This is a review (by no means comprehensive) of how the stem cell niche evolved from an abstract concept to a complex system, implemented with a number of experimental data at the cellular and molecular levels, including metabolic cues,...
moreThis is a review (by no means comprehensive) of how the stem cell niche evolved from an abstract concept to a complex system, implemented with a number of experimental data at the cellular and molecular levels, including metabolic cues, on which we focused in particular. The concept was introduced in 1978 to model bone marrow sites suited to host hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and favor their self-renewal, while restraining clonal expansion and commitment to differentiation. Studies of the effects of low oxygen tension on HSC maintenance in vitro led us to hypothesize niches were located within bone marrow areas where oxygen tension is lower than elsewhere. We named these areas hypoxic stem cell niches, although a low oxygen tension is to be considered physiological for the environment where HSCs are maintained. HSCs were later shown to have the option of cycling in low oxygen, which steers this cycling to the maintenance of stem cell potential. Cell subsets capable of withstanding incubation in very low oxygen were also detected within leukemia cell populations, including chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). The oncogenetic Bcr/Abl protein is completely suppressed in these subsets, whereas Bcr/Abl messenger ribonucleic acid is not, indicating that CML cells resistant to low oxygen are independent of Bcr/Abl for persistence in culture but remain genetically leukemic. Accordingly, leukemia stem cells of CML selected in low oxygen are refractory to the Bcr/Abl inhibitor imatinib mesylate. Bcr/Abl protein suppression turned out to be actually determined when glucose shortage complicated the effects of low oxygen, indicating that ischemia-like conditions are the driving force of leukemia stem cell refractoriness to imatinib mesylate. These studies pointed to “ischemic” stem cell niches as a novel scenario for the maintenance of minimal residual disease of CML. A possible functional relationship of the “ischemic” with the “hypoxic” stem cell niche is discussed.
Keywords: hypoxia, ischemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, stem cell niche, leukemia stem cell, drug resistance
Macrophages, which are found in all tissues, are an essential component of the innate immune system, and they play important roles in host defense, inflammation, autoimmune diseases as well as cancer. Functionally, macrophages are...
moreMacrophages, which are found in all tissues, are an essential component of the innate immune system, and they play important roles in host defense, inflammation, autoimmune diseases as well as cancer. Functionally, macrophages are classified into two types: classically-activated M1 macrophages and alternatively-activated M2 macrophages. The M1 macrophages typically produce high levels of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, whereas M2 macrophages show an efficient phagocytic and scavenging activity. Because the phenotypes of polarized M1 and M2 macrophages can be induced, and reversed to some extent, by various signals, different phases of many diseases are associated with dynamic changes in the balance between M1 and M2 macrophages. The colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF-1R), a class III receptor tyrosine kinase, sustains the survival, proliferation and differentiation of monocytes and macrophages. Drugging CSF-1R may be the only way to target macrophages within a pathological context. However, CSF-1R-dependent signals may be either positive or detrimental depending on the disease and even on the phase of disease. The role of CSF-1R and its ligands, the colony-stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-34, in macrophages with respect to the pathogenesis of several inflammatory or neoplastic diseases has been reviewed previously. This review will focus specifically on evidences obtained about the role of CSF-1R in macrophage polarization in the context of physiological as well as pathological conditions including inflammation and cancer. The possibility to target CSF-1R, using the several inhibitors already available, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases as well as cancer will be also discussed.
We showed that resistance to severe hypoxia defines hierarchical levels within normal hematopoietic populations and that hypoxia modulates the balance between generation of progenitors and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in...
moreWe showed that resistance to severe hypoxia defines hierarchical levels within normal hematopoietic populations and that hypoxia modulates the balance between generation of progenitors and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in favor of the latter. This study deals with the effects of hypoxia (0.1% oxygen) in vitro on Friend's murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cells, addressing the question of whether a clonal leukemia cell population comprise functionally different cell subsets characterized by different hypoxia resistance. To identify leukemia stem cells (LSC), we used the Culture Repopulating Ability (CRA) assay we developed to quantify in vitro stem cells capable of short-term reconstitution (STR). Hypoxia strongly inhibited the overall growth of MEL cell population, which, despite its clonality, comprised progenitors characterized by markedly different hypoxia-resistance. These included hypoxia-sensitive colony-forming cells and hypoxia-resistant STR-type LSC, capable of repopulating secondary liquid cultures of CRA assays, confirming what was previously shown for normal hematopoiesis. STR-type LSC were found capable not only of surviving in hypoxia but also of being mostly in cycle, in contrast with the fact that almost all hypoxia-surviving cells were growth-arrested and with what we previously found for HSC. However, quiescent LSC were also detected, capable of delayed culture repopulation with the same efficiency as STR-like LSC. The fact that even quiescent LSC, believed to sustain minimal residual disease in vivo, were found within the MEL cells indicates that all main components of leukemia cell populations may be present within clonal cell lines, which are therefore suitable to study the sensitivity of individual components to treatments. Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest is found at the end of this article.
SERPINB3 is a cysteine-proteases inhibitor up-regulated in a significant number of cirrhotic patients carrying hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and recently proposed as a prognostic marker for HCC early recurrence. SERPINB3 has been...
moreSERPINB3 is a cysteine-proteases inhibitor up-regulated in a significant number of cirrhotic patients carrying hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and recently proposed as a prognostic marker for HCC early recurrence. SERPINB3 has been reported to stimulate proliferation, inhibit apoptosis and, similar to what reported for hypoxia, to trigger epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and increased invasiveness in liver cancer cells. This study has investigated whether SERPINB3 expression is regulated by hypoxia-related mechanisms in liver cancer cells. Exposure of HepG2 and Huh7 cells to hypoxia up-regulated SERPINB3 transcription, protein synthesis and release in the extracellular medium. Hypoxia-dependent SERPINB3 up-regulation was selective (no change detected for SERPINB4) and operated through hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2α (not HIF-1α) binding to SERPINB3 promoter, as confirmed by chromatin immuno-precipitation assay and silencing experiments employing specific siRNAs. HIF-2α-me...
The Hedgehog-GLI (HH-GLI) signaling is of critical importance during embryonic development, where it regulates a number of cellular processes, including patterning, proliferation and differentiation. Its aberrant activation has been...
moreThe Hedgehog-GLI (HH-GLI) signaling is of critical importance during embryonic development, where it regulates a number of cellular processes, including patterning, proliferation and differentiation. Its aberrant activation has been linked to several types of cancer. HH-GLI signaling is triggered by binding of ligands to the transmembrane receptor patched and is subsequently mediated by transcriptional effectors belonging to the GLI family, whose function is fine tuned by a series of molecular interactions and modifications. Several HH-GLI inhibitors have been developed and are in clinical trials. Similarly, the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are involved in a number of biological processes and play an important role in many diseases including cancer. Inhibiting molecules targeting MAPK signaling, especially those elicited by the MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway, have been developed and are moving into clinical trials. ERK1/2 may be activated as a consequence of aberrant activation of upstream signaling molecules or during development of drug resistance following treatment with kinase inhibitors such as those for PI3K or BRAF. Evidence of a crosstalk between HH-GLI and other oncogenic signaling pathways has been reported in many tumor types, as shown by recent reviews. Here we will focus on the interaction between HH-GLI and the final MAPK effectors ERK1/2, p38 and JNK in cancer in view of its possible implications for cancer therapy. Several reports highlight the existence of a consistent crosstalk between HH signaling and MAPK, especially with the MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway, and this fact should be taken into consideration for designing optimal treatment and prevent tumor relapse.
We defined the stem cell profile of K562 line, demonstrating the expression of the Embryonic Transcription Factors Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4 and Nanog. This profile was associated with a high vulnerability to the physiological oxidizable...
moreWe defined the stem cell profile of K562 line, demonstrating the expression of the Embryonic Transcription Factors Oct3/4, Sox2, Klf4 and Nanog. This profile was associated with a high vulnerability to the physiological oxidizable substrate pyruvate. remarkably, this substrate was shown to be innocuous, even at the highest doses, to normal differentiated cells. This vulnerability is based on a complex metabolic trim centered on the cellular redox state expressed by the NADP/NADPH ratio geared by the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Flow cytometry revealed that the inhibition of this chain by antimycin A produced cell accumulation in the S phase of cell cycle and apoptosis. This block negatively interferes with the aerobic synthesis of purines, without affecting the anaerobic synthesis of pyrimidines. This imbalance was reproduced by using two antifolate agents, LY309887 and raltitrexed (TDX), inhibitors of purine or pyrimidine synthesis, respectively. All this revealed the apparent paradox that low doses of TDX stimulated, instead of inhibiting, leukemia cell growth. This paradox might have significant impact on therapy with regard to the effects of TDX during the intervals of administration, when the drug concentrations become so low as to promote maintenance of dormant cancer cells in hypoxic tissue niches.
The activation of macrophages interferes with their response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), the main growth and differentiation factor for mononuclear phagocytes. We tested the rapid effects of interleukin-4 (IL-4), the...
moreThe activation of macrophages interferes with their response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), the main growth and differentiation factor for mononuclear phagocytes. We tested the rapid effects of interleukin-4 (IL-4), the alternative macrophage activator produced by Th2 helper lymphocytes, on the receptor for M-CSF (M-CSFR) expressed on the cell surface of murine macrophages. IL4 rapidly down-modulated M-CSFR in a dose-dependent fashion. This effect was unique to IL-4 among a number of Th2-produced cytokines, none of which, with the exception of IL4 itself, is able to activate macrophages. The down-modulation of M-CSFR by IL4 was partially prevented by the inhibition of the activity of phospholipase C or protein kinase C. The data are consistent with the hypothesis that the down-modulation of M-CSFR is a property common to, and exclusive of, macrophage activators, and is driven by different activators via a common mechanism.
SERPINB3 is a cysteine-proteases inhibitor up-regulated in a significant number of cirrhotic patients carrying hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and recently proposed as a prognostic marker for HCC early recurrence. SERPINB3 has been...
moreSERPINB3 is a cysteine-proteases inhibitor up-regulated in a significant number of cirrhotic patients carrying hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and recently proposed as a prognostic marker for HCC early recurrence. SERPINB3 has been reported to stimulate proliferation, inhibit apoptosis and, similar to what reported for hypoxia, to trigger epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and increased invasiveness in liver cancer cells. This study has investigated whether SERPINB3 expression is regulated by hypoxia-related mechanisms in liver cancer cells. Exposure of HepG2 and Huh7 cells to hypoxia up-regulated SERPINB3 transcription, protein synthesis and release in the extracellular medium. Hypoxia-dependent SERPINB3 up-regulation was selective (no change detected for SERPINB4) and operated through hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2α (not HIF-1α) binding to SERPINB3 promoter, as confirmed by chromatin immuno-precipitation assay and silencing experiments employing specific siRNAs. HIF-2α-me...
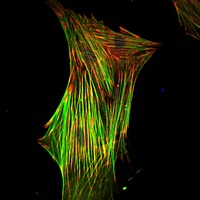
Low M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase interferes in vivo with the activation of several growth factor receptors and is transiently redistributed, following cell stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor, from the cytosol to...
moreLow M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase interferes in vivo with the activation of several growth factor receptors and is transiently redistributed, following cell stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor, from the cytosol to the cytoskeleton. We demonstrate here that this phosphatase also participates in the regulation of cell spreading and migration, pointing to its involvement in cytoskeleton organization. Low M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase-overexpressing fibroblasts are, indeed, less spread than controls and display a significantly decreased number of focal adhesions and increased cell motility. Furthermore, p125 focal adhesion kinase is associated to, and dephosphorylated by, low M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase both in vitro and in vivo. This event is consistent with an altered association of pp60(src) with focal adhesion kinase. The activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, another well known event downstream of the focal adhesion kinase, is also affected. On the other hand, cells overexpressing the dominant-negative form of low M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase exhibit hyperphosphorylated focal adhesion kinase, reduced motility, and an increased number of focal adhesions, which are distributed all over the ventral cell surface. Taken together, the results reported here are in keeping with low M(r) phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase participation in FAK-mediated focal adhesion remodeling.
The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5 or BMK1) is involved in tumour development. The ERK5 gene may be amplified in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but its biological role has not been clarified. In this study, we explored the...
moreThe extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5 or BMK1) is involved in tumour development. The ERK5 gene may be amplified in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but its biological role has not been clarified. In this study, we explored the role of ERK5 expression and activity in HCC in vitro and in vivo. ERK5 expression was evaluated in human liver tissue. Cultured HepG2 and Huh-7 were studied after ERK5 knockdown by siRNA or in the presence of the specific pharmacological inhibitor, XMD8-92. The role of ERK5 in vivo was assessed using mouse Huh-7 xenografts. In tissue specimens from patients with HCC, a higher percentage of cells with nuclear ERK5 expression was found both in HCC and in the surrounding cirrhotic tissue compared with normal liver tissue. Inhibition of ERK5 decreased HCC cell proliferation and increased the proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase. These effects were associated with increased expression of p27 and p15 and decreased CCND1. Treatment with XMD8-92 or ERK5 sile...
We showed that resistance to severe hypoxia defines hierarchical levels within normal hematopoietic populations and that hypoxia modulates the balance between generation of progenitors and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in...
moreWe showed that resistance to severe hypoxia defines hierarchical levels within normal hematopoietic populations and that hypoxia modulates the balance between generation of progenitors and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in favor of the latter. This study deals with the effects of hypoxia (0.1% oxygen) in vitro on Friend's murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cells, addressing the question of whether a clonal leukemia cell population comprise functionally different cell subsets characterized by different hypoxia resistance. To identify leukemia stem cells (LSC), we used the Culture Repopulating Ability (CRA) assay we developed to quantify in vitro stem cells capable of short-term reconstitution (STR). Hypoxia strongly inhibited the overall growth of MEL cell population, which, despite its clonality, comprised progenitors characterized by markedly different hypoxia-resistance. These included hypoxia-sensitive colony-forming cells and hypoxia-resistant STR-type LSC, capable of repopulating secondary liquid cultures of CRA assays, confirming what was previously shown for normal hematopoiesis. STR-type LSC were found capable not only of surviving in hypoxia but also of being mostly in cycle, in contrast with the fact that almost all hypoxia-surviving cells were growth-arrested and with what we previously found for HSC. However, quiescent LSC were also detected, capable of delayed culture repopulation with the same efficiency as STR-like LSC. The fact that even quiescent LSC, believed to sustain minimal residual disease in vivo, were found within the MEL cells indicates that all main components of leukemia cell populations may be present within clonal cell lines, which are therefore suitable to study the sensitivity of individual components to treatments. Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest is found at the end of this article.
We previously demonstrated that severe hypoxia inhibits growth of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) cells and selects stem cells where BCR/Ablprotein is suppressed, although mRNA is not, so that hypoxia-selected stem cells, while remaining...
moreWe previously demonstrated that severe hypoxia inhibits growth of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) cells and selects stem
cells where BCR/Ablprotein is suppressed, although mRNA is not, so that hypoxia-selected stem cells, while remaining
leukemic, are independent of BCR/Abl signaling and thereby refractory to Imatinib-mesylate. The main target of this study
was to address the effects of the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (BZ) on the maintenance of stem or progenitor cells in
hypoxic primary cultures (LC1), by determining the capacity of LC1 cells to repopulate normoxic secondary cultures (LC2)
and the kinetics of this repopulation. Unselected K562 cells from day-2 hypoxic LC1 repopulated LC2 with rapid, progenitortype
kinetics; this repopulation was suppressed by BZ addition to LC1 at time 0, but completely resistant to day-1 BZ,
indicating that progenitors require some time to adapt to stand hypoxia. K562 cells selected in hypoxic day-7 LC1
repopulated LC2 with stem-type kinetics, which was largely resistant to BZ added at either time 0 or day 1, indicating that
hypoxia-selectable stem cells are BZ-resistant per se, i.e. before their selection. Furthermore, these cells were completely
resistant to day-6 BZ, i.e. after selection. On the other hand, hypoxia-selected stem cells from CD34-positive cells of blastcrisis
CML patients appeared completely resistant to either time-0 or day-1 BZ. To exploit in vitro the capacity of CML cells to
adapt to hypoxia enabled to detect a subset of BZ-resistant leukemia stem cells, a finding of particular relevance in light of
the fact that our experimental system mimics the physiologically hypoxic environment of bone marrow niches where
leukemia stem cells most likely home and sustain minimal residual disease in vivo. This suggests the use of BZ as an
enhanced strategy to control CML. in particular to prevent relapse of disease, to be considered with caution and to need
further deepening.
The colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and its receptor CSF-1R physiologically regulate the monocyte/macrophage system, trophoblast implantation and breast development. An abnormal CSF-1R expression has been documented in several human...
moreThe colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) and its receptor CSF-1R physiologically regulate the monocyte/macrophage system, trophoblast implantation and breast development. An abnormal CSF-1R expression has been documented in several human epithelial tumors, including breast carcinomas. We recently demonstrated that CSF-1/CSF-1R signaling drives proliferation of breast cancer cells via 'classical' receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, including activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. In this paper, we show that CSF-1R can also localize within the nucleus of breast cancer cells, either cell lines or tissue specimens, irrespectively of their intrinsic molecular subtype. We found that the majority of nuclear CSF-1R is located in the chromatin-bound subcellular compartment. Chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that CSF-1R, once in the nucleus, binds to the promoters of the proliferation-related genes CCND1, c-JUN and c-MYC. CSF-1R also binds the promoter of its ligand CSF-1 and positively regulates CSF-1 expression. The existence of such a receptor/ligand regulatory loop is a novel aspect of CSF-1R signaling. Moreover, our results provided the first evidence of a novel localization site of CSF-1R in breast cancer cells, suggesting that CSF-1R could act as a transcriptional regulator on proliferation-related genes.
Background Incubation of chronic myeloid leukemia cells in hypoxia inhibits growth and selects BCR/Ablindependent cells with stem cell properties which are refractory to imatinib-mesylate. This study aimed to characterize the relationship...
moreBackground
Incubation of chronic myeloid leukemia cells in hypoxia inhibits growth and selects BCR/Ablindependent cells with stem cell properties which are refractory to imatinib-mesylate. This study aimed to characterize the relationship of this refractoriness with glucose availability in the environment.
Design and Methods
K562 or primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells were cultured at 0.1% O2, different cell densities and glucose concentrations. The stem and progenitor cell potential of these cultures at different times of incubation in relation to BCR/Ablprotein expression and sensitivity to imatinibmesylate was explored by transferring cells to growth-permissive secondary cultures in normoxia, according to the Culture-Repopulating Ability assay methodology.
Results
Hypoxia-resistant cells maintained BCR/Ablprotein expression until glucose was no longer available in primary hypoxic cultures, where glucose availability appeared to regulate cell number and the balance between the enrichment of cells with kinetic properties typical of stem or progenitor cells. Cells surviving merely hypoxic conditions were, upon transfer to secondary cultures,
immediately available for numerical expansion due to the maintained BCR/Ablprotein expression, and were consequently sensitive to imatinib-mesylate. Instead, BCR/Ablprotein–negative cells selected in primary cultures under oxygen/glucose shortage underwent a delayed numerical expansion in secondary cultures, which was completely refractory to imatinib-mesylate. Cells with the latter properties were also found in primary chronic myeloid leukemia
explants.
Conclusions
Glucose shortage in hypoxia was shown to represent the condition selecting BCR/Ablprotein–negative cells refractory to imatinib-mesylate from either chronic myeloid leukemia lines or patients. These cells, exhibiting stem cell properties in vitro, are metabolically suited to home to stem cell niches in vivo and so may represent the chronic myeloid leukemia cell subset responsible for minimal residual disease.
The macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF, CSF-1) regulates survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, as well as macrophage motility and morphology. The latter features are usually regulated by...
moreThe macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF, CSF-1) regulates survival, proliferation and differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes, as well as macrophage motility and morphology. The latter features are usually regulated by ECM-mediated activation of integrins and subsequent tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins, including focal adhesion kinase (FAK). FAK is phosphorylated by downstream receptor tyrosine kinases as well. We addressed the question whether M-CSF regulates FAK tyrosine phosphorylation in macrophages, and found that M-CSF induces FAK phosphorylation at all known tyrosine residues. This phosphorylation was dependent on Src. Extracellularly-regulated kinase (ERK), Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) were found to be negatively involved in M-CSF-induced FAK phosphorylation, as their inhibition resulted in FAK hyper-phosphorylation. Following M-CSF treatment, FAK and the active forms of M-CSFR and Src were redistributed to the c...
We analysed the in vitro effects of a new hydroxamate derivative, ITF2357, on AML cells. ITF2357 potently induced histone acetylation. ITF2357 0.1 microM blocked proliferation and induced apoptosis in AML1/ETO-positive Kasumi-1 cells,...
moreWe analysed the in vitro effects of a new hydroxamate derivative, ITF2357, on AML cells. ITF2357 potently induced histone acetylation. ITF2357 0.1 microM blocked proliferation and induced apoptosis in AML1/ETO-positive Kasumi-1 cells, while AML1/ETO-negative HL60, THP1 and NB4 cell lines were sensitive only to 1 microM ITF2357. Apoptosis was induced by 0.1 microM ITF2357 in AML1/ETO-positive primary blasts and U937-A/E cells induced to express AML1/ETO, but not in U937-A/E cells non-expressing AML1/ETO. In Kasumi-1 cells 0.1 microM ITF2357 induced AML1/ETO degradation through a caspase-dependent mechanism. ITF2357 0.1 microM also determined DNMT1 efflux from, and p300 influx to, the nucleus. Moreover, 0.1 microM ITF2357 determined local H4 acetylation and release of DNMT1, HDAC1 and AML1/ETO, paralleled by recruitment of p300 to the IL-3 gene promoter. ITF2357 treatment, however, did not induce re-expression of IL-3 gene. Accordingly, the methylation level of IL-3 promoter, as well as of several other genes, was unmodified. In conclusion, ITF2357 emerged as an anti-leukaemic agent very potent on AML cells, and on AML1/ETO-positive cells in particular. More relevantly, clearly emerged from our results that ITF2357 could be an ideal agent to treat AML subtypes presenting AML1/ETO fusion protein which determine HDAC involvement in leukaemogenesis.