Frank Neumann
North-West University, School of Geo- and Spatial Sciences, Faculty Member
Research Interests:
South Africa’s urban population is increasing, and in parallel, urban green infrastructure has shown an increase in alien tree species, e.g., mulberry (Morus sp.), oak (Quercus spp.) and plane trees (Platanus spp.) to name a few. This... more
South Africa’s urban population is increasing, and in parallel, urban green infrastructure has shown an increase in alien tree species, e.g., mulberry (Morus sp.), oak (Quercus spp.) and plane trees (Platanus spp.) to name a few. This causes ecological problems since alien trees are often more water-demanding and competitive than indigenous trees, but they also increase the abundance of respiratory diseases often triggered by an allergic reaction towards the pollen of those alien taxa. In the current study, utilizing 7-day volumetric spore traps, we illustrate that the most abundant tree pollen in the two largest cities of South Africa, Cape Town and Johannesburg, is produced by alien trees with a high risk of allergenicity. This adds another aspect related to public health when evaluating plant species composition in urban forestry and urban ecology, which underlines the urgency of more intense monitoring. More importantly, this - for South Africa - newly emphasized risk for public...
Palynology of marine sediment core SBQW4, Saldanha Bay (South Africa), early Miocene, supplement to: Neumann, Frank Harald; Roberts, David; Cawthra, Hayley C; Carr, Andrew S; Scott, Louis; Durugbo, Ernest; Humphries, Marc; Cowling, Richard; Bamford, Marion; Musekiwa, Chiedza; Machutchon, Michael ...more
A multi-proxy study of an offshore core in Saldanha Bay (South Africa) provides new insights into fluvial deposition, ecosystems, phytogeography and sea-level history during the late Paleogene-early Neogene. Offshore seismic data reveal... more
A multi-proxy study of an offshore core in Saldanha Bay (South Africa) provides new insights into fluvial deposition, ecosystems, phytogeography and sea-level history during the late Paleogene-early Neogene. Offshore seismic data reveal bedrock topography, and provide evidence of relative sea levels as low as -100 m during the Oligocene. 3D landscape reconstruction reveals hills, plains and an anastomosing river system. A Chattian or early Miocene age for the sediments is inferred from dinoflagellate taxa Distatodinium craterum, Chiropteridium lobospinosum, Homotryblium plectilum and Impagidinium paradoxum. The subtropical forest revealed by palynology includes lianas and vines, evergreen trees, palms and ferns, implying higher water availability than today, probably reduced seasonal drought and stronger summer rainfall. From topography, sedimentology and palynology we reconstruct Podocarpaceaedominated forests, Proto-Fynbos, and swamp/riparian forests with palms and other angiosper...
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Waterfall Bluff is a rock shelter in eastern Pondoland, South Africa, adjacent to a narrow continental shelf that limited coastline movements across glacial/interglacial cycles. The archaeological deposits are characterized by... more
Waterfall Bluff is a rock shelter in eastern Pondoland, South Africa, adjacent to a narrow continental shelf that limited coastline movements across glacial/interglacial cycles. The archaeological deposits are characterized by well-preserved stratigraphy, faunal, and botanical remains alongside abundant stone artifacts and other materials. A comprehensive dating protocol consisting of 5 optically stimulated luminescence ages and 51 accelerator mass spectrometry 14C ages shows that the record of hunter-gatherer occupations at Waterfall Bluff persisted from the late Pleistocene to the Holocene, spanning the last glacial maximum and the transition from the Pleistocene to the Holocene. Here, we provide detailed descriptions about the sedimentary sequence, chronology, and characteristics of the archaeological deposits at Waterfall Bluff. Remains of marine mollusks and marine fish also show, for the first time, that coastal foraging was a component of some hunter-gatherer groups’ subsiste...
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests: Engineering, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Medicine, and 8 moreMultidisciplinary, South Africa, Bivalvia, Fossils, Animals, PLoS one, Fresh water, and Feces
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Pollen and fungal spores (aerospora) are the major atmospheric bioaerosols. Aerospora occurrence and concentration vary by geographical region and blossoming period, and with meteorological factors. Allergic respiratory diseases affect... more
Pollen and fungal spores (aerospora) are the major atmospheric bioaerosols. Aerospora occurrence and concentration vary by geographical region and blossoming period, and with meteorological factors. Allergic respiratory diseases affect about 20 million South Africans, with pollen and fungal allergens amongst the leading triggers. Asthma triggered by aerospora can be life threatening; allergic rhinitis causes considerable morbidity and carries financial implications for individuals and health systems. Thus, knowledge about geographical variation, seasonal timing and intensity, as well as annual aerospora fluctuations in South Africa, where climate and vegetation are exceptionally diverse, is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment of allergies. Unfortunately, there is a lack of continuous aeropalynological data from South Africa. The longest annual monitoring exists for Cape Town (~20 years), with almost no data out of the Cape since the 1990s, and many parts of South Africa ...
Research Interests:
Pollen and fungal spores (aerospora) are the major atmospheric bioaerosols. Aerospora occurrence and concentration vary by geographical region and blossoming period, and with meteorological factors. Allergic respiratory diseases affect... more
Pollen and fungal spores (aerospora) are the major atmospheric bioaerosols. Aerospora occurrence and concentration vary by geographical region and blossoming period, and with meteorological factors. Allergic respiratory diseases affect about 20 million South Africans, with pollen and fungal allergens amongst the leading triggers. Asthma triggered by aerospora can be life threatening; allergic rhinitis causes considerable morbidity and carries financial implications for individuals and health systems. Thus, knowledge about geographical variation, seasonal timing and intensity, as well as annual aerospora fluctuations in South Africa, where climate and vegetation are exceptionally diverse, is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment of allergies. Unfortunately, there is a lack of continuous aeropalynological data from South Africa. The longest annual monitoring exists for Cape Town (~20 years), with almost no data out of the Cape since the 1990s, and many parts of South Africa ...
Research Interests:
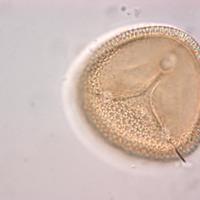
When applying high-resolution microscopy, the pollen morphology of extant taxa can be used to classify fossil pollen, that is, to address the latter in the established systematic-phylogenetic framework. Here we investigate tetrads and... more
When applying high-resolution microscopy, the pollen morphology of extant taxa can be used to classify fossil pollen, that is, to address the latter in the established systematic-phylogenetic framework. Here we investigate tetrads and pollen features of 20 different Winteraceae species, most of them belonging to the early-diverging generic lineagesTasmannia,DrimysandPseudowintera. The tetrads and pollen are grouped into eleven pollen types based on diagnostic features observed by both light and scanning electron microscopy. The high-resolution scanning electron micrographs of recent material allow detailed comparison with fossil material, resulting in a more accurate affiliation of fossil tetrads/pollen to extant lineages. As a case study, early Miocene Winteraceae tetrads from South Africa are re-examined and formally described. The systematic placement of the African fossils is discussed in light of the pollen types presented here.
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
This article presents the role of climate fluctuations in shaping southern Levantine human history from 3600 to 600 BCE (the Bronze and Iron Ages) as evidenced in palynological studies. This time interval is critical in the history of the... more
This article presents the role of climate fluctuations in shaping southern Levantine human history from 3600 to 600 BCE (the Bronze and Iron Ages) as evidenced in palynological studies. This time interval is critical in the history of the region; it includes two phases of rise and decline of urban life, organization of the first territorial kingdoms, and domination of the area by great Ancient Near Eastern empires. The study is based on a comparison of several fossil pollen records that span a north-south transect of 220 km along the southern Levant: Birkat Ram in the northern Golan Heights, Sea of Galilee, and Ein Feshkha and Ze'elim Gully both on the western shore of the Dead Sea. The vegetation history and its climatic implications are as follows: during the Early Bronze Age I (∼3600–3000 BCE) climate conditions were wet; a minor reduction in humidity was documented during the Early Bronze Age II–III (∼3000–2500 BCE). The Intermediate Bronze Age (∼2500–1950 BCE) was character...
Research Interests: Archaeology, Geochemistry, Paleoclimatology, Levantine Archaeology, Paleoenvironment, and 15 morePaleoecology, Palynology, Bronze Age Archaeology, Radiocarbon, Paleoenvironmental Change, Late Bronze Age archaeology, Paleoclimate, Middle Bronze Age, Iron Age, Early Iron Age, Geoarchaeology and Paleoenvironmental Reconstructions, Archaeology of the Southern Levant, Middle Bronze Age Southern Levant, Late Bronze Age Early Iron Age, and Past Environments
Research Interests:
The history of lake-level changes at the Dead Sea during the Holocene was determined mainly by radiocarbon dating of terrestrial organic debris. This article reviews the various studies that have been devoted over the past 2 decades to... more
The history of lake-level changes at the Dead Sea during the Holocene was determined mainly by radiocarbon dating of terrestrial organic debris. This article reviews the various studies that have been devoted over the past 2 decades to defining the Dead Sea levels during the Bronze and Iron Ages (≃5.5 to 2.5 ka cal BP) and adds new data and interpretation. In particular, we focus on research efforts devoted to refining the chronology of the sedimentary sequence in the Ze'elim Gully, a key site of paleoclimate investigation in the European Research Council project titled Reconstructing Ancient Israel. The Bronze and Iron Ages are characterized by significant changes in human culture, reflected in archaeological records in which sharp settlement oscillations over relatively short periods of time are evident. During the Early Bronze, Intermediate Bronze, Middle Bronze, and Late Bronze Ages, the Dead Sea saw significant level fluctuations, reaching in the Middle Bronze an elevation ...
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests: Geology, Sea Level, Sea surface temperature, Iron Age, South Africa, and 15 moreglobal Climate change, Radiocarbon Dating, Land Use, Late Holocene, Water Table, Little Ice Age, Vegetation history, Human impact, Southern Hemisphere, Zea mays, Sedimentation Rate, Vegetation Change, Holocene Thermal Maximum, Climatic condition, and dry period
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Research Interests:
Title: Late Holocene paleoclimate records from Lakes Sibaya and Verlorenvlei, South Africa. Authors: Stager, J. Curt; Neumann, Frank; Chase, Brian M.; Meadows, Michael E.; Fitzpatrick,Jason; Hazzard, Matt; King, Christiaan; Madson,... more
Title: Late Holocene paleoclimate records from Lakes Sibaya and Verlorenvlei, South Africa. Authors: Stager, J. Curt; Neumann, Frank; Chase, Brian M.; Meadows, Michael E.; Fitzpatrick,Jason; Hazzard, Matt; King, Christiaan; Madson, Jerome; White, Jay. ...