGIT、CTLA-4、BTLA和LAIR1。在一個實施方式中,將檢查點抑制劑表現細胞與T調節性例如CD25+細胞同時去除。例如,抗C25抗體或其片段以及抗檢查點抑制劑抗體或其片段可以附接至可以用於去除細胞的同一珠上;或者抗CD25抗體或其片段和抗檢查點抑制劑抗體或其片段可以附接至其混合物可以用於去除細胞的分開的珠上。在一些實施方式中,T調節性細胞(例如,CD25+細胞)的去除和檢查點抑制劑表現細胞的去除係依序的,並且可以例如按任一順序發生。Also provided are methods comprising removing cells (e.g., one or more of PD1+ cells, LAG3+ cells, and TIM3+ cells) from a population expressing a checkpoint inhibitor, such as a checkpoint inhibitor described herein, thereby providing T modulating Populations of depleted (eg CD25+ depleted) cells and checkpoint inhibitor depleted cells (eg PD1+, LAG3+ and/or TIM3+ depleted cells). Exemplary checkpoint inhibitors include B7-H1, B&-1, CD160, P1H, 2B4, PD1, TIM3, CEACAM (e.g., CEACAM-1, CEACAM-3 and/or CEACAM-5), LAG3, TIGIT, CTLA- 4. BTLA and LAIR1. In one embodiment, checkpoint inhibitor expressing cells are depleted simultaneously with T regulatory, eg, CD25+ cells. For example, an anti-C25 antibody or fragment thereof and an anti-checkpoint inhibitor antibody or fragment thereof can be attached to the same bead that can be used to remove cells; or an anti-CD25 antibody or fragment thereof and an anti-checkpoint inhibitor antibody or fragment thereof can be Attached to separate beads whose mixture can be used to remove cells. In some embodiments, depletion of T regulatory cells (eg, CD25+ cells) and depletion of checkpoint inhibitor expressing cells are sequential and can occur, for example, in either order.
本文所述之方法可以包括陽性選擇步驟。例如,可以藉由將T細胞與抗-CD3/抗-CD28(例如,3 x 28)軛合的珠(如DYNABEADS® M-450 CD3/CD28 T)一起孵育足以對所希望的T細胞進行陽性選擇的時間段來分離該等T細胞。在一方面,該時間段係約30分鐘。在另一個方面,該時間段的範圍為30分鐘至36小時或更長以及其間的所有整數值。在另一個方面,該時間段為至少1、2、3、4、5、或6小時。在又另一個較佳的方面,該時間段係10至24小時。在一方面,孵育時間段係24小時。與其他細胞類型相比,在存在較少T細胞的任何情況下,如從腫瘤組織或免疫受損個體分離腫瘤浸潤淋巴球(TIL),可以使用更長的孵育時間來分離T細胞。此外,使用更長的孵育時間可以提高CD8+ T細胞捕獲的效率。因此,藉由簡單地縮短或延長使T細胞與CD3/CD28珠結合的時間和/或藉由增加或減少珠與T細胞的比率(如本文進一步描述的),可以在培養起始時或在該過程期間的其他時間點優先地選擇或針對T細胞亞群。另外,藉由增加或減少抗CD3和/或抗CD28抗體在珠或其他表面上的比率,可以在培養起始時或在其他希望的時間點優先地選擇或針對T細胞亞群。The methods described herein may include a positive selection step. For example, it may be sufficient to positively posit desired T cells by incubating T cells with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 (e.g., 3 x 28) conjugated beads (e.g. DYNABEADS® M-450 CD3/CD28 T) The selected time period is used to isolate the T cells. In one aspect, the period of time is about 30 minutes. In another aspect, the time period ranges from 30 minutes to 36 hours or longer and all integer values therebetween. In another aspect, the period of time is at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 hours. In yet another preferred aspect, the period of time is 10 to 24 hours. In one aspect, the incubation period is 24 hours. In any situation where fewer T cells are present, such as isolating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) from tumor tissue or from immunocompromised individuals, longer incubation times can be used to isolate T cells compared to other cell types. In addition, using longer incubation times can increase the efficiency of CD8+ T cell capture. Thus, by simply shortening or prolonging the time that T cells are allowed to bind to CD3/CD28 beads and/or by increasing or decreasing the ratio of beads to T cells (as further described herein), it is possible to either start the culture or at the beginning of the culture. Other time points during the process preferentially select for or target T cell subsets. Additionally, by increasing or decreasing the ratio of anti-CD3 and/or anti-CD28 antibodies on beads or other surfaces, T cell subsets can be preferentially selected or targeted at the initiation of culture or at other desired time points.
在一個實施方式中,可以選擇表現以下中的一或多種的T細胞群體:IFN-γ、TNFα、IL-17A、IL-2、IL-3、IL-4、GM-CSF、IL-10、IL-13、顆粒酶B、和穿孔素、或其他適當的分子(例如,其他細胞介素)。篩選細胞表現的方法可以藉由例如PCT公開案號WO 2013/126712中描述的方法來確定。In one embodiment, a T cell population can be selected that expresses one or more of: IFN-γ, TNFα, IL-17A, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, GM-CSF, IL-10, IL-13, granzyme B, and perforin, or other appropriate molecules (eg, other cytokines). The method of screening for cell expression can be determined by, for example, the method described in PCT Publication No. WO 2013/126712.
為了藉由陽性或陰性選擇分離希望的細胞群體,可以改變細胞和表面(例如顆粒(如珠))的濃度。在某些方面,可能希望顯著減小其中珠和細胞混合在一起的體積(例如,增加細胞的濃度),以確保細胞和珠的最大接觸。例如,在一方面,使用約100億個細胞/ml、90億個/ml、80億個/ml、70億個/ml、60億個/ml、或50億個/ml的濃度。在一方面,使用10億個細胞/ml的濃度。在一方面,使用7500萬、8000萬、8500萬、9000萬、9500萬、或1億個細胞/ml的細胞濃度。在另外的方面,可以使用125或150百萬個細胞/ml的濃度。To isolate desired cell populations by positive or negative selection, the concentration of cells and surfaces (eg particles such as beads) can be varied. In some aspects, it may be desirable to significantly reduce the volume in which beads and cells are mixed together (eg, increase the concentration of cells) to ensure maximum cell and bead contact. For example, in one aspect, a concentration of about 10 billion cells/ml, 9 billion/ml, 8 billion/ml, 7 billion/ml, 6 billion/ml, or 5 billion/ml is used. In one aspect, a concentration of 1 billion cells/ml is used. In one aspect, a cell concentration of 75 million, 80 million, 85 million, 90 million, 95 million, or 100 million cells/ml is used. In additional aspects, concentrations of 125 or 150 million cells/ml can be used.
使用高濃度可以導致細胞產量增加、細胞活化、和細胞擴增。此外,使用高細胞濃度允許更有效地捕獲可能弱表現感興趣的靶抗原的細胞(如CD28陰性T細胞),或來自存在許多腫瘤細胞的樣本(例如白血病的血、腫瘤組織等)的細胞。此類細胞群體可能具有治療價值,並且係希望獲得的。例如,使用高濃度的細胞允許更有效地選擇通常具有較弱CD28表現的CD8+T細胞。Use of high concentrations can result in increased cell yield, cell activation, and cell expansion. Furthermore, the use of high cell concentrations allows more efficient capture of cells that may weakly express the target antigen of interest (such as CD28-negative T cells), or cells from samples where many tumor cells are present (such as leukemic blood, tumor tissue, etc.). Such cell populations may be of therapeutic value and are desirable. For example, using high concentrations of cells allows for more efficient selection of CD8+ T cells that typically have a weaker CD28 expression.
在相關方面,可能希望使用較低的細胞濃度。藉由顯著稀釋T細胞和表面的混合物(例如顆粒(如珠)),使顆粒與細胞之間的相互作用最小化。這選擇了表現大量有待結合顆粒的所希望抗原的細胞。例如,CD4+ T細胞表現較高水平的CD28,並且在稀釋濃度下比CD8+ T細胞更有效地捕獲。在一方面,所用細胞的濃度為5 × 10 6/ml。在其他方面,使用的濃度可為約1 × 10 5/ml至1 × 10 6/ml,以及其間的任何整數值。 In a related aspect, it may be desirable to use lower cell concentrations. Particle-cell interactions are minimized by significantly diluting the mixture of T cells and surfaces such as particles (eg, beads). This selects for cells expressing large quantities of the desired antigen to be bound to the particle. For example, CD4+ T cells exhibit higher levels of CD28 and are more efficiently captured than CD8+ T cells at dilute concentrations. In one aspect, cells are used at a concentration of 5 x 106 /ml. In other aspects, the concentration used may be from about 1 x 105 /ml to 1 x 106 /ml, and any integer value therebetween.
在其他方面,可以將該等細胞在旋轉器上以不同的速度在2°C-10°C或室溫下孵育不同的時間長度。In other aspects, the cells can be incubated on a rotator at different speeds at 2°C-10°C or at room temperature for different lengths of time.
用於刺激的T細胞也可以在洗滌步驟後冷凍。不希望受理論束縛,冷凍和隨後的解凍步驟藉由在細胞群體中去除粒細胞及在一定程度上去除單核細胞提供更均勻的產物。在除去血漿和血小板的洗滌步驟之後,可以將細胞懸浮在冷凍溶液中。雖然許多冷凍溶液和參數係本領域已知的並且在這種情況下將是有用的,但一種方法涉及使用含有20% DMSO和8%人血清白蛋白的PBS,或含有10%葡聚糖40和5%葡萄糖、20%人血清白蛋白和7.5% DMSO的培養基,或含有31.25% Plasmalyte-A、31.25%葡萄糖5%、0.45% NaCl、10%葡聚糖40和5%葡萄糖、20%人血清白蛋白和7.5% DMSO的培養基,或含有例如Hespan和PlasmaLyte A的其他適合的細胞冷凍培養基,然後將細胞以每分鐘1°的速率冷凍至-80°C並儲存在液氮儲罐的氣相中。可以使用其他控制冷凍的方法以及在-20°C或液氮中立即不受控制的冷凍。T cells used for stimulation can also be frozen after washing steps. Without wishing to be bound by theory, the freezing and subsequent thawing steps provide a more uniform product by removing granulocytes and to some extent monocytes in the cell population. Following a washing step to remove plasma and platelets, cells can be suspended in freezing solution. While many freezing solutions and parameters are known in the art and will be useful in this situation, one method involves the use of PBS containing 20% DMSO and 8% human serum albumin, or 10
在某些方面,將冷凍保存的細胞如本文所描述進行解凍和洗滌,並允許在使用本發明之方法活化之前在室溫靜置1小時。In certain aspects, cryopreserved cells are thawed and washed as described herein and allowed to stand at room temperature for 1 hour prior to activation using the methods of the invention.
在本發明之上下文中還考慮了在可能需要如本文描述的擴增細胞之前的時間段從受試者收集血液樣本或單采血液成分術產物。因此,可以在任何必要的時間點收集待擴增細胞的來源,並且分離和冷凍所需的細胞(如T細胞)以便後續用於免疫效應細胞療法中,以用於將受益於免疫效應細胞療法的任意數目的疾病或病症,如本文所述之那些。在一方面,血液樣本或單采血液成分術取自基本健康的受試者。在某些方面,血液樣本或單采血液成分術取自基本健康的受試者,該受試者處於發展疾病的風險中,但尚未患發展疾病,並且將感興趣的細胞分離並冷凍供以後使用。在某些方面,可以將T細胞擴增、冷凍、並在以後使用。在某些方面,在診斷如本文描述的特定疾病之後但在任何治療之前不久從患者收集樣本。在另一個方面,在任何數量的相關治療方式之前,從受試者的血液樣本或單采血液成分術分離細胞,該等相關治療方式包括但不限於用以下進行治療:藥劑(如那他珠單抗(natalizumab)、依法珠單抗、抗病毒劑)、化學療法、放射、免疫抑制劑(如環孢素、硫唑嘌呤、胺甲喋呤、黴酚酸酯、和FK506)、抗體或其他免疫清除劑(如CAMPATH、抗CD3抗體、環磷醯胺(cytoxan)、氟達拉濱(fludarabine)、環孢素、FK506、雷帕黴素、黴酚酸、類固醇、FR901228)、和照射。It is also contemplated in the context of the present invention that blood samples or apheresis products are collected from a subject for a period of time before expansion of cells as described herein may be required. Thus, a source of cells to be expanded can be harvested at any necessary time point, and the desired cells, such as T cells, can be isolated and frozen for subsequent use in immune effector cell therapy for patients who would benefit from immune effector cell therapy Any number of diseases or conditions, such as those described herein. In one aspect, a blood sample or apheresis is taken from a substantially healthy subject. In certain aspects, a blood sample or apheresis is taken from a substantially healthy subject who is at risk of developing a disease, but has not yet developed a disease, and the cells of interest are isolated and frozen for later use. In certain aspects, T cells can be expanded, frozen, and used later. In certain aspects, samples are collected from patients shortly after diagnosis of a particular disease as described herein but before any treatment. In another aspect, cells are isolated from a blood sample or apheresis of a subject prior to any number of related therapeutic modalities, including but not limited to treatment with agents such as natalizumab monoclonal antibodies (natalizumab, efalizumab, antiviral agents), chemotherapy, radiation, immunosuppressants (such as cyclosporine, azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and FK506), antibodies or Other immune depleting agents (eg, CAMPATH, anti-CD3 antibodies, cyclophosphamide (cytoxan), fludarabine, cyclosporine, FK506, rapamycin, mycophenolic acid, steroids, FR901228), and irradiation .
在本發明之另一個方面,在治療後直接從患者獲得T細胞使得受試者具有功能性T細胞。在這點上,已觀察到在某些癌症治療(特別是使用破壞免疫系統的藥物的治療)之後,在患者通常將從治療恢復期間治療後不久,所獲得的T細胞的品質因其離體擴增的能力可能是最佳或改善的。同樣地,在使用本文描述的方法進行離體操作之後,該等細胞可以處於較佳的狀態以增強植入和體內擴增。因此,在本發明之上下文中,預期在該恢復期期間收集血細胞,包括T細胞、樹突細胞或造血譜系的其他細胞。此外,在某些方面,動員(例如,用GM-CSF動員)和調整方案可以用於在受試者中產生病狀,其中特定細胞類型的再增殖、再循環、再生、和/或擴增係有利的,尤其是在治療後確定的時間視窗期間。例證性細胞類型包括免疫系統的T細胞、B細胞、樹突細胞、和其他細胞。In another aspect of the invention, T cells are obtained directly from the patient after treatment such that the subject has functional T cells. In this regard, it has been observed that following certain cancer treatments (particularly those with drugs that disrupt the immune system), shortly after treatment during which the patient would normally recover from treatment, the quality of the T cells obtained is due to their ex vivo The ability to amplify may be optimal or improved. Likewise, following ex vivo manipulation using the methods described herein, the cells can be in an optimal state for enhanced engraftment and in vivo expansion. Therefore, in the context of the present invention, it is contemplated that blood cells, including T cells, dendritic cells or other cells of the hematopoietic lineage, are collected during this recovery period. Additionally, in certain aspects, mobilization (e.g., with GM-CSF) and adjustment protocols can be used to create a pathology in a subject wherein repopulation, recycling, regeneration, and/or expansion of specific cell types This is advantageous, especially during a defined time window after treatment. Exemplary cell types include T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and other cells of the immune system.
在一個實施方式中,表現CAR分子(例如,本文所述之CAR分子)的免疫效應細胞獲自已接受低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑的受試者。在實施方式中,在足夠的時間後、或在低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑的足夠給藥後收穫經工程化以表現CAR的免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的群體,使得受試者中或從受試者收穫的PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的水平,或PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)/PD1陽性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的比率已經至少是瞬時增加了。In one embodiment, immune effector cells expressing a CAR molecule (eg, a CAR molecule described herein) are obtained from a subject who has received a low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor. In embodiments, the population of immune effector cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) engineered to express a CAR is harvested after sufficient time, or following sufficient administration of a low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor, such that Levels of PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells), or PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., T cells/NK cells)/PD1-positive immune effector cells ( For example, the ratio of T cells or NK cells) has increased at least transiently.
在一些實施方式中,已經工程化或將經工程化以表現CAR的免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的群體可以藉由接觸一定量的mTOR抑制劑進行離體處理,該mTOR抑制劑增加PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞)的數目或增加PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)/PD1陽性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的比率。In some embodiments, a population of immune effector cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that have been engineered or will be engineered to express a CAR can be treated ex vivo by exposure to an amount of an mTOR inhibitor that inhibits The agent increases the number of PD1-negative immune effector cells (eg, T cells) or increases the ratio of PD1-negative immune effector cells (eg, T cells/NK cells)/PD1-positive immune effector cells (eg, T cells or NK cells).
在一個實施方式中,T細胞群體係二醯基甘油激酶(DGK)缺陷型。DGK缺陷型細胞包括不表現DGK RNA或蛋白質,或具有降低或抑制的DGK活性的細胞。DGK缺陷型細胞可以藉由遺傳方法產生,例如投與RNA干擾劑(例如siRNA、shRNA、miRNA)以減少或預防DGK表現。替代性地,可以藉由用本文描述的DGK抑制劑處理產生DGK缺陷型細胞。In one embodiment, the population of T cells is diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) deficient. DGK-deficient cells include cells that do not express DGK RNA or protein, or have reduced or suppressed DGK activity. DGK-deficient cells can be generated by genetic methods, such as administration of RNA interference agents (eg, siRNA, shRNA, miRNA) to reduce or prevent DGK expression. Alternatively, DGK-deficient cells can be generated by treatment with a DGK inhibitor described herein.
在一個實施方式中,T細胞群體係Ikaros缺陷型。Ikaros缺陷型細胞包括不表現Ikaros RNA或蛋白質,或具有降低或抑制的Ikaros活性的細胞,Ikaros缺陷型細胞可以藉由遺傳方法產生,例如投與RNA干擾劑(例如siRNA、shRNA、miRNA)以減少或預防Ikaros表現。替代性地,可以藉由用Ikaros抑制劑(例如,來那度胺(lenalidomide))處理產生Ikaros缺陷型細胞。In one embodiment, the T cell population is Ikaros deficient. Ikaros-deficient cells include cells that do not express Ikaros RNA or protein, or have reduced or suppressed Ikaros activity, and Ikaros-deficient cells can be produced by genetic methods, such as administering RNA interference agents (such as siRNA, shRNA, miRNA) to reduce Or to prevent Ikaros manifestations. Alternatively, Ikaros-deficient cells can be generated by treatment with an Ikaros inhibitor (eg, lenalidomide).
在實施方式中,T細胞群體係DGK缺陷型且Ikaros缺陷型的,例如不表現DGK和Ikaros,或者具有降低或抑制的DGK和Ikaros活性。可以藉由本文描述的任何方法產生此類DGK和Ikaros缺陷型細胞。In an embodiment, the population of T cells is DGK deficient and Ikaros deficient, eg, does not express DGK and Ikaros, or has reduced or suppressed DGK and Ikaros activities. Such DGK and Ikaros deficient cells can be produced by any of the methods described herein.
在實施方式中,從受試者獲得NK細胞。在另一個實施方式中,NK細胞係NK細胞系,例如NK-92細胞系(Conkwest公司)。 同種異體的CART In an embodiment, NK cells are obtained from a subject. In another embodiment, the NK cell line is an NK cell line, such as NK-92 cell line (Conkwest Company). allogeneic CART
在本文所述之實施方式中,免疫效應細胞可為同種異體免疫效應細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞。例如,細胞可為同種異體T細胞,例如缺乏功能性T細胞受體(TCR)和/或人白血球抗原(HLA)(例如,HLA I類和/或HLA II類)表現的同種異體T細胞。In the embodiments described herein, the immune effector cells can be allogeneic immune effector cells, such as T cells or NK cells. For example, the cells can be allogeneic T cells, such as those lacking functional T cell receptor (TCR) and/or human leukocyte antigen (HLA) (eg, HLA class I and/or HLA class II) expression.
缺乏功能性TCR的T細胞可以例如經工程化以使其表面上不表現任何功能性TCR,經工程化以使其不表現包含功能性TCR的一或多個亞基,或者經工程化以使其表面上產生非常少的功能性TCR。替代性地,T細胞可以例如藉由表現TCR的一或多個亞基的突變或截短形式表現嚴重受損的TCR。術語「嚴重受損的TCR」意指該TCR將不在宿主中引發不利的免疫反應。可以通過使用如本文所述之一或多種基因編輯系統來產生此類細胞。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向編碼TCR組分的序列,例如TCRα恒定鏈基因(TRAC)或其調節元件中的序列。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向編碼TCR組分的序列,例如TCRβ恒定鏈基因(TRBC)或其調節元件中的序列。A T cell lacking a functional TCR can be engineered, for example, to not express any functional TCR on its surface, engineered to not express one or more subunits comprising a functional TCR, or engineered to express Very few functional TCRs are produced on its surface. Alternatively, T cells may express a severely impaired TCR, eg, by expressing a mutated or truncated form of one or more subunits of the TCR. The term "severely impaired TCR" means that the TCR will not elicit an adverse immune response in the host. Such cells can be produced by using one or more of the gene editing systems as described herein. In an embodiment, the gene editing system targets sequences encoding TCR components, such as sequences in the TCR alpha constant chain gene (TRAC) or its regulatory elements. In an embodiment, the gene editing system targets sequences encoding TCR components, such as sequences in the TCR beta constant chain gene (TRBC) or its regulatory elements.
本文描述的T細胞可以例如被工程化,使得它在其表面上不表現功能性HLA。例如,可以工程化本文描述的T細胞,使得其細胞表面HLA(例如HLA 1類和/或HLA II類)表現被下調。可以通過使用如本文所述之一或多種基因編輯系統來產生此類細胞。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向編碼一或多種HLA分子的組分的序列。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向編碼影響一或多種HLA分子表現的因子的序列。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向MHC I類表現的調節子,例如編碼β-2微球蛋白(B2M)的序列。在實施方式中,基因編輯系統靶向編碼MHC II類分子表現的調節子(例如,CIITA)的序列。在實施方式中,將靶向MHC I類表現的調節子(例如,B2M)和MHC II類分子表現的調節子(例如,CIITA)的基因編輯系統引入到細胞中,使得至少MHC I類分子和至少一種MHC II類分子表現被下調。A T cell described herein can, for example, be engineered such that it does not express functional HLA on its surface. For example, T cells described herein can be engineered such that their cell surface HLA (eg,
在一些實施方式中,T細胞可缺乏功能性TCR和功能性HLA,例如HLA I類和/或HLA II類。In some embodiments, a T cell may lack a functional TCR and a functional HLA, eg, HLA class I and/or HLA class II.
缺少功能性TCR和/或HLA表現的修飾的T細胞可以藉由任何適合的方式獲得,包括敲除或敲低TCR或HLA的一或多個亞基。例如,T細胞可以包括使用siRNA、shRNA、規律間隔重複短迴文序列簇(CRISPR)轉錄活化因子樣效應核酸酶(TALEN)、或鋅指內切核酸酶(ZFN)敲低TCR和/或HLA。Modified T cells lacking functional TCR and/or HLA expression can be obtained by any suitable means, including knockout or knockdown of one or more subunits of TCR or HLA. For example, T cells can include TCR and/or HLA knockdown using siRNA, shRNA, Cluster of Short Regularly Interspaced Repeat (CRISPR) Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nuclease (TALEN), or Zinc Finger Endonuclease (ZFN) .
在一些實施方式中,同種異體細胞可為例如藉由本文描述的任何方法不表現或以低水平表現抑制性分子的細胞。例如,該細胞可為不表現或以低水平表現抑制性分子的細胞,該抑制性分子例如可以降低表現CAR的細胞產生免疫效應子響應的能力。抑制性分子之實例包括PD1、PD-L1、CTLA4、TIM3、CEACAM(例如,CEACAM-1、CEACAM-3和/或CEACAM-5)、LAG3、VISTA、BTLA、TIGIT、LAIR1、CD160、2B4和TGFβ。抑制性分子的抑制(例如藉由在DNA、RNA或蛋白質水平上的抑制)可以優化表現CAR的細胞的性能。在實施方式中,可以使用例如如本文描述的抑制性核酸,例如抑制性核酸,例如dsRNA,例如siRNA或shRNA、規律間隔重複短迴文序列簇(CRISPR)、轉錄活化因子樣效應核酸酶(TALEN)或鋅指內切核酸酶(ZFN)。 抑制例如TCR或HLA的siRNA和shRNA In some embodiments, an allogeneic cell can be a cell that expresses no or low levels of an inhibitory molecule, eg, by any of the methods described herein. For example, the cell can be a cell that does not express, or expresses at low levels, an inhibitory molecule that, for example, can reduce the ability of the CAR-expressing cell to mount an immune effector response. Examples of inhibitory molecules include PD1, PD-L1, CTLA4, TIM3, CEACAM (e.g., CEACAM-1, CEACAM-3 and/or CEACAM-5), LAG3, VISTA, BTLA, TIGIT, LAIR1, CD160, 2B4, and TGFβ . Inhibition of inhibitory molecules (eg, by inhibition at the DNA, RNA or protein level) can optimize the performance of CAR-expressing cells. In an embodiment, inhibitory nucleic acids such as those described herein, such as inhibitory nucleic acids, such as dsRNA, such as siRNA or shRNA, cluster of regularly interspaced repeat short palindromic sequences (CRISPR), transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN ) or zinc finger endonucleases (ZFNs). siRNA and shRNA that inhibit e.g. TCR or HLA
在一些實施方式中,可以使用靶向編碼T細胞中的TCR和/或HLA的核酸的siRNA或shRNA來抑制TCR表現和/或HLA表現。In some embodiments, TCR expression and/or HLA expression can be inhibited using siRNA or shRNA targeting nucleic acids encoding TCR and/or HLA in T cells.
siRNA和shRNA在T細胞中的表現可以使用任何常規表現系統(例如像慢病毒表現系統)來實現。Expression of siRNA and shRNA in T cells can be achieved using any conventional expression system such as, for example, lentiviral expression system.
下調TCR的組分的表現的示例性shRNA描述於例如美國公開案號:2012/0321667中。下調HLA I類和/或HLA II類基因表現的示例性siRNA和shRNA描述於例如美國公開案號:US 2007/0036773中。 抑制例如TCR或HLA的CRISPR Exemplary shRNAs that down-regulate the expression of components of the TCR are described, eg, in US Publication No.: 2012/0321667. Exemplary siRNAs and shRNAs that down-regulate HLA class I and/or HLA class II gene expression are described, eg, in US Publication No.: US 2007/0036773. Inhibition of CRISPR such as TCR or HLA
如本文所用,「CRISPR」或「針對TCR和/或HLA的CRISPR」或「抑制TCR和/或HLA的CRISPR」係指一組規律間隔重複短迴文序列簇,或包含這組重複序列的系統。如本文所用,「Cas」係指CRISPR相關蛋白。「CRISPR/Cas」系統係指衍生自CRISPR和Cas的系統,該系統可以用於使TCR和/或HLA基因緘默或突變。As used herein, "CRISPR" or "CRISPR targeting TCR and/or HLA" or "CRISPR inhibiting TCR and/or HLA" refers to a cluster of regularly interspaced repeat short palindromic sequences, or a system comprising such repeating sequences . As used herein, "Cas" refers to a CRISPR-associated protein. The "CRISPR/Cas" system refers to a system derived from CRISPR and Cas, which can be used to silence or mutate TCR and/or HLA genes.
在大約40%的定序的真細菌基因組和90%的定序的古細菌中發現了天然存在的CRISPR/Cas系統。Grissa等人 (2007) BMC Bioinformatics[BMC生物資訊學] 8: 172。此系統係賦予對外來遺傳元件(如質體和噬菌體)的抗性並提供獲得性免疫的形式的原核免疫系統。Barrangou等人 (2007) Science[科學] 315: 1709-1712;Marragini等人 (2008) Science[科學] 322: 1843-1845。 Naturally occurring CRISPR/Cas systems are found in approximately 40% of sequenced eubacterial genomes and 90% of sequenced archaea. Grissa et al. (2007) BMC Bioinformatics 8: 172. This system is a prokaryotic immune system that confers resistance to foreign genetic elements such as plastids and phages and provides a form of acquired immunity. Barrangou et al. (2007) Science 315: 1709-1712; Marragini et al. (2008) Science 322: 1843-1845.
已經修飾CRISPR/Cas系統用於真核生物(如小鼠或靈長類動物)的基因編輯(緘默、增強或改變特定基因)。Wiedenheft等人 (2012) Nature[自然] 482: 331-8。這係藉由向真核細胞中引入含有特異設計的CRISPR和一或多種適當的Cas的質體來實現的。 The CRISPR/Cas system has been modified for gene editing (silencing, enhancing, or changing specific genes) in eukaryotic organisms such as mice or primates. Wiedenheft et al. (2012) Nature 482: 331-8. This is achieved by introducing into eukaryotic cells a plastid containing a specifically designed CRISPR and one or more appropriate Cas.
CRISPR序列(有時稱為CRISPR基因座)包含可替代的重複序列和間隔子。在天然存在的CRISPR中,間隔子通常包含對於細菌而言外來的序列,如質體或噬菌體序列;在TCR和/或HLA CRISPR/Cas系統中,間隔子衍生自TCR或HLA基因序列。CRISPR sequences (sometimes called CRISPR loci) contain alternative repeats and spacers. In naturally-occurring CRISPR, spacers usually contain sequences foreign to bacteria, such as plastid or phage sequences; in TCR and/or HLA CRISPR/Cas systems, spacers are derived from TCR or HLA gene sequences.
來自CRISPR基因座的RNA係組成型表現的並由Cas蛋白加工成小RNA。該等包含由重複序列側接的間隔子。RNA指導其他Cas蛋白在RNA或DNA水平緘默外源性遺傳元件。Horvath等人 (2010) Science[科學] 327: 167-170;Makarova等人 (2006) Biology Direct[生物學快訊] 1: 7。因此,類似於siRNA,間隔子充當RNA分子的模板。Pennisi (2013) Science[科學] 341: 833-836。 RNAs from CRISPR loci are constitutively expressed and processed by Cas proteins into small RNAs. These comprise spacers flanked by repeat sequences. RNA guides other Cas proteins to silence exogenous genetic elements at the RNA or DNA level. Horvath et al. (2010) Science 327: 167-170; Makarova et al. (2006) Biology Direct 1: 7. Thus, similar to siRNAs, spacers serve as templates for RNA molecules. Pennisi (2013) Science 341: 833-836.
由於該等天然存在於許多不同類型的細菌中,因此CRISPR的確切排列,和Cas基因的結構、功能和數量及其產物在物種之間略有不同。Haft等人 (2005) PLoS Comput. Biol.[公共科學圖書館醫學雜誌第一版] 1: e60;Kunin等人 (2007) Genome Biol.[基因組生物學] 8: R61;Mojica等人 (2005) J. Mol. Evol.[分子進化雜誌]60: 174-182;Bolotin等人 (2005) Microbiol.[微生物學] 151: 2551-2561;Pourcel等人 (2005) Microbiol.[微生物學] 151: 653-663;和Stern等人 (2010) Trends.Genet. [遺傳學趨勢] 28: 335-340。例如,Cse(Cas亞型,大腸桿菌)蛋白質(例如,CasA)形成功能性複合物Cascade,其將CRISPR RNA轉錄物處理成保留Cascade的間隔子重複單元。Brouns等人 (2008) Science[科學] 321: 960-964。在其他原核生物中,Cas6加工CRISPR轉錄物。大腸桿菌中基於CRISPR的噬菌體失活需要Cascade和Cas3,但不需要Cas1或Cas2。強烈火球菌(Pyrococcus furiosus)和其他原核生物中的Cmr(Cas RAMP模組)蛋白形成具有小CRISPR RNA的功能性複合物,該功能性複合物識別和裂解互補的靶RNA。更簡單的CRISPR系統依賴於蛋白質Cas9,其係具有兩個活性切割位點的核酸酶,各自對應用於雙螺旋的每股。將Cas9和修飾的CRISPR基因座RNA組合可用於基因編輯系統。Pennisi (2013) Science[科學] 341: 833-836。 Because these are naturally present in many different types of bacteria, the exact arrangement of CRISPR, and the structure, function and number of Cas genes and their products vary slightly between species. Haft et al. (2005) PLoS Comput. Biol. [PLOS Med. 1st Edition] 1: e60; Kunin et al. (2007) Genome Biol. [Genome Biology] 8: R61; Mojica et al. (2005) J. Mol. Evol. [Journal of Molecular Evolution] 60: 174-182; Bolotin et al. (2005) Microbiol. [Microbiology] 151: 2551-2561; Pourcel et al. (2005) Microbiol. [Microbiology] 151: 653 -663; and Stern et al. (2010) Trends. Genet . Trends in Genetics 28: 335-340. For example, Cse (Cas subtype, E. coli) proteins (e.g., CasA) form the functional complex Cascade, which processes CRISPR RNA transcripts into Cascade-retaining spacer repeat units. Brouns et al. (2008) Science 321: 960-964. In other prokaryotes, Cas6 processes CRISPR transcripts. CRISPR-based phage inactivation in E. coli requires Cascade and Cas3, but not Cas1 or Cas2. The Cmr (Cas RAMP module) proteins in Pyrococcus furiosus and other prokaryotes form functional complexes with small CRISPR RNAs that recognize and cleave complementary target RNAs. The simpler CRISPR system relies on the protein Cas9, a nuclease with two active cutting sites, one for each strand of the double helix. Combining Cas9 and modified CRISPR locus RNA can be used in gene editing systems. Pennisi (2013) Science 341: 833-836.
因此,CRISPR/Cas系統可用於編輯TCR和/或HLA基因(添加或刪除一或多個鹼基對),或引入提前終止,該提前終止從而降低靶基因或染色體序列如TCR和/或HLA的表現。替代性地,可以像RNA干擾一樣使用CRISPR/Cas系統,以可逆的方式關閉TCR和/或HLA基因。例如,在哺乳動物細胞中,RNA可以將Cas蛋白,例如缺乏核酸酶活性的Cas蛋白(例如,dCas9)引導至TCR和/或HLA啟動子,空間上阻斷RNA聚合酶。Therefore, the CRISPR/Cas system can be used to edit TCR and/or HLA genes (adding or deleting one or more base pairs), or to introduce premature termination, which reduces the activity of target genes or chromosomal sequences such as TCR and/or HLA. Performance. Alternatively, the CRISPR/Cas system can be used like RNA interference to switch off TCR and/or HLA genes in a reversible manner. For example, in mammalian cells, RNA can direct Cas proteins, such as those lacking nuclease activity (e.g., dCas9), to TCR and/or HLA promoters, sterically blocking RNA polymerase.
可以使用本領域已知的技術產生抑制例如TCR和/或HLA的人工CRISPR/Cas系統,例如,描述於美國公開案號20140068797中的技術。可用於本文所述發明的CRISPR系統包括在例如PCT申請公開WO 2017/093969中描述的那些,將該文獻的內容藉由引用以其整體併入本文。 抑制例如TCR和/或HLA的TALEN Artificial CRISPR/Cas systems that inhibit, for example, TCR and/or HLA can be generated using techniques known in the art, eg, techniques described in US Publication No. 20140068797. CRISPR systems that may be used in the invention described herein include those described, for example, in PCT Application Publication WO 2017/093969, the contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety. Inhibition of TALENs such as TCR and/or HLA
「TALEN」或「針對HLA和/或TCR的TALEN」或「抑制HLA和/或TCR的TALEN」係指轉錄激活因子樣效應子核酸酶,一種可以用於編輯HLA和/或TCR基因的人工核酸酶。"TALEN" or "TALEN targeting HLA and/or TCR" or "TALEN inhibiting HLA and/or TCR" refers to a transcription activator-like effector nuclease, an artificial nucleic acid that can be used to edit HLA and/or TCR genes enzyme.
藉由將TAL效應子DNA結合結構域與DNA切割域進行融合來人工產生TALEN。可以工程化轉錄活化因子樣作用(TALE)以結合任何所希望的DNA序列,包括HLA或TCR基因的部分。藉由將工程化的TALE與DNA切割域組合,可以產生對任何所希望的DNA序列(包括HLA或TCR序列)特異的限制酶。然後可以將該等引入細胞中,其中它們可以用於基因組編輯。Boch (2011) Nature Biotech. [自然生物技術] 29: 135-6;和Boch等人 (2009) Science[科學] 326: 1509-12;Moscou等人 (2009) Science[科學] 326: 3501。 TALENs were artificially generated by fusing the TAL effector DNA binding domain to the DNA cleavage domain. Transcription activator-like effects (TALEs) can be engineered to bind any desired DNA sequence, including portions of HLA or TCR genes. By combining engineered TALEs with DNA cleavage domains, restriction enzymes specific for any desired DNA sequence, including HLA or TCR sequences, can be generated. These can then be introduced into cells where they can be used for genome editing. Boch (2011) Nature Biotech 29: 135-6; and Boch et al. (2009) Science 326: 1509-12; Moscou et al. (2009) Science 326: 3501.
TALE係由黃單胞菌屬(Xanthomonas)細菌分泌的蛋白質。DNA結合結構域含有重複的、高度保守的33-34個胺基酸序列,但第12和第13胺基酸除外。這兩個位置高度變化,顯示出與特定核苷酸識別的強相關性。因此,它們可以被工程化以結合所希望的DNA序列。TALEs are proteins secreted by bacteria of the genus Xanthomonas. The DNA binding domain contains a repetitive, highly conserved sequence of 33-34 amino acids, except for the 12th and 13th amino acids. These two positions are highly variable, showing a strong correlation with specific nucleotide recognition. Thus, they can be engineered to bind desired DNA sequences.
為了產生TALEN,將TALE蛋白質與核酸酶(N)融合,該核酸酶係野生型或突變的FokI內切核酸酶。針對其在TALEN中的用途已經對FokI作出若干突變;該等例如,改進切割特異性或活性。Cermak等人 (2011) Nucl.Acids Res.[核酸研究] 39: e82;Miller等人 (2011) Nature Biotech. [自然生物技術] 29: 143-8;Hockemeyer等人 (2011) Nature Biotech. [自然生物技術] 29: 731-734;Wood等人 (2011) Science[科學] 333: 307;Doyon等人 (2010) Nature Methods[自然方法] 8: 74-79;Szczepek等人 (2007) Nature Biotech.[自然生物技術] 25: 786-793;和Guo等人 (2010) J. Mol. Biol.[分子生物學雜誌] 200: 96。 To generate TALENs, TALE proteins are fused to a nuclease (N), which is a wild-type or mutant FokI endonuclease. Several mutations have been made to Fokl for its use in TALENs; these, for example, improve cleavage specificity or activity. Cermak et al. (2011) Nucl.Acids Res. [Nucleic Acids Research] 39: e82; Miller et al. (2011) Nature Biotech . [Nature Biotechnology] 29: 143-8; Hockemeyer et al. (2011) Nature Biotech . Biotechnology] 29: 731-734; Wood et al. (2011) Science 333: 307; Doyon et al. (2010) Nature Methods 8: 74-79; Szczepek et al. (2007) Nature Biotech. [Nature Biotechnology] 25: 786-793; and Guo et al. (2010) J. Mol. Biol. 200: 96.
FokI結構域作為二聚體起作用,這需要兩個具有獨特DNA結合結構域的構建體,用於靶基因組中具有適當方向和間距的位點。TALE DNA結合結構域與FokI切割域之間的胺基酸殘基的數量和兩個單獨TALEN結合位點之間的鹼基的數量似乎都是實現高水平活性的重要參數。Miller等人 (2011) Nature Biotech.[自然生物技術] 29: 143-8。 The FokI domain functions as a dimer, which requires two constructs with unique DNA-binding domains for sites in the target genome with proper orientation and spacing. Both the number of amino acid residues between the TALE DNA binding domain and the FokI cleavage domain and the number of bases between the two individual TALEN binding sites appear to be important parameters for achieving high levels of activity. Miller et al. (2011) Nature Biotech. 29: 143-8.
可以使用HLA或TCR TALEN在細胞內產生雙股斷裂(DSB)。如果修復機制經由非同源末端連接不正確地修復斷裂,則可以在斷裂位點引入突變。例如,不正確的修復可以引入移碼突變。替代性地,可以將外來DNA與TALEN一起引入到細胞中;取決於外來DNA的序列和染色體序列,此過程可以用於校正HLA或TCR基因中的缺陷或將此類缺陷引入wt HLA或TCR基因中,從而降低HLA或TCR的表現。Double-strand breaks (DSBs) can be generated intracellularly using HLA or TCR TALENs. If the repair mechanism incorrectly repairs the break via non-homologous end joining, mutations can be introduced at the site of the break. For example, incorrect repairs can introduce frameshift mutations. Alternatively, foreign DNA can be introduced into cells together with TALENs; depending on the sequence of the foreign DNA and the chromosomal sequence, this process can be used to correct defects in HLA or TCR genes or to introduce such defects into wt HLA or TCR genes , thereby reducing the expression of HLA or TCR.
可以使用本領域已知的任何方法構建對HLA或TCR中的序列特異的TALEN,該等方法包括使用模組組分的各種方案。Zhang等人 (2011) Nature Biotech.[自然生物技術] 29: 149-53;Geibler等人 (2011) PLoS ONE[公共科學圖書館綜合] 6: e19509。 抑制例如HLA和/或TCR的鋅指核酸酶 TALENs specific for sequences in HLA or TCR can be constructed using any method known in the art, including various approaches using modular components. Zhang et al. (2011) Nature Biotech . 29: 149-53; Geibler et al. (2011) PLoS ONE 6: e19509. Inhibition of zinc finger nucleases such as HLA and/or TCR
「ZFN」或「鋅指核酸酶」或「針對HLA和/或TCR的ZFN」或「抑制HLA和/或TCR的ZFN」係指鋅指核酸酶,一種可以用於編輯HLA和/或TCR基因的人工核酸酶。"ZFN" or "zinc finger nuclease" or "ZFN targeting HLA and/or TCR" or "ZFN inhibiting HLA and/or TCR" refers to a zinc finger nuclease, a type that can be used to edit HLA and/or TCR genes artificial nucleases.
像TALEN一樣,ZFN包含與DNA結合結構域融合的FokI核酸酶域(或它的衍生物)。就ZFN而言,DNA結合結構域包含一或多個鋅指。Carroll等人 (2011) Genetics Society of America[美國遺傳學學會] 188: 773-782;和Kim等人 (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA[美國國家科學院院刊] 93: 1156-1160。 Like TALENs, ZFNs contain a FokI nuclease domain (or its derivatives) fused to a DNA-binding domain. In the case of ZFNs, the DNA binding domain comprises one or more zinc fingers. Carroll et al. (2011) Genetics Society of America 188: 773-782; and Kim et al. (1996) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 1156-1160 .
鋅指係被一或多種鋅離子穩定的小蛋白質結構模體。鋅指可包含例如Cys2His2,並且可識別大約3-bp序列。可以將已知特異性的各種鋅指組合以產生識別約6、9、12、15或18-bp序列的多指多肽。各種選擇和模組組裝技術可用於產生識別特定序列的鋅指(及其組合),包括噬菌體展示、酵母單雜交系統、細菌單雜交和雙雜交系統、以及哺乳動物細胞。Zinc fingers are small protein structural motifs stabilized by one or more zinc ions. Zinc fingers can comprise, for example, Cys2His2, and can recognize approximately 3-bp sequences. Various zinc fingers of known specificity can be combined to generate multifinger polypeptides that recognize sequences of about 6, 9, 12, 15 or 18-bp. Various selection and modular assembly techniques can be used to generate zinc fingers (and combinations thereof) that recognize specific sequences, including phage display, yeast one-hybrid systems, bacterial one-hybrid and two-hybrid systems, and mammalian cells.
像TALEN一樣,ZFN必須二聚化以切割DNA。因此,需要一對ZFN來靶向非迴文DNA位點。兩個單獨的ZFN必須與DNA的相反股結合,其中它們的核酸酶適當地間隔開。Bitinaite等人 (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA[美國國家科學院院刊] 95: 10570-5。 Like TALENs, ZFNs must dimerize to cleave DNA. Therefore, a pair of ZFNs is required to target non-palindromic DNA loci. Two separate ZFNs must bind to opposite strands of DNA with their nucleases spaced appropriately. Bitinaite et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 10570-5.
也像TALEN一樣,ZFN可以在DNA中產生雙股斷裂,如果不正確地修復則可以產生移碼突變,這導致細胞中HLA和/或TCR的表現和量的減少。ZFN還可以與同源重組一起使用以在HLA或TCR基因中產生突變。Also like TALENs, ZFNs can create double-strand breaks in the DNA that, if not repaired correctly, can create frameshift mutations, which lead to a reduction in the expression and amount of HLA and/or TCR in the cell. ZFNs can also be used with homologous recombination to generate mutations in HLA or TCR genes.
可以使用本領域已知的任何方法構建對HLA和/或TCR中的序列特異性的ZFN。Cathomen等人 (2008) Mol. Ther.[分子療法] 16: 1200-7;和Guo等人 (2010) J. Mol. Biol.[分子生物學雜誌] 400: 96。 免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞)的活化和擴增 ZFNs specific for sequences in HLA and/or TCR can be constructed using any method known in the art. Cathomen et al. (2008) Mol. Ther. 16: 1200-7; and Guo et al. (2010) J. Mol. Biol. 400: 96. Activation and expansion of immune effector cells (eg, T cells)
免疫效應細胞(如T細胞)通常可以使用如描述於例如以下中的方法進行激活和擴增:美國專利6,352,694;6,534,055;6,905,680;6,692,964;5,858,358;6,887,466;6,905,681;7,144,575;7,067,318;7,172,869;7,232,566;7,175,843;5,883,223;6,905,874;6,797,514;6,867,041;和美國專利申請公開案號 20060121005。Immune effector cells (such as T cells) can generally be activated and expanded using methods as described in, for example, US Patents 6,352,694; 6,534,055; 6,905,680; 6,692,964; 5,858,358; 5,883,223; 6,905,874; 6,797,514; 6,867,041; and US Patent Application Publication No. 20060121005.
通常,本發明的免疫效應細胞群體可以藉由與表面接觸而擴增,該表面附接有刺激CD3/TCR複合物相關的訊息的藥劑和刺激T細胞表面上的共刺激分子的配體。特別地,可以如本文所描述刺激T細胞群體,如藉由與固定在表面上的抗CD3抗體或其抗原結合片段、或抗CD2抗體接觸,或藉由與結合有鈣離子載體的蛋白激酶C活化劑(例如苔蘚抑素)接觸。對於T細胞表面上輔助分子的共刺激,使用結合輔助分子的配體。例如,可以在適於刺激T細胞增殖的條件下,使T細胞群體與抗CD3抗體和抗CD28抗體接觸。為了刺激CD4+ T細胞或CD8+ T細胞的增殖,抗CD3抗體和抗CD28抗體。可以使用抗CD28抗體之實例包括9.3、B-T3、XR-CD28(法國貝桑松Diaclone公司(Diaclone, Besançon, France)),還可以使用本領域公知的其他方法(Berg等人, Transplant Proc.[移植學會會報] 30(8):3975-3977, 1998;Haanen等人, J. Exp. Med.[實驗醫學雜誌] 190(9):13191328, 1999;Garland等人, J. Immunol Meth.[免疫學雜誌] 227(1-2):53-63, 1999)。In general, immune effector cell populations of the invention can be expanded by contacting a surface with attached an agent that stimulates a message associated with the CD3/TCR complex and a ligand that stimulates a co-stimulatory molecule on the surface of the T cell. In particular, T cell populations can be stimulated as described herein, such as by contacting an anti-CD3 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, or an anti-CD2 antibody immobilized on a surface, or by contacting a calcium ionophore-bound protein kinase C Activators (such as bryostatin) exposure. For co-stimulation of accessory molecules on the surface of T cells, ligands that bind the accessory molecules are used. For example, a population of T cells can be contacted with an anti-CD3 antibody and an anti-CD28 antibody under conditions suitable to stimulate T cell proliferation. To stimulate the proliferation of CD4+ T cells or CD8+ T cells, anti-CD3 antibody and anti-CD28 antibody. Examples of anti-CD28 antibodies that can be used include 9.3, B-T3, XR-CD28 (Diaclone, Besançon, France), and other methods known in the art (Berg et al., Transplant Proc. [Proceedings of the Society for Transplantation] 30(8):3975-3977, 1998; Haanen et al., J. Exp. Med. [Journal of Experimental Medicine] 190(9):13191328, 1999; Garland et al., J. Immunol Meth.[ Journal of Immunology] 227(1-2):53-63, 1999).
在某些方面,T細胞的初級刺激訊息和共刺激訊息可以由不同的方案提供。例如,提供每個訊息的藥劑可以在溶液中或偶合到表面。當偶合到表面時,藥劑可以偶合到同一表面(即,為「順式」形成)或偶合到分離表面(即,為「反式」形成)。替代性地,可以將一種藥劑偶合到表面並且使另一種藥劑在溶液中。在一方面,將提供共刺激訊息的藥劑與細胞表面結合,並且使提供初級活化訊息的藥劑在溶液中或偶合到表面。在某些方面,兩種藥劑都可以在溶液中。在一方面,該等試劑可以為可溶形式,並且然後交聯到表面,如表現Fc受體的細胞或將與該等藥劑結合的抗體或其他結合劑。在這方面,參見例如美國專利申請公開案號20040101519和20060034810的人工抗原呈遞細胞(aAPC),其預期用於活化和擴增本發明中的T細胞。In some aspects, primary and co-stimulatory messages to T cells can be provided by different protocols. For example, the agents that provide each message can be in solution or coupled to a surface. When coupled to a surface, the agent can be coupled to the same surface (ie, formed in "cis") or coupled to a separate surface (ie, formed in "trans"). Alternatively, one agent can be coupled to the surface and the other agent left in solution. In one aspect, the agent providing the co-stimulatory message is bound to the cell surface and the agent providing the primary activation message is either in solution or coupled to the surface. In some aspects, both agents can be in solution. In one aspect, the agents may be in soluble form and then cross-linked to surfaces such as cells expressing Fc receptors or antibodies or other binding agents to which the agents will bind. In this regard, see, eg, US Patent Application Publication Nos. 20040101519 and 20060034810 for artificial antigen presenting cells (aAPCs) contemplated for activating and expanding T cells in the present invention.
在一方面,將兩種藥劑固定在珠上,或者在同一珠上,即「順式」,或者在分離的珠上,即「反式」。藉由舉例,提供初級活化訊息的藥劑係抗CD3抗體或其抗原結合片段,並且提供共刺激訊息的藥劑係抗CD28抗體或其抗原結合片段;並且將兩種藥劑以等效分子量共固定到同一珠。在一方面,使用與珠結合的每種抗體的1 : 1比率用於CD4+ T細胞擴增和T細胞生長。在本發明之某些方面,使用與珠結合的抗CD3 : CD28抗體的比率,使得與使用1 : 1的比率觀察到的擴增相比,觀察到T細胞擴增的增加。在一個特定方面,與使用1 : 1比率觀察到的擴增相比,觀察到從約1倍至約3倍的增加。在一方面,與珠結合的CD3 : CD28抗體的比率範圍為從100 : 1至1 : 100以及其間的所有整數值。在本發明之一方面,與抗CD3抗體相比,更多的抗CD28抗體與顆粒結合,即CD3 : CD28的比率小於1。在本發明之某些方面,與珠結合的抗CD28抗體與抗CD3抗體的比率大於2 : 1。在一個特定方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 100 CD3 : CD28比率。在一方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 75 CD3 : CD28比率。在另外的方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 50 CD3 : CD28比率。在一方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 30 CD3 : CD28比率。在一個較佳的方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 10 CD3 : CD28比率。在一方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的1 : 3 CD3 : CD28比率。在又一個方面,使用與珠結合的抗體的3 : 1 CD3 : CD28比率。In one aspect, the two agents are immobilized on beads, either on the same bead, ie "cis", or on separate beads, ie "trans". By way of example, the agent providing the primary activation signal is an anti-CD3 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, and the agent providing the co-stimulatory signal is an anti-CD28 antibody or an antigen-binding fragment thereof; and the two agents are co-immobilized at equivalent molecular weights to the same beads. In one aspect, a 1:1 ratio of each antibody bound to beads is used for CD4+ T cell expansion and T cell growth. In certain aspects of the invention, a ratio of anti-CD3:CD28 antibody bound to beads is used such that an increase in T cell expansion is observed compared to the expansion observed using a 1:1 ratio. In a specific aspect, an increase from about 1-fold to about 3-fold is observed compared to the amplification observed using a 1:1 ratio. In one aspect, the ratio of CD3:CD28 antibody bound to the beads ranges from 100:1 to 1:100 and all integer values therebetween. In one aspect of the invention, more anti-CD28 antibody is bound to the particle than anti-CD3 antibody, ie the CD3:CD28 ratio is less than 1. In certain aspects of the invention, the ratio of anti-CD28 antibody to anti-CD3 antibody bound to the beads is greater than 2:1. In a specific aspect, a 1:100 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In one aspect, a 1:75 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In additional aspects, a 1:50 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In one aspect, a 1:30 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In a preferred aspect, a 1:10 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In one aspect, a 1:3 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used. In yet another aspect, a 3:1 CD3:CD28 ratio of antibody bound to the beads is used.
顆粒與細胞的比率為從1 : 500至500 : 1以及其間的任何整數值可以用於刺激T細胞或其他靶細胞。如熟悉該項技術者可以容易地理解的,顆粒與細胞的比率可以取決於相對於靶細胞的顆粒尺寸。例如,小尺寸的珠僅可以結合少量細胞,而較大的珠可以結合許多細胞。在某些方面範圍從1 : 100至100 : 1以及其間的任何整數值的細胞與顆粒的比率和在另外的方面包括1 : 9至9 : 1的比率以及其間的任何整數值也可以用於刺激T細胞。如以上所指出,導致T細胞刺激的抗CD3和抗CD28偶合顆粒與T細胞的比率可以變化,然而某些較佳的值包括1 : 100、1 : 50、1 : 40、1 : 30、1 : 20、1 : 10、1 : 9、1 : 8、1 : 7、1 : 6、1 : 5、1 : 4、1 : 3、1 : 2、1 : 1、2 : 1、3 : 1、4 : 1、5 : 1、6 : 1、7 : 1、8 : 1、9 : 1、10 : 1、和15 : 1,其中一個較佳的比率係每個T細胞至少1 : 1個顆粒。在一方面,使用1 : 1或更小的顆粒與細胞比率。在一個特定方面,較佳的顆粒 : 細胞的比率為1 : 5。在另外的方面,顆粒與細胞的比率可以根據刺激日而變化。例如,在一方面,顆粒與細胞的比率在第一天為從1 : 1至10 : 1,並且將另外顆粒在之後每天或每隔一天加入到細胞中持續最長10天,最終比率為從1 : 1至1 : 10(基於添加當天的細胞計數)。在一個特定方面,在刺激的第一天,顆粒與細胞的比率為1 : 1,並且在刺激的第三天和第五天調整為1 : 5。在一方面,基於在第一天的最終比率為1 : 1並且在刺激的第三天和第五天為1 : 5,每天或每隔一天添加顆粒。在一方面,在刺激的第一天,顆粒與細胞的比率為2 : 1,並且在刺激的第三天和第五天調整為1 : 10。在一方面,基於在第一天的最終比率為1 : 1並且在刺激的第三天和第五天為1 : 10,每天或每隔一天添加顆粒。熟悉該項技術者將理解,各種其他比率可適用於本發明。特別地,比率將根據粒度和細胞大小和類型而變化。在一方面,在第一天用於使用的最典型比率係1 : 1、2 : 1和3 : 1附近。Particle to cell ratios from 1:500 to 500:1 and any integer value therebetween can be used to stimulate T cells or other target cells. As can be readily understood by those skilled in the art, the ratio of particles to cells may depend on the size of the particles relative to the target cells. For example, small sized beads can bind only a few cells, while larger beads can bind many cells. Cell-to-particle ratios ranging in some aspects from 1:100 to 100:1 and any integer value therebetween and in other aspects including ratios from 1:9 to 9:1 and any integer value therebetween can also be used Stimulates T cells. As noted above, the ratio of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 coupled particles to T cells resulting in T cell stimulation can vary, however some preferred values include 1:100, 1:50, 1:40, 1:30, 1 : 20, 1 : 10, 1 : 9, 1 : 8, 1 : 7, 1 : 6, 1 : 5, 1 : 4, 1 : 3, 1 : 2, 1 : 1, 2 : 1, 3 : 1 , 4:1, 5:1, 6:1, 7:1, 8:1, 9:1, 10:1, and 15:1, with a preferred ratio of at least 1:1 per T cell particles. In one aspect, a particle-to-cell ratio of 1:1 or less is used. In a specific aspect, a preferred particle:cell ratio is 1:5. In additional aspects, the ratio of particles to cells can vary depending on the day of stimulation. For example, in one aspect, the ratio of particles to cells is from 1:1 to 10:1 on the first day, and additional particles are added to the cells every day or every other day thereafter for a maximum of 10 days, with a final ratio of from 1 : 1 to 1 : 10 (based on the cell count on the day of addition). In a specific aspect, the ratio of particles to cells is 1:1 on the first day of stimulation and adjusted to 1:5 on the third and fifth days of stimulation. In one aspect, particles are added daily or every other day based on a final ratio of 1:1 on day one and 1:5 on days three and five of stimulation. In one aspect, the ratio of particles to cells is 2:1 on the first day of stimulation and adjusted to 1:10 on the third and fifth days of stimulation. In one aspect, particles are added daily or every other day based on a final ratio of 1:1 on day one and 1:10 on days three and five of stimulation. Those skilled in the art will understand that various other ratios are applicable to the present invention. In particular, ratios will vary according to particle size and cell size and type. In one aspect, the most typical ratios for use on the first day are around 1:1, 2:1 and 3:1.
在本發明之另外的方面,將細胞(如T細胞)與藥劑包被的珠組合,隨後將珠和細胞分離,並且然後培養細胞。在可替代方面,在培養之前,不將藥劑包被的珠和細胞分開而是一起培養。在另一個方面,首先藉由施加力(如磁力)濃縮珠和細胞,導致細胞表面標誌物的連接增加,從而誘導細胞刺激。In additional aspects of the invention, cells (eg, T cells) are combined with agent-coated beads, the beads and cells are subsequently separated, and the cells are then cultured. In an alternative aspect, the agent-coated beads and cells are not separated but cultured together prior to culturing. In another aspect, cell stimulation is induced by first concentrating the beads and cells by applying a force, such as a magnetic force, resulting in increased attachment of cell surface markers.
藉由舉例,可以藉由使抗CD3和抗CD28附著的順磁珠(3x28珠)接觸T細胞來連接細胞表面蛋白。在一方面,將細胞(例如,10 4至10 9個T細胞)和珠(例如,比率為1 : 1的DYNABEADS® M-450 CD3/CD28 T順磁珠)在緩衝液(例如PBS(不含二價陽離子(如鈣和鎂))中組合。同樣,本領域的普通技術者可易於理解可以使用任何細胞濃度。例如,靶標細胞在樣本中可以非常稀少,僅占樣本的0.01%,或者整個樣本(即100%)可以包含所關注的靶標細胞。因此,任何細胞數量都在本發明之上下文內。在某些方面,可能希望顯著減小其中顆粒和細胞混合在一起的體積(即增加細胞的濃度),以確保細胞和顆粒的最大接觸。例如,在一方面,使用約100億個細胞/ml、90億個/ml、80億個/ml、70億個/ml、60億個/ml、或50億個/ml的濃度。在一方面,使用大於1億個細胞/ml。在另一個方面,使用10、15、20、25、30、35、40、45、或50百萬個細胞/ml的細胞濃度。在又一個方面,使用75、80、85、90、95、或100百萬個細胞/ml的細胞濃度。在另外的方面,可以使用125或150百萬個細胞/ml的濃度。使用高濃度可以導致細胞產量增加、細胞活化、和細胞擴增。此外,使用高細胞濃度允許更有效地捕獲可能弱表現感興趣的靶抗原的細胞,如CD28陰性T細胞。此類細胞群體可能具有治療價值,並且在某些方面係希望獲得的。例如,使用高濃度的細胞允許更有效地選擇通常具有較弱CD28表現的CD8+T細胞。 By way of example, cell surface proteins can be attached by contacting T cells with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 attached paramagnetic beads (3x28 beads). In one aspect, cells (e.g., 104 to 109 T cells) and beads (e.g., DYNABEADS® M-450 CD3/CD28 T paramagnetic beads in a 1:1 ratio) are mixed in a buffer (e.g., PBS (without Divalent cations (such as calcium and magnesium)). Again, any concentration of cells can be readily understood by those of ordinary skill in the art. For example, target cells can be very rare in a sample, accounting for only 0.01% of the sample, or The entire sample (i.e. 100%) may contain the target cells of interest. Therefore, any number of cells is within the context of the present invention. In certain aspects it may be desirable to significantly reduce the volume in which particles and cells are mixed together (i.e. increase concentration of cells) to ensure maximum cell and particle contact. For example, in one aspect, use about 10 billion cells/ml, 9 billion/ml, 8 billion/ml, 7 billion/ml, 6 billion /ml, or a concentration of 5 billion/ml. On the one hand, use greater than 100 million cells/ml. In another aspect, use 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, or 50 A cell concentration of 10,000 cells/ml. In yet another aspect, a cell concentration of 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, or 100 million cells/ml is used. In another aspect, 125 or 150 million can be used Concentration of cells/ml. Using high concentrations can lead to increased cell yield, cell activation, and cell expansion. Additionally, using high cell concentrations allows for more efficient capture of cells that may weakly express the target antigen of interest, such as CD28-negative T cells Such cell populations may be of therapeutic value and are desirable in certain respects. For example, the use of high concentrations of cells allows for more efficient selection of CD8+ T cells that typically have a weaker CD28 expression.
在一個實施方式中,將用編碼CAR(例如本文所述之CAR)的核酸轉導的細胞例如藉由本文所述之方法擴增。在一個實施方式中,將細胞在培養物中擴增數小時(例如,約2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、15、18、21小時)至約14天(例如,1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13或14天)的時間段。在一個實施方式中,將細胞擴增4至9天的時間段。在一個實施方式中,將細胞擴增8天或更短例如7天、6天或5天的時間段。在一個實施方式中,將細胞(例如,包含本文所述之例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)在培養物中擴增5天,並且所得細胞比在相同的培養條件下在培養物中擴增9天的相同細胞更有效力。效力可以例如藉由各種T細胞功能來定義,例如增殖、靶細胞殺傷、細胞介素產生、活化、遷移、或其組合。在一個實施方式中,與在相同的培養條件下在培養物中擴增9天的相同細胞相比,擴增5天的細胞(例如,本文所述之CD19 CAR細胞)顯示抗原刺激後細胞倍增方面至少一倍、兩倍、三倍或四倍的增加。在一個實施方式中,使細胞(例如,包含本文所述之例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)在培養物中擴增5天,與在相同培養條件下在培養物中擴增9天的相同細胞相比,所得的細胞表現出更高的促炎細胞介素產生(例如,IFN-γ和/或GM-CSF水平)。在一個實施方式中,與在相同培養條件下在培養物中擴增9天的相同細胞相比,將包含本文所述之例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞擴增5天,顯示出促炎細胞介素產生(例如,IFN-γ和/或GM-CSF水平)以pg/ml計增加至少一倍、二倍、三倍、四倍、五倍、十倍或更多倍。In one embodiment, cells transduced with a nucleic acid encoding a CAR, such as a CAR described herein, are amplified, eg, by the methods described herein. In one embodiment, cells are expanded in culture for several hours (e.g., about 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 18, 21 hours) to about 14 days ( For example, a period of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, or 14 days). In one embodiment, the cells are expanded for a period of 4 to 9 days. In one embodiment, the cells are expanded for a period of 8 days or less, such as 7 days, 6 days or 5 days. In one embodiment, cells (e.g., comprising cells described herein, e.g., expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) are expanded in culture for 5 days, and the resulting cells are larger than those expanded in culture under the same culture conditions. The same cells grown for 9 days were more potent. Potency can be defined, for example, by various T cell functions, such as proliferation, target cell killing, cytokine production, activation, migration, or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, cells expanded for 5 days (e.g., CD19 CAR cells described herein) exhibit cell doubling after antigen stimulation compared to the same cells expanded for 9 days in culture under the same culture conditions An increase of at least one, two, three or four times. In one embodiment, cells (e.g., comprising cells described herein, e.g., expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) are expanded in culture for 5 days compared to cells expanded in culture for 9 days under the same culture conditions. The resulting cells exhibit higher production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (eg, IFN-γ and/or GM-CSF levels) compared to the same cells. In one embodiment, cells comprising, for example, expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR described herein, expanded for 5 days, were shown to be pro-inflammatory compared to the same cells expanded in culture for 9 days under the same culture conditions. Interleukin production (eg, IFN-γ and/or GM-CSF levels) is increased by at least one-fold, two-fold, three-fold, four-fold, five-fold, ten-fold or more in pg/ml.
在本發明之一方面,可以將混合物培養若干個小時(約3小時)至約14天或其間的任何小時整數值。在一方面,可以將混合物培養21天。在本發明之一個方面,將珠和T細胞一起培養約八天。在一方面,將珠和T細胞一起培養2-3天。還可能希望進行幾個刺激循環,使得T細胞的培養時間可為60天或更長。適於T細胞培養的條件包括適當的培養基(例如,Minimal Essential Media或RPMI Media 1640或X-vivo 15,(龍沙公司(Lonza))),該培養基可以含有增殖和活力所必需的因子,包括血清(例如胎牛或人血清)、介白素-2(IL-2)、胰島素、IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-7、GM-CSF、IL-10、IL-12、IL-15、TGFβ、和TNF-α或熟悉該項技術者已知用於細胞生長的任何其他添加劑。用於細胞生長的其他添加劑包括但不限於界面活性劑、人血漿蛋白製品、和還原劑(如N-乙醯基-半胱胺酸和2-巰基乙醇)。培養基可以包括RPMI 1640、AIM-V、DMEM、MEM、α-MEM、F-12、X-Vivo 15、和X-Vivo 20、優化劑,其中添加胺基酸、丙酮酸鈉、和維生素,無血清或補充有適當量的血清(或血漿)或一組確定的激素、和/或足以使T細胞生長和擴增的一定量細胞介素。抗生素(例如青黴素和鏈黴素)僅包含在實驗培養物中,而不包含在有待注入受試者的細胞培養物中。將靶細胞維持在支持生長所必需的條件下,例如,適當的溫度(例如,37°C)和大氣(例如空氣加5% CO 2)。 In one aspect of the invention, the mixture can be incubated for a number of hours (about 3 hours) to about 14 days or any integer value of hours therebetween. In one aspect, the mixture can be grown for 21 days. In one aspect of the invention, beads and T cells are cultured together for about eight days. In one aspect, beads and T cells are cultured together for 2-3 days. It may also be desirable to perform several cycles of stimulation so that the T cells may be cultured for 60 days or longer. Conditions suitable for T cell culture include appropriate media (e.g., Minimal Essential Media or RPMI Media 1640 or X-vivo 15, (Lonza)), which may contain factors necessary for proliferation and viability, including Serum (eg, fetal calf or human serum), interleukin-2 (IL-2), insulin, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-7, GM-CSF, IL-10, IL-12, IL-15 , TGFβ, and TNF-α or any other additive known to those skilled in the art for cell growth. Other additives for cell growth include, but are not limited to, surfactants, human plasma protein preparations, and reducing agents (such as N-acetyl-cysteine and 2-mercaptoethanol). Media can include RPMI 1640, AIM-V, DMEM, MEM, α-MEM, F-12, X-Vivo 15, and X-Vivo 20, optimizers, in which amino acids, sodium pyruvate, and vitamins are added, without Serum or supplemented with an appropriate amount of serum (or plasma) or a defined set of hormones, and/or an amount of cytokine sufficient to allow T cell growth and expansion. Antibiotics such as penicillin and streptomycin are included only in the experimental cultures, not in the cell cultures to be injected into the subjects. Target cells are maintained under conditions necessary to support growth, eg, appropriate temperature (eg, 37°C) and atmosphere (eg, air plus 5% CO 2 ).
在一個實施方式中,將細胞在包括一或多種白血球介素的適當培養基(例如,本文所述之培養基)中擴增,在14天擴增期中產生至少200倍(例如,200倍、250倍、300倍、350倍)的細胞增加,例如如藉由本文所述之方法如流動式細胞測量術測量的。在一個實施方式中,將細胞在IL-15和/或IL-7(例如,IL-15和IL-7)存在下擴增。In one embodiment, the cells are expanded in an appropriate medium (e.g., as described herein) that includes one or more interleukins to produce at least 200-fold (e.g., 200-fold, 250-fold) over a 14-day expansion period , 300-fold, 350-fold), for example as measured by a method described herein, such as flow cytometry. In one embodiment, the cells are expanded in the presence of IL-15 and/or IL-7 (eg, IL-15 and IL-7).
已暴露於不同刺激時間的T細胞可以表現出不同的特徵。例如,典型的血液或周圍血單核細胞產物具有輔助T細胞群體(TH,CD4+),其大於細胞毒性或抑制性T細胞群體(TC,CD8+)。藉由刺激CD3和CD28受體離體擴增T細胞產生T細胞群體,該T細胞群體在約8-9天之前主要由TH細胞組成,而在約8-9天之後,該T細胞群體包含越來越多的TC細胞群體。因此,取決於治療目的,向受試者輸注主要包含TH細胞的T細胞群體可能是有利的。類似地,如果已分離了TC細胞的抗原特異性子集,則將該子集擴增到更大程度可能是有益的。T cells that have been exposed to different stimulation times can exhibit different characteristics. For example, a typical blood or peripheral blood monocyte product has a helper T cell population (TH, CD4+) that is larger than a cytotoxic or suppressor T cell population (TC, CD8+). Ex vivo expansion of T cells by stimulation of the CD3 and CD28 receptors produces a T cell population that until about 8-9 days consists primarily of TH cells and after about 8-9 days the T cell population comprises Growing population of TC cells. Thus, depending on the purpose of the treatment, it may be advantageous to infuse a subject with a T cell population comprising primarily TH cells. Similarly, if an antigen-specific subset of TC cells has been isolated, it may be beneficial to expand this subset to a greater extent.
此外,在細胞擴增過程期間,除CD4和CD8標誌物之外,其他表型標記物顯著地,但在很大程度上,可重複地變化。因此,這種可重複性使得能夠針對特定目的定製活化的T細胞產物。Furthermore, in addition to the CD4 and CD8 markers, other phenotypic markers changed significantly, but to a large extent, reproducibly, during the cell expansion process. This reproducibility thus enables the tailoring of activated T cell products for specific purposes.
一旦構建CAR,例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR,可以使用各種測定來評價分子活性,如但不限於:在抗原刺激後擴增T細胞、在沒有再刺激的情況下維持T細胞擴增的能力,以及在適當的體外和動物模型中的抗癌活性。用於評價CAR,例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR的效果的測定在下文進一步詳細描述。Once a CAR is constructed, such as a dual CAR or a tandem CAR, various assays can be used to assess molecular activity such as, but not limited to: the ability to expand T cells after antigen stimulation, maintain T cell expansion without restimulation, and Anticancer activity in appropriate in vitro and animal models. Assays for evaluating the effects of CARs, eg, dual CARs or tandem CARs, are described in further detail below.
原代T細胞中CAR表現的西方墨點法分析可用於檢測單體和二聚體的存在。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。非常簡單地,表現CAR的T細胞(CD4 +和CD8 +T細胞的1 : 1混合物)在體外擴增超過10天,然後在還原條件下進行裂解和SDS-PAGE。使用針對TCR-ζ鏈的抗體藉由西方墨點法來檢測含有全長TCR-ζ胞質結構域和內源性TCR-ζ鏈的CAR。相同的T細胞亞群用於在非還原條件下的SDS-PAGE分析,以允許評估共價二聚體的形成。 Western blot analysis of CAR expression in primary T cells can be used to detect the presence of monomers and dimers. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Very briefly, CAR-expressing T cells (1:1 mixture of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells) were expanded in vitro for more than 10 days, followed by lysis and SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. CARs containing the full-length TCR-ζ cytoplasmic domain and endogenous TCR-ζ chain were detected by Western blotting using an antibody against the TCR-ζ chain. The same T cell subsets were used for SDS-PAGE analysis under non-reducing conditions to allow assessment of covalent dimer formation.
可以藉由流動式細胞測量術測量抗原刺激後CAR
+T細胞的體外擴增。例如,將CD4
+和CD8
+T細胞的混合物用αCD3/αCD28 aAPC刺激,隨後用在待分析的啟動子的控制下表現GFP的慢病毒載體轉導。示例性啟動子包括CMV IE基因、EF-1α、泛素C、或磷酸甘油激酶(PGK)啟動子。藉由流動式細胞測量術,在培養的第6天在CD4
+和/或CD8
+T細胞亞群中評估GFP螢光。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。替代性地,在第0天將CD4
+和CD8
+T細胞的混合物用被αCD3/αCD28包被的磁珠刺激,並在第1天使用表現CAR連同eGFP(使用2A核糖體跳躍序列)的雙順反子慢病毒載體用CAR轉導。在洗滌後,用CD19
+K562細胞(K562-CD19)、野生型K562細胞(K562野生型)或在抗CD3和抗CD28抗體存在下表現hCD32和4-1BBL的K562細胞(K562-BBL-3/28)再刺激培養物。每隔一天以100 IU/ml向培養基中添加外源IL-2。使用基於珠的計數藉由流動式細胞測量術計算GFP
+T細胞。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。可以使用抗CD20 T細胞(參見例如,Gill等人 Blood [血液] 2014; 123: 2343)或用抗CD20 CAR T細胞進行類似的測定。
In vitro expansion of CAR + T cells after antigen stimulation can be measured by flow cytometry. For example, a mixture of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells is stimulated with αCD3/αCD28 aAPCs and subsequently transduced with a lentiviral vector expressing GFP under the control of the promoter to be analyzed. Exemplary promoters include the CMV IE gene, EF-la, ubiquitin C, or phosphoglycerol kinase (PGK) promoters. GFP fluorescence was assessed in CD4 + and/or CD8 + T cell subsets on day 6 of culture by flow cytometry. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Alternatively, a mixture of CD4 + and CD8 + T cells was stimulated on
還可以測量在沒有再刺激的情況下持續的CAR
+T細胞擴增。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。簡而言之,在第0天用αCD3/αCD28包被的磁珠刺激,以及在第1天用指示的CAR轉導後,使用Coulter Multisizer III粒子計數器、Nexcelom Cellometer Vision或密理博(Millipore)Scepter在培養的第8天測量平均T細胞體積(fl)。
Sustained CAR + T cell expansion in the absence of restimulation could also be measured. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Briefly, after stimulation with αCD3/αCD28-coated beads on
動物模型也可用於測量CART活性。例如,可以使用異種移植模型,該模型使用人CD19特異性CAR +T細胞來治療免疫缺陷小鼠中的原代人前-B ALL。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。簡而言之,在建立ALL後,將小鼠隨機分配至治療組。將不同數目的αCD19-ζ和αCD19-BB-ζ工程化的T細胞以1 : 1的比率共注射到攜帶B-ALL的NOD-SCID-γ − / −小鼠中。在T細胞注射後的不同時間,評價來自小鼠的脾DNA中的αCD19-ζ和αCD19-BB-ζ載體的拷貝的數目。以每週為間隔評估動物的白血病。在注射了αCD19-ζ CAR +T細胞或模擬轉導的T細胞的小鼠中測量周圍血CD19 +B-ALL母細胞計數。使用對數秩檢定比較組的存活曲線。此外,還可以分析在NOD-SCID-γ − / −小鼠中T細胞注射後4週的絕對外週血CD4 +和CD8 +T細胞計數。給小鼠注射白血病細胞,並在3週後注射T細胞,該等T細胞經工程化以藉由編碼與eGFP連接的CAR的雙順反子慢病毒載體表現CAR。藉由在注射前與模擬轉導的細胞混合將T細胞標準化為45%-50%輸入的GFP +T細胞,並藉由流動式細胞測量術確認。在1週的間隔評估動物的白血病。使用對數秩檢定比較CAR +T細胞組的存活曲線。可以用雙重CART或串聯CART完成相似的實驗。 Animal models can also be used to measure CART activity. For example, a xenograft model using human CD19-specific CAR + T cells to treat primary human pre-B ALL in immunodeficient mice can be used. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Briefly, after the establishment of ALL, mice were randomly assigned to treatment groups. Different numbers of αCD19-ζ and αCD19-BB-ζ engineered T cells were co-injected into B-ALL-bearing NOD-SCID-γ − / − mice at a ratio of 1:1. The number of copies of αCD19-ζ and αCD19-BB-ζ vectors in splenic DNA from mice was assessed at various times after T cell injection. Animals were assessed for leukemia at weekly intervals. Peripheral blood CD19 + B-ALL blast counts were measured in mice injected with αCD19-ζ CAR + T cells or mock-transduced T cells. Survival curves of groups were compared using the log-rank test. In addition, absolute peripheral blood CD4 + and CD8 + T cell counts 4 weeks after T cell injection in NOD-SCID-γ − /− mice could also be analyzed. Mice were injected with leukemia cells and 3 weeks later T cells engineered to express the CAR via a bicistronic lentiviral vector encoding the CAR linked to eGFP. T cells were normalized to 45%-50% input GFP + T cells by mixing with mock-transduced cells prior to injection and confirmed by flow cytometry. Animals were assessed for leukemia at 1 week intervals. The survival curves of the CAR + T cell groups were compared using the log-rank test. Similar experiments can be done with dual CARTs or tandem CARTs.
可以評價劑量依賴性CAR治療響應。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。例如,在第21天用CAR T細胞、相同數量的模擬轉導的T細胞、或無T細胞注射的小鼠中建立白血病之後35-70天獲得周圍血。將每組小鼠隨機放血以確定周圍血CD19 +ALL母細胞計數,並且然後在第35和49天處死。在第57天和第70天評價剩餘的動物。可以用雙重CART或串聯CART完成相似的實驗。 Dose-dependent CAR treatment response can be assessed. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). For example, peripheral blood was obtained 35-70 days after establishment of leukemia in mice injected with CAR T cells on day 21, the same number of mock-transduced T cells, or no T cells. Each group of mice was bled randomly to determine peripheral blood CD19 + ALL blast counts and then sacrificed on days 35 and 49. The remaining animals were evaluated on days 57 and 70. Similar experiments can be done with dual CARTs or tandem CARTs.
先前已經描述了細胞增殖和細胞介素產生的評估,例如在Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)中。簡而言之,藉由將洗滌的T細胞與表現CD19(K19)或CD32和CD137(KT32-BBL)的K562細胞混合(最終T細胞 : K562比率為2 : 1),在微量滴定板中進行對CAR介導的增殖的評估。在使用前用γ射線照射K562細胞。將抗CD3(殖株OKT3)和抗CD28(殖株9.3)單株抗體添加至具有KT32-BBL細胞的培養基以用作用於刺激T細胞增殖的陽性對照,因為該等訊息支持長期CD8 +T細胞離體擴增。使用CountBright™螢光珠(茵維特羅根公司(Invitrogen),卡爾斯巴德,加利福尼亞州(Carlsbad,CA))和流動式細胞測量術(如由製造商描述的)在培養基中計數T細胞。使用用eGFP-2A連接的表現CAR的慢病毒載體進行工程化的T細胞,藉由GFP表現來鑒定CAR +T細胞。對於不表現GFP的CAR+ T細胞,用生物素化的重組CD19蛋白和次級抗生物素蛋白-PE軛合物檢測CAR+ T細胞。還用特異性單株抗體(BD生物科學公司(BD Biosciences))同時檢測T細胞上的CD4+和CD8 +表現。根據製造商的說明書或使用Luminex 30-plex套組(英傑公司(Invitrogen)),使用人TH1/TH2細胞介素細胞計數珠陣列套組(加利福尼亞州聖地牙哥(San Diego, CA)的BD生物科學公司)在再刺激後24小時收集的上清液上進行細胞介素測量。使用BD Fortessa流式細胞儀評估螢光,並根據製造商的說明書分析數據。可以用雙重CART或串聯CART完成相似的實驗。 Assessment of cell proliferation and cytokine production has been described previously, eg in Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Briefly, by mixing washed T cells with K562 cells expressing CD19 (K19) or CD32 and CD137 (KT32-BBL) (final T cell:K562 ratio 2 : 1) in microtiter plates Evaluation of CAR-mediated proliferation. K562 cells were irradiated with gamma rays before use. Anti-CD3 (strain OKT3) and anti-CD28 (strain 9.3) monoclonal antibodies were added to media with KT32-BBL cells to serve as positive controls for stimulating T cell proliferation, as these messages support long-term CD8 + T cells Ex vivo amplification. T cells were counted in culture using CountBright™ fluorescent beads (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and flow cytometry (as described by the manufacturer). CAR + T cells were identified by GFP expression using T cells engineered with a CAR-expressing lentiviral vector linked to eGFP-2A. For CAR+ T cells that do not express GFP, CAR+ T cells were detected with biotinylated recombinant CD19 protein and secondary avidin-PE conjugate. CD4+ and CD8 + expression on T cells were also detected simultaneously with specific monoclonal antibodies (BD Biosciences). Human TH1/TH2 cytokine cytometric bead array kit (BD Biotech, San Diego, CA) was used according to the manufacturer's instructions or using the Luminex 30-plex kit (Invitrogen). Scientific Inc.) Interleukin measurements were performed on supernatants collected 24 hr after restimulation. Fluorescence was assessed using a BD Fortessa flow cytometer and data were analyzed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Similar experiments can be done with dual CARTs or tandem CARTs.
可藉由標準51Cr釋放測定來評估細胞毒性。參見例如,Milone等人, Molecular Therapy [分子療法] 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009)。簡而言之,在37°C下將靶細胞(K562系和原代B-ALL細胞)用51Cr(如NaCrO4,麻塞諸塞州波士頓的新英格蘭核公司(New England Nuclear, Boston, MA))載入2小時伴隨頻繁攪拌,在完全RPMI中洗滌兩次並鋪板到微量滴定板中。將效應T細胞與完全RPMI的孔中的靶細胞以不同比率的效應細胞 : 靶細胞(E : T)混合。還製備了僅含有培養基(自發釋放,SR)或1% triton-X 100洗滌劑溶液(總釋放,TR)的另外的孔。在37°C孵育4小時後,收穫來自每個孔的上清液。然後使用γ顆粒計數器(帕卡德儀器公司(Packard Instrument Co.),沃爾瑟姆(Waltham),麻塞諸塞州)測量釋放的51Cr。每種條件進行至少一式三份,並且使用下式計算裂解百分比:%裂解 = (ER - SR)/(TR - SR),其中ER代表每種實驗條件釋放的平均51Cr。Cytotoxicity can be assessed by standard51Cr release assays. See, eg, Milone et al., Molecular Therapy 17(8): 1453-1464 (2009). Briefly, target cells (K562 line and primary B-ALL cells) were treated with 51Cr (such as NaCrO4, New England Nuclear, Boston, MA) at 37°C. ) loaded for 2 hours with frequent agitation, washed twice in complete RPMI and plated into microtiter plates. Effector T cells were mixed with target cells in wells of complete RPMI at various ratios of effector:target (E:T). Additional wells containing medium alone (spontaneous release, SR) or 1% triton-
成像技術可用於評估荷腫瘤的動物模型中CAR的特定運輸和增殖。例如,Barrett等人, Human Gene Therapy [人基因療法] 22:1575-1586 (2011)中已經描述了此類測定。簡言之,NOD/SCID/γc
-/-(NSG)小鼠IV注射Nalm-6細胞,7天後在用CAR構建體電穿孔後4小時用T細胞注射。將T細胞用慢病毒構建體穩定轉染以表現螢火蟲螢光素酶,並將小鼠針對生物發光成像。可替代地,單次注射CAR
+T細胞在Nalm-6異種移植模型中的治療功效和特異性可以如下測量:向NSG小鼠注射經轉導以穩定表現螢火蟲螢光素酶的Nalm-6,然後在7天後單次尾靜脈注射用CAR電穿孔的T細胞。在注射後的不同時間點對動物成像。例如,可以產生在第5天(處理前2天)和第8天(CAR
+PBL後24小時)的代表性小鼠中螢火蟲螢光素酶陽性白血病的光子密度熱圖。
Imaging techniques can be used to assess the specific trafficking and proliferation of CARs in tumor-bearing animal models. Such assays have been described, for example, in Barrett et al., Human Gene Therapy 22:1575-1586 (2011). Briefly, NOD/SCID/γc -/- (NSG) mice were injected IV with Nalm-6 cells and 7 days later with
其他測定,包括本文實例部分中描述的那些測定以及本領域已知的那些測定也可用於評價本文揭露的雙重CART或串聯CART構建體。 治療應用 Other assays, including those described in the Examples section herein as well as those known in the art, can also be used to evaluate the dual CART or tandem CART constructs disclosed herein. therapeutic application
本發明尤其提供了用於治療與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的癌症或疾病或與表現CD19和/或CD22的細胞相關的病症之組成物及方法。在一些實施方式中,癌症或疾病包括例如增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症(如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病);或與表現CD19和/或CD22的細胞相關的非癌症相關適應症。在一方面,與CD22表現相關的癌症或疾病係血液學癌症。在一方面,血液學癌症包括但不限於B細胞惡性腫瘤。在一方面,血液學癌症係白血病或淋巴瘤。在一方面,癌症,例如與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的癌症包括癌症和惡性腫瘤,包括但不限於:例如一或多種急性白血病,包括但不限於B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)(例如,小兒BALL和/或成人BALL)、T細胞急性淋巴球白血病(TALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL);一或多種慢性白血病,包括但不限於慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)、慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL);其他血液學癌症或血液學病症,包括但不限於套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞或大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、多發性骨髓瘤、骨髓化生不良和骨髓化生不良綜合症、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症、和「前白血病」(這係由髓系血細胞的無效產生(或發育不良)聯合的血液學病症的多樣化集合)。在一些實施方式中,與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的疾病包括但不限於表現CD19和/或CD22的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病,以及其任何組合。In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancers or diseases associated with expression of CD19 and/or CD22 or disorders associated with cells expressing CD19 and/or CD22. In some embodiments, the cancer or disease includes, for example, a proliferative disease (such as cancer or malignancy) or a precancerous condition (such as myelodysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, or preleukemia); or is associated with expression of CD19 and/or CD22 cell-associated non-cancer-related indications. In one aspect, the cancer or disease associated with CD22 expression is a hematological cancer. In one aspect, hematological cancers include, but are not limited to, B cell malignancies. In one aspect, the hematological cancer is leukemia or lymphoma. In one aspect, cancers, e.g., cancers associated with CD19 and/or CD22 expression include cancers and malignancies, including, but not limited to, e.g., one or more acute leukemias, including, but not limited to, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BALL) (e.g. , pediatric BALL and/or adult BALL), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (TALL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); one or more chronic leukemias, including but not limited to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); other hematological cancers or hematological conditions, including but not limited to mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic Lymphoblastic cell neoplasm, Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, small or large cell follicular lymphoma, malignant lymphoproliferative disorder, MALT lymphoma, marginal zone Lymphoma, multiple myeloma, myelodysplasia and myelodysplasia syndrome, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma, plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, and "preleukemias" (a diverse collection of hematological disorders associated with ineffective production (or dysplasia) of myeloid blood cells). In some embodiments, diseases associated with expression of CD19 and/or CD22 include, but are not limited to, atypical and/or atypical cancers, malignancies, precancerous conditions, or proliferative diseases expressing CD19 and/or CD22, and any of these combination.
還可以包括與CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症。與CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症包括但不限於例如自體免疫疾病(例如,狼瘡、類風濕性關節炎、多發性硬化症自體免疫性溶血性貧血、純紅血球再生不良、特發性血小板減少性紫癜、埃文斯綜合症(Evans syndrome)、血管炎、大皰性皮膚病、1型糖尿病、斯耶葛籣氏綜合症(Sjogren's syndrome)、抗NMDA受體腦炎和德維克氏病(Devic's disease)、格雷夫斯眼病(Graves' ophthalmopathy)和自體免疫性胰臟炎)、炎性障礙(過敏和氣喘)和移植。Non-cancer related indications related to CD22 expression may also be included. Non-cancer-related indications associated with CD22 expression include, but are not limited to, for example, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell dysplasia, idiopathic Thrombocytopenic purpura, Evans syndrome, vasculitis, bullous dermatosis,
在一方面,本發明提供了用於治療與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的疾病之方法。在一方面,本發明提供了用於治療其中部分腫瘤對CD19和/或CD22係陰性的並且部分腫瘤對CD19和/或CD22係陽性的疾病之方法。例如,本發明之CAR可用於治療已經受過與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的疾病的治療的受試者,其中已經受過與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的治療的受試者表現出與CD19和/或CD22表現相關的疾病。In one aspect, the invention provides methods for treating diseases associated with CD19 and/or CD22 expression. In one aspect, the present invention provides a method for treating a disease in which some tumors are negative for the CD19 and/or CD22 lineage and some tumors are positive for the CD19 and/or CD22 lineage. For example, the CAR of the present invention can be used to treat a subject who has received treatment for a disease associated with CD19 and/or CD22 expression, wherein the subject who has received treatment associated with CD19 and/or CD22 expression exhibits a combination of CD19 and/or CD22 expression and/or CD22 expression-associated disease.
在一方面,本發明關於一種包含如本文所述之CAR的載體,該CAR與用於在哺乳動物T細胞或NK細胞中表現的啟動子可操作地連接。在一方面,本發明提供了一種表現CAR的重組T細胞,用於在治療表現CD19和/或CD22的腫瘤中使用,其中表現CD19 CAR和CD22 CAR的重組T細胞被稱為雙重CART。在一方面,本發明提供了一種表現CAR的重組T細胞,用於在治療表現CD19和/或CD22的腫瘤中使用,其中表現CD19抗原結合結構域和CD22抗原結合結構域的重組T細胞被稱為串聯CART。在一方面,本發明之雙重CART或串聯CART能夠使腫瘤細胞與其表面上表現的至少一種本發明之CD19 CAR或CD22 CAR接觸,使得CART靶向腫瘤細胞並且抑制腫瘤的生長。In one aspect, the invention pertains to a vector comprising a CAR as described herein operably linked to a promoter for expression in mammalian T cells or NK cells. In one aspect, the present invention provides a recombinant T cell expressing CAR for use in the treatment of tumors expressing CD19 and/or CD22, wherein the recombinant T cell expressing CD19 CAR and CD22 CAR is called dual CART. In one aspect, the present invention provides a CAR-expressing recombinant T cell for use in the treatment of tumors expressing CD19 and/or CD22, wherein the recombinant T cell expressing the CD19 antigen-binding domain and the CD22 antigen-binding domain is referred to as For series CART. In one aspect, the dual CART or tandem CART of the present invention can contact tumor cells with at least one CD19 CAR or CD22 CAR of the present invention expressed on their surface, so that the CART targets the tumor cells and inhibits the growth of the tumor.
在一方面,本發明關於一種抑制表現CD19和/或CD22的腫瘤細胞的生長之方法,該方法包括使腫瘤細胞與本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的NK細胞)接觸,使得表現CAR的細胞響應於抗原而激活並且靶向癌細胞,其中腫瘤的生長受到抑制。In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method of inhibiting the growth of tumor cells expressing CD19 and/or CD22, the method comprising allowing the tumor cells to interact with the CAR-expressing cells of the present invention (for example, NK cells expressing dual CARs or tandem CARs) Upon contact, the CAR-expressing cells are activated in response to the antigen and target the cancer cells, where the growth of the tumor is inhibited.
在一方面,本發明關於治療受試者的癌症之方法。該方法包括將本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)投與於受試者,從而治療受試者中的癌症。可以藉由本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)治療的癌症之實例係與CD22表現相關的癌症。可藉由本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)治療的癌症之實例包括但不限於本文所述之血液學癌症。本發明包括一類細胞療法,其中細胞經遺傳修飾以表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR),並且將表現CAR的細胞輸注給有需要的接受者。輸注的細胞能夠殺傷受體中的腫瘤細胞。與抗體療法不同,CAR修飾的細胞能夠在體內複製,導致長期持久性,從而可導致持續的腫瘤控制。在不同方面,向患者投與T細胞或其子代後,向患者投與的該細胞在患者中持續至少四個月、五個月、六個月、七個月、八個月、九個月、十個月、十一個月、十二個月、十三個月、十四個月、十五個月、十六個月、十七個月、十八個月、十九個月、二十個月、二十一個月、二十二個月、二十三個月、兩年、三年、四年、或五年。In one aspect, the invention pertains to methods of treating cancer in a subject. The method comprises administering a CAR-expressing cell of the invention (eg, a cell expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) to a subject, thereby treating cancer in the subject. An example of a cancer that can be treated by a CAR expressing cell of the invention (eg, a cell expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) is a cancer associated with CD22 expression. Examples of cancers that can be treated by CAR-expressing cells of the invention (eg, cells expressing dual or tandem CARs) include, but are not limited to, hematological cancers described herein. The invention includes a type of cell therapy in which cells are genetically modified to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), and the CAR-expressing cells are infused to a recipient in need thereof. The infused cells were able to kill tumor cells in the recipient. Unlike antibody therapies, CAR-modified cells are able to replicate in vivo, resulting in long-term persistence that can lead to sustained tumor control. In various aspects, following administration of the T cells or their progeny to the patient, the cells administered to the patient persist in the patient for at least four months, five months, six months, seven months, eight months, nine months month, ten months, eleven months, twelve months, thirteen months, fourteen months, fifteen months, sixteen months, seventeen months, eighteen months, nineteen months , twenty months, twenty one months, twenty two months, twenty three months, two years, three years, four years, or five years.
本發明還包括一類細胞療法,其中免疫效應細胞(例如,NK細胞或T細胞)例如藉由體外轉錄的RNA被修飾,以瞬時表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR),並且將表現CAR的細胞(例如,CART細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)輸注給有需要的接受者。輸注的細胞能夠殺傷接受者中的癌細胞。因此,在不同方面,在向患者投與表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)之後,向患者投與的表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)存在少於一個月,例如三週、兩週、一週。The present invention also includes a type of cell therapy in which immune effector cells (e.g., NK cells or T cells) are modified, e.g., by in vitro transcribed RNA, to transiently express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), and the CAR-expressing cells ( For example, CART cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) are infused to recipients in need. The infused cells are able to kill cancer cells in the recipient. Thus, in various aspects, the CAR-expressing cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) administered to the patient are present for less than one month after administration of the CAR-expressing cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) to the patient, For example three weeks, two weeks, one week.
在一方面,本發明之CAR修飾的細胞(例如,表現完全人CAR的細胞)可為用於哺乳動物離體免疫和/或體內治療的疫苗類型。在一方面,哺乳動物係人。In one aspect, the CAR-modified cells of the invention (eg, cells expressing a fully human CAR) can be of the type used in vaccines for ex vivo immunization and/or in vivo treatment of mammals. In one aspect, the mammal is a human.
關於離體免疫,在將細胞投與於哺乳動物中之前,在體外進行以下中的至少一者:i) 擴增細胞,ii) 將編碼CAR的核酸引入細胞,或iii) 冷凍保存細胞。For ex vivo immunization, prior to administering the cells to a mammal, at least one of: i) expanding the cells, ii) introducing a nucleic acid encoding a CAR into the cells, or iii) cryopreserving the cells is performed in vitro.
離體程序係本領域熟知的,並在下文更全面地討論。簡而言之,從哺乳動物(例如,人)分離細胞,並用表現本文揭露的CAR的載體進行遺傳修飾(即,體外轉導或轉染)。可以將CAR修飾的細胞投與於哺乳動物受體以提供治療益處。哺乳動物受體可為人,並且CAR修飾的細胞可以相對於受體係自體的。替代性地,相對於受體,細胞可為同種異體的、同基因的或異種異體的。Ex vivo procedures are well known in the art and are discussed more fully below. Briefly, cells are isolated from a mammal (eg, human) and genetically modified (ie, transduced or transfected in vitro) with a vector expressing a CAR disclosed herein. CAR-modified cells can be administered to mammalian recipients to provide therapeutic benefit. The mammalian receptor can be human, and the CAR-modified cell can be autologous to the receptor. Alternatively, the cells may be allogeneic, syngeneic or xenogeneic with respect to the recipient.
造血幹細胞和先驅細胞的離體擴增程序描述於美國專利案號5,199,942(藉由引用併入本文)中,可以應用於本發明之細胞。其他合適的方法係本領域已知的,因此本發明不限於離體擴增細胞的任何具體方法。簡而言之,T細胞的離體培養和擴增包括:(1) 從哺乳動物收集來自周圍血收穫物或骨髓外植體的CD34+造血幹細胞和先驅細胞;以及 (2) 離體擴增此類細胞。除了美國專利案號5,199,942中描述的細胞生長因子外,其他因子如flt3-L、IL-1、IL-3和c-kit配體也可以用於培養和擴增細胞。Ex vivo expansion procedures for hematopoietic stem cells and precursor cells are described in US Pat. No. 5,199,942 (incorporated herein by reference), and can be applied to the cells of the present invention. Other suitable methods are known in the art, and thus the present invention is not limited to any particular method of ex vivo expansion of cells. Briefly, ex vivo culture and expansion of T cells involves: (1) collection of CD34+ hematopoietic stem and precursor cells from peripheral blood harvests or bone marrow explants from mammals; and (2) ex vivo expansion of these class cells. In addition to the cell growth factors described in US Pat. No. 5,199,942, other factors such as flt3-L, IL-1, IL-3, and c-kit ligands can also be used to culture and expand cells.
除了在離體免疫方面使用基於細胞的疫苗之外,本發明還提供了用於體內免疫以引發針對患者中的抗原的免疫反應之組成物及方法。In addition to the use of cell-based vaccines in ex vivo immunization, the present invention also provides compositions and methods for in vivo immunization to elicit an immune response against an antigen in a patient.
通常,如本文描述活化和擴增的細胞可以用於治療和預防免疫受損個體中出現的疾病。特別地,本發明之CAR修飾的細胞用於治療與CD22和/或CD19表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症。在某些方面,本發明之細胞用於治療處於發展與CD22和/或CD19表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症之風險的患者。因此,本發明提供了用於治療或預防與CD22和/或CD19表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與治療有效量的本發明之CAR修飾的細胞。In general, cells activated and expanded as described herein can be used to treat and prevent diseases occurring in immunocompromised individuals. In particular, the CAR-modified cells of the present invention are used to treat diseases, disorders and conditions associated with CD22 and/or CD19 expression. In certain aspects, the cells of the invention are used to treat patients at risk of developing diseases, disorders and conditions associated with CD22 and/or CD19 expression. Accordingly, the present invention provides methods for treating or preventing diseases, disorders and conditions associated with CD22 and/or CD19 expression, the method comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a CAR-modified cell.
在一方面,本發明之表現CAR的細胞可用於治療增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症(如骨髓化生不良、骨髓化生不良綜合症或前白血病)。在一方面,與CD22和/或CD19表現相關的癌症係血液學癌症前白血病、過度增生性障礙、增生或發育不良,其特徵在於細胞的異常生長。In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells of the invention can be used to treat a proliferative disease (such as cancer or malignancy) or a precancerous condition (such as myelodysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, or preleukemia). In one aspect, the cancer associated with CD22 and/or CD19 expression is a hematologic precancerous leukemia, hyperproliferative disorder, hyperplasia or dysplasia, characterized by abnormal growth of cells.
在一方面,本發明之表現CAR的細胞用於治療癌症,其中癌症係血液學癌症。血液學癌症病症係影響血液、骨髓和淋巴系統的癌症類型,如白血病和惡性淋巴組織增生病症。In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells of the invention are used to treat cancer, wherein the cancer is a hematological cancer. Hematological cancer disorders are types of cancer that affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic systems, such as leukemias and lymphoproliferative disorders.
白血病可分為急性白血病和慢性白血病。急性白血病可以進一步分類為急性髓細胞性白血病(AML)和急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)。慢性白血病包括慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)和慢性淋巴性白血病(CLL)。其他相關病症包括骨髓化生不良綜合症(MDS,以前稱為「前白血病」),這係由髓系血細胞的無效產生(或發育不良)聯合的血液學病症的多樣化集合,並且具有轉化為AML的風險。Leukemia can be divided into acute leukemia and chronic leukemia. Acute leukemia can be further classified into acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Chronic leukemia includes chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Other related conditions include myeloid metaplasia syndromes (MDS, formerly known as "preleukemias"), a diverse collection of hematological disorders associated with ineffective production (or dysplasia) of myeloid blood cells and having the potential to transform into Risk of AML.
淋巴瘤係一組從淋巴球發展的血細胞腫瘤。示例性淋巴瘤包括非何杰金氏淋巴瘤和何杰金氏淋巴瘤。Lymphomas are a group of blood cell tumors that develop from lymphocytes. Exemplary lymphomas include non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
在一方面,本發明之組成物和表現CAR的細胞特別有用於治療B細胞惡性腫瘤,如非何杰金氏淋巴瘤,例如DLBCL、濾泡性淋巴瘤或CLL。In one aspect, the compositions and CAR-expressing cells of the invention are particularly useful in the treatment of B cell malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, eg DLBCL, follicular lymphoma or CLL.
非何杰金氏淋巴瘤(NHL)係由B細胞或T細胞形成的一組淋巴球癌。NHL發生在任何年齡,並且通常特徵在於比正常淋巴結更大、體重減輕、和發燒。不同類型的NHL分為侵襲性(快速生長)和惰性(緩慢生長)類型。B細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤包括柏基特淋巴瘤、慢性淋巴球白血病/小淋巴球淋巴瘤(CLL/SLL)、彌漫性大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)、濾泡性淋巴瘤、免疫母細胞性大細胞淋巴瘤、先質B淋巴母細胞淋巴瘤、和套細胞淋巴瘤。T細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤之實例包括蕈狀肉芽腫、間變性大細胞淋巴瘤、和先質T淋巴母細胞淋巴瘤。在骨髓或幹細胞移植後發生的淋巴瘤通常是B細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤。參見例如,Maloney.NEJM. [新英格蘭醫學雜誌] 366.21(2012):2008-16。Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is a group of cancers of lymphocytes formed by B cells or T cells. NHL occurs at any age and is usually characterized by larger than normal lymph nodes, weight loss, and fever. The different types of NHL are divided into aggressive (fast growing) and indolent (slow growing) types. B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas include Burkitt lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma, immune Blastic large cell lymphoma, precursor B lymphoblastic lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma. Examples of T-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma include mycosis fungoides, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and precursor T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Lymphomas that develop after bone marrow or stem cell transplants are usually B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. See eg, Maloney. NEJM. [New England Journal of Medicine] 366.21(2012):2008-16.
彌漫性大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)係從B細胞發展而來的NHL形式。DLBCL係侵襲性淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤可出現在淋巴結中或淋巴系統外,例如胃腸道、睪丸、甲狀腺、皮膚、乳房、骨骼、或腦部中。在DLBCL中通常觀察到細胞形態學的三種變體:中心母細胞、免疫母細胞和未分化細胞。中心母細胞形態係最常見的並且具有中型到大型淋巴球的外觀、具有最小的細胞質。有若干種DLBCL的亞型。例如,原發性中樞神經系統淋巴瘤係一類僅影響大腦的DLBCL,並且與影響大腦外區域的DLBCL的治療不同。另一種類型的DLBCL係原發性縱隔B細胞淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤通常發生在年輕患者中並且在胸部迅速生長。DLBCL的症狀包括頸部、腋窩或腹股溝無痛性快速腫脹,這係由淋巴結腫大引起的。對於一些受試者,腫脹可能是疼痛的。DLBCL的其他症狀包括盜汗、不明原因的發燒和體重減輕。儘管大多數DLBCL患者係成人,但此類疾病有時會發生在兒童身上。DLBCL的治療包括化學療法(例如,環磷醯胺、多柔比星、長春新鹼、強體松、依託泊苷)、抗體(例如,利妥昔單抗)、輻射或幹細胞移植。Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a form of NHL that develops from B cells. DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma that can develop in lymph nodes or outside the lymphatic system, such as in the gastrointestinal tract, testes, thyroid, skin, breast, bones, or brain. Three variants of cell morphology are commonly observed in DLBCL: centroblasts, immunoblasts, and undifferentiated cells. The centroblastic morphotype is the most common and has the appearance of medium to large lymphocytes with minimal cytoplasm. There are several subtypes of DLBCL. For example, primary central nervous system lymphoma is a type of DLBCL that affects only the brain and is treated differently than DLBCL that affects areas outside the brain. Another type of DLBCL is primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, which usually occurs in young patients and grows rapidly in the chest. Symptoms of DLBCL include painless, rapid swelling of the neck, armpits, or groin caused by enlarged lymph nodes. For some subjects, swelling may be painful. Other symptoms of DLBCL include night sweats, unexplained fever, and weight loss. Although most people with DLBCL are adults, the disease sometimes occurs in children. Treatment of DLBCL includes chemotherapy (eg, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, etoposide), antibodies (eg, rituximab), radiation, or stem cell transplantation.
濾泡性淋巴瘤係一類非何杰金氏淋巴瘤,並且係濾泡中心B細胞(中心細胞和中心母細胞)的淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤具有至少部分濾泡模式。濾泡性淋巴瘤細胞表現B細胞標記物CD10、CD19、CD20、和CD22。濾泡性淋巴瘤細胞通常對CD5係陰性的。在形態學上,濾泡性淋巴瘤腫瘤由含有中心細胞(也稱為裂解的濾泡中心細胞或小細胞)和中心母細胞(也稱為大的未裂解的濾泡中心細胞或大細胞)的混合物的濾泡組成。濾泡被非惡性細胞(大多數是T細胞)包圍。濾泡主要含有中心細胞和少數中心母細胞。世界衛生組織(WHO)對疾病進行如下形態學分類:1級(< 5個中心母細胞/高倍視野(hpf));2級(6-15個中心母細胞/hpf);3級(> 15個中心母細胞/hpf)。3級進一步細分為以下等級:3A級(仍存在中心細胞);3B級(濾泡幾乎全部由中心母細胞組成)。濾泡性淋巴瘤的治療包括化學療法,例如,烷基化劑、核苷類似物、含蒽環的方案(例如,稱為CHOP-環磷醯胺、多柔比星、長春新鹼、強體松/普賴蘇穠的組合療法)、抗體(例如,利妥昔單抗)、放射免疫療法、和造血幹細胞移植。Follicular lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and is a lymphoma of follicular center B cells (centrocytes and centroblasts) that have an at least partial follicular pattern. Follicular lymphoma cells express the B cell markers CD10, CD19, CD20, and CD22. Follicular lymphoma cells are usually negative for the CD5 lineage. Morphologically, follicular lymphoma tumors are composed of centrocytes (also called lysed follicular center cells or small cells) and centroblasts (also called large unlysed follicular center cells or large cells) follicular composition of the mixture. Follicles are surrounded by non-malignant cells, mostly T cells. Follicles mainly contain centrocytes and a few centroblasts. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies the disease as follows morphologically: grade 1 (<5 centroblasts/high power field (hpf)); grade 2 (6-15 centroblasts/hpf); grade 3 (>15 centroblasts/hpf).
CLL係B細胞惡性腫瘤,其特徵在於骨髓、血液、淋巴結和脾中的腫瘤細胞增殖和積累。CLL診斷時的中值年齡約為65歲。當前的治療包括化學療法、輻射療法、生物療法、或骨髓移植。有時症狀藉由外科手術(例如,脾臟切除術去除腫大的脾臟)或藉由輻射療法(例如,對腫脹的淋巴結進行減瘤)。用於治療CLL的化學治療劑包括例如氟達拉濱、2-氯去氧腺苷(克拉屈濱)、氯芥苯丁酸、長春新鹼、噴司他丁、環磷醯胺、阿侖單抗(Campath-1H)、多柔比星和強體松。CLL的生物療法包括抗體,例如阿侖單抗、利妥昔單抗、和奧法木單抗;以及酪胺酸激酶抑制劑療法。許多標準可以用於對CLL的階段進行分類,例如Rai或Binet系統。Rai系統描述了CLL具有五個階段:僅存在淋巴球增多的第0階段;其中存在淋巴結腫大的第I階段;其中存在脾腫大、淋巴結腫大或兩者都存在的第II階段;其中存在貧血、器官腫大或兩者都存在的第III階段(進展由體重減輕、疲勞、發熱、嚴重器官腫大、和淋巴球計數迅速增加定義);和其中存在貧血、血小板減少症、器官腫大或其組合的IV階段。在Binet階段系統下,有三類:其中存在淋巴球增多並且少於3個淋巴結增大(該階段包括所有Rai 0階段患者,Rai I階段患者的一半和Rai II階段患者的三分之一)的階段A;其中涉及三個或更多淋巴結的階段B;和其中存在貧血、或血小板減少症、或兩者的階段C。該等分類系統可以與免疫球蛋白基因突變的測量組合,以提供疾病狀態的更準確的表徵。突變的免疫球蛋白基因的存在與改善的預後相關。CLL is a B-cell malignancy characterized by the proliferation and accumulation of tumor cells in the bone marrow, blood, lymph nodes, and spleen. The median age at diagnosis of CLL is about 65 years. Current treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biological therapy, or bone marrow transplant. Sometimes symptoms are resolved by surgery (eg, splenectomy to remove an enlarged spleen) or by radiation therapy (eg, detumescence of swollen lymph nodes). Chemotherapeutic agents used in the treatment of CLL include, for example, fludarabine, 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (cladribine), erucinate, vincristine, pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, alendramide Monoclonal antibody (Campath-1H), doxorubicin and prednisone. Biological therapies for CLL include antibodies, such as alemtuzumab, rituximab, and ofatumumab; and tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. A number of criteria can be used to classify the stages of CLL, such as the Rai or Binet systems. The Rai system describes CLL as having five stages:
在另一個實施方式中,將本發明之表現CAR的細胞用於治療癌症或白血病(例如具有白血病幹細胞)。例如,白血病幹細胞係CD34 +/CD38 −白血病細胞。 In another embodiment, the CAR-expressing cells of the invention are used to treat cancer or leukemia (eg, with leukemia stem cells). For example, the leukemia stem cell line CD34 + /CD38 − leukemia cells.
本發明尤其提供了用於治療癌症之組成物及方法。在一方面,癌症係血液學癌症,包括但不限於一或多種急性白血病,包括但不限於B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)(例如,小兒BALL和/或成人BALL)、T細胞急性淋巴球白血病(TALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL);一或多種慢性白血病,包括但不限於慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)、慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL);其他血液學癌症或血液學病症,包括但不限於套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞或大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、多發性骨髓瘤、骨髓化生不良和骨髓化生不良綜合症、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症、和「前白血病」(這係由髓系血細胞的無效產生(或發育不良)聯合的血液學病症的多樣化集合),以及與CD22表現相關的疾病,包括但不限於表現CD22的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病;以及其任何組合。In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cancer. In one aspect, the cancer is a hematological cancer, including but not limited to one or more acute leukemias, including but not limited to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BALL) (e.g., pediatric BALL and/or adult BALL), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Leukemia (TALL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); one or more chronic leukemias, including but not limited to chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); other Hematologic cancers or hematologic conditions, including but not limited to mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, small or large cell follicular lymphoma, malignant lymphoproliferative disorders, MALT lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, multiple myeloma, myelodysplasia, and myelosis dysplastic syndrome, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, plasmablastic lymphoma, plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, and "preleukemic ” (a diverse collection of hematological disorders combined with ineffective production (or dysplasia) of myeloid blood cells), and diseases associated with CD22 expression, including but not limited to atypical and/or nonclassical cancers expressing CD22 , malignancy, precancerous condition, or proliferative disease; and any combination thereof.
本發明之CAR修飾的細胞可以單獨地投與,或作為與稀釋劑和/或與其他組分如IL-2或其他細胞介素或細胞群體組合的藥物組成物投與。The CAR-modified cells of the invention can be administered alone, or as a pharmaceutical composition with diluents and/or in combination with other components such as IL-2 or other cytokines or cell populations.
在另一方面,本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)可用於治療先前用表現CD19 CAR的細胞治療的受試者。在一些實施方式中,本發明之表現CAR的細胞在先前用表現CD19 CAR的細胞治療的癌症或其他病症復發後投與。In another aspect, CAR-expressing cells of the invention (eg, cells expressing dual CARs or tandem CARs) can be used to treat subjects previously treated with CD19 CAR-expressing cells. In some embodiments, CAR-expressing cells of the invention are administered following recurrence of a cancer or other disorder previously treated with CD19 CAR-expressing cells.
在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症係表現CD19的。在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症係表現CD22的。在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症係表現CD19和CD22的。In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder expresses CD19. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder expresses CD22. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder expresses CD19 and CD22.
在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症先前未對表現CD19 CAR的細胞沒有響應。在一些實施方式中,受試癌症或其他病症對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應。在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療的響應性比目前的更大。在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應。在一些實施方式中,癌症或其他病症對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應並且不再對表現CD19 CAR的細胞有響應。In some embodiments, the cancer or other condition has not previously been non-responsive to cells expressing the CD19 CAR. In some embodiments, the subject cancer or other condition is responsive to treatment with cells expressing a CD19 CAR. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder is more responsive to treatment with cells expressing the CD19 CAR than is currently the case. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder is responsive to treatment with cells expressing a CD19 CAR. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell and no longer responds to the CD19 CAR expressing cell.
在一些實施方式中,由於對表現CD19 CAR的細胞的響應性降低或喪失,因此投與CAR(例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR)(例如,如本文所述之)。在一些實施方式中,已停止表現CD19 CAR的細胞療法。在一些實施方式中,由於對表現CD19 CAR的細胞的回應性降低或喪失,因此已停止CD19 CAR療法。In some embodiments, a CAR (eg, dual CAR or tandem CAR) is administered due to decreased or lost responsiveness to cells expressing the CD19 CAR (eg, as described herein). In some embodiments, the cell therapy expressing the CD19 CAR has been discontinued. In some embodiments, CD19 CAR therapy has been discontinued due to decreased or lost responsiveness to cells expressing the CD19 CAR.
在一些實施方式中,由於對表現CD22 CAR的細胞的響應性降低或喪失,因此投與CAR(例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR)(例如,如本文所述之)。在一些實施方式中,已停止表現CD22 CAR的細胞療法。在一些實施方式中,由於對CD22 CAR表現細胞的回應性降低或喪失,因此已停止CD22 CAR療法。In some embodiments, a CAR (eg, dual CAR or tandem CAR) is administered due to decreased or lost responsiveness to cells expressing the CD22 CAR (eg, as described herein). In some embodiments, the cell therapy expressing the CD22 CAR has been discontinued. In some embodiments, the CD22 CAR therapy has been discontinued due to decreased or lost responsiveness to the CD22 CAR expressing cells.
本發明還提供了用於預防、治療和/或控制與表現CD22的細胞相關的疾病(例如,表現CD22的血液學癌症或非典型癌症)之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與結合表現CD22的細胞的本發明之表現CD22 CAR的細胞。在一方面,受試者係人。與表現CD22的細胞相關的障礙之非限制性實例包括自體免疫疾病(例如,狼瘡、類風濕性關節炎、多發性硬化症自體免疫性溶血性貧血、純紅血球再生不良、特發性血小板減少性紫癜、埃文斯綜合症、血管炎、大皰性皮膚病、1型糖尿病、斯耶葛籣氏綜合症、抗NMDA受體腦炎和德維克氏病、格雷夫斯眼病和自體免疫性胰臟炎)、炎性障礙(過敏和氣喘)、移植和癌症(如表現CD22的血液學癌症或非典型癌症)。The present invention also provides methods for preventing, treating and/or managing diseases associated with CD22-expressing cells (for example, hematological or atypical cancers expressing CD22), the method comprising administering to a subject in need thereof CD22 CAR-expressing cells of the present invention in combination with CD22-expressing cells. In one aspect, the subject is a human. Non-limiting examples of disorders associated with CD22-expressing cells include autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell dysplasia, idiopathic platelet Attenuated purpura, Evans syndrome, vasculitis, bullous dermatosis,
本發明還提供了用於預防、治療和/或控制與表現CD22的細胞相關的疾病之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與結合表現CD22的細胞的本發明之表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞。在一方面,受試者係人。The present invention also provides a method for preventing, treating and/or controlling diseases associated with CD22-expressing cells, the method comprising administering to a subject in need a dual-expressing CAR or CAR of the present invention that binds to CD22-expressing cells. Cells with tandem CARs. In one aspect, the subject is a human.
在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的無響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的部分響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的完全響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的非復發者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的復發者。In some embodiments, the subject is a non-responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a partial responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a complete responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a non-relapser of CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a relapser of CD19 CAR therapy.
在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症不表現CD19。在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症相對於該癌症或其他病症對表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的時候具有10%、20%、30%、40%、50%或更多的CD19表現水平降低。在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症表現CD22。In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell does not express CD19. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell has a 10%, 20%, 30% relative to when the cancer or other disorder responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell %, 40%, 50% or more of CD19 expression levels were reduced. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell expresses CD22.
在一些實施方式中,本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)在先前用表現CD19 CAR的細胞治療的癌症或其他病症復發後投與。 骨髓消融 In some embodiments, CAR-expressing cells of the invention (eg, cells expressing dual CARs or tandem CARs) are administered after recurrence of a cancer or other disorder previously treated with CD19 CAR-expressing cells. bone marrow ablation
在一方面,本發明提供了用於骨髓消融之組成物及方法。例如,在一方面,本發明提供了用於根除受試者中現有骨髓的至少一部分之組成物及方法。在某些情況下,本文描述了包含本發明之CD22 CAR和CD19 CAR的表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)根除CD19和/或CD22陽性骨髓髓系先驅細胞。In one aspect, the invention provides compositions and methods for bone marrow ablation. For example, in one aspect, the invention provides compositions and methods for eradicating at least a portion of existing bone marrow in a subject. In certain instances, described herein is the eradication of CD19 and/or CD22 positive myeloid lineage precursor cells by CAR-expressing cells (eg, cells expressing dual or tandem CARs) comprising a CD22 CAR and a CD19 CAR of the invention.
在一方面,本發明提供了一種骨髓消融方法,該方法包括向需要骨髓消融的受試者投與本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)。例如,本方法可用於根除患有其中骨髓移植或骨髓再調理係有益的治療策略的疾病或障礙的受試者的一些或所有現有骨髓。在一方面,本發明之骨髓消融方法(包含投與本文其他地方描述的表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)在骨髓移植之前在受試者中進行。因此,在一方面,本發明之方法在骨髓或幹細胞移植之前提供細胞調理方案。在一方面,骨髓移植包含幹細胞移植。骨髓移植可包含自體或同種異體的細胞的移植。In one aspect, the present invention provides a method of bone marrow ablation, the method comprising administering to a subject in need of bone marrow ablation the CAR-expressing cells of the present invention (eg, cells expressing dual CARs or tandem CARs). For example, the method can be used to eradicate some or all of the existing bone marrow in a subject suffering from a disease or disorder in which bone marrow transplantation or bone marrow reconditioning is a beneficial treatment strategy. In one aspect, the bone marrow ablation methods of the invention comprising administering CAR-expressing cells as described elsewhere herein (eg, cells expressing dual or tandem CARs) are performed in a subject prior to bone marrow transplantation. Thus, in one aspect , the method of the invention provides a cell conditioning regimen prior to bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. In one aspect, bone marrow transplantation comprises stem cell transplantation. Bone marrow transplantation may comprise transplantation of autologous or allogeneic cells.
本發明提供了一種治療疾病或障礙之方法,該方法包括投與本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)以根除現有骨髓的至少一部分。該方法可以用作治療方案的至少部分,用於治療骨髓移植有益的任何疾病或障礙。也就是說,本方法可用於需要骨髓移植的任何受試者。在一方面,包含投與表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)的骨髓消融有用於治療AML。在某些方面,藉由本方法的骨髓消融可用於治療血液學癌症、實性瘤、血液學疾病、代謝障礙、HIV、HTLV、溶酶體貯積病、和免疫缺陷。The invention provides a method of treating a disease or disorder comprising administering a CAR-expressing cell of the invention (eg, a cell expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) to eradicate at least a portion of the existing bone marrow. The method can be used as at least part of a therapeutic regimen for any disease or disorder for which bone marrow transplantation would be beneficial. That is, the method can be used in any subject in need of a bone marrow transplant. In one aspect, bone marrow ablation comprising administration of CAR-expressing cells (eg, cells expressing dual or tandem CARs) is useful in the treatment of AML. In certain aspects, bone marrow ablation by the present methods can be used to treat hematological cancers, solid tumors, hematological diseases, metabolic disorders, HIV, HTLV, lysosomal storage diseases, and immunodeficiency.
本文揭露的組成物及方法可用於根除現有骨髓的至少一部分以治療血液學癌症,該等血液學癌症包括但不限於本文所述之癌症,例如白血病、淋巴瘤、骨髓瘤、ALL、AML、CLL、CML、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤(例如,DLBCL或濾泡性淋巴瘤)、和多發性骨髓瘤。The compositions and methods disclosed herein can be used to eradicate at least a portion of existing bone marrow to treat hematological cancers, including but not limited to cancers described herein, such as leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, ALL, AML, CLL , CML, Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (eg, DLBCL or follicular lymphoma), and multiple myeloma.
本文揭露的組成物及方法可用於治療血液學疾病,該等血液學疾病包括但不限於骨髓化生不良、貧血、陣發性夜間血紅素尿、再生不良性貧血、獲得性純紅血球性貧血、戴-布二氏貧血(Diamon-Blackfan anemia)、範可尼(Fanconi)貧血、血球減少症、無症狀性血小板減少症、骨髓增生性障礙、真性紅血球增多症、原發性血小板增多症、骨髓纖維化、血紅素病、鐮形血球貧血症、β地中海貧血症等。The compositions and methods disclosed herein can be used to treat hematological diseases, including but not limited to myelodysplasia, anemia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, aplastic anemia, acquired pure red blood cell anemia, Diamon-Blackfan anemia, Fanconi anemia, cytopenia, asymptomatic thrombocytopenia, myeloproliferative disorder, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, bone marrow Fibrosis, heme disease, sickle cell anemia, beta thalassemia, etc.
在一方面,本發明提供了一種治療癌症(包含骨髓調理)之方法,其中受試者的骨髓的至少一部分被本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)根除。例如,在某些情況下,受試者的骨髓包含惡性先質細胞,其可以被表現CAR的細胞(例如表現雙重CAR或串聯CAR的細胞)的活性靶向和消除。在一方面,骨髓調理療法包括在根除天然骨髓後向受試者投與骨髓或幹細胞移植物。在一方面,將骨髓再調理療法與一或多種其他抗癌療法(包括但不限於抗腫瘤CAR療法、化學療法、輻射等)組合。In one aspect, the invention provides a method of treating cancer comprising bone marrow conditioning, wherein at least a portion of the subject's bone marrow is eradicated by a CAR-expressing cell of the invention (eg, a cell expressing a dual CAR or a tandem CAR). For example, in certain instances, the subject's bone marrow contains malignant precursor cells that can be targeted and eliminated by the activity of CAR-expressing cells, such as cells expressing dual CARs or tandem CARs. In one aspect, bone marrow conditioning therapy involves administering a bone marrow or stem cell transplant to a subject following eradication of native bone marrow. In one aspect, bone marrow reconditioning therapy is combined with one or more other anti-cancer therapies (including but not limited to anti-tumor CAR therapy, chemotherapy, radiation, etc.).
在一方面,在輸注骨髓或幹細胞移植之前可能需要根除投與的表現CAR 的細胞。可以使用任何合適的策略或治療(包括但不限於使用自殺基因、使用RNA編碼的CAR的有限的CAR持久性、或包括抗體或化學療法的抗T細胞模式)來完成根除表現CAR的細胞。 CD22 相關疾病和 / 或障礙 In one aspect, it may be desirable to eradicate administered CAR-expressing cells prior to bone marrow infusion or stem cell transplantation. Eradicating CAR-expressing cells can be accomplished using any suitable strategy or treatment, including but not limited to the use of suicide genes, limited CAR persistence using RNA-encoded CARs, or anti-T cell modalities including antibodies or chemotherapy. CD22 -related diseases and / or disorders
本揭露尤其提供了用於治療與CD22表現相關的疾病或與表現CD22的細胞相關的病症之組成物及方法,該等疾病或病症包括例如增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症;或與表現CD22的細胞相關的非癌症相關適應症。在一方面,與CD22表現相關的癌症係血液學癌症。在一方面,血液學癌症包括但不限於B細胞惡性腫瘤。在一方面,血液學癌症係白血病或淋巴瘤。在一方面,與CD22表現相關的癌症包括癌症和惡性腫瘤,包括但不限於:例如一或多種急性白血病,包括但不限於B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)(例如,小兒BALL和/或成人BALL)、T細胞急性淋巴球白血病(TALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL);一或多種慢性白血病,包括但不限於慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL);其他血液學癌症或血液學病症,包括但不限於套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞或大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、和瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症。在另一個實施方式中,與CD22表現相關的疾病包括但不限於表現CD22的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病;以及其任何組合。Among other things, the present disclosure provides compositions and methods for treating diseases associated with CD22 expression or disorders associated with cells expressing CD22, including, for example, proliferative diseases (such as cancer or malignancy) or precancerous conditions ; or non-cancer-related indications associated with CD22-expressing cells. In one aspect, the cancer associated with CD22 expression is a hematological cancer. In one aspect, hematological cancers include, but are not limited to, B cell malignancies. In one aspect, the hematological cancer is leukemia or lymphoma. In one aspect, cancers associated with CD22 expression include cancers and malignancies, including, but not limited to, for example, one or more acute leukemias, including but not limited to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BALL) (e.g., pediatric BALL and/or adult BALL), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (TALL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); one or more chronic leukemias, including but not limited to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); other blood Cancer or hematological conditions, including but not limited to mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma , follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, small cell or large cell follicular lymphoma, malignant lymphoproliferative disorder, MALT lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma plasmablastic lymphoma, plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. In another embodiment, diseases associated with CD22 expression include, but are not limited to, atypical and/or atypical cancers, malignancies, precancerous conditions, or proliferative diseases expressing CD22; and any combination thereof.
還可以包括與CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症。與CD22表現相關的非癌症相關適應症包括但不限於例如自體免疫疾病(例如,狼瘡、類風濕性關節炎、多發性硬化症自體免疫性溶血性貧血、純紅血球再生不良、特發性血小板減少性紫癜、埃文斯綜合症、血管炎、大皰性皮膚病、1型糖尿病、斯耶葛籣氏綜合症、抗NMDA受體腦炎和德維克氏病、格雷夫斯眼病和自體免疫性胰臟炎)、炎性障礙(過敏和氣喘)和實體器官或造血細胞移植。Non-cancer related indications related to CD22 expression may also be included. Non-cancer-related indications associated with CD22 expression include, but are not limited to, for example, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell dysplasia, idiopathic Thrombocytopenic purpura, Evans syndrome, vasculitis, bullous dermatosis,
在一方面,本揭露提供了用於治療與CD22表現相關的疾病之方法。在一方面,本揭露提供了用於治療疾病之方法,其中部分腫瘤對CD22係陰性的,並且部分腫瘤對CD22係陽性的。例如,本揭露之CAR可用於治療已經受過與CD22表現相關的疾病的治療的受試者,其中已經受過與CD22表現相關的治療的受試者表現出與CD22表現相關的疾病。In one aspect, the present disclosure provides methods for treating diseases associated with CD22 expression. In one aspect, the present disclosure provides methods for treating a disease wherein a portion of the tumor is negative for CD22 and a portion of the tumor is positive for CD22. For example, the CARs of the present disclosure can be used to treat a subject who has been treated for a disease associated with CD22 expression, wherein the subject who has received treatment for a CD22 expression exhibits a disease associated with CD22 expression.
在一方面,本揭露關於一種包含CAR(例如雙重CAR或串聯CAR)的載體,該CAR與用於在哺乳動物細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)中表現的啟動子可操作地連接。在一方面,本揭露提供了表現CAR的重組T細胞,例如,雙重CAR或串聯CAR,用於在治療表現CD22的腫瘤中使用。在一方面,本揭露之表現CAR的T細胞或NK細胞能夠使腫瘤細胞與其表面上表現的至少一種本揭露之CAR接觸,使得表現CAR的T細胞或NK細胞靶向腫瘤細胞並且抑制腫瘤的生長。In one aspect, the disclosure pertains to a vector comprising a CAR (eg, a dual CAR or a tandem CAR) operably linked to a promoter for expression in mammalian cells (eg, T cells or NK cells). In one aspect, the present disclosure provides recombinant T cells expressing a CAR, eg, a dual CAR or a tandem CAR, for use in treating tumors expressing CD22. In one aspect, a CAR-expressing T cell or NK cell of the present disclosure is capable of contacting a tumor cell with at least one CAR of the present disclosure expressed on its surface, such that the CAR-expressing T cell or NK cell targets the tumor cell and inhibits tumor growth .
在一方面,本揭露關於一種抑制表現CD22的腫瘤細胞的生長之方法,該方法包括使腫瘤細胞與本揭露之CAR細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)接觸,使得CART回應於抗原而激活並且靶向癌細胞,其中腫瘤的生長受到抑制。In one aspect, the disclosure pertains to a method of inhibiting the growth of tumor cells expressing CD22, the method comprising contacting the tumor cells with a CAR cell of the disclosure (e.g., a T cell or NK cell), such that the CART is activated in response to the antigen and Targets cancer cells where tumor growth is inhibited.
在一方面,本揭露關於一種治療受試者的癌症之方法。該方法包括向受試者投與本揭露之表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞),使得治療受試者的癌症。可藉由本揭露之表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)治療的癌症之實例係與CD22表現相關的癌症。可藉由本揭露之表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)治療的癌症之實例包括但不限於本文所述之血液學癌症。In one aspect, the disclosure pertains to a method of treating cancer in a subject. The method includes administering to a subject a CAR-expressing cell (eg, a T cell or NK cell) of the present disclosure, such that the cancer in the subject is treated. An example of a cancer that can be treated by a CAR expressing cell (eg, T cell or NK cell) of the present disclosure is a cancer associated with CD22 expression. Examples of cancers that can be treated by the CAR-expressing cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) of the present disclosure include, but are not limited to, the hematological cancers described herein.
本揭露包括一類細胞療法,其中細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)經遺傳修飾以表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR),並將表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)輸注給有需要的接受者。輸注的細胞能夠殺傷受體中的腫瘤細胞。與抗體療法不同,CAR修飾的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)能夠在體內複製,導致長期持久性,從而可導致持續的腫瘤控制。在不同方面,向患者投與細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)後,向患者投與的T細胞在患者中持續至少四個月、五個月、六個月、七個月、八個月、九個月、十個月、十一個月、十二個月、十三個月、十四個月、十五個月、十六個月、十七個月、十八個月、十九個月、二十個月、二十一個月、二十二個月、二十三個月、兩年、三年、四年、或五年。The present disclosure includes a type of cell therapy in which cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) are genetically modified to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), and the CAR-expressing cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) are infused into an Recipient of need. The infused cells were able to kill tumor cells in the recipient. Unlike antibody therapies, CAR-modified cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) are able to replicate in vivo, resulting in long-term persistence that can lead to sustained tumor control. In various aspects, after administration of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) to the patient, the T cells administered to the patient persist in the patient for at least four months, five months, six months, seven months, eight months month, nine months, ten months, eleven months, twelve months, thirteen months, fourteen months, fifteen months, sixteen months, seventeen months, eighteen months, Nineteen months, twenty months, twenty one months, twenty two months, twenty three months, two years, three years, four years, or five years.
本揭露還包括一類細胞療法,其中免疫效應細胞(例如,NK細胞或T細胞)例如藉由體外轉錄的RNA被修飾,以瞬時表現嵌合抗原受體(CAR),並且將表現CAR的細胞(例如,CART細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)輸注給有需要的接受者。輸注的細胞能夠殺傷接受者中的癌細胞。因此,在不同方面,在向患者投與表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)之後,向患者投與的表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)存在少於一個月,例如三週、兩週、一週。The present disclosure also includes a type of cell therapy in which immune effector cells (e.g., NK cells or T cells) are modified to transiently express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), e.g., by in vitro transcribed RNA, and CAR-expressing cells ( For example, CART cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) are infused to recipients in need. The infused cells are able to kill cancer cells in the recipient. Thus, in various aspects, the CAR-expressing cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) administered to the patient are present for less than one month after administration of the CAR-expressing cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) to the patient, For example three weeks, two weeks, one week.
不希望受任何具體理論的束縛,由CAR修飾的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)引發的抗腫瘤免疫反應可為主動或被動免疫反應,或可替代地可為由於直接與間接免疫反應。在一方面,CAR轉導的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)響應於表現CD22的人癌細胞表現出特異性促炎細胞介素分泌和有效的細胞溶解活性,抵抗可溶性CD22抑制,介導旁觀者殺傷,並且介導建立的人腫瘤的消退。例如,在表現CD22的腫瘤的異質區域內的無抗原腫瘤細胞可能易受先前已經針對鄰近的抗原陽性癌細胞反應的CD22重定向T細胞的間接破壞。Without wishing to be bound by any particular theory, anti-tumor immune responses elicited by CAR-modified cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) can be active or passive immune responses, or alternatively can be due to direct and indirect immune responses. In one aspect, CAR-transduced cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) exhibit specific pro-inflammatory interleukin secretion and potent cytolytic activity in response to CD22-expressing human cancer cells, resist inhibition by soluble CD22, and mediate Bystander killing and mediating regression of established human tumors. For example, antigen-free tumor cells within heterogeneous regions of CD22-expressing tumors may be vulnerable to indirect destruction by CD22-redirected T cells that have previously responded against neighboring antigen-positive cancer cells.
在一方面,本揭露之CAR細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)(例如,表現完全人CAR的細胞)可為用於哺乳動物離體免疫和/或體內治療的疫苗類型。在一方面,哺乳動物係人。In one aspect, the CAR cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) of the present disclosure (eg, cells expressing a fully human CAR) can be a type of vaccine for ex vivo immunization and/or in vivo treatment of mammals. In one aspect, the mammal is a human.
關於離體免疫,在將細胞投與於哺乳動物中之前,在體外進行以下中的至少一者:i) 擴增細胞,ii) 將編碼CAR的核酸引入細胞,或iii) 冷凍保存細胞。For ex vivo immunization, prior to administering the cells to a mammal, at least one of: i) expanding the cells, ii) introducing a nucleic acid encoding a CAR into the cells, or iii) cryopreserving the cells is performed in vitro.
離體程序係本領域熟知的,並在下文更全面地討論。簡而言之,從哺乳動物(例如,人)分離細胞,並用表現本文揭露的CAR的載體進行遺傳修飾(即,體外轉導或轉染)。可以將CAR細胞投與於哺乳動物接受者以提供治療益處。哺乳動物受體可為人,並且CAR細胞可以相對於受體係自體的。替代性地,相對於受體,細胞可為同種異體的、同基因的或異種異體的。Ex vivo procedures are well known in the art and are discussed more fully below. Briefly, cells are isolated from a mammal (eg, human) and genetically modified (ie, transduced or transfected in vitro) with a vector expressing a CAR disclosed herein. CAR cells can be administered to a mammalian recipient to provide a therapeutic benefit. The mammalian recipient can be a human, and the CAR cell can be autologous to the recipient. Alternatively, the cells may be allogeneic, syngeneic or xenogeneic with respect to the recipient.
造血幹細胞和先驅細胞的離體擴增程序描述於美國專利案號5,199,942(將該文獻藉由引用併入本文)中,可以應用於本揭露之細胞。其他合適的方法在本領域中係已知的,因此本揭露不限於離體擴增細胞的任何具體方法。簡而言之,T細胞的離體培養和擴增包括:(1) 從哺乳動物收集來自周圍血收穫物或骨髓外植體的CD34+造血幹細胞和先驅細胞;以及 (2) 離體擴增此類細胞。除了美國專利案號5,199,942中描述的細胞生長因子外,其他因子如flt3-L、IL-1、IL-3和c-kit配體也可以用於培養和擴增細胞。Ex vivo expansion procedures for hematopoietic stem cells and precursor cells are described in US Pat. No. 5,199,942 (herein incorporated by reference), and can be applied to cells of the present disclosure. Other suitable methods are known in the art, and thus this disclosure is not limited to any particular method of ex vivo expansion of cells. Briefly, ex vivo culture and expansion of T cells involves: (1) collection of CD34+ hematopoietic stem and precursor cells from peripheral blood harvests or bone marrow explants from mammals; and (2) ex vivo expansion of these class cells. In addition to the cell growth factors described in US Pat. No. 5,199,942, other factors such as flt3-L, IL-1, IL-3, and c-kit ligands can also be used to culture and expand cells.
除了在離體免疫方面使用基於細胞的疫苗之外,本揭露還提供了用於體內免疫以引發針對患者中的抗原的免疫反應之組成物及方法。In addition to the use of cell-based vaccines in ex vivo immunization, the present disclosure also provides compositions and methods for in vivo immunization to elicit an immune response against an antigen in a patient.
通常,如本文描述活化和擴增的細胞可以用於治療和預防免疫受損個體中出現的疾病。特別地,本揭露之CAR修飾的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)用於治療與CD22表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症。在某些方面,本揭露之細胞用於治療處於發展與CD22表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症之風險的患者。因此,本揭露提供了用於治療或預防與CD22表現相關的疾病、障礙和病症之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與治療有效量的本揭露之CAR細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)。In general, cells activated and expanded as described herein can be used to treat and prevent diseases occurring in immunocompromised individuals. In particular, the CAR-modified cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) of the present disclosure are used to treat diseases, disorders and conditions associated with CD22 expression. In certain aspects, cells of the present disclosure are used to treat patients at risk of developing diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with CD22 expression. Accordingly, the present disclosure provides methods for treating or preventing diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with CD22 expression comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a CAR cell (e.g., a T cell) of the present disclosure. or NK cells).
在一方面,本揭露之表現CAR的細胞可用於治療增生性疾病(如癌症或惡性腫瘤)或癌前病症。在一方面,與CD22表現相關的癌症係血液學癌症前白血病、過度增生性障礙、增生或發育不良,其特徵在於細胞的異常生長。In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure can be used to treat proliferative diseases (such as cancer or malignancy) or precancerous conditions. In one aspect, the cancer associated with CD22 expression is a hematological precancerous leukemia, hyperproliferative disorder, hyperplasia or dysplasia, characterized by abnormal growth of cells.
在一方面,本揭露之表現CAR的細胞用於治療癌症,其中癌症係血液學癌症。血液學癌症病症係影響血液、骨髓和淋巴系統的癌症類型,如白血病和惡性淋巴組織增生病症。In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure are used to treat cancer, wherein the cancer is a hematological cancer. Hematological cancer disorders are types of cancer that affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic systems, such as leukemias and lymphoproliferative disorders.
白血病可分為急性白血病和慢性白血病。急性白血病可以進一步分類為急性髓細胞性白血病(AML)和急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)。慢性白血病包括慢性髓細胞性白血病(CML)和慢性淋巴性白血病(CLL)。其他相關病症包括骨髓化生不良綜合症(MDS,以前稱為「前白血病」),這係由髓系血細胞的無效產生(或發育不良)聯合的血液學病症的多樣化集合,並且具有轉化為AML的風險。Leukemia can be divided into acute leukemia and chronic leukemia. Acute leukemia can be further classified into acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Chronic leukemia includes chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Other related conditions include myeloid metaplasia syndromes (MDS, formerly known as "preleukemias"), a diverse collection of hematological disorders associated with ineffective production (or dysplasia) of myeloid blood cells and having the potential to transform into Risk of AML.
淋巴瘤係一組從淋巴球發展的血細胞腫瘤。示例性淋巴瘤包括非何杰金氏淋巴瘤和何杰金氏淋巴瘤。Lymphomas are a group of blood cell tumors that develop from lymphocytes. Exemplary lymphomas include non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
在一方面,本揭露之組成物和CART細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞特別有用於治療B細胞惡性腫瘤,如非何杰金氏淋巴瘤,例如DLBCL、濾泡性淋巴瘤或CLL。In one aspect, the compositions of the present disclosure and CAR T cells or CAR expressing NK cells are particularly useful in the treatment of B cell malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, eg DLBCL, follicular lymphoma or CLL.
非何杰金氏淋巴瘤(NHL)係由B細胞或T細胞形成的一組淋巴球癌。NHL發生在任何年齡,並且通常特徵在於比正常淋巴結更大、體重減輕、和發燒。不同類型的NHL分為侵襲性(快速生長)和惰性(緩慢生長)類型。B細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤包括柏基特淋巴瘤、慢性淋巴球白血病/小淋巴球淋巴瘤(CLL/SLL)、彌漫性大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)、濾泡性淋巴瘤、免疫母細胞性大細胞淋巴瘤、先質B淋巴母細胞淋巴瘤、和套細胞淋巴瘤。T細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤之實例包括蕈狀肉芽腫、間變性大細胞淋巴瘤、和先質T淋巴母細胞淋巴瘤。在骨髓或幹細胞移植後發生的淋巴瘤通常是B細胞非何杰金氏淋巴瘤。參見例如,Maloney. NEJM. [新英格蘭醫學雜誌] 366.21(2012):2008-16。Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is a group of cancers of lymphocytes formed by B cells or T cells. NHL occurs at any age and is usually characterized by larger than normal lymph nodes, weight loss, and fever. The different types of NHL are divided into aggressive (fast growing) and indolent (slow growing) types. B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas include Burkitt lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma, immune Blastic large cell lymphoma, precursor B lymphoblastic lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma. Examples of T-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma include mycosis fungoides, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, and precursor T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Lymphomas that develop after bone marrow or stem cell transplants are usually B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. See eg, Maloney. NEJM. [New England Journal of Medicine] 366.21(2012):2008-16.
彌漫性大B細胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)係從B細胞發展而來的NHL形式。DLBCL係侵襲性淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤可出現在淋巴結中或淋巴系統外,例如胃腸道、睪丸、甲狀腺、皮膚、乳房、骨骼、或腦部中。在DLBCL中通常觀察到細胞形態學的三種變體:中心母細胞、免疫母細胞和未分化細胞。中心母細胞形態係最常見的並且具有中型到大型淋巴球的外觀、具有最小的細胞質。有若干種DLBCL的亞型。例如,原發性中樞神經系統淋巴瘤係一類僅影響大腦的DLBCL,並且與影響大腦外區域的DLBCL的治療不同。另一種類型的DLBCL係原發性縱隔B細胞淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤通常發生在年輕患者中並且在胸部迅速生長。DLBCL的症狀包括頸部、腋窩或腹股溝無痛性快速腫脹,這係由淋巴結腫大引起的。對於一些受試者,腫脹可能是疼痛的。DLBCL的其他症狀包括盜汗、不明原因的發燒和體重減輕。儘管大多數DLBCL患者係成人,但此類疾病有時會發生在兒童身上。DLBCL的治療包括化學療法(例如,環磷醯胺、多柔比星、長春新鹼、強體松、依託泊苷)、抗體(例如,利妥昔單抗)、輻射或幹細胞移植。Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a form of NHL that develops from B cells. DLBCL is an aggressive lymphoma that can develop in lymph nodes or outside the lymphatic system, such as in the gastrointestinal tract, testes, thyroid, skin, breast, bones, or brain. Three variants of cell morphology are commonly observed in DLBCL: centroblasts, immunoblasts, and undifferentiated cells. The centroblastic morphotype is the most common and has the appearance of medium to large lymphocytes with minimal cytoplasm. There are several subtypes of DLBCL. For example, primary central nervous system lymphoma is a type of DLBCL that affects only the brain and is treated differently than DLBCL that affects areas outside the brain. Another type of DLBCL is primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, which usually occurs in young patients and grows rapidly in the chest. Symptoms of DLBCL include painless, rapid swelling of the neck, armpits, or groin caused by enlarged lymph nodes. For some subjects, swelling may be painful. Other symptoms of DLBCL include night sweats, unexplained fever, and weight loss. Although most people with DLBCL are adults, the disease sometimes occurs in children. Treatment of DLBCL includes chemotherapy (eg, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, etoposide), antibodies (eg, rituximab), radiation, or stem cell transplantation.
濾泡性淋巴瘤係一類非何杰金氏淋巴瘤,並且係濾泡中心B細胞(中心細胞和中心母細胞)的淋巴瘤,該淋巴瘤具有至少部分濾泡模式。濾泡性淋巴瘤細胞表現B細胞標記物CD10、CD19、CD20、和CD22。濾泡性淋巴瘤細胞通常對CD5係陰性的。在形態學上,濾泡性淋巴瘤腫瘤由含有中心細胞(也稱為裂解的濾泡中心細胞或小細胞)和中心母細胞(也稱為大的未裂解的濾泡中心細胞或大細胞)的混合物的濾泡組成。濾泡被非惡性細胞(大多數是T細胞)包圍。濾泡主要含有中心細胞和少數中心母細胞。世界衛生組織(WHO)對疾病進行如下形態學分類:1級(< 5個中心母細胞/高倍視野(hpf));2級(6-15個中心母細胞/hpf);3級(> 15個中心母細胞/hpf)。3級進一步細分為以下等級:3A級(仍存在中心細胞);3B級(濾泡幾乎全部由中心母細胞組成)。濾泡性淋巴瘤的治療包括化學療法,例如,烷基化劑、核苷類似物、含蒽環的方案(例如,稱為CHOP-環磷醯胺、多柔比星、長春新鹼、強體松/普賴蘇穠的組合療法)、抗體(例如,利妥昔單抗)、放射免疫療法、和造血幹細胞移植。Follicular lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and is a lymphoma of follicular center B cells (centrocytes and centroblasts) that have an at least partial follicular pattern. Follicular lymphoma cells express the B cell markers CD10, CD19, CD20, and CD22. Follicular lymphoma cells are usually negative for the CD5 lineage. Morphologically, follicular lymphoma tumors are composed of centrocytes (also called lysed follicular center cells or small cells) and centroblasts (also called large unlysed follicular center cells or large cells) follicular composition of the mixture. Follicles are surrounded by non-malignant cells, mostly T cells. Follicles mainly contain centrocytes and a few centroblasts. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies the disease as follows morphologically: grade 1 (<5 centroblasts/high power field (hpf)); grade 2 (6-15 centroblasts/hpf); grade 3 (>15 centroblasts/hpf).
CLL係B細胞惡性腫瘤,其特徵在於骨髓、血液、淋巴結和脾中的腫瘤細胞增殖和積累。CLL診斷時的中值年齡約為65歲。當前的治療包括化學療法、輻射療法、生物療法、或骨髓移植。有時症狀藉由外科手術(例如,脾臟切除術去除腫大的脾臟)或藉由輻射療法(例如,對腫脹的淋巴結進行減瘤)。用於治療CLL的化學治療劑包括例如氟達拉濱、2-氯去氧腺苷(克拉屈濱)、氯芥苯丁酸、長春新鹼、噴司他丁、環磷醯胺、阿侖單抗(Campath-1H)、多柔比星和強體松。CLL的生物療法包括抗體,例如阿侖單抗、利妥昔單抗、和奧法木單抗;以及酪胺酸激酶抑制劑療法。許多標準可以用於對CLL的階段進行分類,例如Rai或Binet系統。Rai系統描述了CLL具有五個階段:僅存在淋巴球增多的第0階段;其中存在淋巴結腫大的第I階段;其中存在脾腫大、淋巴結腫大或兩者都存在的第II階段;其中存在貧血、器官腫大或兩者都存在的第III階段(進展由體重減輕、疲勞、發熱、嚴重器官腫大、和淋巴球計數迅速增加定義);和其中存在貧血、血小板減少症、器官腫大或其組合的IV階段。在Binet階段系統下,有三類:其中存在淋巴球增多並且少於3個淋巴結增大(該階段包括所有Rai 0階段患者,Rai I階段患者的一半和Rai II階段患者的三分之一)的階段A;其中涉及三個或更多淋巴結的階段B;和其中存在貧血、或血小板減少症、或兩者的階段C。該等分類系統可以與免疫球蛋白基因突變的測量組合,以提供疾病狀態的更準確的表徵。突變的免疫球蛋白基因的存在與改善的預後相關。CLL is a B-cell malignancy characterized by the proliferation and accumulation of tumor cells in the bone marrow, blood, lymph nodes, and spleen. The median age at diagnosis of CLL is about 65 years. Current treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, biological therapy, or bone marrow transplant. Sometimes symptoms are resolved by surgery (eg, splenectomy to remove an enlarged spleen) or by radiation therapy (eg, detumescence of swollen lymph nodes). Chemotherapeutic agents used in the treatment of CLL include, for example, fludarabine, 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (cladribine), erucinate, vincristine, pentostatin, cyclophosphamide, alendramide Monoclonal antibody (Campath-1H), doxorubicin and prednisone. Biological therapies for CLL include antibodies, such as alemtuzumab, rituximab, and ofatumumab; and tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. A number of criteria can be used to classify the stages of CLL, such as the Rai or Binet systems. The Rai system describes CLL as having five stages:
在另一個實施方式中,將本揭露之表現CAR的細胞用於治療癌症或白血病(例如,具有白血病幹細胞)。例如,白血病幹細胞係CD34 +/CD38 −白血病細胞。 In another embodiment, CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure are used to treat cancer or leukemia (eg, with leukemia stem cells). For example, the leukemia stem cell line CD34 + /CD38 − leukemia cells.
本揭露尤其提供了用於治療癌症之組成物及方法。在一方面,癌症係血液學癌症,包括但不限於一或多種急性白血病,包括但不限於B細胞急性淋巴球白血病(BALL)(例如,小兒BALL和/或成人BALL)、T細胞急性淋巴球白血病(TALL)、小淋巴球淋巴瘤(SLL)、急性淋巴球白血病(ALL);一或多種慢性白血病,包括但不限於慢性淋巴球白血病(CLL);其他血液學癌症或血液學病症,包括但不限於套細胞淋巴瘤(MCL)、B細胞前淋巴球白血病、母細胞性漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、柏基特淋巴瘤、彌漫大B細胞淋巴瘤、濾泡性淋巴瘤、毛細胞白血病、小細胞或大細胞濾泡性淋巴瘤、惡性淋巴組織增生病症、MALT淋巴瘤、緣帶淋巴瘤、非何杰金氏淋巴瘤、何杰金氏淋巴瘤、漿母細胞淋巴瘤、漿細胞樣樹突狀細胞腫瘤、瓦爾登斯特倫巨球蛋白血症,以及與CD22表現相關的疾病,包括但不限於表現CD22的非典型和/或非經典癌症、惡性腫瘤、癌前病症或增生性疾病;以及其任何組合。Among other things, the disclosure provides compositions and methods for treating cancer. In one aspect, the cancer is a hematological cancer, including but not limited to one or more acute leukemias, including but not limited to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BALL) (e.g., pediatric BALL and/or adult BALL), T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia Leukemia (TALL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL); one or more chronic leukemias, including but not limited to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); other hematological cancers or hematological conditions, including But not limited to mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, Burkitt lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, hair follicular lymphoma, Cellular Leukemia, Small or Large Cell Follicular Lymphoma, Malignant Lymphoproliferative Disorder, MALT Lymphoma, Marginal Lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Plasmablastic Lymphoma, Plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, and disorders associated with CD22 expression, including but not limited to atypical and/or atypical cancers, malignancies, precancerous conditions expressing CD22 or a proliferative disease; and any combination thereof.
本揭露之CAR細胞可以單獨地投與,或作為與稀釋劑和/或與其他組分如IL-2或其他細胞介素或細胞群體組合的藥物組成物投與。The CAR cells of the present disclosure can be administered alone, or as a pharmaceutical composition with diluents and/or in combination with other components such as IL-2 or other cytokines or cell populations.
本揭露還提供了用於抑制表現CD22的細胞群體的增殖或減少表現CD22的細胞群體之方法,該方法包括使包含表現CD22的細胞的細胞群體與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之表現CAR的細胞接觸。在一個方面,本揭露提供了用於抑制表現CD22的癌細胞群體的增殖或減少表現CD22的癌細胞群體之方法,該方法包括使表現CD22的癌細胞群體與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之表現CAR的細胞接觸。在一方面,本揭露提供了用於抑制表現CD22的癌細胞群體的增殖或減少表現CD22的癌細胞群體之方法,該方法包括使表現CD22的癌細胞群體與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之CART接觸。在某些方面,在患有B細胞惡性腫瘤或與表現CD22的細胞相關的另一種癌症的受試者中、或B細胞惡性腫瘤或與表現CD22的細胞相關的另一種癌症的動物模型中,相對於陰性對照,本揭露之表現CAR的細胞將細胞和/或癌細胞的數量、數目、量或百分比減少了至少25%、至少30%、至少40%、至少50%、至少65%、至少75%、至少85%、至少95%、或至少99%。在一方面,受試者係人。The present disclosure also provides a method for inhibiting the proliferation of a CD22-expressing cell population or reducing a CD22-expressing cell population, the method comprising combining a cell population comprising the CD22-expressing cells with a CAR-expressing CAR of the present disclosure in combination with the CD22-expressing cells. cell contact. In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a method for inhibiting the proliferation of a population of CD22-expressing cancer cells or reducing a population of CD22-expressing cancer cells, the method comprising combining the population of CD22-expressing cancer cells with a CD22-expressing cell according to the present disclosure. Cells expressing the CAR are contacted. In one aspect, the present disclosure provides a method for inhibiting the proliferation of a population of CD22-expressing cancer cells or reducing a population of CD22-expressing cancer cells, the method comprising combining the population of CD22-expressing cancer cells with a CD22-expressing cell according to the present disclosure. CART contact. In certain aspects, in a subject having a B-cell malignancy or another cancer associated with CD22-expressing cells, or in an animal model of a B-cell malignancy or another cancer associated with CD22-expressing cells, The CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure reduce the number, number, amount or percentage of cells and/or cancer cells by at least 25%, at least 30%, at least 40%, at least 50%, at least 65%, at least 75%, at least 85%, at least 95%, or at least 99%. In one aspect, the subject is a human.
本揭露還提供了用於預防、治療和/或控制與表現CD22的細胞相關的疾病(例如,表現CD22的血液學癌症或非典型癌症)之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之表現CAR的細胞。在一方面,受試者係人。與表現CD22的細胞相關的障礙的非限制性實例包括自體免疫疾病(例如,狼瘡、類風濕性關節炎、多發性硬化症自體免疫性溶血性貧血、純紅血球再生不良、特發性血小板減少性紫癜、埃文斯綜合症、血管炎、大皰性皮膚病、1型糖尿病、斯耶葛籣氏綜合症、抗NMDA受體腦炎和德維克氏病、格雷夫斯眼病和自體免疫性胰臟炎)、炎性障礙(過敏和氣喘)、移植和癌症(如表現CD22的血液學癌症或非典型癌症)。The disclosure also provides methods for preventing, treating and/or managing diseases associated with CD22-expressing cells (eg, CD22-expressing hematological or atypical cancers), the method comprising administering to a subject in need thereof CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure in combination with CD22-expressing cells. In one aspect, the subject is a human. Non-limiting examples of disorders associated with CD22-expressing cells include autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell dysplasia, idiopathic platelet Attenuated purpura, Evans syndrome, vasculitis, bullous dermatosis,
本揭露還提供了用於預防、治療和/或控制與表現CD22的細胞相關的疾病之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之表現CAR的細胞。在一方面,受試者係人。The present disclosure also provides methods for preventing, treating and/or managing diseases associated with CD22-expressing cells, the method comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a CAR-expressing cell of the present disclosure that binds to a CD22-expressing cell . In one aspect, the subject is a human.
本揭露提供了用於預防與表現CD22的細胞相關的癌症復發之方法,該方法包括向有需要的受試者投與結合表現CD22的細胞的本揭露之表現CAR的細胞。在一方面,該等方法包括向有需要的受試者投與有效量的結合表現CD22的細胞的本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與有效量的另一種療法的組合。The present disclosure provides methods for preventing recurrence of cancer associated with CD22-expressing cells, the method comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a CAR-expressing cell of the present disclosure that binds to a CD22-expressing cell. In one aspect, the methods comprise administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a CAR-expressing cell described herein that binds a CD22-expressing cell in combination with an effective amount of another therapy.
在一些實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞表現CD19、CD123、FLT-3、ROR-1、CD79b、CD179b、CD79a、CD10、CD34和/或CD20。在某些實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞表現CD19。在一些實施方式中,表現CD22的細胞不表現CD19。In some embodiments, the CD22-expressing cells express CD19, CD123, FLT-3, ROR-1, CD79b, CD179b, CD79a, CD10, CD34, and/or CD20. In certain embodiments, the cells expressing CD22 express CD19. In some embodiments, the cells expressing CD22 do not express CD19.
在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的無響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的部分響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的完全響應者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的非復發者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的部分復發者。在一些實施方式中,受試者係CD19 CAR療法的完全復發者。In some embodiments, the subject is a non-responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a partial responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a complete responder to CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a non-relapser of CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a partial relapser of CD19 CAR therapy. In some embodiments, the subject is a complete relapser of CD19 CAR therapy.
在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症不表現CD19。在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症相對於該癌症或其他病症對表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的時候具有10%、20%、30%、40%、50%或更多的CD19表現水平降低。在一些實施方式中,先前對用表現CD19 CAR的細胞的治療有響應的癌症或其他病症表現CD22。In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell does not express CD19. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell has a 10%, 20%, 30% relative to when the cancer or other disorder responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell %, 40%, 50% or more of CD19 expression levels were reduced. In some embodiments, the cancer or other disorder that previously responded to treatment with a CD19 CAR expressing cell expresses CD22.
在一些實施方式中,本揭露之表現CAR的細胞在先前用表現CD19 CAR的細胞治療的癌症或其他病症復發後投與。 在治療多發性骨髓瘤中使用的 CD19 CAR T 細胞 In some embodiments, the CAR-expressing cells of the present disclosure are administered following recurrence of a cancer or other disorder previously treated with a CD19 CAR-expressing cell. CD19 CAR T cells used in the treatment of multiple myeloma
即使採用化學療法、靶向療法和自體幹細胞移植的目前方案,骨髓瘤也被認為是一種無法治癒的疾病。在一項研究(未揭露)中,描述了用具有嵌合抗原受體(慢病毒/CD19:4-1BB:CD3ζ;也稱為「CART19」或CTL019)的針對CD19的自體T細胞治療多發性骨髓瘤(MM)。該實例證明CD19定向的CAR療法具有基於靶向表現非常低(藉由大多數方法檢測不到)水平的CD19的骨髓瘤幹細胞和/或腫瘤細胞而建立深度、長期持久緩解的潛力。 用於何杰金氏淋巴瘤的 CAR19 T 細胞療法 Even with current regimens of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and autologous stem cell transplantation, myeloma is considered an incurable disease. In one (unpublished) study, the use of CD19-targeted autologous T cells with a chimeric antigen receptor (lentivirus/CD19:4-1BB:CD3ζ; also known as "CART19" or CTL019) was described for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM). This example demonstrates the potential of CD19-directed CAR therapy to establish deep, long-term durable responses based on targeting myeloma stem cells and/or tumor cells expressing very low (undetectable by most methods) levels of CD19. CAR19 T cell therapy for Hodgkin's lymphoma
CAR19 T細胞療法也可用於治療何杰金氏淋巴瘤(HL)。何杰金氏淋巴瘤的特徵在於存在衍生自選殖生發中心B細胞的惡性霍奇金裡德-斯騰伯格(HRS)細胞。有若干個指示CAR19 T細胞療法對HL的治療功效的因素。對HL腫瘤的CD19染色顯示腫瘤和腫瘤微環境內的表現CD19的(CD19 +)細胞。一項研究顯示,表現CD19的選殖B細胞群體(CD20 +CD27 +ALDH +)負責何杰金氏淋巴瘤細胞系的產生和維持,並且還在大多數HL患者的血液中循環(Jones等人, Blood [血液], 2009, 113(23):5920-5926)。還提出該選殖B細胞群體引起或有助於惡性HRS細胞的產生。因此,CART19療法將耗減這種有助於腫瘤發生或維持腫瘤細胞的B細胞群體。另一項研究顯示,B細胞耗減延緩了多種鼠模型中的實性腫瘤生長(Kim等人, J Immunotherapy [免疫療法雜誌], 2008, 31(5):446-57)。為了支持HL腫瘤微環境中B細胞的耗減導致一些抗腫瘤作用的觀點,在臨床上正在測試目前療法(如利妥昔單抗)用於靶向和消減HL中的腫瘤B細胞(Younes等人, Blood [血液], 2012, 119(18):4123-8)。與慢性炎症相關的從頭開始的癌發生也已顯示出B細胞依賴性(de Visser等人, Cancer Cell [癌細胞], 2005, 7(5):411-23)。該等研究的結果表明,靶向特別是在HL腫瘤微環境中的B細胞群體可用於藉由減少或抑制疾病進展或腫瘤生長來治療HL。 CLL 患者的無響應者亞群表現出免疫檢查點抑制劑分子的表現增加 CAR19 T cell therapy can also be used to treat Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the presence of malignant Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells derived from selective germinal center B cells. There are several factors indicative of the therapeutic efficacy of CAR19 T cell therapy for HL. CD19 staining of HL tumors revealed CD19 expressing (CD19 + ) cells within the tumor and tumor microenvironment. One study showed that a CD19-expressing clonal B-cell population (CD20 + CD27 + ALDH + ) was responsible for the generation and maintenance of Hodgkin's lymphoma cell lines and also circulated in the blood of most HL patients (Jones et al. , Blood [blood], 2009, 113(23):5920-5926). It has also been suggested that this colonized B cell population causes or contributes to the generation of malignant HRS cells. Therefore, CART19 therapy will deplete this population of B cells that contribute to tumorigenesis or maintenance of tumor cells. Another study showed that B cell depletion delayed solid tumor growth in various mouse models (Kim et al., J Immunotherapy, 2008, 31(5):446-57). In support of the idea that depletion of B cells in the HL tumor microenvironment results in some antitumor effects, current therapies (such as rituximab) are being tested in the clinic for targeting and depleting tumor B cells in HL (Younes et al. People, Blood, 2012, 119(18):4123-8). De novo carcinogenesis associated with chronic inflammation has also been shown to be B cell dependent (de Visser et al., Cancer Cell, 2005, 7(5):411-23). The results of these studies suggest that targeting B cell populations particularly in the HL tumor microenvironment can be used to treat HL by reducing or inhibiting disease progression or tumor growth. Non-responder subpopulation of CLL patients exhibits increased expression of immune checkpoint inhibitor molecules
在一項研究(數據未公開)中,評估來自34名CLL患者的臨床製造的CART19細胞的免疫檢查點抑制劑分子(如PD-1、LAG3和TIM3)的表現。該群組對CART19的響應係已知的,並且因此可以評估響應與生物標記物表現模式之間的相關性。 mTOR 抑制對老年人中免疫衰老的影響 In one study (unpublished data), the performance of immune checkpoint inhibitor molecules such as PD-1, LAG3, and TIM3 was assessed in clinically manufactured CART19 cells from 34 CLL patients. The response of this cohort to CART19 is known, and thus the correlation between the response and the biomarker expression pattern can be assessed. Effects of mTOR inhibition on immune senescence in the elderly
mTOR抑制對免疫衰老的功效描述於例如國際申請WO/2015/073644的實例1中,並且該申請的全部內容藉由引用併入本文。 增強老年人受試者中對疫苗的免疫反應 The efficacy of mTOR inhibition on immune senescence is described eg in Example 1 of International Application WO/2015/073644, and the entire content of this application is incorporated herein by reference. Enhanced immune response to vaccines in elderly subjects
mTOR抑制對增強免疫反應的功效描述於例如國際申請WO/2015/073644的實例2中,並且該申請的全部內容藉由引用併入本文。 低劑量 mTOR 抑制增加能量和運動; The efficacy of mTOR inhibition to enhance the immune response is described eg in Example 2 of International Application WO/2015/073644, and the entire content of this application is incorporated herein by reference. Low-dose mTOR inhibition increases energy and locomotion;
mTOR抑制對能量和運動的影響描述於例如20國際申請WO/2015/073644的實例3中,並且該申請的全部內容藉由引用併入本文。 用 RAD001 抑制 P70 S6 激酶 The effect of mTOR inhibition on energy and movement is described eg in Example 3 of 20 International Application WO/2015/073644, and the entire content of this application is incorporated herein by reference. Inhibition of P70 S6 Kinase with RAD001
mTOR抑制對P70 S6激酶抑制的影響描述於例如國際申請WO/2015/073644的實例4中,並且該申請的全部內容藉由引用併入本文。 外源性 IL-7 增強 CAR T 細胞的功能 The effect of mTOR inhibition on P70 S6 kinase inhibition is described eg in Example 4 of International Application WO/2015/073644, and the entire content of this application is incorporated herein by reference. Exogenous IL-7 enhances the function of CAR T cells
在過繼轉移CAR T細胞後,一些患者經歷CAR T細胞的有限持久性,這可導致次優水平的抗腫瘤活性。在該實例中,在小鼠異種移植模型中評估外源性人IL-7的投與效果,其中已觀察到對CAR T細胞的初始次優響應。 組合療法 After adoptive transfer of CAR T cells, some patients experience limited persistence of CAR T cells, which can lead to suboptimal levels of antitumor activity. In this example, the effect of administration of exogenous human IL-7 was evaluated in a mouse xenograft model where an initial suboptimal response to CAR T cells had been observed. combination therapy
本文所述之表現CAR的細胞可以與其他已知的藥劑和療法組合使用。如本文所用,「組合」投與意指在受試者患病期間將兩種(或更多種)不同的治療遞送至受試者,例如在受試者被診斷患有障礙後並且在該障礙被治癒或清除前或者在由於其他原因終止治療前遞送兩種或多種治療。在一些實施方式中,當第二治療的遞送開始時,第一治療的遞送仍在進行,所以就投與而言存在重疊。這在本文中有時被稱為「同時遞送」或「並行遞送」。在一些實施方式中,一種治療的遞送在另一種治療遞送開始之前結束。在每一種情況的一些實施方式中,由於是組合投與,該治療更有效。例如,與不存在第一治療的條件下投與第二治療所觀察到的結果相比,第二治療更有效,例如使用更少的第二治療觀察到等效的作用,或者第二治療將症狀減少更大的程度,或者觀察到對第一治療而言類似的情況。在一些實施方式中,與不存在另一種治療的條件下遞送一種治療所觀察到的結果相比,遞送使得症狀或與該障礙相關的其他參數減少更多。兩種治療的作用可以部分累加、完全累加、或大於累加。該遞送可以使得當遞送第二治療時,遞送的第一治療的作用仍然是可檢測的。The CAR-expressing cells described herein can be used in combination with other known agents and therapies. As used herein, "combination" administration means the delivery of two (or more) different treatments to a subject during the subject's illness, for example after the subject has been diagnosed with the disorder and in the Two or more treatments were delivered before the disorder was cured or cleared or before treatment was discontinued for other reasons. In some embodiments, when the delivery of the second therapy begins, the delivery of the first therapy is still in progress, so there is an overlap in terms of administration. This is sometimes referred to herein as "simultaneous delivery" or "parallel delivery." In some embodiments, delivery of one therapy ends before delivery of another therapy begins. In some embodiments in each case, the treatment is more effective due to the combined administration. For example, the second treatment is more effective than that observed when the second treatment is administered in the absence of the first treatment, e.g., an equivalent effect is observed with less of the second treatment, or the second treatment will Symptoms were reduced to a greater extent, or a similar situation was observed for the first treatment. In some embodiments, delivery results in a greater reduction in symptoms or other parameters associated with the disorder than is observed with delivery of one treatment in the absence of the other treatment. The effects of the two treatments can be partially additive, fully additive, or more than additive. The delivery may be such that the effect of the first therapy delivered is still detectable when the second therapy is delivered.
可以將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞和至少一種另外的治療劑同時(以相同或分開的組成物)、或依序投與。對於依次投與,可以首先投與本文所述之表現CAR的細胞並且可以其次投與另外的藥劑,或者可以顛倒投與順序。The CAR-expressing cells described herein and at least one additional therapeutic agent can be administered simultaneously (in the same or separate compositions), or sequentially. For sequential administration, the CAR-expressing cells described herein can be administered first and the additional agent can be administered second, or the order of administration can be reversed.
可以將CAR療法和/或其他治療劑、程序或方式在活性障礙期間,或在緩解期或活性較低的疾病期間投與。可以將CAR療法在其他治療之前、與治療並行、治療後或在障礙緩解期間投與。CAR therapy and/or other therapeutic agents, procedures or modalities may be administered during active disorders, or during remission or less active disease. CAR therapy can be administered before other treatments, concurrently with treatment, after treatment, or during remission of the disorder.
當組合投與時,可以將CAR療法和另外的藥劑(例如,第二藥劑或第三藥劑)或全部以比單獨使用(例如,作為單一療法)的每種藥劑的量或劑量更高、更低或相同的量或劑量投與。在某些實施方式中,CAR療法、另外的藥劑(例如,第二藥劑或第三藥劑)、或全部的投與量或劑量比單獨使用(例如,作為單一療法)的每種藥劑的量或劑量低(例如,至少20%、至少30%、至少40%、或至少50%)。在一些實施方式中,CAR療法、另外的藥劑(例如,第二或第三藥劑)、或全部的導致期望效果(例如,治療癌症)的量或劑量比單獨使用(例如,作為單一療法)的每種藥劑實現相同治療效果所需的量或劑量低(例如,低至少20%、至少30%、至少40%、或至少50%)。When administered in combination, the CAR therapy and the additional agent (e.g., a second agent or a third agent) or both may be administered in higher, lower amounts or doses than each agent used alone (e.g., as a monotherapy). Low or the same amount or dose is administered. In certain embodiments, the amount or dose of CAR therapy, additional agent (e.g., second agent or third agent), or all administered is greater than the amount of each agent used alone (e.g., as a monotherapy) or The dose is low (eg, at least 20%, at least 30%, at least 40%, or at least 50%). In some embodiments, the CAR therapy, the additional agent (e.g., a second or third agent), or both, results in a desired effect (e.g., treating cancer) in an amount or dose that is greater than that used alone (e.g., as a monotherapy). The amount or dose of each agent required to achieve the same therapeutic effect is lower (eg, at least 20%, at least 30%, at least 40%, or at least 50% lower).
在另外的方面,本文所述之表現CAR的細胞可以用於與以下項組合的治療方案中:手術、細胞介素、輻射或化學療法(如,環磷醯胺、氟達拉濱、組蛋白脫乙醯化酶抑制劑、去甲基化劑或肽疫苗),例如在Izumoto等人 2008 J Neurosurg,[神經外科雜誌] 108:963-971中所述。在一方面,本文所述之表現CAR的細胞可以與CD20xCD3雙特異性抗體組合使用。In additional aspects, the CAR-expressing cells described herein can be used in a treatment regimen in combination with surgery, cytokines, radiation, or chemotherapy (e.g., cyclophosphamide, fludarabine, histone deacetylase inhibitors, demethylating agents or peptide vaccines) as described, for example, in Izumoto et al. 2008 J Neurosurg, 108:963-971. In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells described herein can be used in combination with a CD20xCD3 bispecific antibody.
在某些情況下,將本發明化合物與其他治療劑組合,如其他抗癌劑、抗過敏劑、抗噁心劑(或抗嘔劑)、鎮痛藥、細胞保護劑及其組合。In certain instances, the compounds of the invention are combined with other therapeutic agents, such as other anticancer agents, antiallergic agents, antinausea (or antiemetic), analgesics, cytoprotective agents, and combinations thereof.
考慮用於組合療法的一般化學治療劑包括阿那曲唑(Arimidex®)、比卡魯胺(Casodex®)、硫酸博來黴素(Blenoxane®)、白消安(Myleran®)、白消安注射液(Busulfex®)、卡培他濱(Xeloda®)、N4-戊氧羰基-5-去氧-5-氟胞苷、卡鉑(Paraplatin®)、卡莫司汀(BiCNU®)、氯芥苯丁酸(Leukeran®)、順鉑(Platinol®)、克拉屈濱(Leustatin®)、環磷醯胺(Cytoxan®或Neosar®)、阿糖胞苷、胞嘧啶阿拉伯糖苷(Cytosar-U®)、阿糖胞苷脂質體注射液(DepoCyt®)、達卡巴𠯤(DTIC-Dome®)、更生黴素(放線菌素D、Cosmegan)、鹽酸柔紅黴素(Cerubidine®)、檸檬酸道諾黴素脂質體注射液(DaunoXome®)、地塞米松、多西他賽(Taxotere®)、鹽酸多柔比星(Adriamycin®、Rubex®)、依託泊苷(Vepesid®)、磷酸氟達拉濱(Fludara®)、5-氟尿嘧啶(Adrucil®、Efudex®)、氟他胺(Eulexin®)、替紮他濱(tezacitibine)、吉西他濱(二氟去氧胞苷)、羥基脲(Hydrea®)、伊達比星(Idamycin®)、依弗醯胺(IFEX®)、伊立替康(Camptosar®)、L-天冬醯胺酶(ELSPAR®)、醛葉酸鈣、黴法蘭(Alkeran®)、6-巰基嘌呤(Purinethol®)、胺甲喋呤(Folex®)、米托蒽醌(Novantrone®)、麥羅塔、紫杉醇(Taxol®)、nab-紫杉醇(Abraxane®)、phoenix(Yttrium90/MX-DTPA)、噴司他丁、聚苯丙生(polifeprosan)20與卡莫司汀的植入物(Gliadel®)、枸櫞酸他莫昔芬(Nolvadex®)、替尼泊苷(Vumon®)、6-硫代鳥嘌呤、噻替派、替拉紮明(Tirazone®)、注射用鹽酸托泊替康(Hycamptin®)、長春花鹼(Velban®)、長春新鹼(Oncovin®)和長春瑞濱(Navelbine®)。Common chemotherapeutic agents to consider for combination therapy include anastrozole (Arimidex®), bicalutamide (Casodex®), bleomycin sulfate (Blenoxane®), busulfan (Myleran®), busulfan injection (Busulfex®), capecitabine (Xeloda®), N4-pentyloxycarbonyl-5-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine, carboplatin (Paraplatin®), carmustine (BiCNU®), chlorine mustard Phenylbutyric acid (Leukeran®), cisplatin (Platinol®), cladribine (Leustatin®), cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan® or Neosar®), cytarabine, cytosine arabinoside (Cytosar-U®) , Cytarabine Liposomal Injection (DepoCyt®), Dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome®), Dactinomycin (Actinomycin D, Cosmegan), Daunorubicin Hydrochloride (Cerubidine®), Daunorubicin Citrate Mycin liposome injection (DaunoXome®), dexamethasone, docetaxel (Taxotere®), doxorubicin hydrochloride (Adriamycin®, Rubex®), etoposide (Vepesid®), fludarabine phosphate (Fludara®), 5-fluorouracil (Adrucil®, Efudex®), flutamide (Eulexin®), tezacitabine (tezacitibine), gemcitabine (difluorodeoxycytidine), hydroxyurea (Hydrea®), Ida Idamycin®, Ifexamide (IFEX®), Irinotecan (Camptosar®), L-Asparaginase (ELSPAR®), Aldehyde Calcium Folate, Alkeran®, 6- Mercaptopurine (Purinethol®), methotrexate (Folex®), mitoxantrone (Novantrone®), mylotar, paclitaxel (Taxol®), nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane®), phoenix (Yttrium90/MX-DTPA ), pentostatin, pofeprosan 20 and carmustine implants (Gliadel®), tamoxifen citrate (Nolvadex®), teniposide (Vumon®), 6-thioguanine, thiotepa, tirapazamine (Tirazone®), topotecan hydrochloride for injection (Hycamptin®), vinblastine (Velban®), vincristine (Oncovin®), and vinorel Bin (Navelbine®).
與本發明化合物組合的特別感興趣的抗癌劑包括:抗腫瘤抗生素;酪胺酸激酶抑制劑;烷基化劑;抗微管或抗有絲分裂劑;或溶瘤細胞病毒。Anticancer agents of particular interest in combination with the compounds of the invention include: antineoplastic antibiotics; tyrosine kinase inhibitors; alkylating agents; antimicrotubule or antimitotic agents; or oncolytic viruses.
示例性酪胺酸激酶抑制劑包括但不限於鹽酸埃羅替尼(Tarceva®);利尼法尼(Linifanib)(N-[4-(3-胺基-1H-吲唑-4-基)苯基]-N'-(2-氟-5-甲基苯基)脲,也稱為ABT 869,可購自基因泰克公司(Genentech));蘋果酸舒尼替尼(Sutent®);柏舒替尼(Bosutinib)(4-[(2,4-二氯-5-甲氧基苯基)胺基]-6-甲氧基-7-[3-(4-甲基哌𠯤-1-基)丙氧基]喹啉-3-甲腈,也稱為SKI-606,並且描述於美國專利案號6,780,996);達沙替尼(Sprycel®);帕唑帕尼(Votrient®);索拉非尼(Nexavar®);凡德他尼(ZD6474);和伊馬替尼或甲磺酸伊馬替尼(Gilvec®和Gleevec®)。Exemplary tyrosine kinase inhibitors include, but are not limited to, erlotinib hydrochloride (Tarceva®); Linifanib (N-[4-(3-amino-1H-indazol-4-yl) Phenyl]-N'-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenyl)urea, also known as ABT 869, available from Genentech); sunitinib malate (Sutent®); Bosutinib (4-[(2,4-dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)amino]-6-methoxy-7-[3-(4-methylpiperone-1 -yl)propoxy]quinoline-3-carbonitrile, also known as SKI-606 and described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,780,996); dasatinib (Sprycel®); pazopanib (Votrient®); Sorafenib (Nexavar®); vandetanib (ZD6474); and imatinib or imatinib mesylate (Gilvec® and Gleevec®).
示例性烷基化劑包括而不限於奧沙利鉑(Eloxatin®);替莫唑胺(Temodar®和Temodal®);更生黴素(也稱為放線菌素-D、Cosmegen®);黴法蘭(也稱為L-PAM、L-溶肉瘤素和苯丙胺酸氮芥、Alkeran®);六甲蜜胺(也稱為六甲基三聚氰胺(HMM)、Hexalen®);卡莫司汀(BiCNU®);苯達莫司汀(Treanda®);白消安(Busulfex®和Myleran®);卡鉑(Paraplatin®);洛莫司汀(也稱為CCNU、CeeNU®);順鉑(也稱為CDDP、Platinol®和Platinol®-AQ);氯芥苯丁酸(Leukeran®);環磷醯胺(Cytoxan®和Neosar®);達卡巴𠯤(也稱為DTIC、DIC和咪唑甲醯胺、DTIC-Dome®);六甲蜜胺(也稱為六甲基三聚氰胺(HMM)、Hexalen®);依弗醯胺(Ifex®);Prednumustine;丙卡巴肼(Matulane®);二氯甲基二乙胺(也稱為氮芥、鹽酸氮芥和鹽酸二氯甲基二乙胺、Mustargen®);鏈脲佐菌素(Zanosar®);噻替派(也稱為硫代磷醯胺、TESPA和TSPA、Thioplex®);環磷醯胺(Endoxan®、Cytoxan®、Neosar®、Procytox®、Revimmune®);和鹽酸苯達莫司汀(Treanda®)。Exemplary alkylating agents include, without limitation, oxaliplatin (Eloxatin®); temozolomide (Temodar® and Temodal®); dactinomycin (also known as Actinomycin-D, Cosmegen®); known as L-PAM, L-sarcolysin and melphalan, Alkeran®); hexamethylmelamine (also known as hexamethylmelamine (HMM), Hexalen®); carmustine (BiCNU®); Damustine (Treanda®); Busulfan (Busulfex® and Myleran®); Carboplatin (Paraplatin®); Lomustine (also known as CCNU, CeeNU®); Cisplatin (also known as CDDP, Platinol ® and Platinol®-AQ); chlorambucil (Leukeran®); cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan® and Neosar®); ); hexamethylmelamine (also known as hexamethylmelamine (HMM), Hexalen®); everamide (Ifex®); Prednumustine; procarbazine (Matulane®); Streptozotocin (Zanosar®); Thiotepa (also known as Thiophosphoramide, TESPA and TSPA, Thioplex® ); cyclophosphamide (Endoxan®, Cytoxan®, Neosar®, Procytox®, Revimmune®); and bendamustine hydrochloride (Treanda®).
示例性抗腫瘤抗生素包括例如多柔比星(Adriamycin®和Rubex®);博萊黴素(lenoxane®);道諾黴素(鹽酸道諾黴素、道諾黴素和鹽酸紅比黴素、Cerubidine®);道諾黴素脂質體(檸檬酸道諾黴素脂質體、DaunoXome®);米托蒽醌(DHAD、Novantrone®);表柔比星(Ellence™);伊達比星(Idamycin®、Idamycin PFS®);絲裂黴素C(Mutamycin®);格爾德黴素(geldanamycin);除莠黴素(herbimycin);近灰黴素(ravidomycin);和去乙基近灰黴素(Desacetylravidomycin)。Exemplary antineoplastic antibiotics include, for example, doxorubicin (Adriamycin® and Rubex®); bleomycin (lenoxane®); daunomycin (daunomycin hydrochloride, daunomycin hydrochloride, Cerubidine®); liposomal daunomycin (daunomycin citrate liposome, DaunoXome®); mitoxantrone (DHAD, Novantrone®); epirubicin (Ellence™); idarubicin (Idamycin® , Idamycin PFS®); mitomycin C (Mutamycin®); geldanamycin; herbimycin; ravidomycin; Desacetylravidomycin).
示例性抗微管或抗有絲分裂劑包括但不限於長春花生物鹼(如酒石酸長春瑞濱(Navelbine®)、長春新鹼(Oncovin®)和長春地辛(Eldisine®));紫杉烷(如紫杉醇和多西他賽);和雌莫司汀(Emcyl®或Estracyt®)。Exemplary anti-microtubule or anti-mitotic agents include, but are not limited to, vinca alkaloids (such as vinorelbine tartrate (Navelbine®), vincristine (Oncovin®), and vindesine (Eldisine®)); taxanes (such as paclitaxel and docetaxel); and estramustine (Emcyl® or Estracyt®).
在一些實施方式中,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與溶瘤細胞病毒組合投與。在實施方式中,溶瘤病毒能夠選擇性地複製並引發癌細胞的死亡或減緩其生長。在一些情況下,溶瘤病毒對非癌細胞沒有影響或影響很小。溶瘤病毒包括但不限於溶瘤腺病毒、溶瘤性單純皰疹病毒、溶瘤性反轉錄病毒、溶瘤性細小病毒、溶瘤性痘瘡病毒、溶瘤性辛奈病毒(oncolytic Sinbis viru)、溶瘤性流感病毒、或溶瘤性RNA病毒(例如,溶瘤性裏奧病毒、溶瘤性新城雞瘟病毒(NDV)、溶瘤性麻疹病毒、或溶瘤性水泡性口炎病毒(VSV))。In some embodiments, a CAR-expressing cell described herein is administered in combination with an oncolytic virus. In an embodiment, the oncolytic virus is capable of selectively replicating and triggering the death or slowing the growth of cancer cells. In some cases, oncolytic viruses had no or minimal effect on non-cancerous cells. Oncolytic viruses include but are not limited to oncolytic adenovirus, oncolytic herpes simplex virus, oncolytic retrovirus, oncolytic parvovirus, oncolytic pox virus, oncolytic Sinbis viru , oncolytic influenza virus, or oncolytic RNA virus (e.g., oncolytic Leo virus, oncolytic Newcastle disease virus (NDV), oncolytic measles virus, or oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) )).
在一些實施方式中,溶瘤病毒係US 2010/0178684 A1中描述的病毒,例如重組溶瘤病毒,該專利藉由引用以其全文併入本文。在一些實施方式中,重組溶瘤病毒包含編碼免疫反應或炎性響應抑制劑的核酸序列(例如,異源核酸序列),例如如US 2010/0178684 A1中所述,該專利藉由引用以其全文併入本文。在實施方式中,重組溶瘤病毒(例如溶瘤NDV)包含促凋亡蛋白(例如凋亡蛋白)、細胞介素(例如GM-CSF、干擾素-γ、白血球介素-2(IL-2)、腫瘤壞死因子-α)、免疫球蛋白(例如針對ED-B firbonectin的抗體)、腫瘤相關抗原、雙特異性銜接蛋白(例如針對NDV HN蛋白的雙特異性抗體或抗體片段以及T細胞共刺激受體,如CD3或CD28;或人IL-2與針對NDV HN蛋白的單鏈抗體之間的融合蛋白)。參見例如,Zamarin等人 Future Microbiol. [未來微生物學] 7.3(2012):347-67,該文獻藉由引用以其全文併入本文。在一些實施方式中,溶瘤病毒係描述於US 8591881 B2、US 2012/0122185 A1、或US 2014/0271677 A1(每個專利均藉由引用以其全文併入本文)中的嵌合溶瘤NDV。In some embodiments, the oncolytic virus is a virus described in US 2010/0178684 A1, such as a recombinant oncolytic virus, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. In some embodiments, the recombinant oncolytic virus comprises a nucleic acid sequence (e.g., a heterologous nucleic acid sequence) encoding an inhibitor of an immune response or an inflammatory response, e.g., as described in US 2010/0178684 A1, which is incorporated by reference in its The entire text is incorporated herein. In an embodiment, the recombinant oncolytic virus (eg, oncolytic NDV) comprises pro-apoptotic proteins (eg, apoptotic proteins), cytokines (eg, GM-CSF, interferon-γ, interleukin-2 (IL-2 ), tumor necrosis factor-α), immunoglobulins (such as antibodies against ED-B firbonectin), tumor-associated antigens, bispecific adapter proteins (such as bispecific antibodies or antibody fragments against NDV HN protein, and T cell co- stimulatory receptors, such as CD3 or CD28; or a fusion protein between human IL-2 and a single-chain antibody against NDV HN protein). See, eg, Zamarin et al. Future Microbiol. 7.3 (2012): 347-67, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. In some embodiments, the oncolytic virus is a chimeric oncolytic NDV described in US 8591881 B2, US 2012/0122185 A1, or US 2014/0271677 A1 (each incorporated herein by reference in its entirety) .
在一些實施方式中,溶瘤病毒包含條件複製型腺病毒(CRAd),其被設計成僅在癌細胞中複製。參見例如,Alemany等人 Nature Biotechnol. [自然生物技術] 18(2000):723-27。在一些實施方式中,溶瘤腺病毒包含描述於Alemany等人的第725頁的表1中的一種溶瘤腺病毒,該文獻藉由引用以其全文併入本文。In some embodiments, the oncolytic virus comprises a conditionally replicating adenovirus (CRAd) that is engineered to replicate only in cancer cells. See, eg, Alemany et al. Nature Biotechnol. 18(2000):723-27. In some embodiments, the oncolytic adenovirus comprises one of the oncolytic adenoviruses described in Table 1 on page 725 of Alemany et al., which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety.
示例性溶瘤病毒包括但不限於以下: B組溶瘤腺病毒(ColoAd1)(皮斯奧克斯治療有限公司(PsiOxus Therapeutics Ltd.))(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT02053220); ONCOS-102(以前稱為CGTG-102),其係包含粒細胞-巨噬細胞集落刺激因子(GM-CSF)(昂克斯治療公司(Oncos Therapeutics))的腺病毒(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT01598129); VCN-01,其係基因修飾的溶瘤人腺病毒,編碼人PH20透明質酸酶(VCN Biosciences,S.L.)(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT02045602和NCT02045589); 條件複製型腺病毒ICOVIR-5,其係衍生自野生型人腺病毒血清型5(Had5)的病毒,該病毒經過修飾以在癌細胞中選擇性地複製,並具有解除調節的視網膜母細胞瘤/E2F途徑(加泰羅尼亞腫瘤研究所(Institut Català d'Oncologia))(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT01864759); Celyvir,其包含用ICOVIR5感染的骨髓衍生的自體間充質幹細胞(MSC),係一種溶瘤腺病毒(Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, 馬德里, 西班牙/Ramon Alemany)(參見例如臨床試驗識別字:NCT01844661); CG0070,其係條件性複製型溶瘤血清型5腺病毒(Ad5),其中人E2F-1啟動子驅動必需的E1a病毒基因的表現,從而限制病毒複製和對Rb途徑缺陷型腫瘤細胞的細胞毒性(Cold Genesys公司)(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT02143804);或 DNX-2401(以前命名為δ-24-RGD),其係腺病毒,該腺病毒經工程化以在視網膜母細胞瘤(Rb)途徑缺陷型細胞中選擇性地複製並感染更高效地表現某些RGD結合整聯蛋白的細胞(那瓦勒大學醫院(Clinica Universidad de Navarra), 那瓦勒大學(Universidad de Navarra)/德那翠絲有限公司(DNAtrix, Inc.))(參見例如,臨床試驗識別字:NCT01956734)。 Exemplary oncolytic viruses include, but are not limited to the following: Group B Oncolytic Adenovirus (ColoAd1) (PsiOxus Therapeutics Ltd.) (See eg, Clinical Trial Identifier: NCT02053220); ONCOS-102 (formerly known as CGTG-102), which is an adenovirus containing granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (Oncos Therapeutics) (see e.g., Clinical Trial Identification Word: NCT01598129); VCN-01, which is a genetically modified oncolytic human adenovirus encoding human PH20 hyaluronidase (VCN Biosciences, S.L.) (see, eg, Clinical Trial Identifiers: NCT02045602 and NCT02045589); Conditionally replicating adenovirus ICOVIR-5, a line of virus derived from wild-type human adenovirus serotype 5 (Had5), modified to replicate selectively in cancer cells with deregulated retinoblastoma /E2F pathway (Institut Català d'Oncologia) (see for example, clinical trial identifier: NCT01864759); Celyvir, which comprises bone marrow-derived autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) infected with ICOVIR5, an oncolytic adenovirus (Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús, Madrid, Spain/Ramon Alemany) (see e.g. Clinical Trial Identifier: NCT01844661 ); CG0070, a conditionally replicative oncolytic serotype 5 adenovirus (Ad5) in which the human E2F-1 promoter drives the expression of essential E1a viral genes, thereby limiting viral replication and cytotoxicity to Rb pathway-deficient tumor cells (Cold Genesys) (see for example, Clinical Trial Identifier: NCT02143804); or DNX-2401 (formerly named delta-24-RGD), which is an adenovirus engineered to selectively replicate and infect cells with defects in the retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway to more efficiently express certain cells in which RGD binds integrins (Clinica Universidad de Navarra, Universidad de Navarra/DNAtrix, Inc.) (see e.g., Clinical Trials Identification word: NCT01956734).
在一些實施方式中,藉由注射(例如,皮下、動脈內、靜脈內、肌內、鞘內、或腹膜內注射)投與本文描述的溶瘤病毒。在實施方式中,將本文所述之溶瘤病毒通過腫瘤內、透皮、經黏膜、口服、鼻內、或經由肺部給藥投與。In some embodiments, an oncolytic virus described herein is administered by injection (eg, subcutaneous, intraarterial, intravenous, intramuscular, intrathecal, or intraperitoneal injection). In an embodiment, an oncolytic virus described herein is administered by intratumoral, transdermal, transmucosal, oral, intranasal, or via pulmonary administration.
在一個實施方式中,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與靶向GITR和/或調節GITR功能的分子(如GITR促效劑和/或耗減調節性T細胞(Treg)的GITR抗體)組合投與至受試者。在一個實施方式中,GITR結合分子和/或調節GITR功能的分子(例如,GITR促效劑和/或耗減Treg的GITR抗體)在表現CAR的細胞之前投與。例如,在一個實施方式中,GITR促效劑可以在細胞的單采血液成分術之前投與。在一個實施方式中,受試者患有CLL。示例性GITR促效劑包括例如GITR融合蛋白和抗GITR抗體(例如,二價抗GITR抗體),例如像描述於以下中的GITR融合蛋白,美國專利案號:6,111,090、歐洲專利案號:090505B1、美國專利案號:8,586,023、PCT公開案號:WO 2010/003118和2011/090754,或描述於以下中的抗GITR抗體,例如在美國專利案號:7,025,962、歐洲專利案號:1947183 B1、美國專利案號:7,812,135、美國專利案號:8,388,967、美國專利案號:8,591,886、歐洲專利案號:EP 1866339、PCT公開案號:WO 2011/028683、PCT公開案號:WO 2013/039954、PCT公開案號:WO 2005/007190、PCT公開案號:WO 2007/133822、PCT公開案號:WO 2005/055808、PCT公開案號:WO 99/40196、PCT公開案號:WO 2001/03720、PCT公開案號:WO 99/20758、PCT公開案號:WO 2006/083289、PCT公開案號:WO 2005/115451、美國專利案號:7,618,632、和PCT公開案號:WO 2011/051726。In one embodiment, the CAR-expressing cells described herein are combined with molecules that target GITR and/or modulate GITR function, such as GITR agonists and/or GITR antibodies that deplete regulatory T cells (Treg) Administer to subjects. In one embodiment, a GITR binding molecule and/or a molecule that modulates GITR function (eg, a GITR agonist and/or a Treg-depleting GITR antibody) is administered prior to the CAR-expressing cells. For example, in one embodiment, a GITR agonist can be administered prior to apheresis of the cells. In one embodiment, the subject has CLL. Exemplary GITR agonists include, for example, GITR fusion proteins and anti-GITR antibodies (e.g., bivalent anti-GITR antibodies), such as GITR fusion proteins as described in U.S. Patent No. 6,111,090, European Patent No. 090505B1, U.S. Patent No.: 8,586,023, PCT Publication Nos.: WO 2010/003118 and 2011/090754, or anti-GITR antibodies described, for example, in U.S. Patent No.: 7,025,962, European Patent No.: 1947183 B1, U.S. Patent No. Case No.: 7,812,135, U.S. Patent No.: 8,388,967, U.S. Patent No.: 8,591,886, European Patent No.: EP 1866339, PCT Publication No.: WO 2011/028683, PCT Publication No.: WO 2013/039954, PCT Publication No.: WO 2005/007190, PCT Publication No.: WO 2007/133822, PCT Publication No.: WO 2005/055808, PCT Publication No.: WO 99/40196, PCT Publication No.: WO 2001/03720, PCT Publication No.: WO 99/20758, PCT Publication No.: WO 2006/083289, PCT Publication No.: WO 2005/115451, US Patent No.: 7,618,632, and PCT Publication No.: WO 2011/051726.
在一個實施方式中,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與mTOR抑制劑,例如本文所述之mTOR抑制劑(例如,rapalog如依維莫司)組合投與至受試者。在一個實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑在表現CAR的細胞之前投與。例如,在一個實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑可以在細胞的單采血液成分術之前投與。In one embodiment, a CAR-expressing cell described herein is administered to a subject in combination with an mTOR inhibitor, eg, an mTOR inhibitor described herein (eg, rapalog such as everolimus). In one embodiment, the mTOR inhibitor is administered prior to the CAR expressing cells. For example, in one embodiment, the mTOR inhibitor can be administered prior to apheresis of the cells.
在一個實施方式中,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與GITR促效劑(例如,本文所述之GITR促效劑)組合投與至受試者。在一個實施方式中,在表現CAR的細胞之前投與GITR促效劑。例如,在一個實施方式中,GITR促效劑可以在細胞的單采血液成分術之前投與。In one embodiment, a CAR-expressing cell described herein is administered to a subject in combination with a GITR agonist (eg, a GITR agonist described herein). In one embodiment, the GITR agonist is administered prior to the CAR-expressing cells. For example, in one embodiment, a GITR agonist can be administered prior to apheresis of the cells.
在一個實施方式中,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞與蛋白酪胺酸磷酸酶抑制劑(例如,本文所述之蛋白酪胺酸磷酸酶抑制劑)組合投與至受試者。在一個實施方式中,蛋白酪胺酸磷酸酶抑制劑係SHP-1抑制劑,例如本文所述之SHP-1抑制劑,例如像葡萄糖酸銻鈉。在一個實施方式中,蛋白酪胺酸磷酸酶抑制劑係SHP-2抑制劑。In one embodiment, a CAR-expressing cell described herein is administered to a subject in combination with a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor (eg, a protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor described herein). In one embodiment, the protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor is a SHP-1 inhibitor, such as a SHP-1 inhibitor described herein, such as, for example, sodium stibogluconate. In one embodiment, the protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor is a SHP-2 inhibitor.
在一個實施方式中,本文所述之表現CAR的細胞可以與激酶抑制劑組合給予。In one embodiment, the CAR-expressing cells described herein can be administered in combination with a kinase inhibitor.
在實施方式中,該方法可以用於優化本文所述之CAR細胞在受試者中的性能。雖然不希望受理論束縛,但據信,在實施方式中,內源性未修飾的免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的性能得到改善。雖然不希望受理論束縛,但據信,在實施方式中,表現CAR的細胞的性能得到改善。在一些實施方式中,已經工程化或將經工程化以表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的群體可以藉由接觸一定量的mTOR抑制劑進行離體處理,該mTOR抑制劑增加PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)的數目或增加PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)/PD1陽性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的比率。In embodiments, the method can be used to optimize the performance of the CAR cells described herein in a subject. While not wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that, in embodiments, the performance of endogenous unmodified immune effector cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) is improved. While not wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that, in embodiments, the performance of cells expressing the CAR is improved. In some embodiments, a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that have been engineered or will be engineered to express a CAR can be treated ex vivo by exposure to an amount of an mTOR inhibitor that increases The number of PD1-negative immune effector cells (eg, T cells/NK cells) or increase the ratio of PD1-negative immune effector cells (eg, T cells/NK cells)/PD1-positive immune effector cells (eg, T cells or NK cells).
在實施方式中,在投與本文所述之表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)之前,開始投與低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑,例如變構抑制劑(例如,RAD001),或催化性抑制劑。在實施方式中,在足夠的時間、或mTOR抑制劑的足夠給藥後投與CAR細胞,使得PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)的水平,或PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)/PD1陽性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的比率已經至少是瞬時增加了。In an embodiment, administration of a low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor, such as an allosteric inhibitor (e.g., RAD001 ), is initiated prior to administration of a CAR-expressing cell (e.g., a T cell or NK cell) described herein, or catalytic inhibitors. In an embodiment, the CAR cells are administered at a sufficient time, or following sufficient administration of the mTOR inhibitor, to achieve levels of PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., T cells/NK cells), or PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., , T cells/NK cells)/PD1-positive immune effector cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) have increased at least transiently.
在實施方式中,在足夠的時間後、或在低免疫增強劑量的mTOR抑制劑的足夠給藥後收穫經工程化以表現CAR的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞),使得受試者中或從受試者收穫的PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的水平,或PD1陰性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞/NK細胞)/PD1陽性免疫效應細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)的比率已經至少是瞬時增加了。In embodiments, cells engineered to express a CAR (e.g., T cells or NK cells) are harvested after sufficient time, or after sufficient administration of a low immunoenhancing dose of an mTOR inhibitor, such that in a subject or the level of PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells), or PD1-negative immune effector cells (e.g., T cells/NK cells)/PD1-positive immune effector cells (e.g., T cells) harvested from the subject or NK cells) have increased at least transiently.
在一些實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑投與足夠的時間量以在受試者的周圍血或從受試者分離的T細胞的製備物中降低PD-1陽性T細胞的比率、增加PD-1陰性T細胞的比率、或增加PD-1陰性T細胞/PD-1陽性T細胞的比率。In some embodiments, the mTOR inhibitor is administered for a sufficient amount of time to reduce the rate of PD-1 positive T cells, increase the rate of PD-1 positive T cells in the subject's peripheral blood or a preparation of T cells isolated from the subject. The ratio of negative T cells, or increase the ratio of PD-1 negative T cells/PD-1 positive T cells.
在一些實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑的劑量與至少5%但不超過90%的mTOR抑制相關聯,例如,如藉由p70 S6K抑制測量的。在一些實施方式中,mTOR抑制劑的劑量與至少10%但不超過40%的mTOR抑制相關聯,例如,如藉由p70 S6K抑制測量的。In some embodiments, the dose of mTOR inhibitor correlates with at least 5% but no more than 90% inhibition of mTOR, eg, as measured by p70 S6K inhibition. In some embodiments, the dose of the mTOR inhibitor correlates with at least 10% but no more than 40% inhibition of mTOR, eg, as measured by p70 S6K inhibition.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係CDK4抑制劑,例如本文所述之CDK4抑制劑,例如CD4/6抑制劑,如6-乙醯基-8-環戊基-5-甲基-2-(5-哌𠯤-1-基-吡啶-2-基胺基)-8 H-吡啶并[2,3- d]嘧啶-7-酮, 鹽酸鹽(也稱為帕博西尼(palbociclib)或PD0332991)。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係BTK抑制劑,例如本文所述之BTK抑制劑,例如像依魯替尼。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係mTOR抑制劑,例如本文所述之mTOR抑制劑,例如像雷帕黴素、雷帕黴素類似物、OSI-027。該mTOR抑制劑可為例如mTORC1抑制劑和/或mTORC2抑制劑,例如本文描述的mTORC1抑制劑和/或mTORC2抑制劑。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係MNK抑制劑,例如本文所述之MNK抑制劑,例如像4-胺基-5-(4-氟苯胺基)-吡唑并[3,4- d]嘧啶。該MNK抑制劑可為例如MNK1a、MNK1b、MNK2a和/或MNK2b抑制劑。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係DGK抑制劑,例如本文所述之DGK抑制劑,例如像DGKinh1(D5919)或DGKinh2(D5794)。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係選自以下的CDK4抑制劑:阿洛新A(aloisine A);夫拉平度(flavopiridol)或HMR-1275,2-(2-氯苯基)-5,7-二羥基-8-[(3S,4R)-3-羥基-1-甲基-4-哌啶基]-4-苯并哌喃酮;克唑替尼(PF-02341066;2-(2-氯苯基)-5,7-二羥基-8-[(2 R,3 S)-2-(羥甲基)-1-甲基-3-吡咯啶基]-4 H-1-苯并哌喃-4-酮 鹽酸鹽(P276-00);1-甲基-5-[[2-[5-(三氟甲基)-1 H-咪唑-2-基]-4-吡啶基]氧基]- N-[4-(三氟甲基)苯基] -1H-苯并咪唑-2-胺(RAF265);吲地橫胺(indisulam)(E7070);洛斯可維汀(roscovitine)(CYC202);帕博西尼(PD0332991);地那西利(dinaciclib)(SCH727965);N-[5-[[(5-三級丁基㗁唑-2-基)甲基]硫代]噻唑-2-基]哌啶-4-甲醯胺(BMS 387032);4-[[9-氯-7-(2,6-二氟苯基)-5 H-嘧啶并[5,4- d][2]苯并氮雜-2-基]胺基]-苯甲酸(MLN8054);5-[3-(4,6-二氟-1H-苯并咪唑-2-基)-1H-吲唑-5-基]-N-乙基-4-甲基-3-吡啶甲胺(AG-024322);4-(2,6-二氯苯甲醯基胺基)-1H-吡唑-3-羧酸N-(哌啶-4-基)醯胺(AT7519);4-[2-甲基-1-(1-甲基乙基)-1 H-咪唑-5-基]- N-[4-(甲基磺醯基)苯基]-2-嘧啶胺(AZD5438);和XL281(BMS908662)。 In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a CDK4 inhibitor, such as a CDK4 inhibitor described herein, such as a CD4/6 inhibitor, such as 6-acetyl-8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-2- (5-Piperyl-1-yl-pyridin-2-ylamino) -8H -pyrido[2,3- d ]pyrimidin-7-one, hydrochloride (also known as palbociclib ) or PD0332991). In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a BTK inhibitor, eg a BTK inhibitor as described herein, eg ibrutinib. In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is an mTOR inhibitor, eg, an mTOR inhibitor as described herein, eg, like rapamycin, rapamycin analogs, OSI-027. The mTOR inhibitor can be, for example, an mTORCl inhibitor and/or an mTORC2 inhibitor, such as an mTORCl inhibitor and/or an mTORC2 inhibitor described herein. In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a MNK inhibitor, such as a MNK inhibitor described herein, such as, for example, 4-amino-5-(4-fluoroanilino)-pyrazolo[3,4- d ] pyrimidine. The MNK inhibitor can be, for example, a MNK1a, MNK1b, MNK2a and/or MNK2b inhibitor. In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a DGK inhibitor, eg a DGK inhibitor as described herein, eg like DGKinh1 (D5919) or DGKinh2 (D5794). In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a CDK4 inhibitor selected from the group consisting of: aloisine A; flavopiridol or HMR-1275, 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-5, 7-Dihydroxy-8-[(3S,4R)-3-hydroxy-1-methyl-4-piperidinyl]-4-benzopyrone; Crizotinib (PF-02341066; 2-( 2-chlorophenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-8-[(2 R ,3 S )-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methyl-3-pyrrolidinyl]-4 H -1- Benzopyran-4-one hydrochloride (P276-00); 1-methyl-5-[[2-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1 H -imidazol-2-yl]-4- Pyridyl]oxy] -N- [4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl] -1H- benzimidazol-2-amine (RAF265); indisulam (E7070); loscovitine (roscovitine) (CYC202); Palbociclib (PD0332991); Denaciclib (SCH727965); N-[5-[[(5-tertiary butylzol-2-yl)methyl]sulfur Substitute]thiazol-2-yl]piperidine-4-carboxamide (BMS 387032); 4-[[9-chloro-7-(2,6-difluorophenyl) -5H -pyrimido[5, 4- d ][2]Benzazepin-2-yl]amino]-benzoic acid (MLN8054); 5-[3-(4,6-difluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)- 1H-Indazol-5-yl]-N-Ethyl-4-methyl-3-pyridinemethylamine (AG-024322); 4-(2,6-dichlorobenzoylamino)-1H- Pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid N-(piperidin-4-yl)amide (AT7519); 4-[2-methyl-1-(1-methylethyl)-1 H -imidazol-5-yl ] -N- [4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-2-pyrimidinamine (AZD5438); and XL281 (BMS908662).
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係CDK4抑制劑,例如帕博西尼(PD0332991),並且將帕博西尼以每天約50 mg、60 mg、70 mg、75 mg、80 mg、90 mg、100 mg、105 mg、110 mg、115 mg、120 mg、125 mg、130 mg、135 mg(例如,75 mg、100 mg或125 mg)的劑量投與一段時間,例如,每天投與持續28天週期的14-21天,或每天投與持續21天週期的7-12天。在一個實施方式中,帕博西尼投與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12個或更多個週期。In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a CDK4 inhibitor, such as palbociclib (PD0332991), and palbociclib is administered at about 50 mg, 60 mg, 70 mg, 75 mg, 80 mg, 90 mg, Doses of 100 mg, 105 mg, 110 mg, 115 mg, 120 mg, 125 mg, 130 mg, 135 mg (eg, 75 mg, 100 mg, or 125 mg) administered over a period of time, eg, daily for 28 days Days 14-21 of a cycle, or administered daily for days 7-12 of a 21-day cycle. In one embodiment, palbociclib is administered for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or more cycles.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係選自以下項的BTK抑制劑:依魯替尼(PCI-3 2765);GDC-0834;RN-486;CGI-560;CGI-1764;HM-71224;CC-292;ONO-4059;CNX-774;和LFM-A13。 In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a BTK inhibitor selected from: ibrutinib (PCI-3 2 765); GDC-0834; RN-486; CGI-560; CGI-1764; HM-71224 ; CC-292; ONO-4059; CNX-774; and LFM-A13.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係 BTK抑制劑,例如依魯替尼(PCI-32765),並且將依魯替尼以每天約250 mg、300 mg、350 mg、400 mg、420 mg、440 mg、460 mg、480 mg、500 mg、520 mg、540 mg、560 mg、580 mg、600 mg(例如,250 mg、420 mg或560 mg)的劑量投與一段時間,例如,每天投與持續21天週期、或每天投與持續28天週期。在一個實施方式中,依魯替尼投與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12個或更多個週期。 In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a BTK inhibitor, such as ibrutinib (PCI-32765), and ibrutinib is administered at about 250 mg, 300 mg, 350 mg, 400 mg, 420 mg, 440 mg per day Doses of mg, 460 mg, 480 mg, 500 mg, 520 mg, 540 mg, 560 mg, 580 mg, 600 mg (eg, 250 mg, 420 mg, or 560 mg) administered over a period of time, eg, daily 21-day cycle, or daily administration for a 28-day cycle. In one embodiment, ibrutinib is administered for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or more cycles.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係選自以下的mTOR抑制劑:坦羅莫司;地磷莫司(1 R,2 R,4 S)-4-[(2 R)-2[(1 R,9 S,12 S,15 R,16 E,18 R,19 R,21 R, 23 S,24 E,26 E,28 Z,30 S,32 S,35 R)-1,18-二羥基-19,30-二甲氧基-15,17,21,23,29,35-六甲基-2,3,10,14,20-五氧雜-11,36-二氧雜-4-氮雜三環[30.3.1.0 4,9] 三十六碳-16,24,26,28-四烯-12-基]丙基]-2-甲氧基環己基二甲基次膦酸酯,也稱為AP23573和MK8669;依維莫司(RAD001);雷帕黴素(AY22989);塞馬莫德(simapimod);(5-{2,4-雙[(3 S)-3-甲基𠰌啉-4-基]吡啶并[2,3- d]嘧啶-7-基}-2-甲氧基苯基)甲醇(AZD8055);2-胺基-8-[反式-4-(2-羥基乙氧基)環己基]-6-(6-甲氧基-3-吡啶基)-4-甲基-吡啶并[2,3- d]嘧啶-7(8 H)-酮(PF04691502);和 N 2-[1,4-二側氧基-4-[[4-(4-側氧基-8-苯基-4 H-1-苯并哌喃-2-基)𠰌啉-4-基]甲氧基]丁基]-L-精胺醯甘胺醯-L-α-天冬胺醯L-絲胺酸-內鹽(SF1126);和XL765。 In one embodiment , the kinase inhibitor is an mTOR inhibitor selected from the group consisting of temsirolimus ; R ,9 S ,12 S ,15 R ,16 E ,18 R ,19 R ,21 R , 23 S ,24 E ,26 E ,28 Z ,30 S ,32 S , 35 R )-1,18-Two Hydroxy-19,30-Dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-Hexamethyl-2,3,10,14,20-Pentoxa-11,36-Dioxa-4 -Azatricyclo[30.3.1.0 4,9 ]hexadecyl-16,24,26,28-tetraen-12-yl]propyl]-2-methoxycyclohexyldimethylphosphinic acid Esters, also known as AP23573 and MK8669; everolimus (RAD001); rapamycin (AY22989); simapimod; (5-{2,4-bis[(3 S )-3- Methyl 𠰌line-4-yl]pyrido[2,3- d ]pyrimidin-7-yl}-2-methoxyphenyl)methanol (AZD8055); -(2-Hydroxyethoxy)cyclohexyl]-6-(6-methoxy-3-pyridyl)-4-methyl-pyrido[2,3- d ]pyrimidine-7(8 H )- Ketone (PF04691502); and N 2 -[1,4-dioxo-4-[[4-(4-oxo-8-phenyl- 4H -1-benzopyran-2-yl )𠰌line-4-yl]methoxy]butyl]-L-spernilylglycinyl-L-alpha-asparticyl L-serine-inner salt (SF1126); and XL765.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係mTOR抑制劑,例如雷帕黴素,並且將雷帕黴素以每天約3 mg、4 mg、5 mg、6 mg、7 mg、8 mg、9 mg、10mg(例如,每天6 mg)的劑量投與一段時間,例如每天投與持續21天週期、或每天投與持續28天週期。在一個實施方式中,雷帕黴素投與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12個或更多個週期。在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係mTOR抑制劑,例如依維莫司,並且將依維莫司以每天約2 mg、2.5 mg、3 mg、4 mg、5 mg、6 mg、7 mg、8 mg、9 mg、10 mg、11 mg、12 mg、13 mg、14 mg、15 mg(例如,10 mg)的劑量投與一段時間,例如每天投與持續28天循環。在一個實施方式中,依維莫司投與1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12個或更多個週期。In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is an mTOR inhibitor, such as rapamycin, and rapamycin is administered at about 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 6 mg, 7 mg, 8 mg, 9 mg, A dose of 10 mg (eg, 6 mg per day) is administered for a period of time, eg, daily for a 21-day cycle, or daily for a 28-day cycle. In one embodiment, rapamycin is administered for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or more cycles. In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is an mTOR inhibitor, such as everolimus, and everolimus is administered at about 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 6 mg, 7 mg, Doses of 8 mg, 9 mg, 10 mg, 11 mg, 12 mg, 13 mg, 14 mg, 15 mg (eg, 10 mg) are administered over a period of time, eg, daily for a 28-day cycle. In one embodiment, everolimus is administered for 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 or more cycles.
在一個實施方式中,激酶抑制劑係選自以下的MNK抑制劑:CGP052088;4-胺基-3-(對氟苯基胺基)-吡唑并[3,4- d]嘧啶(CGP57380);尾孢醯胺(cercosporamide);ETC-1780445-2;和4-胺基-5-(4-氟苯胺基)-吡唑并[3,4- d]嘧啶。 In one embodiment, the kinase inhibitor is a MNK inhibitor selected from the group consisting of: CGP052088; 4-amino-3-(p-fluorophenylamino)-pyrazolo[3,4- d ]pyrimidine (CGP57380) ; cercosporamide; ETC-1780445-2; and 4-amino-5-(4-fluoroanilino)-pyrazolo[3,4- d ]pyrimidine.
也可以使用抑制鈣依賴性磷酸酶鈣調神經磷酸酶的藥物(環孢素和FK506)或抑制對生長因子誘導的傳訊重要的p70S6激酶的藥物(雷帕黴素)。(Liu等人, Cell [細胞] 66:807-815, 1991;Henderson等人, Immun. [免疫學] 73:316-321, 1991;Bierer等人, Curr.Opin. Immun. [免疫學新觀點] 5:763-773, 1993)。在另一個方面,本發明之細胞組成物可以與以下聯合投與(例如,之前、同時或之後)至患者:骨髓移植,使用化學治療劑(如氟達拉濱)、外部光束輻射療法(XRT)、環磷醯胺、和/或抗體(如OKT3或CAMPATH)進行的T細胞消融療法。在一方面,將本發明之細胞組成物在B細胞消融療法(如,與CD20反應的藥劑,例如利妥昔單抗)後投與。例如,在一個實施方式中,受試者可以經受用高劑量化學療法、然後進行周圍血幹細胞移植的標準療法。在某些實施方式中,在移植後,受試者接受本發明之擴增的免疫細胞的輸注。在另外的實施方式中,在手術之前或之後投與擴增的細胞。Drugs that inhibit the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin (cyclosporine and FK506) or p70S6 kinase, which is important for growth factor-induced signaling (rapamycin), may also be used. (Liu et al., Cell [cell] 66:807-815, 1991; Henderson et al., Immun. [immunology] 73:316-321, 1991; Bierer et al., Curr.Opin. Immun. [New perspectives on immunology ] 5:763-773, 1993). In another aspect, the cellular composition of the invention can be administered to a patient in combination (eg, before, concurrently or after) with: bone marrow transplantation, use of chemotherapeutic agents (such as fludarabine), external beam radiation therapy (XRT ), cyclophosphamide, and/or T cell ablation therapy with antibodies such as OKT3 or CAMPATH. In one aspect, a cellular composition of the invention is administered following B cell ablation therapy (eg, an agent reactive with CD20, such as rituximab). For example, in one embodiment, the subject may undergo standard therapy with high dose chemotherapy followed by peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. In certain embodiments, following transplantation, the subject receives an infusion of expanded immune cells of the invention. In additional embodiments, the expanded cells are administered before or after surgery.
一些患者在給藥期間或之後可以經歷對本發明化合物和/或一或多種其他抗癌劑的過敏反應;因此,通常投與抗過敏劑以最小化過敏反應的風險。適合的抗過敏劑包括皮質類固醇,如地塞米松(例如,Decadron®)、倍氯米松(例如,Beclovent®)、氫化可體松(也稱為可體松、氫化可體松琥珀酸鈉、氫化可體松磷酸鈉,並在商品名Ala-Cort®、氫化可體松磷酸鹽、Solu-Cortef®、Hydrocort Acetate®和Lanacort®下出售)、普賴蘇穠(在商品名Delta-Cortel®、Orapred®、Pediapred®和Prelone®下出售)、強體松(在商品名Deltasone®、Liquid Red®、Meticorten®和Orasone®下出售)、甲基普賴蘇穠(也稱為6-甲基普賴蘇穠、醋酸甲基普賴蘇穠、丁二酸鈉甲基普賴蘇穠,在商品名Duralone®、Medralone®、Medrol®、M-Prednisol®和Solu-Medrol®下出售);抗組胺藥,如苯海拉明(例如,Benadryl®)、羥𠯤、和賽庚啶;和支氣管擴張劑,如β-腎上腺素能受體促效劑、沙丁胺醇(例如,Proventil®)、和特布他林(Brethine®)組合投與於受試者。Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the compounds of the invention and/or one or more other anticancer agents during or after administration; therefore, antiallergic agents are typically administered to minimize the risk of allergic reactions. Suitable antiallergic agents include corticosteroids such as dexamethasone (eg, Decadron®), beclomethasone (eg, Beclovent®), hydrocortisone (also known as cortisone, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, Hydrocortisone Sodium Phosphate and sold under the trade names Ala-Cort®, Hydrocortisone Phosphate, Solu-Cortef®, Hydrocort Acetate®, and Lanacort®), Prysolone (under the trade name Delta-Cortel® , Orapred®, Pediapred®, and Prelone®), prednisone (sold under the tradenames Deltasone®, Liquid Red®, Meticorten®, and Orasone®), methylpresulone (also known as 6-methyl presulone, methylpresulone acetate, methylpresulone sodium succinate, sold under the tradenames Duralone®, Medralone®, Medrol®, M-Prednisol®, and Solu-Medrol®); Histamines, such as diphenhydramine (eg, Benadryl®), hydroxymethazine, and cyproheptadine; and bronchodilators, such as beta-adrenergic agonists, albuterol (eg, Proventil®), and The terbutaline (Brethine®) combination was administered to the subjects.
一些患者在投與本發明之化合物和/或一或多種其他抗癌劑期間和之後可能會出現噁心;因此,使用止吐藥用於預防噁心(反胃)和嘔吐。合適的止吐藥包括阿瑞匹坦(Emend®)、安坦息吐(Zofran®)、HCl格拉司瓊(Kytril®)、蘿拉西泮(Ativan®)、地塞米松(Decadron®)、丙氯拉𠯤(Compazine®)、casopitant(Rezonic®和Zunrisa®)、及其組合。Some patients may experience nausea during and after administration of a compound of the invention and/or one or more other anticancer agents; therefore, antiemetics are used to prevent nausea (nausea) and vomiting. Suitable antiemetics include aprepitant (Emend®), antanzamet (Zofran®), granisetron HCl (Kytril®), lorazepam (Ativan®), dexamethasone (Decadron®), Prochloraz (Compazine®), casopitant (Rezonic® and Zunrisa®), and combinations thereof.
通常開具用於緩解治療期間經歷的疼痛的藥物以使患者更舒適。通常使用常見的非處方鎮痛藥,如Tylenol®。然而,類鴉片類鎮痛藥如氫可酮/對乙醯胺基酚或氫可酮/醋胺酚(例如Vicodin®)、嗎啡(例如Astramorph®或Avinza®)、羥考酮(例如OxyContin®或Percocet®)、鹽酸羥嗎啡酮(Opana®)和芬太尼(例如Duragesic®)也可用於中度或重度疼痛。Medications are often prescribed to relieve pain experienced during treatment to make the patient more comfortable. Common over-the-counter pain relievers such as Tylenol® are usually used. However, opioid analgesics such as hydrocodone/acetaminophen or hydrocodone/acetaminophen (eg Vicodin®), morphine (eg Astramorph® or Avinza®), oxycodone (eg OxyContin® or Percocet®), oxymorphone hydrochloride (Opana®), and fentanyl (such as Duragesic®) may also be used for moderate or severe pain.
為了保護正常細胞免受治療毒性並限制器官毒性,可以使用細胞保護劑(如神經保護劑、自由基清除劑、心臟保護劑、蒽環類外滲中和劑、營養素等)作為輔助療法。合適的細胞保護劑包括胺磷汀(Amifostine)(Ethyol®)、麩醯胺酸、地美司鈉(dimesna)(Tavocept®)、美司納(mesna)(Mesnex®)、右丙亞胺(dexrazoxane)(Zinecard®或Totect®)、紮利羅登(xaliproden)(Xaprila®)、和甲醯四氫葉酸(也稱為甲醯四氫葉酸鈣、嗜橙菌(citrovorum)因子和醛葉酸)。To protect normal cells from treatment toxicity and limit organ toxicity, cytoprotective agents (e.g., neuroprotectants, free radical scavengers, cardioprotectants, anthracycline extravasation neutralizers, nutrients, etc.) can be used as adjuvant therapy. Suitable cytoprotective agents include Amifostine (Ethyol®), glutamine, dimesna (Tavocept®), mesna (Mesnex®), dextropropimide ( dexrazoxane) (Zinecard® or Totect®), xaliproden (Xaprila®), and folate (also known as calcium folate, citrovorum factor, and aldehyde folate) .
由編號、通用名或商品名識別的活性化合物的結構可以取自標準綱要「默克索引(The Merck Index)」的、或來自數據庫(例如,國際專利(例如IMS世界出版物))的實際版本。The structure of the active compounds identified by number, generic or trade name can be taken from the actual version of the standard compendium "The Merck Index", or from databases such as international patents (e.g. IMS World Publications) .
可以與本發明化合物組合使用的上述化合物可以如本領域所述(如在上面引用的文獻中)製備和投與。The aforementioned compounds, which may be used in combination with the compounds of the present invention, can be prepared and administered as described in the art (eg, in the above-cited documents).
在一個實施方式中,本發明提供了藥物組成物,該藥物組成物包含至少一種本發明之化合物(例如,本發明化合物)或其藥學上可接受的鹽以及適於投與至人或動物受試者的藥學上可接受的載體,單獨地或與其他抗癌藥物一起。In one embodiment, the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one compound of the invention (eg, a compound of the invention) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and suitable for administration to a human or animal subject. A pharmaceutically acceptable carrier for the subject, alone or with other anticancer drugs.
在一個實施方式中,本發明提供了治療罹患細胞增生性疾病(如癌症)的人或動物受試者之方法。本發明提供了治療需要這種治療的人或動物受試者之方法,該方法包括向受試者單獨地或與其他抗癌藥物組合投與治療有效量的本發明之化合物(例如,本發明化合物)或其藥學上可接受的鹽。In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating a human or animal subject suffering from a cell proliferative disease, such as cancer. The invention provides methods of treating a human or animal subject in need of such treatment comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention (e.g., compound) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
特別地,組成物可以作為組合治療劑配製在一起或分開投與。In particular, the compositions can be formulated together or administered separately as a combination therapy.
在組合療法中,本發明化合物和一或多種其他抗癌劑可以同時、並行或依序(沒有特定的時間限制)投與,其中這種投與在患者的體內提供治療有效水平的這兩種化合物。In combination therapy, a compound of the invention and one or more other anticancer agents may be administered simultaneously, concurrently, or sequentially (with no particular time limit), wherein such administration provides a therapeutically effective level of both compounds in the patient's body. compound.
在較佳的實施方式中,將本發明化合物和一或多種其他抗癌劑通常藉由輸注或口服以任何順序依序投與。給藥方案可以取決於疾病的階段、患者的身體健康、單個藥物的安全性、單個藥物的耐受性、以及主治醫師和一或多個執業醫師熟知的投與該組合的其他標準而變化。本發明化合物和一或多種其他抗癌劑可以在彼此數分鐘、數小時、數天或甚至數週內投與,這取決於用於治療的特定週期。此外,該週期可包括在治療週期期間比另一種藥物更頻繁地投與一種藥物,並且每次投與藥物時的劑量不同。In a preferred embodiment, the compound of the invention and one or more other anticancer agents are administered sequentially, in any order, usually by infusion or orally. The dosing regimen can vary depending on the stage of the disease, the physical health of the patient, the safety of the individual agents, the tolerability of the individual agents, and other criteria well known to the attending physician and one or more practicing physicians for administering the combination. The compound of the invention and the one or more other anticancer agents can be administered within minutes, hours, days, or even weeks of each other, depending on the particular period used for the treatment. In addition, the cycle can include administering one drug more frequently than the other drug during the treatment cycle, with each drug being administered at a different dosage.
在本發明之另一方面,提供了套組,該等套組包括一或多種本發明之化合物和本文揭露的組合配偶體。代表性套組包括 (a) 本發明之化合物或其藥學上可接受的鹽,(b) 至少一種組合配偶體,例如,如上所指出的,其中這種套組可包含包裝插頁或包含給藥指導的其他標籤。In another aspect of the invention, there are provided kits comprising one or more compounds of the invention and a combination partner disclosed herein. A representative kit comprises (a) a compound of the invention, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, (b) at least one combination partner, e.g., as indicated above, wherein such a kit may comprise a package insert or contain a other labels of the Medicines Directive.
本發明化合物還可以與已知的療法方法(例如,投與激素或特別是輻射)組合使用。本發明之化合物特別地可以用作放射增敏劑,尤其用於治療對放射療法表現出差的敏感性的腫瘤。The compounds of the invention may also be used in combination with known methods of therapy, eg administration of hormones or especially radiation. The compounds of the invention are particularly useful as radiosensitizers, especially for the treatment of tumors which exhibit poor sensitivity to radiotherapy.
在一個實施方式中,可以向受試者投與降低或改善與投與表現CAR的細胞相關的副作用的藥劑。與投與表現CAR的細胞相關的副作用包括但不限於CRS和噬血細胞性淋巴組織細胞增多症(HLH)(也稱為巨噬細胞激活綜合症(MAS))。CRS的症狀包括高燒、噁心、短暫性低血壓、缺氧等。CRS可以包括臨床體質上體征和症狀,如發燒、疲勞、厭食、肌痛、眩暈、噁心、嘔吐和頭痛。CRS可以包括臨床皮膚體征和症狀,如皮疹。CRS可以包括臨床胃腸道體征和症狀,如噁心、嘔吐和腹瀉。CRS可以包括臨床呼吸道體征和症狀,如呼吸急促和低氧血症。CRS可以包括臨床心血管體征和症狀,如心動過速、脈壓加寬、低血壓、心輸出量增加(早期)和潛在的心輸出量減少(晚期)。CRS可以包括臨床凝血體征和症狀,如升高的d-二聚體、伴有或不伴有出血的低纖維蛋白原血症。CRS可以包括臨床腎體征和症狀,如氮血症。CRS可以包括臨床肝體征和症狀,如轉胺酶升高(transaminitis)和高膽紅素血症。CRS可以包括臨床神經的體征和症狀,如頭痛、精神狀態改變、精神錯亂、發狂、喚詞困難或明顯失語、幻覺、震顫、辨距不良、步態改變、和癲癇發作。因此,本文所述之方法可包括向受試者投與本文所述之表現CAR的細胞,並且進一步投與一或多種藥劑以控制由表現CAR的細胞治療引起的可溶性因子水平升高。在一個實施方式中,該受試者體內升高的可溶性因子係IFN-γ、TNFα、IL-2和IL-6中的一或多種。在實施方式中,受試者中升高的因子係IL-1、GM-CSF、IL-10、IL-8、IL-5和不規則趨化因子(fraktalkine)中的一或多種。因此,投與以治療此副作用的藥劑可為中和該等可溶性因子中的一或多種的藥劑。在一個實施方式中,中和該等可溶形式中的一或多種的藥劑係抗體或其抗原結合片段。此類藥劑之實例包括但不限於類固醇(例如,皮質類固醇)、TNFα抑制劑、和IL-6抑制劑。TNFα抑制劑之實例係抗TNFα抗體分子如英夫利昔單抗、阿達木單抗、塞妥珠單抗、和戈利木單抗。TNFα抑制劑的另一個實例係融合蛋白,如依那西普(entanercept)。TNFα的小分子抑制劑包括但不限於黃嘌呤衍生物(例如己酮可哥鹼)和安非他酮。IL-6抑制劑之實例係抗IL-6抗體分子如托珠單抗(toc)、薩瑞魯單抗、伊斯利莫、CNTO 328、ALD518/BMS-945429、CNTO 136、CPSI-2364、CDP6038、VX30、ARGX-109、FE301、和FM101。在一個實施方式中,抗IL-6抗體分子係托珠單抗。基於IL-1R的抑制劑之實例係阿那白滯素(anakinra)。In one embodiment, agents that reduce or ameliorate side effects associated with administration of CAR-expressing cells can be administered to a subject. Side effects associated with administration of CAR-expressing cells include, but are not limited to, CRS and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) (also known as macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)). Symptoms of CRS include high fever, nausea, transient hypotension, and hypoxia. CRS can include clinical physical signs and symptoms such as fever, fatigue, anorexia, myalgia, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and headache. CRS can include clinical cutaneous signs and symptoms, such as rashes. CRS can include clinical gastrointestinal signs and symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. CRS can include clinical respiratory signs and symptoms, such as shortness of breath and hypoxemia. CRS can include clinical cardiovascular signs and symptoms such as tachycardia, widened pulse pressure, hypotension, increased cardiac output (early) and potentially decreased cardiac output (late). CRS can include clinical coagulation signs and symptoms such as elevated d-dimer, hypofibrinogenemia with or without bleeding. CRS can include clinical renal signs and symptoms, such as azotemia. CRS can include clinical liver signs and symptoms, such as elevated transaminases (transaminitis) and hyperbilirubinemia. CRS can include clinical neurological signs and symptoms, such as headache, altered mental status, confusion, delirium, difficulty in recalling words or pronounced aphasia, hallucinations, tremors, dysmetria, altered gait, and seizures. Accordingly, the methods described herein may comprise administering to a subject a CAR-expressing cell described herein, and further administering one or more agents to control elevated levels of soluble factors resulting from treatment with the CAR-expressing cells. In one embodiment, the elevated soluble factor in the subject is one or more of IFN-γ, TNFα, IL-2 and IL-6. In an embodiment, the factor that is elevated in the subject is one or more of IL-1, GM-CSF, IL-10, IL-8, IL-5, and fraktalkine. Thus, the agent administered to treat this side effect may be an agent that neutralizes one or more of these soluble factors. In one embodiment, the agent that neutralizes one or more of these soluble forms is an antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof. Examples of such agents include, but are not limited to, steroids (eg, corticosteroids), TNFα inhibitors, and IL-6 inhibitors. Examples of TNFα inhibitors are anti-TNFα antibody molecules such as infliximab, adalimumab, certolizumab, and golimumab. Another example of a TNFα inhibitor is a fusion protein such as entanercept. Small molecule inhibitors of TNFα include, but are not limited to, xanthine derivatives (eg, pentoxifylline) and bupropion. Examples of IL-6 inhibitors are anti-IL-6 antibody molecules such as tocilizumab (toc), sarrelumab, Islimo, CNTO 328, ALD518/BMS-945429, CNTO 136, CPSI-2364, CDP6038, VX30, ARGX-109, FE301, and FM101. In one embodiment, the anti-IL-6 antibody molecule is tocilizumab. An example of an IL-1R based inhibitor is anakinra.
在一些實施方式中,向受試者投與皮質類固醇,例如像甲基普賴蘇穠、氫化可體松等。In some embodiments, a corticosteroid is administered to the subject, such as, for example, methylpresulone, hydrocortisone, and the like.
在一些實施方式中,向受試者投與血管加壓藥,例如像去甲腎上腺素、多巴胺、去氧腎上腺素、腎上腺素、加壓素、或其組合。In some embodiments, the subject is administered a vasopressor, such as, for example, norepinephrine, dopamine, phenylephrine, epinephrine, vasopressin, or combinations thereof.
在實施方式中,可以向受試者投與解熱劑。在實施方式中,可以向受試者投與鎮痛劑。In embodiments, an antipyretic agent may be administered to the subject. In embodiments, an analgesic may be administered to the subject.
在一個實施方式中,可以向受試者投與增強表現CAR的細胞活性的藥劑。例如,在一個實施方式中,藥劑可為對抑制性分子進行抑制的藥劑。在一些實施方式中,抑制性分子(例如,計畫性死亡受體1(PD1))可以降低表現CAR的細胞產生免疫效應子響應的能力。抑制性分子之實例包括PD1、PD-L1、CTLA4、TIM3、CEACAM(例如,CEACAM-1、CEACAM-3和/或CEACAM-5)、LAG3、VISTA、BTLA、TIGIT、LAIR1、CD160、2B4和TGFβ。抑制性分子的抑制(例如藉由在DNA、RNA或蛋白質水平上的抑制)可以優化表現CAR的細胞的性能。在實施方式中,可以使用抑制性核酸(例如,抑制性核酸,例如dsRNA,例如siRNA或shRNA)、或規律間隔重複短迴文序列簇(CRISPR)、轉錄激活子樣效應子核酸酶(TALEN)、或鋅指內切核酸酶(ZFN)來抑制表現CAR的細胞中抑制性分子的表現。在實施方式中,抑制劑係shRNA。在實施方式中,抑制性分子在表現CAR的細胞內被抑制。在該等實施方式中,對抑制性分子的表現進行抑制的dsRNA分子與編碼CAR的組分(例如,所有組分)的核酸連接。在一個實施方式中,抑制性訊息的抑制劑可為例如結合抑制性分子的抗體或抗體片段。例如,藥劑可為結合PD1、PD-L1、PD-L2或CTLA4的抗體或抗體片段(例如,易普利姆瑪(ipilimumab)(也稱為MDX-010和MDX-101,並以Yervoy®銷售;百時美施貴寶公司(Bristol-Myers Squibb);曲美利木單抗(Tremelimumab)(從輝瑞公司(Pfizer)可獲得的IgG2單株抗體,以前稱為ticilimumab,CP-675,206)。在實施方式中,該藥劑係結合TIM3的抗體或抗體片段。在實施方式中,該藥劑係結合LAG3的抗體或抗體片段。在實施方式中,該藥劑係結合CEACAM(例如,CEACAM-1、CEACAM-3和/或CEACAM-5)的抗體或抗體片段。In one embodiment, an agent that enhances the activity of a cell expressing a CAR can be administered to the subject. For example, in one embodiment, the agent can be an agent that inhibits an inhibitory molecule. In some embodiments, an inhibitory molecule (eg, programmed death receptor 1 (PD1) ) can reduce the ability of CAR-expressing cells to mount an immune effector response. Examples of inhibitory molecules include PD1, PD-L1, CTLA4, TIM3, CEACAM (e.g., CEACAM-1, CEACAM-3 and/or CEACAM-5), LAG3, VISTA, BTLA, TIGIT, LAIR1, CD160, 2B4, and TGFβ . Inhibition of inhibitory molecules (eg, by inhibition at the DNA, RNA or protein level) can optimize the performance of CAR-expressing cells. In embodiments, inhibitory nucleic acids (e.g., inhibitory nucleic acids, such as dsRNA, such as siRNA or shRNA), or Cluster of Regularly Interspaced Repeat Short Palindromic Sequences (CRISPR), Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN) may be used , or zinc finger endonuclease (ZFN) to inhibit the expression of inhibitory molecules in CAR-expressing cells. In an embodiment, the inhibitor is shRNA. In an embodiment, the inhibitory molecule is inhibited in a cell expressing the CAR. In such embodiments, the dsRNA molecule that inhibits the expression of the inhibitory molecule is linked to a nucleic acid that encodes components (eg, all components) of the CAR. In one embodiment, an inhibitor of an inhibitory message can be, for example, an antibody or antibody fragment that binds an inhibitory molecule. For example, the agent can be an antibody or antibody fragment that binds PD1, PD-L1, PD-L2, or CTLA4 (e.g., ipilimumab (also known as MDX-010 and MDX-101 and marketed as Yervoy® ; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Tremelimumab (IgG2 monoclonal antibody available from Pfizer, formerly known as ticilimumab, CP-675, 206). In In an embodiment, the medicament is an antibody or antibody fragment that binds TIM3. In an embodiment, the medicament is an antibody or antibody fragment that binds LAG3. In an embodiment, the medicament is a CEACAM (for example, CEACAM-1, CEACAM- 3 and/or CEACAM-5) antibodies or antibody fragments.
PD1係受體的CD28家族的抑制性成員,該家族還包括CD28、CTLA-4、ICOS和BTLA。PD1在激活的B細胞、T細胞和髓系細胞上表現(Agata等人 1996 Int. Immunol [國際免疫學] 8:765-75)。PD1的兩個配體,PD-L1和PD-L2已證明在與PD1結合後下調T細胞活化(Freeman等人 2000 J Exp Med [實驗醫學雜誌] 192:1027-34;Latchman等人 2001 Nat Immunol [自然免疫學] 2:261-8;Carter等人 2002 Eur J Immunol [歐洲免疫學雜誌] 32:634-43)。PD-L1在人癌症中很豐富(Dong等人 2003 J Mol Med [分子醫學雜誌] 81:281-7;Blank等人 2005 Cancer Immunol. Immunother [癌症免疫學免疫療法] 54:307-314;Konishi等人 2004 Clin Cancer Res [臨床癌症研究] 10:5094)。藉由抑制PD1與PD-L1的局部相互作用可以逆轉免疫抑制。PD1、PD-L1和PD-L2的抗體、抗體片段和其他抑制劑係本領域可獲得的,並且可以與本文所述之CAR組合使用。例如,尼沃魯單抗(nivolumab)(也稱為BMS-936558或MDX1106;百時美施貴寶公司)係特異性阻斷PD1的全人IgG4單株抗體。尼沃魯單抗(殖株5C4)和特異性結合PD1的其他人單株抗體揭露於US 8,008,449和WO 2006/121168中。匹地利珠單抗(Pidilizumab)(CT-011;治療科技公司(Cure Tech))係與PD1結合的人源化IgG1k單株抗體(匹地利珠單抗和其他人源化抗PD1單株抗體揭露於WO 2009/101611中)。派姆單抗(pembrolizumab)(以前稱為蘭布羅利珠單抗(lambrolizumab),也稱為Keytruda、MK03475;默克公司(Merck))係結合PD1的人源化IgG4單株抗體。派姆單抗和其他人源化抗PD1抗體揭露於US 8,354,509和WO 2009/114335中。MEDI4736(醫學免疫公司(Medimmune))係結合PDL1的人單株抗體,並抑制配體與PD1的相互作用。MDPL3280A(基因泰克公司/羅氏公司(Roche))係結合PD-L1的人Fc優化的IgG1單株抗體。MDPL3280A和針對PD-L1的其他人單株抗體揭露於美國專利案號:7,943,743和美國公開案號:20120039906。其他抗PD-L1結合劑包括YW243.55.S70(重鏈和輕鏈可變區顯示於WO 2010/077634中的SEQ ID NO: 20和21中)和MDX-1 105(也稱為BMS-936559,並且例如,WO 2007/005874中揭露的抗PD-L1結合劑)。AMP-224(B7-DCIg;安普利穆尼公司(Amplimmune);例如,在WO 2010/027827和WO 2011/066342中揭露)係阻斷PD1與B7-H1之間的相互作用的PD-L2 Fc融合可溶性受體。其他抗PD1抗體包括AMP 514(安普利穆尼公司),尤其是例如US 8,609,089、US 2010028330和/或US 20120114649中揭露的抗PD1抗體。Inhibitory member of the CD28 family of PD1 receptors, which also includes CD28, CTLA-4, ICOS and BTLA. PD1 is expressed on activated B cells, T cells and myeloid cells (Agata et al. 1996 Int. Immunol 8:765-75). Two ligands of PD1, PD-L1 and PD-L2, have been shown to downregulate T cell activation upon binding to PD1 (Freeman et al 2000 J Exp Med 192:1027-34; Latchman et al 2001 Nat Immunol [Nature Immunol] 2:261-8; Carter et al 2002 Eur J Immunol 32:634-43). PD-L1 is abundant in human cancers (Dong et al 2003 J Mol Med 81:281-7; Blank et al 2005 Cancer Immunol. Immunother 54:307-314; Konishi et al 2004 Clin Cancer Res 10:5094). Immunosuppression can be reversed by inhibiting the local interaction of PD1 with PD-L1. Antibodies, antibody fragments and other inhibitors of PD1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 are available in the art and can be used in combination with the CARs described herein. For example, nivolumab (also known as BMS-936558 or MDX1106; Bristol-Myers Squibb) is a fully human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that specifically blocks PD1. Nivolumab (colon 5C4) and other human monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind PD1 are disclosed in US 8,008,449 and WO 2006/121168. Pidilizumab (CT-011; Cure Tech) is a humanized IgG1k monoclonal antibody that binds to PD1 (Pidilizumab and other humanized anti-PD1 monoclonal antibodies revealed in WO 2009/101611). Pembrolizumab (formerly lambrolizumab, also known as Keytruda, MK03475; Merck) is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds PD1. Pembrolizumab and other humanized anti-PD1 antibodies are disclosed in US 8,354,509 and WO 2009/114335. MEDI4736 (Medimmune) is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to PDL1 and inhibits the interaction of the ligand with PD1. MDPL3280A (Genentech/Roche) is a human Fc-optimized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds PD-L1. MDPL3280A and other human monoclonal antibodies against PD-L1 are disclosed in US Patent No.: 7,943,743 and US Publication No.: 20120039906. Other anti-PD-L1 binders include YW243.55.S70 (heavy and light chain variable regions are shown in SEQ ID NO: 20 and 21 in WO 2010/077634) and MDX-1 105 (also known as BMS- 936559, and, for example, the anti-PD-L1 binders disclosed in WO 2007/005874). AMP-224 (B7-DCIg; Amplimmune; eg disclosed in WO 2010/027827 and WO 2011/066342) is a PD-L2 that blocks the interaction between PD1 and B7-H1 Fc is fused to a soluble receptor. Other anti-PD1 antibodies include AMP 514 (Amply Mooney), especially anti-PD1 antibodies such as disclosed in US 8,609,089, US 2010028330 and/or US 20120114649.
TIM3(T細胞免疫球蛋白-3)也負調節T細胞功能,特別是在分泌IFN-g的CD4 + T輔助細胞1和CD8 + T細胞毒性細胞1中,並且在T細胞耗竭中起關鍵作用。抑制TIM3與其配體(例如,半乳糖凝集素-9(Gal9)、磷脂醯絲胺酸(PS)和HMGB1)之間的相互作用可以增強免疫反應。TIM3及其配體的抗體、抗體片段和其他抑制劑係本領域可獲得的,並且可以與CAR(例如本文所述之)組合使用。例如,靶向TIM3的抗體、抗體片段、小分子或肽抑制劑結合TIM3的IgV域以抑制與其配體的相互作用。抑制TIM3的抗體和肽揭露於WO 2013/006490和US 20100247521中。其他抗TIM3抗體包括人源化形式的RMT3-23(在Ngiow等人, 2011, Cancer Res [癌症研究], 71:3540-3551中揭露)和殖株8B.2C12(在Monney等人, 2002, Nature [自然], 415:536-541中揭露)。在US 20130156774中揭露了抑制TIM3和PD-1的雙特異性抗體。TIM3 (T cell immunoglobulin-3) also negatively regulates T cell function, especially in IFN-g-secreting
在一些實施方式中,增強表現CAR的細胞活性的藥劑係CEACAM抑制劑(例如,CEACAM-1、CEACAM-3、和/或CEACAM-5抑制劑)。在一個實施方式中,CEACAM的抑制劑係抗CEACAM抗體分子。示例性抗CEACAM-1抗體描述於WO 2010/125571、WO 2013/082366、WO 2014/059251、和WO 2014/022332中,例如,單株抗體34B1、26H7、和5F4;或其重組形式,如例如US 2004/0047858、US 7,132,255、和WO 99/052552中所述。在一些實施方式中,抗CEACAM抗體結合CEACAM-5,如例如描述於Zheng等人 PLoS One. [公共科學圖書館綜合] 2010年9月2日; 5(9). pii: e12529 (DOI:10:1371/journal.pone.0021146),或與CEACAM-1和CEACAM-5交叉反應,如WO 2013/054331和US 2014/0271618中所述。In some embodiments, the agent that enhances the activity of a CAR-expressing cell is a CEACAM inhibitor (eg, a CEACAM-1, CEACAM-3, and/or CEACAM-5 inhibitor). In one embodiment, the inhibitor of CEACAM is an anti-CEACAM antibody molecule. Exemplary anti-CEACAM-1 antibodies are described in WO 2010/125571, WO 2013/082366, WO 2014/059251, and WO 2014/022332, e.g., monoclonal antibodies 34B1, 26H7, and 5F4; or recombinant forms thereof, such as e.g. Described in US 2004/0047858, US 7,132,255, and WO 99/052552. In some embodiments, an anti-CEACAM antibody binds CEACAM-5, as described, e.g., in Zheng et al. PLoS One. [PLOS ONE] 2010
不希望受理論的約束,據信癌胚抗原細胞黏附分子(CEACAM)(如CEACAM-1和CEACAM-5)至少部分地介導抗腫瘤免疫反應的抑制(參見例如,Markel等人 J Immunol.[免疫學雜誌] 2002年3月15日; 168(6):2803-10;Markel等人 J Immunol. [免疫學雜誌] 2006年11月1日; 177(9):6062-71;Markel等人 Immunology. [免疫學] 2009年2月; 126(2):186-200;Markel等人 Cancer Immunol Immunother. [癌症免疫學免疫療法] 2010年2月; 59(2):215-30;Ortenberg等人 Mol Cancer Ther. [分子癌症治療學] 2012年6月;11(6):1300-10;Stern等人 J Immunol. [免疫學雜誌] 2005年6月1日; 174(11):6692-701;Zheng等人 PLoS One. [公共科學圖書館綜合] 2010年9月2日; 5(9). pii: e12529)。例如,CEACAM-1已被描述為TIM-3的嗜異性配體,並且在TIM-3介導的T細胞耐受性和耗竭中起作用(參見例如,WO 2014/022332;Huang等人 (2014) Nature [自然] doi: 10.1038/nature13848)。在實施方式中,已顯示CEACAM-1和TIM-3的共同阻斷增強異種移植結腸直腸癌模型中的抗腫瘤免疫反應(參見例如,WO 2014/022332;Huang等人 (2014), 同上)。在一些實施方式中,CEACAM-1和PD-1的共同阻斷降低了T細胞耐受性,如例如WO 2014/059251中所述。因此,CEACAM抑制劑可與本文所述之其他免疫調節劑(例如,抗PD-1和/或抗TIM-3抑制劑)一起使用以增強針對癌症(例如,黑色素瘤、肺癌(例如,NSCLC)、膀胱癌、結腸癌、卵巢癌、和本文所述之其他癌症)的免疫反應。Without wishing to be bound by theory, it is believed that carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs), such as CEACAM-1 and CEACAM-5, mediate at least in part the suppression of antitumor immune responses (see, eg, Markel et al. J Immunol.[ J Immunol] 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2803-10; Markel et al J Immunol. [J Immunol] 2006
LAG3(淋巴球激活基因-3或CD223)係在激活的T細胞和B細胞上表現的細胞表面分子,已顯示該細胞表面分子在CD8+ T細胞耗竭中起作用。LAG3及其配體的抗體、抗體片段和其他抑制劑係本領域可獲得的,並且可以與CAR(例如本文所述之CAR)組合使用。例如,BMS-986016(百時美施貴寶公司)係靶向LAG3的單株抗體。IMP701(伊繆泰普公司(Immutep))係拮抗性LAG3抗體,並且IMP731(伊繆泰普公司和葛蘭素史克(GlaxoSmithKline))係耗減性LAG3抗體。其他LAG3抑制劑包括IMP321(伊繆泰普公司),它係LAG3的可溶性部分和Ig的重組融合蛋白,結合MHC II類分子並激活抗原呈遞細胞(APC)。其他抗體揭露於例如WO 2010/019570中。LAG3 (lymphocyte-activating gene-3 or CD223), a cell surface molecule expressed on activated T cells and B cells, has been shown to play a role in CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Antibodies, antibody fragments and other inhibitors of LAG3 and its ligands are available in the art and can be used in combination with CARs such as those described herein. For example, BMS-986016 (Bristol-Myers Squibb) is a monoclonal antibody targeting LAG3. IMP701 (Immutep) is an antagonistic LAG3 antibody and IMP731 (Immutep and GlaxoSmithKline) is a depleting LAG3 antibody. Other LAG3 inhibitors include IMP321 (Imutep), which is a recombinant fusion protein of the soluble portion of LAG3 and Ig, which binds MHC class II molecules and activates antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Other antibodies are disclosed eg in WO 2010/019570.
在一些實施方式中,增強表現CAR的細胞活性的藥劑可為例如包含第一結構域和第二結構域的融合蛋白,其中第一結構域係抑制性分子或其片段,並且第二結構域係與正訊息相關的多肽,例如包含如本文所述之細胞內傳訊結構域的多肽。在一些實施方式中,與陽性訊息相關的多肽可以包括CD28、CD27、ICOS的共刺激結構域(例如,CD28、CD27和/或ICOS的細胞內傳訊結構域)和/或初級傳訊結構域(例如,如本文所述之CD3ζ的初級傳訊結構域)。在一個實施方式中,融合蛋白由表現CAR的相同細胞表現。In some embodiments, the agent that enhances the activity of a cell expressing a CAR can be, for example, a fusion protein comprising a first domain and a second domain, wherein the first domain is an inhibitory molecule or a fragment thereof, and the second domain is a Polypeptides associated with positive signaling, eg, polypeptides comprising an intracellular signaling domain as described herein. In some embodiments, a polypeptide associated with a positive message can include a co-stimulatory domain of CD28, CD27, ICOS (e.g., an intracellular signaling domain of CD28, CD27, and/or ICOS) and/or a primary signaling domain (e.g., , the primary signaling domain of CD3ζ as described herein). In one embodiment, the fusion protein is expressed by the same cell that expresses the CAR.
在一個實施方式中,增強本文所述之表現CAR的細胞活性的藥劑係miR-17-92。 藥物組成物 In one embodiment, the agent that enhances the activity of a CAR-expressing cell described herein is miR-17-92. drug composition
本發明之藥物組成物可以包含表現CAR的細胞(例如如本文描述的多種表現CAR的細胞),以及一或多種藥學上或生理學上可接受的載體、稀釋劑或賦形劑。此類組成物可以包含緩衝液,如中性緩衝鹽水、磷酸鹽緩衝鹽水等;碳水化合物,如葡萄糖、甘露糖、蔗糖或葡聚糖、甘露醇;蛋白質;多肽或胺基酸如甘胺酸;抗氧化劑;螯合劑,如EDTA或麩胱甘肽;佐劑(例如氫氧化鋁);以及防腐劑。在一方面,本發明之組成物被配製用於靜脈內投與。在另一方面,可以將本發明之組成物配製為用於顱內投與和/或脊柱注射。The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention may comprise CAR-expressing cells (eg, various CAR-expressing cells as described herein), and one or more pharmaceutically or physiologically acceptable carriers, diluents or excipients. Such compositions may comprise buffers such as neutral buffered saline, phosphate buffered saline, etc.; carbohydrates such as glucose, mannose, sucrose or dextran, mannitol; proteins; polypeptides or amino acids such as glycine ; antioxidants; chelating agents, such as EDTA or glutathione; adjuvants (such as aluminum hydroxide); and preservatives. In one aspect, compositions of the invention are formulated for intravenous administration. In another aspect, compositions of the invention may be formulated for intracranial administration and/or spinal injection.
本發明之藥物組成物能以適合於待治療(或預防)的疾病的方式投與。投與的總量和頻率將由如患者的狀況以及患者的疾病的類型和嚴重程度等因素來確定,然而適當的劑量可以藉由臨床試驗來確定。The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be administered in a manner suitable for the disease to be treated (or prevented). The total amount and frequency of administration will be determined by factors such as the condition of the patient and the type and severity of the patient's disease, although appropriate dosages can be determined by clinical trials.
在一個實施方式中,藥物組成物基本上不含,例如沒有可檢測水平的污染物,該污染物例如選自下組,該組由以下組成:內毒素、黴漿菌、有複製能力的慢病毒(RCL)、p24、VSV-G核酸、HIV gag、殘留的抗CD3/抗CD28包被的珠、小鼠抗體、合併的人血清、牛血清白蛋白、牛血清、培養基組分、載體包裝細胞或質體組分、細菌和真菌。在一個實施方式中,細菌係選自由以下組成之群組中至少一種:鹼性糞便菌(Alcaligenes faecalis)、白色念珠菌(Candida albicans)、大腸桿菌、流感嗜血桿菌(Haemophilus influenza)、腦膜炎奈瑟氏菌(Neisseria meningitides)、綠膿桿菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)、金黃色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)、肺炎鏈球菌(Streptococcus pneumonia)、和釀膿鏈球菌A群(Streptococcus pyogenes group A)。In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical composition is substantially free, e.g., free of detectable levels of contaminants, e.g., selected from the group consisting of endotoxins, mycoplasma, replication-competent slow Virus (RCL), p24, VSV-G nucleic acid, HIV gag, residual anti-CD3/anti-CD28 coated beads, mouse antibody, pooled human serum, bovine serum albumin, bovine serum, media components, vector packaging Cellular or plastid components, bacteria and fungi. In one embodiment, the bacteria is at least one selected from the group consisting of Alcaligenes faecalis, Candida albicans, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenza, meningitis Neisseria meningitides, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, and Streptococcus pyogenes group A.
當指示「免疫有效量」、「抗腫瘤有效量」、「腫瘤抑制有效量」或「治療量」時,醫生可以考慮到年齡、體重、腫瘤大小、感染或轉移的程度以及患者(受試者)的狀況的個體差異來確定待投與的本發明組成物的精確量。 給藥方案 When indicating "immune effective dose", "antitumor effective dose", "tumor inhibitory effective dose" or "therapeutic dose", the physician may take into account age, weight, tumor size, degree of infection or metastasis, and patient (subject ) to determine the precise amount of the composition of the invention to be administered. Dosing regimen
本文描述了治療疾病(例如,ALL)之方法,該方法包括以基於細胞/kg體重和該藥物組成物中的總CAR+細胞的劑量,向有需要的患者投與包含細胞(例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22結合的嵌合抗原受體(CAR)分子的核酸分子。在一個實施方式中,如全文所述,總CAR+細胞被測量為表現CD19 CAR和CD22 CAR的CAR細胞群體。在另一個實施方式中,如全文所述,總CAR+細胞被測量為表現CD19 CAR、CD22 CAR以及兩者的CAR細胞群體。在另一個實施方式中,本文測量的總CAR+細胞不包括患者在CD19-CD22 CAR治療前接受的CAR+細胞,例如在用Kymriah(CD19 CAR;替沙侖賽)、Yescarta(CD19 CAR;阿基侖賽)、Tecartus(CD19 CAR;布奧侖賽)、和/或Breyanzi(CD19 CAR;利基邁侖賽)治療前。Described herein is a method of treating a disease (e.g., ALL) comprising administering to a patient in need thereof comprising cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) at a dose based on cells/kg body weight and total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition. A pharmaceutical composition of a population of cells) comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecule that binds to CD19 and CD22. In one embodiment, total CAR+ cells are measured as a population of CAR cells expressing CD19 CAR and CD22 CAR, as described throughout. In another embodiment, total CAR+ cells are measured as a population of CAR cells expressing CD19 CAR, CD22 CAR, and both, as described throughout. In another embodiment, the total CAR+ cells measured herein do not include the CAR+ cells received by the patient prior to CD19-CD22 CAR treatment, for example, after treatment with Kymriah (CD19 CAR; tesarenside), Yescarta (CD19 CAR; before treatment with Tecartus (CD19 CAR; Buolens), and/or Breyanzi (CD19 CAR; Leakemyrons).
在一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中總CAR+細胞,可以對於體重≤50 kg的患者,以劑量為約3 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 > 50 kg的患者以劑量為約1.5 × 10 6個細胞,投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子。在一個實施方式中,體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者在1和30歲之間。 In one embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, a dose of about 3 × 104 cells/kg body weight can be used for patients with body weight ≤ 50 kg, or a dose of About 1.5 x 106 cells, administered (e.g., intravenously) of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) comprising a gene encoding a protein associated with CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171 , c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduction CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules. In one embodiment, the patient is between 1 and 30 years old weighing ≤ 50 kg.
在一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中總CAR+細胞,可以對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,以劑量為約10 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 >50 kg的患者以劑量為約5 × 10 6個細胞,投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子。在一個實施方式中,體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者在1和30歲之間。 In one embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, a dose of about 10 x 104 cells/kg body weight can be used for patients with body weight ≤ 50 kg, or a dose of About 5 x 106 cells, administered (e.g., intravenously) with a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) comprising , c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduction CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules. In one embodiment, the patient is between 1 and 30 years old weighing ≤ 50 kg.
在一個實施方式中,基於該藥物組成物中總CAR+細胞,可以對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,以劑量為約30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重,或對於體重 > 50 kg的患者以劑量為約15 × 10 6個細胞,投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子。在一個實施方式中,體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者在1和30歲之間。 In one embodiment, based on the total CAR+ cells in the pharmaceutical composition, a dose of about 30 × 104 cells/kg body weight can be used for patients with body weight ≤ 50 kg, or a dose of About 15 x 106 cells, administered (e.g., intravenously) in a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) comprising a protein encoding a protein associated with CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171 , c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduction CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules. In one embodiment, the patient is between 1 and 30 years old weighing ≤ 50 kg.
在另一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約1 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、2 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、3 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、4 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、5 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、6 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、7 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、8 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、9 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、10 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、11 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、12 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、13 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、14 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、15 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、16 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、17 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、18 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、19 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、20 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、21 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、22 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、23 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、24 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、25 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、26 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、27 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、28 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、29 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、40 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、50 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、60 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、70 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、80 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重、或90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 ≤ 50 kg體重和/或在1和30歲之間。 In another embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that encodes CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230) can be administered (e.g., intravenously) at a dose of , c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: about 1 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 2 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 3 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 4 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 5 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 6 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 7 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 8 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 9 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 10 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 11 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 12 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 13 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 14 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 15 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 16 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 17 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 18 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 19 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 20 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 21 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 22 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 23 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 24 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 25 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 26 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 27 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 28 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 29 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 30 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 40 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 50 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 60×10 4 cells/kg body weight, 70×10 4 cells/kg body weight, 80×10 4 cells/kg body weight, or 90×10 4 cells/kg body weight. In one embodiment, the patient has a body weight of ≤ 50 kg and/or is between 1 and 30 years old.
在另一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約1 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、2 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、3 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、4 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、5 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、6 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、7 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、8 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、9 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、10 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、11 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、12 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、13 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、14 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、15 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、16 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、17 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、18 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、19 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、20 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、21 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、22 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、23 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、24 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、25 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、26 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、27 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、28 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、29 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、30 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、40 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、50 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、60 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、70 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、或80 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 ≤ 50 kg體重和/或在1和30歲之間。 In another embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) encoding a protein encoding a protein associated with CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230) can be administered (e.g., intravenously) at a dose that is as follows: , c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: between about 1 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 2 × 10 Between 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 3 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 4 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 5 × Between 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 6 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 7 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 8 Between × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 9 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 10 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 11 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 12 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 13 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight , between 14 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 15 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 16 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight Between, between 17 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 18 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 19 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight Between, between 20 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 21 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 22 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg between 23 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 24 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 25 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg Between kg body weight, between 26 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 27 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 28 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells Between 29 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight /kg body weight, between 30 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 40 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 50 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells Between cells/kg body weight, between 60 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 70 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, or between 80 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 Between 4 cells/kg body weight. In one embodiment, the patient has a body weight of ≤ 50 kg and/or is between 1 and 30 years old.
在另一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約1 × 10 4和80 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和70 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和60 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和50 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和40 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和29 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和28 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和27 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和26 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和25 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和24 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和23 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和22 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和21 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和20 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和19 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和18 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和17 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和16 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和15 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和14 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和13 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和12 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和11 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和10 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和9 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和8 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和7 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和6 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和5 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和4 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、1 × 10 4和3 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、或1 × 10 4和2 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 ≤ 50 kg體重和/或在1和30歲之間。 In another embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that encodes CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230) can be administered (e.g., intravenously) at a dose of , c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: between about 1 × 10 4 and 80 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 1 × 10 Between 4 and 70 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 60 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 50 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 1 × Between 10 4 and 40 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 30 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 29 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 1 Between × 10 4 and 28 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 1 × 10 4 and 27 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 1 × 10 4 and 26 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 1 × 10 4 and 25 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 24 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 23 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight , between 1 × 10 4 and 22 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 21 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 20 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight between 1 × 10 4 and 19 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 18 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 17 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight Between, between 1 × 10 4 and 16 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 15 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 14 × 10 4 cells/kg between 1 × 10 4 and 13 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 12 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 11 × 10 4 cells/kg Between kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 10 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 9 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 8 × 10 4 cells /kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 7 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 6 × 10 Between 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 5 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 4 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 1 × 10 4 and 3 × Between 10 4 cells/kg body weight, or between 1×10 4 and 2×10 4 cells/kg body weight. In one embodiment, the patient has a body weight of ≤ 50 kg and/or is between 1 and 30 years old.
在另一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約2 × 10 4和80 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、3 × 10 4和70 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、4 × 10 4和60 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、5 × 10 4和50 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、6 × 10 4和40 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、7 × 10 4和30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、8 × 10 4和29 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、9 × 10 4和28 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、10 × 10 4和27 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、11 × 10 4和26 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、12 × 10 4和25 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、13 × 10 4和24 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、14 × 10 4和23 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、15 × 10 4和22 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、16 × 10 4和21 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、17 × 10 4和20 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、或18 × 10 4和19 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 ≤ 50 kg體重和/或在1和30歲之間。 In another embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that encodes CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230) can be administered (e.g., intravenously) at a dose of , c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: between about 2 × 10 4 and 80 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 3 × 10 Between 4 and 70 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 4 × 10 4 and 60 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 5 × 10 4 and 50 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 6 × Between 10 4 and 40 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 7 × 10 4 and 30 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 8 × 10 4 and 29 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 9 Between × 10 4 and 28 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 10 × 10 4 and 27 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 11 × 10 4 and 26 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 12 × 10 4 and 25 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 13 × 10 4 and 24 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 14 × 10 4 and 23 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight , between 15 × 10 4 and 22 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 16 × 10 4 and 21 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 17 × 10 4 and 20 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight Between, or between 18 × 10 4 and 19 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight. In one embodiment, the patient has a body weight of ≤ 50 kg and/or is between 1 and 30 years old.
在另一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約1 × 10 4和2 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、2 × 10 4和4 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、4 × 10 4和6 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、6 × 10 4和8 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、8 × 10 4和10 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、10 × 10 4和12 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、12 × 10 4和14 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、14 × 10 4和16 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、16 × 10 4和18 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、18 × 10 4和20 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、20 × 10 4和22 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、22 × 10 4和24 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、24 × 10 4和26 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、26 × 10 4和28 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、28 × 10 4和30 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、30 × 10 4和40 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、40 × 10 4和50 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、50 × 10 4和60 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、60 × 10 4和70 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、70 × 10 4和80 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間、或80 × 10 4和90 × 10 4個細胞/kg體重之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 ≤ 50 kg體重和/或在1和30歲之間。 In another embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) that encodes CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230) can be administered (e.g., intravenously) at a dose of , c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: between about 1 × 10 4 and 2 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 2 × 10 Between 4 and 4 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 4 × 10 4 and 6 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 6 × 10 4 and 8 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, 8 × Between 10 4 and 10 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 10 × 10 4 and 12 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 12 × 10 4 and 14 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 14 Between × 10 4 and 16 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 16 × 10 4 and 18 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 18 × 10 4 and 20 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, Between 20 × 10 4 and 22 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 22 × 10 4 and 24 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 24 × 10 4 and 26 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight , between 26 × 10 4 and 28 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 28 × 10 4 and 30 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 30 × 10 4 and 40 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight Between, between 40 × 10 4 and 50 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 50 × 10 4 and 60 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, between 60 × 10 4 and 70 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight between 70 × 10 4 and 80 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight, or between 80 × 10 4 and 90 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight. In one embodiment, the patient has a body weight of ≤ 50 kg and/or is between 1 and 30 years old.
在一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約0.3 × 10 6個細胞、0.35 × 10 6個細胞、0.4 × 10 6個細胞、0.45 × 10 6個細胞、0.5 × 10 6個細胞、0.55 × 10 6個細胞、0.6 × 10 6個細胞、0.65 × 10 6個細胞、0.7 × 10 6個細胞、0.75 × 10 6個細胞、0.8 × 10 6個細胞、0.85 × 10 6個細胞、0.9 × 10 6個細胞、0.95 × 10 6個細胞、5 × 10 6個細胞、1 × 10 6個細胞、1.5 × 10 6個細胞、2 × 10 6個細胞、2.5 × 10 6個細胞、3 × 10 6個細胞、3.5 × 10 6個細胞、4 × 10 6個細胞、4.5 × 10 6個細胞、5 × 10 6個細胞、5.5 × 10 6個細胞、6 × 10 6個細胞、6.5 × 10 6個細胞、7 × 10 6個細胞、7.5 × 10 6個細胞、8 × 10 6個細胞、8.5 × 10 6個細胞、9 × 10 6個細胞、9.5 × 10 6個細胞、10 × 10 6個細胞、10.5 × 10 6個細胞、11 × 10 6個細胞、11.5 × 10 6個細胞、12 × 10 6個細胞、12.5 × 10 6個細胞、13 × 10 6個細胞、13.5 × 10 6個細胞、14 × 10 6個細胞、14.5 × 10 6個細胞、15 × 10 6個細胞、16 × 10 6個細胞、17 × 10 6個細胞、18 × 10 6個細胞、19 × 10 6個細胞、20 × 10 6個細胞、21 × 10 6個細胞、22 × 10 6個細胞、23 × 10 6個細胞、24 × 10 6個細胞、25 × 10 6個細胞、26 × 10 6個細胞、27 × 10 6個細胞、28 × 10 6個細胞、29 × 10 6個細胞、30 × 10 6個細胞、31 × 10 6個細胞、32 × 10 6個細胞、33 × 10 6個細胞、34 × 10 6個細胞、35 × 10 6個細胞、36 × 10 6個細胞、37 × 10 6個細胞、38 × 10 6個細胞、39 × 10 6個細胞、40 × 10 6個細胞、41 × 10 6個細胞、42 × 10 6個細胞、43 × 10 6個細胞、44 × 10 6個細胞、或45 × 10 6個細胞。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 > 50 kg體重。 In one embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) coding for CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: about 0.3 × 10 6 cells, 0.35 × 10 6 cells, 0.4 × 10 6 cells, 0.45 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × 10 6 cells, 0.55 × 10 6 cells, 0.6 × 10 6 cells, 0.65 × 10 6 cells, 0.7 × 10 6 cells, 0.75 × 10 6 cells, 0.8 × 10 6 cells, 0.85 × 10 6 cells, 0.9 × 10 6 cells, 0.95 × 10 6 cells, 5 × 10 6 cells, 1 × 10 6 cells, 1.5 × 10 6 cells, 2 × 10 6 cells, 2.5 × 10 6 cells, 3 × 10 6 cells, 3.5 × 10 6 cells, 4 × 10 6 cells , 4.5 × 10 6 cells, 5 × 10 6 cells, 5.5 × 10 6 cells, 6 × 10 6 cells, 6.5 × 10 6 cells, 7 × 10 6 cells, 7.5 × 10 6 cells , 8 × 10 6 cells, 8.5 × 10 6 cells, 9 × 10 6 cells cells, 9.5 × 10 6 cells, 10 × 10 6 cells, 10.5 × 10 6 cells, 11 × 10 6 cells, 11.5 × 10 6 cells, 12 × 10 6 cells, 12.5 × 10 6 cells Cells, 13 × 10 6 cells, 13.5 × 10 6 cells, 14 × 10 6 cells, 14.5 × 10 6 cells, 15 × 10 6 cells, 16 × 10 6 cells, 17 × 10 6 cells , 18 × 10 6 cells, 19 × 10 6 cells, 20 × 10 6 cells, 21 × 10 6 cells , 22 × 10 6 cells, 23 × 10 6 cells, 24 × 10 6 cells, 25 × 10 6 cells, 26 × 10 6 cells, 27 × 10 6 cells, 28 × 10 6 cells, 29 × 10 6 cells , 30 × 10 6 cells, 31 × 10 6 cells, 32 × 10 6 cells, 33 × 10 6 cells, 34 × 10 6 cells, 35 × 10 6 cells, 36 × 10 6 cells, 37 × 10 6 cells, 38 × 10 6 cells, 39 × 10 6 cells , 40 × 10 6 cells, 41 × 10 6 cells, 42 × 10 6 cells, 43 × 10 6 cells, 44 × 10 6 cells, or 45 × 10 6 cells. In one embodiment, the patient has >50 kg body weight.
在一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約0.45 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、1 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、1.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、2 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、2.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、3 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、3.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、4 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、4.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、5.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、6 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、6.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、7 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、7.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、8 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、8.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、9 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、9.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、10 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、10.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、11 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、11.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、12 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、12.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、13 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、13.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、14 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、14.5 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、15 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、16 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、17 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、18 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、19 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、20 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、21 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、22 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、23 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、24 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、25 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、26 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、27 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、28 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、29 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、30 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、31 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、32 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、33 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、34 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、35 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、36 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、37 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、38 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、39 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、40 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、41 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、42 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、43 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間、或44 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 > 50 kg體重。 In one embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) coding for CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: about 0.45 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × 10 6 and 45 × Between 10 6 cells, between 1 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 1.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 2 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, 2.5 Between × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 3 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 3.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 4 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells between 4.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 5.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, 6 × 10 Between 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 6.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 7 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 7.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells Between, between 8 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 8.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 9 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 9.5 × 10 6 and Between 45 × 10 6 cells, between 10 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 10.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 11 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells , between 11.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 12 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 12.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 13 × 10 6 and 45 × Between 10 6 cells, between 13.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 14 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 14.5 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 15 Between × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 16 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 17 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 18 × 10 6 and 45 × 1 0 6 cells, between 19 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 20 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 21 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, 22 Between × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 23 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 24 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 25 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 between 26 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 27 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 28 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, 29 × 10 Between 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 30 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 31 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 32 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells Between, between 33 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 34 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 35 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 36 × 10 6 and Between 45 × 10 6 cells, between 37 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 38 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 39 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells , between 40 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 41 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 42 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells, between 43 × 10 6 and 45 × Between 10 6 cells, or between 44 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells. In one embodiment, the patient has >50 kg body weight.
在一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約0.5 × 10 6和44 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和43 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和42 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和41 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和40 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和39 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和38 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和37 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和36 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和35 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和34 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和33 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和32 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和31 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和30 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和29 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和28 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和27 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和26 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和25 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和24 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和23 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和22 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和21 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和20 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和19 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和18 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和17 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和16 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和15 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和14.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和14 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和13.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和13 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和12.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和12 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和11.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和11 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和10.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和10 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和9.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和9 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和8.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和8 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和7.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和7 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和6.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和6 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和5.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和4.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和4 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和3.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和3 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和2.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和2 × 10 6個細胞之間、0.5 × 10 6和1.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、或0.5 × 10 6和1 × 10 6個細胞之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 > 50 kg體重。 In one embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) coding for CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: about 0.5 × 10 6 and 44 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × 10 6 and 43 × Between 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 42 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 41 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 40 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 Between × 10 6 and 39 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 38 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 37 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 36 × 10 6 cells between 0.5 × 10 6 and 35 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 34 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 33 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × 10 Between 6 and 32 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 31 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 30 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 29 × 10 6 cells Between, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 28 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 27 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 26 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and Between 25 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 24 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 23 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 22 × 10 6 cells , between 0.5 × 10 6 and 21 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 20 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 19 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 18 × Between 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 17 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 16 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 15 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 Between × 10 6 and 14.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 14 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 13.5 × 10 Between 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 13 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 12.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 12 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × Between 10 6 and 11.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 11 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 10.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 10 × 10 6 cells Between cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 9.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 9 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 8.5 × 10 6 cells, 0.5 × 10 6 and 8 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 7.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 7 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 6.5 × 10 6 cells between 0.5 × 10 6 and 6 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 5.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 4.5 Between × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 4 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 3.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 3 × 10 6 cells, Between 0.5 × 10 6 and 2.5 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 2 × 10 6 cells, between 0.5 × 10 6 and 1.5 × 10 6 cells, or between 0.5 × 10 6 and 1 × 10 between 6 cells. In one embodiment, the patient has >50 kg body weight.
在一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約1 × 10 6和44 × 10 6個細胞之間、1.5 × 10 6和43 × 10 6個細胞之間、2 × 10 6和42 × 10 6個細胞之間、2.5 × 10 6和41 × 10 6個細胞之間、3 × 10 6和40 × 10 6個細胞之間、3.5 × 10 6和39 × 10 6個細胞之間、4 × 10 6和38 × 10 6個細胞之間、4.5 × 10 6和37 × 10 6個細胞之間、5 × 10 6和36 × 10 6個細胞之間、5.5 × 10 6和35 × 10 6個細胞之間、6 × 10 6和34 × 10 6個細胞之間、6.5 × 10 6和33 × 10 6個細胞之間、7 × 10 6和32 × 10 6個細胞之間、7.5 × 10 6和31 × 10 6個細胞之間、8 × 10 6和30 × 10 6個細胞之間、8.5 × 10 6和29 × 10 6個細胞之間、9 × 10 6和28 × 10 6個細胞之間、9.5 × 10 6和27 × 10 6個細胞之間、10 × 10 6和26 × 10 6個細胞之間、10.5 × 10 6和25 × 10 6個細胞之間、11 × 10 6和24 × 10 6個細胞之間、11.5 × 10 6和23 × 10 6個細胞之間、12 × 10 6和22 × 10 6個細胞之間、12.5 × 10 6和21 × 10 6個細胞之間、13 × 10 6和20 × 10 6個細胞之間、13.5 × 10 6和19 × 10 6個細胞之間、14 × 10 6和18 × 10 6個細胞之間、14.5 × 10 6和17 × 10 6個細胞之間、或15 × 10 6和16 × 10 6個細胞之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 > 50 kg體重。 In one embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) coding for CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: between about 1 × 10 6 and 44 × 10 6 cells, 1.5 × 10 6 and 43 × Between 10 6 cells, between 2 × 10 6 and 42 × 10 6 cells, between 2.5 × 10 6 and 41 × 10 6 cells, between 3 × 10 6 and 40 × 10 6 cells, 3.5 Between × 10 6 and 39 × 10 6 cells, between 4 × 10 6 and 38 × 10 6 cells, between 4.5 × 10 6 and 37 × 10 6 cells, between 5 × 10 6 and 36 × 10 6 cells between 5.5 × 10 6 and 35 × 10 6 cells, between 6 × 10 6 and 34 × 10 6 cells, between 6.5 × 10 6 and 33 × 10 6 cells, 7 × 10 Between 6 and 32 × 10 6 cells, between 7.5 × 10 6 and 31 × 10 6 cells, between 8 × 10 6 and 30 × 10 6 cells, between 8.5 × 10 6 and 29 × 10 6 cells Between, between 9 × 10 6 and 28 × 10 6 cells, between 9.5 × 10 6 and 27 × 10 6 cells, between 10 × 10 6 and 26 × 10 6 cells, between 10.5 × 10 6 and Between 25 × 10 6 cells, between 11 × 10 6 and 24 × 10 6 cells, between 11.5 × 10 6 and 23 × 10 6 cells, between 12 × 10 6 and 22 × 10 6 cells , between 12.5 × 10 6 and 21 × 10 6 cells, between 13 × 10 6 and 20 × 10 6 cells, between 13.5 × 10 6 and 19 × 10 6 cells, between 14 × 10 6 and 18 × Between 10 6 cells, between 14.5 x 10 6 and 17 x 10 6 cells, or between 15 x 10 6 and 16 x 10 6 cells. In one embodiment, the patient has >50 kg body weight.
在一個實施方式中,可以以如下劑量投與(例如靜脈內)包含細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)群體的藥物組成物,該細胞群體包含編碼與CD19和CD22(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)結合的CAR分子的核酸分子:約0.5 × 10 6和1.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、1.5 × 10 6和2.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、2.5 × 10 6和3.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、3.5 × 10 6和4.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、4.5 × 10 6和5.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、5.5 × 10 6和6.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、6.5 × 10 6和7.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、7.5 × 10 6和8.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、8.5 × 10 6和9.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、9.5 × 10 6和10.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、10.5 × 10 6和11.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、11.5 × 10 6和12.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、12.5 × 10 6和13.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、13.5 × 10 6和14.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、14.5 × 10 6和15.5 × 10 6個細胞之間、15.5 × 10 6和16 × 10 6個細胞之間、16 × 10 6和17 × 10 6個細胞之間、17 × 10 6和18 × 10 6個細胞之間、18 × 10 6和19 × 10 6個細胞之間、19 × 10 6和20 × 10 6個細胞之間、20 × 10 6和21 × 10 6個細胞之間、21 × 10 6和22 × 10 6個細胞之間、22 × 10 6和23 × 10 6個細胞之間、23 × 10 6和24 × 10 6個細胞之間、24 × 10 6和25 × 10 6個細胞之間、25 × 10 6和26 × 10 6個細胞之間、26 × 10 6和27 × 10 6個細胞之間、27 × 10 6和28 × 10 6個細胞之間、28 × 10 6和29 × 10 6個細胞之間、29 × 10 6和30 × 10 6個細胞之間、30 × 10 6和31 × 10 6個細胞之間、31 × 10 6和32 × 10 6個細胞之間、32 × 10 6和33 × 10 6個細胞之間、33 × 10 6和34 × 10 6個細胞之間、34 × 10 6和35 × 10 6個細胞之間、35 × 10 6和36 × 10 6個細胞之間、36 × 10 6和37 × 10 6個細胞之間、37 × 10 6和38 × 10 6個細胞之間、38 × 10 6和39 × 10 6個細胞之間、39 × 10 6和40 × 10 6個細胞之間、40 × 10 6和41 × 10 6個細胞之間、41 × 10 6和42 × 10 6個細胞之間、42 × 10 6和43 × 10 6個細胞之間、43 × 10 6和44 × 10 6個細胞之間、或44 × 10 6和45 × 10 6個細胞之間。在一個實施方式中,患者具有 > 50 kg體重。 In one embodiment, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a population of cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) coding for CD19 and CD22 (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) nucleic acid molecules combined with CAR molecules: about 0.5 × 10 6 and 1.5 × 10 6 cells, 1.5 × 10 6 and 2.5 × Between 10 6 cells, between 2.5 × 10 6 and 3.5 × 10 6 cells, between 3.5 × 10 6 and 4.5 × 10 6 cells, between 4.5 × 10 6 and 5.5 × 10 6 cells, 5.5 Between × 10 6 and 6.5 × 10 6 cells, between 6.5 × 10 6 and 7.5 × 10 6 cells, between 7.5 × 10 6 and 8.5 × 10 6 cells, between 8.5 × 10 6 and 9.5 × 10 6 cells between 9.5 × 10 6 and 10.5 × 10 6 cells, between 10.5 × 10 6 and 11.5 × 10 6 cells, between 11.5 × 10 6 and 12.5 × 10 6 cells, 12.5 × 10 Between 6 and 13.5 × 10 6 cells, between 13.5 × 10 6 and 14.5 × 10 6 cells, between 14.5 × 10 6 and 15.5 × 10 6 cells, between 15.5 × 10 6 and 16 × 10 6 cells Between, between 16 × 10 6 and 17 × 10 6 cells, between 17 × 10 6 and 18 × 10 6 cells, between 18 × 10 6 and 19 × 10 6 cells, between 19 × 10 6 and Between 20 × 10 6 cells, between 20 × 10 6 and 21 × 10 6 cells, between 21 × 10 6 and 22 × 10 6 cells, between 22 × 10 6 and 23 × 10 6 cells , between 23 × 10 6 and 24 × 10 6 cells, between 24 × 10 6 and 25 × 10 6 cells, between 25 × 10 6 and 26 × 10 6 cells, between 26 × 10 6 and 27 × Between 10 6 cells, between 27 × 10 6 and 28 × 10 6 cells, between 28 × 10 6 and 29 × 10 6 cells, between 29 × 10 6 and 30 × 10 6 cells, between 30 Between × 10 6 and 31 × 10 6 cells, between 31 × 10 6 and 32 × 10 6 cells, between 32 × 10 6 and 3 Between 3 × 10 6 cells, between 33 × 10 6 and 34 × 10 6 cells, between 34 × 10 6 and 35 × 10 6 cells, between 35 × 10 6 and 36 × 10 6 cells , between 36 × 10 6 and 37 × 10 6 cells, between 37 × 10 6 and 38 × 10 6 cells, between 38 × 10 6 and 39 × 10 6 cells, between 39 × 10 6 and 40 × Between 10 6 cells, between 40 × 10 6 and 41 × 10 6 cells, between 41 × 10 6 and 42 × 10 6 cells, between 42 × 10 6 and 43 × 10 6 cells, between 43 Between × 10 6 and 44 × 10 6 cells, or between 44 × 10 6 and 45 × 10 6 cells. In one embodiment, the patient has >50 kg body weight.
在一方面,以如全文所述之劑量,單次輸注投與藥物組成物,例如,經由靜脈內投與。在另一方面,以如全文所述之劑量,多次投與藥物組成物,例如,經由靜脈內投與。可以藉由使用在免疫療法中通常已知的輸注技術來投與細胞(參見例如Rosenberg等人, New Eng. J. of Med.[新英格蘭醫學雜誌] 319:1676, 1988)。In one aspect, the pharmaceutical composition is administered as a single infusion, eg, intravenously, at dosages as described throughout. In another aspect, the pharmaceutical composition is administered multiple times, eg, via intravenous administration, at dosages as described throughout. Cells can be administered by using infusion techniques generally known in immunotherapy (see eg Rosenberg et al., New Eng. J. of Med. 319:1676, 1988).
在某些方面,可能需要將激活的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)投與至受試者,並且然後隨後重新抽取血液(或進行單采血液成分術),根據本發明激活來自血液的細胞,並用該等激活和擴增的細胞重新輸注入患者。該過程可以每隔幾週進行多次。在某些方面,可以將來自10cc至400cc抽血的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)激活。在某些方面,將來自20cc、30cc、40cc、50cc、60cc、70cc、80cc、90cc、或100cc抽血的細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)激活。In certain aspects, it may be desirable to administer activated cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells) to a subject, and then subsequently redraw blood (or perform an apheresis) to activate cells from the blood in accordance with the present invention. cells and re-infuse the patient with these activated and expanded cells. This procedure can be done several times every few weeks. In certain aspects, cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) from a 10cc to 400cc blood draw can be activated. In certain aspects, cells (eg, T cells or NK cells) from a 20cc, 30cc, 40cc, 50cc, 60cc, 70cc, 80cc, 90cc, or 100cc blood draw are activated.
能以任何常規方式投與主題組成物,包括藉由霧化吸入、注射、攝取、輸血、植入或移植。可以向患者經動脈、皮下、真皮內、瘤內、結內、髓內、肌內、顱內、藉由脊柱注射、藉由靜脈內(i.v.)注射(例如,i.v.推注和/或i.v.輸注)、或者腹膜內投與本文所述之組成物。在一方面,藉由皮內或皮下注射將本發明之細胞組成物(例如,T細胞或NK細胞組成物)投與至患者。在一方面,藉由i.v.注射來投與本發明之細胞組成物(例如,T細胞或NK細胞組成物)。可以將細胞組成物(例如,T細胞或NK細胞組成物)直接注射到腫瘤、淋巴結或感染位點中。A subject composition can be administered in any conventional manner, including by aerosol inhalation, injection, ingestion, transfusion, implantation or transplantation. Patients may be administered arterially, subcutaneously, intradermally, intratumorally, intranodally, intramedullary, intramuscularly, intracranially, by spinal injection, by intravenous (i.v.) injection (e.g., i.v. bolus injection and/or i.v. infusion ), or administer a composition described herein intraperitoneally. In one aspect, a cellular composition (eg, a T cell or NK cell composition) of the invention is administered to a patient by intradermal or subcutaneous injection. In one aspect, a cellular composition (eg, a T cell or NK cell composition) of the invention is administered by i.v. injection. Cellular compositions (eg, T cell or NK cell compositions) can be injected directly into tumors, lymph nodes, or sites of infection.
在具體的示例性方面,受試者可經歷白血球去除術,其中離體收集、富集或耗減白血球以選擇和/或分離感興趣的細胞,例如T細胞或NK細胞。可以將該等細胞分離物(例如,T細胞或NK細胞分離物)藉由本領域已知的方法擴增,並進行處理,使得可以引入本發明之一或多種CAR構建體,從而產生本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)。有需要的受試者可以隨後經歷使用高劑量化學療法的標準治療,隨後進行周圍血幹細胞移植。在某些方面,在移植後或與移植同時,受試者接受擴增的本發明之表現CAR的細胞的輸注。在另外的方面,在手術之前或之後投與擴增的細胞。In specific exemplary aspects, a subject may undergo leukapheresis, wherein leukocytes are collected, enriched, or depleted ex vivo to select and/or isolate cells of interest, such as T cells or NK cells. These cell isolates (e.g., T cell or NK cell isolates) can be expanded by methods known in the art and processed so that one or more CAR constructs of the invention can be introduced to produce the CAR constructs of the invention. CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells). Subjects in need can then undergo standard treatment with high-dose chemotherapy followed by peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. In certain aspects, the subject receives an infusion of expanded CAR-expressing cells of the invention following or concurrently with transplantation. In additional aspects, the expanded cells are administered before or after surgery.
在實施方式中,例如在投與表現本文所述之CAR的一或多種細胞之前,對受試者進行淋巴球耗減。在實施方式中,淋巴球耗減包含投與黴法蘭、環磷醯胺、環磷醯胺和氟達拉濱中的一或多種。在另一個實施方式中,淋巴球耗減包含投與阿糖胞苷和/或依託泊苷。In embodiments, the subject is lymphocyte depleted, eg, prior to administration of one or more cells expressing a CAR described herein. In an embodiment, the lymphocyte depletion comprises administering one or more of myoflan, cyclophosphamide, cyclophosphamide, and fludarabine. In another embodiment, lymphocyte depletion comprises administering cytarabine and/or etoposide.
有待向患者投與的以上治療的劑量將隨著所治療病症的確切性質和該治療的受者而變化。可以根據本領域接受的做法來進行人類投與的劑量的縮放。治療劑,例如抗體,例如CAMPATH對於成人患者的劑量例如可以通常在1至約100 mg的範圍內,例如每天投與,持續1天與30天之間的時間段。合適的日劑量為每天1至10 mg,但在一些情況下,可以使用每天多達40 mg的較大劑量(描述於美國專利案號6,120,766中)。The dosage of the above treatments to be administered to a patient will vary with the precise nature of the condition being treated and the recipient of the treatment. Dosage scaling for human administration can be performed according to art-accepted practices. The dosage of a therapeutic agent, eg an antibody, eg CAMPATH, eg, for an adult patient may generally range from 1 to about 100 mg, eg administered daily, for a period of between 1 and 30 days. A suitable daily dose is 1 to 10 mg per day, although in some cases larger doses of up to 40 mg per day may be used (described in US Pat. No. 6,120,766).
在一個實施方式中,例如使用體外轉錄將CAR引入到細胞(例如,T細胞或NK細胞)中,並且使受試者(例如,人)接受本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的初始投與以及本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的一次或多次後續投與,其中將一次或多次後續投與在先前的投與之後少於15天,例如在14、13、12、11、10、9、8、7、6、5、4、3、或2天進行投與。在一個實施方式中,將本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的多於一次投與每週投與至受試者(例如,人),例如每週投與本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的2、3、或4次投與。在一個實施方式中,受試者(例如,人受試者)每週接受多於一次表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的投與(例如每週2、3或4次投與)(在本文中也稱為週期),隨後一週未投與表現CAR的細胞(例如,未投與CAR T細胞或未投與表現CAR的NK細胞),並且然後將表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的一次或多次另外的投與(例如,每週表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的多於一次的投與)投與至受試者。在另一個實施方式中,受試者(例如,人受試者)接受表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)的多於一次的週期,並且每個週期之間的時間小於10天、9天、8天、7天、6天、5天、4天或3天。在一個實施方式中,每隔一天投與表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞),每週投與3次。在一個實施方式中,投與本發明之表現CAR的細胞(例如,CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞)持續至少兩週、三週、四週、五週、六週、七週、八週或更多週。In one embodiment, the CAR is introduced into cells (e.g., T cells or NK cells), e.g., using in vitro transcription, and a subject (e.g., a human) receives the CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells) of the invention. or CAR-expressing NK cells) and one or more subsequent administrations of CAR-expressing cells of the invention (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells), wherein the one or more subsequent administrations The administration is performed less than 15 days after the previous administration, eg, at 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, or 2 days. In one embodiment, more than one administration of a CAR-expressing cell (e.g., a CAR T cell or a CAR-expressing NK cell) of the invention is administered to a subject (e.g., a human) weekly, such as weekly 2, 3, or 4 administrations of CAR-expressing cells (eg, CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) of the invention are administered. In one embodiment, the subject (e.g., a human subject) receives more than one administration of CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) per week (e.g., 2, 3 or 4 administrations) (also referred to herein as a cycle), followed by one week of no administration of CAR-expressing cells (e.g., no administration of CAR T cells or no administration of CAR-expressing NK cells), and then will express CAR One or more additional administrations of cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) (e.g., more than one weekly administration of CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) administration) administered to the subject. In another embodiment, the subject (e.g., a human subject) receives more than one cycle of CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells), and the The period is less than 10 days, 9 days, 8 days, 7 days, 6 days, 5 days, 4 days or 3 days. In one embodiment, CAR-expressing cells (eg, CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) are administered every other day, 3 times per week. In one embodiment, CAR-expressing cells (e.g., CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells) of the invention are administered for at least two weeks, three weeks, four weeks, five weeks, six weeks, seven weeks, eight weeks, or more weeks.
在一些實施方式中,受試者可為成人受試者(即18歲及以上)。在某些實施方式中,受試者可以在1歲與30歲之間。在一些實施方式中,受試者為16歲或以上。在某些實施方式中,受試者在16與30歲之間。在一些實施方式中,受試者係兒童受試者(即1與18歲之間)。In some embodiments, the subject can be an adult subject (ie, 18 years and older). In certain embodiments, the subject may be between 1 and 30 years old. In some embodiments, the subject is 16 years or older. In certain embodiments, the subject is between 16 and 30 years old. In some embodiments, the subject is a child subject (ie, between 1 and 18 years of age).
在一方面,使用慢病毒病毒載體(例如,慢病毒)產生表現CAR的細胞。以這種方式產生的表現CAR的細胞,例如CART將具有穩定的CAR表現。In one aspect, CAR-expressing cells are generated using lentiviral viral vectors (eg, lentiviruses). CAR-expressing cells generated in this manner, such as CART, will have stable CAR expression.
在一方面,轉導後,表現CAR的細胞,例如CART瞬時表現CAR載體,持續4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、12、13、14、15天。CAR的瞬時表現可能受RNA CAR載體遞送的影響。在一方面,藉由電穿孔將CAR RNA轉導到細胞(例如,NK細胞或T細胞)中。In one aspect, the CAR-expressing cells, e.g., CART, transiently express the CAR vector for 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 days after transduction. The transient expression of CAR may be affected by the delivery of RNA CAR vectors. In one aspect, the CAR RNA is transduced into cells (eg, NK cells or T cells) by electroporation.
在使用瞬時表現CAR T細胞或表現CAR的NK細胞(特別是採用攜帶鼠scFv的表現CAR的細胞時)治療的患者中可能出現的潛在問題係多次治療後的過敏反應。A potential problem that may arise in patients treated with transient CAR T cells or CAR-expressing NK cells (especially with CAR-expressing cells carrying murine scFv) is hypersensitivity reactions after multiple treatments.
不受該理論的束縛,認為這種過敏反應可能是由患者發展體液抗CAR響應,即具有抗IgE同種型的抗CAR抗體引起的。認為當存在暴露於抗原的10至14天中斷時,患者的抗體產生細胞經歷從IgG同種型(不引起過敏反應)到IgE同種型的類別轉換。Without being bound by this theory, it is believed that this allergic reaction may be caused by the patient developing a humoral anti-CAR response, ie, anti-CAR antibodies with an anti-IgE isotype. It is thought that when there is a 10 to 14 day break in exposure to the antigen, the patient's antibody producing cells undergo a class switch from the IgG isotype (which does not elicit anaphylaxis) to the IgE isotype.
如果患者在瞬時CAR療法(如藉由RNA轉導產生的那些)過程期間處於產生抗CAR抗體響應的高風險中,則CART輸注中斷時間不應持續超過10至14天。 生物聚合物遞送方法 If a patient is at high risk of developing an anti-CAR antibody response during the course of transient CAR therapy (such as those generated by RNA transduction), the interruption of CART infusion should not last longer than 10 to 14 days. Biopolymer Delivery Methods
在一些實施方式中,如本文所揭露的一或多種表現CAR的細胞可以經由生物聚合物支架(例如,生物聚合物植入物)投與或遞送至受試者。生物聚合物支架可以支持或增強本文所述之表現CAR的細胞的遞送、擴增和/或分散。生物聚合物支架包含可為天然存在的或合成的生物相容的(例如,基本上不誘導炎性或免疫反應)和/或可生物降解的聚合物。In some embodiments, one or more CAR-expressing cells as disclosed herein can be administered or delivered to a subject via a biopolymer scaffold (eg, a biopolymer implant). Biopolymer scaffolds can support or enhance the delivery, expansion and/or dispersion of the CAR-expressing cells described herein. Biopolymer scaffolds comprise biocompatible (eg, do not substantially induce an inflammatory or immune response) and/or biodegradable polymers that may be naturally occurring or synthetic.
合適的生物聚合物之實例包括但不限於瓊脂、瓊脂糖、藻酸鹽、藻酸鹽/磷酸鈣水泥(CPC)、β-半乳糖苷酶(β-GAL)、(1,2,3,4,6-戊乙醯基a-D-半乳糖)、纖維素、幾丁質、殼聚糖、膠原蛋白、彈性蛋白、明膠、透明質酸膠原、羥基磷灰石、聚(3-羥基丁酸酯-共-3-羥基-己酸酯)(PHBHHx)、聚(丙交酯)、聚(己內酯)(PCL)、聚(丙交酯-共-乙交酯)(PLG)、聚環氧乙烷(PEO)、聚(乳酸-共-羥基乙酸)(PLGA)、聚環氧丙烷(PPO)、聚乙烯醇(PVA)、絲、大豆蛋白、和大豆蛋白分離物,單獨地或以任何濃度和任何比率與任何其他聚合物組成物組合。生物聚合物可以用黏附或遷移促進分子(例如,與淋巴球的膠原受體結合的膠原模擬肽、和/或刺激性分子)強化或修飾以增強待遞送細胞的遞送、擴增或功能(例如,抗癌活性)。生物聚合物支架可為可注射的,例如凝膠或半固體、或固體組成物。 Examples of suitable biopolymers include, but are not limited to, agar, agarose, alginate, alginate/calcium phosphate cement (CPC), β-galactosidase (β-GAL), (1,2,3, 4,6-pentaacetyl a-D-galactose), cellulose, chitin, chitosan, collagen, elastin, gelatin, hyaluronic acid collagen, hydroxyapatite, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate ester-co-3-hydroxy-hexanoate) (PHBHHx), poly(lactide), poly(caprolactone) (PCL), poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLG), poly Ethylene oxide (PEO), poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), polypropylene oxide (PPO), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), silk, soy protein, and soy protein isolate, alone or Combine with any other polymer composition in any concentration and in any ratio. Biopolymers can be enhanced or modified with adhesion or migration promoting molecules (e.g., collagen-mimetic peptides that bind to lymphocyte collagen receptors, and/or stimulatory molecules) to enhance delivery, expansion, or function of the cells to be delivered (e.g., , anticancer activity). Biopolymer scaffolds can be injectable, eg gel or semi-solid, or solid compositions.
在一些實施方式中,在遞送至受試者之前,將本文所述之表現CAR的細胞接種到生物聚合物支架上。在實施方式中,生物聚合物支架進一步包含一或多種本文所述之另外的治療劑(例如,另一種表現CAR的細胞、抗體、或小分子)或例如併入或軛合到支架的生物聚合物的增強表現CAR的細胞活性的藥劑。在實施方式中,生物聚合物支架被注射(例如,瘤內、或通過外科手術植入)到腫瘤處或足以介導抗腫瘤作用的腫瘤附近。生物聚合物組成物及其遞送方法的另外的實例描述於Stephan等人, Nature Biotechnology[自然生物技術], 2015, 33:97-101;和WO 2014/110591中。 實例 In some embodiments, the CAR-expressing cells described herein are seeded onto a biopolymer scaffold prior to delivery to a subject. In embodiments, the biopolymer scaffold further comprises one or more additional therapeutic agents described herein (e.g., another CAR-expressing cell, antibody, or small molecule) or a biopolymer, e.g., incorporated or conjugated to the scaffold. Agents that enhance the cellular activity of CARs. In an embodiment, the biopolymer scaffold is injected (eg, intratumorally, or surgically implanted) at or near the tumor sufficient to mediate an anti-tumor effect. Additional examples of biopolymer compositions and methods of delivery thereof are described in Stephan et al., Nature Biotechnology , 2015, 33:97-101; and WO 2014/110591. example
藉由參考以下實驗實例進一步詳細描述本發明。提供該等實例僅用於說明之目的,除非另有說明,否則不應旨在是限制性的。因此,本發明決不應被解釋為限於以下實例,而是應該被解釋為涵蓋由於本文提供的傳授內容而變得明顯的任何和所有變化。 實例1:靶向CD19和CD22的串聯和雙重CAR T細胞體外活性 The present invention is described in further detail by referring to the following experimental examples. These examples are provided for illustrative purposes only and should not be intended to be limiting unless otherwise indicated. Accordingly, the present invention should in no way be construed as limited to the following examples, but rather should be construed to cover any and all variations which become apparent as a result of the teachings provided herein. Example 1: In vitro activity of tandem and dual CAR T cells targeting CD19 and CD22
本實例證明了串聯和雙重CAR T細胞的體外活性。This example demonstrates the in vitro activity of tandem and dual CAR T cells.
串聯嵌合抗原受體(CAR)作為相同蛋白的一部分,串聯表現兩個不同的scFv結構域。雙重CAR係由兩個全長的CAR組成。此處,這兩個CAR係藉由單個慢病毒載體編碼,藉由P2A核糖體跳過元件分離。這裡描述的串聯和雙重CAR均使用相同的4-1BB和CD3ζ刺激結構域。將串聯和雙重CAR選殖到慢病毒表現載體(Pelp)中,用於原代T細胞的轉導。Tandem chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) express two distinct scFv domains in tandem as part of the same protein. The dual CAR line consists of two full-length CARs. Here, the two CARs are encoded by a single lentiviral vector, separated by a P2A ribosomal skipping element. Both the tandem and dual CARs described here use the same 4-1BB and CD3ζ stimulatory domains. Tandem and dual CARs were cloned into a lentiviral expression vector (Pelp) for transduction of primary T cells.
在本實例中使用的串聯CAR係:c171、c182、c224和c227。在本實例中測試的雙重CAR係c201和c230(這兩個CAR在CD19 CAR的上游有CD22 CAR),和c203(在CD22 CAR的上游有CD19 CAR)。C230雖然與c201具有相同的胺基酸序列,但它係使用不同的密碼子生成的,因此具有不同的DNA序列。在本實例中還使用的係相關的單CAR:CD22-65s(識別CD22)和c206(識別CD19)。Tandem CAR lines used in this example: c171, c182, c224 and c227. The dual CAR lines tested in this example were c201 and c230 (these two CARs have the CD22 CAR upstream of the CD19 CAR), and c203 (these two CARs have the CD19 CAR upstream of the CD22 CAR). Although C230 has the same amino acid sequence as c201, it is produced using different codons and therefore has a different DNA sequence. Line-related single CARs also used in this example: CD22-65s (recognizes CD22) and c206 (recognizes CD19).
藉由測試串聯和雙重CAR轉導的T細胞響應於表現CD19和CD22(Nalm6)、表現CD22(CD19KO)或表現CD19(CD22KO)靶標的效應T細胞反應進行比較。效應T細胞響應包括但不限於細胞擴增、增殖、倍增、細胞介素產生和靶細胞殺傷或細胞溶解活性(去顆粒)。 結果 CAR T 細胞的產生 Comparisons were made by testing tandem and dual CAR-transduced T cells in response to effector T cell responses expressing CD19 and CD22 (Nalm6), expressing CD22 (CD19KO), or expressing CD19 (CD22KO) targets. Effector T cell responses include, but are not limited to, cell expansion, proliferation, doubling, cytokine production, and target cell killing or cytolytic activity (degranulation). Results Generation of CAR T cells
使用編碼CAR的Pelp慢病毒轉移載體來產生包裝到VSVg假型化慢病毒顆粒中的基因組病毒材料。將編碼CAR的慢病毒載體DNA與三個包裝組分VSVg、gag/pol和rev與lipofectamine試劑的組合混合以轉染Lenti-X 293T細胞(克羅泰克公司),然後在12-18小時後更換培養基。在培養基更換後30小時,收集培養基,過濾,藉由沈澱濃縮並儲存在-80°C下。The CAR-encoding Pelp lentiviral transfer vector was used to generate genomic viral material packaged into VSVg pseudotyped lentiviral particles. CAR-encoding lentiviral vector DNA was mixed with the three packaging components VSVg, gag/pol and rev in combination with lipofectamine reagent to transfect Lenti-X 293T cells (Crotec) and then replaced after 12-18 hours Medium. Thirty hours after the medium change, the medium was collected, filtered, concentrated by precipitation and stored at -80°C.
將CAR T細胞藉由從被單采血液成分的健康供體的血液開始而產生,藉由陰性選擇(Pan T細胞分離,美天旎公司)而獲得該健康供體的T細胞。然後藉由以1 : 3(T細胞與珠)的比率添加CD3/CD28珠(Dynabeads® Human T-Expander(人T擴增劑)CD3/CD28,賽默飛世爾科技公司(ThermoFisher Scientific))並在37°C、5% CO 2下、在T細胞培養基(RPMI1640、10%熱滅活的胎牛血清(FCS)、2 Mm L-麩醯胺酸、1x青黴素/鏈黴素、100 mM非必需胺基酸、1 mM丙酮酸鈉、10 mM Hepes和55 mM 2-巰基乙醇)中培養來激活T細胞。將T細胞以24孔板每孔1 ml培養基中0.5 × 10 6個T細胞培養。24小時後,當T細胞出胚時,添加病毒上清液;以5的感染複數(MOI)轉導T細胞。T細胞開始增殖,藉由測量細胞濃度(如每Ml的計數)來進行監測,並且每兩天將T細胞稀釋在新鮮T細胞培養基中。隨著T細胞在大約10天後開始靜息,對數生長減弱。生長速度減緩和T細胞大小減小(接近350 Fl)的組合決定了T細胞被冷凍保存以供以後分析的時間。所有CAR T細胞均在研究級(即,非臨床級)製造條件下製備。在冷凍保存之前,藉由FACS Fortessa(BD)上的流動式細胞測量術分析確定轉導的細胞的百分比(在細胞表面上表現CD22特異性和/或CD19特異性CAR)。病毒轉導顯示出相當的表現水平,這表明對應CAR的相似的轉導效率。CAR T細胞培養物的細胞計數表明,當與未轉導的T細胞(「UTD」)相比時,CAR對T細胞增殖能力沒有可檢測的負面影響。 評價 CAR 重定向的 T 細胞的效能: CAR T cells were generated by starting from the blood of an apheresis healthy donor whose T cells were obtained by negative selection (Pan T cell isolation, Miltenyi). Then by adding CD3/CD28 beads (Dynabeads® Human T-Expander (Human T-Expander) CD3/CD28, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a ratio of 1:3 (T cells to beads) and In T cell medium (RPMI1640, 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum ( FCS ), 2 Mm L-glutamine, 1x penicillin/streptomycin, 100 mM non- essential amino acids, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 mM Hepes, and 55 mM 2-mercaptoethanol) to activate T cells. T cells were cultured at 0.5 × 106 T cells in 1 ml medium per well of a 24-well plate. After 24 hours, when T cells emerged from the embryos, viral supernatant was added; T cells were transduced at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5. T cells start to proliferate, monitored by measuring cell concentration (eg, counts per Ml), and T cells are diluted in fresh T cell medium every two days. Logarithmic growth attenuated as T cells became quiescent after about 10 days. The combination of slowed growth rate and reduced T cell size (approximately 350 Fl) dictates how long T cells are cryopreserved for later analysis. All CAR T cells were prepared under research-grade (i.e., not clinical-grade) manufacturing conditions. The percentage of transduced cells (expressing CD22-specific and/or CD19-specific CAR on the cell surface) was determined by flow cytometry analysis on a FACS Fortessa (BD) prior to cryopreservation. Viral transductions showed comparable levels of expression, suggesting similar transduction efficiencies for CARs. Cell counts of CAR T cell cultures indicated that CAR had no detectable negative effect on T cell proliferative capacity when compared to untransduced T cells (“UTD”). Evaluate the potency of CAR- redirected T cells:
為了評價該等雙重CAR T細胞的功能性能力,將如上所述產生的CAR-T解凍、計數並與癌細胞共培養以讀出它們的殺傷能力和細胞介素的分泌。在一個實驗中,雙重CAR-T c201和c203與單CAR對應物c206(CART19)和CD22-65s進行了比較。第二個實驗比較了雙重CAR-T c201和c230與串聯CAR-T c171、c182、c188、c224和c227,並與單CAR對應物c206(CART19)和CD22-65s進行了比較。在兩個實驗中,將未轉導的T細胞(UTD)作為非靶向T細胞對照。To evaluate the functional capabilities of these dual CAR T cells, the CAR-Ts generated as described above were thawed, counted, and co-cultured with cancer cells to read out their killing ability and cytokine secretion. In one experiment, the dual CAR-T c201 and c203 were compared with the single CAR counterparts c206 (CART19) and CD22-65s. The second experiment compared the dual CAR-T c201 and c230 with the tandem CAR-T c171, c182, c188, c224 and c227, and with the single CAR counterpart c206 (CART19) and CD22-65s. In both experiments, untransduced T cells (UTD) served as non-targeted T cell controls.
T細胞殺傷針對急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)株Nalm6(RRID:CVCL 0092)和相應的CD22陰性株(CD22KO)以及藉由CRISPR修飾Nalm6而產生的CD19陰性株(CD19KO)。轉導所有細胞系以表現作為細胞活力/殺傷的報告基因的螢光素酶。在10 : 1、5 : 1、2.5 : 1、1.25 : 1、0.63 : 1和0.31 : 1的效應子 : 靶細胞比率(E : T)的滴定下測量CAR-T的細胞溶解活性。藉由將對應數目的T細胞與恒定數目的靶細胞(96孔板每孔25,000個細胞)混合來開始測定。20小時後,藉由添加Bright-Glo™螢光素酶測定系統(普洛麥格公司(Promega))試劑溶解孔中剩餘的細胞,以定量每個孔中剩餘的表現Luc的癌細胞。「殺傷%」係相對於僅含有靶細胞的孔(0%殺傷,最大Luc訊息)計算的。CD22KO Nalm6-Luc的數據表明,用編碼慢雙重或c206 CART的病毒轉導,將抗CD19殺傷活性轉移到T細胞( 圖 3A)。CD19KO Nalm6-Luc的數據表明,用編碼雙重、串聯或CD22-65s CART的慢病毒轉導,將抗CD22殺傷活性轉移到T細胞( 圖 3B)。UTD T細胞僅顯示出背景殺傷。所有三種雙重CAR-T均顯示出對CD19和CD22介導的KO Nalm6靶細胞的殺傷略高。 T cell killing against the acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) strain Nalm6 (RRID: CVCL 0092) and the corresponding CD22-negative strain (CD22KO) as well as the CD19-negative strain (CD19KO) generated by CRISPR modification of Nalm6. All cell lines were transduced to express luciferase as a reporter gene for cell viability/killing. The cytolytic activity of CAR-T was measured at titrations of effector:target cell ratios (E:T) of 10:1, 5:1, 2.5:1, 1.25:1, 0.63:1, and 0.31:1. The assay was initiated by mixing the corresponding number of T cells with a constant number of target cells (25,000 cells per well of a 96-well plate). After 20 hours, the remaining Luc-expressing cancer cells in each well were quantified by adding Bright-Glo™ Luciferase Assay System (Promega) reagent to lyse the remaining cells in the wells. "Killing %" is calculated relative to wells containing only target cells (0% killing, maximum Luc message). Data from CD22KO Nalm6-Luc demonstrated that transduction with viruses encoding slow double or c206 CART transferred anti-CD19 killing activity to T cells ( Fig. 3A ). Data from CD19KO Nalm6-Luc demonstrated that transduction with lentiviruses encoding double, tandem, or CD22-65s CARTs transferred anti-CD22 killing activity to T cells ( Fig. 3B ). UTD T cells showed only background killing. All three dual CAR-Ts showed slightly higher killing of KO Nalm6 target cells mediated by CD19 and CD22.
為了測量回應於表現CD22和/或CD19的靶細胞的CAR T細胞的細胞介素產生,將CAR T細胞與上述相同的ALL系共培養。另外,用ALL系SEM共培養CAR-T。將細胞以1 : 1的效應子 : 靶標比率和96孔板每孔25,000個細胞培養24 h,之後取出培養基以用於使用V-PLEX人IFN-g套組(Meso Scale Diagnostics公司)進行細胞介素分析。藉由表現CD19的靶細胞(Nalm6、CD22KO Nalm6和SEM; 圖 3C和 3D)強烈刺激所有雙重、串聯和單CAR-T。然而,通過單獨藉由CD22刺激的CAR T(CD19KO Nalm6)分泌的IFN-g水平的數據顯示,與c203和串聯CAR-T相比,c201和c230雙重CAR-T的刺激有所提高。IFN-g的C201和c230分泌水平與CD22-65s單CAR-T分泌水平相當(圖3C和3D)。 To measure the cytokine production of CAR T cells in response to target cells expressing CD22 and/or CD19, CAR T cells were co-cultured with the same ALL lines described above. In addition, CAR-T was co-cultured with ALL line SEM. Cells were cultured at an effector:target ratio of 1 : 1 and 25,000 cells per well in a 96-well plate for 24 h, after which the medium was removed for cell mediation using the V-PLEX Human IFN-g Kit (Meso Scale Diagnostics, Inc.) prime analysis. All dual, tandem and single CAR-Ts were strongly stimulated by CD19-expressing target cells (Nalm6, CD22KO Nalm6 and SEM; Figures 3C and 3D ). However, the data on IFN-g levels secreted by CAR T (CD19KO Nalm6) stimulated by CD22 alone showed that the stimulation of c201 and c230 dual CAR-T was improved compared with c203 and tandem CAR-T. The C201 and C230 secretion levels of IFN-g were comparable to CD22-65s single CAR-T secretion levels (Fig. 3C and 3D).
在本研究中,雙重CAR-T c201、c203和c230比串聯和單CAR-T表現出更好的殺傷活性。在與表現CD19的靶細胞共培養時,雖然雙重CAR-T相對於IFN-g的分泌具有相似的活性,但與c203相比c201顯示出的優異的活化。與本研究中測試的串聯CAR-T相比,c201和c230都表現出更好的活性。 實例2:靶向CD19和CD22的雙重和串聯CAR-T的體內活性研究活性 In this study, dual CAR-T c201, c203 and c230 showed better killing activity than tandem and single CAR-T. While the dual CAR-T had similar activity with respect to the secretion of IFN-g when co-cultured with CD19-expressing target cells, c201 showed superior activation compared with c203. Compared with the tandem CAR-T tested in this study, both c201 and c230 showed better activity. Example 2: In vivo activity study of dual and tandem CAR-T targeting CD19 and CD22
本實例證明了雙重和串聯CAR-T細胞的體內活性。This example demonstrates the in vivo activity of dual and tandem CAR-T cells.
串聯嵌合抗原受體(CAR)作為相同蛋白的一部分,串聯表現兩個不同的scFv結構域。雙重CAR係由兩個全長的CAR組成。在此示例中,這兩個CAR係藉由單個慢病毒載體編碼,藉由P2A核糖體跳過元件分離。這裡描述的串聯和雙重CAR均使用相同的4-1BB和CD3ζ刺激結構域。將串聯和雙重CAR選殖到慢病毒表現載體(Pelp)中,用於原代T細胞的轉導。Tandem chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) express two distinct scFv domains in tandem as part of the same protein. The dual CAR line consists of two full-length CARs. In this example, the two CARs are encoded by a single lentiviral vector, separated by a P2A ribosomal skipping element. Both the tandem and dual CARs described here use the same 4-1BB and CD3ζ stimulatory domains. Tandem and dual CARs were cloned into a lentiviral expression vector (Pelp) for transduction of primary T cells.
在本實例中使用的串聯CAR係:c171、c182、c224和c227。本例中使用的雙重CAR係c201和c230,其在CD19 CAR的上游有CD22 CAR。C230雖然與c201具有相同的胺基酸序列,但它係使用不同的密碼子生成的,因此具有不同的DNA序列。本研究中使用的相關單CAR係CD22-65s(識別CD22)和c206(識別CD19)。在ALL異種移植復發模型中體內評估雙重和串聯CAR T細胞的抗腫瘤活性。 材料與方法 Tandem CAR lines used in this example: c171, c182, c224 and c227. The dual CAR lines used in this example, c201 and c230, have a CD22 CAR upstream of the CD19 CAR. Although C230 has the same amino acid sequence as c201, it is produced using different codons and therefore has a different DNA sequence. The related single CAR lines used in this study were CD22-65s (recognizing CD22) and c206 (recognizing CD19). In vivo assessment of antitumor activity of dual and tandem CAR T cells in an ALL xenograft recurrence model. Materials and Methods
細胞系:Nalm6(RRID:CVCL_0092)為人急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)細胞系。利用CRISPR技術,將CD19基因敲除(CD19KO)。將細胞在含有10%胎牛血清的RMPI培養基中生長並且兩者均懸浮生長。當靜脈內植入時,細胞在小鼠中持續存在並擴增。已經將細胞修飾以表現螢光素酶,使得在它們注射底物螢光素酶之後也可以藉由對小鼠成像來監測腫瘤細胞生長。Cell line: Nalm6 (RRID: CVCL_0092) is a human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell line. Using CRISPR technology, the CD19 gene is knocked out (CD19KO). Cells were grown in RMPI medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and both were grown in suspension. The cells persisted and expanded in mice when implanted intravenously. Cells have been modified to express luciferase so that tumor cell growth can also be monitored by imaging mice after they have been injected with the substrate luciferase.
小鼠:6週齡NSG(NOD.Cg- Prkdc scidIl2rg tm1Wjl/ SzJ)小鼠接收自傑克遜實驗室(Jackson Laboratory)(庫存號005557)。在實驗之前使動物適應至少3天。根據相關條例和指南處理動物。在腫瘤植入前一天,將用於動物標識的電子轉發器植入在左側肋腹部。 Mice: 6-week-old NSG (NOD.Cg- Prkdc scid Il2rg tm1Wjl / SzJ) mice were received from Jackson Laboratory (stock number 005557). Animals were acclimatized for at least 3 days prior to experimentation. Animals were handled according to relevant regulations and guidelines. One day before tumor implantation, electron transponders for animal identification were implanted in the left flank abdomen.
腫瘤移植:收穫處於對數生長期的Nalm6和CD19KO Nalm6細胞,並且在50 ml falcon管中以1200 rpm洗滌5分鐘,在生長培養基中洗滌一次,並且然後在冷的無菌PBS中洗滌兩次。將細胞以5 × 10 6/ml的濃度和以Nalm6與CD19KO Nalm6按20 : 1的比率重懸於PBS中,置於冰上,並且注射在小鼠中。通過尾靜脈以200 μl靜脈內注射癌細胞。當靜脈內植入在小鼠中時該模型生長良好,可以成像以測量腫瘤負荷。在注射1 × 10 6個癌細胞後,腫瘤建立並且可在3天內準確測量。基線測量值為4-6 × 10 5光子/秒(p/s)。在7天內,平均生物發光測量值為2-4 × 10 6p/s,並且未治療的腫瘤在20-30天達到終點測量(2-3 × 10 9)。一旦腫瘤完全移植,通常測試治療劑的抗腫瘤活性。因此,該等模型存在期間可以觀察到CAR T細胞的抗腫瘤活性的大視窗。 Tumor implantation: Nalm6 and CD19KO Nalm6 cells in logarithmic growth phase were harvested and washed in 50 ml falcon tubes at 1200 rpm for 5 minutes, once in growth medium and then twice in cold sterile PBS. Cells were resuspended in PBS at a concentration of 5 x 106 /ml in a 20:1 ratio of Nalm6 to CD19KO Nalm6, placed on ice, and injected in mice. Cancer cells were injected intravenously in 200 μl through the tail vein. The model grows well when implanted intravenously in mice and can be imaged to measure tumor burden. After injection of 1 × 106 cancer cells, tumors were established and could be accurately measured within 3 days. Baseline measurements are 4-6 × 10 5 photons per second (p/s). Within 7 days, mean bioluminescence measurements were 2-4 × 10 6 p/s, and untreated tumors reached endpoint measurements (2-3 × 10 9 ) in 20-30 days. Once the tumor is fully implanted, the therapeutic agent is usually tested for anti-tumor activity. Therefore, a large window of anti-tumor activity of CAR T cells can be observed during the existence of these models.
CAR T細胞產生:所有CAR T細胞均在研究級(即,非臨床級)製造條件下製備。傳統製造:將CAR T細胞藉由從被單采血液成分的健康供體的血液開始而產生,藉由陰性選擇(Pan T細胞分離,美天旎公司)而獲得該健康供體的T細胞。然後藉由以1 : 3(T細胞與珠)的比率添加CD3/CD28珠(Dynabeads® Human T-Expander(人T擴增劑)CD3/CD28,賽默飛世爾科技公司)並在37°C、5% CO 2下、在T細胞培養基(RPMI1640、10%熱滅活的胎牛血清(FCS)、2 mM L-麩醯胺酸、1x青黴素/鏈黴素、100 mM非必需胺基酸、1 mM丙酮酸鈉、10 mM Hepes和55 mM 2-巰基乙醇)中培養來激活T細胞。將T細胞以24孔板每孔1 mL培養基中0.5 × 10 6個T細胞培養。24小時後,當T細胞出胚時,添加病毒上清液;以5的感染複數(MOI)轉導T細胞。T細胞開始增殖,藉由測量細胞濃度(如每mL的計數)來進行監測,並且每兩天將T細胞稀釋在新鮮T細胞培養基中。隨著T細胞在大約10天後開始靜息,對數生長減弱。生長速度減緩和T細胞大小減小(接近350 Fl)的組合決定了T細胞被冷凍保存以供以後分析的時間。在冷凍保存之前,藉由FACS Fortessa(BD)上的流動式細胞測量術分析確定轉導的細胞的百分比(在細胞表面上表現CD22特異性和/或CD19特異性CAR)。病毒轉導顯示出相當的表現水平,這表明對應CAR的相似的轉導效率。CAR T細胞培養物的細胞計數表明,當與未轉導的T細胞(「UTD」)相比時,CAR對T細胞增殖能力沒有可檢測的負面影響。 CAR T cell production: All CAR T cells were produced under research-grade (i.e., not clinical-grade) manufacturing conditions. Conventional manufacturing: CAR T cells are generated by starting from the blood of a healthy donor whose blood components are apheresis, and the T cells of this healthy donor are obtained by negative selection (Pan T cell isolation, Miltenyi). Then by adding CD3/CD28 beads (Dynabeads® Human T-Expander (Human T-Expander) CD3/CD28, Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a ratio of 1:3 (T cells to beads) and incubated at 37°C , 5% CO, in T cell medium (RPMI1640, 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS), 2 mM L-glutamine, 1x penicillin/streptomycin, 100 mM non-essential amino acids , 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 mM Hepes, and 55 mM 2-mercaptoethanol) to activate T cells. T cells were cultured at 0.5 × 106 T cells in 1 mL medium per well of a 24-well plate. After 24 hours, when T cells emerged from the embryos, viral supernatant was added; T cells were transduced at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5. T cell initiation of proliferation was monitored by measuring cell concentration (eg, counts per mL), and T cells were diluted in fresh T cell medium every two days. Logarithmic growth attenuated as T cells became quiescent after about 10 days. The combination of slowed growth rate and reduced T cell size (approximately 350 Fl) dictates how long T cells are cryopreserved for later analysis. The percentage of transduced cells (expressing CD22-specific and/or CD19-specific CAR on the cell surface) was determined by flow cytometry analysis on a FACS Fortessa (BD) prior to cryopreservation. Viral transductions showed comparable levels of expression, suggesting similar transduction efficiencies for CARs. Cell counts of CAR T cell cultures indicated that CAR had no detectable negative effect on T cell proliferative capacity when compared to untransduced T cells (“UTD”).
CAR T細胞給藥:在Nalm6研究中,小鼠在腫瘤植入後7天給藥。藉由傳統製造產生的CAR T細胞以1 x 10 6CAR+ T細胞給藥。用快速法產生的細胞以0.3和0.1 x 10 6的CAR+ T細胞給藥。對於混合給藥,c206和CD22-65s 單CAR-T以1 : 1的比率,以如下所示劑量混合。在TMD8研究中,在腫瘤植入後9天向小鼠投與1 × 10 6或3 × 10 6個CAR+ T細胞。作為對照,小鼠接受媒劑物(PBS)或UTD。對於給藥,將細胞在37°C水浴中部分解凍,並且然後藉由添加1 ml溫熱的T細胞培養基完全解凍。將解凍的細胞轉移到50 ml falcon管中,並且用T細胞培養基調節至終體積12 ml。將細胞洗滌兩次並以300 g旋轉10分鐘,並且然後藉由血細胞計數器(Nexcelom)計數。然後將T細胞以對應濃度重懸浮於冷PBS中並且保持在冰上直至向小鼠給予。經由尾靜脈以200 μl靜脈內注射CAR-T。所有細胞均由相同的供體平行製備。 CAR T cell administration: In the Nalm6 study, mice were dosed 7 days after tumor implantation. CAR T cells produced by conventional manufacturing were administered at 1 x 10 6 CAR+ T cells. Cells generated by the rapid method were administered at 0.3 and 0.1 x 106 CAR+ T cells. For mixed administration, c206 and CD22-65s single CAR-T are mixed at a ratio of 1:1 at the doses shown below. In the TMD8 study, mice were administered 1 × 106 or 3 × 106 CAR+ T cells 9 days after tumor implantation. As controls, mice received vehicle (PBS) or UTD. For dosing, cells were partially thawed in a 37°C water bath and then completely thawed by adding 1 ml of warmed T cell medium. Thawed cells were transferred to 50 ml falcon tubes and brought to a final volume of 12 ml with T cell medium. Cells were washed twice and spun at 300 g for 10 minutes, and then counted by a hemocytometer (Nexcelom). T cells were then resuspended at corresponding concentrations in cold PBS and kept on ice until administration to mice. CAR-T was injected intravenously in 200 μl via the tail vein. All cells were prepared in parallel from the same donor.
動物監測:每天監測小鼠的健康狀況,包括每週兩次體重測量。對於Nalm6研究,腫瘤也藉由成像每週監測兩次。 結果 Animal Monitoring: Monitor the health of mice daily, including body weight measurements twice a week. For the Nalm6 study, tumors were also monitored twice weekly by imaging. result
在B細胞急性淋巴球白血病異種移植復發模型中評估雙重和串聯CAR T細胞的抗腫瘤活性。5%的CD19陰性,CD22陽性Nalm6細胞(CD19KO)混入Nalm6野生型細胞中,其表現CD22和CD19。將癌細胞作為一個混合群體計數,合併和注射。在第0天腫瘤細胞植入後,將攜帶腫瘤小鼠隨機化到治療組中,並且在腫瘤植入後第7天經由側尾靜脈經靜脈內投與CAR T細胞。監測腫瘤生長和動物健康狀態直至動物達到終點。Evaluation of antitumor activity of dual and tandem CAR T cells in a B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft relapse model. 5% of CD19-negative, CD22-positive Nalm6 cells (CD19KO) were mixed with Nalm6 wild-type cells, which express CD22 and CD19. Cancer cells were counted, pooled and injected as a mixed population. After tumor cell implantation on
在研究中,使用傳統製造的CAR-T,將c171、c182、c224和c227串聯CAR-T與c201和c230雙重CAR-T進行了比較。作為參考,c206和CD22-65s單CAR-T單獨注射或以1 : 1混合注射。當所有單個CAR-T群體以1 x 10
6CAR+劑量注射時,混合CAR-T以每個1 x 10
6CAR+細胞的劑量注射(2 x 10
6總CAR T,1e6混合)或0.5 x 10
6CAR+細胞的劑量注射(1 x 10
6總CAR T,5e5混合)。在第3週(在腫瘤致使後肢活動性降低前)對接受PBS或UTD T細胞的小鼠實施安樂死。其他組在第4週和第7週之間實施安樂死。所有治療組的平均生物發光繪製在
圖 4A中。
In the study, a c171, c182, c224, and c227 tandem CAR-T was compared to a c201 and c230 dual CAR-T using a conventionally manufactured CAR-T. For reference, c206 and CD22-65s single CAR-T were injected alone or mixed at 1:1. When all individual CAR-T populations were injected at a dose of 1 x 10 6 CAR+, pooled CAR-Ts were injected at a dose of 1 x 10 6 CAR+ cells (2 x 10 6 total CAR T, 1e6 pooled) or 0.5 x 10 6 Dose injection of CAR+ cells (1 x 10 6 total CAR T, 5e5 pooled). Mice receiving PBS or UTD T cells were euthanized at week 3 (before tumors reduced hindlimb mobility). The other groups were euthanized between
未接受任何T細胞的PBS治療組在靜脈內注射的NSG小鼠中展示出基線Nalm6腫瘤生長動力學。UTD治療組充當T細胞對照以顯示人供體T細胞在此模型中的非特異性響應(其無法檢測)。在這個復發模型中,在使用的劑量下,c206,CD22-65s單CAR-T顯示出最少反應。所有的串聯CAR-T顯示出明顯減慢腫瘤生長,但最終由於腫瘤負荷,小鼠被安樂死。雙重CAR-T,c201和c230在治療組的幾隻小鼠中顯示腫瘤完全根除(見 圖 4A)。1e6混合組顯示相似的功效,但與雙重組比較,其需要的CAR+ T細胞係兩倍。5e5混合組,其得到的CAR-T的總數與雙重組相同,但與這裡測試的串聯CAR-T相比,表現不好。 The PBS-treated group that did not receive any T cells exhibited baseline Nalm6 tumor growth kinetics in intravenously injected NSG mice. The UTD treatment group served as a T cell control to show non-specific responses (which were not detectable) of human donor T cells in this model. In this relapse model, c206, CD22-65s single CAR-T showed the least response at the doses used. All tandem CAR-Ts were shown to significantly slow tumor growth, but eventually the mice were euthanized due to tumor burden. The dual CAR-T, c201 and c230, showed complete tumor eradication in several mice in the treatment group (see Figure 4A ). The 1e6 pooled arm showed similar efficacy but required twice as many CAR+ T cell lines as compared to the dual arm. The 5e5 hybrid arm, which yielded the same total number of CAR-Ts as the dual arm, did not perform as well compared to the tandem CAR-Ts tested here.
藉由每週用流動式細胞測量術分析該等動物血液測試CAR-T的擴張動力學和持續性。針對在CAR-T注射後2週的分析( 圖 4B)顯示代表性數據。雙重CAR-T以及串聯CAR-T c182、c224和c227均顯示循環T細胞數量與1e6混合組相似。與單CAR-T和5e5混合組相比,該等數字更高。 The expansion kinetics and persistence of CAR-T were tested by analyzing blood of these animals weekly by flow cytometry. Representative data are shown for analysis at 2 weeks after CAR-T injection ( Fig. 4B ). Dual CAR-T as well as tandem CAR-T c182, c224 and c227 all showed circulating T cell numbers similar to the 1e6 mixed group. These numbers were higher compared to the single CAR-T and 5e5 mixed group.
前兩項研究證明,雙重CAR T細胞c201和c230能夠根除NALM6癌及其CD19陰性變體。在此測試的功效優於相應的單CAR-T和串聯CAR-T。 實例3:使用活化過程按小規模製造c201細胞 The first two studies demonstrated that dual CAR T cells, c201 and c230, were able to eradicate NALM6 cancer and its CD19-negative variant. The efficacy tested here was superior to the corresponding single and tandem CAR-Ts. Example 3: Manufacturing c201 cells on a small scale using the activation process
本實例描述了使用活化過程按小規模來評估靶向CD19和CD22的雙重CAR-T細胞的可以製造性。This example describes the use of an activation process to assess the manufacturability of dual CAR-T cells targeting CD19 and CD22 at a small scale.
將冷凍T細胞的等分試樣在37°C水浴中解凍,放入優化器CM(具有補充劑 + 100 U/mL人IL2的Gibco優化器培養基),並以1500 rpm旋轉5分鐘。計數細胞,並以3 × 10 6細胞/mL,1 mL/孔鋪板到24孔板。以1/100(10 µL/孔)將TransAct添加到每個孔中。基於qPCR滴度,以不同的感染複數(MOI)添加GMP級c201病毒。還將未轉導的對照(UTD)進行鋪板。在培養物中24小時後,收穫細胞並在PBS + 1% HSA中洗滌三次。然後對細胞進行計數,並以最終1 × 10 6細胞/mL重新鋪板到24孔板中。 Thaw an aliquot of frozen T cells in a 37 °C water bath, place in Optimizer CM (Gibco Optimizer Medium with supplements + 100 U/mL human IL2), and spin at 1500 rpm for 5 min. Count cells and plate at 3 × 106 cells/mL, 1 mL/well into 24-well plates. Add TransAct to each well at 1/100 (10 µL/well). GMP-grade c201 virus was added at different multiplicity of infection (MOI) based on qPCR titer. Untransduced controls (UTD) were also plated. After 24 hours in culture, cells were harvested and washed three times in PBS + 1% HSA. Cells were then counted and replated into 24-well plates at a final 1 × 106 cells/mL.
重新鋪板72小時後,收穫細胞,計數,並從每個樣本中取5 × 10
5個細胞的等分試樣進行流動式細胞測量術分析。將細胞用Live/Dead Aqua(BV510)以100 µl/孔中染色15分鐘,然後洗滌兩次。然後將抗體混合物(表6)以50 µl/孔添加,在4°C下持續25分鐘。將細胞再次洗滌兩次,然後在100 µl/孔PBS中的1.6% PFA中固定15分鐘。固定後,將細胞如先前所述進行洗滌,並在流動式細胞測量術緩衝液中以150 µl/樣本的終體積進行重懸。在BD LSRFortessa(BD生物科技公司,聖約瑟,加利福尼亞州)上的每個樣本的活CD3陽性門控上獲取5e4細胞,並使用FlowJo v.10軟體(亞什蘭公司(Ashland),俄勒岡州)分析數據。在重新鋪板144 h後重複此程序。
[
表 6 ]
. 抗體和其他試劑
流分析顯示,大多數CAR+細胞表現靶向CD19和CD22兩者的CAR,如藉由相應的抗獨特型抗體檢測到的(圖5A和5B)。單CAR比雙重CAR表現的比率隨著時間的推移向雙重CAR表現轉移,並在144 h後穩定。同時,總CAR的表現也增加。在這兩個時間點,CAR表現取決於MOI,顯示出MOI越高CAR表現增加。這裡示出了來自若干個供體的一個代表的數據。 實例4:使用活化過程按大規模製造c201細胞 Flow analysis revealed that the majority of CAR+ cells expressed CARs targeting both CD19 and CD22, as detected by the corresponding anti-idiotypic antibodies (Figures 5A and 5B). The ratio of single CAR to dual CAR expression shifted towards dual CAR expression over time and stabilized after 144 h. At the same time, the performance of total CAR also increased. At both time points, CAR performance was dependent on MOI, showing increased CAR performance at higher MOI. Data from one representative of several donors are shown here. Example 4: Production of c201 cells on a large scale using the activation process
本實例描述了使用活化過程按大、完整臨床規模來評估靶向CD19和CD22的雙重CAR-T細胞的可以製造性。This example describes the use of an activation process to assess the manufacturability of dual CAR-T cells targeting CD19 and CD22 at a large, full clinical scale.
CAR-T細胞的活化過程始於培養基的製備,如在表7中概述的。將冷凍保存的白血球分離產物用作起始原料,並加工用於T細胞富集。
[
表 7 ]
:在 CART 製造期間培養基和緩衝液類型和使用時間點
將冷凍保存的白血球分離產物解凍、洗滌,並且然後使用CliniMACS ®微珠技術進行T細胞選擇和富集。將用Miltenyi微球選擇的活細胞接種到Prodigy ®上的centricult中,該centricult為未加濕的孵育室。在培養時,將細胞懸浮於快速培養基中,該快速培養基係基於OpTmizer TMCTS TM的培養基(含有CTS TM補充劑(賽默飛世爾公司)、Glutamax、IL-2和2%免疫細胞血清替代物(在其組分中促進T細胞活化和轉導))。用TransACT(美天旎公司(Miltenyi))激活活核細胞(VNC)並用編碼兩種CAR的c201慢病毒載體轉導。向培養基中稀釋的細胞中添加TransACT後,於接種當天進行慢病毒轉導。基於qPCR滴度,使用以感染複數(MOI)為1添加的GMP級c201病毒轉導細胞。慢病毒載體在使用前立即在室溫下解凍多達30分鐘。 Cryopreserved leukapheresis was thawed, washed, and then subjected to T cell selection and enrichment using CliniMACS ® microbead technology. Live cells selected with Miltenyi microspheres were inoculated into the centricult on the Prodigy® , which is a non-humidified incubation chamber. In culture, cells were suspended in Fast Medium, an OpTmizer ™ CTS ™ -based medium (containing CTS ™ Supplement (Thermo Fisher), Glutamax, IL-2, and 2% Immune Cell Serum Replacement (promotes T cell activation and transduction among its components)). Viable nuclear cells (VNC) were activated with TransACT (Miltenyi) and transduced with the c201 lentiviral vector encoding the two CARs. Lentiviral transduction was performed on the day of inoculation after TransACT was added to cells diluted in culture medium. Cells were transduced with GMP-grade c201 virus added at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 based on qPCR titers. Thaw lentiviral vectors at room temperature for up to 30 minutes immediately before use.
從第0天的過程開始到起始洗滌和收穫培養物,將CAR-T細胞自接種培養20小時。培養後,將細胞懸浮液在centricult室中進行兩次培養洗滌和一次收穫洗滌。CAR-T cells were cultured from seeding for 20 hours from the start of the
在第1天在CliniMACS
®Prodigy
®上進行收穫洗滌後,對細胞懸浮液進行取樣,以確定活細胞計數和生活力。然後將細胞懸浮液轉移到待手動沈澱的離心機中。除去上清液,並將細胞沈澱重懸浮於CS10(生物生命溶液公司(BioLife Solution))中,產生終DMSO濃度為約10%的產品配製物。然後將細胞分配到單獨的凍存袋中,並分析採樣入冷凍小瓶中。
After harvest washes on the CliniMACS ® Prodigy ® on
將哨兵小瓶解凍,然後對細胞進行計數,並以最終1 × 10 6細胞/mL重新鋪板到24孔板中。重新鋪板72小時後,收穫細胞,計數,並從每個樣本中取5 × 10 5個細胞的等分試樣進行流動式細胞測量術分析。將細胞用Live/Dead Aqua(BV510)以100 µl/孔中染色15分鐘,然後洗滌兩次。然後將抗體混合物(表5)以50 µl/孔添加,在4°C下持續25分鐘。將細胞再次洗滌兩次,然後在100 µl/孔PBS中的1.6% PFA中固定15分鐘。固定後,將細胞如先前所述進行洗滌,並在流動式細胞測量術緩衝液中以150 µl/樣本的終體積進行重懸。在BD LSRFortessa(BD生物科技公司,聖約瑟,加利福尼亞州)上的每個樣本的活CD3陽性門控上獲取5e4細胞,並使用FlowJo v.10軟體(亞什蘭公司(Ashland),俄勒岡州)分析數據。在重新鋪板144 h後重複此程序。 Thaw the sentinel vials, then count the cells and replate into 24-well plates at a final 1 x 106 cells/mL. Seventy-two hours after re-plating, cells were harvested, counted, and aliquots of 5 x 105 cells from each sample were analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were stained with Live/Dead Aqua (BV510) at 100 µl/well for 15 minutes, then washed twice. Antibody mix (Table 5) was then added at 50 µl/well for 25 min at 4°C. Cells were washed twice again and then fixed in 1.6% PFA in 100 µl/well PBS for 15 minutes. After fixation, cells were washed as previously described and resuspended in flow cytometry buffer in a final volume of 150 µl/sample. 5e4 cells were acquired on the live CD3-positive gate of each sample on BD LSRFortessa (BD Biotechnology, San Jose, CA) and analyzed using FlowJo v.10 software (Ashland, OR) )analyze data. This procedure was repeated 144 h after replating.
如轉導後144 h確定的,全規模的ARM過程產生總CAR表現為12%的CAR-T產物;9%雙重CAR+細胞和3%單CAR22+細胞(圖5C)。如小規模活化過程實驗所看到的,總CAR%以及雙重CAR比單CAR的比率隨時間增加。 實例5:靶向CD19和/或CD22的雙重和單CAR-T的體內活性 As determined at 144 h post-transduction, the full-scale ARM process yielded total CAR manifested as 12% CAR-T product; 9% dual CAR+ cells and 3% single CAR22+ cells (Fig. 5C). As seen in the small-scale activation process experiments, the overall CAR % as well as the ratio of dual CAR to single CAR increased over time. Example 5: In vivo activity of dual and single CAR-T targeting CD19 and/or CD22
本實例證明了根據傳統方法(TM)和活化過程(AP)製造的雙重和單CAR-T細胞的體內活性。本實例中使用的雙重CAR-T係c201,其在CD19 CAR的上游具有CD22 CAR,由活化過程產生。在本研究中使用的相關單CAR-T係CD22-65s(識別CD22並由TM產生)和CAR19(鼠scFv)(識別CD19並由TM和AP產生)。在ALL異種移植模型中體內評估雙重和單CAR-T細胞的抗腫瘤活性。 材料與方法 This example demonstrates the in vivo activity of dual and single CAR-T cells fabricated according to traditional method (TM) and activation process (AP). The dual CAR-T line c201 used in this example, which has a CD22 CAR upstream of the CD19 CAR, was generated by the activation process. The related single CAR-T lines CD22-65s (recognizing CD22 and produced by TM) and CAR19 (murine scFv) (recognizing CD19 and produced by TM and AP) used in this study. Antitumor activity of dual and single CAR-T cells was assessed in vivo in an ALL xenograft model. Materials and Methods
實例2概述了動物研究。在本實例中,使用野生型Nalm6(RRID: CVCL_0092)(人急性淋巴球白血病(ALL)細胞系)。Example 2 outlines animal studies. In this example, wild-type Nalm6 (RRID: CVCL_0092), a human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell line, was used.
CAR T細胞給藥:小鼠在腫瘤植入後7天給藥。藉由傳統製造業產生的CD22-65s CAR-T細胞以3、1、和0.3 x 10 6CAR+ T細胞給藥。用AP產生的CAR19細胞以1和0.3 x 10 6CAR+ T細胞給藥;藉由TM產生的CAR19以1、0.3、和0.1 x 10 6CAR+ T細胞給藥。用AP產生的C201雙重CAR-T細胞以0.3、0.1、和0.03 x 10 6CAR+ T細胞給藥。作為對照,小鼠接受媒劑物(PBS)或UTD。 結果 CAR T cell administration: Mice were dosed 7 days after tumor implantation. CD22-65s CAR-T cells produced by traditional manufacturing were administered at 3, 1, and 0.3 x 10 6 CAR+ T cells. CAR19 cells generated by AP were dosed at 1 and 0.3 x 10 6 CAR+ T cells; CAR19 generated by TM were dosed at 1, 0.3, and 0.1 x 10 6 CAR+ T cells. C201 dual CAR-T cells generated with AP were dosed at 0.3, 0.1, and 0.03 x 10 6 CAR+ T cells. As controls, mice received vehicle (PBS) or UTD. result
在B細胞急性淋巴球白血病異種移植模型中評估雙重和單CAR T細胞的抗腫瘤活性;Nalm6細胞表現CD19和CD22。在第0天腫瘤細胞植入後,將攜帶腫瘤小鼠隨機化到治療組中,並且在腫瘤植入後第7天經由側尾靜脈經靜脈內投與CAR T細胞。監測腫瘤生長和動物健康狀態直至動物達到終點。Antitumor activity of dual and single CAR T cells evaluated in a B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft model; Nalm6 cells express CD19 and CD22. After tumor cell implantation on
在第3週(在腫瘤致使後肢活動性降低前)對接受PBS或UTD T細胞的小鼠實施安樂死。其他組在第4週和第7週之間實施安樂死。所有治療組的平均生物發光繪製在
圖 6A中。未接受任何T細胞的PBS治療組在靜脈內注射的NSG小鼠中展示出基線Nalm6腫瘤生長動力學。UTD治療組充當T細胞對照以顯示人供體T細胞在此模型中的非特異性響應(其無法檢測)。為了更好地進行比較,
圖 6B中,0.3 x 10
6劑量組的不同CAR-T繪製在一起。兩種TM產生的CAR-T均顯示出較低的活性,對CAR19(TM)的腫瘤生長有適度的延遲。相比之下,兩種AP CAR-T均能顯著降低腫瘤負荷,並且c201(AP)CAR-T致使5隻小鼠中有4隻小鼠的腫瘤根除(BLI基線水平)。
Mice receiving PBS or UTD T cells were euthanized at week 3 (before tumors reduced hindlimb mobility). The other groups were euthanized between
藉由每週用流動式細胞測量術分析該等動物血液測試CAR-T的擴張動力學和持續性。編譯的數據示於 圖 6C中。將跨0.3 x 10 6劑量的CAR-T組進行了比較,AP加工的CAR-T表現出更好的擴增。c201和CAR19(兩種AP)的比較分別示出了對0.3和1 x 10 6劑量,CAR-T的擴增相似。 The expansion kinetics and persistence of CAR-T were tested by analyzing blood of these animals weekly by flow cytometry. The compiled data is shown in Figure 6C . Comparing CAR-T groups across doses of 0.3 x 106 , the AP-processed CAR-T showed better expansion. A comparison of c201 and CAR19 (both APs) showed similar expansion of CAR-T for doses of 0.3 and 1 x 10 6 , respectively.
本研究還突出了c201當與AP製造時的效力。對於體內抗腫瘤活性和細胞擴增,C201 AP優於CAR19(AP)以及CAR19和CD22-65s(TM)。 實例6:臨床研究設計 This study also highlights the potency of c201 when produced with AP. For in vivo antitumor activity and cell expansion, C201 AP was superior to CAR19 (AP) as well as CAR19 and CD22-65s (TM). Example 6: Clinical Study Design
進行了對CD19-CD22 CAR(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224或c227)的I期、開放標籤、多中心、劑量遞增以及擴展研究。該研究在兩個獨立組的患者中進行調查:29歲以下的小兒、青少年和年輕成人(AYA)ALL患者和成人ALL患者(≥ 30歲)安全群組。Phase I, open-label, multicenter, dose-escalation, and extension studies of CD19-CD22 CARs (eg, c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, or c227) were conducted. The study was investigated in two separate cohorts of patients: a pediatric, adolescent and young adult (AYA) ALL patient under the age of 29 and a safety cohort of adult ALL patients (≥30 years).
小兒和AYA ALL組由兩部分組成:用於評估可行性、表徵安全性並確定CD19-CD22 CAR的推薦劑量(RD)的劑量遞增部分;和用於進一步表徵安全性、細胞動力學和評估初步抗腫瘤活性的劑量擴展部分。一旦確定該組的RD,就可以開始對應的擴展部分。The Pediatric and AYA ALL cohorts consisted of two parts: a dose-escalation part to assess feasibility, characterize safety, and determine the recommended dose (RD) of the CD19-CD22 CAR; and a dose-escalation part to further characterize safety, cellular kinetics and assess initial Dose Expansion Portion of Antitumor Activity. Once the RD of the group is determined, the corresponding expansion part can be started.
一旦確定了小兒和AYA組的RD,就可以與上述擴展部分平行,開始 ≥ 30歲的成人ALL患者的安全群組。該組的目的係以來自小兒和AYA ALL患者確定的RD,表徵在成人ALL患者中CD19-CD22 CAR的安全性和耐受性。如果成人患者對小兒和AYA ALL患者的RD不耐受,則可以測試較低的劑量(圖7)。Once the RD in the pediatric and AYA groups has been identified, a safety cohort of adult ALL patients ≥30 years of age can be initiated in parallel with the expansion described above. The aim of this group was to characterize the safety and tolerability of CD19-CD22 CAR in adult ALL patients with established RD from pediatric and AYA ALL patients. Lower doses can be tested if adult patients are not tolerant to RD in pediatric and AYA ALL patients (Figure 7).
隨著研究的進展,並且基於從本研究中收集的新出現的臨床數據,可能修改該方案,以在擴展部分包括另外的患者,從而進一步表徵安全性、細胞動力學,並且評估先前未暴露於CAR- T的小兒和AYA ALL患者的初步抗腫瘤活性。As the study progresses, and based on emerging clinical data collected from this study, the protocol may be modified to include additional patients in the extension to further characterize safety, cellular kinetics, and assess Preliminary antitumor activity of CAR-T in pediatric and AYA ALL patients.
研究流程如圖7所示。首先將對患者進行臨床資格評估,並且只有在具有臨床資格的情況下,才會安排白血球去除術。一旦確認白血球去除術適合治療,該過程將開始。患者將僅在確認最終產品可用後才接受淋巴球耗減化學療法。淋巴球耗減化學療法後,在第一天作為單次靜脈內(i.v.)投與來給予CD19-CD22 CAR。The research process is shown in Figure 7. Patients will first be assessed for clinical eligibility and only if clinically eligible will leukapheresis be scheduled. Once leukapheresis is confirmed to be suitable for treatment, the process will begin. Patients will receive lymphocyte-depleting chemotherapy only after confirmation that the final product is available. Following lymphocyte-depleting chemotherapy, the CD19-CD22 CAR was administered as a single intravenous (i.v.) administration on day one.
每位患者在CD19-CD22雙重CAR輸注後都要住院最少72小時。如果HA或IEC/IRB要求,或基於當地實踐,治療醫師可以實施較長時間的住院治療。Each patient was hospitalized for a minimum of 72 hours after CD19-CD22 dual CAR infusion. The treating physician may administer longer inpatient care if required by the HA or IEC/IRB, or based on local practice.
一旦研究完成,將患者納入長達15年的慢病毒載體安全性的研究後長期跟蹤。將在單獨方案下繼續進行慢病毒載體安全性的研究後長期跟蹤。 實例7:給藥方案和治療 Once the study is complete, patients will be followed long-term after enrolling in the study of lentiviral safety for up to 15 years. Long-term follow-up will continue after the study of lentiviral vector safety under a separate protocol. Example 7: Dosing regimen and treatment
基於該產品中總CAR+ T細胞,CD19-CD22 CAR(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)的起始劑量(或劑量水平1),對於 ≤ 50 kg的患者係3 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重,並且對於 > 50 kg(劑量上限(dose cap)為50 kg)的患者係1.5 × 10
6個細胞。在另一方面,劑量水平1基於總CAR+ T細胞減去患者在CD19-CD22 CAR治療前(例如在用Kymriah(CD19 CAR;替沙侖賽)、Yescarta(CD19 CAR;阿基侖賽)、Tecartus(CD19 CAR;布奧侖賽)、和/或Breyanzi(CD19 CAR;利基邁侖賽)治療前)接受的CAR+ T細胞。對於體重 ≤ 50 kg的患者,根據每kg體重給藥細胞,而在> 50 kg的患者中給藥則不考慮體重。處於起始劑量的患者需要最小體重為10 kg。可替代地,處於起始劑量的患者需要最小體重為15 kg。具有較低體重的患者將需要輸注非常低的細胞數量。如果起始劑量被認為是不可耐受的,可以推薦較低的起始劑量。起始劑量將滿足控制過量用藥的劑量遞增(EWOC)標準。
Starting dose (or dose level 1) of CD19-CD22 CAR (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR) based on total CAR+ T cells in this product , 3 × 10 4 cells/kg body weight for patients ≤ 50 kg and 1.5 × 10 6 cells for patients > 50 kg (
在患有ALL的患者中進行劑量遞增研究,如下表8所示。以上提供了起始劑量(或劑量水平1)。基於該產品中總CAR+ T細胞,劑量水平2對於 ≤ 50 kg的患者係10 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重,並且對於 > 50 kg的患者(劑量上限為50 kg)係5 × 10
6個細胞。基於該產品中總CAR+ T細胞,劑量水平3對於 ≤ 50 kg的患者係30 × 10
4個細胞/kg體重,並且對於 > 50 kg的患者(劑量上限為50 kg)係15 × 10
6個細胞。每個目標劑量都與±30%的劑量範圍有關。在另一方面,劑量水平2和劑量水平3基於總CAR+ T細胞減去患者在CD19-CD22 CAR治療前(例如在用Kymriah(CD19 CAR;替沙侖賽)、Yescarta(CD19 CAR;阿基侖賽)、Tecartus(CD19 CAR;布奧侖賽)、和/或Breyanzi(CD19 CAR;利基邁侖賽)治療前)接受的CAR+ T細胞。在研究期間可以添加另外的和/或中等劑量水平。
[
表 8]
. ALL 中 CD19-CD22 CAR 的臨時劑量水平
每個劑量遞增群組將從3至6個新治療的患者開始。他們必須有足夠的暴露和跟蹤,才能被認為可評估劑量遞增決策。可以按任何劑量水平、或低於先前測試的安全的最高劑量招募具有1至6名患者的另外的群組。Each dose escalation cohort will start with 3 to 6 newly treated patients. They must have sufficient exposure and follow-up to be considered assessable for dose-escalation decisions. Additional cohorts of 1 to 6 patients may be enrolled at any dose level, or lower than the highest dose previously tested as safe.
在劑量遞增期間,任何先前未測試過的較高劑量水平的前兩名患者將被錯開28天進行治療,即在對第一名和第二名患者給藥之間將存在28天的時間段。如果沒有安全性訊息阻止招募更多的患者,則將進行淋巴球耗減化學療法以及相同劑量水平的給藥,無需進一步錯開。During dose escalation, the first two patients at any higher dose level not previously tested will be treated 28 days apart, ie there will be a 28-day period between dosing the first and second patient. If no safety information prevents enrolling more patients, lymphocyte-depleting chemotherapy and dosing at the same dose level will be administered without further staggering.
取決於體積,CD19-CD22 CAR(例如c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR),將經由注射器進行靜脈內(i.v.)推注(對於較小體積)給予或通過無乳膠管(無白血球過濾器)從凍存袋中進行i.v.輸注(大約每分鐘10 - 20 mL,根據較小的兒童和較小的體積進行適當調整)給予。初次輸注完成後應沖洗管,以允許回收並輸注任何剩餘產品。建議在解凍冷凍保存產品後90分鐘內完成i.v.推注/輸注(較佳的是經由中心線),以保存細胞活力。Depending on the volume, CD19-CD22 CAR (e.g. c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR), will be given as an intravenous (i.v.) bolus via syringe (for smaller volume) or as an i.v. infusion (approximately 10 - 20 mL per minute, with appropriate adjustments for smaller children and smaller volumes) from a cryopreservation bag through latex-free tubing (no leukocyte filter). The tubing should be flushed after the initial infusion is complete to allow any remaining product to be retrieved and infused. It is recommended that i.v. boluses/infusions (preferably via the centerline) be completed within 90 minutes of thawing cryopreserved product to preserve cell viability.
在CD19-CD22 CAR輸注前,每名患者都應進行淋巴球耗減。如果患者具有顯著的血球減少症(例如,白血球計數(WBC)≤ 1,000個細胞/µL)或研究人員認為排除淋巴球耗減的任何病症,不需要淋巴球耗減。淋巴球耗減應該在輸注前約一週開始,即在淋巴球耗減後的2至5天,取決於淋巴球耗減方案。在輸注延遲超過四週的情況下,可以重複淋巴球耗減。Each patient should be lymphodepleted prior to CD19-CD22 CAR infusion. Lymphocyte depletion was not required if the patient had significant cytopenias (eg, white blood cell count (WBC) ≤ 1,000 cells/µL) or any condition that, in the opinion of the investigator, precluded lymphodepletion. Lymphocyte depletion should begin approximately one week prior to infusion,
所有患者在輸注後的至少前72小時內都要住院。 實例8:研究群體 All patients were hospitalized for at least the first 72 hours after the infusion. Example 8: Study groups
初始目標群體由年齡為1-29歲(具有r/r ALL)的小兒和年輕成人患者組成,對於該等患者,至少一項先前的CD19和/或CD22定向療法(具有或不具有後續同種異體-HCT)失敗。一旦鑒定出該群體的RD,則可以招募年齡 ≥ 30歲的患者,以評估CD19-CD22 CAR(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)在老年人中的安全性。小兒和AYA患者在劑量遞增部分期間被分配至特定群組,或在本研究的劑量擴展部分期間,被分配至擴展組。將 ≥ 30歲的成人患者分配至安全群組。The initial target population consisted of pediatric and young adult patients aged 1-29 years (with r/r ALL) for whom at least one prior CD19 and/or CD22-directed therapy (with or without subsequent allogeneic -HCT) failed. Once RD in this population is identified, patients aged ≥30 years can be recruited for evaluation of CD19-CD22 CAR (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CAR ) safety in the elderly. Pediatric and AYA patients were assigned to specific cohorts during the dose-escalation portion, or to an expansion group during the dose-expansion portion of the study. Adult patients ≥30 years of age were assigned to the safety cohort.
需要在復發時或進入研究前藉由流動式細胞測量術證明骨髓或周圍血中B-ALL母細胞上CD19和/或CD22的細胞表面表現。如果r/r費城染色體陽性B-ALL患者對酪胺酸激酶抑制劑和化學療法組合療法不耐受或酪胺酸激酶抑制劑和化學療法組合療法對該等患者失敗,則該等患者有資格。Cell surface expression of CD19 and/or CD22 on B-ALL blasts in bone marrow or peripheral blood needs to be demonstrated by flow cytometry at relapse or prior to study entry. Patients with r/r Philadelphia chromosome positive B-ALL are eligible if they are intolerant to tyrosine kinase inhibitor and chemotherapy combination therapy or if such patients have failed tyrosine kinase inhibitor and chemotherapy combination therapy .
有資格納入本研究的患者必須符合以下所有標準。 所有患者: • 在復發時或進入研究前藉由流動式細胞測量術證明骨髓或周圍血中B-ALL母細胞上CD19和/或CD22的細胞表面表現。 之前接受過/沒有資格接受CD19 CAR-T療法的小兒、青少年和年輕成人ALL患者: • 在知情同意書(ICF)簽名時,年齡為1-29歲。 • 3個或更多治療線之後或同種異體HCT之後的復發或難治性CD19 +和/或CD22 +ALL。 • 必須接受過CD19定向CAR-T治療(聯合或不聯合博納吐單抗(blinatumomab)),除非之前出現CD19細胞表面表現缺失或不具有CD19定向CAR-T治療的資格。 • Lansky(年齡 < 16歲)、Karnofsky(年齡為16-25歲)表現狀態 ≥ 60%。篩選時的ECOG(年齡 > 25歲)體能狀態為0或1。 年齡 ≥ 30歲的成人ALL患者: • 在知情同意書(ICF)簽名時,年齡 ≥ 30歲。 • 難治性或復發的CD19 +和/或CD22 +ALL,包括以下至少一種: o 同種異體HCT之後 o 兩個或更多個治療線之後,包括博納吐單抗和/或奧英妥珠單抗 o 原發性難治性疾病(定義為在至少一次誘導化學療法結束時未能達到CR) o 首次復發發生在自首次緩解的12個月內 • 篩選時的ECOG體能狀態為0或1。 符合以下任一標準的患者不具有納入本研究的資格。 • 篩選前12週內進行同種異體HCT。 • 存在孤立的髓外疾病、睪丸受累或大包塊疾病。 • 伴有與骨髓衰竭狀態相關的遺傳綜合症的患者:如患有範科尼貧血、柯士文綜合症(Kostmann syndrome)、舒瓦克曼綜合症(Shwachman syndrome)的患者。 • 患有柏基特淋巴瘤/白血病的患者。 • 活動性神經性自體免疫或炎性障礙病史。 Patients eligible for inclusion in this study must meet all of the following criteria. All patients: • Demonstrated cell surface expression of CD19 and/or CD22 on B-ALL blasts in bone marrow or peripheral blood by flow cytometry at relapse or prior to study entry. Pediatric, adolescent and young adult ALL patients who have previously received/not been eligible for CD19 CAR-T therapy: • Age 1-29 at the time of signing the Informed Consent Form (ICF). • Relapsed or refractory CD19 + and/or CD22 + ALL after 3 or more lines of therapy or after allogeneic HCT. • Must have received CD19-directed CAR-T therapy (with or without blinatumomab), unless prior CD19 cell surface expression loss or ineligibility for CD19-directed CAR-T therapy. • Lansky (age < 16 years old), Karnofsky (age 16-25 years old) performance status ≥ 60%. ECOG (age >25 years) performance status of 0 or 1 at screening. Adult ALL patients aged ≥ 30 years: • Age ≥ 30 years at the time of signing the Informed Consent Form (ICF). • Refractory or relapsed CD19 + and/or CD22 + ALL, including at least one of the following: o After allogeneic HCT o After two or more lines of therapy, including blinatumomab and/or intuzumab Anti o Primary refractory disease (defined as failure to achieve CR at the end of at least one induction chemotherapy session) o First relapse occurred within 12 months from first remission • ECOG performance status of 0 or 1 at Screening. Patients meeting any of the following criteria were not eligible for inclusion in this study. • Allogeneic HCT within 12 weeks prior to screening. • Presence of isolated extramedullary disease, testicular involvement, or bulky disease. • Patients with genetic syndromes associated with bone marrow failure states: eg patients with Fanconi anemia, Kostmann syndrome, Shwachman syndrome. • Patients with Burkitt's lymphoma/leukemia. • History of active neurological autoimmune or inflammatory disorder.
可以應用其他方案定義的納入/排除標準。 實例9:生物標記物 Inclusion/exclusion criteria defined by other protocols may apply. Example 9: Biomarkers
生物標記物分析用於研究CD19-CD22 CAR(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)在分子和細胞水平上的作用,以及確定標記物的變化如何與暴露和臨床結果相關。此外,還可以探索功效的潛在預測標記物以及對CD19-CD22 CAR的耐藥機制。 收集以下生物標記物: • 用於微量殘存疾病(MRD)和免疫調節和/或IgH定序的骨髓抽吸物;和/或 • 用於可溶性細胞介素(例如,IFN-γ、IL-2、IL-4、IL-6、IL-8、IL-10、IL-15、TNF-α、IP-10、MCP1、MIP1α),MRD和免疫調節,聯合PK和免疫表型分型;和/或DNA/RNA定序的血液。 實例10:主要終點和其他終點的分析 Biomarker analysis to investigate the role of CD19-CD22 CARs (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227, or co-transduced CD19-CD22 CARs) at the molecular and cellular levels, as well as to identify markers how changes in the drug relate to exposure and clinical outcomes. In addition, potential predictive markers of efficacy and mechanisms of resistance to CD19-CD22 CARs could also be explored. Collect the following biomarkers: • Bone marrow aspirate for minimal residual disease (MRD) and immunomodulation and/or IgH sequencing; and/or • For soluble interkines (eg, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-15, TNF-α, IP-10, MCP1, MIP1α) , MRD and immune modulation, combined PK and immunophenotyping; and/or DNA/RNA sequenced blood. Example 10: Analysis of primary and other endpoints
主要終點包括DLT、實驗室測量、生命體征、不良事件以及ECG。其他終點包括製造成功率(MSR),定義為在劑量遞增和劑量擴展部分輸注計畫目標劑量範圍的CD19-CD22 CAR(例如,c201、c230、c203、c171、c182、c188、c224、c227或共轉導CD19-CD22 CAR)的患者數量除以兩個研究組中輸注CD19-CD22 CAR的患者總數量。按治療組總結MSR,以及準確的雙側90%信賴區間。Primary endpoints included DLTs, laboratory measures, vital signs, adverse events, and ECG. Additional endpoints include manufacturing success rate (MSR), defined as CD19-CD22 CAR infusion program target dose range (e.g., c201, c230, c203, c171, c182, c188, c224, c227 or co- The number of patients transduced with CD19-CD22 CAR) was divided by the total number of patients infused with CD19-CD22 CAR in both study groups. The MSRs are summarized by treatment group, along with accurate two-sided 90% confidence intervals.
其他終點包括製造成功率(MSR),定義為在劑量遞增和劑量擴展部分輸注計畫目標劑量範圍的CD19-CD22 CAR的患者數量除以兩個研究組中輸注CD19-CD22 CAR的患者總數量。按治療組總結MSR,以及準確的雙側90%信賴區間。Additional endpoints included manufacturing success rate (MSR), defined as the number of patients infused with a CD19-CD22 CAR in the dose-escalation and dose-expansion portion of the program's target dose range divided by the total number of patients infused with a CD19-CD22 CAR in both study arms. The MSRs are summarized by treatment group, along with accurate two-sided 90% confidence intervals.
成人ALL組的安全終點包括DLT、實驗室測量、生命體征、不良事件以及ECG。成人ALL的安全群組目的係獲得CD19-CD22 CAR在成人ALL患者中的安全特性,並表徵在小兒和AYA ALL中對成人ALL的RD。因此,它將從小兒和AYA ALL患者中鑒定的RD開始。Safety endpoints in the adult ALL group included DLT, laboratory measurements, vital signs, adverse events, and ECG. The safety cohort in adult ALL aims to obtain the safety profile of CD19-CD22 CAR in adult ALL patients and characterize the RD in adult ALL in pediatric and AYA ALL. Therefore, it will start with RD identified in pediatric and AYA ALL patients.
對於所有的功效參數,都按治療組對數據進行了分析、總結和列出。將使用FAS。按照當地研究人員對小兒患者的評估確定腫瘤響應。For all efficacy parameters, data were analyzed, summarized and presented by treatment group. FAS will be used. Tumor response was determined as assessed by local investigators in pediatric patients.
CR/CRi率定義為根據當地研究人員在CD19-CD22 CAR輸注後和任何新的抗腫瘤療法開始前對CR/CRi響應的患者比例。按研究組和治療組當地研究人員對RD下治療的患者使用FAS,總結了第28天、第3、6和12個月的CR/CRi率以及對應的90%精確的CI。The CR/CRi rate was defined as the proportion of patients responding to CR/CRi after CD19-CD22 CAR infusion and before the initiation of any new antitumor therapy according to the local investigators. The CR/CRi rates at
BOR被定義為從治療開始到疾病進展/復發或死亡或開始新的抗腫瘤療法之前所記錄的最佳響應。BOR率按研究組和治療組使用FAS進行總結。BOR was defined as the best response recorded from the start of treatment until disease progression/relapse or death or initiation of new antineoplastic therapy. BOR rates were summarized by study and treatment groups using FAS.
響應持續時間(DOR)僅適用於最佳總體響應為CR或CRi的患者。它被定義為從第一次記錄的疾病響應(CR或CRi)到第一次記錄的進展或因潛在疾病而死亡的日期的時間。DOR的分佈係用Kaplan-Meier法估計的,並且中位響應持續時間以及達到響應後3、6、9和12個月仍有響應的患者比例以及90%的CI將按研究組列出。另外的時間點可適當報告。DOR將按RD由當地研究人員審查報告。僅在當該研究組在RD下至少有5名響應者,才會進行DOR分析。DOR將基於研究人員的評估按治療組列出。Duration of response (DOR) was only available for patients whose best overall response was CR or CRi. It was defined as the time from the first documented disease response (CR or CRi) to the date of the first documented progression or death from the underlying disease. The distribution of DOR was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the median duration of response and the proportion of patients remaining in
已經詳細描述了本揭露,將顯而易見的是,在不脫離如本文和所附申請專利範圍中所描述的本揭露之精神和範圍的情況下,修改、變化和等同方面係可能的。此外,應當理解,本揭露中的所有實例均作為非限制性實例提供。Having described the disclosure in detail, it will be apparent that modifications, variations and equivalents are possible without departing from the spirit and scope of the disclosure as described herein and in the appended claims. Furthermore, it should be understood that all examples in this disclosure are provided as non-limiting examples.
無none
[ 圖 1A-1C]係本文揭露的雙重CAR構建體之示意圖。該雙重CAR構建體包括CD22 CAR和CD19 CAR。 圖 1A顯示出從N末端至C末端具有CD22 CAR,隨後CD19 CAR的雙重CAR構建體。 圖 1B顯示出從N末端至C末端具有CD22 CAR,隨後CD19 CAR的不同的雙重CAR構建體。 圖 1C顯示出從N末端至C末端具有CD19 CAR,隨後CD22 CAR的雙重CAR構建體。 [ FIGS. 1A-1C ] are schematic diagrams of the dual CAR constructs disclosed herein. The dual CAR construct includes a CD22 CAR and a CD19 CAR. Figure 1A shows a dual CAR construct with CD22 CAR followed by CD19 CAR from N-terminus to C-terminus. Figure 1B shows different dual CAR constructs with CD22 CAR followed by CD19 CAR from N-terminus to C-terminus. Figure 1C shows a dual CAR construct with CD19 CAR followed by CD22 CAR from N-terminus to C-terminus.
[ 圖 2]係本揭露之串聯CD19/CD22 CAR構建體之示意圖。每個串聯CAR包含含有CD19抗原結合結構域和CD22抗原結合結構域的雙特異性抗原結合結構域。 [ FIG. 2 ] is a schematic diagram of the tandem CD19/CD22 CAR construct of the present disclosure. Each tandem CAR contains a bispecific antigen-binding domain containing a CD19 antigen-binding domain and a CD22 antigen-binding domain.
[ 圖 3A-3D]顯示出靶向CD19和CD22的串聯和雙重CAR T細胞之體外活性。 圖 3A係描繪針對CD22陰性ALL細胞系(CD22KO Nalm6-Luc)的各種構建體的細胞溶解活性(細胞殺傷)之圖。 圖 3B係描繪針對CD19陰性ALL細胞系(CD19KO Nalm6-Luc)的各種構建體的細胞溶解活性(細胞殺傷)之圖。 圖 3C-3D係顯示出藉由回應於表現CD22和/或CD19的靶細胞的各種CAR構建體產生IFNg細胞介素之圖。 [ FIG. 3A-3D ] In vitro activity of tandem and dual CAR T cells targeting CD19 and CD22 was shown. Figure 3A is a graph depicting the cytolytic activity (cell killing) of various constructs against a CD22 negative ALL cell line (CD22KO Nalm6-Luc). Figure 3B is a graph depicting the cytolytic activity (cell killing) of various constructs against a CD19-negative ALL cell line (CD19KO Nalm6-Luc). Figures 3C-3D are graphs showing the production of IFNg cytokines by various CAR constructs in response to target cells expressing CD22 and/or CD19.
[ 圖 4A-4B]顯示出在B細胞急性淋巴球白血病異種移植復發模型中靶向CD19和CD22的串聯和雙重CAR T細胞之體內活性。 圖 4A係顯示出所有治療組的總流量(平均生物發光)之圖。 圖 4B係描繪各種CAR-T細胞的擴增動力學之圖。 [ FIGS. 4A-4B ] Demonstrated in vivo activity of tandem and dual CAR T cells targeting CD19 and CD22 in a B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft relapse model. Figure 4A is a graph showing total flux (mean bioluminescence) for all treatment groups. Figure 4B is a graph depicting the expansion kinetics of various CAR-T cells.
[ 圖 5A-5C]顯示出藉由活化過程製造的靶向CD19和CD22的CAR19+、CAR22+、和雙陽性CAR T細胞的流動式細胞測量術百分比分析。 圖 5A和 圖 5B分別描繪了收穫後72小時和收穫後144小時小規模製造過程的結果。 圖 5C描述了大規模製造過程之結果。 [ FIGS. 5A-5C ] show flow cytometry percentage analysis of CAR19+, CAR22+, and double-positive CAR T cells targeting CD19 and CD22 produced by the activation process. Figures 5A and 5B depict the results of the small-scale manufacturing process at 72 hours post-harvest and 144 hours post-harvest , respectively. Figure 5C depicts the results of the large-scale fabrication process.
[ 圖 6A-6B]顯示出在B細胞急性淋巴球白血病異種移植模型中靶向CD19和/或CD22的單和雙重CAR T細胞的體內活性。 圖 6A係顯示出所有治療組的總流量(平均生物發光)之圖。 圖 6B顯示出0.3 x 10 6(0.3e6)劑量組之直接比較。 圖 6C係描繪各種CAR-T細胞擴增動力學之圖,顯示出每20 μl血液中的CAR+細胞的數目(CAR-T細胞的數目,nCARtot)。 [ FIG. 6A-6B ] showing the in vivo activity of single and dual CAR T cells targeting CD19 and/or CD22 in a B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft model. Figure 6A is a graph showing total flux (mean bioluminescence) for all treatment groups. Figure 6B shows a direct comparison of the 0.3 x 106 (0.3e6) dose groups. Figure 6C is a graph depicting the expansion kinetics of various CAR-T cells, showing the number of CAR+ cells per 20 μl of blood (number of CAR-T cells, nCARtot).
[ 圖 7]係顯示出臨床試驗研究設計之流程圖。LD CT:淋巴球耗減化學療法;PD:疾病進展;EOS:研究結束;以及FU:跟蹤。 [ FIG. 7 ] is a flowchart showing the study design of the clinical trial. LD CT: lymphocyte-depleting chemotherapy; PD: disease progression; EOS: end of study; and FU: follow-up.
無none
<![CDATA[<110> 瑞士商諾華公司(Novartis AG)]]>
<![CDATA[<120> CD19和CD22嵌合抗原受體及其用途]]>
<![CDATA[<130> PAT059124-US-PSP]]>
<![CDATA[<160> 109 ]]>
<![CDATA[<170> PatentIn 3.5版]]>
<![CDATA[<210> 1]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2238]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 1]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaaattg tgatgaccca gtcacccgcc actcttagcc tttcacccgg tgagcgcgca 120
accctgtctt gcagagcctc ccaagacatc tcaaaatacc ttaattggta tcaacagaag 180
cccggacagg ctcctcgcct tctgatctac cacaccagcc ggctccattc tggaatccct 240
gccaggttca gcggtagcgg atctgggacc gactacaccc tcactatcag ctcactgcag 300
ccagaggact tcgctgtcta tttctgtcag caagggaaca ccctgcccta cacctttgga 360
cagggcacca agctcgagat taaaggtgga ggtggcagcg gaggaggtgg gtccggcggt 420
ggaggaagcc aggtccaact ccaagaaagc ggaccgggtc ttgtgaagcc atcagaaact 480
ctttcactga cttgtactgt gagcggagtg tctctccccg attacggggt gtcttggatc 540
agacagccac cggggaaggg tctggaatgg attggagtga tttggggctc tgagactact 600
tactaccaat catccctcaa gtcacgcgtc accatctcaa aggacaactc taagaatcag 660
gtgtcactga aactgtcatc tgtgaccgca gccgacaccg ccgtgtacta ttgcgctaag 720
cattactatt atggcgggag ctacgcaatg gattactggg gacagggtac tctggtcacc 780
gtgtccagct tggcagaagc cgccgcgaaa gaagtgcagc ttcaacaatc aggaccagga 840
ctcgtcaaac catcacagac cctctccctc acatgtgcca tctccgggga ctccatgttg 900
agcaattccg acacttggaa ttggattaga caaagcccgt cccggggtct ggaatggttg 960
ggacgcacct accaccggtc tacttggtac gacgactacg cgtcatccgt gcggggaaga 1020
gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac cagtacagcc tgcagcttaa tgccgtgact 1080
cctgaggata cgggcgtcta ctactgcgcc cgcgtccgcc tgcaagacgg gaacagctgg 1140
agcgatgcat tcgatgtctg gggccaggga actatggtca ccgtgtcgtc tgggggcggt 1200
ggatcgggtg gcgggggttc ggggggcggc ggctctcagt ccgctcttac ccaaccggcc 1260
tcagcctcgg ggagccccgg ccagagcgtg accatttcct gcaccggcac ttcatccgac 1320
gtgggcggct acaactacgt gtcctggtac caacagcacc cgggaaaggc ccccaagctc 1380
atgatctacg acgtgtccaa caggccctcg ggagtgtcca accggttctc gggttcgaaa 1440
tcgggaaaca cagccagcct gaccatcagc ggactgcagg ctgaagatga agccgactac 1500
tactgctcct cctacacctc gtcatccacg ctctacgtgt tcggcactgg aactcagctg 1560
actgtgctga ccactacccc agcaccgagg ccacccaccc cggctcctac catcgcctcc 1620
cagcctctgt ccctgcgtcc ggaggcatgt agacccgcag ctggtggggc cgtgcatacc 1680
cggggtcttg acttcgcctg cgatatctac atttgggccc ctctggctgg tacttgcggg 1740
gtcctgctgc tttcactcgt gatcactctt tactgtaagc gcggtcggaa gaagctgctg 1800
tacatcttta agcaaccctt catgaggcct gtgcagacta ctcaagagga ggacggctgt 1860
tcatgccggt tcccagagga ggaggaaggc ggctgcgaac tgcgcgtgaa attcagccgc 1920
agcgcagatg ctccagccta ccagcagggg cagaaccagc tctacaacga actcaatctt 1980
ggtcggagag aggagtacga cgtgctggac aagcggagag gacgggaccc agaaatgggc 2040
gggaagccgc gcagaaagaa tccccaagag ggcctgtaca acgagctcca aaaggataag 2100
atggcagaag cctatagcga gattggtatg aaaggggaac gcagaagagg caaaggccac 2160
gacggactgt accagggact cagcaccgcc accaaggaca cctatgacgc tcttcacatg 2220
caggccctgc cgcctcgg 2238
<![CDATA[<210> 2]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 746]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 2]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Leu Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Lys Glu Val
260 265 270
Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu
275 280 285
Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp
290 295 300
Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu
305 310 315 320
Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser
325 330 335
Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr
340 345 350
Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr
355 360 365
Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe
370 375 380
Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu
405 410 415
Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile
420 425 430
Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser
435 440 445
Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp
450 455 460
Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys
465 470 475 480
Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp
485 490 495
Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr
500 505 510
Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala
515 520 525
Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser
530 535 540
Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr
545 550 555 560
Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala
565 570 575
Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys
580 585 590
Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met
595 600 605
Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe
610 615 620
Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg
625 630 635 640
Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn
645 650 655
Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg
660 665 670
Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro
675 680 685
Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala
690 695 700
Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His
705 710 715 720
Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp
725 730 735
Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740 745
<![CDATA[<210> 3]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 3]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaagtgc agcttcaaca atcaggacca ggactcgtca aaccatcaca gaccctctcc 120
ctcacatgtg ccatctccgg ggactccatg ttgagcaatt ccgacacttg gaattggatt 180
agacaaagcc cgtcccgggg tctggaatgg ttgggacgca cctaccaccg gtctacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgcgtcatc cgtgcgggga agagtgtcca tcaacgtgga cacctccaag 300
aaccagtaca gcctgcagct taatgccgtg actcctgagg atacgggcgt ctactactgc 360
gcccgcgtcc gcctgcaaga cgggaacagc tggagcgatg cattcgatgt ctggggccag 420
ggaactatgg tcaccgtgtc gtctgggggc ggtggatcgg gtggcggggg ttcggggggc 480
ggcggctctc agtccgctct tacccaaccg gcctcagcct cggggagccc cggccagagc 540
gtgaccattt cctgcaccgg cacttcatcc gacgtgggcg gctacaacta cgtgtcctgg 600
taccaacagc acccgggaaa ggcccccaag ctcatgatct acgacgtgtc caacaggccc 660
tcgggagtgt ccaaccggtt ctcgggttcg aaatcgggaa acacagccag cctgaccatc 720
agcggactgc aggctgaaga tgaagccgac tactactgct cctcctacac ctcgtcatcc 780
acgctctacg tgttcggcac tggaactcag ctgactgtgc tgggaggggg agggagtgaa 840
attgtgatga cccagtcacc cgccactctt agcctttcac ccggtgagcg cgcaaccctg 900
tcttgcagag cctcccaaga catctcaaaa taccttaatt ggtatcaaca gaagcccgga 960
caggctcctc gccttctgat ctaccacacc agccggctcc attctggaat ccctgccagg 1020
ttcagcggta gcggatctgg gaccgactac accctcacta tcagctcact gcagccagag 1080
gacttcgctg tctatttctg tcagcaaggg aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacagggc 1140
accaagctcg agattaaagg tggaggtggc agcggaggag gtgggtccgg cggtggagga 1200
agccaggtcc aactccaaga aagcggaccg ggtcttgtga agccatcaga aactctttca 1260
ctgacttgta ctgtgagcgg agtgtctctc cccgattacg gggtgtcttg gatcagacag 1320
ccaccgggga agggtctgga atggattgga gtgatttggg gctctgagac tacttactac 1380
caatcatccc tcaagtcacg cgtcaccatc tcaaaggaca actctaagaa tcaggtgtca 1440
ctgaaactgt catctgtgac cgcagccgac accgccgtgt actattgcgc taagcattac 1500
tattatggcg ggagctacgc aatggattac tggggacagg gtactctggt caccgtgtcc 1560
agcaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccaccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggaggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agagaggagt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg acccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc gg 2232
<![CDATA[<210> 4]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 4]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly
145 150 155 160
Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser
165 170 175
Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val
180 185 190
Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala
195 200 205
Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser
210 215 220
Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile
225 230 235 240
Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr
245 250 255
Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr
260 265 270
Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
290 295 300
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
305 310 315 320
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
325 330 335
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
340 345 350
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
355 360 365
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
370 375 380
Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
405 410 415
Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp
420 425 430
Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp
435 440 445
Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu
450 455 460
Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser
465 470 475 480
Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys
485 490 495
Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly
500 505 510
Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[<210> 5]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2202]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 5]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
ccccagtccg ctcttaccca accggcctca gcctcgggga gccccggcca gagcgtgacc 120
atttcctgca ccggcacttc atccgacgtg ggcggctaca actacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcacccgg gaaaggcccc caagctcatg atctacgacg tgtccaacag gccctcggga 240
gtgtccaacc ggttctcggg ttcgaaatcg ggaaacacag ccagcctgac catcagcgga 300
ctgcaggctg aagatgaagc cgactactac tgctcctcct acacctcgtc atccacgctc 360
tacgtgttcg gcactggaac tcagctgact gtgctgggcg gaggaggctc cgaagtgcag 420
cttcaacaat caggaccagg actcgtcaaa ccatcacaga ccctctccct cacatgtgcc 480
atctccgggg actccatgtt gagcaattcc gacacttgga attggattag acaaagcccg 540
tcccggggtc tggaatggtt gggacgcacc taccaccggt ctacttggta cgacgactac 600
gcgtcatccg tgcggggaag agtgtccatc aacgtggaca cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
ctgcagctta atgccgtgac tcctgaggat acgggcgtct actactgcgc ccgcgtccgc 720
ctgcaagacg ggaacagctg gagcgatgca ttcgatgtct ggggccaggg aactatggtc 780
accgtgtcgt ctggaggggg agggagtgaa attgtgatga cccagtcacc cgccactctt 840
agcctttcac ccggtgagcg cgcaaccctg tcttgcagag cctcccaaga catctcaaaa 900
taccttaatt ggtatcaaca gaagcccgga caggctcctc gccttctgat ctaccacacc 960
agccggctcc attctggaat ccctgccagg ttcagcggta gcggatctgg gaccgactac 1020
accctcacta tcagctcact gcagccagag gacttcgctg tctatttctg tcagcaaggg 1080
aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacagggc accaagctcg agattaaagg tggaggtggc 1140
agcggaggag gtgggtccgg cggtggagga agccaggtcc aactccaaga aagcggaccg 1200
ggtcttgtga agccatcaga aactctttca ctgacttgta ctgtgagcgg agtgtctctc 1260
cccgattacg gggtgtcttg gatcagacag ccaccgggga agggtctgga atggattgga 1320
gtgatttggg gctctgagac tacttactac caatcatccc tcaagtcacg cgtcaccatc 1380
tcaaaggaca actctaagaa tcaggtgtca ctgaaactgt catctgtgac cgcagccgac 1440
accgccgtgt actattgcgc taagcattac tattatggcg ggagctacgc aatggattac 1500
tggggacagg gtactctggt caccgtgtcc agcaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccaccc 1560
accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct ctgtccctgc gtccggaggc atgtagaccc 1620
gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg 1680
gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt 1740
aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag 1800
actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc cggttcccag aggaggagga aggcggctgc 1860
gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac 1920
cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg agagaggagt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg 1980
agaggacggg acccagaaat gggcgggaag ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg 2040
tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg 2100
gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag 2160
gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc ctgccgcctc gg 2202
<![CDATA[<210> 6]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 734]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 6]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val
260 265 270
Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp
290 295 300
Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr
305 310 315 320
Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser
325 330 335
Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe
340 345 350
Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly
355 360 365
Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
370 375 380
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro
385 390 395 400
Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser
405 410 415
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro
420 425 430
Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr
435 440 445
Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn
450 455 460
Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp
465 470 475 480
Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr
485 490 495
Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr
500 505 510
Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser
515 520 525
Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly
530 535 540
Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp
545 550 555 560
Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile
565 570 575
Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys
580 585 590
Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys
595 600 605
Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val
610 615 620
Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn
625 630 635 640
Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val
645 650 655
Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg
660 665 670
Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys
675 680 685
Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg
690 695 700
Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys
705 710 715 720
Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
725 730
<![CDATA[<210> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 7]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cctcagtccg ctctgactca gccggcctca gcttcggggt cccctggtca aagcgtcact 120
atttcctgta ccggaacctc atcagacgtg ggcggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcaccccg gaaaggctcc taagcttatg atctacgacg tgtccaaccg gccgtcagga 240
gtgtccaaca gattctccgg ctccaagagc ggaaacactg ccagcttgac cattagcggc 300
ttgcaggccg aggacgaagc cgactactac tgctctagct acacatcctc gtctaccctc 360
tacgtgtttg gaacggggac ccagctgact gtgctcgggg gtggaggatc agaggtgcaa 420
ctccagcagt ccggtcctgg cctcgtgaaa ccgtcccaaa ccctgtccct gacttgcgcc 480
atctcgggcg actccatgct gtccaattcc gacacctgga actggattag acaatcgcct 540
agccggggac tcgaatggct gggccggacc taccaccggt ccacgtggta tgacgactac 600
gcaagctccg tccggggaag ggtgtccatt aacgtcgata cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
cttcagctga acgctgtgac ccccgaggat accggcgtct actactgtgc aagagtgcga 720
ttgcaggatg gaaactcgtg gtcggacgca ttcgatgtct ggggacaggg aactatggtg 780
accgtgtcct cgggcggagg cgggagcgga ggaggaggct ctggcggagg aggaagcgag 840
attgtcatga ctcagtcccc ggccacactc tccctgtcac ccggagaaag agcaaccctg 900
agctgcaggg cgtcccagga catctcgaag tacctgaact ggtaccagca gaagcctgga 960
caagcacccc gcctcctgat ctaccacacc tcgcggctgc attcgggaat ccccgccaga 1020
ttctcaggga gcggatcagg aaccgactac accctgacta tctcgagcct gcaaccagag 1080
gatttcgccg tgtacttctg ccagcaagga aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacaggga 1140
accaagctcg agattaaggg gggtggtgga tcgggagggg gtggatcagg aggaggcggc 1200
tcacaagtcc agctgcaaga atccggtccg ggacttgtga agccgtccga aaccctgtca 1260
ctgacttgca ctgtgtccgg ggtgtcattg cccgactacg gcgtgagctg gattcggcag 1320
ccccctggaa agggattgga atggatcggc gtgatctggg gttcggaaac tacctactat 1380
cagtcctcac tgaagtcccg cgtgaccatc agcaaggata attccaaaaa ccaagtgtct 1440
ctgaagctct ccagcgtcac tgccgccgat actgccgtgt actactgcgc caagcactac 1500
tattacggcg gttcgtacgc catggactac tggggccaag ggacactcgt gaccgtgtca 1560
tccaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccaccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggaggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agagaggagt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg acccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc gg 2232
<![CDATA[<210> 8]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 8]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
260 265 270
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
290 295 300
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
305 310 315 320
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
325 330 335
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
340 345 350
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
355 360 365
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
370 375 380
Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
405 410 415
Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp
420 425 430
Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp
435 440 445
Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu
450 455 460
Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser
465 470 475 480
Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys
485 490 495
Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly
500 505 510
Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[<210> 9]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 9]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cctcagtccg ctctgactca gccggcctca gcttcggggt cccctggtca aagcgtcact 120
atttcctgta ccggaacctc atcagacgtg ggcggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcaccccg gaaaggctcc taagcttatg atctacgacg tgtccaaccg gccgtcagga 240
gtgtccaaca gattctccgg ctccaagagc ggaaacactg ccagcttgac cattagcggc 300
ttgcaggccg aggacgaagc cgactactac tgctctagct acacatcctc gtctaccctc 360
tacgtgtttg gaacggggac ccagctgact gtgctcgggg gtggaggatc agaggtgcaa 420
ctccagcagt ccggtcctgg cctcgtgaaa ccgtcccaaa ccctgtccct gacttgcgcc 480
atctcgggcg actccatgct gtccaattcc gacacctgga actggattag acaatcgcct 540
agccggggac tcgaatggct gggccggacc taccaccggt ccacgtggta tgacgactac 600
gcaagctccg tccggggaag ggtgtccatt aacgtcgata cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
cttcagctga acgctgtgac ccccgaggat accggcgtct actactgtgc aagagtgcga 720
ttgcaggatg gaaactcgtg gtcggacgca ttcgatgtct ggggacaggg aactatggtc 780
actgtgtcct ccggcggtgg aggctcgggg gggggcggct caggaggagg cggctcacaa 840
gtccagctgc aagaatccgg tccgggactt gtgaagccgt ccgaaaccct gtcactgact 900
tgcactgtgt ccggggtgtc attgcccgac tacggcgtga gctggattcg gcagccccct 960
ggaaagggat tggaatggat cggcgtgatc tggggttcgg aaactaccta ctatcagtcc 1020
tcactgaagt cccgcgtgac catcagcaag gataattcca aaaaccaagt gtctctgaag 1080
ctctccagcg tcactgccgc cgatactgcc gtgtactact gcgccaagca ctactattac 1140
ggcggttcgt acgccatgga ctactgggga caaggcactc ttgtgactgt gtcaagcggc 1200
ggtggaggga gcggtggggg cggttcagga ggaggcggat cagagatcgt gatgacccaa 1260
tccccagcca ccctgtccct cagccctgga gaaagagcca ccctgagctg ccgggcctcc 1320
caggatatca gcaagtactt gaactggtac caacaaaagc cggggcaggc gccccggctc 1380
ctgatctacc acacctcgcg cctccactca ggtatccccg ccagattctc agggagcggc 1440
tccggtactg actacaccct gactatttcc tcactgcagc cagaggactt tgccgtgtac 1500
ttctgccagc agggaaacac tctgccgtac accttcgggc agggaacgaa gcttgaaatt 1560
aagaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccaccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggaggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agagaggagt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg acccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc gg 2232
<![CDATA[<210> 10]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 10]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
260 265 270
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro
275 280 285
Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser
290 295 300
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro
305 310 315 320
Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr
325 330 335
Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn
340 345 350
Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp
355 360 365
Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr
370 375 380
Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly
385 390 395 400
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile
405 410 415
Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg
420 425 430
Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn
435 440 445
Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His
450 455 460
Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly
465 470 475 480
Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp
485 490 495
Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe
500 505 510
Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[<210> 11]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 11]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaagtgc agctgcagca gtcagggcct ggcctggtca agccgtcgca gaccctctcc 120
ctgacatgcg ccattagcgg ggactccatg ctgagcaact cggacacctg gaactggatt 180
cggcagtccc cttcccgggg actcgagtgg ctcggacgca cctaccatcg gagcacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgcctcctc cgtgagaggt cgcgtgtcga tcaacgtgga tacctcgaag 300
aaccagtata gcttgcaact gaacgccgtg acccctgagg ataccggagt gtactattgt 360
gcgagagtca ggctgcaaga cggaaactcc tggtccgacg catttgatgt ctggggacag 420
ggtactatgg tcacggtgtc atctggaggc ggaggatcgc aaagcgccct gactcagccg 480
gcttcggcta gcggttcacc ggggcagtcc gtgactatct cctgcaccgg gacttcctcc 540
gacgtgggag gctacaatta cgtgtcctgg taccagcaac accccggcaa agccccaaag 600
ctgatgatct acgacgtcag caacagaccc agcggagtgt ccaaccggtt cagcggctcc 660
aagtccggca acaccgcctc cctgaccatc agcgggcttc aggccgaaga tgaggcggat 720
tactactgct cctcgtacac ctcaagctca actctgtacg tgttcggcac cggtactcag 780
ctcaccgtgc tgaccactac cccagcaccg aggccaccca ccccggctcc taccatcgcc 840
tcccagcctc tgtccctgcg tccggaggca tgtagacccg cagctggtgg ggccgtgcat 900
acccggggtc ttgacttcgc ctgcgatatc tacatttggg cccctctggc tggtacttgc 960
ggggtcctgc tgctttcact cgtgatcact ctttactgta agcgcggtcg gaagaagctg 1020
ctgtacatct ttaagcaacc cttcatgagg cctgtgcaga ctactcaaga ggaggacggc 1080
tgttcatgcc ggttcccaga ggaggaggaa ggcggctgcg aactgcgcgt gaaattcagc 1140
cgcagcgcag atgctccagc ctaccagcag gggcagaacc agctctacaa cgaactcaat 1200
cttggtcgga gagaggagta cgacgtgctg gacaagcgga gaggacggga cccagaaatg 1260
ggcgggaagc cgcgcagaaa gaatccccaa gagggcctgt acaacgagct ccaaaaggat 1320
aagatggcag aagcctatag cgagattggt atgaaagggg aacgcagaag aggcaaaggc 1380
cacgacggac tgtaccaggg actcagcacc gccaccaagg acacctatga cgctcttcac 1440
atgcaggccc tgccgcctcg gggaagcgga gctactaact tcagcctgct gaagcaggct 1500
ggagacgtgg aggagaaccc tggacctatg gccttaccag tgaccgcctt gctcctgccg 1560
ctggccttgc tgctccacgc cgccaggccg gaaattgtga tgacccagtc acccgccact 1620
cttagccttt cacccggtga gcgcgcaacc ctgtcttgca gagcctccca agacatctca 1680
aaatacctta attggtatca acagaagccc ggacaggctc ctcgccttct gatctaccac 1740
accagccggc tccattctgg aatccctgcc aggttcagcg gtagcggatc tgggaccgac 1800
tacaccctca ctatcagctc actgcagcca gaggacttcg ctgtctattt ctgtcagcaa 1860
gggaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag ggcaccaagc tcgagattaa aggtggaggt 1920
ggcagcggag gaggtgggtc cggcggtgga ggaagccagg tccaactcca agaaagcgga 1980
ccgggtcttg tgaagccatc agaaactctt tcactgactt gtactgtgag cggagtgtct 2040
ctccccgatt acggggtgtc ttggatcaga cagccaccgg ggaagggtct ggaatggatt 2100
ggagtgattt ggggctctga gactacttac taccaatcat ccctcaagtc acgcgtcacc 2160
atctcaaagg acaactctaa gaatcaggtg tcactgaaac tgtcatctgt gaccgcagcc 2220
gacaccgccg tgtactattg cgctaagcat tactattatg gcgggagcta cgcaatggat 2280
tactggggac agggtactct ggtcaccgtg tccagcacca cgacgccagc gccgcgacca 2340
ccaacaccgg cgcccaccat cgcgtcgcag cccctgtccc tgcgcccaga ggcgtgccgg 2400
ccagcggcgg ggggcgcagt gcacacgagg gggctggact tcgcctgtga tatctacatc 2460
tgggcgccct tggccgggac ttgtggggtc cttctcctgt cactggttat caccctttac 2520
tgcaaacggg gcagaaagaa actcctgtat atattcaaac aaccatttat gagaccagta 2580
caaactactc aagaggaaga tggctgtagc tgccgatttc cagaagaaga agaaggagga 2640
tgtgaactga gagtgaagtt cagcaggagc gcagacgccc ccgcgtacca gcagggccag 2700
aaccagctct ataacgagct caatctagga cgaagagagg agtacgatgt tttggacaag 2760
agacgtggcc gggaccctga gatgggggga aagccgagaa ggaagaaccc tcaggaaggc 2820
ctgtacaatg aactgcagaa agataagatg gcggaggcct acagtgagat tgggatgaaa 2880
ggcgagcgcc ggaggggcaa ggggcacgat ggcctttacc agggtctcag tacagccacc 2940
aaggacacct acgacgccct tcacatgcag gccctgcccc ctcgc 2985
<![CDATA[<210> 12]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 995]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 12]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro
145 150 155 160
Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr
165 170 175
Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln
180 185 190
Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn
195 200 205
Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn
210 215 220
Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp
225 230 235 240
Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly
245 250 255
Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu
485 490 495
Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro Met Ala Leu
500 505 510
Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu His Ala Ala
515 520 525
Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser
530 535 540
Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser
545 550 555 560
Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu
565 570 575
Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe
580 585 590
Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu
595 600 605
Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu
610 615 620
Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly
625 630 635 640
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu
645 650 655
Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu
660 665 670
Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp
675 680 685
Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp
690 695 700
Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr
705 710 715 720
Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser
725 730 735
Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr
740 745 750
Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val
755 760 765
Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala
770 775 780
Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg
785 790 795 800
Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys
805 810 815
Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu
820 825 830
Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu
835 840 845
Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln
850 855 860
Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly
865 870 875 880
Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr
885 890 895
Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg
900 905 910
Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met
915 920 925
Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu
930 935 940
Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys
945 950 955 960
Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu
965 970 975
Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu
980 985 990
Pro Pro Arg
995
<![CDATA[<210> 13]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 508]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 13]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro
145 150 155 160
Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr
165 170 175
Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln
180 185 190
Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn
195 200 205
Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn
210 215 220
Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp
225 230 235 240
Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly
245 250 255
Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu
485 490 495
Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly
500 505
<![CDATA[<210> 14]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 487]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 14]]>
Pro Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
Leu His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr
20 25 30
Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln
50 55 60
Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile
65 70 75 80
Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
130 135 140
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
145 150 155 160
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
165 170 175
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
180 185 190
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
210 215 220
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
225 230 235 240
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[<210> 15]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 15]]>
atggccttac cagtgaccgc cttgctcctg ccgctggcct tgctgctcca cgccgccagg 60
ccggaaattg tgatgaccca gtcacccgcc actcttagcc tttcacccgg tgagcgcgca 120
accctgtctt gcagagcctc ccaagacatc tcaaaatacc ttaattggta tcaacagaag 180
cccggacagg ctcctcgcct tctgatctac cacaccagcc ggctccattc tggaatccct 240
gccaggttca gcggtagcgg atctgggacc gactacaccc tcactatcag ctcactgcag 300
ccagaggact tcgctgtcta tttctgtcag caagggaaca ccctgcccta cacctttgga 360
cagggcacca agctcgagat taaaggtgga ggtggcagcg gaggaggtgg gtccggcggt 420
ggaggaagcc aggtccaact ccaagaaagc ggaccgggtc ttgtgaagcc atcagaaact 480
ctttcactga cttgtactgt gagcggagtg tctctccccg attacggggt gtcttggatc 540
agacagccac cggggaaggg tctggaatgg attggagtga tttggggctc tgagactact 600
tactaccaat catccctcaa gtcacgcgtc accatctcaa aggacaactc taagaatcag 660
gtgtcactga aactgtcatc tgtgaccgca gccgacaccg ccgtgtacta ttgcgctaag 720
cattactatt atggcgggag ctacgcaatg gattactggg gacagggtac tctggtcacc 780
gtgtccagca ccacgacgcc agcgccgcga ccaccaacac cggcgcccac catcgcgtcg 840
cagcccctgt ccctgcgccc agaggcgtgc cggccagcgg cggggggcgc agtgcacacg 900
agggggctgg acttcgcctg tgatatctac atctgggcgc ccttggccgg gacttgtggg 960
gtccttctcc tgtcactggt tatcaccctt tactgcaaac ggggcagaaa gaaactcctg 1020
tatatattca aacaaccatt tatgagacca gtacaaacta ctcaagagga agatggctgt 1080
agctgccgat ttccagaaga agaagaagga ggatgtgaac tgagagtgaa gttcagcagg 1140
agcgcagacg cccccgcgta ccagcagggc cagaaccagc tctataacga gctcaatcta 1200
ggacgaagag aggagtacga tgttttggac aagagacgtg gccgggaccc tgagatgggg 1260
ggaaagccga gaaggaagaa ccctcaggaa ggcctgtaca atgaactgca gaaagataag 1320
atggcggagg cctacagtga gattgggatg aaaggcgagc gccggagggg caaggggcac 1380
gatggccttt accagggtct cagtacagcc accaaggaca cctacgacgc ccttcacatg 1440
caggccctgc cccctcgcgg aagcggagct actaacttca gcctgctgaa gcaggctgga 1500
gacgtggagg agaaccctgg acctatggcc ctccctgtca ccgccctgct gcttccgctg 1560
gctcttctgc tccacgccgc tcggcccgaa gtgcagctgc agcagtcagg gcctggcctg 1620
gtcaagccgt cgcagaccct ctccctgaca tgcgccatta gcggggactc catgctgagc 1680
aactcggaca cctggaactg gattcggcag tccccttccc ggggactcga gtggctcgga 1740
cgcacctacc atcggagcac ttggtacgac gactacgcct cctccgtgag aggtcgcgtg 1800
tcgatcaacg tggatacctc gaagaaccag tatagcttgc aactgaacgc cgtgacccct 1860
gaggataccg gagtgtacta ttgtgcgaga gtcaggctgc aagacggaaa ctcctggtcc 1920
gacgcatttg atgtctgggg acagggtact atggtcacgg tgtcatctgg aggcggagga 1980
tcgcaaagcg ccctgactca gccggcttcg gctagcggtt caccggggca gtccgtgact 2040
atctcctgca ccgggacttc ctccgacgtg ggaggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccag 2100
caacaccccg gcaaagcccc aaagctgatg atctacgacg tcagcaacag acccagcgga 2160
gtgtccaacc ggttcagcgg ctccaagtcc ggcaacaccg cctccctgac catcagcggg 2220
cttcaggccg aagatgaggc ggattactac tgctcctcgt acacctcaag ctcaactctg 2280
tacgtgttcg gcaccggtac tcagctcacc gtgctgacca ctaccccagc accgaggcca 2340
cccaccccgg ctcctaccat cgcctcccag cctctgtccc tgcgtccgga ggcatgtaga 2400
cccgcagctg gtggggccgt gcatacccgg ggtcttgact tcgcctgcga tatctacatt 2460
tgggcccctc tggctggtac ttgcggggtc ctgctgcttt cactcgtgat cactctttac 2520
tgtaagcgcg gtcggaagaa gctgctgtac atctttaagc aacccttcat gaggcctgtg 2580
cagactactc aagaggagga cggctgttca tgccggttcc cagaggagga ggaaggcggc 2640
tgcgaactgc gcgtgaaatt cagccgcagc gcagatgctc cagcctacca gcaggggcag 2700
aaccagctct acaacgaact caatcttggt cggagagagg agtacgacgt gctggacaag 2760
cggagaggac gggacccaga aatgggcggg aagccgcgca gaaagaatcc ccaagagggc 2820
ctgtacaacg agctccaaaa ggataagatg gcagaagcct atagcgagat tggtatgaaa 2880
ggggaacgca gaagaggcaa aggccacgac ggactgtacc agggactcag caccgccacc 2940
aaggacacct atgacgctct tcacatgcag gccctgccgc ctcgg 2985
<![CDATA[<210> 16]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 995]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 16]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu
485 490 495
Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro Met Ala Leu Pro
500 505 510
Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu His Ala Ala Arg
515 520 525
Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
530 535 540
Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser
545 550 555 560
Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu
565 570 575
Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr
580 585 590
Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys
595 600 605
Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly
610 615 620
Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser
645 650 655
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
660 665 670
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
675 680 685
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
690 695 700
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
705 710 715 720
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
725 730 735
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
740 745 750
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
755 760 765
Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala
770 775 780
Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg
785 790 795 800
Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys
805 810 815
Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu
820 825 830
Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu
835 840 845
Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln
850 855 860
Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly
865 870 875 880
Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr
885 890 895
Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg
900 905 910
Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met
915 920 925
Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu
930 935 940
Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys
945 950 955 960
Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu
965 970 975
Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu
980 985 990
Pro Pro Arg
995
<![CDATA[<210> 17]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 507]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 17]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu
485 490 495
Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly
500 505
<![CDATA[<210> 18]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 488]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213>]]> 人工序列
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 18]]>
Pro Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
Leu His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly
20 25 30
Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly
35 40 45
Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser
50 55 60
Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr
65 70 75 80
Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn
85 90 95
Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr
100 105 110
Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp
115 120 125
Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met
130 135 140
Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln
145 150 155 160
Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys
165 170 175
Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr
180 185 190
Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser
195 200 205
Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly
210 215 220
Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala
225 230 235 240
Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe
245 250 255
Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
260 265 270
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
275 280 285
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
290 295 300
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
305 310 315 320
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
325 330 335
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
340 345 350
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
370 375 380
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
385 390 395 400
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
405 410 415
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
420 425 430
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
435 440 445
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
450 455 460
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
465 470 475 480
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[<210> 19]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 19]]>
atggcacttc ccgtcaccgc cctgctgctc ccactcgccc tccttctgca cgccgcccgc 60
cccgaagtgc agctgcagca gtcaggaccg ggcctggtca aaccttcgca gactctgtcc 120
ctgacttgcg ctataagcgg ggactccatg ctgagcaatt cggacacttg gaactggatt 180
cgccaaagcc ccagccgggg tctggaatgg ctgggaagga cctaccatcg ctctacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgccagctc cgtgcgagga cgcgtgtcca tcaacgtgga cacctccaag 300
aaccagtact cgcttcaact caacgcagtg acccctgaag ataccggagt ctactattgc 360
gcccgcgtgc ggctccagga cgggaactcc tggtcggacg ctttcgatgt ctggggacag 420
ggcactatgg tcaccgtcag ctccggcggc ggcggtagcc aatcggcgct gacacagccg 480
gcttccgcct cgggatcgcc tggacagtcg gtgaccatct cgtgcactgg aacctcctcc 540
gacgtgggcg gctacaatta tgtgtcatgg taccagcagc acccgggaaa ggcccctaag 600
ctgatgatct acgacgtgtc caatagacct agcggggtgt caaacagatt ctccggatcc 660
aaatccggaa acactgcctc cctgaccatt tccggactgc aggccgagga cgaagccgat 720
tactactgct cctcttacac ctcctcatcc accctctacg tgtttgggac tgggacccag 780
ctgaccgtcc tcactaccac cccggccccg cggcccccta caccggcacc gactattgcc 840
agccagcctc tctcgctgcg gccggaggcc tgccgcccag ccgccggcgg agccgtgcac 900
acccgcggtc tggacttcgc gtgcgatatc tacatctggg ctccgctggc cgggacttgt 960
ggcgtgctgc tgctgtctct ggtcatcaca ctgtactgca agcgcggaag aaagaagctg 1020
ctctacatct tcaagcaacc cttcatgcgg cctgtgcaga ccacccagga agaggatggc 1080
tgctcctgcc ggttcccgga ggaagaagag ggcggatgcg aactgcgcgt gaagttcagc 1140
cgaagcgccg acgccccggc ctaccagcag ggccagaacc aactgtacaa cgaactcaac 1200
ctgggtcgga gagaagagta cgacgtgctg gacaaaagac gcggcaggga ccccgagatg 1260
ggcggaaagc ctcgccgcaa gaacccgcag gagggcctct acaacgagct gcagaaggac 1320
aagatggccg aagcctactc agagatcggc atgaaggggg agcggaggcg cgggaagggc 1380
cacgacggtt tgtaccaagg actttccact gcgaccaagg acacctacga tgccctccat 1440
atgcaagccc tgccgccccg gggttccgga gctaccaact tctcgctgtt gaagcaggcc 1500
ggagatgtcg aggaaaaccc gggacctatg gccctgccag tgaccgcgct cctgctgccc 1560
ctggctctgc tgcttcacgc ggcccggcct gagattgtga tgactcagag cccggcgacc 1620
ctgtccctgt cccccgggga gagagcaacc ctgtcgtgcc gggcctccca agacatctca 1680
aagtacctca attggtatca gcagaagcca ggacaggctc cacggttgct gatctaccac 1740
acttcgagac tgcactcagg aatccccgcg cggttttccg gttccggctc cgggaccgac 1800
tacaccctga ccatcagctc gctccagcct gaggatttcg cagtgtactt ctgtcagcaa 1860
ggaaacaccc ttccatacac cttcggacag ggtaccaagc tggaaatcaa gggaggagga 1920
ggatctgggg gcggtggttc cggaggcggt ggaagccaag tgcagctcca ggaaagcgga 1980
cccgggctgg tcaagccgag cgaaaccctc tcactgactt gtactgtgtc cggagtgtcc 2040
ctgcctgact atggagtgtc ctggatccga cagccccccg gaaagggtct ggagtggatt 2100
ggggtcatct ggggctccga aactacctac taccagagca gcctcaagag ccgggtcacc 2160
atttcaaagg ataactccaa gaatcaagtg tccctgaagc tgtcctcagt gacagccgca 2220
gacaccgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac tactactacg gaggctccta cgcaatggac 2280
tactggggac aaggcacttt ggtcactgtg tcaagcacca ccacccctgc gcctcggcct 2340
cctaccccgg ctcccactat cgcgagccag ccgctgagcc tgcggcctga ggcttgccga 2400
ccggccgctg gcggcgccgt gcatactcgg ggcctcgact ttgcctgtga catctacatc 2460
tgggcccccc tggccggaac gtgcggagtg ctgctgctgt cgctggtcat taccctgtat 2520
tgcaaacgcg gaaggaagaa gctgttgtac attttcaagc agcccttcat gcgcccggtg 2580
caaactactc aggaggaaga tggctgttcc tgtcggttcc ccgaagagga agaaggcggc 2640
tgcgagttga gggtcaagtt ctcccggtcc gccgatgctc ccgcctacca acaggggcag 2700
aaccagcttt ataacgaact gaacctgggc aggagggagg aatatgatgt gttggataag 2760
cgccggggcc gggacccaga aatgggggga aagcccagaa gaaagaaccc tcaagaggga 2820
ctttacaacg aattgcagaa agacaaaatg gccgaggcct actccgagat tgggatgaag 2880
ggcgaaagac ggagaggaaa ggggcacgac gggctctacc agggactcag caccgccacc 2940
aaagatacct acgacgccct gcatatgcag gcgctgccgc cgcgc 2985
<![CDATA[<210> 20]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 20]]>
Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 21]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 18]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 21]]>
Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val
1 5 10 15
Arg Gly
<![CDATA[<210> 22]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 22]]>
Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[<210> 23]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 23]]>
Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 24]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 24]]>
Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 25]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 25]]>
Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 26]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 26]]>
Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 27]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 17]]>
<![CDATA[<212>]]> PRT
<![CDATA[<213> 人工]]>序列
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 27]]>
Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp
1 5 10 15
Val
<![CDATA[<210> 28]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 14]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 28]]>
Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 29]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 29]]>
Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 30]]>
<![CDATA[<211> ]]>11
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 30]]>
Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 31]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 31]]>
Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 32]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 3]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 32]]>
Asp Val Ser
1
<![CDATA[<210> 33]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 8]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 33]]>
Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 34]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 34]]>
Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 35]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 35]]>
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 36]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 36]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[<210> 37]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 37]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[<210> 38]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 38]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[<210> 39]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 12]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 39]]>
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 40]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 11]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 40]]>
Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn
1 5 10
<![CDATA[<210> 41]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 41]]>
His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 42]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 42]]>
Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 43]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 43]]>
gaaattgtga tgacccagtc acccgccact cttagccttt cacccggtga gcgcgcaacc 60
ctgtcttgca gagcctccca agacatctca aaatacctta attggtatca acagaagccc 120
ggacaggctc ctcgccttct gatctaccac accagccggc tccattctgg aatccctgcc 180
aggttcagcg gtagcggatc tgggaccgac tacaccctca ctatcagctc actgcagcca 240
gaggacttcg ctgtctattt ctgtcagcaa gggaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag 300
ggcaccaagc tcgagattaa aggtggaggt ggcagcggag gaggtgggtc cggcggtgga 360
ggaagccagg tccaactcca agaaagcgga ccgggtcttg tgaagccatc agaaactctt 420
tcactgactt gtactgtgag cggagtgtct ctccccgatt acggggtgtc ttggatcaga 480
cagccaccgg ggaagggtct ggaatggatt ggagtgattt ggggctctga gactacttac 540
taccaatcat ccctcaagtc acgcgtcacc atctcaaagg acaactctaa gaatcaggtg 600
tcactgaaac tgtcatctgt gaccgcagcc gacaccgccg tgtactattg cgctaagcat 660
tactattatg gcgggagcta cgcaatggat tactggggac agggtactct ggtcaccgtg 720
tccagc 726
<![CDATA[<210> 44]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 44]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[<210> 45]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 45]]>
gagattgtca tgactcagtc cccggccaca ctctccctgt cacccggaga aagagcaacc 60
ctgagctgca gggcgtccca ggacatctcg aagtacctga actggtacca gcagaagcct 120
ggacaagcac cccgcctcct gatctaccac acctcgcggc tgcattcggg aatccccgcc 180
agattctcag ggagcggatc aggaaccgac tacaccctga ctatctcgag cctgcaacca 240
gaggatttcg ccgtgtactt ctgccagcaa ggaaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag 300
ggaaccaagc tcgagattaa ggggggtggt ggatcgggag ggggtggatc aggaggaggc 360
ggctcacaag tccagctgca agaatccggt ccgggacttg tgaagccgtc cgaaaccctg 420
tcactgactt gcactgtgtc cggggtgtca ttgcccgact acggcgtgag ctggattcgg 480
cagccccctg gaaagggatt ggaatggatc ggcgtgatct ggggttcgga aactacctac 540
tatcagtcct cactgaagtc ccgcgtgacc atcagcaagg ataattccaa aaaccaagtg 600
tctctgaagc tctccagcgt cactgccgcc gatactgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac 660
tactattacg gcggttcgta cgccatggac tactggggcc aagggacact cgtgaccgtg 720
tcatcc 726
<![CDATA[<210> 46]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 46]]>
caagtccagc tgcaagaatc cggtccggga cttgtgaagc cgtccgaaac cctgtcactg 60
acttgcactg tgtccggggt gtcattgccc gactacggcg tgagctggat tcggcagccc 120
cctggaaagg gattggaatg gatcggcgtg atctggggtt cggaaactac ctactatcag 180
tcctcactga agtcccgcgt gaccatcagc aaggataatt ccaaaaacca agtgtctctg 240
aagctctcca gcgtcactgc cgccgatact gccgtgtact actgcgccaa gcactactat 300
tacggcggtt cgtacgccat ggactactgg ggacaaggca ctcttgtgac tgtgtcaagc 360
ggcggtggag ggagcggtgg gggcggttca ggaggaggcg gatcagagat cgtgatgacc 420
caatccccag ccaccctgtc cctcagccct ggagaaagag ccaccctgag ctgccgggcc 480
tcccaggata tcagcaagta cttgaactgg taccaacaaa agccggggca ggcgccccgg 540
ctcctgatct accacacctc gcgcctccac tcaggtatcc ccgccagatt ctcagggagc 600
ggctccggta ctgactacac cctgactatt tcctcactgc agccagagga ctttgccgtg 660
tacttctgcc agcagggaaa cactctgccg tacaccttcg ggcagggaac gaagcttgaa 720
attaag 726
<![CDATA[<210> 47]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 47]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[<210> 48]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 48]]>
gagattgtga tgactcagag cccggcgacc ctgtccctgt cccccgggga gagagcaacc 60
ctgtcgtgcc gggcctccca agacatctca aagtacctca attggtatca gcagaagcca 120
ggacaggctc cacggttgct gatctaccac acttcgagac tgcactcagg aatccccgcg 180
cggttttccg gttccggctc cgggaccgac tacaccctga ccatcagctc gctccagcct 240
gaggatttcg cagtgtactt ctgtcagcaa ggaaacaccc ttccatacac cttcggacag 300
ggtaccaagc tggaaatcaa gggaggagga ggatctgggg gcggtggttc cggaggcggt 360
ggaagccaag tgcagctcca ggaaagcgga cccgggctgg tcaagccgag cgaaaccctc 420
tcactgactt gtactgtgtc cggagtgtcc ctgcctgact atggagtgtc ctggatccga 480
cagccccccg gaaagggtct ggagtggatt ggggtcatct ggggctccga aactacctac 540
taccagagca gcctcaagag ccgggtcacc atttcaaagg ataactccaa gaatcaagtg 600
tccctgaagc tgtcctcagt gacagccgca gacaccgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac 660
tactactacg gaggctccta cgcaatggac tactggggac aaggcacttt ggtcactgtg 720
tcaagc 726
<![CDATA[<210> 49]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 49]]>
gaagtgcagc tgcagcagtc agggcctggc ctggtcaagc cgtcgcagac cctctccctg 60
acatgcgcca ttagcgggga ctccatgctg agcaactcgg acacctggaa ctggattcgg 120
cagtcccctt cccggggact cgagtggctc ggacgcacct accatcggag cacttggtac 180
gacgactacg cctcctccgt gagaggtcgc gtgtcgatca acgtggatac ctcgaagaac 240
cagtatagct tgcaactgaa cgccgtgacc cctgaggata ccggagtgta ctattgtgcg 300
agagtcaggc tgcaagacgg aaactcctgg tccgacgcat ttgatgtctg gggacagggt 360
actatggtca cggtgtcatc tggaggcgga ggatcgcaaa gcgccctgac tcagccggct 420
tcggctagcg gttcaccggg gcagtccgtg actatctcct gcaccgggac ttcctccgac 480
gtgggaggct acaattacgt gtcctggtac cagcaacacc ccggcaaagc cccaaagctg 540
atgatctacg acgtcagcaa cagacccagc ggagtgtcca accggttcag cggctccaag 600
tccggcaaca ccgcctccct gaccatcagc gggcttcagg ccgaagatga ggcggattac 660
tactgctcct cgtacacctc aagctcaact ctgtacgtgt tcggcaccgg tactcagctc 720
accgtgctg 729
<![CDATA[<210> 50]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 243]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 50]]>
Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn
20 25 30
Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu
35 40 45
Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala
50 55 60
Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn
65 70 75 80
Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val
85 90 95
Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp
100 105 110
Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly
130 135 140
Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp
145 150 155 160
Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys
165 170 175
Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val
180 185 190
Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr
195 200 205
Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser
210 215 220
Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu
225 230 235 240
Thr Val Leu
<![CDATA[<210> 51]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 51]]>
gaagtgcagc tgcagcagtc aggaccgggc ctggtcaaac cttcgcagac tctgtccctg 60
acttgcgcta taagcgggga ctccatgctg agcaattcgg acacttggaa ctggattcgc 120
caaagcccca gccggggtct ggaatggctg ggaaggacct accatcgctc tacttggtac 180
gacgactacg ccagctccgt gcgaggacgc gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac 240
cagtactcgc ttcaactcaa cgcagtgacc cctgaagata ccggagtcta ctattgcgcc 300
cgcgtgcggc tccaggacgg gaactcctgg tcggacgctt tcgatgtctg gggacagggc 360
actatggtca ccgtcagctc cggcggcggc ggtagccaat cggcgctgac acagccggct 420
tccgcctcgg gatcgcctgg acagtcggtg accatctcgt gcactggaac ctcctccgac 480
gtgggcggct acaattatgt gtcatggtac cagcagcacc cgggaaaggc ccctaagctg 540
atgatctacg acgtgtccaa tagacctagc ggggtgtcaa acagattctc cggatccaaa 600
tccggaaaca ctgcctccct gaccatttcc ggactgcagg ccgaggacga agccgattac 660
tactgctcct cttacacctc ctcatccacc ctctacgtgt ttgggactgg gacccagctg 720
accgtcctc 729
<![CDATA[<210> 52]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 759]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 52]]>
gaagtgcagc ttcaacaatc aggaccagga ctcgtcaaac catcacagac cctctccctc 60
acatgtgcca tctccgggga ctccatgttg agcaattccg acacttggaa ttggattaga 120
caaagcccgt cccggggtct ggaatggttg ggacgcacct accaccggtc tacttggtac 180
gacgactacg cgtcatccgt gcggggaaga gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac 240
cagtacagcc tgcagcttaa tgccgtgact cctgaggata cgggcgtcta ctactgcgcc 300
cgcgtccgcc tgcaagacgg gaacagctgg agcgatgcat tcgatgtctg gggccaggga 360
actatggtca ccgtgtcgtc tgggggcggt ggatcgggtg gcgggggttc ggggggcggc 420
ggctctcagt ccgctcttac ccaaccggcc tcagcctcgg ggagccccgg ccagagcgtg 480
accatttcct gcaccggcac ttcatccgac gtgggcggct acaactacgt gtcctggtac 540
caacagcacc cgggaaaggc ccccaagctc atgatctacg acgtgtccaa caggccctcg 600
ggagtgtcca accggttctc gggttcgaaa tcgggaaaca cagccagcct gaccatcagc 660
ggactgcagg ctgaagatga agccgactac tactgctcct cctacacctc gtcatccacg 720
ctctacgtgt tcggcactgg aactcagctg actgtgctg 759
<![CDATA[<210> 53]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 253]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 53]]>
Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn
20 25 30
Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu
35 40 45
Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala
50 55 60
Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn
65 70 75 80
Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val
85 90 95
Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp
100 105 110
Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser
130 135 140
Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val
145 150 155 160
Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile
180 185 190
Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly
195 200 205
Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala
210 215 220
Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr
225 230 235 240
Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu
245 250
<![CDATA[<210> 54]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 54]]>
cagtccgctc ttacccaacc ggcctcagcc tcggggagcc ccggccagag cgtgaccatt 60
tcctgcaccg gcacttcatc cgacgtgggc ggctacaact acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
cacccgggaa aggcccccaa gctcatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaacaggcc ctcgggagtg 180
tccaaccggt tctcgggttc gaaatcggga aacacagcca gcctgaccat cagcggactg 240
caggctgaag atgaagccga ctactactgc tcctcctaca cctcgtcatc cacgctctac 300
gtgttcggca ctggaactca gctgactgtg ctgggcggag gaggctccga agtgcagctt 360
caacaatcag gaccaggact cgtcaaacca tcacagaccc tctccctcac atgtgccatc 420
tccggggact ccatgttgag caattccgac acttggaatt ggattagaca aagcccgtcc 480
cggggtctgg aatggttggg acgcacctac caccggtcta cttggtacga cgactacgcg 540
tcatccgtgc ggggaagagt gtccatcaac gtggacacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctg 600
cagcttaatg ccgtgactcc tgaggatacg ggcgtctact actgcgcccg cgtccgcctg 660
caagacggga acagctggag cgatgcattc gatgtctggg gccagggaac tatggtcacc 720
gtgtcgtct 729
<![CDATA[<210> 55]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 243]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 55]]>
Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln
1 5 10 15
Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr
20 25 30
Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu
35 40 45
Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu
65 70 75 80
Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser
85 90 95
Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Gly
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val
115 120 125
Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser
130 135 140
Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser
145 150 155 160
Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp
180 185 190
Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu
195 200 205
Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn
210 215 220
Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr
225 230 235 240
Val Ser Ser
<![CDATA[<210> 56]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 56]]>
cagtccgctc tgactcagcc ggcctcagct tcggggtccc ctggtcaaag cgtcactatt 60
tcctgtaccg gaacctcatc agacgtgggc ggctacaatt acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
caccccggaa aggctcctaa gcttatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaaccggcc gtcaggagtg 180
tccaacagat tctccggctc caagagcgga aacactgcca gcttgaccat tagcggcttg 240
caggccgagg acgaagccga ctactactgc tctagctaca catcctcgtc taccctctac 300
gtgtttggaa cggggaccca gctgactgtg ctcgggggtg gaggatcaga ggtgcaactc 360
cagcagtccg gtcctggcct cgtgaaaccg tcccaaaccc tgtccctgac ttgcgccatc 420
tcgggcgact ccatgctgtc caattccgac acctggaact ggattagaca atcgcctagc 480
cggggactcg aatggctggg ccggacctac caccggtcca cgtggtatga cgactacgca 540
agctccgtcc ggggaagggt gtccattaac gtcgatacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctt 600
cagctgaacg ctgtgacccc cgaggatacc ggcgtctact actgtgcaag agtgcgattg 660
caggatggaa actcgtggtc ggacgcattc gatgtctggg gacagggaac tatggtgacc 720
gtgtcctcg 729
<![CDATA[<210> 57]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 57]]>
cagtccgctc tgactcagcc ggcctcagct tcggggtccc ctggtcaaag cgtcactatt 60
tcctgtaccg gaacctcatc agacgtgggc ggctacaatt acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
caccccggaa aggctcctaa gcttatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaaccggcc gtcaggagtg 180
tccaacagat tctccggctc caagagcgga aacactgcca gcttgaccat tagcggcttg 240
caggccgagg acgaagccga ctactactgc tctagctaca catcctcgtc taccctctac 300
gtgtttggaa cggggaccca gctgactgtg ctcgggggtg gaggatcaga ggtgcaactc 360
cagcagtccg gtcctggcct cgtgaaaccg tcccaaaccc tgtccctgac ttgcgccatc 420
tcgggcgact ccatgctgtc caattccgac acctggaact ggattagaca atcgcctagc 480
cggggactcg aatggctggg ccggacctac caccggtcca cgtggtatga cgactacgca 540
agctccgtcc ggggaagggt gtccattaac gtcgatacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctt 600
cagctgaacg ctgtgacccc cgaggatacc ggcgtctact actgtgcaag agtgcgattg 660
caggatggaa actcgtggtc ggacgcattc gatgtctggg gacagggaac tatggtcact 720
gtgtcctcc 729
<![CDATA[<210> 58]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 58]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
ccc 63
<![CDATA[<210> 59]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 21]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 59]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro
20
<![CDATA[<210> 60]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 60]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cct 63
<![CDATA[<210> 61]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 61]]>
atggccttac cagtgaccgc cttgctcctg ccgctggcct tgctgctcca cgccgccagg 60
ccg 63
<![CDATA[<210> 62]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 62]]>
atggcacttc ccgtcaccgc cctgctgctc ccactcgccc tccttctgca cgccgcccgc 60
ccc 63
<![CDATA[<210> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 63]]>
atggccctgc cagtgaccgc gctcctgctg cccctggctc tgctgcttca cgcggcccgg 60
cct 63
<![CDATA[<210> 64]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 64]]>
accactaccc cagcaccgag gccacccacc ccggctccta ccatcgcctc ccagcctctg 60
tccctgcgtc cggaggcatg tagacccgca gctggtgggg ccgtgcatac ccggggtctt 120
gacttcgcct gcgatatcta catttgggcc cctctggctg gtacttgcgg ggtcctgctg 180
ctttcactcg tgatcactct ttactgt 207
<![CDATA[<210> 65]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 69]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 65]]>
Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala
1 5 10 15
Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly
20 25 30
Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile
35 40 45
Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val
50 55 60
Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys
65
<![CDATA[<210> 66]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 66]]>
actaccaccc cggccccgcg gccccctaca ccggcaccga ctattgccag ccagcctctc 60
tcgctgcggc cggaggcctg ccgcccagcc gccggcggag ccgtgcacac ccgcggtctg 120
gacttcgcgt gcgatatcta catctgggct ccgctggccg ggacttgtgg cgtgctgctg 180
ctgtctctgg tcatcacact gtactgc 207
<![CDATA[<210> 67]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 67]]>
accacgacgc cagcgccgcg accaccaaca ccggcgccca ccatcgcgtc gcagcccctg 60
tccctgcgcc cagaggcgtg ccggccagcg gcggggggcg cagtgcacac gagggggctg 120
gacttcgcct gtgatatcta catctgggcg cccttggccg ggacttgtgg ggtccttctc 180
ctgtcactgg ttatcaccct ttactgc 207
<![CDATA[<210> 68]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 68]]>
accaccaccc ctgcgcctcg gcctcctacc ccggctccca ctatcgcgag ccagccgctg 60
agcctgcggc ctgaggcttg ccgaccggcc gctggcggcg ccgtgcatac tcggggcctc 120
gactttgcct gtgacatcta catctgggcc cccctggccg gaacgtgcgg agtgctgctg 180
ctgtcgctgg tcattaccct gtattgc 207
<![CDATA[<210> 69]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 69]]>
aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag 60
actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc cggttcccag aggaggagga aggcggctgc 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[<210> 70]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 42]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 70]]>
Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met
1 5 10 15
Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe
20 25 30
Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu
35 40
<![CDATA[<210> 71]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 71]]>
aaacggggca gaaagaaact cctgtatata ttcaaacaac catttatgag accagtacaa 60
actactcaag aggaagatgg ctgtagctgc cgatttccag aagaagaaga aggaggatgt 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[<210> 72]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 72]]>
aagcgcggaa gaaagaagct gctctacatc ttcaagcaac ccttcatgcg gcctgtgcag 60
accacccagg aagaggatgg ctgctcctgc cggttcccgg aggaagaaga gggcggatgc 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[<210> 73]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 73]]>
aaacgcggaa ggaagaagct gttgtacatt ttcaagcagc ccttcatgcg cccggtgcaa 60
actactcagg aggaagatgg ctgttcctgt cggttccccg aagaggaaga aggcggctgc 120
gagttg 126
<![CDATA[<210> 74]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 74]]>
cgcgtgaaat tcagccgcag cgcagatgct ccagcctacc agcaggggca gaaccagctc 60
tacaacgaac tcaatcttgg tcggagagag gagtacgacg tgctggacaa gcggagagga 120
cgggacccag aaatgggcgg gaagccgcgc agaaagaatc cccaagaggg cctgtacaac 180
gagctccaaa aggataagat ggcagaagcc tatagcgaga ttggtatgaa aggggaacgc 240
agaagaggca aaggccacga cggactgtac cagggactca gcaccgccac caaggacacc 300
tatgacgctc ttcacatgca ggccctgccg cctcgg 336
<![CDATA[<210> 75]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 112]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 75]]>
Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly
1 5 10 15
Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr
20 25 30
Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys
35 40 45
Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys
50 55 60
Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg
65 70 75 80
Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala
85 90 95
Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
100 105 110
<![CDATA[<210> 76]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 76]]>
agagtgaagt tcagcaggag cgcagacgcc cccgcgtacc agcagggcca gaaccagctc 60
tataacgagc tcaatctagg acgaagagag gagtacgatg ttttggacaa gagacgtggc 120
cgggaccctg agatgggggg aaagccgaga aggaagaacc ctcaggaagg cctgtacaat 180
gaactgcaga aagataagat ggcggaggcc tacagtgaga ttgggatgaa aggcgagcgc 240
cggaggggca aggggcacga tggcctttac cagggtctca gtacagccac caaggacacc 300
tacgacgccc ttcacatgca ggccctgccc cctcgc 336
<![CDATA[<210> 77]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 77]]>
cgcgtgaagt tcagccgaag cgccgacgcc ccggcctacc agcagggcca gaaccaactg 60
tacaacgaac tcaacctggg tcggagagaa gagtacgacg tgctggacaa aagacgcggc 120
agggaccccg agatgggcgg aaagcctcgc cgcaagaacc cgcaggaggg cctctacaac 180
gagctgcaga aggacaagat ggccgaagcc tactcagaga tcggcatgaa gggggagcgg 240
aggcgcggga agggccacga cggtttgtac caaggacttt ccactgcgac caaggacacc 300
tacgatgccc tccatatgca agccctgccg ccccgg 336
<![CDATA[<210> 78]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 78]]>
agggtcaagt tctcccggtc cgccgatgct cccgcctacc aacaggggca gaaccagctt 60
tataacgaac tgaacctggg caggagggag gaatatgatg tgttggataa gcgccggggc 120
cgggacccag aaatgggggg aaagcccaga agaaagaacc ctcaagaggg actttacaac 180
gaattgcaga aagacaaaat ggccgaggcc tactccgaga ttgggatgaa gggcgaaaga 240
cggagaggaa aggggcacga cgggctctac cagggactca gcaccgccac caaagatacc 300
tacgacgccc tgcatatgca ggcgctgccg ccgcgc 336
<![CDATA[<210> 79]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 21]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 79]]>
ttggcagaag ccgccgcgaa a 21
<![CDATA[<210> 80]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 80]]>
Leu Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Lys
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 81]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 81]]>
ggtggaggtg gcagcggagg aggtgggtcc ggcggtggag gaagc 45
<![CDATA[<210> 82]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 82]]>
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[<210> 83]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 83]]>
ggcggaggcg ggagcggagg aggaggctct ggcggaggag gaagc 45
<![CDATA[<210> 84]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 84]]>
ggcggtggag gctcgggggg gggcggctca ggaggaggcg gctca 45
<![CDATA[<210> 85]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 66]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 85]]>
ggaagcggag ctactaactt cagcctgctg aagcaggctg gagacgtgga ggagaaccct 60
ggacct 66
<![CDATA[<210> 86]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 22]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 86]]>
Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val
1 5 10 15
Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro
20
<![CDATA[<210> 87]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 66]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 87]]>
ggttccggag ctaccaactt ctcgctgttg aagcaggccg gagatgtcga ggaaaacccg 60
ggacct 66
<![CDATA[<210> 88]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[<212> DNA]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多核苷酸]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 88]]>
ggtggaggtg gcagc 15
<![CDATA[<210> ]]>89
<![CDATA[<211> 5]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 89]]>
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[<210> 90]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 90]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[<210> 91]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 271]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 91]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser His His His His His His His His
260 265 270
<![CDATA[<210> 92]]>
<![CDATA[<211>]]> 486
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 92]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[<210> 93]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 465]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 93]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr
245 250 255
Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala
260 265 270
Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile
275 280 285
Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser
290 295 300
Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr
305 310 315 320
Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu
325 330 335
Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu
340 345 350
Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln
355 360 365
Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu
370 375 380
Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln
405 410 415
Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu
420 425 430
Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr
435 440 445
Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro
450 455 460
Arg
465
<![CDATA[<210> 94]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 94]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[<210> 95]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 95]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[<210> 96]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 96]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[<210> 97]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 97]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[<210> 98]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 98]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[<210> 99]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 99]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[<210> 100]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 100]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[<210> 101]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 101]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[<210> 102]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 102]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[<210> 103]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 489]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 103]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser
20 25 30
Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly
50 55 60
Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val
65 70 75 80
Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser
130 135 140
Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala
145 150 155 160
Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu
165 170 175
Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu
180 185 190
Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser
195 200 205
Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln
210 215 220
Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr
225 230 235 240
Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
245 250 255
Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ala Ala Ala Ile Glu
260 265 270
Val Met Tyr Pro Pro Pro Tyr Leu Asp Asn Glu Lys Ser Asn Gly Thr
275 280 285
Ile Ile His Val Lys Gly Lys His Leu Cys Pro Ser Pro Leu Phe Pro
290 295 300
Gly Pro Ser Lys Pro Phe Trp Val Leu Val Val Val Gly Gly Val Leu
305 310 315 320
Ala Cys Tyr Ser Leu Leu Val Thr Val Ala Phe Ile Ile Phe Trp Val
325 330 335
Arg Ser Lys Arg Ser Arg Leu Leu His Ser Asp Tyr Met Asn Met Thr
340 345 350
Pro Arg Arg Pro Gly Pro Thr Arg Lys His Tyr Gln Pro Tyr Ala Pro
355 360 365
Pro Arg Asp Phe Ala Ala Tyr Arg Ser Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser
370 375 380
Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu
385 390 395 400
Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg
405 410 415
Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln
420 425 430
Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr
435 440 445
Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp
450 455 460
Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala
465 470 475 480
Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[<210> 104]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 245]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 104]]>
Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly
1 5 10 15
Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly
100 105 110
Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys
115 120 125
Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser
130 135 140
Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
145 150 155 160
Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile
165 170 175
Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu
180 185 190
Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn
195 200 205
Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr
210 215 220
Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser
225 230 235 240
Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[<210> 105]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 461]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 105]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser
20 25 30
Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly
50 55 60
Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val
65 70 75 80
Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser
130 135 140
Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala
145 150 155 160
Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu
165 170 175
Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu
180 185 190
Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser
195 200 205
Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln
210 215 220
Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr
225 230 235 240
Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
245 250 255
Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser Val Thr Val Ser Ser Glu Ser Lys Tyr Gly
260 265 270
Pro Pro Cys Pro Pro Cys Pro Met Phe Trp Val Leu Val Val Val Gly
275 280 285
Gly Val Leu Ala Cys Tyr Ser Leu Leu Val Thr Val Ala Phe Ile Ile
290 295 300
Phe Trp Val Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln
305 310 315 320
Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser
325 330 335
Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys
340 345 350
Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln
355 360 365
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu
370 375 380
Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg
385 390 395 400
Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met
405 410 415
Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly
420 425 430
Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp
435 440 445
Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
450 455 460
<![CDATA[<210> 106]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 245]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 106]]>
Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly
1 5 10 15
Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly
100 105 110
Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys
115 120 125
Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser
130 135 140
Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
145 150 155 160
Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile
165 170 175
Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu
180 185 190
Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn
195 200 205
Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr
210 215 220
Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser
225 230 235 240
Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[<210> 107]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 22]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 107]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro
20
<![CDATA[<210> 108]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 112]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 108]]>
Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln Gly
1 5 10 15
Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr
20 25 30
Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys
35 40 45
Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys
50 55 60
Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg
65 70 75 80
Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala
85 90 95
Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
100 105 110
<![CDATA[<210> 109]]>
<![CDATA[<211> 284]]>
<![CDATA[<212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[<213> 人工序列]]>
<![CDATA[<220>]]>
<![CDATA[<223> 合成多肽]]>
<![CDATA[<400> 109]]>
Asn Trp Val Asn Val Ile Ser Asp Leu Lys Lys Ile Glu Asp Leu Ile
1 5 10 15
Gln Ser Met His Ile Asp Ala Thr Leu Tyr Thr Glu Ser Asp Val His
20 25 30
Pro Ser Cys Lys Val Thr Ala Met Lys Cys Phe Leu Leu Glu Leu Gln
35 40 45
Val Ile Ser Leu Glu Ser Gly Asp Ala Ser Ile His Asp Thr Val Glu
50 55 60
Asn Leu Ile Ile Leu Ala Asn Asn Ser Leu Ser Ser Asn Gly Asn Val
65 70 75 80
Thr Glu Ser Gly Cys Lys Glu Cys Glu Glu Leu Glu Glu Lys Asn Ile
85 90 95
Lys Glu Phe Leu Gln Ser Phe Val His Ile Val Gln Met Phe Ile Asn
100 105 110
Thr Ser Ile Thr Cys Pro Pro Pro Met Ser Val Glu His Ala Asp Ile
115 120 125
Trp Val Lys Ser Tyr Ser Leu Tyr Ser Arg Glu Arg Tyr Ile Cys Asn
130 135 140
Ser Gly Phe Lys Arg Lys Ala Gly Thr Ser Ser Leu Thr Glu Cys Val
145 150 155 160
Leu Asn Lys Ala Thr Asn Val Ala His Trp Thr Thr Pro Ser Leu Lys
165 170 175
Cys Ile Arg Asp Pro Ala Leu Val His Gln Arg Pro Ala Pro Pro Ser
180 185 190
Thr Val Thr Thr Ala Gly Val Thr Pro Gln Pro Glu Ser Leu Ser Pro
195 200 205
Ser Gly Lys Glu Pro Ala Ala Ser Ser Pro Ser Ser Asn Asn Thr Ala
210 215 220
Ala Thr Thr Ala Ala Ile Val Pro Gly Ser Gln Leu Met Pro Ser Lys
225 230 235 240
Ser Pro Ser Thr Gly Thr Thr Glu Ile Ser Ser His Glu Ser Ser His
245 250 255
Gly Thr Pro Ser Gln Thr Thr Ala Lys Asn Trp Glu Leu Thr Ala Ser
260 265 270
Ala Ser His Gln Pro Pro Gly Val Tyr Pro Gln Gly
275 280
<![CDATA[ <110> Novartis AG]]>
<![CDATA[ <120> CD19 and CD22 chimeric antigen receptors and their uses]]>
<![CDATA[ <130> PAT059124-US-PSP]]>
<![CDATA[ <160> 109 ]]>
<![CDATA[ <170> PatentIn Version 3.5]]>
<![CDATA[ <210> 1]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2238]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 1]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaaattg tgatgaccca gtcacccgcc actcttagcc tttcacccgg tgagcgcgca 120
accctgtctt gcagagcctc ccaagacatc tcaaaatacc ttaattggta tcaacagaag 180
cccggacagg ctcctcgcct tctgatctac cacaccagcc ggctccattc tggaatccct 240
gccaggttca gcggtagcgg atctgggacc gactacaccc tcactatcag ctcactgcag 300
ccagaggact tcgctgtcta tttctgtcag caagggaaca ccctgcccta cacctttgga 360
cagggcacca agctcgagat taaaggtgga ggtggcagcg gaggaggtgg gtccggcggt 420
ggaggaagcc aggtccaact ccaagaaagc ggaccgggtc ttgtgaagcc atcagaaact 480
ctttcactga cttgtactgt gagcggagtg tctctccccg attacggggt gtcttggatc 540
agacagccac cggggaaggg tctggaatgg attggagtga tttggggctc tgagactact 600
tactaccaat catccctcaa gtcacgcgtc accatctcaa aggacaactc taagaatcag 660
gtgtcactga aactgtcatc tgtgaccgca gccgacaccg ccgtgtacta ttgcgctaag 720
cattactatt atggcggggag ctacgcaatg gattactggg gacagggtac tctggtcacc 780
gtgtccagct tggcagaagc cgccgcgaaa gaagtgcagc ttcaacaatc aggaccagga 840
ctcgtcaaac catcacagac cctctccctc acatgtgcca tctccgggga ctccatgttg 900
agcaattccg acacttggaa ttggattaga caaagcccgt cccggggtct ggaatggttg 960
ggacgcacct accaccggtc tacttggtac gacgactacg cgtcatccgt gcggggaaga 1020
gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac cagtacagcc tgcagcttaa tgccgtgact 1080
cctgaggata cgggcgtcta ctactgcgcc cgcgtccgcc tgcaagacgg gaacagctgg 1140
agcgatgcat tcgatgtctg gggccaggga actatggtca ccgtgtcgtc tgggggcggt 1200
ggatcgggtg gcgggggttc ggggggcggc ggctctcagt ccgctcttac ccaaccggcc 1260
tcagcctcgg ggagccccgg ccagagcgtg accatttcct gcaccggcac ttcatccgac 1320
gtgggcggct acaactacgt gtcctggtac caacagcacc cgggaaaggc ccccaagctc 1380
atgatctacg acgtgtccaa caggccctcg ggagtgtcca accggttctc gggttcgaaa 1440
tcgggaaaca cagccagcct gaccatcagc ggactgcagg ctgaagatga agccgactac 1500
tactgctcct cctacacctc gtcatccacg ctctacgtgt tcggcactgg aactcagctg 1560
actgtgctga ccactaccccc agcaccgagg ccaccccaccc cggctcctac catcgcctcc 1620
cagcctctgt ccctgcgtcc ggaggcatgt agacccgcag ctggtggggc cgtgcatacc 1680
cggggtcttg acttcgcctg cgatatctac atttgggccc ctctggctgg tacttgcggg 1740
gtcctgctgc tttcactcgt gatcactctt tactgtaagc gcggtcggaa gaagctgctg 1800
tacatcttta agcaaccctt catgaggcct gtgcagacta ctcaagagga ggacggctgt 1860
tcatgccggt tcccagagga ggaggaaggc ggctgcgaac tgcgcgtgaa attcagccgc 1920
agcgcagatg ctccagccta ccagcagggg cagaaccagc tctacaacga actcaatctt 1980
ggtcggagag aggagtacga cgtgctggac aagcggagag gacgggaccc agaaatgggc 2040
gggaagccgc gcagaaagaa tccccaagag ggcctgtaca acgagctcca aaaggataag 2100
atggcagaag cctatagcga gattggtatg aaaggggaac gcagaagagg caaaggccac 2160
gacggactgt accagggact cagcaccgcc accaaggaca cctatgacgc tcttcacatg 2220
caggccctgc cgcctcgg 2238
<![CDATA[ <210> 2]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 746]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 2]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Leu Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Lys Glu Val
260 265 270
Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu
275 280 285
Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp
290 295 300
Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu
305 310 315 320
Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser
325 330 335
Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr
340 345 350
Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr
355 360 365
Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe
370 375 380
Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu
405 410 415
Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile
420 425 430
Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser
435 440 445
Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp
450 455 460
Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys
465 470 475 480
Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp
485 490 495
Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr
500 505 510
Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala
515 520 525
Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser
530 535 540
Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr
545 550 555 560
Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala
565 570 575
Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys
580 585 590
Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met
595 600 605
Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe
610 615 620
Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg
625 630 635 640
Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn
645 650 655
Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg
660 665 670
Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro
675 680 685
Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala
690 695 700
Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His
705 710 715 720
Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp
725 730 735
Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740 745
<![CDATA[ <210> 3]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 3]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaagtgc agcttcaaca atcaggacca ggactcgtca aaccatcaca gaccctctcc 120
ctcacatgtg ccatctccgg ggactccatg ttgagcaatt ccgacacttg gaattggatt 180
agacaaagcc cgtcccgggg tctggaatgg ttgggacgca cctaccaccg gtctacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgcgtcatc cgtgcgggga agagtgtcca tcaacgtgga cacctccaag 300
aaccagtaca gcctgcagct taatgccgtg actcctgagg atacgggcgt ctactactgc 360
gcccgcgtcc gcctgcaaga cgggaacagc tggagcgatg cattcgatgt ctggggccag 420
ggaactatgg tcaccgtgtc gtctgggggc ggtggatcgg gtggcggggg ttcggggggc 480
ggcggctctc agtccgctct tacccaaccg gcctcagcct cggggagccc cggccagagc 540
gtgaccattt cctgcaccgg cacttcatcc gacgtgggcg gctacaacta cgtgtcctgg 600
taccaacagc acccgggaaa ggcccccaag ctcatgatct acgacgtgtc caacaggccc 660
tcgggagtgt ccaaccggtt ctcgggttcg aaatcgggaa acacagccag cctgaccatc 720
agcggactgc aggctgaaga tgaagccgac tactactgct cctcctacac ctcgtcatcc 780
acgctctacg tgttcggcac tggaactcag ctgactgtgc tgggagggggg agggagtgaa 840
attgtgatga cccagtcacc cgccactctt agcctttcac ccggtgagcg cgcaaccctg 900
tcttgcagag cctcccaaga catctcaaaa taccttaatt ggtatcaaca gaagcccgga 960
caggctcctc gccttctgat ctaccacacc agccggctcc attctggaat ccctgccagg 1020
ttcagcggta gcggatctgg gaccgactac accctcacta tcagctcact gcagccagag 1080
gacttcgctg tctatttctg tcagcaaggg aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacagggc 1140
accaagctcg agattaaagg tggaggtggc agcgggaggag gtgggtccgg cggtggagga 1200
agccaggtcc aactccaaga aagcggaccg ggtcttgtga agccatcaga aactctttca 1260
ctgacttgta ctgtgagcgg agtgtctctc cccgattacg gggtgtcttg gatcagacag 1320
ccaccgggga agggtctgga atggattgga gtgatttggg gctctgagac tacttactac 1380
caatcatccc tcaagtcacg cgtcaccatc tcaaaggaca actctaagaa tcaggtgtca 1440
ctgaaactgt catctgtgac cgcagccgac accgccgtgt actattgcgc taagcattac 1500
tattatggcg ggagctacgc aatggattac tggggacagg gtactctggt caccgtgtcc 1560
agcaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccacccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccgggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggagggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agaggaggt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg accccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc-gg 2232
<![CDATA[ <210> 4]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 4]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly
145 150 155 160
Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser
165 170 175
Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val
180 185 190
Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala
195 200 205
Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser
210 215 220
Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile
225 230 235 240
Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr
245 250 255
Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr
260 265 270
Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
290 295 300
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
305 310 315 320
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
325 330 335
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
340 345 350
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
355 360 365
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
370 375 380
Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
405 410 415
Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp
420 425 430
Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp
435 440 445
Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu
450 455 460
Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser
465 470 475 480
Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys
485 490 495
Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly
500 505 510
Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[ <210> 5]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2202]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 5]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
ccccagtccg ctcttaccca accggcctca gcctcgggga gccccggcca gagcgtgacc 120
atttcctgca ccggcacttc atccgacgtg ggcggctaca actacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcacccgg gaaaggcccc caagctcatg atctacgacg tgtccaacag gccctcggga 240
gtgtccaacc ggttctcggg ttcgaaatcg ggaaacacag ccagcctgac catcagcgga 300
ctgcaggctg aagatgaagc cgactactac tgctcctcct acacctcgtc atccacgctc 360
tacgtgttcg gcactggaac tcagctgact gtgctgggcg gaggaggctc cgaagtgcag 420
cttcaacaat caggaccagg actcgtcaaa ccatcacaga ccctctccct cacatgtgcc 480
atctccgggg actccatgtt gagcaattcc gacacttgga attggattag acaaagcccg 540
tcccggggtc tggaatggtt gggacgcacc taccaccggt ctacttggta cgacgactac 600
gcgtcatccg tgcggggaag agtgtccatc aacgtggaca cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
ctgcagctta atgccgtgac tcctgaggat acgggcgtct actactgcgc ccgcgtccgc 720
ctgcaagacg ggaacagctg gagcgatgca ttcgatgtct ggggccaggg aactatggtc 780
accgtgtcgt ctggaggggg agggagtgaa attgtgatga cccagtcacc cgccactctt 840
agcctttcac ccggtgagcg cgcaaccctg tcttgcagag cctcccaaga catctcaaaa 900
taccttaatt ggtatcaaca gaagcccgga caggctcctc gccttctgat ctaccacacc 960
agccggctcc attctggaat ccctgccagg ttcagcggta gcggatctgg gaccgactac 1020
accctcacta tcagctcact gcagccagag gacttcgctg tctatttctg tcagcaaggg 1080
aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacagggc accaagctcg agattaaagg tggaggtggc 1140
agcggaggag gtgggtccgg cggtggagga agccaggtcc aactccaaga aagcggaccg 1200
ggtcttgtga agccatcaga aactctttca ctgacttgta ctgtgagcgg agtgtctctc 1260
cccgattacg gggtgtcttg gatcagacag ccaccgggga agggtctgga atggattgga 1320
gtgatttggg gctctgagac tacttactac caatcatccc tcaagtcacg cgtcaccatc 1380
tcaaaggaca actctaagaa tcaggtgtca ctgaaactgt catctgtgac cgcagccgac 1440
accgccgtgt actattgcgc taagcattac tattatggcg ggagctacgc aatggattac 1500
tggggacagg gtactctggt caccgtgtcc agcaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccaccc 1560
accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct ctgtccctgc gtccggaggc atgtagaccc 1620
gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg 1680
gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt 1740
aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag 1800
actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc cggttcccag aggagggagga aggcggctgc 1860
gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac 1920
cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg agagaggagt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg 1980
agaggacggg accccagaaat gggcgggaag ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg 2040
tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg 2100
gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag 2160
gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc ctgccgcctc gg 2202
<![CDATA[ <210> 6]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 734]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 6]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val
260 265 270
Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp
290 295 300
Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr
305 310 315 320
Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser
325 330 335
Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe
340 345 350
Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly
355 360 365
Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
370 375 380
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro
385 390 395 400
Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser
405 410 415
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro
420 425 430
Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr
435 440 445
Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn
450 455 460
Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp
465 470 475 480
Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr
485 490 495
Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr
500 505 510
Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser
515 520 525
Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly
530 535 540
Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp
545 550 555 560
Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile
565 570 575
Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys
580 585 590
Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys
595 600 605
Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val
610 615 620
Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn
625 630 635 640
Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val
645 650 655
Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg
660 665 670
Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys
675 680 685
Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg
690 695 700
Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys
705 710 715 720
Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
725 730
<![CDATA[ <210> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 7]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cctcagtccg ctctgactca gccggcctca gcttcggggt cccctggtca aagcgtcact 120
atttcctgta ccggaacctc atcagacgtg ggcggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcaccccg gaaaggctcc taagcttatg atctacgacg tgtccaaccg gccgtcagga 240
gtgtccaaca gattctccgg ctccaagagc ggaaacactg ccagcttgac cattagcggc 300
ttgcaggccg aggacgaagc cgactactac tgctctagct acacatcctc gtctaccctc 360
tacgtgtttg gaacggggac ccagctgact gtgctcgggg gtggaggatc agaggtgcaa 420
ctccagcagt ccggtcctgg cctcgtgaaa ccgtcccaaa ccctgtccct gacttgcgcc 480
atctcgggcg actccatgct gtccaattcc gacacctgga actggattag acaatcgcct 540
agccggggac tcgaatggct gggccggacc taccaccggt ccacgtggta tgacgactac 600
gcaagctccg tccggggaag ggtgtccatt aacgtcgata cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
cttcagctga acgctgtgac ccccgaggat accggcgtct actactgtgc aagagtgcga 720
ttgcaggatg gaaactcgtg gtcggacgca ttcgatgtct ggggacaggg aactatggtg 780
accgtgtcct cgggcggagg cgggagcgga ggaggaggct ctggcggagg aggaagcgag 840
attgtcatga ctcagtcccc ggccaacactc tccctgtcac ccggagaaag agcaaccctg 900
agctgcaggg cgtcccagga catctcgaag tacctgaact ggtaccagca gaagcctgga 960
caagcacccc gcctcctgat ctaccacacc tcgcggctgc attcgggaat ccccgccaga 1020
ttctcaggga gcggatcagg aaccgactac accctgacta tctcgagcct gcaaccagag 1080
gatttcgccg tgtacttctg ccagcaagga aacaccctgc cctacacctt tggacaggga 1140
accaagctcg agattaaggg gggtggtgga tcgggagggg gtggatcagg aggaggcggc 1200
tcacaagtcc agctgcaaga atccggtccg ggacttgtga agccgtccga aaccctgtca 1260
ctgacttgca ctgtgtccgg ggtgtcattg cccgactacg gcgtgagctg gattcggcag 1320
ccccctggaa agggatgga atggatcggc gtgatctggg gttcggaaac tacctactat 1380
cagtcctcac tgaagtcccg cgtgaccatc agcaaggata attccaaaaa ccaagtgtct 1440
ctgaagctct ccagcgtcac tgccgccgat actgccgtgt actactgcgc caagcactac 1500
tattacggcg gttcgtacgc catggactac tggggccaag ggacactcgt gaccgtgtca 1560
tccaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccacccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccgggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggagggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agaggaggt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg accccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc-gg 2232
<![CDATA[ <210> 8]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 8]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
260 265 270
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
275 280 285
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
290 295 300
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
305 310 315 320
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
325 330 335
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
340 345 350
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
355 360 365
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
370 375 380
Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
405 410 415
Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp
420 425 430
Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp
435 440 445
Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu
450 455 460
Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser
465 470 475 480
Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys
485 490 495
Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly
500 505 510
Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[ <210> 9]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2232]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 9]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cctcagtccg ctctgactca gccggcctca gcttcggggt cccctggtca aagcgtcact 120
atttcctgta ccggaacctc atcagacgtg ggcggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccaa 180
cagcaccccg gaaaggctcc taagcttatg atctacgacg tgtccaaccg gccgtcagga 240
gtgtccaaca gattctccgg ctccaagagc ggaaacactg ccagcttgac cattagcggc 300
ttgcaggccg aggacgaagc cgactactac tgctctagct acacatcctc gtctaccctc 360
tacgtgtttg gaacggggac ccagctgact gtgctcgggg gtggaggatc agaggtgcaa 420
ctccagcagt ccggtcctgg cctcgtgaaa ccgtcccaaa ccctgtccct gacttgcgcc 480
atctcgggcg actccatgct gtccaattcc gacacctgga actggattag acaatcgcct 540
agccggggac tcgaatggct gggccggacc taccaccggt ccacgtggta tgacgactac 600
gcaagctccg tccggggaag ggtgtccatt aacgtcgata cctccaagaa ccagtacagc 660
cttcagctga acgctgtgac ccccgaggat accggcgtct actactgtgc aagagtgcga 720
ttgcaggatg gaaactcgtg gtcggacgca ttcgatgtct ggggacaggg aactatggtc 780
actgtgtcct ccggcggtgg aggctcgggg gggggcggct caggaggagg cggctcacaa 840
gtccagctgc aagaatccgg tccgggactt gtgaagccgt ccgaaaccct gtcactgact 900
tgcactgtgt ccggggtgtc attgcccgac tacggcgtga gctggattcg gcagccccct 960
ggaaagggat tggaatggat cggcgtgatc tggggttcgg aaactaccta ctatcagtcc 1020
tcactgaagt cccgcgtgac catcagcaag gataattcca aaaaccaagt gtctctgaag 1080
ctctccagcg tcactgccgc cgatactgcc gtgtactact gcgccaagca ctactattac 1140
ggcggttcgt acgccatgga ctactgggga caaggcactc ttgtgactgt gtcaagcggc 1200
ggtggaggga gcggtggggg cggttcagga ggaggcggat cagagatcgt gatgacccaa 1260
tccccagcca ccctgtccct cagccctgga gaaagagcca ccctgagctg ccgggcctcc 1320
caggatatca gcaagtactt gaactggtac caacaaaagc cggggcaggc gccccggctc 1380
ctgatctacc acacctcgcg cctccactca ggtatccccg ccagattctc agggagcggc 1440
tccggtactg actacaccct gactatttcc tcactgcagc cagaggactt tgccgtgtac 1500
ttctgccagc agggaaacac tctgccgtac accttcgggc agggaacgaa gcttgaaatt 1560
aagaccacta ccccagcacc gaggccacccc accccggctc ctaccatcgc ctcccagcct 1620
ctgtccctgc gtccgggaggc atgtagaccc gcagctggtg gggccgtgca tacccggggt 1680
cttgacttcg cctgcgatat ctacatttgg gcccctctgg ctggtacttg cggggtcctg 1740
ctgctttcac tcgtgatcac tctttactgt aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc 1800
tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc 1860
cggttcccag aggagggagga aggcggctgc gaactgcgcg tgaaattcag ccgcagcgca 1920
gatgctccag cctaccagca ggggcagaac cagctctaca acgaactcaa tcttggtcgg 1980
agaggaggt acgacgtgct ggacaagcgg agaggacggg accccagaaat gggcgggaag 2040
ccgcgcagaa agaatcccca agagggcctg tacaacgagc tccaaaagga taagatggca 2100
gaagcctata gcgagattgg tatgaaaggg gaacgcagaa gaggcaaagg ccacgacgga 2160
ctgtaccagg gactcagcac cgccaccaag gacacctatg acgctcttca catgcaggcc 2220
ctgccgcctc-gg 2232
<![CDATA[ <210> 10]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 744]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 10]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
20 25 30
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
35 40 45
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
50 55 60
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
65 70 75 80
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
85 90 95
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
100 105 110
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
115 120 125
Leu Thr Val Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser
130 135 140
Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala
145 150 155 160
Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile
165 170 175
Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His
180 185 190
Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val
195 200 205
Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn
210 215 220
Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg
225 230 235 240
Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
260 265 270
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro
275 280 285
Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser
290 295 300
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro
305 310 315 320
Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr
325 330 335
Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn
340 345 350
Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp
355 360 365
Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr
370 375 380
Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly
385 390 395 400
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile
405 410 415
Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg
420 425 430
Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn
435 440 445
Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His
450 455 460
Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly
465 470 475 480
Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp
485 490 495
Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe
500 505 510
Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
515 520 525
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
530 535 540
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
545 550 555 560
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
565 570 575
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
580 585 590
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
595 600 605
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
610 615 620
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
645 650 655
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
660 665 670
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
675 680 685
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
690 695 700
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
705 710 715 720
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
725 730 735
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
740
<![CDATA[ <210> 11]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 11]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
cccgaagtgc agctgcagca gtcagggcct ggcctggtca agccgtcgca gaccctctcc 120
ctgacatgcg ccattagcgg ggactccatg ctgagcaact cggacacctg gaactggatt 180
cggcagtccc cttcccgggg actcgagtgg ctcggacgca cctaccatcg gagcacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgcctcctc cgtgagaggt cgcgtgtcga tcaacgtgga tacctcgaag 300
aaccagtata gcttgcaact gaacgccgtg acccctgagg ataccggagt gtactattgt 360
gcgagagtca ggctgcaaga cggaaactcc tggtccgacg catttgatgt ctggggacag 420
ggtactatgg tcacggtgtc atctggaggc ggaggatcgc aaagcgccct gactcagccg 480
gcttcggcta gcggttcacc ggggcagtcc gtgactatct cctgcaccgg gacttcctcc 540
gacgtgggag gctacaatta cgtgtcctgg taccagcaac accccggcaa agccccaaag 600
ctgatgatct acgacgtcag caacagaccc agcggagtgt ccaaccggtt cagcggctcc 660
aagtccggca acaccgcctc cctgaccatc aggcgggcttc aggccgaaga tgaggcggat 720
tactactgct cctcgtacac ctcaagctca actctgtacg tgttcggcac cggtactcag 780
ctcaccgtgc tgaccactac cccagcaccg aggccaccca ccccggctcc taccatcgcc 840
tcccagcctc tgtccctgcg tccggaggca tgtagacccg cagctggtgg ggccgtgcat 900
acccggggtc ttgacttcgc ctgcgatatc tacatttggg cccctctggc tggtacttgc 960
ggggtcctgc tgctttcact cgtgatcact ctttactgta agcgcggtcg gaagaagctg 1020
ctgtacatct ttaagcaacc cttcatgagg cctgtgcaga ctactcaaga ggaggacggc 1080
tgttcatgcc ggttcccaga ggaggaggaa ggcggctgcg aactgcgcgt gaaattcagc 1140
cgcagcgcag atgctccagc ctaccagcag gggcagaacc agctctacaa cgaactcaat 1200
cttggtcgga gagaggagta cgacgtgctg gacaagcgga gaggacggga cccagaaatg 1260
ggcgggaagc cgcgcagaaa gaatccccaa gagggcctgt acaacgagct ccaaaaggat 1320
aagatggcag aagcctatag cgagattggt atgaaagggg aacgcagaag aggcaaaggc 1380
cacgacggac tgtaccaggg actcagcacc gccaccaagg acacctatga cgctcttcac 1440
atgcaggccc tgccgcctcg gggaagcgga gctactaact tcagcctgct gaagcaggct 1500
ggagacgtgg aggagaaccc tggacctatg gccttaccag tgaccgcctt gctcctgccg 1560
ctggccttgc tgctccacgc cgccaggccg gaaattgtga tgacccagtc acccgccact 1620
cttagccttt cacccggtga gcgcgcaacc ctgtcttgca gagcctccca agacatctca 1680
aaatacctta attggtatca acagaagccc gcacaggctc ctcgccttct gatctaccac 1740
accagccggc tccatctgg aatccctgcc aggttcagcg gtagcggatc tgggaccgac 1800
tacaccctca ctatcagctc actgcagcca gaggacttcg ctgtctattt ctgtcagcaa 1860
gggaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag ggcaccaagc tcgagattaa aggtggaggt 1920
ggcagcggag gaggtgggtc cggcggtgga ggaagccagg tccaactcca agaaagcgga 1980
ccgggtcttg tgaagccatc agaaactctt tcactgactt gtactgtgag cggagtgtct 2040
ctccccgatt acggggtgtc ttggatcaga cagccaccgg ggaagggtct ggaatggatt 2100
ggagtgattt ggggctctga gactacttac taccaatcat ccctcaagtc acgcgtcacc 2160
atctcaaagg acaactctaa gaatcaggtg tcactgaaac tgtcatctgt gaccgcagcc 2220
gacaccgccg tgtactattg cgctaagcat tactattatg gcgggagcta cgcaatggat 2280
tactggggac agggtactct ggtcaccgtg tccagcacca cgacgccagc gccgcgacca 2340
ccaacaccgg cgcccaccat cgcgtcgcag cccctgtccc tgcgcccaga ggcgtgccgg 2400
ccagcggcgg ggggcgcagt gcacacgagg gggctggact tcgcctgtga tatctacatc 2460
tgggcgccct tggccgggac ttgtggggtc cttctcctgt cactggttat caccctttac 2520
tgcaaacggg gcagaaagaa actcctgtat atattcaaac aaccatttat gagaccagta 2580
caaactactc aagaggaaga tggctgtagc tgccgatttc cagaagaaga agaaggagga 2640
tgtgaactga gagtgaagtt cagcaggagc gcagacgccc ccgcgtacca gcagggccag 2700
aaccagctct ataacgagct caatctagga cgaagagagg agtacgatgt tttggacaag 2760
agacgtggcc gggaccctga gatgggggga aagccgagaa ggaagaaccc tcaggaaggc 2820
ctgtacaatg aactgcagaa agataagatg gcggaggcct acagtgagat tgggatgaaa 2880
ggcgagcgcc ggaggggcaa ggggcacgat ggcctttacc agggtctcag tacagccacc 2940
aaggacacct acgacgccct tcacatgcag gccctgcccc ctcgc 2985
<![CDATA[ <210> 12]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 995]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 12]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro
145 150 155 160
Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr
165 170 175
Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln
180 185 190
Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn
195 200 205
Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn
210 215 220
Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp
225 230 235 240
Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly
245 250 255
Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu
485 490 495
Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro Met Ala Leu
500 505 510
Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu His Ala Ala
515 520 525
Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser
530 535 540
Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser
545 550 555 560
Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu
565 570 575
Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe
580 585 590
Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Ser Leu
595 600 605
Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu
610 615 620
Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly
625 630 635 640
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu
645 650 655
Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu
660 665 670
Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp
675 680 685
Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp
690 695 700
Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr
705 710 715 720
Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser
725 730 735
Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr
740 745 750
Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val
755 760 765
Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala
770 775 780
Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg
785 790 795 800
Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys
805 810 815
Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu
820 825 830
Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu
835 840 845
Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln
850 855 860
Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly
865 870 875 880
Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr
885 890 895
Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg
900 905 910
Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met
915 920 925
Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu
930 935 940
Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys
945 950 955 960
Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu
965 970 975
Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu
980 985 990
Pro Pro Arg
995
<![CDATA[ <210> 13]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 508]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 13]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu
20 25 30
Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp
35 40 45
Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro
50 55 60
Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp
65 70 75 80
Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val
85 90 95
Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro
100 105 110
Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly
115 120 125
Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro
145 150 155 160
Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr
165 170 175
Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln
180 185 190
Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn
195 200 205
Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn
210 215 220
Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp
225 230 235 240
Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly
245 250 255
Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu
485 490 495
Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly
500 505
<![CDATA[ <210> 14]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 487]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 14]]>
Pro Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
Leu His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr
20 25 30
Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln
50 55 60
Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile
65 70 75 80
Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
130 135 140
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
145 150 155 160
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
165 170 175
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
180 185 190
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
210 215 220
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
225 230 235 240
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
245 250 255
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro
260 265 270
Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro
275 280 285
Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu
290 295 300
Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys
305 310 315 320
Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly
325 330 335
Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val
340 345 350
Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp
370 375 380
Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn
385 390 395 400
Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg
405 410 415
Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly
420 425 430
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu
435 440 445
Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu
450 455 460
Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His
465 470 475 480
Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[ <210> 15]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 15]]>
atggccttac cagtgaccgc cttgctcctg ccgctggcct tgctgctcca cgccgccagg 60
ccggaaattg tgatgaccca gtcacccgcc actcttagcc tttcacccgg tgagcgcgca 120
accctgtctt gcagagcctc ccaagacatc tcaaaatacc ttaattggta tcaacagaag 180
cccggacagg ctcctcgcct tctgatctac cacaccagcc ggctccattc tggaatccct 240
gccaggttca gcggtagcgg atctgggacc gactacaccc tcactatcag ctcactgcag 300
ccagaggact tcgctgtcta tttctgtcag caagggaaca ccctgcccta cacctttgga 360
cagggcacca agctcgagat taaaggtgga ggtggcagcg gaggaggtgg gtccggcggt 420
ggaggaagcc aggtccaact ccaagaaagc ggaccgggtc ttgtgaagcc atcagaaact 480
ctttcactga cttgtactgt gagcggagtg tctctccccg attacggggt gtcttggatc 540
agacagccac cggggaaggg tctggaatgg attggagtga tttggggctc tgagactact 600
tactaccaat catccctcaa gtcacgcgtc accatctcaa aggacaactc taagaatcag 660
gtgtcactga aactgtcatc tgtgaccgca gccgacaccg ccgtgtacta ttgcgctaag 720
cattactatt atggcggggag ctacgcaatg gattactggg gacagggtac tctggtcacc 780
gtgtccagca ccacgacgcc agcgccgcga ccaccaacac cggcgcccac catcgcgtcg 840
cagcccctgt ccctgcgccc agaggcgtgc cggccagcgg cggggggcgc agtgcacacg 900
aggggggctgg acttcgcctg tgatatctac atctgggcgc ccttggccgg gacttgtggg 960
gtccttctcc tgtcactggt tatcaccctt tactgcaaac ggggcagaaa gaaactcctg 1020
tatatattca aacaaccatt tatgagacca gtacaaacta ctcaagagga agatggctgt 1080
agctgccgat ttccagaaga agaagaagga ggatgtgaac tgagagtgaa gttcagcagg 1140
agcgcagacg cccccgcgta ccagcagggc cagaaccagc tctataacga gctcaatcta 1200
ggacgaagag aggagtacga tgttttggac aagagacgtg gccgggaccc tgagatgggg 1260
ggaaagccga gaaggaagaa ccctcaggaa ggcctgtaca atgaactgca gaaagataag 1320
atggcggagg cctacagtga gattgggatg aaaggcgagc gccgggagggg caaggggcac 1380
gatggccttt accagggtct cagtacagcc accaaggaca cctacgacgc ccttcacatg 1440
caggccctgc cccctcgcgg aagcggagct actaacttca gcctgctgaa gcaggctgga 1500
gacgtggagg agaaccctgg acctatggcc ctccctgtca ccgccctgct gcttccgctg 1560
gctcttctgc tccacgccgc tcggcccgaa gtgcagctgc agcagtcagg gcctggcctg 1620
gtcaagccgt cgcagaccct ctccctgaca tgcgccatta gcggggactc catgctgagc 1680
aactcggaca cctggaactg gattcggcag tccccttccc ggggactcga gtggctcgga 1740
cgcacctacc atcggagcac ttggtacgac gactacgcct cctccgtgag aggtcgcgtg 1800
tcgatcaacg tggataccctc gaagaaccag tatagcttgc aactgaacgc cgtgacccct 1860
gaggataccg gagtgtacta ttgtgcgaga gtcaggctgc aagacggaaa ctcctggtcc 1920
gacgcatttg atgtctgggg acagggtact atggtcacgg tgtcatctgg aggcggagga 1980
tcgcaaagcg ccctgactca gccggcttcg gctagcggtt caccggggca gtccgtgact 2040
atctcctgca ccgggacttc ctccgacgtg ggaggctaca attacgtgtc ctggtaccag 2100
caacacccccg gcaaagcccc aaagctgatg atctacgacg tcagcaacag accccagcgga 2160
gtgtccaacc ggttcagcgg ctccaagtcc ggcaacaccg cctccctgac catcagcggg 2220
cttcaggccg aagatgaggc ggattactac tgctcctcgt acacctcaag ctcaactctg 2280
tacgtgttcg gcaccggtac tcagctcacc gtgctgacca ctaccccagc accgaggcca 2340
cccaccccgg ctcctaccat cgcctcccag cctctgtccc tgcgtccgga ggcatgtaga 2400
cccgcagctg gtggggccgt gcatacccgg ggtcttgact tcgcctgcga tatctacatt 2460
tgggcccctc tggctggtac ttgcggggtc ctgctgcttt cactcgtgat cactctttac 2520
tgtaagcgcg gtcggaagaa gctgctgtac atctttaagc aacccttcat gaggcctgtg 2580
cagactactc aagaggagga cggctgttca tgccggttcc cagaggagga ggaaggcggc 2640
tgcgaactgc gcgtgaaatt cagccgcagc gcagatgctc cagcctacca gcaggggcag 2700
aaccagctct acaacgaact caatcttggt cggagagagg agtacgacgt gctggacaag 2760
cggagaggac gggacccaga aatgggcggg aagccgcgca gaaagaatcc ccaagagggc 2820
ctgtacaacg agctccaaaa ggataagatg gcagaagcct atagcgagat tggtatgaaa 2880
ggggaacgca gaagaggcaa aggccacgac ggactgtacc agggactcag caccgccacc 2940
aaggacacct atgacgctct tcacatgcag gccctgccgc ctcgg 2985
<![CDATA[ <210> 16]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 995]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 16]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu
485 490 495
Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro Met Ala Leu Pro
500 505 510
Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu His Ala Ala Arg
515 520 525
Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser
530 535 540
Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser
545 550 555 560
Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu
565 570 575
Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr
580 585 590
Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys
595 600 605
Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly
610 615 620
Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser
625 630 635 640
Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser
645 650 655
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser
660 665 670
Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser
675 680 685
Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly
690 695 700
Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly
705 710 715 720
Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu
725 730 735
Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser
740 745 750
Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln
755 760 765
Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala
770 775 780
Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg
785 790 795 800
Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys
805 810 815
Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu
820 825 830
Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu
835 840 845
Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln
850 855 860
Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly
865 870 875 880
Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr
885 890 895
Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg
900 905 910
Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met
915 920 925
Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu
930 935 940
Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys
945 950 955 960
Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu
965 970 975
Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu
980 985 990
Pro Pro Arg
995
<![CDATA[ <210> 17]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 507]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 17]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu
485 490 495
Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly
500 505
<![CDATA[ <210> 18]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 488]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213>]]> Artificial Sequence
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 18]]>
Pro Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
Leu His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly
20 25 30
Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly
35 40 45
Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser
50 55 60
Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr
65 70 75 80
Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn
85 90 95
Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr
100 105 110
Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp
115 120 125
Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met
130 135 140
Val Thr Val Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln
145 150 155 160
Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys
165 170 175
Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr
180 185 190
Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser
195 200 205
Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly
210 215 220
Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala
225 230 235 240
Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe
245 250 255
Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg
260 265 270
Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg
275 280 285
Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly
290 295 300
Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr
305 310 315 320
Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg
325 330 335
Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro
340 345 350
Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu
355 360 365
Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala
370 375 380
Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu
385 390 395 400
Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly
405 410 415
Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu
420 425 430
Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser
435 440 445
Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly
450 455 460
Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu
465 470 475 480
His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[ <210> 19]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 2985]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 19]]>
atggcacttc ccgtcaccgc cctgctgctc ccactcgccc tccttctgca cgccgcccgc 60
cccgaagtgc agctgcagca gtcaggaccg ggcctggtca aaccttcgca gactctgtcc 120
ctgacttgcg ctataagcgg ggactccatg ctgagcaatt cggacacttg gaactggatt 180
cgccaaagcc ccagccgggg tctggaatgg ctgggaagga cctaccatcg ctctacttgg 240
tacgacgact acgccagctc cgtgcgagga cgcgtgtcca tcaacgtgga cacctccaag 300
aaccagtact cgcttcaact caacgcagtg accccctgaag ataccggagt ctactattgc 360
gcccgcgtgc ggctccagga cgggaactcc tggtcggacg ctttcgatgt ctggggacag 420
ggcactatgg tcaccgtcag ctccggcggc ggcggtagcc aatcggcgct gacacagccg 480
gcttccgcct cgggatcgcc tggacagtcg gtgaccatct cgtgcactgg aacctcctcc 540
gacgtgggcg gctacaatta tgtgtcatgg taccagcagc acccgggaaa ggcccctaag 600
ctgatgatct acgacgtgtc caatagacct agcggggtgt caaacagatt ctccggatcc 660
aaatccggaa acactgcctc cctgaccatt tccggactgc aggccgagga cgaagccgat 720
tactactgct cctcttacac ctcctcatcc accctctacg tgtttgggac tgggacccag 780
ctgaccgtcc tcactaccac cccggccccg cggcccccta caccggcacc gactattgcc 840
agccagcctc tctcgctgcg gccggaggcc tgccgcccag ccgccggcgg agccgtgcac 900
acccgcggtc tggacttcgc gtgcgatatc tacatctggg ctccgctggc cgggacttgt 960
ggcgtgctgc tgctgtctct ggtcatcaca ctgtactgca agcgcggaag aaagaagctg 1020
ctctacatct tcaagcaacc cttcatgcgg cctgtgcaga ccaccccagga agaggatggc 1080
tgctcctgcc ggttcccgga ggaagaagag ggcggatgcg aactgcgcgt gaagttcagc 1140
cgaagcgccg acgccccggc ctaccagcag ggccagaacc aactgtacaa cgaactcaac 1200
ctgggtcgga gagaagagta cgacgtgctg gacaaaagac gcggcaggga ccccgagatg 1260
ggcggaaagc ctcgccgcaa gaacccgcag gagggcctct acaacgagct gcagaaggac 1320
aagatggccg aagcctactc agagatcggc atgaaggggg agcggaggcg cgggaagggc 1380
cacgacggtt tgtaccaagg actttccact gcgaccaagg acacctacga tgccctccat 1440
atgcaagccc tgccgccccg gggttccgga gctaccaact tctcgctgtt gaagcaggcc 1500
ggagatgtcg aggaaaaccc gggacctatg gccctgccag tgaccgcgct cctgctgccc 1560
ctggctctgc tgcttcacgc ggcccggcct gagattgtga tgactcagag cccggcgacc 1620
ctgtccctgt cccccgggga gagagcaacc ctgtcgtgcc gggcctccca agacatctca 1680
aagtacctca attggtatca gcagaagcca ggacaggctc cacggttgct gatctaccac 1740
acttcgagac tgcactcagg aatccccgcg cggttttccg gttccggctc cgggaccgac 1800
tacaccctga ccatcagctc gctccagcct gaggatttcg cagtgtactt ctgtcagcaa 1860
ggaaacaccc ttccataacac cttcggacag ggtaccaagc tggaaatcaa gggaggagga 1920
ggatctgggg gcggtggttc cggaggcggt ggaagccaag tgcagctcca ggaaagcgga 1980
cccgggctgg tcaagccgag cgaaaccctc tcactgactt gtactgtgtc cggagtgtcc 2040
ctgcctgact atggagtgtc ctggatccga cagccccccg gaaagggtct ggagtggatt 2100
ggggtcatct ggggctccga aactacctac taccagagca gcctcaagag ccgggtcacc 2160
atttcaaagg ataactccaa gaatcaagtg tccctgaagc tgtcctcagt gacagccgca 2220
gacaccgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac tactactacg gaggctccta cgcaatggac 2280
tactggggac aaggcacttt ggtcactgtg tcaagcacca ccaccccctgc gcctcggcct 2340
cctaccccgg ctcccactat cgcgagccag ccgctgagcc tgcggcctga ggcttgccga 2400
ccggccgctg gcggcgccgt gcatactcgg ggcctcgact ttgcctgtga catctacatc 2460
tgggcccccc tggccggaac gtgcggagtg ctgctgctgt cgctggtcat taccctgtat 2520
tgcaaacgcg gaaggaagaa gctgttgtac attttcaagc agcccttcat gcgcccggtg 2580
caaactactc aggaggaaga tggctgttcc tgtcggttcc ccgaagagga agaaggcggc 2640
tgcgagttga gggtcaagtt ctcccggtcc gccgatgctc ccgcctacca acaggggcag 2700
aaccagcttt ataacgaact gaacctgggc aggagggagg aatatgatgt gttggataag 2760
cgccggggcc gggacccaga aatgggggga aagcccagaa gaaagaaccc tcaagaggga 2820
ctttacaacg aattgcagaa agacaaaatg gccgaggcct actccgagat tgggatgaag 2880
ggcgaaagac ggagaggaaa ggggcacgac gggctctacc agggactcag caccgccacc 2940
aaagatacct acgacgccct gcatatgcag gcgctgccgc cgcgc 2985
<![CDATA[ <210> 20]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 20]]>
Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 21]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 18]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 21]]>
Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val
1 5 10 15
Arg Gly
<![CDATA[ <210> 22]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 22]]>
Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[ <210> 23]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 23]]>
Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 24]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 24]]>
Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 25]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 25]]>
Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 26]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 26]]>
Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 27]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 17]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>]]> PRT
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial]]> sequence
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 27]]>
Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp
1 5 10 15
Val
<![CDATA[ <210> 28]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 14]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 28]]>
Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 29]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 29]]>
Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 30]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> ]]>11
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 30]]>
Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 31]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 31]]>
Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 32]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 3]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 32]]>
Asp Val Ser
1
<![CDATA[ <210> 33]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 8]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 33]]>
Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 34]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 34]]>
Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 35]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 10]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 35]]>
Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 36]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 36]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[ <210> 37]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 37]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[ <210> 38]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 16]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 38]]>
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[ <210> 39]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 12]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 39]]>
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 40]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 11]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 40]]>
Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn
1 5 10
<![CDATA[ <210> 41]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 41]]>
His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 42]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 9]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 42]]>
Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 43]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 43]]>
gaaattgtga tgacccagtc acccgccact cttagccttt cacccggtga gcgcgcaacc 60
ctgtcttgca gagcctccca agacatctca aaatacctta attggtatca acagaagccc 120
ggacaggctc ctcgccttct gatctaccac accagccggc tccatctgg aatccctgcc 180
aggttcagcg gtagcggatc tgggaccgac tacaccctca ctatcagctc actgcagcca 240
gaggacttcg ctgtctattt ctgtcagcaa gggaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag 300
ggcaccaagc tcgagattaa aggtggaggt ggcagcggag gaggtgggtc cggcggtgga 360
ggaagccagg tccaactcca agaaagcgga ccgggtcttg tgaagccatc agaaactctt 420
tcactgactt gtactgtgag cggagtgtct ctccccgatt acggggtgtc ttggatcaga 480
cagccaccgg ggaagggtct ggaatggatt ggagtgattt ggggctctga gactacttac 540
taccaatcat ccctcaagtc acgcgtcacc atctcaaagg acaactctaa gaatcaggtg 600
tcactgaaac tgtcatctgt gaccgcagcc gacaccgccg tgtactattg cgctaagcat 660
tactattatg gcgggagcta cgcaatggat tactggggac agggtactct ggtcaccgtg 720
tccagc 726
<![CDATA[ <210> 44]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 44]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[ <210> 45]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 45]]>
gagattgtca tgactcagtc cccggccaca ctctccctgt cacccggaga aagagcaacc 60
ctgagctgca gggcgtccca ggacatctcg aagtacctga actggtacca gcagaagcct 120
ggacaagcac cccgcctcct gatctaccac acctcgcggc tgcattcggg aatccccgcc 180
agattctcag ggagcggatc aggaaccgac tacaccctga ctatctcgag cctgcaacca 240
gaggatttcg ccgtgtactt ctgccagcaa ggaaacaccc tgccctacac ctttggacag 300
ggaaccaagc tcgagattaa gggggtggt ggatcgggag ggggtggatc aggaggaggc 360
ggctcacaag tccagctgca agaatccggt ccgggacttg tgaagccgtc cgaaaccctg 420
tcactgactt gcactgtgtc cggggtgtca ttgcccgact acggcgtgag ctggattcgg 480
cagccccctg gaaagggatt ggaatggatc ggcgtgatct ggggttcgga aactacctac 540
tatcagtcct cactgaagtc ccgcgtgacc atcagcaagg ataattccaa aaaccaagtg 600
tctctgaagc tctccagcgt cactgccgcc gatactgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac 660
tactattacg gcggttcgta cgccatggac tactggggcc aagggacact cgtgaccgtg 720
tcatcc 726
<![CDATA[ <210> 46]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 46]]>
caagtccagc tgcaagaatc cggtccggga cttgtgaagc cgtccgaaac cctgtcactg 60
acttgcactg tgtccggggt gtcattgccc gactacggcg tgagctggat tcggcagccc 120
cctggaaagg gattggaatg gatcggcgtg atctggggtt cggaaactac ctactatcag 180
tcctcactga agtcccgcgt gaccatcagc aaggataatt ccaaaaacca agtgtctctg 240
aagctctcca gcgtcactgc cgccgatact gccgtgtact actgcgccaa gcactactat 300
tacggcggtt cgtacgccat ggactactgg ggacaaggca ctcttgtgac tgtgtcaagc 360
ggcggtggag ggagcggtgg gggcggttca ggaggaggcg gatcagagat cgtgatgacc 420
caatccccag ccaccctgtc cctcagccct ggagaaagag ccaccctgag ctgccgggcc 480
tcccaggata tcagcaagta cttgaactgg taccaacaaa agccggggca ggcgccccgg 540
ctcctgatct accacacctc gcgcctccac tcaggtatcc ccgccagatt ctcagggagc 600
ggctccggta ctgactacac cctgactatt tcctcactgc agccagagga ctttgccgtg 660
tacttctgcc agcagggaaa cactctgccg tacaccttcg ggcagggaac gaagcttgaa 720
attaag 726
<![CDATA[ <210> 47]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 47]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[ <210> 48]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 726]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 48]]>
gagattgtga tgactcagag cccggcgacc ctgtccctgt cccccgggga gagagcaacc 60
ctgtcgtgcc gggcctccca agacatctca aagtacctca attggtatca gcagaagcca 120
ggacaggctc cacggttgct gatctaccac acttcgagac tgcactcagg aatccccgcg 180
cggttttccg gttccggctc cgggaccgac tacaccctga ccatcagctc gctccagcct 240
gaggatttcg cagtgtactt ctgtcagcaa ggaaacaccc ttccatacac cttcggacag 300
ggtaccaagc tggaaatcaa gggaggagga ggatctgggg gcggtggttc cggaggcggt 360
ggaagccaag tgcagctcca ggaaagcgga cccgggctgg tcaagccgag cgaaaccctc 420
tcactgactt gtactgtgtc cggagtgtcc ctgcctgact atggagtgtc ctggatccga 480
cagccccccg gaaagggtct ggagtggatt ggggtcatct ggggctccga aactacctac 540
taccagagca gcctcaagag ccgggtcacc atttcaaagg ataactccaa gaatcaagtg 600
tccctgaagc tgtcctcagt gacagccgca gacaccgccg tgtactactg cgccaagcac 660
tactactacg gaggctccta cgcaatggac tactggggac aaggcacttt ggtcactgtg 720
tcaagc 726
<![CDATA[ <210> 49]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 49]]>
gaagtgcagc tgcagcagtc agggcctggc ctggtcaagc cgtcgcagac cctctccctg 60
acatgcgcca ttagcgggga ctccatgctg agcaactcgg acacctggaa ctggattcgg 120
cagtccccctt cccggggact cgagtggctc ggacgcacct accatcggag cacttggtac 180
gacgactacg cctcctccgt gagaggtcgc gtgtcgatca acgtggatac ctcgaagaac 240
cagtatagct tgcaactgaa cgccgtgacc cctgaggata ccggagtgta ctattgtgcg 300
agagtcaggc tgcaagacgg aaactcctgg tccgacgcat ttgatgtctg gggacagggt 360
actatggtca cggtgtcatc tggaggcgga ggatcgcaaa gcgccctgac tcagccggct 420
tcggctagcg gttcaccggg gcagtccgtg actatctcct gcaccgggac ttcctccgac 480
gtgggaggct acaattacgt gtcctggtac cagcaacacc ccggcaaagc cccaaagctg 540
atgatctacg acgtcagcaa cagacccagc ggagtgtcca accggttcag cggctccaag 600
tccggcaaca ccgcctccct gaccatcagc gggcttcagg ccgaagatga ggcggattac 660
tactgctcct cgtacacctc aagctcaact ctgtacgtgt tcggcaccgg tactcagctc 720
accgtgctg 729
<![CDATA[ <210> 50]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 243]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 50]]>
Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn
20 25 30
Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu
35 40 45
Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala
50 55 60
Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn
65 70 75 80
Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val
85 90 95
Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp
100 105 110
Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly
130 135 140
Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Ser Asp
145 150 155 160
Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys
165 170 175
Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val
180 185 190
Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr
195 200 205
Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser
210 215 220
Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu
225 230 235 240
Thr Val Leu
<![CDATA[ <210> 51]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 51]]>
gaagtgcagc tgcagcagtc aggaccgggc ctggtcaaac cttcgcagac tctgtccctg 60
acttgcgcta taagcgggga ctccatgctg agcaattcgg acacttggaa ctggattcgc 120
caaagcccca gccggggtct ggaatggctg ggaaggacct accatcgctc tacttggtac 180
gacgactacg ccagctccgt gcgaggacgc gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac 240
cagtactcgc ttcaactcaa cgcagtgacc cctgaagata ccggagtcta ctattgcgcc 300
cgcgtgcggc tccaggacgg gaactcctgg tcggacgctt tcgatgtctg gggacagggc 360
actatggtca ccgtcagctc cggcggcggc ggtagccaat cggcgctgac acagccggct 420
tccgcctcgg gatcgcctgg acagtcggtg accatctcgt gcactggaac ctcctccgac 480
gtgggcggct acaattatgt gtcatggtac cagcagcacc cgggaaaggc ccctaagctg 540
atgatctacg acgtgtccaa tagacctagc ggggtgtcaa acagattctc cggatccaaa 600
tccggaaaca ctgcctccct gaccatttcc ggactgcagg ccgaggacga agccgattac 660
tactgctcct cttacacctc ctcatccacc ctctacgtgtttgggactgg gacccagctg 720
accgtcctc 729
<![CDATA[ <210> 52]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 759]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 52]]>
gaagtgcagc ttcaacaatc aggaccagga ctcgtcaaac catcacagac cctctccctc 60
acatgtgcca tctccgggga ctccatgttg agcaattccg acacttggaa ttggattaga 120
caaagcccgt cccggggtct ggaatggttg ggacgcacct accaccggtc tacttggtac 180
gacgactacg cgtcatccgt gcggggaaga gtgtccatca acgtggacac ctccaagaac 240
cagtacagcc tgcagcttaa tgccgtgact cctgaggata cgggcgtcta ctactgcgcc 300
cgcgtccgcc tgcaagacgg gaacagctgg agcgatgcat tcgatgtctg gggccaggga 360
actatggtca ccgtgtcgtc tgggggcggt ggatcgggtg gcgggggttc ggggggcggc 420
ggctctcagt ccgctcttac ccaaccggcc tcagcctcgg ggagccccgg ccagagcgtg 480
accatttcct gcaccggcac ttcatccgac gtgggcggct acaactacgt gtcctggtac 540
caacagcacc cgggaaaggc ccccaagctc atgatctacg acgtgtccaa caggccctcg 600
ggagtgtcca accggttctc gggttcgaaa tcgggaaaca cagccagcct gaccatcagc 660
ggactgcagg ctgaagatga agccgactac tactgctcct cctacacctc gtcatccacg 720
ctctacgtgt tcggcactgg aactcagctg actgtgctg 759
<![CDATA[ <210> 53]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 253]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 53]]>
Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Gln
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser Met Leu Ser Asn
20 25 30
Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser Arg Gly Leu Glu
35 40 45
Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr Asp Asp Tyr Ala
50 55 60
Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp Thr Ser Lys Asn
65 70 75 80
Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu Asp Thr Gly Val
85 90 95
Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn Ser Trp Ser Asp
100 105 110
Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Ser
130 135 140
Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln Ser Val
145 150 155 160
Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr Asn Tyr
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu Met Ile
180 185 190
Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe Ser Gly
195 200 205
Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu Gln Ala
210 215 220
Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser Ser Ser Thr
225 230 235 240
Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu
245 250
<![CDATA[ <210> 54]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 54]]>
cagtccgctc ttacccaacc ggcctcagcc tcggggagcc ccggccagag cgtgaccatt 60
tcctgcaccg gcacttcatc cgacgtgggc ggctacaact acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
cacccgggaa aggcccccaa gctcatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaacaggcc ctcgggagtg 180
tccaaccggt tctcgggttc gaaatcggga aacacagcca gcctgaccat cagcggactg 240
caggctgaag atgaagccga ctactactgc tcctcctaca cctcgtcatc cacgctctac 300
gtgttcggca ctggaactca gctgactgtg ctgggcggag gaggctccga agtgcagctt 360
caacaatcag gaccaggact cgtcaaacca tcacagaccc tctccctcac atgtgccatc 420
tccggggact ccatgttgag caattccgac acttggaatt ggattagaca aagcccgtcc 480
cggggtctgg aatggttggg acgcacctac caccggtcta cttggtacga cgactacgcg 540
tcatccgtgc ggggaagagt gtccatcaac gtggacacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctg 600
cagcttaatg ccgtgactcc tgaggatacg ggcgtctact actgcgcccg cgtccgcctg 660
caagacggga acagctggag cgatgcattc gatgtctggg gccagggaac tatggtcacc 720
gtgtcgtct 729
<![CDATA[ <210> 55]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 243]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 55]]>
Gln Ser Ala Leu Thr Gln Pro Ala Ser Ala Ser Gly Ser Pro Gly Gln
1 5 10 15
Ser Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Thr Gly Thr Ser Ser Asp Val Gly Gly Tyr
20 25 30
Asn Tyr Val Ser Trp Tyr Gln Gln His Pro Gly Lys Ala Pro Lys Leu
35 40 45
Met Ile Tyr Asp Val Ser Asn Arg Pro Ser Gly Val Ser Asn Arg Phe
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Lys Ser Gly Asn Thr Ala Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Gly Leu
65 70 75 80
Gln Ala Glu Asp Glu Ala Asp Tyr Tyr Cys Ser Ser Tyr Thr Ser Ser
85 90 95
Ser Thr Leu Tyr Val Phe Gly Thr Gly Thr Gln Leu Thr Val Leu Gly
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Val Gln Leu Gln Gln Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val
115 120 125
Lys Pro Ser Gln Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Ala Ile Ser Gly Asp Ser
130 135 140
Met Leu Ser Asn Ser Asp Thr Trp Asn Trp Ile Arg Gln Ser Pro Ser
145 150 155 160
Arg Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Arg Thr Tyr His Arg Ser Thr Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Asp Asp Tyr Ala Ser Ser Val Arg Gly Arg Val Ser Ile Asn Val Asp
180 185 190
Thr Ser Lys Asn Gln Tyr Ser Leu Gln Leu Asn Ala Val Thr Pro Glu
195 200 205
Asp Thr Gly Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Arg Val Arg Leu Gln Asp Gly Asn
210 215 220
Ser Trp Ser Asp Ala Phe Asp Val Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Met Val Thr
225 230 235 240
Val Ser Ser
<![CDATA[ <210> 56]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 56]]>
cagtccgctc tgactcagcc ggcctcagct tcggggtccc ctggtcaaag cgtcactatt 60
tcctgtaccg gaacctcatc agacgtgggc ggctacaatt acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
caccccggaa aggctcctaa gcttatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaaccggcc gtcaggagtg 180
tccaacagat tctccggctc caagagcgga aacactgcca gcttgaccat tagcggcttg 240
caggccgagg acgaagccga ctactactgc tctagctaca catcctcgtc taccctctac 300
gtgtttggaa cggggaccca gctgactgtg ctcgggggtg gaggatcaga ggtgcaactc 360
cagcagtccg gtcctggcct cgtgaaaccg tcccaaaccc tgtccctgac ttgcgccatc 420
tcgggcgact ccatgctgtc caattccgac acctggaact ggattagaca atcgcctagc 480
cggggactcg aatggctggg ccggacctac caccggtcca cgtggtatga cgactacgca 540
agctccgtcc ggggaagggt gtccattaac gtcgatacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctt 600
cagctgaacg ctgtgacccc cgaggatacc ggcgtctact actgtgcaag agtgcgattg 660
caggatggaa actcgtggtc ggacgcattc gatgtctggg gacagggaac tatggtgacc 720
gtgtcctcg 729
<![CDATA[ <210> 57]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 729]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 57]]>
cagtccgctc tgactcagcc ggcctcagct tcggggtccc ctggtcaaag cgtcactatt 60
tcctgtaccg gaacctcatc agacgtgggc ggctacaatt acgtgtcctg gtaccaacag 120
caccccggaa aggctcctaa gcttatgatc tacgacgtgt ccaaccggcc gtcaggagtg 180
tccaacagat tctccggctc caagagcgga aacactgcca gcttgaccat tagcggcttg 240
caggccgagg acgaagccga ctactactgc tctagctaca catcctcgtc taccctctac 300
gtgtttggaa cggggaccca gctgactgtg ctcgggggtg gaggatcaga ggtgcaactc 360
cagcagtccg gtcctggcct cgtgaaaccg tcccaaaccc tgtccctgac ttgcgccatc 420
tcgggcgact ccatgctgtc caattccgac acctggaact ggattagaca atcgcctagc 480
cggggactcg aatggctggg ccggacctac caccggtcca cgtggtatga cgactacgca 540
agctccgtcc ggggaagggt gtccattaac gtcgatacct ccaagaacca gtacagcctt 600
cagctgaacg ctgtgacccc cgaggatacc ggcgtctact actgtgcaag agtgcgattg 660
caggatggaa actcgtggtc ggacgcattc gatgtctggg gacagggaac tatggtcact 720
gtgtcctcc 729
<![CDATA[ <210> 58]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 58]]>
atggccctcc ctgtcaccgc cctgctgctt ccgctggctc ttctgctcca cgccgctcgg 60
ccc 63
<![CDATA[ <210> 59]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 21]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 59]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro
20
<![CDATA[ <210> 60]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 60]]>
atggccctgc ccgtgactgc gctcctgctt ccgttggccc tgctcctgca tgccgccaga 60
cct 63
<![CDATA[ <210> 61]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 61]]>
atggccttac cagtgaccgc cttgctcctg ccgctggcct tgctgctcca cgccgccagg 60
ccg 63
<![CDATA[ <210> 62]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 62]]>
atggcacttc ccgtcaccgc cctgctgctc ccactcgccc tccttctgca cgccgcccgc 60
ccc 63
<![CDATA[ <210> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 63]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 63]]>
atggccctgc cagtgaccgc gctcctgctg cccctggctc tgctgcttca cgcggcccgg 60
cct 63
<![CDATA[ <210> 64]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 64]]>
accactaccc cagcaccgag gccaccccacc ccggctccta ccatcgcctc ccagcctctg 60
tccctgcgtc cggaggcatg tagacccgca gctggtgggg ccgtgcatac ccggggtctt 120
gacttcgcct gcgatatcta catttgggcc cctctggctg gtacttgcgg ggtcctgctg 180
ctttcactcg tgatcactct ttactgt 207
<![CDATA[ <210> 65]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 69]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 65]]>
Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala
1 5 10 15
Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly
20 25 30
Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile
35 40 45
Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val
50 55 60
Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys
65
<![CDATA[ <210> 66]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 66]]>
actaccaccc cggccccgcg gccccctaca ccggcaccga ctattgccag ccagcctctc 60
tcgctgcggc cggaggcctg ccgcccagcc gccggcggag ccgtgcacac ccgcggtctg 120
gacttcgcgt gcgatatcta catctgggct ccgctggccg ggacttgtgg cgtgctgctg 180
ctgtctctgg tcatcacact gtactgc 207
<![CDATA[ <210> 67]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 67]]>
accacgacgc cagcgccgcg accaccaaca ccggcgccca ccatcgcgtc gcagcccctg 60
tccctgcgcc cagaggcgtg ccggccagcg gcggggggcg cagtgcacac gagggggctg 120
gacttcgcct gtgatatcta catctgggcg cccttggccg ggacttgtgg ggtccttctc 180
ctgtcactgg ttatcaccct ttactgc 207
<![CDATA[ <210> 68]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 207]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 68]]>
accacccaccc ctgcgcctcg gcctcctacc ccggctccca ctatcgcgag ccagccgctg 60
agcctgcggc ctgaggcttg ccgaccggcc gctggcggcg ccgtgcatac tcggggcctc 120
gactttgcct gtgacatcta catctgggcc cccctggccg gaacgtgcgg agtgctgctg 180
ctgtcgctgg tcattaccct gtattgc 207
<![CDATA[ <210> 69]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 69]]>
aagcgcggtc ggaagaagct gctgtacatc tttaagcaac ccttcatgag gcctgtgcag 60
actactcaag aggaggacgg ctgttcatgc cggttcccag aggagggagga aggcggctgc 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[ <210> 70]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 42]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 70]]>
Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met
1 5 10 15
Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe
20 25 30
Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu
35 40
<![CDATA[ <210> 71]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 71]]>
aaacggggca gaaagaaact cctgtatata ttcaaacaac catttatgag accagtacaa 60
actactcaag aggaagatgg ctgtagctgc cgatttccag aagaagaaga aggaggatgt 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[ <210> 72]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 72]]>
aagcgcggaa gaaagaagct gctctacatc ttcaagcaac ccttcatgcg gcctgtgcag 60
accacccagg aagaggatgg ctgctcctgc cggttcccgg aggaagaaga gggcggatgc 120
gaactg 126
<![CDATA[ <210> 73]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 126]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 73]]>
aaacgcggaa ggaagaagct gttgtacatt ttcaagcagc ccttcatgcg cccggtgcaa 60
actactcagg aggaagatgg ctgttcctgt cggttccccg aagaggaaga aggcggctgc 120
gagttg 126
<![CDATA[ <210> 74]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 74]]>
cgcgtgaaat tcagccgcag cgcagatgct ccagcctacc agcaggggca gaaccagctc 60
tacaacgaac tcaatcttgg tcggagagag gagtacgacg tgctggacaa gcggagagga 120
cgggacccag aaatgggcgg gaagccgcgc agaaagaatc cccaagaggg cctgtacaac 180
gagctccaaa aggtaagat ggcagaagcc tatagcgaga ttggtatgaa agggggaacgc 240
agaagaggca aaggccacga cggactgtac cagggactca gcaccgccac caaggacacc 300
tatgacgctc ttcacatgca ggccctgccg cctcgg 336
<![CDATA[ <210> 75]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 112]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 75]]>
Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly
1 5 10 15
Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr
20 25 30
Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys
35 40 45
Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys
50 55 60
Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg
65 70 75 80
Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala
85 90 95
Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
100 105 110
<![CDATA[ <210> 76]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 76]]>
agagtgaagt tcagcaggag cgcagacgcc cccgcgtacc agcagggcca gaaccagctc 60
tataacgagc tcaatctagg acgaagagag gagtacgatg ttttggacaa gagacgtggc 120
cgggaccctg agatgggggg aaagccgaga aggaagaacc ctcaggaagg cctgtacaat 180
gaactgcaga aagataagat ggcggaggcc tacagtgaga ttgggatgaa aggcgagcgc 240
cggaggggca aggggcacga tggcctttac cagggtctca gtacagccac caaggacacc 300
tacgacgccc ttcacatgca ggccctgccc cctcgc 336
<![CDATA[ <210> 77]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 77]]>
cgcgtgaagt tcagccgaag cgccgacgcc ccggcctacc agcagggcca gaaccaactg 60
tacaacgaac tcaacctggg tcggagagaa gagtacgacg tgctggacaa aagacgcggc 120
agggaccccg agatgggcgg aaagcctcgc cgcaagaacc cgcaggaggg cctctacaac 180
gagctgcaga aggacaagat ggccgaagcc tactcagaga tcggcatgaa gggggagcgg 240
aggcgcggga agggccacga cggtttgtac caaggacttt ccactgcgac caaggacacc 300
tacgatgccc tccatatgca agccctgccg ccccgg 336
<![CDATA[ <210> 78]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 336]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 78]]>
agggtcaagt tctcccggtc cgccgatgct cccgcctacc aacaggggca gaaccagctt 60
tataacgaac tgaacctggg caggagggag gaatatgatg tgttggataa gcgccggggc 120
cgggacccag aaatgggggg aaagccccaga agaaagaacc ctcaagagggg actttacaac 180
gaattgcaga aagacaaaat ggccgaggcc tactccgaga ttgggatgaa gggcgaaaga 240
cggagaggaa aggggcacga cgggctctac cagggactca gcaccgccac caaagatacc 300
tacgacgccc tgcatatgca ggcgctgccg ccgcgc 336
<![CDATA[ <210> 79]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 21]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 79]]>
ttggcagaag ccgccgcgaa a 21
<![CDATA[ <210> 80]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 7]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 80]]>
Leu Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Lys
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 81]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 81]]>
ggtggaggtg gcagcggagg aggtgggtcc ggcggtggag gaagc 45
<![CDATA[ <210> 82]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 82]]>
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
1 5 10 15
<![CDATA[ <210> 83]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 83]]>
ggcggaggcg ggagcggagg aggaggctct ggcggaggag gaagc 45
<![CDATA[ <210> 84]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 45]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 84]]>
ggcggtggag gctcgggggg gggcggctca ggaggaggcg gctca 45
<![CDATA[ <210> 85]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 66]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 85]]>
ggaagcggag ctactaactt cagcctgctg aagcaggctg gagacgtgga ggagaaccct 60
ggacct 66
<![CDATA[ <210> 86]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 22]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 86]]>
Gly Ser Gly Ala Thr Asn Phe Ser Leu Leu Lys Gln Ala Gly Asp Val
1 5 10 15
Glu Glu Asn Pro Gly Pro
20
<![CDATA[ <210> 87]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 66]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 87]]>
ggttccggag ctaccaactt ctcgctgttg aagcaggccg gagatgtcga ggaaaacccg 60
ggacct 66
<![CDATA[ <210> 88]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 15]]>
<![CDATA[ <212>DNA]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic polynucleotides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 88]]>
ggtggaggtg gcagc 15
<![CDATA[ <210> ]]>89
<![CDATA[ <211> 5]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 89]]>
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
1 5
<![CDATA[ <210> 90]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 90]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[ <210> 91]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 271]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 91]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser His His His His His His His His His His His
260 265 270
<![CDATA[ <210> 92]]>
<![CDATA[ <211>]]> 486
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 92]]>
Met Ala Leu Pro Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Leu Pro Leu Ala Leu Leu Leu
1 5 10 15
His Ala Ala Arg Pro Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu
20 25 30
Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln
35 40 45
Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala
50 55 60
Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro
65 70 75 80
Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile
85 90 95
Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly
100 105 110
Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
115 120 125
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
130 135 140
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
165 170 175
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
180 185 190
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
195 200 205
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
210 215 220
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
225 230 235 240
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
245 250 255
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro
260 265 270
Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu
275 280 285
Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp
290 295 300
Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly
305 310 315 320
Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg
325 330 335
Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln
340 345 350
Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu
355 360 365
Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala
370 375 380
Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu
385 390 395 400
Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp
405 410 415
Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu
420 425 430
Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile
435 440 445
Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr
450 455 460
Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met
465 470 475 480
Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[ <210> 93]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 465]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 93]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser Thr Thr Thr Thr Pro Ala Pro Arg Pro Pro Thr Pro Ala Pro Thr
245 250 255
Ile Ala Ser Gln Pro Leu Ser Leu Arg Pro Glu Ala Cys Arg Pro Ala
260 265 270
Ala Gly Gly Ala Val His Thr Arg Gly Leu Asp Phe Ala Cys Asp Ile
275 280 285
Tyr Ile Trp Ala Pro Leu Ala Gly Thr Cys Gly Val Leu Leu Leu Ser
290 295 300
Leu Val Ile Thr Leu Tyr Cys Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr
305 310 315 320
Ile Phe Lys Gln Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu
325 330 335
Asp Gly Cys Ser Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu
340 345 350
Leu Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln
355 360 365
Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu
370 375 380
Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly
385 390 395 400
Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln
405 410 415
Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu
420 425 430
Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr
435 440 445
Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro
450 455 460
Arg
465
<![CDATA[ <210> 94]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 94]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[ <210> 95]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 95]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 96]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 96]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 97]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 97]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Ser Ser Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 98]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 98]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Gln Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 99]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 99]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln
115 120 125
Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr
130 135 140
Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly
145 150 155 160
Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly
165 170 175
Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser
180 185 190
Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys
195 200 205
Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys
210 215 220
His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly
225 230 235 240
Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 100]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 247]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 100]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met
130 135 140
Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr
145 150 155 160
Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr
165 170 175
Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser
180 185 190
Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly
195 200 205
Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala
210 215 220
Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln
225 230 235 240
Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 101]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 101]]>
Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly
1 5 10 15
Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Lys Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser
100 105 110
Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu
115 120 125
Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys
130 135 140
Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg
145 150 155 160
Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser
165 170 175
Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser
180 185 190
Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr
195 200 205
Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly
210 215 220
Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val
225 230 235 240
Ser Ser
<![CDATA[ <210> 102]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 242]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 102]]>
Gln Val Gln Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Lys Pro Ser Glu
1 5 10 15
Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr
20 25 30
Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Gly Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Ile
35 40 45
Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ser Leu Lys
50 55 60
Ser Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Asn Gln Val Ser Leu
65 70 75 80
Lys Leu Ser Ser Val Thr Ala Ala Asp Thr Ala Val Tyr Tyr Cys Ala
85 90 95
Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln
100 105 110
Gly Thr Leu Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly
115 120 125
Gly Ser Gly Gly Gly Gly Ser Glu Ile Val Met Thr Gln Ser Pro Ala
130 135 140
Thr Leu Ser Leu Ser Pro Gly Glu Arg Ala Thr Leu Ser Cys Arg Ala
145 150 155 160
Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Gly
165 170 175
Gln Ala Pro Arg Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly
180 185 190
Ile Pro Ala Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Thr Leu
195 200 205
Thr Ile Ser Ser Leu Gln Pro Glu Asp Phe Ala Val Tyr Phe Cys Gln
210 215 220
Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gln Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu
225 230 235 240
Ile Lys
<![CDATA[ <210> 103]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 489]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 103]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser
20 25 30
Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly
50 55 60
Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val
65 70 75 80
Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser
130 135 140
Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala
145 150 155 160
Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu
165 170 175
Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu
180 185 190
Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser
195 200 205
Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln
210 215 220
Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr
225 230 235 240
Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
245 250 255
Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser Val Thr Val Ser Ser Ala Ala Ala Ile Glu
260 265 270
Val Met Tyr Pro Pro Pro Tyr Leu Asp Asn Glu Lys Ser Asn Gly Thr
275 280 285
Ile Ile His Val Lys Gly Lys His Leu Cys Pro Ser Pro Leu Phe Pro
290 295 300
Gly Pro Ser Lys Pro Phe Trp Val Leu Val Val Val Gly Gly Val Leu
305 310 315 320
Ala Cys Tyr Ser Leu Leu Val Thr Val Ala Phe Ile Ile Phe Trp Val
325 330 335
Arg Ser Lys Arg Ser Arg Leu Leu His Ser Asp Tyr Met Asn Met Thr
340 345 350
Pro Arg Arg Pro Gly Pro Thr Arg Lys His Tyr Gln Pro Tyr Ala Pro
355 360 365
Pro Arg Asp Phe Ala Ala Tyr Arg Ser Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser
370 375 380
Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu
385 390 395 400
Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg
405 410 415
Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln
420 425 430
Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr
435 440 445
Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp
450 455 460
Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala
465 470 475 480
Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
485
<![CDATA[ <210> 104]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 245]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 104]]>
Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser Ser Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly
1 5 10 15
Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly
100 105 110
Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys
115 120 125
Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser
130 135 140
Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
145 150 155 160
Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile
165 170 175
Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu
180 185 190
Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn
195 200 205
Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr
210 215 220
Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser
225 230 235 240
Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 105]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 461]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 105]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser
20 25 30
Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser
35 40 45
Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly
50 55 60
Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val
65 70 75 80
Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr
85 90 95
Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln
100 105 110
Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile
115 120 125
Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser
130 135 140
Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala
145 150 155 160
Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu
165 170 175
Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu
180 185 190
Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser
195 200 205
Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln
210 215 220
Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr
225 230 235 240
Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr
245 250 255
Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser Val Thr Val Ser Ser Glu Ser Lys Tyr Gly
260 265 270
Pro Pro Cys Pro Pro Cys Pro Met Phe Trp Val Leu Val Val Val Gly
275 280 285
Gly Val Leu Ala Cys Tyr Ser Leu Leu Val Thr Val Ala Phe Ile Ile
290 295 300
Phe Trp Val Lys Arg Gly Arg Lys Lys Leu Leu Tyr Ile Phe Lys Gln
305 310 315 320
Pro Phe Met Arg Pro Val Gln Thr Thr Gln Glu Glu Asp Gly Cys Ser
325 330 335
Cys Arg Phe Pro Glu Glu Glu Glu Gly Gly Cys Glu Leu Arg Val Lys
340 345 350
Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Gln Gln Gly Gln Asn Gln
355 360 365
Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr Asp Val Leu
370 375 380
Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys Pro Arg Arg
385 390 395 400
Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys Asp Lys Met
405 410 415
Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg Arg Arg Gly
420 425 430
Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala Thr Lys Asp
435 440 445
Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
450 455 460
<![CDATA[ <210> 106]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 245]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 106]]>
Asp Ile Gln Met Thr Gln Thr Thr Ser Ser Ser Leu Ser Ala Ser Leu Gly
1 5 10 15
Asp Arg Val Thr Ile Ser Cys Arg Ala Ser Gln Asp Ile Ser Lys Tyr
20 25 30
Leu Asn Trp Tyr Gln Gln Lys Pro Asp Gly Thr Val Lys Leu Leu Ile
35 40 45
Tyr His Thr Ser Arg Leu His Ser Gly Val Pro Ser Arg Phe Ser Gly
50 55 60
Ser Gly Ser Gly Thr Asp Tyr Ser Leu Thr Ile Ser Asn Leu Glu Gln
65 70 75 80
Glu Asp Ile Ala Thr Tyr Phe Cys Gln Gln Gly Asn Thr Leu Pro Tyr
85 90 95
Thr Phe Gly Gly Gly Thr Lys Leu Glu Ile Thr Gly Ser Thr Ser Gly
100 105 110
Ser Gly Lys Pro Gly Ser Gly Glu Gly Ser Thr Lys Gly Glu Val Lys
115 120 125
Leu Gln Glu Ser Gly Pro Gly Leu Val Ala Pro Ser Gln Ser Leu Ser
130 135 140
Val Thr Cys Thr Val Ser Gly Val Ser Leu Pro Asp Tyr Gly Val Ser
145 150 155 160
Trp Ile Arg Gln Pro Pro Arg Lys Gly Leu Glu Trp Leu Gly Val Ile
165 170 175
Trp Gly Ser Glu Thr Thr Tyr Tyr Asn Ser Ala Leu Lys Ser Arg Leu
180 185 190
Thr Ile Ile Lys Asp Asn Ser Lys Ser Gln Val Phe Leu Lys Met Asn
195 200 205
Ser Leu Gln Thr Asp Asp Thr Ala Ile Tyr Tyr Cys Ala Lys His Tyr
210 215 220
Tyr Tyr Gly Gly Ser Tyr Ala Met Asp Tyr Trp Gly Gln Gly Thr Ser
225 230 235 240
Val Thr Val Ser Ser
245
<![CDATA[ <210> 107]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 22]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 107]]>
Met Leu Leu Leu Val Thr Ser Leu Leu Leu Cys Glu Leu Pro His Pro
1 5 10 15
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Pro
20
<![CDATA[ <210> 108]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 112]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 108]]>
Arg Val Lys Phe Ser Arg Ser Ala Asp Ala Pro Ala Tyr Lys Gln Gly
1 5 10 15
Gln Asn Gln Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Asn Leu Gly Arg Arg Glu Glu Tyr
20 25 30
Asp Val Leu Asp Lys Arg Arg Gly Arg Asp Pro Glu Met Gly Gly Lys
35 40 45
Pro Arg Arg Lys Asn Pro Gln Glu Gly Leu Tyr Asn Glu Leu Gln Lys
50 55 60
Asp Lys Met Ala Glu Ala Tyr Ser Glu Ile Gly Met Lys Gly Glu Arg
65 70 75 80
Arg Arg Gly Lys Gly His Asp Gly Leu Tyr Gln Gly Leu Ser Thr Ala
85 90 95
Thr Lys Asp Thr Tyr Asp Ala Leu His Met Gln Ala Leu Pro Pro Arg
100 105 110
<![CDATA[ <210> 109]]>
<![CDATA[ <211> 284]]>
<![CDATA[ <212> PRT]]>
<![CDATA[ <213> Artificial Sequence]]>
<![CDATA[ <220>]]>
<![CDATA[ <223> Synthetic peptides]]>
<![CDATA[ <400> 109]]>
Asn Trp Val Asn Val Ile Ser Asp Leu Lys Lys Ile Glu Asp Leu Ile
1 5 10 15
Gln Ser Met His Ile Asp Ala Thr Leu Tyr Thr Glu Ser Asp Val His
20 25 30
Pro Ser Cys Lys Val Thr Ala Met Lys Cys Phe Leu Leu Glu Leu Gln
35 40 45
Val Ile Ser Leu Glu Ser Gly Asp Ala Ser Ile His Asp Thr Val Glu
50 55 60
Asn Leu Ile Ile Leu Ala Asn Asn Ser Leu Ser Ser Asn Gly Asn Val
65 70 75 80
Thr Glu Ser Gly Cys Lys Glu Cys Glu Glu Leu Glu Glu Lys Asn Ile
85 90 95
Lys Glu Phe Leu Gln Ser Phe Val His Ile Val Gln Met Phe Ile Asn
100 105 110
Thr Ser Ile Thr Cys Pro Pro Pro Met Ser Val Glu His Ala Asp Ile
115 120 125
Trp Val Lys Ser Tyr Ser Leu Tyr Ser Arg Glu Arg Tyr Ile Cys Asn
130 135 140
Ser Gly Phe Lys Arg Lys Ala Gly Thr Ser Ser Leu Thr Glu Cys Val
145 150 155 160
Leu Asn Lys Ala Thr Asn Val Ala His Trp Thr Thr Pro Ser Leu Lys
165 170 175
Cys Ile Arg Asp Pro Ala Leu Val His Gln Arg Pro Ala Pro Pro Ser
180 185 190
Thr Val Thr Thr Ala Gly Val Thr Pro Gln Pro Glu Ser Leu Ser Pro
195 200 205
Ser Gly Lys Glu Pro Ala Ala Ser Ser Pro Ser Ser Asn Asn Thr Ala
210 215 220
Ala Thr Thr Ala Ala Ile Val Pro Gly Ser Gln Leu Met Pro Ser Lys
225 230 235 240
Ser Pro Ser Thr Gly Thr Thr Glu Ile Ser Ser His Glu Ser Ser His
245 250 255
Gly Thr Pro Ser Gln Thr Thr Ala Lys Asn Trp Glu Leu Thr Ala Ser
260 265 270
Ala Ser His Gln Pro Pro Gly Val Tyr Pro Gln Gly
275 280
Claims (20)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US202163195573P | 2021-06-01 | 2021-06-01 | |
| US63/195,573 | 2021-06-01 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| TW202307210A true TW202307210A (en) | 2023-02-16 |
Family
ID=82258402
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW111120303A TW202307210A (en) | 2021-06-01 | 2022-05-31 | Cd19 and cd22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| TW (1) | TW202307210A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2022254337A1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (112)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2116183B (en) | 1982-03-03 | 1985-06-05 | Genentech Inc | Human antithrombin iii dna sequences therefore expression vehicles and cloning vectors containing such sequences and cell cultures transformed thereby a process for expressing human antithrombin iii and pharmaceutical compositions comprising it |
| US6905680B2 (en) | 1988-11-23 | 2005-06-14 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Methods of treating HIV infected subjects |
| US6534055B1 (en) | 1988-11-23 | 2003-03-18 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells |
| US6352694B1 (en) | 1994-06-03 | 2002-03-05 | Genetics Institute, Inc. | Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate using agents which recognize TCR/CD3 and ligands which stimulate an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells |
| US5858358A (en) | 1992-04-07 | 1999-01-12 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells |
| US5703055A (en) | 1989-03-21 | 1997-12-30 | Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation | Generation of antibodies through lipid mediated DNA delivery |
| US5399346A (en) | 1989-06-14 | 1995-03-21 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Department Of Health And Human Services | Gene therapy |
| US5585362A (en) | 1989-08-22 | 1996-12-17 | The Regents Of The University Of Michigan | Adenovirus vectors for gene therapy |
| US5199942A (en) | 1991-06-07 | 1993-04-06 | Immunex Corporation | Method for improving autologous transplantation |
| GB9125768D0 (en) | 1991-12-04 | 1992-02-05 | Hale Geoffrey | Therapeutic method |
| US5350674A (en) | 1992-09-04 | 1994-09-27 | Becton, Dickinson And Company | Intrinsic factor - horse peroxidase conjugates and a method for increasing the stability thereof |
| US7175843B2 (en) | 1994-06-03 | 2007-02-13 | Genetics Institute, Llc | Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells |
| US6692964B1 (en) | 1995-05-04 | 2004-02-17 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Methods for transfecting T cells |
| US7067318B2 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2006-06-27 | The Regents Of The University Of Michigan | Methods for transfecting T cells |
| AU4055697A (en) | 1996-08-16 | 1998-03-06 | Schering Corporation | Mammalian cell surface antigens; related reagents |
| US6111090A (en) | 1996-08-16 | 2000-08-29 | Schering Corporation | Mammalian cell surface antigens; related reagents |
| DE69839147T2 (en) | 1997-06-12 | 2009-02-19 | Novartis International Pharmaceutical Ltd. | ARTIFICIAL ANTIBODY POLYPEPTIDE |
| AU1102399A (en) | 1997-10-21 | 1999-05-10 | Human Genome Sciences, Inc. | Human tumor necrosis factor receptor-like proteins tr11, tr11sv1, and tr11sv2 |
| IL137409A0 (en) | 1998-02-09 | 2001-07-24 | Genentech Inc | Novel tumor necrosis factor receptor homolog and nucleic acids encoding the same |
| WO1999052552A1 (en) | 1998-04-15 | 1999-10-21 | Brigham & Women's Hospital, Inc. | T cell inhibitory receptor compositions and uses thereof |
| WO2001003720A2 (en) | 1999-07-12 | 2001-01-18 | Genentech, Inc. | Promotion or inhibition of angiogenesis and cardiovascularization by tumor necrosis factor ligand/receptor homologs |
| WO2001029058A1 (en) | 1999-10-15 | 2001-04-26 | University Of Massachusetts | Rna interference pathway genes as tools for targeted genetic interference |
| US6326193B1 (en) | 1999-11-05 | 2001-12-04 | Cambria Biosciences, Llc | Insect control agent |
| US6797514B2 (en) | 2000-02-24 | 2004-09-28 | Xcyte Therapies, Inc. | Simultaneous stimulation and concentration of cells |
| US6867041B2 (en) | 2000-02-24 | 2005-03-15 | Xcyte Therapies, Inc. | Simultaneous stimulation and concentration of cells |
| US7572631B2 (en) | 2000-02-24 | 2009-08-11 | Invitrogen Corporation | Activation and expansion of T cells |
| ES2302726T3 (en) | 2000-02-24 | 2008-08-01 | Invitrogen Corporation | STIMULATION AND SIMULTANEOUS CONCENTRATION OF CELLS. |
| WO2001096584A2 (en) | 2000-06-12 | 2001-12-20 | Akkadix Corporation | Materials and methods for the control of nematodes |
| US7745140B2 (en) | 2002-01-03 | 2010-06-29 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Activation and expansion of T-cells using an engineered multivalent signaling platform as a research tool |
| TWI275390B (en) | 2002-04-30 | 2007-03-11 | Wyeth Corp | Process for the preparation of 7-substituted-3- quinolinecarbonitriles |
| US20040047858A1 (en) | 2002-09-11 | 2004-03-11 | Blumberg Richard S. | Therapeutic anti-BGP(C-CAM1) antibodies and uses thereof |
| JP4511943B2 (en) | 2002-12-23 | 2010-07-28 | ワイス エルエルシー | Antibody against PD-1 and use thereof |
| KR20060052681A (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2006-05-19 | 와이어쓰 | Gitr ligand and gitr ligand-related molecules and antibody and uses thereof |
| WO2005007190A1 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2005-01-27 | Schering Corporation | Agonists or antagonists of the clucocorticoid-induced tumour necrosis factor receptor (gitr) or its ligand for the treatment of immune disorders, infections and cancer |
| WO2005055808A2 (en) | 2003-12-02 | 2005-06-23 | Genzyme Corporation | Compositions and methods to diagnose and treat lung cancer |
| GB0409799D0 (en) | 2004-04-30 | 2004-06-09 | Isis Innovation | Method of generating improved immune response |
| WO2005118788A2 (en) | 2004-05-27 | 2005-12-15 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Novel artificial antigen presenting cells and uses therefor |
| EP1765402A2 (en) | 2004-06-04 | 2007-03-28 | Duke University | Methods and compositions for enhancement of immunity by in vivo depletion of immunosuppressive cell activity |
| CA2602777C (en) | 2005-03-25 | 2018-12-11 | Tolerrx, Inc. | Gitr binding molecules and uses therefor |
| PL2161336T5 (en) | 2005-05-09 | 2017-10-31 | Ono Pharmaceutical Co | Human monoclonal antibodies to programmed death 1(PD-1) and methods for treating cancer using anti-PD-1 antibodies alone or in combination with other immunotherapeutics |
| CN104356236B (en) | 2005-07-01 | 2020-07-03 | E.R.施贵宝&圣斯有限责任公司 | Human monoclonal antibody against programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
| US20070036773A1 (en) | 2005-08-09 | 2007-02-15 | City Of Hope | Generation and application of universal T cells for B-ALL |
| AP2911A (en) | 2005-12-02 | 2014-05-31 | Sinai School Medicine | Chimeric Viruses presenting non-native surface proteins and uses thereof |
| WO2007133822A1 (en) | 2006-01-19 | 2007-11-22 | Genzyme Corporation | Gitr antibodies for the treatment of cancer |
| US20100178684A1 (en) | 2006-12-21 | 2010-07-15 | Woo Savio L C | Transgenic oncolytic viruses and uses thereof |
| CA2691357C (en) | 2007-06-18 | 2014-09-23 | N.V. Organon | Antibodies to human programmed death receptor pd-1 |
| ES2591281T3 (en) | 2007-07-12 | 2016-11-25 | Gitr, Inc. | Combination therapies that employ GITR binding molecules |
| US9416165B2 (en) | 2007-10-26 | 2016-08-16 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods of inhibiting viral replication and improving T cell function employing soluble Tim-3 inhibitors |
| HUE034465T2 (en) | 2008-02-11 | 2018-02-28 | Cure Tech Ltd | Monoclonal antibodies for tumor treatment |
| US8168757B2 (en) | 2008-03-12 | 2012-05-01 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | PD-1 binding proteins |
| AU2009266873A1 (en) | 2008-07-02 | 2010-01-07 | Emergent Product Development Seattle, Llc | TGF-beta antagonist multi-target binding proteins |
| AR072999A1 (en) | 2008-08-11 | 2010-10-06 | Medarex Inc | HUMAN ANTIBODIES THAT JOIN GEN 3 OF LYMPHOCYTARY ACTIVATION (LAG-3) AND THE USES OF THESE |
| EP2328919A2 (en) | 2008-08-25 | 2011-06-08 | Amplimmune, Inc. | Pd-i antagonists and methods for treating infectious disease |
| PL2350129T3 (en) | 2008-08-25 | 2015-12-31 | Amplimmune Inc | Compositions of pd-1 antagonists and methods of use |
| JPWO2010030002A1 (en) | 2008-09-12 | 2012-02-02 | 国立大学法人三重大学 | Foreign GITR ligand expressing cells |
| EP4331604B9 (en) | 2008-12-09 | 2025-07-23 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG | Anti-pd-l1 antibodies and their use to enhance t-cell function |
| ES2550179T3 (en) | 2009-02-05 | 2015-11-05 | Icahn School Of Medicine At Mount Sinai | Chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and uses thereof |
| ES2629337T3 (en) | 2009-02-09 | 2017-08-08 | Inserm - Institut National De La Santé Et De La Recherche Médicale | Antibodies against PD-1 and antibodies against PD-L1 and uses thereof |
| KR20180077322A (en) | 2009-04-30 | 2018-07-06 | 텔 하쇼머 메디컬 리서치 인프라스트럭쳐 앤드 서비시스 리미티드. | Anti ceacam1 antibodies and methods of using same |
| CA2772613C (en) | 2009-09-03 | 2020-03-10 | Schering Corporation | Anti-gitr antibodies |
| WO2011059836A2 (en) | 2009-10-29 | 2011-05-19 | Trustees Of Dartmouth College | T cell receptor-deficient t cell compositions |
| GB0919054D0 (en) | 2009-10-30 | 2009-12-16 | Isis Innovation | Treatment of obesity |
| US20130017199A1 (en) | 2009-11-24 | 2013-01-17 | AMPLIMMUNE ,Inc. a corporation | Simultaneous inhibition of pd-l1/pd-l2 |
| HUE029257T2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2017-02-28 | Aptevo Res And Dev Llc | Heterodimer binding proteins and uses thereof |
| CA2802344C (en) | 2010-06-18 | 2023-06-13 | The Brigham And Women's Hospital, Inc. | Bi-specific antibodies against tim-3 and pd-1 for immunotherapy in chronic immune conditions |
| ES2872077T3 (en) | 2011-04-08 | 2021-11-02 | Us Health | Chimeric antigen receptor anti-variant III epidermal growth factor receptor and use of the same for the treatment of cancer |
| WO2013006490A2 (en) | 2011-07-01 | 2013-01-10 | Cellerant Therapeutics, Inc. | Antibodies that specifically bind to tim3 |
| US20130108641A1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2013-05-02 | Sanofi | Anti-gitr antibodies |
| WO2013054320A1 (en) | 2011-10-11 | 2013-04-18 | Tel Hashomer Medical Research Infrastructure And Services Ltd. | Antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule (ceacam) |
| EP2785743B1 (en) | 2011-12-01 | 2019-08-14 | The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc. | Anti-ceacam1 recombinant antibodies for cancer therapy |
| BR112014020499A2 (en) | 2012-02-22 | 2019-09-24 | Univ Pennsylvania | isolated nucleic acid sequence, t-cell, vector, and persistent t-cell population |
| PT3241902T (en) | 2012-05-25 | 2018-05-28 | Univ California | METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR MODIFICATION OF TARGETED TARGET DNA BY RNA AND FOR MODULATION DIRECTED BY TRANSCRIPTION RNA |
| EP2879709B1 (en) | 2012-07-31 | 2020-01-08 | The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc. | Modulation of the immune response |
| AR092745A1 (en) | 2012-10-01 | 2015-04-29 | Univ Pennsylvania | COMPOSITIONS THAT INCLUDE AN ANTI-FAP UNION DOMAIN AND METHODS TO MAKE WHITE IN STROMAL CELLS FOR THE TREATMENT OF CANCER |
| US10117896B2 (en) | 2012-10-05 | 2018-11-06 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Use of a trans-signaling approach in chimeric antigen receptors |
| EP2906241B1 (en) | 2012-10-12 | 2020-01-08 | The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc. | Enhancement of the immune response |
| WO2014110591A1 (en) | 2013-01-14 | 2014-07-17 | Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center | Compositions and methods for delivery of immune cells to treat un-resectable or non-resected tumor cells and tumor relapse |
| CA2905272A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2014-10-02 | Icahn School Of Medicine At Mount Sinai | Newcastle disease viruses and uses thereof |
| EP3783098A1 (en) | 2013-05-14 | 2021-02-24 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Human application of engineered chimeric antigen receptor (car) t-cells |
| CA2929181A1 (en) | 2013-11-13 | 2015-05-21 | Novartis Ag | Mtor inhibitors for enhancing the immune response |
| JP7114457B2 (en) | 2015-04-17 | 2022-08-08 | ザ トラスティーズ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ ペンシルバニア | Methods for Improving Efficacy and Growth of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Expressing Cells |
| WO2016180467A1 (en) | 2015-05-11 | 2016-11-17 | Biontech Cell & Gene Therapies Gmbh | Enhancing the effect of car-engineered t cells by means of nucleic acid vaccination |
| WO2016196388A1 (en) | 2015-05-29 | 2016-12-08 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Composition and methods for regulating inhibitory interactions in genetically engineered cells |
| HK1256130A1 (en) | 2015-07-21 | 2019-09-13 | City Of Hope | T cells for expression of chimeric antigen receptors and other receptors |
| AU2016297014B2 (en) | 2015-07-21 | 2021-06-17 | Novartis Ag | Methods for improving the efficacy and expansion of immune cells |
| CN108472314A (en) | 2015-07-31 | 2018-08-31 | 明尼苏达大学董事会 | Modified Cells and Therapeutics |
| MA45488A (en) | 2015-10-22 | 2018-08-29 | Juno Therapeutics Gmbh | CELL CULTURE PROCESSES, KITS AND APPARATUS |
| MX2018006767A (en) | 2015-12-04 | 2019-03-14 | Novartis Ag | COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR IMMUNOLOGICAL ONCOLOGY. |
| GB201522097D0 (en) | 2015-12-15 | 2016-01-27 | Cellular Therapeutics Ltd | Cells |
| SG11201805449PA (en) | 2015-12-28 | 2018-07-30 | Novartis Ag | Methods of making chimeric antigen receptor -expressing cells |
| WO2017114497A1 (en) | 2015-12-30 | 2017-07-06 | Novartis Ag | Immune effector cell therapies with enhanced efficacy |
| US20190030151A1 (en) | 2016-01-15 | 2019-01-31 | Etubics Corporation | Methods and compositions for t-cell immunotherapy |
| US11413309B2 (en) | 2016-01-20 | 2022-08-16 | Fate Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions and methods for immune cell modulation in adoptive immunotherapies |
| KR102457098B1 (en) | 2016-03-19 | 2022-10-21 | 엑수마 바이오테크, 코포레이션 | Methods and compositions for transducing lymphocytes, and controlled expansion thereof |
| WO2017190100A1 (en) | 2016-04-28 | 2017-11-02 | The Trustees Of Dartmouth College | Nucleic acid constructs for co-expression of chimeric antigen receptor and transcription factor, cells containing and therapeutic use thereof |
| MA45341A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2019-04-10 | Hutchinson Fred Cancer Res | METHODS FOR TREATING B-LYMPHOCYTE MALIGNITIES USING ADOPTIVE CELL THERAPY |
| IL321834A (en) | 2016-06-08 | 2025-08-01 | Precigen Inc | Chimeric receptors for the CD33 antigen |
| JP7160482B2 (en) * | 2016-09-02 | 2022-10-25 | レンティジェン・テクノロジー・インコーポレイテッド | Compositions and methods for treating cancer with DUOCAR |
| WO2018052947A1 (en) | 2016-09-16 | 2018-03-22 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Platform for activation and expansion of virus-specific t-cells |
| AU2017330379B2 (en) | 2016-09-23 | 2023-07-13 | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Generation and use in adoptive immunotherapy of stem cell-like memory T cells |
| EP3523290A4 (en) | 2016-09-30 | 2020-07-29 | Novartis AG | IMMUNE EFFECTOR CELL THERAPIES WITH IMPROVED EFFECTIVENESS |
| WO2018075813A1 (en) | 2016-10-19 | 2018-04-26 | City Of Hope | Use of endogenous viral vaccine in chimeric antigen receptor t cell therapy |
| WO2018102761A1 (en) | 2016-12-02 | 2018-06-07 | City Of Hope | Methods for manufacturing and expanding t cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors and other receptors |
| WO2018106732A1 (en) | 2016-12-05 | 2018-06-14 | Juno Therapeutics, Inc. | Production of engineered cells for adoptive cell therapy |
| CN106957822B (en) | 2017-05-10 | 2020-08-11 | 成都美杰赛尔生物科技有限公司 | Culture method, kit and application of in-vitro amplified gene editing activated T cells |
| CN107287164A (en) | 2017-07-07 | 2017-10-24 | 青岛协和华美医学诊断技术有限公司 | Target CD19 Chimeric antigen receptor T cell, preparation method and application |
| CN108018312B (en) | 2017-12-20 | 2019-09-10 | 上海优卡迪生物医药科技有限公司 | The CAR-T therapy vector and its construction method of a kind of T lymphocyte leukaemia and application |
| CN108085342A (en) | 2017-12-29 | 2018-05-29 | 深圳市茵冠生物科技有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of the T lymphocytes of Chimeric antigen receptor genetic modification, CAR-T cells obtained and application thereof |
| CN108103105A (en) | 2017-12-29 | 2018-06-01 | 深圳市茵冠生物科技有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of CAR-T cells, CAR-T cells obtained and its application |
| CA3163104A1 (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | Novartis Ag | Chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
| KR20220104217A (en) * | 2019-11-26 | 2022-07-26 | 노파르티스 아게 | CD19 and CD22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
| GB202006820D0 (en) * | 2020-05-07 | 2020-06-24 | Autolus Ltd | Cell |
-
2022
- 2022-05-31 TW TW111120303A patent/TW202307210A/en unknown
- 2022-05-31 WO PCT/IB2022/055088 patent/WO2022254337A1/en not_active Ceased
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2022254337A1 (en) | 2022-12-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12344651B2 (en) | CD19 and CD22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof | |
| US20240398913A1 (en) | Methods for improving the efficacy and expansion of chimeric antigen receptor-expressing cells | |
| TWI890660B (en) | Bcma chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof | |
| AU2015292811B2 (en) | Treatment of cancer using a CLL-1 chimeric antigen receptor | |
| KR20180118175A (en) | Cells expressing multiple chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) molecules and their uses | |
| US20240033358A1 (en) | Combination therapies with chimeric antigen receptor (car)-expressing cells | |
| RU2847299C1 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptors for cd19 and cd22 and ways of their application | |
| US20260042812A1 (en) | Cd19 and cd22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof | |
| TW202307210A (en) | Cd19 and cd22 chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof | |
| WO2025096673A1 (en) | Compositions comprising cells targeting cancer and methods of using the same | |
| WO2026006794A1 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof | |
| WO2026006795A1 (en) | Chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |