Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 25mg
Toxoplasmosis
50-75 mg qD PO for 1-3 weeks, THEN
25-37.5 mg qD PO for 4-5 weeks
P jiroveci Pneumonia (Off-label)
Prophylaxis p P jiroveci pneumonia (formerly Pneumocystis pneumonia); administer with dapsone
50-75 mg PO once/week
Tay-Sachs & Sandhoff Disease (Orphan)
Treatment of GM-2 gangliosidoses (Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff disease)
Orphan indication sponsor
- ExSAR Corporation; 11 Deer Park Drive; Monmouth Junction, NJ 08852
Other Indications & Uses
Treatment & prevention of toxoplasmosis (with sulfadiazine, clindamycin, or atovaquone); malaria
Off-label: prophylaxis of P. jiroveci pneumonia (with dapsone), isosporiasis
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 25mg
>2 Months Old
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
- Loading dose: 2 mg/kg/day divided q12hr PO for 2 days
- Maintenance.: First 2-6 months old: 1 mg/kg PO qD for 2-6 months old; THEN remainder of 12 months old; 1 mg/kg PO 3 times/week
Toxoplasmosis
- Loading dose: 2 mg/kg/d divided q12hr PO for 3 days
- Maintenance: 1 mg/kg PO qD for 4 weeks
< 2 months old: Safety and efficacy not established
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results
Contraindicated
Serious
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor
Contraindicated (1)
- eliglustat
pyrimethamine increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Contraindicated. If coadministered with strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors, reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive and intermediate metabolizers; eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
Serious (5)
- dapsone topical
pyrimethamine, dapsone topical. unspecified interaction mechanism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of dapsone topical with oral dapsone or antimalarial medications because of the potential for hemolytic reactions.
- deferiprone
deferiprone, pyrimethamine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid use of deferiprone with other drugs known to be associated with neutropenia or agranulocytosis; if an alternative is not possible, monitor absolute neutrophil count more frequently.
- erdafitinib
pyrimethamine will increase the level or effect of erdafitinib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of a strong CYP2C9 inhibitors is unavoidable, closely monitor adverse reactions and modify dose of erdafitinib accordingly. If strong CYP2C9 inhibitor is discontinued, consider increasing erdafitinib dose in the absence of any drug-related toxicities.
- ropeginterferon alfa 2b
ropeginterferon alfa 2b, pyrimethamine. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Myelosuppressive agents can produce additive myelosuppression. Avoid use and monitor patients receiving the combination for effects of excessive myelosuppression.
- siponimod
pyrimethamine will increase the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with drugs that cause moderate CYP2C9 AND a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibition is not recommended. Caution if siponimod coadministered with moderate CYP2C9 inhibitors alone.
Monitor Closely (9)
- acalabrutinib
acalabrutinib, pyrimethamine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may increase risk of myelosuppressive effects.
- brexpiprazole
pyrimethamine will increase the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Administer a quarter of brexpiprazole dose if coadministered with a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor PLUS a strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- bupivacaine implant
pyrimethamine, bupivacaine implant. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Local anesthetics may increase the risk of developing methemoglobinemia when concurrently exposed to drugs that also cause methemoglobinemia.
- folic acid
folic acid, pyrimethamine. Either decreases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- hydroxyurea
pyrimethamine, hydroxyurea. Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Combination may increase risk of myelosuppression.
- ifosfamide
ifosfamide, pyrimethamine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Ifosfamide may enhance the toxicities of myelosuppressive agents. Monitor for increased risk of myelosuppression.
- L-methylfolate
L-methylfolate, pyrimethamine. pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oliceridine
pyrimethamine will increase the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If concomitant use is necessary, may require less frequent oliceridine dosing. Closely monitor for respiratory depression and sedation and titrate subsequent doses accordingly. If inhibitor is discontinued, consider increase oliceridine dosage until stable drug effects are achieved. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal.
- tamsulosin
pyrimethamine increases levels of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (18)
- chlorpromazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of chlorpromazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- dapsone
dapsone, pyrimethamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased bone marrow toxicity.
- ethotoin
pyrimethamine decreases effects of ethotoin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluphenazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of fluphenazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fosphenytoin
pyrimethamine decreases effects of fosphenytoin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lorazepam
lorazepam, pyrimethamine. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Additive hepatotoxicity.
- perphenazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of perphenazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- phenytoin
pyrimethamine decreases effects of phenytoin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- prochlorperazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of prochlorperazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of promazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- promethazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of promethazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sapropterin
pyrimethamine decreases levels of sapropterin by Other (see comment). Minor/Significance Unknown. Comment: Mechanism: Inhibition of dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR).
- sulfadiazine
sulfadiazine, pyrimethamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased bone marrow toxicity.
- sulfamethoxazole
sulfamethoxazole, pyrimethamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased bone marrow toxicity.
- sulfisoxazole
sulfisoxazole, pyrimethamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased bone marrow toxicity.
- thioridazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of thioridazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- trifluoperazine
pyrimethamine increases levels of trifluoperazine by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- zidovudine
zidovudine, pyrimethamine. Mechanism: pharmacodynamic synergism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Increased bone marrow toxicity.
Adverse Effects
Frequency Not Defined
Abdominal cramps
Abnormal skin pigmentation
Anaphylaxis
Anorexia
Arrhythmias (large doses)
Atrophic glossitis
Depression
Fever
Insomnia
Lightheadedness
Malaise
Seizures
Dermatitis
Erythema multiforme
Rash
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Xerostomia
Megaloblastic anemia
Leukopenia
Pancytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Pulmonary eosinophilia
Neutropenia
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Megaloblastic or folate-deficiency anemia
Cautions
Use with caution in patients with G6PD deficiency
Use with caution in hepatic/renal impairment and history of seizure disorders
Dosage of pyrimethamine required for treatment of toxoplasmosis. has a narrow therapeutic window; if signs of folate deficiency develop, reduce dosage or discontinue drug according to response of patient; folinic acid (leucovorin) should be administered in a dosage of 5 to 15 mg daily (orally, IV, or IM) until normal hematopoiesis restored
Megaloblastic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and pancytopenia reported with high doses; monitor CBC and platelets twice weekly in patients receiving high dose therapy
Use caution in patients with possible folate deficiency, including pregnancy, malabsorption syndrome, and alcoholism and those receiving therapy, such as phenytoin, affecting folate levels
Administer with leucovorin, especially at high doses, to prevent hematologic complications, due to pyrimethamine-induced folic acid deficiency; continue leucovorin during therapy and for 1 week after discontinuing therapy
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women; this drug should be used during pregnancy only if potential benefit justifies potential risk to the fetus
Concurrent administration of folinic acid is strongly recommended when used during pregnancy
Animal data
- Pyrimethamine has been shown to be teratogenic in rats when given in oral doses 2.5 times the human dose for treatment of toxoplasmosis; at these doses in rats, there was a significant increase in abnormalities such as cleft palate, brachygnathia, oligodactyly, and microphthalmia; This drug has also been shown to produce terata such as meningocele in hamsters and cleft palate in miniature pigs when given in oral doses 5 times human dose for treatment of toxoplasmosis
Lactation
This drug is excreted in human milk; because of potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from therapy and from concurrent use of a sulfonamide with this drug for treatment of some patients with toxoplasmosis, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Onset: ~1 hr
Absorption: well absorbed
Distribution: widely, mainly in blood cells, kidneys, lungs, liver, & spleen; crosses into CSF; crosses placenta; enters breast milk
Protein Bound: 80-87%
Metabolism: hepatic
Half-life elimination: 80-95 hr
Peak Plasma Time: 1.5-8 hr
Excretion: urine (20-30% as unchanged drug)
Mechanism of Action
Folic acid antagonist
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daraprim oral - | 25 mg tablet | 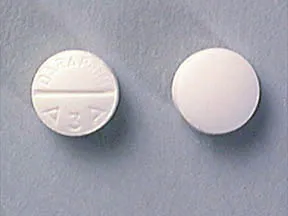 | |
| pyrimethamine oral - | 25 mg tablet |  | |
| pyrimethamine oral - | 25 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
pyrimethamine oral
PYRIMETHAMINE - ORAL
(pir-ih-METH-uh-meen)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Daraprim
USES: This medication is used with other medication (such as a sulfonamide) to treat a serious parasite infection (toxoplasmosis) of the body, brain, or eye or to prevent toxoplasmosis infection in people with HIV infection. Pyrimethamine belongs to a class of drugs known as antiparasitics. It works by killing parasites.
HOW TO USE: Take this medication by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once or twice daily. Take this medication with food to decrease nausea and vomiting. If vomiting is severe or continues, your doctor may lower your dose or direct you to stop taking this medication. Your doctor will prescribe another medication (folic/folinic acid) to prevent blood problems caused by pyrimethamine. Follow your doctor's directions carefully. Drink plenty of fluids to prevent kidney problems if you are taking a "sulfa" medication with pyrimethamine.This medication works best when the amount of drug in your body is kept at a constant level. Take this drug and other antiparasitic drugs regularly, exactly as prescribed by your doctor. To help you remember, take it at the same time(s) each day.Dosage is based on the type of infection, your medical condition, age, and response to treatment. The length of time you will take this medication depends on your infection. Your dose must be carefully adjusted by your doctor to treat your infection and prevent serious side effects. Follow your doctor's directions carefully.Do not take more or less of this drug than prescribed. Do not stop taking it before completing this prescription unless directed to do so by your doctor, even if you feel better. Skipping or changing your dose without approval from your doctor may cause the amount of parasites to increase, make the infection more difficult to treat (resistant), or worsen side effects.Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also How to Use section.Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Some people using this medication may develop serious side effects including blood problems, especially at higher doses. This risk can be reduced with the use of folic/folinic acid and regular blood tests. Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: easy bruising/bleeding, signs of serious infection (such as sore throat that doesn't go away, high fever, severe chills), signs of low red blood cell count (such as severe tiredness, pale lips/nails/skin, fast heartbeat/breathing with usual activities), swollen/painful tongue.Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: bloody/pink urine, chest pain, slow/fast/irregular heartbeat.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before taking pyrimethamine, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: seizures, kidney problems, liver problems, a certain type of low red blood cell count (megaloblastic anemia due to low blood folate), low folic acid levels from other conditions (such as malnutrition, problems with absorption of food, alcoholism), low red/white blood cell counts, low blood-clotting cell (platelet) count.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. Folic acid is very important during pregnancy. Your doctor will prescribe folic/folinic acid to prevent low folate levels.This medication passes into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: lorazepam, penicillamine, sulfa drugs (such as sulfamethoxazole), drugs that can lower folate levels (such as phenytoin, trimethoprim), drugs that can lower blood counts (such as proguanil, zidovudine, chemotherapy including methotrexate, daunorubicin, cytosine).This medication can slow down the removal of other medications from your body, which may affect how they work. An example of an affected drug is dofetilide, among others.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669. Symptoms of overdose may include: abdominal pain, severe/repeated vomiting, vomiting blood, seizures, slow/shallow breathing, inability to wake up.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as complete blood count, liver function) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised October 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.


