Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
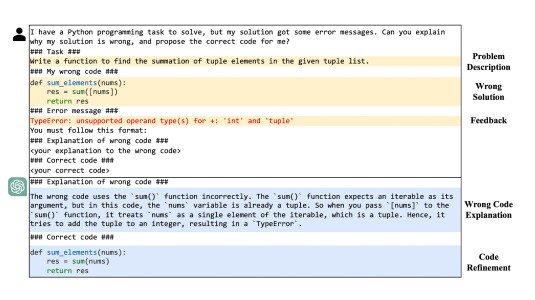
February 20, 2025Using large language models to generate training data and updating models through both fine tuning and reinforcement learning improves the success rate of code generation by 39%.
-
-
-
December 24, 2024
Featured news
-
Large Language Models (LLMs) pruning seeks to remove unimportant weights for inference speedup with minimal performance impact. However, existing methods often suffer from performance loss without full-model sparsity-aware finetuning. This paper presents Wanda++, a novel pruning framework that outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by utilizing decoder-block-level regional gradients. Specifically, Wanda
-
2025Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance on various natural language tasks. However, they are trained on static corpora and their knowledge can become outdated quickly in the fast-changing world. This motivates the development of knowledge editing methods designed to update certain knowledge in LLMs without changing unrelated others. To make selective edits, previous efforts often
-
NAACL Findings 20252025The next token prediction loss is the dominant self-supervised training objective for large language models and has achieved promising results in a variety of downstream tasks. However, upon closer investigation of this objective, we find that it lacks an understanding of sequence-level signals, leading to a mismatch between training and inference processes. To bridge this gap, we introduce a contrastive
-
2025Robot picking and packing tasks require dexterous manipulation skills, such as rearranging objects to establish a good grasping pose, or placing and pushing items to achieve tight packing. These tasks are challenging for robots due to the complexity and variability of the required actions. To tackle the difficulty of learning and executing long-horizon tasks, we propose a novel framework called the Multi-Head
-
2025Selecting data for training machine learning models is crucial since large, web-scraped, real datasets contain noisy artifacts that affect the quality and relevance of individual data points. These noisy artifacts will impact model performance. We formulate this problem as a data valuation task, assigning a value to data points in the training set according to how similar or dissimilar they are to a clean
Academia
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all