CN108083679B - Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN108083679B CN108083679B CN201711393195.0A CN201711393195A CN108083679B CN 108083679 B CN108083679 B CN 108083679B CN 201711393195 A CN201711393195 A CN 201711393195A CN 108083679 B CN108083679 B CN 108083679B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- concrete
- agent
- reducing agent
- water
- cement
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004567 concrete Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 104
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 44
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 title abstract description 10
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title abstract description 10
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000004088 foaming agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000012744 reinforcing agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000004721 Polyphenylene oxide Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium laurylsulphate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229920000570 polyether Polymers 0.000 claims description 8
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Betaine Natural products C[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O N,N,N-trimethylglycinium Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 claims description 7
- 229960003237 betaine Drugs 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 claims description 6
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,2-tetramine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCN VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- MRUAUOIMASANKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cocamidopropyl betaine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NCCC[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O MRUAUOIMASANKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229940073507 cocamidopropyl betaine Drugs 0.000 claims description 4
- GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexamethylphosphoric triamide Chemical compound CN(C)P(=O)(N(C)C)N(C)C GNOIPBMMFNIUFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920000141 poly(maleic anhydride) Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920000058 polyacrylate Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- MAQDBUNNVYRNQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N pent-2-ene-1,1,1,2-tetramine Chemical compound NC(C(N)(N)N)=CCC MAQDBUNNVYRNQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920001529 polyepoxysuccinic acid Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004568 cement Substances 0.000 abstract description 27
- 230000001603 reducing effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 9
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 21
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- NHWGPUVJQFTOQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl-[2-[2-[ethyl(dimethyl)azaniumyl]ethyl-methylamino]ethyl]-dimethylazanium Chemical compound CC[N+](C)(C)CCN(C)CC[N+](C)(C)CC NHWGPUVJQFTOQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000006703 hydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011056 performance test Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920005646 polycarboxylate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004576 sand Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008030 superplasticizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052918 calcium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000378 calcium silicate Substances 0.000 description 1
- OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N calcium;dioxido(oxo)silane Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-][Si]([O-])=O OYACROKNLOSFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005056 compaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052593 corundum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004134 energy conservation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003912 environmental pollution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010881 fly ash Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000036571 hydration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001845 yogo sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C04—CEMENTS; CONCRETE; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES
- C04B—LIME, MAGNESIA; SLAG; CEMENTS; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF, e.g. MORTARS, CONCRETE OR LIKE BUILDING MATERIALS; ARTIFICIAL STONE; CERAMICS; REFRACTORIES; TREATMENT OF NATURAL STONE
- C04B40/00—Processes, in general, for influencing or modifying the properties of mortars, concrete or artificial stone compositions, e.g. their setting or hardening ability
- C04B40/0028—Aspects relating to the mixing step of the mortar preparation
- C04B40/0039—Premixtures of ingredients
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Curing Cements, Concrete, And Artificial Stone (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a concrete gel reducing agent and a preparation method thereof, wherein the concrete gel reducing agent comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 16-25% of reinforcing agent, 12-20% of dispersing agent, 0.1-0.5% of foaming agent, 0.05-0.2% of foam stabilizer and 55-71% of water. The concrete glue reducing agent provided by the invention can reduce the using amount of cement in concrete by 10.7-18.4%, has a remarkable enhancing effect on the strength of the concrete, has good workability, and also has a water reducing effect.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of concrete admixtures, in particular to a concrete glue reducing agent and a preparation method thereof.
Background
Concrete is a general term for engineering composite materials in which aggregate is cemented into a whole by a cementing material. The concrete is characterized in that cement is used as a cementing material, and sand and stone are used as aggregate; the concrete, also called common concrete, is prepared by mixing the concrete with water (which can contain additives and admixtures) according to a certain proportion, uniformly stirring, densely forming, curing and hardening, has the characteristics of rich raw materials, low price and simple production process, and is widely applied to civil engineering.
Research shows that under the conventional environment, about 20-30% of cement cementing materials in concrete have insufficient hydration reaction, only play a filling role and cannot effectively play a role of cement; on the other hand, the cement production process has large resource consumption and serious environmental pollution, so that the consumption of the cement in the concrete is reduced as much as possible on the basis of ensuring the service performance of the concrete, the cost is reduced, and the purpose of green environmental protection is favorably realized.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention mainly aims to provide a concrete glue reducing agent and a preparation method thereof, aiming at improving the strength of concrete while reducing the dosage of cement in the concrete.
In order to achieve the purpose, the concrete gel reducing agent provided by the invention comprises the following components in percentage by mass:
16-25% of reinforcing agent, 12-20% of dispersing agent, 0.1-0.5% of foaming agent, 0.05-0.2% of foam stabilizer and 55-71% of water.
Preferably, the enhancer comprises at least one of hexametaphosphoric triamide, pentaenetetramine and triethylenetetramine.
Preferably, the dispersant comprises at least one of polyepoxysuccinic acid (sodium), polymaleic anhydride, phosphonopolyacrylic acid, and carboxylic acid-sulfonic acid-acrylate terpolymer.
Preferably, the foaming agent comprises at least one of cocamidoethyl betaine, cocamidopropyl betaine, cocamidobutyl betaine, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and sodium dodecyl sulfate.
Preferably, the foam stabilizer is a silicone polyether emulsion.
The invention also provides a preparation method of the concrete gel reducing agent, which comprises the following steps:
and stirring the reinforcing agent, the dispersing agent, the foaming agent, the foam stabilizer and water at 25-40 ℃ for 2-4 h to obtain the concrete gel reducer.
The concrete gel reducing agent provided by the invention can reduce the using amount of cement in concrete by 10.7-18.4%, has a remarkable enhancing effect on the strength of the concrete, has good workability, and also has a water reducing effect.
Detailed Description
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below. The examples, in which specific conditions are not specified, were conducted under conventional conditions or conditions recommended by the manufacturer. The reagents or instruments used are not indicated by the manufacturer, and are all conventional products available commercially.
The invention provides a concrete gel reducing agent which comprises the following components in percentage by mass:
16-25% of reinforcing agent, 12-20% of dispersing agent, 0.1-0.5% of foaming agent, 0.05-0.2% of foam stabilizer and 55-71% of water.
The concrete gel reducing agent provided by the invention can reduce the using amount of cement in concrete by 10.7-18.4%, has a remarkable enhancing effect on the strength of the concrete, is good in workability, and also has a water reducing effect and good adaptability. The strength of the concrete can be improved while the using amount of cement in the concrete is reduced, so that the cost of the concrete can be reduced, and the purpose of green environmental protection is facilitated.
The reinforcing agent has the function of improving the strength of concrete, and after being mixed into the concrete, the reinforcing agent can be uniformly distributed to the interface area of concrete aggregate and cement paste, so that SiO in the sandstone2And Al2O3Hydrate of cement Ca (OH)2The hydration is carried out for many times to produce hydrated calcium silicate gel, thereby greatly improving the performances of the concrete such as strength, durability, corrosion resistance and the like. In the embodiment of the invention, the reinforcing agent comprises at least one of hexamethylphosphoric triamide, pentaenetetramine and triethylenetetramine, and the cement particles are arranged more densely by changing the electric potential through forming an adsorption film on the surfaces of the cement particles through adsorption, thereby achieving the effects of reinforcing and reducing the water consumption.
The dispersant has the functions of uniformly dispersing cement particles when concrete is mixed and improving the rheological property of the concrete when the concrete is mixed. In an embodiment of the invention, the dispersant comprises at least one of polyepoxysuccinic acid (sodium), polymaleic anhydride, phosphonopolyacrylic acid, and carboxylic acid-sulfonic acid-acrylate terpolymer.
The foaming agent has the function of enabling concrete to form a more compact pore structure and an interface microstructure during compaction forming, so that the physical and mechanical properties of the concrete are improved. In embodiments of the invention, the foaming agent comprises at least one of cocamidoethyl betaine, cocamidopropyl betaine, cocamidobutyl betaine, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and sodium dodecyl sulfate.
The foam stabilizer has the function of stabilizing a porous structure generated by the action of the foaming agent, and is not easy to crack or form holes (the strength of the porous structure is reduced due to the cracking or the forming of the holes). In the embodiment of the invention, the foam stabilizer is a silicone polyether emulsion.
The invention also provides a preparation method of the concrete gel reducing agent, which comprises the following steps:
and stirring the reinforcing agent, the dispersing agent, the foaming agent, the foam stabilizer and water at 25-40 ℃ for 2-4 h to obtain the concrete gel reducer.
Wherein, the mass fraction of each raw material component in the total amount of the raw materials is as follows: 16-25% of reinforcing agent, 12-20% of dispersing agent, 0.1-0.5% of foaming agent, 0.05-0.2% of foam stabilizer and 55-71% of water. The concrete size reducer prepared by the method provided above can be incorporated during the process of mixing concrete, and the incorporation amount is generally not more than 5% of the mass of cement (except in special cases). In the embodiment of the invention, the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 0.5-1.0% of the mass of the cement.
The preparation method of the concrete gel reducing agent provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple process and easiness in mass production, and the temperature required in the preparation process is lower, so that the purposes of energy conservation and environmental protection can be achieved.
The technical solutions of the present invention are further described in detail with reference to the following specific examples, which should be understood as merely illustrative and not limitative.
Example 1
(1) Stirring 20% of hexamethylphosphoric triamide, 14% of polymaleic anhydride, 0.4% of sodium dodecyl sulfate, 0.15% of silicone resin polyether emulsion and 65.45% of water at 25 ℃ for 4 hours to obtain the concrete gel reducer for later use.
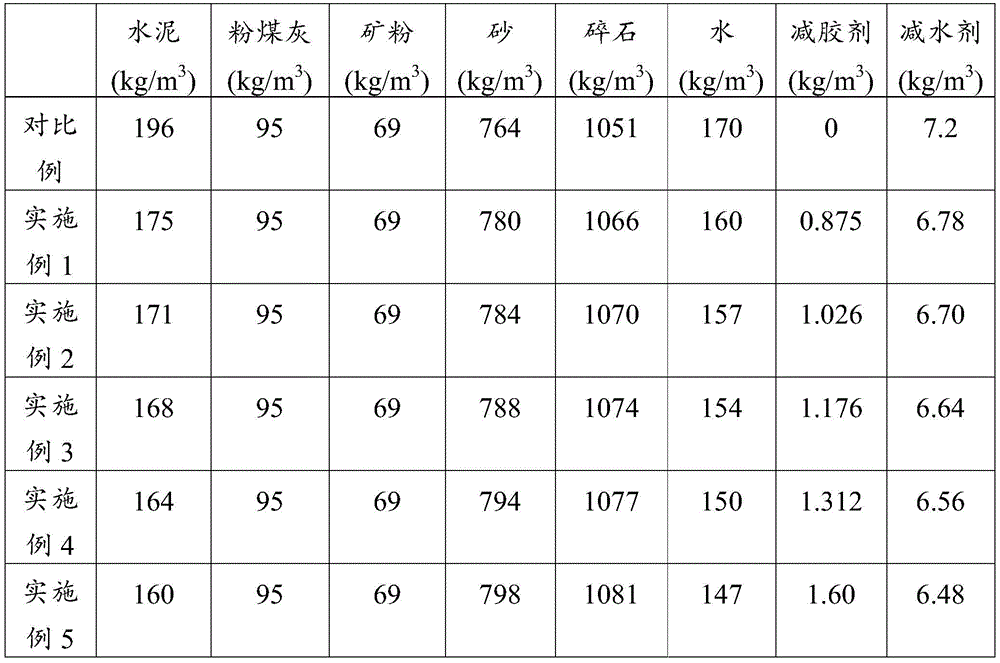
(2) The concrete glue reducing agent prepared in the step (1) is mixed into concrete (mixed in the concrete mixing process), and then standard curing is carried out for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 0.5% of the mass of cement in the concrete, and the mixing ratio of the concrete is shown in table 1.
It should be noted that in all the examples and comparative examples, the reduced amounts of cement and water were added to the amounts of sand and crushed stone, respectively, to avoid the difference in performance test results due to the inconsistent overall quality of the concrete; in addition, in all the examples and comparative examples, a commercial polycarboxylate-type high-performance water reducing agent is added at the same time, wherein the solid content of the water reducing agent is 10%, and the addition amount of the water reducing agent is 2.0% of the total mass of the cement, the fly ash and the mineral powder.
TABLE 1 mixing ratio of concrete in each example
Example 2
(1) 25% of pentamine, 15% of (sodium) polyepoxysuccinate, 0.3% of cocamidopropyl betaine, 0.1% of silicone polyether emulsion and 59.6% of water are stirred for 3.5 hours at the temperature of 30 ℃ to obtain the concrete gel reducing agent for later use.
(2) The concrete glue reducing agent prepared in the step (1) is mixed into concrete (mixed in the concrete mixing process), and then standard curing is carried out for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 0.6 percent of the mass of cement in the concrete, and the mixing ratio of the concrete is shown in table 1.
Example 3
(1) Stirring 16.3% of triethylenetetramine, 12% of phosphonopolyacrylic acid, 0.5% of cocamidobutyl betaine, 0.2% of silicone polyether emulsion and 71% of water at 35 ℃ for 3 hours to obtain the concrete gel reducing agent for later use.
(2) The concrete glue reducing agent prepared in the step (1) is mixed into concrete (mixed in the concrete mixing process), and then standard curing is carried out for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 0.7% of the mass of cement in the concrete, and the mixing ratio of the concrete is shown in table 1.
Example 4
(1) Stirring 23% of hexamethylphosphoric triamide, 20% of carboxylic acid-sulfonic acid-acrylate terpolymer, 0.1% of cocamidoethylbetaine, 0.05% of silicone polyether emulsion and 56.85% of water at 40 ℃ for 2h to obtain the concrete gel reducer for later use.
(2) The concrete glue reducing agent prepared in the step (1) is mixed into concrete (mixed in the concrete mixing process), and then standard curing is carried out for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 0.8% of the mass of cement in the concrete, and the mixing ratio of the concrete is shown in table 1.
Example 5
(1) 25% of pentamine, 18% of (sodium) polyepoxysuccinate, 0.5% of sodium dodecyl sulfate, 0.2% of silicone resin polyether emulsion and 56.3% of water are stirred for 2.5 hours at 33 ℃ to obtain the concrete gel reducer for later use.
(2) The concrete glue reducing agent prepared in the step (1) is mixed into concrete (mixed in the concrete mixing process), and then standard curing is carried out for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducing agent is 1.0% of the mass of cement in the concrete, and the mixing ratio of the concrete is shown in table 1.
Comparative example
Only adding a commercial polycarboxylate superplasticizer into concrete as a comparative example, and then carrying out standard curing for 3d, 7d and 28 d; the concrete mixing ratio is shown in table 1.
The water reducing rate, slump/expansion, workability and compressive strength of the concrete in each example and comparative example were respectively tested according to the test method of the properties of the mixture of ordinary concrete of GB/T50080-2002, and the results are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 results of performance tests of the concrete in each example and comparative example
As can be seen from tables 1 and 2, when the mixing amount of the concrete gel reducer prepared in the embodiment of the invention is 0.5-1.0% of the mass of cement in concrete, the using amount of the cement in the concrete can be reduced by 10.7-18.4%, compared with the concrete only mixed with the commercial polycarboxylate superplasticizer, the concrete gel reducer has slightly improved water reducing rate, and has remarkable reinforcing effect on the strength of the concrete and good workability.
In conclusion, the concrete gel reducing agent provided by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, capability of greatly reducing the using amount of cement in concrete, remarkable enhancement effect on the strength of the concrete, good workability, certain water reducing effect and good adaptability.
The above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, and all modifications of equivalent structures and equivalent processes, which are made by the present specification, or directly or indirectly applied to other related technical fields, are included in the scope of the present invention.
Claims (4)
1. The concrete gel reducing agent is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by mass:
16-25% of a reinforcing agent, 12-20% of a dispersing agent, 0.1-0.5% of a foaming agent, 0.05-0.2% of a foam stabilizer and 55-71% of water; wherein the reinforcing agent comprises at least one of hexamethylphosphoric triamide, pentaenetetramine and triethylenetetramine, and the dispersing agent comprises at least one of polyepoxysuccinic acid (sodium), polymaleic anhydride, phosphonopolyacrylic acid and carboxylic acid-sulfonic acid-acrylate terpolymer.
2. The concrete size reducer of claim 1, wherein the foaming agent comprises at least one of cocamidoethyl betaine, cocamidopropyl betaine, cocamidobutyl betaine, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and sodium dodecyl sulfate.
3. The concrete gel reducer of claim 1, wherein the foam stabilizer is a silicone polyether emulsion.
4. A method for preparing the concrete gel reducing agent according to any one of claims 1 to 3, comprising the steps of:
and stirring the reinforcing agent, the dispersing agent, the foaming agent, the foam stabilizer and water at 25-40 ℃ for 2-4 h to obtain the concrete gel reducer.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201711393195.0A CN108083679B (en) | 2017-12-21 | 2017-12-21 | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201711393195.0A CN108083679B (en) | 2017-12-21 | 2017-12-21 | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN108083679A CN108083679A (en) | 2018-05-29 |
| CN108083679B true CN108083679B (en) | 2020-10-09 |
Family
ID=62177802
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201711393195.0A Active CN108083679B (en) | 2017-12-21 | 2017-12-21 | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN108083679B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109437643B (en) * | 2018-09-12 | 2021-03-02 | 湖北工业大学 | A kind of method for preparing glue reducer from amphoteric polyester polycarboxylate compound |
| CN109534713B (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2021-07-02 | 武汉优城科技有限公司 | Glue reducing agent for high-strength concrete and preparation method thereof |
| CN110386773A (en) * | 2019-06-28 | 2019-10-29 | 浙江老虎山建材有限公司 | A kind of concrete subtracts the preparation method of jelly |
| CN111646729A (en) * | 2020-05-15 | 2020-09-11 | 湖南武源建材有限责任公司 | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation process thereof |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104129943A (en) * | 2014-08-18 | 2014-11-05 | 四川恒泽建材有限公司 | Wet-mixed mortar admixture as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN105217995A (en) * | 2015-11-06 | 2016-01-06 | 科之杰新材料集团有限公司 | A kind of Concrete synergist and preparation method thereof |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101456693B (en) * | 2008-12-31 | 2012-06-27 | 王本淼 | Modifying agent for building expansion material |
| KR101242729B1 (en) * | 2011-04-27 | 2013-03-12 | 우진산업주식회사 | shrinkage-reducing cement dispersant and concret composition containing that |
| CN106946488A (en) * | 2017-02-23 | 2017-07-14 | 杭州筑乐科技有限公司 | Concrete synergist and preparation method thereof |
| CN107244844B (en) * | 2017-07-26 | 2019-11-29 | 盐城爱乐科网络科技股份有限公司 | A kind of green geology polymer heat preserving material and preparation method thereof |
-
2017
- 2017-12-21 CN CN201711393195.0A patent/CN108083679B/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104129943A (en) * | 2014-08-18 | 2014-11-05 | 四川恒泽建材有限公司 | Wet-mixed mortar admixture as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN105217995A (en) * | 2015-11-06 | 2016-01-06 | 科之杰新材料集团有限公司 | A kind of Concrete synergist and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN108083679A (en) | 2018-05-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108059382B (en) | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110304872B (en) | Nano modified cement-based underwater non-dispersible material and preparation method thereof | |
| Türkel et al. | The effect of limestone powder, fly ash and silica fume on the properties of self-compacting repair mortars | |
| CN109455992A (en) | A kind of machine-made sand concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN111807777B (en) | Concrete with gold mine tailing powder as full aggregate and preparation method thereof | |
| CN105693173B (en) | A kind of sleeve grouting material for assembled architecture | |
| CN108083679B (en) | Concrete glue reducing agent and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114014613B (en) | A kind of salt corrosion-resistant concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103265253A (en) | High-performance grouting material for prefabricated building construction, and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110981299A (en) | A kind of high-performance geopolymer concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN102815910A (en) | Cement glue with adjustable performances | |
| CN110498630B (en) | Concrete composite additive, preparation method thereof and concrete | |
| CN115073093A (en) | A kind of low-shrinkage high-strength self-compacting recycled concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104386969A (en) | High-strength and high-durability lightweight aggregate concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN105236879A (en) | Masonry mortar doped with geopolymer and phosphorus slag powder and use method | |
| CN116535147B (en) | Method for preparing self-compacting concrete by utilizing tailing sand and application | |
| CN103755252A (en) | Novel concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN115180915B (en) | High-performance concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110563376B (en) | Concrete reinforcing agent suitable for being prepared from machine-made sand and preparation method of mother liquor of concrete reinforcing agent | |
| CN116496058A (en) | High-strength waterproof gypsum-based self-leveling mortar and preparation method thereof | |
| CN111517740A (en) | A kind of cement-based composite material for 3D printing and preparation method thereof | |
| CN113149577A (en) | Impervious concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN115849838B (en) | Low-alkali concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN115353349B (en) | C60 high-mud-content machine-made sand large-flow-state concrete and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110407541A (en) | A large-volume anti-crack concrete for hydraulic engineering and its preparation method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |