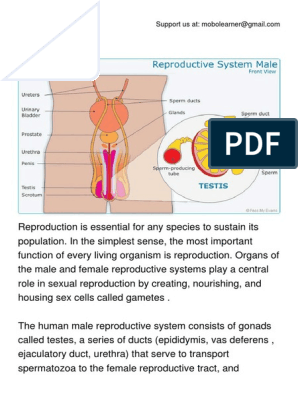
L(+) Lactates for Skin Whitening
Content of the presentation
Content L(+) Lactates for Skin Whitening
1. Mechanism of skin-whitening
2. Whitening the start
3. In vitro data
4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
5. More whitening research
6. Costs / Concentrations
7. pH effect / AHA
8. Conclusions
9. Discussion
�1. Mechanism of skin-whitening
Mechanisms of whitening
A
CH2
COOH
CH
Tyrosinase formation-suppressive
(Lactates)
Tyrosinase
N H2
HO
se
ida )
x
-o ase
pa
Do rosin
(Ty
B
CH2
COOH
CH
N H2
CH2
CH
Dopaquinone
COOH
NH2
HO
Tyrosine
Inhibition
Tyrosinase activity
HO
3,4-Dihydroxy-phenylalanine
(Dopa)
HO
HO
COOH
N
H
Leucodopachrome
HO
COOH
N
H
Dopachrome
O
O
HO
N
H
5,6-Dihydroxyindole
O
N
H
Indole-5,6-Quinone
N
H
Melanin
Reduction
of Melanin
�1. Mechanism of skin-whitening
Types of whitening action
Denaturation and death of pigment cells (C)
Tyrosinase inhibiting action (B)
Suppressing the formation of Tyrosinase (A)
�1. Mechanism of skin-whitening
Whitening ingredients overview
Tyrosinase
suppressive
action (A)
Tyrosinase
inhibiting
action (B)
Ascorbic acid (Vit-C) derivatives
Kojic Acid
Arbutin
Licorice
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3)
Mulberry extract
Vegetable/Herb extracts
Lactates
Hydroquinone
Reduction
of melanin
(C)
�2. Whitening the start
Whitening of lactates the start
Tyrosinase inhibitory/suppressive action of organic acids
(in vitro) ( + = activity, = no activity)
Organic acids/salts
Tyrosinase Melanogenenis
inhibitory
suppressive
activity
activity
Tyrosinase
formation
suppressive
activity
Lactic acid/Sodium Lactate
Asparaginic acid
Glutaminic acid
Citric acid
Fumaric acid
Malic acid
Ascorbic acid (Vit. C)
European patent application 0423 929 A1.
�2. Whitening the start
Whitening of lactates the start
L (+) Lactic acid and lactates in vivo whitening experiment
Percentage of test-objects with significant whitening results
Lactate concentration (w%)
2%
5%
8%
20%
Sodium Lactate
35%
80%
95%
100%
Ammonium Lactate
35%
75%
100%
Magnesium Lactate
30%
75%
90%
100%
Conditions: 20 test-subjects
pH=5.5
measurement after 24 days
applying cream 3 times daily
European patent application 0423 929 A1.
�3. In vitro data
In Vitro Data Melanoderm
Objective:
To assess effect of whitening agents on tyrosinase
suppression/inhibition (in vitro measurement; Melanoderm)
Conditions:
Whitening ingredients tested: Lactic acid(3%), Kojic acid(1%),
Ascorbic acid (1%) and MAP (1%)
Melanoderm: in vitro model of human epidermis. Model can
be used to evaluate efficacy, stability and toxicity of whitening
agents.
Journal of Cosmetic Science. Nov/Dec 98. Vol 49, p.361-367
�3. In vitro data
In Vitro Data Melanoderm
Effect of whitening agents on tyrosinase inhibition/suppression
50
40
30
20
10
0
Lactic
acid
(3%)
Kojic
acid
(1%)
MAP Ascorbic
(1%)
acid
(1%)
Ascorbic acid only reveals modest results (oxidation?)
Lactic acid and kojic acid reduce resp. 46% and 48%
Journal of Cosmetic Science. Nov/Dec 98. Vol 49, p.361-367
�4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
In vivo research Vitamin C + Lactates
Objective:
To determine whether L(+) Lactic acid by itself or supplemented
with ascorbic acid can whiten the skin
To asses if synergistic effects between A and B type whitening
ingredients could possibly take place.
Conditions:
70 test subjects, Caucasian females ages 25-70
(rated 3 or 4 via Fitzpatrick Scale)
3 formulations, applying twice a day
Objective (Minolta Chroma meter) and subjective (clinical
grading; 1-100 scale) whitening measurement
Duration whitening test 12 weeks (t=0, 4, 8, 12 weeks)
Smith, International Journal of Cosmetic Science 21: 33-40 (1999)
�4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
Methodology Test subjects
Caucasian skin type 3 to 4 on Fitzpatrick scale
Fitzpatrick scale
Skin type: Sun burning and Tanning
1. Always burns easily; never tans
2. Always burns easily; tans minimally
3. Burns moderately; tans gradually
4. Burns minimally; always tans well
5. Rarely burns; tans profusely
6. Never burns; deeply pigmented.
Smith, International Journal of Cosmetic Science 21: 33-40 (1999)
�4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
Formulations
1.) Vitamin C (1%)
2.) Lactic acid (8.8%)
3.) Vitamin C (1%) + Lactic acid (8.8%)
Conditions:
pH 5, mild formulations, but not stable
New formulations freshly prepared every 2 weeks
3 formulations, applying twice a day
Smith, International Journal of Cosmetic Science 21: 33-40 (1999)
�4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
Measurement by Clinical grading
Vitamin C +
Lactic acid
80
75
Lactic acid
70
65
Vitamin C
s
th
s
on
th
3
on
m
2
on
th
60
Vitamin C + Lactic acid significant whitening after 3 months
Smith, International Journal of Cosmetic Science 21: 33-40 (1999)
�4. In vivo data Vitamin C + Lactates
Measurement by Clinical grading
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
Vit C (1%)
Lactic acid (8.8%)
Vit C (1%) +
Lactic acid (8.8%)
Months
Synergistic whitening effects achieved when Vitamin C is
combined with Lactates in one formulation
Smith, International Journal of Cosmetic Science 21: 33-40 (1999)
�5. More Clinical Research
More Clinical Research
Objective:
To assess and compare the performance/ effectiveness of
frequently used whitening ingredients in vivo.
Conditions:
Vehicle controlled double blind not randomized clinical trial
7 formulations, applying twice a day
30 test subjects; female, Asian skin type, 18-45 yr. old
Objective (Mexameter) and subjective (4 point scale)
whitening measurement
Duration whitening test 12 weeks (t=0, 4, 6, 8, 12 weeks)
Philippine Dermatological Research and Testing foundation
�5. More Clinical Research
Formulations
Products
Concentration
Control/Placebo
0%
Sodium Lactate 60%
15%
Arbutin
1%
Licorice
0.3%
Kojic acid
1%
Sodium Lactate 60% + Arbutin
15% + 1%
Sodium Lactate 60% + Licorice
15% + 0.3%
Sodium Lactate 60% + Kojic
15% + 1%
G
H
K2 Glycyrrhizinate = licorice
Mild, stable and commercial formulations; pH=5
All formulations equal except for whitening ingredient
F,G, H included to asses possible synergistic effects
Philippine Dermatological Research and Testing foundation
�5. More Clinical Research
Methodology
Objective measurement
Mexameter (M16), Courage and Khasaka, Germany
(Melanin Index)
Scale 400-700, dark-skins range 450-550
Duration whitening test 12 weeks (t=0, 4, 6, 8, 12 weeks)
Photo-types and ranges Mexameter
I:
II:
III:
IV:
V:
VI:
Celtic type (very fair skin, red hairs, freckles) 400-470
Caucasian white (fair skin, blond, blue eyes): 410-490
Mixed type (blond-brown hair, brown eyes): 420-510
Mediterranean type (dark hair, brown eyes): 420-520
Dark skin: 450-550
Black Skin: 520-700
Philippine Dermatological Research and Testing foundation
�5. More Clinical Research
Methodology
Subjective Measurement
On a 4-point scale.
Assessment by dermatologist and panelist themselves
Subjective measurements predominantly used:
Clinical grading: using color cards, comparison with skin
color; expensive, 0-100 point scale, trained staff needed
but very reliable
4-point scales: scaling of skin-color on 4 point scale,
cheap, to be used in combination with objective
measurement.
Philippine Dermatological Research and Testing foundation
�5. More Clinical Research
Objective measurement
Whitening effect in time (3 months)
Mexameter-values
550
Control/Placebo
545
Sodium Lactate 15%
Arbutin 1%
Licorice 0.3%
540
Kojic acid 1%
SL + Arbutin
SL + Licorice
535
SL + Kojic
530
T=0
4 weeks
6 weeks
8 weeks
12 weeks
Significant whitening effect for all treatments after 6 weeks
C&T Jan 2001, whitening effect of frequently used whitening ingredients
�5. More Clinical Research
Objective measurement; T=0 is index 100
Whitening effect in time (3 months)
100.5
Control/Placebo
100
Sodium Lactate 15%
99.5
Arbutin 1%
99
Licorice 0.3%
98.5
Kojic acid 1%
SL 15% + Arbutin 1%
98
SL 15% + Licorice 0.3%
97.5
SL 15% + Kojic 1%
97
1
Form. without Sodium Lactate show stabilizing after week 6
C&T Jan 2001, whitening effect of frequently used whitening ingredients
�5. More Clinical Research
Objective measurement
mean mexameter differences (versus T=0)
Differences in mexameter readings between T=0 and wk 8 resp. 12
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
Control/Placebo
Sodium Lactate 15%
Arbutin 1%
Licorice 0.3%
Kojic acid 1%
SL+Arbutin
SL+Licorice
SL+Kojic
Week 8
Week 12
5 points difference on mexameter scales is significant
Sodium Lactate, SL+Kojic and SL+Licorice best performing
C&T Jan 2001, whitening effect of frequently used whitening ingredients
�6. Costs / Concentrations
Cost comparison formulations
Products
Sodium Lactate 60%
Price
4 US$/kg
Arbutin
750 US$/kg
Licorice
325 US$/kg
Kojic acid
400 US$/kg
10
Control/Placebo
Sodium Lactate 15%
Arbutin 1%
Licorice 0.3%
Kojic acid 1%
SL + Arbutin
SL + Licorice
Costs in formulation (USD/kg formulation)
SL + Kojic
Sodium Lactate cheapest and most effective whitening ingredient
C&T Jan 2001, whitening effect of frequently used whitening ingredients
�6. Costs / Concentrations
6. Summary on concentrations needed
Whitening effect is related to the lactate ion
Nr
Product
Product 100%
Lactate
ion
8.8% Lactic acid 90%
8% Lactic acid (100%)
7.9%
15% Sodium Lactate 60%
9% Sodium lactate (100%)
7.2%
Correction for concentration
Correction for Mw (H=1; Na=23; L=98)
Conclusion: At least 7% Lactate ion should be added
Equivalent to:
15% Sodium Lactate 60%
(= 7.2% Lactate)
8% Lactic acid 90%
(= 7.1% Lactate)
12% Calcium Lactate
(= 7.0% Lactate)
Calcium lactate: Mw=308 g/mole, 5H20 =90 g/mole, Ca2+= 40 g/mole, Lactate = 178 g/mole
�7. pH-effect / AHA
Lactates and pH
Experiments carried out at relatively neutral pH (5)
At pH 5, hardly any Lactic acid is available in final formulation
8
pH
pH=5 in formula:
100 Sodium Lactate
6 Lactic acid
4
3
2
0
% Lactic acid / %Sodium lactate
10
�7. pH-effect / AHA
pH-effect / AHA
Rejuvenating benefits of Lactates; improvement in % after 8 weeks treatment
60
50
Skin cell renewal
increase
40
Increase in skin
firmness
% 30
20
Reduction of
lines and
wrinkles
10
0
pH=7
pH=3
Exfoliating effect of Lactates increases at lower pH levels
Exfoliating effect Lactates could enhance pace of whitening
�8. Conclusions
Conclusions L (+) Lactates in whitening
L(+) Lactates are safe and effective and low
cost whitening ingredients
Formulated at lower pH incorporates additional
peeling/exfoliating properties
Additional moisturizing properties added to
the whitening formulation
Possibility to add properties such as ceramide
increase and mineral enrichment
�9. Discussion
Intended Future Clinical Research
Determine whitening capability/performance
of Lactate salts (Zn-L, Ca-L vs. Na-L)
Study the synergistic effects (if any) with
other popular whitening active ingredients
like Nicotin amide, Ascorbic acid, vegetable
extracts like Brassica rapa juice extract
�9. Discussion
Safety concerns Hydroquinone / Kojic acid
Hydroquinone is suspected to be carcinogenic
FDA ruling due for 30 December 2006 on
imposing a ban on Hydroquinone
Japanese dermatologists suspect Kojic acid
may be carcinogenic (?)
Japanese and Korean government ordered to
stop using Kojic acid until investigations end
Switzerland has banned Kojic acid