CN114690866A - Temperature control method and data storage system - Google Patents
Temperature control method and data storage system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114690866A CN114690866A CN202011597774.9A CN202011597774A CN114690866A CN 114690866 A CN114690866 A CN 114690866A CN 202011597774 A CN202011597774 A CN 202011597774A CN 114690866 A CN114690866 A CN 114690866A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- memory device
- count value
- busy state
- temperature
- threshold
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/16—Constructional details or arrangements
- G06F1/20—Cooling means
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/3003—Monitoring arrangements specially adapted to the computing system or computing system component being monitored
- G06F11/3037—Monitoring arrangements specially adapted to the computing system or computing system component being monitored where the computing system component is a memory, e.g. virtual memory, cache
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/3051—Monitoring arrangements for monitoring the configuration of the computing system or of the computing system component, e.g. monitoring the presence of processing resources, peripherals, I/O links, software programs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/3058—Monitoring arrangements for monitoring environmental properties or parameters of the computing system or of the computing system component, e.g. monitoring of power, currents, temperature, humidity, position, vibrations
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Debugging And Monitoring (AREA)
- Read Only Memory (AREA)
Abstract
本发明提供一种温度控制方法与数据存储系统。所述方法包括:检测存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态;检测所述存储器装置的温度是否高于第一门槛值;响应于所述存储器装置处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度高于所述第一门槛值,指示所述存储器装置执行降温程序;以及响应于所述存储器装置不处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度低于第二门槛值,指示所述存储器装置结束所述降温程序。因此,可提高对于存储器装置的温度控制能力。
The invention provides a temperature control method and a data storage system. The method includes: detecting whether a memory device is in a busy state; detecting whether a temperature of the memory device is above a first threshold; in response to the memory device being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device being above a the first threshold, instructing the memory device to perform a cooling procedure; and in response to the memory device not being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device being below a second threshold, instructing the memory device End the cooling procedure. Therefore, the temperature control capability for the memory device can be improved.
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种温度控制技术,且尤其涉及一种温度控制方法与数据存储系统。The present invention relates to a temperature control technology, and in particular, to a temperature control method and a data storage system.
背景技术Background technique
一般来说,存储器装置或其他类型的电子装置普遍都内建有温度控制机制。当装置内部的温度过高时,此温度控制机制就可被启动以进行降温。然而,大部分的电子装置所采用的温度控制机制都是根据厂商评估的温度变化曲线所预先设定的。以存储器装置为例,当温度高于默认的门槛值时,存储器装置一般可采用默认的降温手段(例如降低数据存取效能)来进行降温。但是,实际在存储器装置与主机系统的配合操作中,当存储器装置处于忙碌状态时,即便存储器装置的温度暂时下降,但一旦停止降温程序则存储器装置的温度可能会马上又飙高。反复的启动与停止降温程序除了容易造成存储器装置的存取效能不稳定外,也可能导致存储器装置降温不及而造成装置损坏。Generally, memory devices or other types of electronic devices generally have built-in temperature control mechanisms. When the temperature inside the device is too high, this temperature control mechanism can be activated to cool down. However, most of the temperature control mechanisms used in electronic devices are preset according to temperature change curves evaluated by manufacturers. Taking a memory device as an example, when the temperature is higher than a default threshold, the memory device can generally use a default cooling method (eg, reducing data access performance) to cool down. However, in the actual cooperative operation of the memory device and the host system, when the memory device is in a busy state, even if the temperature of the memory device drops temporarily, once the cooling process is stopped, the temperature of the memory device may immediately rise again. Repeatedly starting and stopping the cooling process may not only easily lead to unstable access performance of the memory device, but also may cause the memory device to not cool enough to cause damage to the device.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明提供一种温度控制方法与数据存储系统,可提高对于存储器装置的温度控制能力。The present invention provides a temperature control method and a data storage system, which can improve the temperature control capability of a memory device.
本发明的实施例提供一种温度控制方法,其用于控制存储器装置的温度,所述温度控制方法包括:检测所述存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态;检测所述存储器装置的所述温度是否高于第一门槛值;响应于所述存储器装置处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度高于所述第一门槛值,指示所述存储器装置执行降温程序;以及响应于所述存储器装置不处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度低于第二门槛值,指示所述存储器装置结束所述降温程序。An embodiment of the present invention provides a temperature control method for controlling the temperature of a memory device, the temperature control method comprising: detecting whether the memory device is in a busy state; detecting whether the temperature of the memory device is higher than a first threshold; instructing the memory device to perform a cool-down procedure in response to the memory device being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device being above the first threshold; and in response to the memory device Not being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device is lower than a second threshold, instructing the memory device to end the cooling process.
本发明的实施例另提供一种数据存储系统,其包括主机系统与存储器装置。所述存储器装置连接至所述主机系统。所述主机系统用以检测所述存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态。所述主机系统更用以检测所述存储器装置的温度是否高于第一门槛值。所述主机系统更用以响应于所述存储器装置处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度高于所述第一门槛值,指示所述存储器装置执行降温程序。所述主机系统更用以响应于所述存储器装置不处于所述忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的所述温度低于第二门槛值,指示所述存储器装置结束所述降温程序。Embodiments of the present invention further provide a data storage system, which includes a host system and a memory device. The memory device is connected to the host system. The host system is used to detect whether the memory device is in a busy state. The host system is further configured to detect whether the temperature of the memory device is higher than a first threshold. The host system is further configured to instruct the memory device to perform a cooling process in response to the memory device being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device being higher than the first threshold. The host system is further configured to instruct the memory device to end the cooling process in response to the memory device not being in the busy state and the temperature of the memory device being lower than a second threshold.
基于上述,本发明可根据存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态以及存储器装置的温度是否高于第一门槛值(或低于第二门槛值)来作为是否启动(或停止)降温程序的双重验证。藉此,可有效提高对于存储器装置的温度控制能力。Based on the above, according to the present invention, whether the memory device is in a busy state and whether the temperature of the memory device is higher than the first threshold value (or lower than the second threshold value) can be used as a double verification of whether to start (or stop) the cooling process. Thereby, the temperature control capability of the memory device can be effectively improved.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是根据本发明的实施例所示出的数据存储系统的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a data storage system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是根据本发明的实施例所示出的计数值与存储器装置的累积忙碌时间之间的对应的示意图;2 is a schematic diagram illustrating the correspondence between a count value and an accumulated busy time of a memory device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是根据本发明的实施例所示出的第一计数值与第二计数值在时间上的相关关系的示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of the time correlation between the first count value and the second count value according to an embodiment of the present invention;
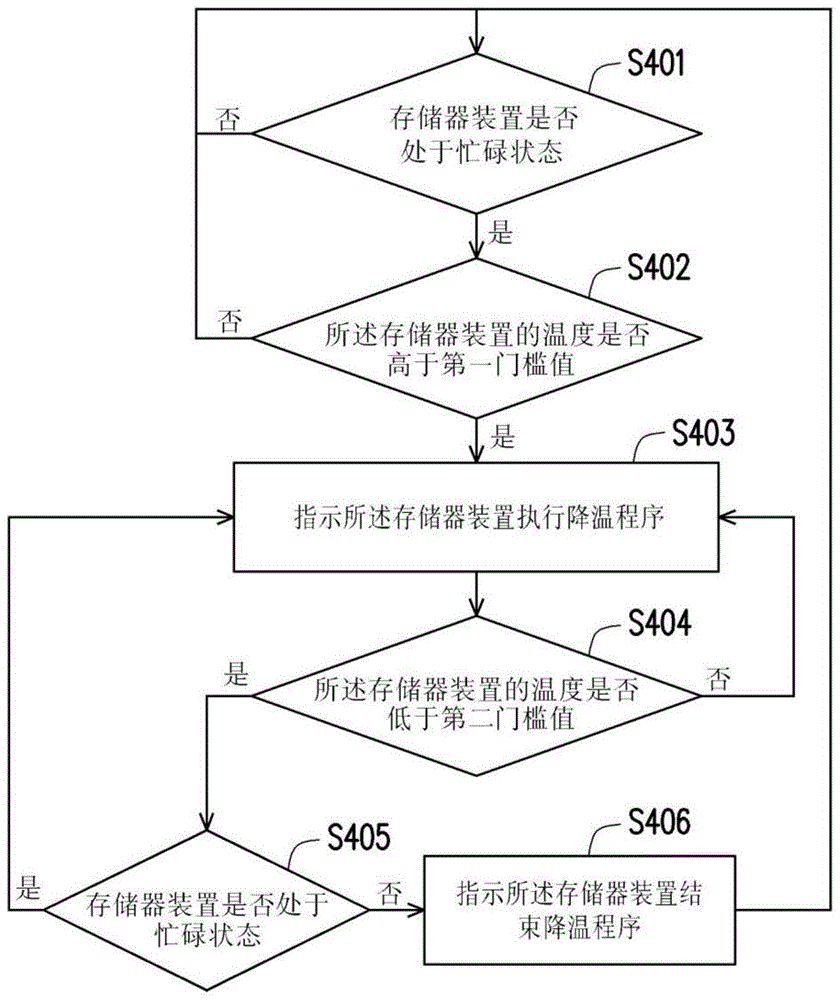
图4是根据本发明的实施例所示出的温度控制方法的流程图。FIG. 4 is a flow chart of a temperature control method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
现将详细地参考本发明的示范性实施例,示范性实施例的实例说明于附图中。只要有可能,相同元件符号在附图和描述中用来表示相同或相似部分。Reference will now be made in detail to the exemplary embodiments of the present invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Wherever possible, the same reference numerals are used in the drawings and description to refer to the same or like parts.
图1是根据本发明的实施例所示出的数据存储系统的示意图。请参照图1,数据存储系统10包括主机系统11与存储器装置12。主机系统11可将数据存储至存储器装置12中,或从存储器装置12中读取数据。例如,主机系统11为可实质地与存储器装置12配合以存储数据的任意系统,例如,计算机系统、数码相机、摄相机、通信装置、音频播放器、视频播放器或平板计算机等,而存储器装置12则可为U盘、存储卡、固态硬盘(Solid State Drive,SSD)、安全数字(Secure Digital,SD)卡、小型快闪(Compact Flash,CF)卡或嵌入式存储装置等各式非易失性存储器装置。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a data storage system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 1 , the
在本实施例中,主机系统11包括处理器111与连接接口112。处理器111可包括中央处理单元(CPU)、或是其他可编程的一般用途或特殊用途的微处理器、数字信号处理器(Digital Signal Processor,DSP)、可编程控制器、专用集成电路(Application SpecificIntegrated Circuits,ASIC)、可编程逻辑器件(Programmable Logic Device,PLD)或其他类似装置或这些装置的组合。处理器111用以控制主机系统11的整体或部分运作。以下实施例中,对主机系统11的操作的描述可等同于对处理器111的操作的描述。In this embodiment, the
连接接口112连接至处理器111并用以将数据传输至存储器装置12或从存储器装置12接收数据。在一实施例中,主机系统11还包含任何实务上所需的硬件装置,例如电池单元、网络接口卡、键盘(或触控板)、屏幕和/或扬声器等等。The
存储器装置12包括连接接口121、存储器控制器122及存储器模块123。连接接口121用以连接主机系统11的连接接口112并经由连接接口112与主机系统11通信。在一实施例中,连接接口112与121符合NVM Express(NVMe)接口规范。在另一实施例中,连接接口112与121亦可以符合串行高级技术附件(Serial Advanced Technology Attachment,SATA)、并行高级技术附件(Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment,PATA)、高速周边零件连接接口(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express,PCI Express)或通用串行总线(Universal Serial Bus,USB)等各式连接接口标准。The
存储器控制器122连接至连接接口121与存储器模块123。存储器控制器122用以执行以硬件型式或固件型式实作的多个逻辑门或控制指令并且根据主机系统11的指令在存储器模块123中进行数据的写入、读取与抹除等运作。此外,存储器控制器122也可控制存储器装置12的整体运作。在一实施例中,存储器控制器122亦称为快闪存储器控制器。The
存储器模块123用以存储主机系统11所写入的数据。例如,存储器模块123可包括单阶单元(single level cell,SLC)NAND型快闪存储器模块(即,一个存储单元可存储1个比特的快闪存储器模块)、多阶单元(multi level cell,MLC)NAND型快闪存储器模块(即,一个存储单元可存储2个比特的快闪存储器模块)、三阶单元(triple level cell,TLC)NAND型快闪存储器模块(即,一个存储单元可存储3个比特的快闪存储器模块)和/或四阶单元(quad level cell,QLC)NAND型快闪存储器模块(即,一个存储单元可存储4个比特的快闪存储器模块)。此外,存储器模块123中的存储单元是以临界电压的改变来存储数据。The
在一实施例中,主机系统11可检测存储器装置12是否处于忙碌状态。在忙碌状态下,由于存储器装置12可能需要持续处理来自主机系统11的指令和/或执行其他数据存取操作(例如对存储器模块123执行写入或读取操作),故存储器装置12的温度较容易升高。In one embodiment, the
在一实施例中,主机系统11可检测存储器装置12的温度。例如,存储器装置12内部可配置有一温度传感器。此温度传感器可用于检测并记录存储器装置12的温度。主机系统11可从存储器装置12读取由此温度传感器记录的温度数据。此外,主机系统11可检测存储器装置12的温度是否高于一门槛值(亦称为第一门槛值)。例如,第一门槛值可为65度或其他温度值。In one embodiment, the
在一实施例中,假设主机系统11判定存储器装置12处于忙碌状态且同时存储器装置12的温度高于第一门槛值。此时,响应于存储器装置12处于忙碌状态且存储器装置12的温度高于第一门槛值,主机系统11可指示存储器装置12执行一降温程序。此降温程序可用以降低存储器装置12的温度。In one embodiment, it is assumed that the
在一实施例中,此降温程序是专用于对处于忙碌状态下的存储器装置12进行降温。例如,在此降温程序中,存储器控制器122可采用的降温手段可包括但不限于,改变存储器装置12的工作状态(例如PS0至PS1)、降低存储器装置12的时钟频率、降低存储器装置12的工作电压、降低对于存储器模块123的存取速度和/或降低存储器装置12的解码引擎耗电量等任何可用于对存储器装置12进行降温的技术手段。In one embodiment, the cooling procedure is dedicated to cooling the
在一实施例中,在启动降温程序后,主机系统11仍可持续检测存储器装置12是否处于忙碌状态以及存储器装置12的温度是否低于另一门槛值(亦称为第二门槛值)。例如,第二门槛值可为55度或低于第一门槛值的其他温度值。In one embodiment, after the cooling process is started, the
在一实施例中,假设主机系统11判定存储器装置12已不处于忙碌状态且同时存储器装置12的温度低于第二门槛值。此时,响应于存储器装置12不处于忙碌状态且存储器装置12的温度低于第二门槛值,主机系统11可指示存储器装置12停止所述降温程序。In one embodiment, it is assumed that the
在一实施例中,主机系统11可从存储器装置12读取一个计数值。此计数值可反映存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的累积时间长度。主机系统11可根据此计数值来决定存储器装置12是否处于忙碌状态。In one embodiment,
在一实施例中,存储器控制器122可根据存储器装置12当前的运作状态决定存储器装置12是否处于忙碌状态。响应于存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的时间增加一个默认时间长度,存储器控制器122可更新此计数值。例如,假设默认时间长度为1分钟,当存储器控制器122持续处于忙碌状态(例如执行写入或读取操作)的时间增加1分钟时,存储器控制器122可将此计数值加1。In one embodiment, the
在一实施例中,从此计数值被重置后开始,此计数值即可反映存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的累积时间长度。例如,假设当前的计数值为5,表示从计数值被重置后开始,存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的累积时间长度为5分钟。此外,若存储器控制器122进入闲置状态(例如停止执行写入或读取操作),则存储器控制器122可暂停累积存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的累积时间并可暂停更新此计数值。In one embodiment, after the count value is reset, the count value can reflect the accumulated time length that the
图2是根据本发明的实施例所示出的计数值与存储器装置的累积忙碌时间之间的对应的示意图。请参照图2,在一实施例中,所述计数值与存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间(即存储器装置12处于忙碌状态的累积时间长度)之间的对应关系可以如图2所示。亦即,随着存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间持续增加(例如从T(0)增加至T(i+1)),所述计数值也可持续更新(例如从V(1)增加至V(i+1))。例如,当存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间从0增加至T(0)时,所述计数值也可从0被更新为V(1);当存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间从T(0)增加至T(1)时,所述计数值也可从V(1)被更新为V(2);依此类推,当存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间从T(i)增加至T(i+1)时,所述计数值也可从V(i)被更新为V(i+1)。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating the correspondence between the count value and the accumulated busy time of the memory device according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 2 , in an embodiment, the corresponding relationship between the count value and the accumulated busy time of the memory device 12 (ie, the accumulated time length of the
在一实施例中,主机系统11可从存储器装置12读取于某一时间点(亦称为第一时间点)记录的计数值(亦称为第一计数值)。稍后,主机系统11可从存储器装置12读取于另一时间点(亦称为第二时间点)记录的计数值(亦称为第二计数值)。第一时间点可早于第二时间点。例如,第一时间点与第二时间点之间可间隔3分钟或某一采样时间间隔。In one embodiment, the
图3是根据本发明的实施例所示出的第一计数值与第二计数值在时间上的相关关系的示意图。请参照图3,假设第一时间点为时间点T(S1),第二时间点为时间点T(S2),且时间点T(S1)早于时间点T(S2)。时间点T(S1)与时间点T(S2)之间可间隔一个采样时间间隔(例如3分钟)。计数值V(S1)可表示,于时间点T(S1)上,对图2的计数值进行读取或采样所获得的数值。计数值V(S2)可表示,于时间点T(S2)上,对图2的计数值进行读取或采样所获得的数值。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the correlation between the first count value and the second count value in time according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 3, it is assumed that the first time point is time point T(S1), the second time point is time point T(S2), and time point T(S1) is earlier than time point T(S2). A sampling time interval (eg, 3 minutes) may be spaced between the time point T(S1) and the time point T(S2). The count value V(S1) may represent a value obtained by reading or sampling the count value of FIG. 2 at the time point T(S1). The count value V(S2) may represent a value obtained by reading or sampling the count value of FIG. 2 at the time point T(S2).
在一实施例中,主机系统11可根据第一计数值与第二计数值之间的数值相对关系决定存储器装置12是否处于忙碌状态。例如,此数值相对关系可以是指第一计数值与第二计数值之间的数值大小关系。例如,此数值相对关系可包括第二计数值大于第一计数值、第二计数值等于第一计数值及第二计数值小于第一计数值。In one embodiment, the
在一实施例中,若第一计数值与第二计数值之间的数值相对关系为第二计数值大于第一计数值,表示在这两个计数值的采样时间间隔中,存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间持续增加(导致所述计数值的数值改变或增加)。因此,主机系统11可根据第二计数值大于第一计数值而判定存储器装置11处于忙碌状态。In one embodiment, if the numerical relative relationship between the first count value and the second count value is that the second count value is greater than the first count value, it means that in the sampling time interval of the two count values, the The cumulative busy time continues to increase (resulting in a numerical change or increase in the count value). Therefore, the
在一实施例中,若第一计数值与第二计数值之间的数值相对关系为第二计数值不大于(或等于)第一计数值,表示在这两个计数值的采样时间间隔中,存储器装置12的累积忙碌时间并未持续增加(两次采样的计数值并未改变或增加)。因此,主机系统11可根据第二计数值不大于(或等于)第一计数值而判定存储器装置11不处于忙碌状态。In one embodiment, if the numerical relative relationship between the first count value and the second count value is that the second count value is not greater than (or equal to) the first count value, it means that in the sampling time interval of the two count values , the accumulated busy time of the
在一实施例中,只有当主机系统11判定存储器装置12已不处于忙碌状态(或离开忙碌状态)且存储器装置12的温度低于第二门槛值这两个条件同时满足时,主机系统11可指示存储器装置12停止降温程序。换言之,在一实施例中,若主机系统11判定存储器装置12仍处于忙碌状态,则无论存储器装置12的温度是否低于第二门槛值,主机系统11皆不指示存储器装置12停止降温程序。或者,在一实施例中,若主机系统11判定存储器装置12不处于忙碌状态但存储器装置12的温度未低于第二门槛值,则主机系统11也不指示存储器装置12停止降温程序。In one embodiment, only when the
从另一角度而言,在一实施例中,一旦在存储器装置12处于忙碌状态下启动所述降温程序,则后续只有当主机系统11判定存储器装置12已离开忙碌状态且存储器装置12的温度低于第二门槛值这两个条件同时满足时,主机系统11可指示存储器装置12停止当前执行中的降温程序。藉此,可减少在存储器装置12离开忙碌状态之前反复启动与停止降温程序,从而提升存储器装置12的操作稳定度。From another perspective, in one embodiment, once the cooling process is started when the
在一实施例中,在启动降温程序后,存储器控制器122可将存储器装置12的温度与至少两个门槛值(例如称为第三门槛值与第四门槛值)中的至少一者进行比较。第四门槛值高于第三门槛值。例如,第三门槛值可为67度,且第四门槛值可为69度。存储器控制器122可根据比较结果来调整降温程序中采用的降温手段,直到停止降温程序为止。须注意的是,前述各个门槛值皆可根据实务需求调整,本发明不加以限制。In one embodiment, after initiating the cooling process, the
例如,在一实施例的降温程序中,若存储器装置12的温度不高于第三门槛值,存储器控制器122可执行一个初阶降温手段,以对存储器装置12进行初始降温。若存储器装置12的温度介于第三门槛值与第四门槛值之间,存储器控制器122可执行一个进阶降温手段,以对存储器装置12进行进阶降温。此外,若存储器装置12的温度高于第四门槛值,则存储器控制器122可执行一个强烈降温手段,以对存储器装置12进行强烈降温。其中,强烈降温手段的降温效率高于进阶降温手段的降温效率,且进阶降温手段的降温效率高于初阶降温手段的降温效率。此外,每一阶段的降温手段皆可采用前述多种降温手段的至少其中之一,从而达到所需的降温需求。For example, in the cooling procedure of an embodiment, if the temperature of the
图4是根据本发明的一实施例所示出的温度控制方法的流程图。请参照图4,在步骤S401中,检测存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态。若存储器装置处于忙碌状态,在步骤S402中,检测所述存储器装置的温度是否高于第一门槛值。响应于所述存储器装置处于忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的温度高于第一门槛值,在步骤S403中,指示所述存储器装置执行降温程序。然而,若在步骤S401中判定所述存储器装置未处于忙碌状态,或于步骤S402中判定所述存储器装置的温度未高于第一门槛值,则可不进入步骤S403而回到步骤S401。FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a temperature control method according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 4 , in step S401 , it is detected whether the memory device is in a busy state. If the memory device is in a busy state, in step S402, it is detected whether the temperature of the memory device is higher than a first threshold value. In response to the memory device being in a busy state and the temperature of the memory device being higher than the first threshold value, in step S403 , instructing the memory device to perform a cooling procedure. However, if it is determined in step S401 that the memory device is not in a busy state, or it is determined in step S402 that the temperature of the memory device is not higher than the first threshold value, then step S401 may be returned without going to step S403.
在启动降温程序后,在步骤S404中,检测所述存储器装置的温度是否低于第二门槛值。若所述存储器装置的温度低于第二门槛值,在步骤S405中,检测存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态。响应于所述存储器装置不处于忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的温度低于第二门槛值,在步骤S406中,指示所述存储器装置结束所述降温程序。然而,须注意的是,在启动降温程序后,若所述存储器装置不处于忙碌状态且所述存储器装置的温度低于第二门槛值此两个条件未同时满除,则可回到步骤S403指示所述存储器装置维持所述降温程序,直到前述两个条件同时满足为止。After the cooling procedure is started, in step S404, it is detected whether the temperature of the memory device is lower than a second threshold value. If the temperature of the memory device is lower than the second threshold, in step S405, it is detected whether the memory device is in a busy state. In response to the memory device not being in a busy state and the temperature of the memory device being lower than the second threshold, in step S406, instructing the memory device to end the cooling process. However, it should be noted that, after the cooling process is started, if the memory device is not in a busy state and the temperature of the memory device is lower than the second threshold, the two conditions are not fully divided at the same time, then the process can go back to step S403 The memory device is instructed to maintain the cool down procedure until both the aforementioned conditions are met simultaneously.
然而,图4中各步骤已详细说明如上,在此便不再赘述。值得注意的是,图4中各步骤可以实作为多个程序码或是电路,本发明不加以限制。此外,图4的方法可以搭配以上范例实施例使用,也可以单独使用,本发明不加以限制。However, each step in FIG. 4 has been described in detail as above, and will not be repeated here. It should be noted that each step in FIG. 4 can be implemented as a plurality of program codes or circuits, which is not limited in the present invention. In addition, the method of FIG. 4 can be used in conjunction with the above exemplary embodiments, and can also be used alone, which is not limited in the present invention.
综上所述,本发明的实施例提出可根据存储器装置是否处于忙碌状态以及存储器装置的温度是否高于第一门槛值(或低于第二门槛值)来作为主机系统是否启动(或停止)降温程序的双重验证。藉此,可减少在存储器装置离开忙碌状态之前反复启动与停止降温程序,从而提升存储器装置的操作稳定度和/或提高对于存储器装置的温度控制能力。To sum up, the embodiments of the present invention propose whether the host system is started (or stopped) according to whether the memory device is in a busy state and whether the temperature of the memory device is higher than the first threshold value (or lower than the second threshold value) Two-factor validation of cooling procedures. Thereby, it is possible to reduce repeatedly starting and stopping the cooling process before the memory device leaves the busy state, thereby improving the operation stability of the memory device and/or improving the temperature control capability of the memory device.
最后应说明的是:以上各实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述各实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分或者全部技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的范围。Finally, it should be noted that the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, but not to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: The technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments can still be modified, or some or all of the technical features thereof can be equivalently replaced; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention. scope.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011597774.9A CN114690866B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Temperature control method and data storage system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011597774.9A CN114690866B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Temperature control method and data storage system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114690866A true CN114690866A (en) | 2022-07-01 |
| CN114690866B CN114690866B (en) | 2024-06-11 |
Family
ID=82133098
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011597774.9A Active CN114690866B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Temperature control method and data storage system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114690866B (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104898982A (en) * | 2014-03-03 | 2015-09-09 | 群联电子股份有限公司 | Data transmission method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage device |
| CN108594971A (en) * | 2018-02-01 | 2018-09-28 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | control method and control system |
| US20190339881A1 (en) * | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Increasing flash memory retention time using waste heat |
| CN110556139A (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2019-12-10 | 晨星半导体股份有限公司 | Circuit for controlling memory and related method |
| CN111831024A (en) * | 2019-04-19 | 2020-10-27 | 群联电子股份有限公司 | Temperature control circuit, memory storage device and temperature control method |
-
2020
- 2020-12-29 CN CN202011597774.9A patent/CN114690866B/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104898982A (en) * | 2014-03-03 | 2015-09-09 | 群联电子股份有限公司 | Data transmission method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage device |
| CN108594971A (en) * | 2018-02-01 | 2018-09-28 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | control method and control system |
| US20190339881A1 (en) * | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Increasing flash memory retention time using waste heat |
| CN110556139A (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2019-12-10 | 晨星半导体股份有限公司 | Circuit for controlling memory and related method |
| CN111831024A (en) * | 2019-04-19 | 2020-10-27 | 群联电子股份有限公司 | Temperature control circuit, memory storage device and temperature control method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114690866B (en) | 2024-06-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI447733B (en) | Methods for calculating compensating voltage and adjusting threshold voltage and memory apparatus and controller | |
| US9424177B2 (en) | Clock switching method, memory controller and memory storage apparatus | |
| TW201314455A (en) | Memory storage device, memory controller, and temperature management method | |
| US12045460B2 (en) | Temperature control method and data storage system | |
| CN102592677A (en) | Memory device, memory control method, and program | |
| TWI802324B (en) | Method of sudden power off recovery, memory controlling circuit unit and memory storage device | |
| CN114327265B (en) | Read interference checking method, memory storage device and control circuit unit | |
| CN113885692B (en) | Memory efficiency optimization method, memory control circuit unit and memory device | |
| TWI526818B (en) | Method of enabling sleep mode, memory control circuit unit and storage appartus | |
| CN108428467A (en) | Read voltage tracking method, memory storage device and control circuit unit | |
| TWI840148B (en) | Performance match method of memory, memory storage device and memory control circuit unit | |
| CN103914391A (en) | Data reading method, memory controller and memory storage device | |
| CN106325764A (en) | Memory management method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage device | |
| TWI757216B (en) | Temperature control method, memory storage device and memory control circuit unit | |
| CN114690866B (en) | Temperature control method and data storage system | |
| KR102730283B1 (en) | Data storage device and operating method thereof | |
| TWI768829B (en) | Parameter adjusting method for a memory device and a memory storage system | |
| CN117289873A (en) | Device control method, memory storage device and memory control circuit unit | |
| CN103985403B (en) | Working clock switching method, memory controller and memory storage device | |
| CN103777732B (en) | Connector control method, connector and memory storage device | |
| CN114765035A (en) | Storage device and storage device management method | |
| US20250103228A1 (en) | Power state control method and data storage system | |
| TWI871806B (en) | Device control method and a data storage system | |
| US12216933B1 (en) | Memory management method, memory storage device, and memory control circuit unit | |
| TWI521354B (en) | Controlling method for connector, connector and memory storage device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |