JP5139190B2 - Magnetic switch - Google Patents
Magnetic switch Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5139190B2 JP5139190B2 JP2008195403A JP2008195403A JP5139190B2 JP 5139190 B2 JP5139190 B2 JP 5139190B2 JP 2008195403 A JP2008195403 A JP 2008195403A JP 2008195403 A JP2008195403 A JP 2008195403A JP 5139190 B2 JP5139190 B2 JP 5139190B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- magnetic
- magnetic field
- layer
- magnetization
- magnetic layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Magnetic Variables (AREA)
Description
本発明は、特に、小型化、且つ製造コストを低減できる磁気スイッチに関する。 The present invention particularly relates to a magnetic switch that can be reduced in size and reduced in manufacturing cost.
磁化方向が固定された固定磁性層、非磁性層、及び磁化方向が外部磁界に対して変動するフリー磁性層の積層構造を備える巨大磁気抵抗効果素子(GMR素子)は、外部磁界に対して検出信号を得るための磁気スイッチ内に組み込まれる。 A giant magnetoresistive element (GMR element) having a laminated structure of a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a nonmagnetic layer, and a free magnetic layer whose magnetization direction fluctuates with respect to an external magnetic field is detected with respect to the external magnetic field. Embedded in a magnetic switch for obtaining a signal.
従来では、第1方向の外部磁界の磁界強度変化、及び、第1方向とは逆方向の第2方向の外部磁界の磁界強度変化を、夫々、検知するために、第1方向の外部磁界用GMR素子と、第2方向の外部磁界用GMR素子の2種類を必要とした。しかもブリッジ回路を組む場合、各GMR素子の素子特性(温度特性等)に合わせて、固定抵抗素子も2種類必要となった。すなわち従来では、異なる4種類の素子を必要とした。 Conventionally, in order to detect the change in the magnetic field strength of the external magnetic field in the first direction and the change in the magnetic field strength of the external magnetic field in the second direction opposite to the first direction, respectively, Two types of GMR element and a GMR element for external magnetic field in the second direction are required. In addition, when a bridge circuit is assembled, two types of fixed resistance elements are required in accordance with the element characteristics (temperature characteristics, etc.) of each GMR element. That is, conventionally, four different types of elements are required.
また、GMR素子や固定抵抗素子を備える回路に電気的に接続される制御部(集積回路)には、第1GMR素子の電気抵抗変化に基づいて変化するセンサ出力により、検出信号を生成し出力するための第1電気回路と、第2GMR素子の電気抵抗変化に基づいて変化するセンサ出力により、検出信号を生成し出力するための第2電気回路との2系統が必要であった。 In addition, a control signal (integrated circuit) electrically connected to a circuit including a GMR element or a fixed resistance element generates and outputs a detection signal based on a sensor output that changes based on a change in electric resistance of the first GMR element. Therefore, two systems of a first electric circuit for generating and a second electric circuit for generating and outputting a detection signal by a sensor output that changes based on a change in electric resistance of the second GMR element are required.
以上により、従来の双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチでは、2種類のGMR素子が必要となり、固定抵抗も合わせると4種類の素子が必要であったため素子形成の材料費(製造コスト)が高くなった。また、制御部も2系統の電気回路が必要あるためチップサイズが大きくなり、磁気スイッチの小型化を促進できない問題があった。 As described above, in the conventional magnetic switch for bipolar detection, two types of GMR elements are required, and when combined with the fixed resistance, four types of elements are required. Therefore, the material cost for manufacturing the element (manufacturing cost) is increased. . In addition, since the control unit also requires two electric circuits, the chip size becomes large, and there is a problem that the miniaturization of the magnetic switch cannot be promoted.
特許文献1,2には上記した磁気スイッチの従来課題の認識がなく、当然、その解決手段も示されていない。
そこで本発明は上記従来課題を解決するためのものであり、特に、1種類の磁気検出素子で足り、また、制御部を共通回路で構成できる双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチを提供することを目的としている。 Accordingly, the present invention is to solve the above-described conventional problems, and in particular, to provide a magnetic switch for bipolar detection that can suffice with one kind of magnetic detection element and that can be configured with a common circuit as a control unit. It is said.
本発明は、感度軸方向からの外部磁界に対して電気抵抗値が変化する磁気検出素子と、前記磁気検出素子の電気抵抗変化に基づいて変化するセンサ出力に基づき、検出信号を出力する制御部とを有して成る磁気スイッチにおいて、
1種類の前記磁気検出素子を内蔵しており、前記磁気検出素子は、外部磁界に対して磁化変動可能な第1磁性層及び第2磁性層が非磁性層を介して積層された素子部を備えて、前記感度軸方向のうち第1の方向、及び前記第1の方向とは逆方向の第2の方向の外部磁界の磁界強度変化に対して、夫々、電気抵抗値が変動する構成であり、
前記制御部は、共通回路にて、第1の方向からの外部磁界の磁界強度変化、及び第2の方向からの外部磁界の磁界強度変化により得られた夫々の前記センサ出力に基づいて、各検出信号を出力できるものであり、
前記素子部は、前記感度軸方向を長手方向とした細長形状で形成されており、
無磁場状態では、前記第1磁性層の磁化方向が、前記感度軸方向に直交する素子幅方向から前記第1の方向に傾いており、前記第2磁性層の磁化方向が、素子幅方向から前記第2の方向に傾いており、前記第1磁性層の磁化方向と、前記第2磁性層の磁化方向は、前記感度軸方向と平行な方向に向けて略反平行であることを特徴とするものである。
The present invention provides a magnetic detection element whose electric resistance value changes with respect to an external magnetic field from the sensitivity axis direction, and a control unit that outputs a detection signal based on a sensor output that changes based on a change in electric resistance of the magnetic detection element. In a magnetic switch comprising:
One kind of the magnetic detection element is built in, and the magnetic detection element includes an element portion in which a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer that can change magnetization with respect to an external magnetic field are stacked via a nonmagnetic layer. provided, the first direction of the sensitivity axis direction, and with respect to the magnetic field strength change of the second direction of the external magnetic field of said first direction backward, respectively, in the configuration electric resistance value varies Yes,
In the common circuit, each of the control units is based on the sensor outputs obtained by the magnetic field strength change of the external magnetic field from the first direction and the magnetic field strength change of the external magnetic field from the second direction. It can output detection signals ,
The element portion is formed in an elongated shape having the sensitivity axis direction as a longitudinal direction,
In the absence of a magnetic field, the magnetization direction of the first magnetic layer is inclined in the first direction from the element width direction orthogonal to the sensitivity axis direction, and the magnetization direction of the second magnetic layer is changed from the element width direction. Inclined in the second direction, the magnetization direction of the first magnetic layer and the magnetization direction of the second magnetic layer are substantially anti-parallel toward a direction parallel to the sensitivity axis direction. To do.
本発明の磁気スイッチは、双極検出対応型である。すなわち第1の方向の外部磁界が作用したときは、第1の方向の外部磁界を検知して検出信号(オン信号)を出力し、第1の方向とは逆方向の第2の方向の外部磁界が作用したときは、第2の方向の外部磁界を検知して検出信号(オン信号)を出力する。 The magnetic switch of the present invention is a bipolar detection compatible type. That is, when an external magnetic field in the first direction acts, the external magnetic field in the first direction is detected and a detection signal (ON signal) is output, and the external in the second direction opposite to the first direction. When a magnetic field is applied, an external magnetic field in the second direction is detected and a detection signal (ON signal) is output.
本発明では、上記した双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチにおいて、外部磁界に対して磁化変動可能な第1磁性層及び第2磁性層を備える磁気検出素子を用いている。この磁気検出素子は、第1の方向からの外部磁界、及び第2の方向からの外部磁界に対して夫々、電気抵抗値が変動する。よって、本発明では、このような1種類の磁気検出素子をセンサ部に組み込めば双極検知が可能になる。そして上記磁気検出素子と電気的に接続され、検出信号を生成し出力するための制御部を共通回路(1系統)で構成できる。 In the present invention, the magnetic detection element including the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer that can change the magnetization with respect to the external magnetic field is used in the above-described magnetic switch for bipolar detection. This magnetic detection element varies in electrical resistance value with respect to an external magnetic field from the first direction and an external magnetic field from the second direction. Therefore, in the present invention, bipolar detection is possible by incorporating such one type of magnetic detection element into the sensor unit. And the control part which is electrically connected with the said magnetic detection element, and produces | generates and outputs a detection signal can be comprised by a common circuit (1 system | strain).
以上により、本発明における双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチによれば、製造コストの低減を図ることができ、さらに、小型化が可能となる。 As described above, according to the magnetic switch for bipolar detection according to the present invention, the manufacturing cost can be reduced, and further, the size can be reduced.
また本発明では、感度軸方向からの外部磁界に対して良好な磁気感度を備えるとともに感度軸方向とは異なる方向からの磁界に対する外乱耐性を向上させることができる。
Further, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a good magnetic sensitivity with respect to an external magnetic field from the sensitivity axis direction, and to improve disturbance resistance against a magnetic field from a direction different from the sensitivity axis direction.
本発明では、双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチにおいて、外部磁界に対して磁化変動可能な第1磁性層及び第2磁性層を備える磁気検出素子を用いている。この磁気検出素子は、第1の方向からの外部磁界、及び第2の方向(第1の方向に対して逆方向)からの外部磁界に対して夫々、電気抵抗値が変動する。よって、本発明では、このような1種類の磁気検出素子をセンサ部に組み込めば双極検知が可能になる。そして上記磁気検出素子と電気的に接続され、検出信号を生成し出力するための制御部を共通回路(1系統)で構成できる。 In the present invention, a magnetic detection element including a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer that can change magnetization with respect to an external magnetic field is used in a magnetic switch that supports bipolar detection. The magnetic detection element varies in electrical resistance value with respect to an external magnetic field from the first direction and an external magnetic field from the second direction (the direction opposite to the first direction). Therefore, in the present invention, bipolar detection is possible by incorporating such one type of magnetic detection element into the sensor unit. And the control part which is electrically connected with the said magnetic detection element, and produces | generates and outputs a detection signal can be comprised by a common circuit (1 system | strain).
以上により、本発明における双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチによれば、製造コストの低減を図ることができ、さらに、小型化が可能となる。 As described above, according to the magnetic switch for bipolar detection according to the present invention, the manufacturing cost can be reduced, and further, the size can be reduced.
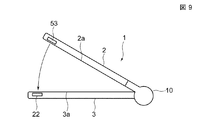
図1は、磁気スイッチに組み込まれる磁気検出素子の拡大平面図、図2は図1に示す磁気検出素子をA−A線に沿って切断し矢印方向から見た部分拡大断面図、図3は、第1磁性層と第2磁性層の磁化関係を平面的に見た模式図、図4は、外部磁界と本実施形態における磁気検出素子の電気抵抗値との関係を示すグラフ、図5は本実施形態の磁気スイッチの回路図、図6は、外部磁界と本実施形態における磁気スイッチのセンサ出力(電圧値)との関係を示すグラフ、図7は、折畳み式携帯電話を開いた状態の平面図、図8は図7に示す折畳み式携帯電話の斜視図、図9は、図8の状態から折畳み式携帯電話を閉じる途中の状態を示す折畳み式携帯電話の側面図、図10は、図9の状態から完全に折畳み式携帯電話の閉じた状態を横から見た側面図、図11は、図10に示す閉じた状態の折畳み式携帯電話をB−B線から切断し矢印方向から見た部分断面図、図12は、図8の状態から表示筐体を反転させる途中状態を示す折畳み式携帯電話の斜視図、図13は、表示筐体の表裏面を反転させた状態を示す折畳み式携帯電話の平面図、である。 FIG. 1 is an enlarged plan view of a magnetic detection element incorporated in a magnetic switch, FIG. 2 is a partially enlarged cross-sectional view of the magnetic detection element shown in FIG. FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing the magnetization relationship between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer in a plan view, FIG. 4 is a graph showing the relationship between the external magnetic field and the electric resistance value of the magnetic detection element in the present embodiment, and FIG. 6 is a circuit diagram of the magnetic switch of the present embodiment, FIG. 6 is a graph showing the relationship between the external magnetic field and the sensor output (voltage value) of the magnetic switch of the present embodiment, and FIG. 7 is a state in which the folding cellular phone is opened. FIG. 8 is a perspective view of the foldable mobile phone shown in FIG. 7, FIG. 9 is a side view of the foldable mobile phone showing a state in the middle of closing the foldable mobile phone from the state of FIG. From the side of the closed state of the completely folding mobile phone from the state of FIG. FIG. 11 is a partial cross-sectional view of the closed folding cellular phone shown in FIG. 10 taken along the line BB and viewed from the direction of the arrow, and FIG. 12 is an inverted view of the display housing from the state of FIG. FIG. 13 is a plan view of the foldable mobile phone showing a state in which the front and back surfaces of the display housing are reversed.
各図におけるX1−X2方向、Y1−Y2方向、及びZ1−Z2方向の各方向は残り2つの方向に対して直交した関係となっている。 Each direction of the X1-X2 direction, the Y1-Y2 direction, and the Z1-Z2 direction in each figure has a relationship orthogonal to the remaining two directions.
本実施形態の磁気スイッチ22は、双極検知可能な磁気センサである。例えば図7に示すように、磁気スイッチ22は、折畳み式携帯電話1に内蔵される。
The
図7に示すように、折畳み式携帯電話1は、表示筐体2と操作筐体3と、表示筐体2と操作筐体3とを連結するヒンジ部4とを有して構成される。
As shown in FIG. 7, the foldable
図7のように折畳み式携帯電話1を開いた状態では、表示筐体2の液晶ディスプレイ等の表示画面5が設けられた表示面2aと、操作筐体3の各種の操作釦6が配置された操作面3aとが同じ側を向いた状態となる。
When the foldable
また表示筐体2の表示面2aにはスピーカ45が設けられ、操作筐体3の操作面3aにはマイク7が設けられている。
A
図8に示すように、ヒンジ部4には、横方向(図示Y1−Y2方向)に延びる第1回転軸50が設けられる。そして表示筐体2が操作筐体3に対して、第1回転軸50を中心として開閉方向に回動するように構成される。
As shown in FIG. 8, the
また図8に示すように、ヒンジ部4には、第1回転軸50に対して直交する方向(図示X1−X2方向)であって、ヒンジ部4の横方向(図示Y1−Y2方向)の中央に第2回転軸56が設けられ、表示筐体2は第2回転軸56に接続されている。そして表示筐体2は第2回転軸56を中心として反転可能に支持されている。よって本形態の折畳み式携帯電話1では図8の通常の使用状態から図12のように表示筐体2の表裏面を反転させて図13に示す反転状態に移行することができる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 8, the
図7に示すように、磁気スイッチ22は操作筐体3に、磁石53は表示筐体2に内蔵される。なお配置は逆であってもよい。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
磁石53は、例えば、図7に示すようにN極とS極とが横方向(図示Y1−Y2方向)に向くように配置されている。
For example, as shown in FIG. 7, the
本形態では、磁気スイッチ22は、図10に示すように表示筐体2と操作筐体3とを閉じた状態では、磁石53と高さ方向(図示Z方向)にて対向する位置に配置される。あるいは磁気スイッチ22は、磁石53に対しY1−Y2方向にずれた位置に配置されてもよい。
In this embodiment, the
折畳み式携帯電話1を図9の状態から図10に示すように閉じるまでの間に、磁石53から磁気スイッチ22に作用する外部磁界Hの磁界強度が徐々に強くなる。図11に示すように、閉じた状態では、磁気スイッチ22に対してY1方向に向う外部磁界Hが作用する。
The magnetic field strength of the external magnetic field H acting on the
また、図10の閉じた状態から図9のように折畳み式携帯電話1を開くと、磁気スイッチ22に作用する外部磁界Hの磁界強度は徐々に弱くなる。そして図12に示すように表示筐体2の表裏面を反転させ、図13の状態から再び、折畳み式携帯電話1を閉じると、磁気スイッチ22は、磁石53からの外部磁界Hを受けるが、今度は、図11と違って、磁気スイッチ22にはY2方向に向く外部磁界Hが作用することになる。
When the folding
本実施形態の磁気スイッチ22の構成について説明する。
図1,図5に示すように磁気スイッチ22は、1種類の磁気検出素子A1を内蔵する。
The configuration of the
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 5, the
図1に示すように磁気検出素子A1は、Y1−Y2方向に帯状に延びる素子部10を備える。素子部10のX1−X2方向における素子幅はW1で形成され、素子部10のY1−Y2方向における長さ寸法はL1で形成される。図1に示すように長さ寸法L1は素子幅W1より大きい。よって素子部10はY1−Y2方向を長手方向とした細長形状で形成される。
As shown in FIG. 1, the magnetic detection element A1 includes an
図1に示すように素子部10は複数設けられ、各素子部10はX1−X2方向に所定の間隔T1を空けて並設されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, a plurality of
図1に示すように、各素子部10のY1−Y2方向における端部間は接続部11により接続されている。接続部11は非磁性導電材料による電極層で形成されたり、あるいはハードバイアス層等で形成される。磁気検出素子A1は、素子部10と接続部11によりミアンダ形状で形成される。なお接続部11は、素子部10と同じ層構成で形成され、素子部10の層構成で一体化されたミアンダ形状であってもよい。接続部11が素子部10と同じ層構成で形成されている場合でも接続部11の部分を除外して素子部10の長さ寸法L1を規定する(図2の長さ寸法L1に一致)。
As shown in FIG. 1, the end portions in the Y1-Y2 direction of each
図1に示すようにX1−X2方向の両側に位置する素子部10の端部には非磁性導電材料で形成された配線パターン部12が接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, a
素子部10は、基板23の上に図2に示す多層構造で形成される。図2に示すように素子部10は下からシード層30、第1磁性層31、非磁性層32、第2磁性層33及び保護層34の順に積層される。シード層30はNiFeCrあるいはCr等によって形成される。シード層30は、その上に形成される各層の結晶配向性を整えるために設けられる層である。シード層30は形成されなくてもよい。また、シード層30の下にTa等で形成される非磁性の下地層が形成されていてもよい。またシード層30を形成しない場合、基板23上に下地層を介して第1磁性層31を形成することが好ましい。
The
第1磁性層31は、下からNi−Fe層35、Co−Fe層36の順に積層されている。
The first
非磁性層32はCu、Ru、Rh、Ir、Cr、Reのうち1種あるいは2種以上の合金で形成されていることが好ましい。
The
第2磁性層33は、下からCo−Fe層37、Ni−Fe層38の順に積層されている。
The second
保護層34は、例えばTaで形成される。保護層34の形成は必須でないが、形成したほうがよい。
The
図2に示すように第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33は非磁性層32を介して積層されている。第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33は、共にCo−Fe層36,37とNi−Fe層35,38との積層構造である。そして図2に示すように第1磁性層31を構成するCo−Fe層36と、第2磁性層33を構成するCo−Fe層37とが非磁性層32を介して対向している。
As shown in FIG. 2, the first
第1磁性層31及び第2磁性層33は、共に同じ磁性材料で形成されることが好ましい。これにより後述する第1磁性層31及び第2磁性層33のMs・t(Msは飽和磁化、tは膜厚)の調整を行いやすい。
Both the first
第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33は、Ni−Fe、Co−Fe以外の磁性材料で形成されてもよい。また、各磁性層31,33は単層構造であっても積層構造であってもどちらでもよい。
The first
ただし図2のように、各磁性層31,33がNi−Fe層35,38とCo−Fe層36,37の積層構造で形成され、Co−Fe層36,37が非磁性層32を介して対向した形態であることが好ましい。これにより、熱を加えたときにNi−Feが非磁性層32へ拡散するのを抑制できる。
However, as shown in FIG. 2, each
第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33は共に外部磁界に対して磁化変動可能となっている。すなわちGMR素子の固定磁性層のように磁化固定されていない。
Both the first
本実施形態では、Y1−Y2方向は磁気検出素子A1の感度軸方向である。
図3に示すように、無磁場状態(外部磁界が作用していない状態)では、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1が、感度軸方向(Y1−Y2方向)に対して直交する素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からY1方向(第1の方向)に傾いており、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2が、素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からY2方向(第2の方向)に傾いている。そして、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2間の角度θは、90度〜180度の範囲内となっている。なお、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1の素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からの傾きθ1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2の素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からの傾きθ2はほぼ同じとなっている。
In the present embodiment, the Y1-Y2 direction is the sensitivity axis direction of the magnetic detection element A1.
As shown in FIG. 3, in the non-magnetic state (state where no external magnetic field is applied), the magnetization direction F1 of the first
また、図2に示すように、本実施形態では、無磁場状態では、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが、感度軸方向(Y1−Y2方向)に向けて、略反平行となっていることが好ましい。
As shown in FIG. 2, in the present embodiment, in the non-magnetic state, the magnetization direction F1 of the first
ここで「略反平行」とは、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2間の角度θ(鈍角)が150度〜180度の範囲内を意味する。
Here, “substantially antiparallel” means that the angle θ (obtuse angle) between the magnetization direction F1 of the first
第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33との間にはRKKY相互作用による結合磁界が生じている。よって、図2に示す素子部10を積層した後、Y1方向、あるいはY2方向のどちらかに磁界をかけながらアニール処理すると、一旦、第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F1,F2は同一方向を向くが、磁場中アニールを停止すると、RKKY相互作用による結合磁界により、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2が反平行となろうとする。
A coupling magnetic field is generated between the first
図4は、本実施形態の磁気検出素子A1に対してY1−Y2方向(感度軸方向)に外部磁界を作用させたときの抵抗値を示すグラフである。図4では、−100Oeから+100Oeの範囲内での抵抗値を示している。 FIG. 4 is a graph showing resistance values when an external magnetic field is applied in the Y1-Y2 direction (sensitivity axis direction) to the magnetic detection element A1 of the present embodiment. FIG. 4 shows resistance values within a range of −100 Oe to +100 Oe.
図4に示す実験で用いた磁気検出素子A1は、無磁場状態(外部磁界が0Oe)での第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2との間の角度θ(鈍角)が、約170度である。
The magnetic detection element A1 used in the experiment shown in FIG. 4 has an angle θ between the magnetization direction F1 of the first
図3に示す無磁場状態(外部磁界が0Oe)からY1方向に外部磁界Hの磁界強度を強くしていくと、外部磁界と、RKKY相互作用による結合磁界とにより、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが反平行、あるいは反平行により近づき、抵抗値がより大きくなる(反平行になれば最大値となる)。なお無磁場状態で、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが反平行であれば、抵抗値が一旦大きくなる現象は生じない。
When the magnetic field strength of the external magnetic field H is increased in the Y1 direction from the no magnetic field state (external magnetic field is 0 Oe) shown in FIG. 3, the magnetization of the first
さらにY1方向に外部磁界を大きくしていくと、反平行状態が崩れ、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2がY2方向からY1方向に回転する。よって第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが平行状態に近づき、抵抗値が徐々に低下する。
When the external magnetic field is further increased in the Y1 direction, the antiparallel state is lost, and the magnetization direction F2 of the second
一方、図3に示す無磁場状態(外部磁界が0Oe)からY2方向に外部磁界を大きくしていくと、外部磁界と、RKKY相互作用による結合磁界とにより、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが反平行、あるいは反平行に近づき、抵抗値がより大きくなる(反平行になれば最大値となる)。さらにY2方向に外部磁界を大きくしていくと、反平行状態が崩れ、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1がY1方向からY2方向に回転する。よって第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが平行状態に近づき、抵抗値が徐々に低下する。
On the other hand, when the external magnetic field is increased in the Y2 direction from the no magnetic field state (external magnetic field is 0 Oe) shown in FIG. 3, the magnetization direction F1 of the first
なお、図4に示すように、R−H曲線にはヒステリシスが生じている。よって、第1磁性層31及び第2磁性層33は保磁力(Hc)が有していることがわかる。
As shown in FIG. 4, hysteresis occurs in the RH curve. Therefore, it can be seen that the first
また、図4に示すように、外部磁界が0Oeのラインを対称軸としてY1方向に外部磁界Hを作用させたときと、Y2方向に外部磁界Hを作用させたときとで抵抗値変化の波形が略対称関係となっている。したがって、Y1方向からの外部磁界HとY2方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度が夫々、ほぼ同じである。このようにY1方向及びY2方向からの外部磁界Hに対してほぼ同じ磁気感度に調整するには、第1磁性層31のMs1・t1(Msは飽和磁化、tは膜厚)と、第2磁性層33のMs2・t2との比を小さくすることが好ましい。例えば、本実施形態では、(Ms2・t2/Ms1・t1)は1より大きく2より小さい。
Further, as shown in FIG. 4, the resistance value change waveform when the external magnetic field H is applied in the Y1 direction with the line having the external magnetic field of 0 Oe as the axis of symmetry and when the external magnetic field H is applied in the Y2 direction. Is substantially symmetrical. Therefore, the magnetic sensitivities to the external magnetic field H from the Y1 direction and the external magnetic field H from the Y2 direction are substantially the same. In order to adjust the magnetic sensitivity to substantially the same with respect to the external magnetic field H from the Y1 direction and the Y2 direction in this way, the Ms1 · t1 (Ms is saturation magnetization and t is the film thickness) of the first
ただし、Y1方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度とY2方向からの外部磁界に対する磁気感度Hとが夫々、異なるように調整してもよい。例えば、磁気スイッチ22を折畳み式携帯電話1に内蔵したとき、図7の通常の使用状態から折畳み式携帯電話1を閉じたときの磁気スイッチ22と磁石53間の距離D1(図11参照)と、図13の表示筐体2の表裏面を反転させた状態から折畳み式携帯電話1を閉じたときの磁気スイッチ22と磁石53間の距離とが、異なる場合がある。係る場合、両者間で同じタイミングで検出信号(オン信号)を得るには、Y1方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度とY2方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度とを異ならすことで調整することができる。例えば、図3に示す無磁場状態での第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1の傾きθ1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2の傾きθ2とを異ならして、Y1方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度とY2方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度とが異なるように調整できる。
However, the magnetic sensitivity to the external magnetic field H from the Y1 direction may be adjusted to be different from the magnetic sensitivity H to the external magnetic field from the Y2 direction. For example, when the
また本実施形態では、磁気検出素子を構成する素子部10がY1−Y2方向(感度軸方向)を長手方向とした細長形状で形成される。よって、形状磁気異方性により素子部10のY1−Y2方向が磁化容易軸方向となっている。したがって、Y1−Y2方向に対して直交するX1−X2方向に外部磁界(外乱磁場)が作用しても磁気検出素子は抵抗変化しにくく外乱耐性を向上させることができる。
Moreover, in this embodiment, the
図5に示すように磁気スイッチ22は、磁気検出素子A1を備えるセンサ部15と、センサ部15からのセンサ出力に基づいて、オン/オフの2値信号を生成し出力するための制御部(集積回路(IC))16とを有して構成される。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
図5に示すようにセンサ部15は1つの磁気検出素子A1と1つの固定抵抗素子17とが直列回路を構成している。また制御部16内には直列接続された2つの固定抵抗素子17が設けられ、合わせてブリッジ回路を構成している。
As shown in FIG. 5, in the
本実施形態では、ブリッジ回路には1種類の磁気検出素子A1のみが組み込まれる。1種類であれば、図5のように磁気検出素子1が1つだけ配置されても同じ磁気検出素子A1が、ブリッジ回路に複数組み込まれてもよい。また、磁気検出素子A1の温度特性等の素子特性と合わせるために固定抵抗素子17も1種類で足りる。
In the present embodiment, only one type of magnetic detection element A1 is incorporated in the bridge circuit. If there is one type, even if only one
図5に示すように、ブリッジ回路は、制御部16に設けられた入力端子24、グランド端子25、及び差動増幅器18に接続される。
As shown in FIG. 5, the bridge circuit is connected to an
磁気検出素子A1の電気抵抗値の変化に基づいて差動増幅器18から得られた差動出力は、閾値を備えるコンパレータ(比較回路)19に送られ、図6のように波形整形される。図6に示すように、外部磁界Hの磁界強度が強まり、外部磁界がHonになったとき、波形整形されたセンサ出力が、ハイレベル(V Hi)からローレベル(V Lo)になり、検出信号(オン信号)が出力される。一方、外部磁界Hの磁界強度が弱まり、外部磁界がHoffになったとき、波形整形されたセンサ出力がローレベル(V Lo)からハイレベル(V Hi)になり、オフ信号が出力される(オン信号が出力されない)。
The differential output obtained from the
図5に示すように、コンパレータ19の出力側にはラッチ回路20が接続され、さらにラッチ回路20の出力側には出力端子21が接続されている。ラッチ回路20が設けられているため、オン信号を出力しているとき、センサ出力がハイレベルになったことを検出しない限り、オン信号を出力し続ける。またオフ信号を出力しているとき、センサ出力がローレベルになったことを検出しない限り、オフ信号を出力し続ける。また、図5に示すように制御部16には、クロック回路26やスイッチ回路27がある。図5の回路構成では、スイッチ回路27がオフされると、入力端子24からブリッジ回路への通電が停止するようになっている。スイッチ回路27のスイッチのオン・オフは、クロック回路26からのクロック信号に連動しており、スイッチ回路27は通電状態を間欠的に行う節電機能を有している。
As shown in FIG. 5, a
図7以降に示した折畳み式携帯電話1について考察する。まず図7に示す通常の使用状態では、磁気スイッチ22は磁石53から距離的に離れており、磁石53から磁気スイッチ22に外部磁界Hが作用していない。すなわち無磁場状態である。よってセンサ出力は図6に示すハイレベルにあり、出力端子21からはオフ信号が出力されている(オン信号が出力されていない)。
Consider the folding
図7の開いた状態から図9の状態に移行し、さらに図10のように閉じると、磁気スイッチ22に作用する磁石53からY1方向に向く外部磁界Hの磁界強度が徐々に強まる。すると磁気検出素子A1の第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F1,F2の略反平行状態が崩れて、図4に示すように電気抵抗値が徐々に低下する。そして、図6に示すように、外部磁界Hが磁界強度Hon以上となったとき、センサ出力がハイレベルからローレベルに移行し、出力端子21から検出信号(オン信号)が出力される。
When shifting from the open state of FIG. 7 to the state of FIG. 9 and further closing as shown in FIG. 10, the magnetic field strength of the external magnetic field H from the
次に、図10の閉じた状態から図7の開いた状態に移行させると、外部磁界Hが磁界強度Hoff以下になったとき、センサ出力がローレベルからハイレベルに移行しオフ信号が出力される。図6に示すようにセンサ出力にはヒステリシスが生じているため、図7の状態から図10の状態に移行させたときにオン信号が生成されるタイミングと、図10の状態から図7の状態に移行させたときにオフ信号が生成されるタイミングとにずれが生じる。このようなタイミングのずれはチャタリングの抑制に貢献できる。 Next, when the closed state in FIG. 10 is shifted to the open state in FIG. 7, when the external magnetic field H becomes lower than the magnetic field strength Hoff, the sensor output shifts from the low level to the high level and an off signal is output. The Since hysteresis occurs in the sensor output as shown in FIG. 6, the timing at which an ON signal is generated when the state of FIG. 7 is shifted to the state of FIG. 10, and the state of FIG. 10 to the state of FIG. There is a deviation from the timing at which the off signal is generated when the shift to. Such timing shift can contribute to suppression of chattering.
図7の状態から図12のように表示筐体2の表裏面を反転させ、図13の状態の開いた状態から折畳み式携帯電話1を閉じる。すると磁気スイッチ22にはY2方向からの外部磁界Hが作用し、その外部磁界Hの磁界強度が徐々に強まる。
From the state of FIG. 7, the front and back surfaces of the
これにより、磁気検出素子A1の第1磁性層31と第2磁性層33の磁化方向F1,F2の略反平行状態が崩れて、図4に示すように電気抵抗値が徐々に低下する。そして、図6に示すように、Y2方向における外部磁界Hが磁界強度Hon以上となったとき、センサ出力がハイレベルからローレベルに移行し、出力端子21から検出信号(オン信号)が出力される。
Thereby, the substantially antiparallel state of the magnetization directions F1 and F2 of the first
以下、本実施形態の磁気スイッチ22の特徴的構成について説明する。
センサ部15には、1種類の磁気検出素子A1が配置されている(図5参照)。この磁気検出素子A1は、外部磁界Hに対して磁化変動可能な第1磁性層31及び第2磁性層33が非磁性層32を介して積層された構成である(図2参照)。この磁気検出素子A1は、感度軸方向(Y1−Y2方向)に対して両方向からの外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化に対して電気抵抗値が変動する(図4参照)。図4に示すように、Y1方向の外部磁界の磁界強度変化に対する電気抵抗値と、Y2方向の外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化に対する電気抵抗値が同傾向で変動する。すなわち、Y1方向及びY2方向の外部磁界Hの磁界強度が大きくなるほど、電気抵抗値は夫々、同じように低下していき、Y1方向及びY2方向の外部磁界の磁界強度が小さくなるほど、電気抵抗値は夫々、同じように上昇していく。このように、Y1方向の外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化に対する電気抵抗値と、Y2方向の外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化に対する電気抵抗値を同傾向で変動させるには、無磁場状態では、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1が、感度軸方向に直交する素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)から感度軸方向(Y1−Y2方向)のうち第1の方向(図4ではY1方向)に傾き、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2が、素子幅方向から感度軸方向の第1の方向とは逆方向の第2の方向(図4ではY2方向)に傾くように制御すればよい。
Hereinafter, a characteristic configuration of the
One type of magnetic detection element A1 is disposed in the sensor unit 15 (see FIG. 5). The magnetic detection element A1 has a configuration in which a first
そして本実施形態では、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2との間の角度θが90度〜180度の範囲内であることが好ましい。また、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2とが略反平行であることがより好適である。さらに本実施形態では、図1に示すように各素子部10が、感度軸方向(Y1−Y2方向)を長手方向とした細長形状で形成されていることが好適である。これにより、感度軸方向からの外部磁界Hに対して良好な磁気感度を備えるとともに感度軸方向とは異なる方向からの磁界に対する外乱耐性を向上させることができる。
In this embodiment, the angle θ between the magnetization direction F1 of the first
このように本実施形態における磁気検出素子A1をセンサ部15内に組み込めば、双極検知が可能である。
In this manner, if the magnetic detection element A1 in the present embodiment is incorporated in the
そして本実施形態では図5,図6に示すように、制御部16は、共通回路にて、Y1方向からの外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化、及び、Y2方向からの外部磁界Hの磁界強度変化により得られた夫々のセンサ出力に基づいて、各検出信号(オン信号)を出力できる。
In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, the
図5に示すようにブリッジ回路は1つであり、このブリッジ回路から出力端子21までの主信号ラインは1系統で済む。すなわち従来のように、Y1方向の外部磁界用の電気回路と、Y2方向の外部磁界用の電気回路との2系統を必要としない。よって制御部16の小型化を実現できる。
As shown in FIG. 5, there is one bridge circuit, and only one main signal line from the bridge circuit to the
以上により、本実施形態における双極検知用の磁気スイッチ22によれば、製造コストの低減を図ることができ、さらに小型化を実現できる。
As described above, according to the
磁気スイッチ22の用途の一例として折畳み式携帯電話1を用いて説明したが、当然、これに限定されない。距離が変動する2つの筐体があり、一方の筐体には磁気スイッチ22が、他方の筐体には磁石53が内蔵され、筐体間の距離の変動により磁気スイッチ22が磁石53からの外部磁界を検知する用途に好ましく使用される。上記した折畳み式携帯電話1では、双極検知が必要な用途であったが、必ずしも双極検知が必要な用途だけに限定されない。例えば、図12,図13に示す反転動作を行うことが出来ず、開閉動作のみ行える折畳み式携帯電話1にも本実施形態を好ましく適用できる。かかる場合、一方向の外部磁界Hのみを検知することになるが、例えば、図1に示す磁気検出素子A1を、180度反転させて設置しても、本実施形態は双極対応型であるので、外部磁界Hの検知が可能になる。すなわち本実施形態の磁気スイッチ22を用いれば、磁気スイッチ(磁気検出素子)の配置(向き)の自由度を向上できる。なお、係る用途の場合、図3に示すように、第1磁性層31の磁化方向F1の素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からの傾きθ1と、第2磁性層33の磁化方向F2の素子幅方向(X1−X2方向)からの傾きθ2をほぼ同じにして、Y1方向の感度軸方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度と、Y2方向の感度軸方向からの外部磁界Hに対する磁気感度をほぼ同じに調整することが好適である。
Although the foldable
A1 磁気検出素子
H 外部磁界
1 折畳み式携帯電話
2 表示筐体
3 操作筐体
4 ヒンジ部
10 素子部
15 センサ部
16 制御部
17 固定抵抗素子
18 差動増幅器
19 コンパレータ
20 ラッチ回路
21 出力端子
22 磁気スイッチ
24 入力端子
25 グランド端子
31 第1磁性層
32 非磁性層
33 第2磁性層
50 第1回転軸
53 磁石
56 第2回転軸
A1 Magnetic detection element H External
Claims (1)
1種類の前記磁気検出素子を内蔵しており、前記磁気検出素子は、外部磁界に対して磁化変動可能な第1磁性層及び第2磁性層が非磁性層を介して積層された素子部を備えて、前記感度軸方向のうち第1の方向、及び前記第1の方向とは逆方向の第2の方向の外部磁界の磁界強度変化に対して、夫々、電気抵抗値が変動する構成であり、
前記制御部は、共通回路にて、第1の方向からの外部磁界の磁界強度変化、及び第2の方向からの外部磁界の磁界強度変化により得られた夫々の前記センサ出力に基づいて、各検出信号を出力できるものであり、
前記素子部は、前記感度軸方向を長手方向とした細長形状で形成されており、
無磁場状態では、前記第1磁性層の磁化方向が、前記感度軸方向に直交する素子幅方向から前記第1の方向に傾いており、前記第2磁性層の磁化方向が、素子幅方向から前記第2の方向に傾いており、前記第1磁性層の磁化方向と、前記第2磁性層の磁化方向は、前記感度軸方向と平行な方向に向けて略反平行であることを特徴とする双極検出対応型の磁気スイッチ。 A magnetic detection element whose electric resistance value changes with respect to an external magnetic field from the sensitivity axis direction; and a control unit which outputs a detection signal based on a sensor output which changes based on a change in electric resistance of the magnetic detection element. In the magnetic switch consisting of
One kind of the magnetic detection element is built in, and the magnetic detection element includes an element portion in which a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer that can change magnetization with respect to an external magnetic field are stacked via a nonmagnetic layer. provided, the first direction of the sensitivity axis direction, and with respect to the magnetic field strength change of the second direction of the external magnetic field of said first direction backward, respectively, in the configuration electric resistance value varies Yes,
In the common circuit, each of the control units is based on the sensor outputs obtained by the magnetic field strength change of the external magnetic field from the first direction and the magnetic field strength change of the external magnetic field from the second direction. It can output detection signals ,
The element portion is formed in an elongated shape having the sensitivity axis direction as a longitudinal direction,
In the absence of a magnetic field, the magnetization direction of the first magnetic layer is inclined in the first direction from the element width direction orthogonal to the sensitivity axis direction, and the magnetization direction of the second magnetic layer is changed from the element width direction. Inclined in the second direction, the magnetization direction of the first magnetic layer and the magnetization direction of the second magnetic layer are substantially anti-parallel toward a direction parallel to the sensitivity axis direction. Magnetic switch for bipolar detection.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195403A JP5139190B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Magnetic switch |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195403A JP5139190B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Magnetic switch |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010032390A JP2010032390A (en) | 2010-02-12 |
| JP5139190B2 true JP5139190B2 (en) | 2013-02-06 |
Family
ID=41737033
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195403A Active JP5139190B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Magnetic switch |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5139190B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6697144B2 (en) * | 2016-01-27 | 2020-05-20 | アルプスアルパイン株式会社 | Magnetic sensor |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3657916B2 (en) * | 2001-02-01 | 2005-06-08 | 株式会社東芝 | Magnetoresistive head and perpendicular magnetic recording / reproducing apparatus |
| JP4232808B2 (en) * | 2006-09-19 | 2009-03-04 | 日立金属株式会社 | Magnetic encoder device |
| JP2008112496A (en) * | 2006-10-30 | 2008-05-15 | Fujitsu Ltd | Magnetoresistive reproducing magnetic head and magnetic recording apparatus using the reproducing magnetic head |
| JPWO2008059914A1 (en) * | 2006-11-17 | 2010-03-04 | アルプス電気株式会社 | Magnetic detector and electronic apparatus using the same |
-
2008
- 2008-07-29 JP JP2008195403A patent/JP5139190B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010032390A (en) | 2010-02-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4810275B2 (en) | Magnetic switch | |
| JP5297539B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP5297442B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| US20030070497A1 (en) | Rotation angle sensor capable of accurately detecting rotation angle | |
| JPWO2008029519A1 (en) | Electronics | |
| JP5899012B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP5066524B2 (en) | Magnetic detector | |
| JP4668818B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP5171933B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP5066581B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor and magnetic sensor module | |
| WO2011074488A1 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| US7414393B2 (en) | Magnetic detection device including circuit switching and processing input of two bridge circuits | |
| JP5139190B2 (en) | Magnetic switch | |
| JP5898986B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5523149B2 (en) | Magnetic switch | |
| JP5174676B2 (en) | Magnetic detection device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4331630B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP2010175359A (en) | Mems inclination sensor | |
| JP5006339B2 (en) | Magnetic detector | |
| JP5341865B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| JP5184380B2 (en) | Magnetic detector | |
| JP2010156543A (en) | Magnetic detecting device | |
| JP4316836B2 (en) | Magnetic sensor | |
| WO2010032823A1 (en) | Magnetic coupling-type isolator | |
| JPWO2008102786A1 (en) | Magnetic detector |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101119 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120302 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120327 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120518 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121106 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121115 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5139190 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151122 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |