WO2003105850A1 - 2-aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists - Google Patents
2-aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2003105850A1 WO2003105850A1 PCT/US2003/018959 US0318959W WO03105850A1 WO 2003105850 A1 WO2003105850 A1 WO 2003105850A1 US 0318959 W US0318959 W US 0318959W WO 03105850 A1 WO03105850 A1 WO 03105850A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- amine
- quinolin
- oxy
- methylbutoxy
- methyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 108010047068 Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor Proteins 0.000 title claims abstract description 16
- 102000029828 Melanin-concentrating hormone receptor Human genes 0.000 title abstract description 15
- 150000005013 2-aminoquinolines Chemical class 0.000 title description 2
- 229940123502 Hormone receptor antagonist Drugs 0.000 title description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 378
- 101800002739 Melanin-concentrating hormone Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 239000000651 prodrug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 229940002612 prodrug Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 208000008589 Obesity Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 235000020824 obesity Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 230000004584 weight gain Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 235000019786 weight gain Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 208000030814 Eating disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 208000019454 Feeding and Eating disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 208000021017 Weight Gain Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 235000014632 disordered eating Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 193
- GCMNJUJAKQGROZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dihydroquinolin-2-imine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=NC(N)=CC=C21 GCMNJUJAKQGROZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 124
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 104
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 63
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 63
- -1 4-(2-(benzyloxy)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy Chemical group 0.000 claims description 58
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 claims description 57
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 51
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 49
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 46
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 33
- 125000004356 hydroxy functional group Chemical group O* 0.000 claims description 31
- 125000004438 haloalkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 28
- 125000003710 aryl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 26
- 125000002102 aryl alkyloxo group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 17
- 125000005129 aryl carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 17
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 17
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004183 alkoxy alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000001188 haloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910001868 water Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000004575 3-pyrrolidinyl group Chemical group [H]N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005160 aryl oxy alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001316 cycloalkyl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- QRRPXJAEHNIECX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentan-1-ol Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCO)C)=CC=CC2=C1 QRRPXJAEHNIECX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004106 butoxy group Chemical group [*]OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 6
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000028327 secretion Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- QBRAFUNNWHXUPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropan-1-ol Chemical compound C1=CC=C(OCCCO)C2=NC(N)=CC=C21 QBRAFUNNWHXUPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- AYSVKPVLDFGRKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropylamino]-6-methylchromen-2-one Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCNC3=CC(=O)OC4=CC=C(C=C43)C)=CC=CC2=C1 AYSVKPVLDFGRKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- VHOVADGQCCWIRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)-3-methylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CC1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 VHOVADGQCCWIRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- PXTDASDBFFAWDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)-n-methylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C(OC(C)CC(C)(C)C)C2=NC(NC)=CC=C21 PXTDASDBFFAWDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- WTCUMHGWTNPEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-hexylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(CCCCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 WTCUMHGWTNPEAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000019901 Anxiety disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 206010010904 Convulsion Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000004880 Polyuria Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- AUYYCJSJGJYCDS-LBPRGKRZSA-N Thyrolar Chemical class IC1=CC(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=CC(I)=C1OC1=CC=C(O)C(I)=C1 AUYYCJSJGJYCDS-LBPRGKRZSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000036506 anxiety Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000037007 arousal Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000035619 diuresis Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000019948 ion homeostasis Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000004770 neurodegeneration Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000020016 psychiatric disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000031893 sensory processing Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000009329 sexual behaviour Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005495 thyroid hormone Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229940036555 thyroid hormone Drugs 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000007279 water homeostasis Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- WBUCAPKBKQMUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzamide Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1C(N)=O WBUCAPKBKQMUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- FUTCVQCKZXKFMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzonitrile Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1C#N FUTCVQCKZXKFMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GTQGNQTYZVZKES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC(N)=NC2=C1 GTQGNQTYZVZKES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- IUBJZEVUFSPDTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenyl]butan-2-one Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(CCC(C)=O)C=C1 IUBJZEVUFSPDTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UFQVNDCBSNGUPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-acetyl-2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzamide Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C(C)=O)C=C1C(N)=O UFQVNDCBSNGUPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- NRJWSTLYXSKKGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropoxy]-1h-quinolin-2-one Chemical compound N1=C(O)C=CC2=CC(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=C21 NRJWSTLYXSKKGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- NPQHPGOWIVAOJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-ethoxypropan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)COCC)=CC=CC2=C1 NPQHPGOWIVAOJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- HFVYCRXMQPWHFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-methoxypropan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)COC)=CC=CC2=C1 HFVYCRXMQPWHFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YLIRVLXATQGNTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCC(C)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 YLIRVLXATQGNTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MXXMNBSDHISKHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylcyclohexyl)oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CC1CCCCC1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 MXXMNBSDHISKHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JZRCCMGLVXGYEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylsulfanylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCSC)=CC=CC2=C1 JZRCCMGLVXGYEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- ZGZSZXFSLMTFBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3,3,3-trifluoropropoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C(OCCC(F)(F)F)C2=NC(N)=CC=C21 ZGZSZXFSLMTFBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GUJKDUVYIJMAPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCC(C)(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 GUJKDUVYIJMAPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UMDWRYRCTHHCNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-ethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)C(CC)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 UMDWRYRCTHHCNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- LPHQANHABFNXJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCC(C)(C)OC)=CC=CC2=C1 LPHQANHABFNXJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UQTSQIVXJFEZMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methylbutan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)C(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 UQTSQIVXJFEZMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- AZGLOGDXDJFQFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methylcyclohexyl)oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1C(C)CCCC1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 AZGLOGDXDJFQFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- XSBYTVRYECCAPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methylcyclopentyl)oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1C(C)CCC1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 XSBYTVRYECCAPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- QGLXWYBIBRYORH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-phenoxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCCCOC1=CC=CC=C1 QGLXWYBIBRYORH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JVIHCEMPSHGRLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-quinolin-8-yloxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CN=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 JVIHCEMPSHGRLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YWQZUTGHEIPYKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)-n-propylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C(OC(C)CC(C)(C)C)C2=NC(NCCC)=CC=C21 YWQZUTGHEIPYKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- OQURIDUAVDCPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4-methylcyclohexyl)oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1CC(C)CCC1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 OQURIDUAVDCPLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GSVPQQXISZNZHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(5-isoquinolin-5-yloxypentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C4=CC=NC=C4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 GSVPQQXISZNZHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GBEABJHOCPCNAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(5-naphthalen-2-yloxypentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4C=CC=CC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 GBEABJHOCPCNAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YGVPVRLYSXAJMW-INIZCTEOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C2OCOC2=CC(CN2CC[C@@H](C2)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)=C1 YGVPVRLYSXAJMW-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- CEMMJEPLXDXUPL-FQEVSTJZSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(O[C@H]3CCN(C3)CC=3C=C4CCC(OC4=CC=3)(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 CEMMJEPLXDXUPL-FQEVSTJZSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- QHBHFKWCHIQSGC-HNNXBMFYSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(2,3-difluorophenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC1=CC=CC(F)=C1F QHBHFKWCHIQSGC-HNNXBMFYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MPINHPJSKBFKKI-KRWDZBQOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(3-methyl-1-benzothiophen-2-yl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound S1C2=CC=CC=C2C(C)=C1CN1C[C@@H](OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)CC1 MPINHPJSKBFKKI-KRWDZBQOSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YVEBLYYXHIIAJG-QHCPKHFHSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(4-phenylphenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 YVEBLYYXHIIAJG-QHCPKHFHSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YDBNKIYLWFCYOA-FQEVSTJZSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(4-tert-butylphenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=C1CN1C[C@@H](OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)CC1 YDBNKIYLWFCYOA-FQEVSTJZSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MRBRLGAGSUSFMW-JTQLQIEISA-N 8-[(3s)-pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1O[C@H]1CCNC1 MRBRLGAGSUSFMW-JTQLQIEISA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- HYHLPCMDRXVXBT-NSCUHMNNSA-N 8-[(e)-but-2-enoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC/C=C/C)=CC=CC2=C1 HYHLPCMDRXVXBT-NSCUHMNNSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- KEQMRPOCAKSNND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxybutoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCOC=3C4=NC(N)=CC=C4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 KEQMRPOCAKSNND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- HRNXVHUKNBMEQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropoxy]-1h-quinolin-2-one Chemical compound C1=C(O)N=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 HRNXVHUKNBMEQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- WXGUEWJPFLONQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)propoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCCCOC1=CC(Cl)=CC(Cl)=C1 WXGUEWJPFLONQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MBSNSEXHXBJNEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-[[8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-yl]amino]propoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCNC3=CC=C4C=CC=C(C4=N3)OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 MBSNSEXHXBJNEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MMAVLLAFFLFSLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C4=NC(N)=CC=C4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 MMAVLLAFFLFSLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JZWRTLSUMOLCKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4OCOC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 JZWRTLSUMOLCKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YTTXVZLWCAXKSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-5-yloxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4CCCC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 YTTXVZLWCAXKSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- QFOXEDDQJHNVQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-benzylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1 QFOXEDDQJHNVQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- RVIGDFVTTVQSNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-chloro-4-methoxyphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound ClC1=CC(OC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 RVIGDFVTTVQSNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- XKIVIKLDTICZPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1F XKIVIKLDTICZPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- XWQRPRSULNLQJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=CC=C1F XWQRPRSULNLQJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GWXYMQOPDWVIAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-methyl-5-nitrophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC=C1C GWXYMQOPDWVIAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- CCAKTCMGHUFDTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxypentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C4=NC(C)=CC=C4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 CCAKTCMGHUFDTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- ZMEBIEGVPHIGNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3,4,5-trimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=C(C)C(C)=C1 ZMEBIEGVPHIGNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- XYPOFCPPPRANTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(Cl)=CC(Cl)=C1 XYPOFCPPPRANTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JHMJEVMHNAAOMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-anilinophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC(C=1)=CC=CC=1NC1=CC=CC=C1 JHMJEVMHNAAOMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- WJKWMYVHOOJEFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-propan-2-ylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C(C)C)=C1 WJKWMYVHOOJEFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- SKGPQIGPVPYWRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-amino-2-chlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(N)C=C1Cl SKGPQIGPVPYWRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- KLCCOQDNLMNWOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1F KLCCOQDNLMNWOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- QKANEKPZRXLELG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-methoxynaphthalen-1-yl)oxypentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2C(OC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 QKANEKPZRXLELG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- SCIIZVSLUQSJOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-propylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC(CCC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 SCIIZVSLUQSJOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- ZRKCVBIWFGDPPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(5-aminonaphthalen-1-yl)oxypentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C4=CC=CC(N)=C4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 ZRKCVBIWFGDPPG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- VXVWPTOGFYADOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[(2,2-dimethyl-3h-1-benzofuran-7-yl)oxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=4OC(C)(C)CC=4C=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 VXVWPTOGFYADOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- JLUUHHRAWRXZIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[2-(1,2-oxazol-5-yl)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=NO1 JLUUHHRAWRXZIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- PJFCCHZNBSVWFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[3-(diethylamino)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CCN(CC)C1=CC=CC(OCCCC(C)OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)=C1 PJFCCHZNBSVWFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- RDHSHZSWPBWALB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-butan-2-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 RDHSHZSWPBWALB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- RANHBKGFWNIVKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-butoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 RANHBKGFWNIVKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YLYMSWOMERSHNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-cyclobutyloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OC1CCC1 YLYMSWOMERSHNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MPHNEJNPZMBSBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-cyclohexyloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OC1CCCCC1 MPHNEJNPZMBSBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- QFJPSIRKKLVRQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-cyclopentyloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OC1CCCC1 QFJPSIRKKLVRQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- YFFRPYGSSBQXDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-ethoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCC)=CC=CC2=C1 YFFRPYGSSBQXDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- FVXCMWHSIIELPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-heptan-3-ylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(C(CC)CCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 FVXCMWHSIIELPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GWRHFSWAYZHHKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-hexan-2-ylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(C(C)CCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 GWRHFSWAYZHHKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- UTETWLJKMIYQHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-hexan-3-ylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(C(CC)CCC)=CC=CC2=C1 UTETWLJKMIYQHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- SBZZEIZRHJBKKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-hexoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 SBZZEIZRHJBKKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- KMEFXXMANWGJCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-pentan-2-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)CCC)=CC=CC2=C1 KMEFXXMANWGJCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- CTMPUINXCIZFAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-pentoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 CTMPUINXCIZFAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- LMFCQQCADRHNMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [2-[[8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-yl]carbamoyl]phenyl]methyl benzoate Chemical compound N1=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=CC=C1NC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1COC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 LMFCQQCADRHNMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- VMSNKSRXIAPKGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenyl]urea Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(NC(N)=O)=C1 VMSNKSRXIAPKGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- BAMHHWOYHJTPLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]-5-methylbenzoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC(C)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 BAMHHWOYHJTPLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- HJMYSTZDGXIDRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 HJMYSTZDGXIDRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- NFBNMXIRFUDQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]-4-methoxybenzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=C(OC)C=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 NFBNMXIRFUDQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- BOPKOMXJIDBIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]-5-methoxybenzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 BOPKOMXJIDBIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- OGBRSXAENKWROK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenyl]propan-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC(C(=O)CC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 OGBRSXAENKWROK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BPFGFDHSAUVHDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropylamino]-6-chlorochromen-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC(Cl)=CC2=C1OC(=O)C=C2NCCCOC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C21 BPFGFDHSAUVHDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VTYIHSXNLDSDNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]-1,3-benzoxathiol-2-one Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4OC(=O)SC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 VTYIHSXNLDSDNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FLASHIIQOAUHMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)C1CCCCC1 FLASHIIQOAUHMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- UBZRQWZLPAJNMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-ethoxypentan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)CCOCC)=CC=CC2=C1 UBZRQWZLPAJNMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BWCBAXDDNXQALA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-methoxybutan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(COC)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 BWCBAXDDNXQALA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YBADJPOEQACJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-phenylbutan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(CC)CC1=CC=CC=C1 YBADJPOEQACJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ILJWLKADTTTWOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-phenylpropan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 ILJWLKADTTTWOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VNDSAADHGZOVGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1C2=CC=CC=C2CC1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C21 VNDSAADHGZOVGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SPVVIGOQSLJWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylheptan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCC)C(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 SPVVIGOQSLJWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MJODBRIOACDMBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylhex-5-en-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC=C)C(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 MJODBRIOACDMBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GWWOFCQTGOKWHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylpentan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)C(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 GWWOFCQTGOKWHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XOSRTYMPIZHJAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-naphthalen-1-ylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(CCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 XOSRTYMPIZHJAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PBTVGUVBILTOJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methoxybutoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCC(C)OC)=CC=CC2=C1 PBTVGUVBILTOJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RGLJKEQVQXDAIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCC(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 RGLJKEQVQXDAIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RSDZXDCGGFCJHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)-n-[[5-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]furan-2-yl]methyl]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound N1=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=CC=C1NCC(O1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1C(F)(F)F RSDZXDCGGFCJHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZDVPLVAZUCNXKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 ZDVPLVAZUCNXKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GGKOMICFVNBEDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4-ethylhexan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)C(CC)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 GGKOMICFVNBEDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LZSDRAOYYHUVST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4-methylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)CC(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 LZSDRAOYYHUVST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FNQZDJXDWDDAHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(5-dibenzofuran-2-yloxypentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4C5=CC=CC=C5OC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 FNQZDJXDWDDAHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DXJFZQRZDRNPFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(5-quinolin-7-yloxypentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCCOC=3C=C4N=CC=CC4=CC=3)C)=CC=CC2=C1 DXJFZQRZDRNPFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IXAWCFLVQOOABZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(6-ethyloctan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)CCC(CC)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 IXAWCFLVQOOABZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HPSBUHJYYFNYCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(6-methylhept-5-en-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCC=C(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 HPSBUHJYYFNYCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LFSKOEPBLSZZCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(6-methylheptan-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CCC(C)C)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 LFSKOEPBLSZZCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XJMDWXUURVOWTQ-CMPLNLGQSA-N 8-[(1r,2s)-2-methylcyclopentyl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C[C@H]1CCC[C@H]1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 XJMDWXUURVOWTQ-CMPLNLGQSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZKOBEHNFUIUBDX-TZMCWYRMSA-N 8-[(1r,5s)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1C(C)(C)C[C@H](C)C[C@H]1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 ZKOBEHNFUIUBDX-TZMCWYRMSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RHJVYTFUGSPPAA-QGZVFWFLSA-N 8-[(3r)-1-benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 RHJVYTFUGSPPAA-QGZVFWFLSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JQLXGGJOOAASBA-KRWDZBQOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 JQLXGGJOOAASBA-KRWDZBQOSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RHJVYTFUGSPPAA-KRWDZBQOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 RHJVYTFUGSPPAA-KRWDZBQOSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AJUQXIZMSKXJLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 AJUQXIZMSKXJLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- QWKDFDKSXZCXNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)C1=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C1 QWKDFDKSXZCXNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- CRHWIVWRZVBOFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[2-(1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CN1CCCC1CCOC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 CRHWIVWRZVBOFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WHNPLRVDCBVSSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[2-[2-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxyethoxy]ethoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCOCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 WHNPLRVDCBVSSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BUVCLAZAWXIHOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxypropoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)C)=CC=CC2=C1 BUVCLAZAWXIHOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- CAOSETWYINZWHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-[2-(methylamino)quinolin-8-yl]oxypropoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)NC)=CC=CC2=C1 CAOSETWYINZWHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MFZONDKDNNNZJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 MFZONDKDNNNZJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SXSQWOHHYFDBFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-phenylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC(C=1)=CC=CC=1C1=CC=CC=C1 SXSQWOHHYFDBFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GFCDTYYGEKKLKI-LXKBMQFRSA-N 8-[[(1r,4s)-3-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl]methoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCC3[C@@]4([H])CC[C@](C4)(C3)[H])=CC=CC2=C1 GFCDTYYGEKKLKI-LXKBMQFRSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KWBRXPIYAUDRPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 KWBRXPIYAUDRPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MGAFXFCQBHUFIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-cycloheptyloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OC1CCCCCC1 MGAFXFCQBHUFIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RXUQTWRDGXBPCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-heptan-3-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)CCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 RXUQTWRDGXBPCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZYSOQSQXCCTFTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-pentan-3-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 ZYSOQSQXCCTFTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YKBUHPDDGIYRSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-phenylmethoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 YKBUHPDDGIYRSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IJQWZUBUZMKYCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-propan-2-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 IJQWZUBUZMKYCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SZBXIIUHFFFWME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-propoxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCC)=CC=CC2=C1 SZBXIIUHFFFWME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MQEDILQFCFYUGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-[4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenyl]acetate Chemical compound C1=CC(CC(=O)OC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 MQEDILQFCFYUGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SCMWXTYCTKFPPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CC(OCCCC(C)OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)=C1 SCMWXTYCTKFPPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- STLABSIVKBHWHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenyl]acetamide Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(NC(C)=O)C=C1 STLABSIVKBHWHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LZNBFPPKQCZSEZ-ZDUSSCGKSA-N tert-butyl (3s)-3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypyrrolidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1N(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CC[C@@H]1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 LZNBFPPKQCZSEZ-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001475 halogen functional group Chemical group 0.000 claims 12
- JFDZBHWFFUWGJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzonitrile Chemical compound N#CC1=CC=CC=C1 JFDZBHWFFUWGJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 6
- GLHRQXXVMGWCEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]-3-methylphenyl]ethanone Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C(C)=O)C=C1C GLHRQXXVMGWCEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- DNJXIEGYABPHEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OC(CC1)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 DNJXIEGYABPHEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- GIWXUQNJYCESBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(1-cyclohexylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(CC)C1CCCCC1 GIWXUQNJYCESBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- RDHSHZSWPBWALB-SECBINFHSA-N 8-[(2r)-butan-2-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(O[C@H](C)CC)=CC=CC2=C1 RDHSHZSWPBWALB-SECBINFHSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 102000006953 melanin-concentrating hormone receptor activity proteins Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- SEZSKZKVXIFHDR-DEOSSOPVSA-N n-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)-8-[(3s)-1-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound O1CCOC2=CC(CNC=3N=C4C(O[C@@H]5CN(CC=6C=C7OCCOC7=CC=6)CC5)=CC=CC4=CC=3)=CC=C21 SEZSKZKVXIFHDR-DEOSSOPVSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 125000000951 phenoxy group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(O*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims 1
- ORRDHOMWDPJSNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N melanin concentrating hormone Chemical compound N1C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCNC(N)=N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCCNC(N)=N)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(N)CC(O)=O)C(C)O)CCSC)CSSCC(C(=O)NC(CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3NC=2)C(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(O)=O)NC(=O)C2CCCN2C(=O)C(CCCNC(N)=N)NC(=O)C1CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 ORRDHOMWDPJSNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 abstract description 31
- 102000047659 melanin-concentrating hormone Human genes 0.000 abstract description 31
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 10
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 abstract description 7
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- YKUCHDXIBAQWSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=CC(O)=C1 YKUCHDXIBAQWSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 152
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 144
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 120
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 115
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 107
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 104
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 95
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N Dimethyl sulfoxide Chemical compound [2H]C([2H])([2H])S(=O)C([2H])([2H])[2H] IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N 0.000 description 90
- 229940120152 methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate Drugs 0.000 description 76
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 69
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 52
- RZKSECIXORKHQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Heptan-3-ol Chemical compound CCCCC(O)CC RZKSECIXORKHQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 52
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 47
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 44
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 44
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- 229960004592 isopropanol Drugs 0.000 description 40
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 37
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 36
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 33
- WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzyl alcohol Chemical compound OCC1=CC=CC=C1 WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 30
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical class CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 28
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 24
- RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylphosphine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 21
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 21
- 235000019439 ethyl acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 20
- ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylamine Chemical compound CNC ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 19
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 19
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 17
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 17
- UFVLIVCXTIGACT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-aminoquinolin-8-ol Chemical compound C1=CC=C(O)C2=NC(N)=CC=C21 UFVLIVCXTIGACT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000004007 reversed phase HPLC Methods 0.000 description 14
- NBYLBWHHTUWMER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Methylquinolin-8-ol Chemical compound C1=CC=C(O)C2=NC(C)=CC=C21 NBYLBWHHTUWMER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 13
- 235000019445 benzyl alcohol Nutrition 0.000 description 10
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 10
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 9
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- NBBJYMSMWIIQGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propionic aldehyde Chemical compound CCC=O NBBJYMSMWIIQGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000010898 silica gel chromatography Methods 0.000 description 8
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium hydroxide Inorganic materials [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 8
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 8
- NHQDETIJWKXCTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chloroperbenzoic acid Chemical compound OOC(=O)C1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 NHQDETIJWKXCTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 125000004448 alkyl carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 7
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 7
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 7
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 102000016267 Leptin Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 108010092277 Leptin Proteins 0.000 description 6
- SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylmorpholine Chemical compound CN1CCOCC1 SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 6
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 6
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- NRYBAZVQPHGZNS-ZSOCWYAHSA-N leptin Chemical compound O=C([C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CC(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(C)C)CCSC)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CS)C(O)=O NRYBAZVQPHGZNS-ZSOCWYAHSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 229940039781 leptin Drugs 0.000 description 6
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 6
- WJKHJLXJJJATHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N triflic anhydride Chemical compound FC(F)(F)S(=O)(=O)OS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F WJKHJLXJJJATHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- JOZICAJUSHUZLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dibenzyltetramethyldisiloxane Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C[Si](C)(C)O[Si](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 JOZICAJUSHUZLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 125000004453 alkoxycarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 5
- 239000013058 crude material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N trifluoroacetic acid Substances OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- AQJFATAFTQCRGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Chloro-4-methylphenol Chemical group CC1=CC=C(O)C(Cl)=C1 AQJFATAFTQCRGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- SRVXSISGYBMIHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[3-[3-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)phenyl]-5-chlorophenyl]-3-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)propanoic acid Chemical compound S1C(C)=CN=C1C(CC(O)=O)C1=CC(Cl)=CC(C=2C=C(CC(N)=O)C=CC=2)=C1 SRVXSISGYBMIHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 125000005078 alkoxycarbonylalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000005093 alkyl carbonyl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000005196 alkyl carbonyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000004390 alkyl sulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000004414 alkyl thio group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000000304 alkynyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- ZTQSAGDEMFDKMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyric aldehyde Natural products CCCC=O ZTQSAGDEMFDKMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011203 carbon fibre reinforced carbon Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000004181 carboxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000004966 cyanoalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000037406 food intake Effects 0.000 description 4
- 235000012631 food intake Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 125000002768 hydroxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 210000003016 hypothalamus Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000003760 magnetic stirring Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 125000001147 pentyl group Chemical group C(CCCC)* 0.000 description 4
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- DAEPDZWVDSPTHF-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium pyruvate Chemical compound [Na+].CC(=O)C([O-])=O DAEPDZWVDSPTHF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- KZPYGQFFRCFCPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene Chemical compound [Fe+2].C1=CC=C[C-]1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=C[C-]1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 KZPYGQFFRCFCPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MNBIBGDICHMQFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-Methylheptan-3-ol Chemical compound CCC(O)CCC(C)C MNBIBGDICHMQFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
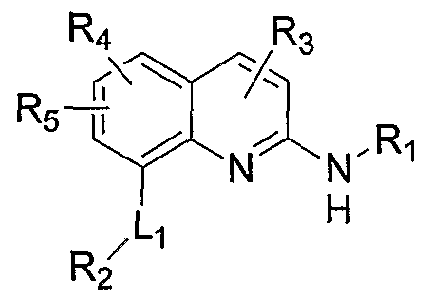
- 0 CC(C(IC)=C(C(C=C1)=*)N=C1N*)=C Chemical compound CC(C(IC)=C(C(C=C1)=*)N=C1N*)=C 0.000 description 3
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000005361 D2 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 3
- OUVXYXNWSVIOSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluo-4 Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)C(OCCOC=2C(=CC=C(C=2)C2=C3C=C(F)C(=O)C=C3OC3=CC(O)=C(F)C=C32)N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O)=C1 OUVXYXNWSVIOSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical group CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butyllithium Chemical compound [Li]CCCC MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ORILYTVJVMAKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N adamantane Chemical compound C1C(C2)CC3CC1CC2C3 ORILYTVJVMAKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000013019 agitation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 3
- 125000002619 bicyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 3
- BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butan-2-ol Chemical group CCC(C)O BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 3
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002485 formyl group Chemical group [H]C(*)=O 0.000 description 3
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 125000002950 monocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen group Chemical group [N] QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium Substances [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 3
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical group CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 3
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- PUPZLCDOIYMWBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N (+/-)-1,3-Butanediol Chemical group CC(O)CCO PUPZLCDOIYMWBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PAMIQIKDUOTOBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylpiperidine Chemical compound CN1CCCCC1 PAMIQIKDUOTOBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OVSKIKFHRZPJSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4-D Chemical compound OC(=O)COC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl OVSKIKFHRZPJSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DDUJXMGQLFUYGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinoline Chemical compound C1=C(Cl)N=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 DDUJXMGQLFUYGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JWAZRIHNYRIHIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-naphthol Chemical group C1=CC=CC2=CC(O)=CC=C21 JWAZRIHNYRIHIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VPOMSPZBQMDLTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,5-dichlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC(Cl)=CC(Cl)=C1 VPOMSPZBQMDLTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KTPVWKOMUBEGJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzonitrile Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C#N)=C1 KTPVWKOMUBEGJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ASHGTJPOSUFTGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxyphenol Chemical group COC1=CC=CC(O)=C1 ASHGTJPOSUFTGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methyl-2-butanol Chemical group CC(C)C(C)O MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HTSABYAWKQAHBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methylcyclohexanol Chemical group CC1CCCC(O)C1 HTSABYAWKQAHBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VLJSLTNSFSOYQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-propan-2-ylphenol Chemical group CC(C)C1=CC=CC(O)=C1 VLJSLTNSFSOYQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OIBKGNPMOMMSSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4-dimethylpentan-2-ol Chemical group CC(O)CC(C)(C)C OIBKGNPMOMMSSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MRNFAUHRORFWLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-hydroxypropylamino)-6-methylchromen-2-one Chemical compound O1C(=O)C=C(NCCCO)C2=CC(C)=CC=C21 MRNFAUHRORFWLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PWSOCWCYYRZPBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]benzonitrile Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C#N)C=C1 PWSOCWCYYRZPBH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LXAPIGYOALPLHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[4-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypentoxy]phenol Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 LXAPIGYOALPLHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WIRGBZBGYNIZIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-hydroxy-6-methylchromen-2-one Chemical compound O1C(=O)C=C(O)C2=CC(C)=CC=C21 WIRGBZBGYNIZIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MQWCXKGKQLNYQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group CC1CCC(O)CC1 MQWCXKGKQLNYQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AOHXYYVHOZAORT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-4-(3-hydroxypropylamino)chromen-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC(Cl)=CC2=C1OC(=O)C=C2NCCCO AOHXYYVHOZAORT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ONNSHYCNYWSADL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCCC1CCCCC1 ONNSHYCNYWSADL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YLXQVSWEPLSGKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-cyclopropylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCCC1CC1 YLXQVSWEPLSGKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MSMWHUFWYBBGPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(2-methylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCC(C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 MSMWHUFWYBBGPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OJXYMHGLLDPJKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)-n-[[5-(2-nitrophenyl)furan-2-yl]methyl]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound N1=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=CC=C1NCC(O1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O OJXYMHGLLDPJKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KEDALJISEBJSHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinoline Chemical compound C1=CN=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 KEDALJISEBJSHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LOSCSSHHWRUJGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(cyclobutylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1CCC1 LOSCSSHHWRUJGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OTJOSBTUERTNPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(cyclohexylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1CCCCC1 OTJOSBTUERTNPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KGRRNRLJYPHJMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(cyclopentylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1CCCC1 KGRRNRLJYPHJMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XDXQUTKCAWSEPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC=C(S(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F)C2=NC(N)=CC=C21 XDXQUTKCAWSEPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005725 8-Hydroxyquinoline Substances 0.000 description 2
- RBZIDWZVYVTJSA-IBGZPJMESA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1CN1C[C@@H](OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)CC1 RBZIDWZVYVTJSA-IBGZPJMESA-N 0.000 description 2
- AWFDJPYQAVDLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1Cl AWFDJPYQAVDLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WKCIVILTKONPPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,3-dimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C)=C1C WKCIVILTKONPPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HQPWHUMUBZEYAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl HQPWHUMUBZEYAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LBXRRANMPXTMQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,4-dimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C)C=C1C LBXRRANMPXTMQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DQKORESXOFARFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1Cl DQKORESXOFARFC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AXUPOYNEIDFPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=CC=C1C AXUPOYNEIDFPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JDXZRLWSACTFNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-bromophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1Br JDXZRLWSACTFNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QYLVEIHPJPPXOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-chloro-4-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C)C=C1Cl QYLVEIHPJPPXOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MKBZGKZJFLXKAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-chloro-5-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=CC=C1Cl MKBZGKZJFLXKAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CULPHADKVYXKSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-chlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1Cl CULPHADKVYXKSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JGMWFUPJHJYTEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-fluorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1F JGMWFUPJHJYTEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LIOVDNVYTPTASJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-methoxy-4-propylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound COC1=CC(CCC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 LIOVDNVYTPTASJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XNJMNGAAHQGVGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 XNJMNGAAHQGVGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SGGHGLMUAHJPAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1C SGGHGLMUAHJPAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YIOZNFWTMSNNDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(2-phenylmethoxyphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 YIOZNFWTMSNNDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SZOVVKJQKLEPDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 SZOVVKJQKLEPDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SRRXJYATSPVMIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3,4-dimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C)C(C)=C1 SRRXJYATSPVMIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- REKXKRDTFNKHIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3,5-dimethylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=CC(C)=C1 REKXKRDTFNKHIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HENJNBYDMHSLFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-bromophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(Br)=C1 HENJNBYDMHSLFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HCBGIFILBPFOKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-chlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 HCBGIFILBPFOKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KIOLJOQMBNWGFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-fluorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(F)=C1 KIOLJOQMBNWGFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KNRSYJLFLOUCOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-methyl-5-propan-2-ylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC(C)=CC(C(C)C)=C1 KNRSYJLFLOUCOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AUPMBAYONMMARB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C)=C1 AUPMBAYONMMARB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OQZFCJKJJYHYAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-bromophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 OQZFCJKJJYHYAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YKEPZZZQQDDICJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-chloro-3-fluorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Cl)C(F)=C1 YKEPZZZQQDDICJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YRYYXEGPKXDRRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-methoxyphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1OCCCC(C)OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 YRYYXEGPKXDRRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YDLSMPSCQRXVGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-methylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 YDLSMPSCQRXVGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CRXNKFCCMKDVJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1Cl CRXNKFCCMKDVJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CLBZKKDIOGYZAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(OC(F)(F)F)=C1 CLBZKKDIOGYZAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ARFFIIFNDFPECT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 ARFFIIFNDFPECT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WNZMQWRCJGTIJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C1 WNZMQWRCJGTIJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MGMDYHZRUILBFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[[4-[(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxymethyl]phenyl]methoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCC3=CC=C(C=C3)COC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 MGMDYHZRUILBFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LNFBSVZJULNONE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-cyclohexylquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1C1CCCCC1 LNFBSVZJULNONE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PFBVEQQRQHCQHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-pent-4-en-2-yloxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OC(CC=C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 PFBVEQQRQHCQHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IKHGUXGNUITLKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetaldehyde Chemical compound CC=O IKHGUXGNUITLKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetaminophen Chemical group CC(=O)NC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia chloride Chemical compound [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 2
- QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylamine Chemical compound CCN QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000003688 G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108090000045 G-Protein-Coupled Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 2
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 2
- BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylamine Chemical compound NC BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JLTDJTHDQAWBAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-dimethylaniline Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=CC=C1 JLTDJTHDQAWBAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AMQJEAYHLZJPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Pentanol Chemical group CCCCCO AMQJEAYHLZJPGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108090000189 Neuropeptides Proteins 0.000 description 2
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ALQSHHUCVQOPAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pentane-1,5-diol Chemical compound OCCCCCO ALQSHHUCVQOPAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1 GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WUGQZFFCHPXWKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanolamine Chemical compound NCCCO WUGQZFFCHPXWKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-WFGJKAKNSA-N acetone d6 Chemical compound [2H]C([2H])([2H])C(=O)C([2H])([2H])[2H] CSCPPACGZOOCGX-WFGJKAKNSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 208000026935 allergic disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000008485 antagonism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000005604 azodicarboxylate group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzaldehyde Chemical compound O=CC1=CC=CC=C1 HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011461 current therapy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- UZVGSSNIUNSOFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzofuran-1-carboxylic acid Chemical group O1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=C1C=CC=C2C(=O)O UZVGSSNIUNSOFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- RRAFCDWBNXTKKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N eugenol Chemical group COC1=CC(CC=C)=CC=C1O RRAFCDWBNXTKKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000002541 furyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000592 heterocycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexan-1-ol Chemical group CCCCCCO ZSIAUFGUXNUGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000009200 high fat diet Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 description 2
- NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxybenzotriazole Substances O=C1C=CC=C2NNN=C12 NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003701 inert diluent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007794 irritation Effects 0.000 description 2
- PHTQWCKDNZKARW-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoamylol Chemical group CC(C)CCO PHTQWCKDNZKARW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutanol Chemical group CC(C)CO ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 239000008297 liquid dosage form Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- OTCKOJUMXQWKQG-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium bromide Chemical group [Mg+2].[Br-].[Br-] OTCKOJUMXQWKQG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229910001623 magnesium bromide Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZICRWXFGZCVTBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate Chemical group COC(=O)C1=CC=C(OC)C=C1O ZICRWXFGZCVTBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DFNBGZODMHWKKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoate Chemical group COC(=O)C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1O DFNBGZODMHWKKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000004170 methylsulfonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 2
- 239000004530 micro-emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 description 2
- BKIMMITUMNQMOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N nonane Chemical compound CCCCCCCCC BKIMMITUMNQMOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000486 o-cresyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(O*)=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- QWVGKYWNOKOFNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-methyl phenol Natural products CC1=CC=CC=C1O QWVGKYWNOKOFNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 description 2
- 229960003540 oxyquinoline Drugs 0.000 description 2
- NWVVVBRKAWDGAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N p-methoxyphenol Chemical group COC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 NWVVVBRKAWDGAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZHZCYWWNFQUZOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N pent-4-en-2-ol Chemical compound CC(O)CC=C ZHZCYWWNFQUZOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JYVLIDXNZAXMDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentan-2-ol Chemical group CCCC(C)O JYVLIDXNZAXMDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AQIXEPGDORPWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentan-3-ol Chemical group CCC(O)CC AQIXEPGDORPWBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002304 perfume Substances 0.000 description 2
- XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphoryl trichloride Chemical compound ClP(Cl)(Cl)=O XHXFXVLFKHQFAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFUASNAHBMBJIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-one Chemical group CC[C]=O UFUASNAHBMBJIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002572 propoxy group Chemical group [*]OC([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 2
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MCJGNVYPOGVAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinolin-8-ol Chemical group C1=CN=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=C1 MCJGNVYPOGVAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000005962 receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108020003175 receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003333 secondary alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- BEOOHQFXGBMRKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium cyanoborohydride Chemical compound [Na+].[B-]C#N BEOOHQFXGBMRKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940054269 sodium pyruvate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000007909 solid dosage form Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 2
- OHEFFKYYKJVVOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulcatol Chemical group CC(O)CCC=C(C)C OHEFFKYYKJVVOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000005931 tert-butyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(OC(*)=O)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001544 thienyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000001988 toxicity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000419 toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylamine Chemical compound CN(C)C GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003039 volatile agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004580 weight loss Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009736 wetting Methods 0.000 description 2
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N (+)-propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N (+/-)-Camphoric acid Chemical compound CC1(C)C(C(O)=O)CCC1(C)C(O)=O LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (1,1-dioxo-1,4-thiazinan-4-yl)-[6-[[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]methoxy]pyridin-3-yl]methanone Chemical compound CC=1ON=C(C=2C=CC(F)=CC=2)C=1COC(N=C1)=CC=C1C(=O)N1CCS(=O)(=O)CC1 VCGRFBXVSFAGGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GMDYDZMQHRTHJA-SNVBAGLBSA-N (1r)-2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-1-ol Chemical group CC(C)[C@@H](O)C1=CC=CC=C1 GMDYDZMQHRTHJA-SNVBAGLBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-RNFRBKRXSA-N (1r,2r)-2-methylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group C[C@@H]1CCCC[C@H]1O NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-RNFRBKRXSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVIJQMCYYASIFP-PHDIDXHHSA-N (1r,2r)-2-methylcyclopentan-1-ol Chemical group C[C@@H]1CCC[C@H]1O BVIJQMCYYASIFP-PHDIDXHHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-NKWVEPMBSA-N (1r,2s)-2-methylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group C[C@H]1CCCC[C@H]1O NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-NKWVEPMBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BRRVXFOKWJKTGG-YUMQZZPRSA-N (1s,5r)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group C[C@H]1C[C@H](O)CC(C)(C)C1 BRRVXFOKWJKTGG-YUMQZZPRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BRRVXFOKWJKTGG-SFYZADRCSA-N (1s,5s)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group C[C@@H]1C[C@H](O)CC(C)(C)C1 BRRVXFOKWJKTGG-SFYZADRCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QUIMJTKRVOBTQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,4-dimethylphenyl)methanol Chemical group CC1=CC=C(CO)C(C)=C1 QUIMJTKRVOBTQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CLKRHIBHXHFDSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,4-dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)methanol Chemical group CC1=NC=C(CO)C(C)=N1 CLKRHIBHXHFDSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RCIVUMDLBQZEHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbamic acid Chemical compound CC(C)(C)ONC(O)=O RCIVUMDLBQZEHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-SCSAIBSYSA-N (2R)-butan-2-ol Chemical group CC[C@@H](C)O BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-SCSAIBSYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-BYPYZUCNSA-N (2S)-butan-2-ol Chemical group CC[C@H](C)O BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-BYPYZUCNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-RXMQYKEDSA-N (2r)-3-methylbutan-2-ol Chemical group CC(C)[C@@H](C)O MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-RXMQYKEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-YFKPBYRVSA-N (2s)-3-methylbutan-2-ol Chemical group CC(C)[C@H](C)O MXLMTQWGSQIYOW-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MAYZWDRUFKUGGP-VIFPVBQESA-N (3s)-1-[5-tert-butyl-3-[(1-methyltetrazol-5-yl)methyl]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-7-yl]pyrrolidin-3-ol Chemical compound CN1N=NN=C1CN1C2=NC(C(C)(C)C)=NC(N3C[C@@H](O)CC3)=C2N=N1 MAYZWDRUFKUGGP-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- YQMXOIAIYXXXEE-NSHDSACASA-N (3s)-1-benzylpyrrolidin-3-ol Chemical group C1[C@@H](O)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 YQMXOIAIYXXXEE-NSHDSACASA-N 0.000 description 1
- NBDZSOKCOAWVPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N (6-chloro-2-oxochromen-3-yl) trifluoromethanesulfonate Chemical compound ClC1=CC=C2OC(=O)C(OS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F)=CC2=C1 NBDZSOKCOAWVPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VCIMYHBCONLMCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (6-methyl-2-oxochromen-3-yl) trifluoromethanesulfonate Chemical compound O1C(=O)C(OS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F)=CC2=CC(C)=CC=C21 VCIMYHBCONLMCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WAPNOHKVXSQRPX-ZETCQYMHSA-N (S)-1-phenylethanol Chemical group C[C@H](O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WAPNOHKVXSQRPX-ZETCQYMHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZGYIXVSQHOKQRZ-COIATFDQSA-N (e)-n-[4-[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-[(3s)-oxolan-3-yl]oxyquinolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide Chemical compound N#CC1=CN=C2C=C(O[C@@H]3COCC3)C(NC(=O)/C=C/CN(C)C)=CC2=C1NC(C=C1Cl)=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=N1 ZGYIXVSQHOKQRZ-COIATFDQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MOWXJLUYGFNTAL-DEOSSOPVSA-N (s)-[2-chloro-4-fluoro-5-(7-morpholin-4-ylquinazolin-4-yl)phenyl]-(6-methoxypyridazin-3-yl)methanol Chemical compound N1=NC(OC)=CC=C1[C@@H](O)C1=CC(C=2C3=CC=C(C=C3N=CN=2)N2CCOCC2)=C(F)C=C1Cl MOWXJLUYGFNTAL-DEOSSOPVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SCYULBFZEHDVBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1-Dichloroethane Chemical compound CC(Cl)Cl SCYULBFZEHDVBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JPRPJUMQRZTTED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dioxolanyl Chemical group [CH]1OCCO1 JPRPJUMQRZTTED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-propanediol Substances OCCCO YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Benzenediol Natural products OC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- APWRZPQBPCAXFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(1-oxo-2H-isoquinolin-5-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]pyrazole-4-carboxamide Chemical compound O=C1NC=CC2=C(C=CC=C12)N1N=CC(=C1C(F)(F)F)C(=O)NC1=CC(=NC=C1)C(F)(F)F APWRZPQBPCAXFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABDDQTDRAHXHOC-QMMMGPOBSA-N 1-[(7s)-5,7-dihydro-4h-thieno[2,3-c]pyran-7-yl]-n-methylmethanamine Chemical compound CNC[C@@H]1OCCC2=C1SC=C2 ABDDQTDRAHXHOC-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YMXIDIAEXNLCFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol Chemical group CC(O)C1=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C1 YMXIDIAEXNLCFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004972 1-butynyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C#C* 0.000 description 1
- JMSUNAQVHOHLMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-cyclohexylethanol Chemical group CC(O)C1CCCCC1 JMSUNAQVHOHLMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVTXOMXEPFDMHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-cyclohexylpropan-1-ol Chemical group CCC(O)C1CCCCC1 JVTXOMXEPFDMHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PJUPKRYGDFTMTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-hydroxybenzotriazole;hydrate Chemical compound O.C1=CC=C2N(O)N=NC2=C1 PJUPKRYGDFTMTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000530 1-propynyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C#C* 0.000 description 1
- YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-indene Natural products C1=CC=C2CC=CC2=C1 YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DNCYBUMDUBHIJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1h-pyrimidin-6-one Chemical compound O=C1C=CN=CN1 DNCYBUMDUBHIJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IDUKOSGEQABOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydrochromene-6-carbaldehyde Chemical group O=CC1=CC=C2OC(C)(C)CCC2=C1 IDUKOSGEQABOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003562 2,2-dimethylpentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- PXSSNPBEHHJLDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,5-tetramethylphenol Chemical group CC1=CC(O)=C(C)C(C)=C1C PXSSNPBEHHJLDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UMPSXRYVXUPCOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dichlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1Cl UMPSXRYVXUPCOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KMGCKSAIIHOKCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dihydro-1h-inden-2-ol Chemical group C1=CC=C2CC(O)CC2=C1 KMGCKSAIIHOKCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003660 2,3-dimethylpentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000098 2,3-xylenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C(C(O*)=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- GISVICWQYMUPJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4-Dimethylbenzaldehyde Chemical group CC1=CC=C(C=O)C(C)=C1 GISVICWQYMUPJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HFZWRUODUSTPEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4-dichlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl HFZWRUODUSTPEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001287 2,4-xylenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C(O*)C(=C([H])C(=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- RANCECPPZPIPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dichlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1Cl RANCECPPZPIPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001257 2,5-xylenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C(O*)C([H])=C1C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- LWGUCIXHBVVATR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-1h-quinolin-4-one Chemical group C1=CC=C2NC(N)=CC(=O)C2=C1 LWGUCIXHBVVATR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GOJUJUVQIVIZAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde Chemical group NC1=NC(Cl)=C(C=O)C(Cl)=N1 GOJUJUVQIVIZAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CDMGNVWZXRKJNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzylphenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1 CDMGNVWZXRKJNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VADKRMSMGWJZCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-bromophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1Br VADKRMSMGWJZCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000143 2-carboxyethyl group Chemical group [H]OC(=O)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- GNVRRKLFFYSLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-4-methoxyphenol Chemical group COC1=CC=C(O)C(Cl)=C1 GNVRRKLFFYSLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ISPYQTSUDJAMAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1Cl ISPYQTSUDJAMAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001731 2-cyanoethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C#N 0.000 description 1
- QJQZRLXDLORINA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-cyclohexylethanol Chemical group OCCC1CCCCC1 QJQZRLXDLORINA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XEHPMVZYZDQLDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-fluoro-5-methylphenol Chemical group CC1=CC=C(F)C(O)=C1 XEHPMVZYZDQLDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004777 2-fluoroethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])(F)C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- CHZCERSEMVWNHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxybenzonitrile Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1C#N CHZCERSEMVWNHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxybenzothiazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SC(O)=NC2=C1 YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HGIDRHWWNZRUEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxydibenzofuran Chemical group C1=CC=C2C3=CC(O)=CC=C3OC2=C1 HGIDRHWWNZRUEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000954 2-hydroxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])O[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000004200 2-methoxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LHGVFZTZFXWLCP-WBJZHHNVSA-N 2-methoxyphenol Chemical group CO[13C]1=[13CH][13CH]=[13CH][13CH]=[13C]1O LHGVFZTZFXWLCP-WBJZHHNVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006022 2-methyl-2-propenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ISTJMQSHILQAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methyl-3-pentanol Chemical group CCC(O)C(C)C ISTJMQSHILQAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UMFDLIXUUJMPSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol Chemical group CC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1O UMFDLIXUUJMPSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QPRQEDXDYOZYLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylbutan-1-ol Chemical group CCC(C)CO QPRQEDXDYOZYLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylcyclohexan-1-ol Chemical group CC1CCCCC1O NDVWOBYBJYUSMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QGVFLDUEHSIZIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylheptan-3-ol Chemical group CCCCC(O)C(C)C QGVFLDUEHSIZIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JKGMJZOZIJHPOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylhex-5-en-3-ol Chemical group CC(C)C(O)CC=C JKGMJZOZIJHPOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WBBPRCNXBQTYLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylthioethanol Chemical group CSCCO WBBPRCNXBQTYLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RXWNCMHRJCOWDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-naphthalen-1-ylethanol Chemical group C1=CC=C2C(CCO)=CC=CC2=C1 RXWNCMHRJCOWDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000094 2-phenylethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- CCZCXFHJMKINPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylmethoxyphenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1OCC1=CC=CC=C1 CCZCXFHJMKINPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003903 2-propenyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000001494 2-propynyl group Chemical group [H]C#CC([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- HDBGBTNNPRCVND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3,3-trifluoropropan-1-ol Chemical group OCCC(F)(F)F HDBGBTNNPRCVND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DUXCSEISVMREAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3-dimethylbutan-1-ol Chemical group CC(C)(C)CCO DUXCSEISVMREAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WDNBURPWRNALGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4-Dichlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 WDNBURPWRNALGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002862 3,4-xylenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C(O*)C([H])=C(C(=C1[H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- TUAMRELNJMMDMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,5-di-methylphenol Natural products CC1=CC(C)=CC(O)=C1 TUAMRELNJMMDMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002852 3,5-xylenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C(O*)C([H])=C(C([H])=C1C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- HCDMJFOHIXMBOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-4,7-dihydropyrrolo[4,5]pyrido[1,2-d]pyrimidin-2-one Chemical compound C=1C2=C3N(CC)C(=O)N(C=4C(=C(OC)C=C(OC)C=4F)F)CC3=CN=C2NC=1CN1CCOCC1 HCDMJFOHIXMBOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BYHQTRFJOGIQAO-GOSISDBHSA-N 3-(4-bromophenyl)-8-[(2R)-2-hydroxypropyl]-1-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one Chemical compound C[C@H](CN1CCC2(CC1)CN(C(=O)N2CC3=CC(=CC=C3)OC)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Br)O BYHQTRFJOGIQAO-GOSISDBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WAVOOWVINKGEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(diethylamino)phenol Chemical group CCN(CC)C1=CC=CC(O)=C1 WAVOOWVINKGEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WNEODWDFDXWOLU-QHCPKHFHSA-N 3-[3-(hydroxymethyl)-4-[1-methyl-5-[[5-[(2s)-2-methyl-4-(oxetan-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]pyridin-2-yl]amino]-6-oxopyridin-3-yl]pyridin-2-yl]-7,7-dimethyl-1,2,6,8-tetrahydrocyclopenta[3,4]pyrrolo[3,5-b]pyrazin-4-one Chemical compound C([C@@H](N(CC1)C=2C=NC(NC=3C(N(C)C=C(C=3)C=3C(=C(N4C(C5=CC=6CC(C)(C)CC=6N5CC4)=O)N=CC=3)CO)=O)=CC=2)C)N1C1COC1 WNEODWDFDXWOLU-QHCPKHFHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDGIBHQWFYCMOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[[8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-yl]amino]propan-1-ol Chemical compound C1=C(NCCCO)N=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 BDGIBHQWFYCMOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LWHKUVOYICRGGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanylmethanol Chemical group C1CC2C(CO)CC1C2 LWHKUVOYICRGGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MNOJRWOWILAHAV-YROCTSJKSA-N 3-bromophenol Chemical group O[14C]1=[14CH][14CH]=[14CH][14C](Br)=[14CH]1 MNOJRWOWILAHAV-YROCTSJKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004975 3-butenyl group Chemical group C(CC=C)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000474 3-butynyl group Chemical group [H]C#CC([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- VZGLVCFVUREVDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chlorobut-1-ene Chemical compound CC(Cl)C=C VZGLVCFVUREVDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HORNXRXVQWOLPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-chlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1 HORNXRXVQWOLPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NEHRITNOSGFGGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-ethylpentan-2-ol Chemical group CCC(CC)C(C)O NEHRITNOSGFGGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SGHBRHKBCLLVCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxybenzonitrile Chemical group OC1=CC=CC(C#N)=C1 SGHBRHKBCLLVCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NDACNGSDAFKTGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxydiphenylamine Chemical group OC1=CC=CC(NC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 NDACNGSDAFKTGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JSGVZVOGOQILFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxy-1-butanol Chemical group COC(C)CCO JSGVZVOGOQILFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MFKRHJVUCZRDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methoxy-3-methylbutan-1-ol Chemical group COC(C)(C)CCO MFKRHJVUCZRDTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DRZGHNXLEQHVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methyl-1-benzothiophene-2-carbaldehyde Chemical group C1=CC=C2C(C)=C(C=O)SC2=C1 DRZGHNXLEQHVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZDUIHRJGDMTBEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methyl-5-propan-2-ylphenol Chemical group CC(C)C1=CC(C)=CC(O)=C1 ZDUIHRJGDMTBEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VEALHWXMCIRWGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-methylcyclopentan-1-ol Chemical group CC1CCC(O)C1 VEALHWXMCIRWGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003469 3-methylhexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- XMIIGOLPHOKFCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 3-phenylpropionate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC1=CC=CC=C1 XMIIGOLPHOKFCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000006201 3-phenylpropyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- CYKCUAPYWQDIKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1h-imidazol-1-yl)phenol Chemical group C1=CC(O)=CC=C1N1C=NC=C1 CYKCUAPYWQDIKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BOTGCZBEERTTDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Methoxy-1-naphthol Chemical group C1=CC=C2C(OC)=CC=C(O)C2=C1 BOTGCZBEERTTDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KLSLBUSXWBJMEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Propylphenol Chemical group CCCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 KLSLBUSXWBJMEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFCIFWOJYYFDQP-PTWZRHHISA-N 4-[3-amino-6-[(1S,3S,4S)-3-fluoro-4-hydroxycyclohexyl]pyrazin-2-yl]-N-[(1S)-1-(3-bromo-5-fluorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-2-fluorobenzamide Chemical compound CNC[C@@H](NC(=O)c1ccc(cc1F)-c1nc(cnc1N)[C@H]1CC[C@H](O)[C@@H](F)C1)c1cc(F)cc(Br)c1 YFCIFWOJYYFDQP-PTWZRHHISA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZYZQSCWSPFLAFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-amino-2-chlorophenol Chemical group NC1=CC=C(O)C(Cl)=C1 ZYZQSCWSPFLAFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVCQTKNUUQOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-amino-n-[1-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-6-methylisoquinolin-5-yl]thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-7-carboxamide Chemical compound N=1C=CC2=C(NC(=O)C=3C4=NC=NC(N)=C4SC=3)C(C)=CC=C2C=1NC1=CC=CC(Cl)=C1F KVCQTKNUUQOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RYVOZMPTISNBDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromo-2-fluorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1F RYVOZMPTISNBDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GZFGOTFRPZRKDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 GZFGOTFRPZRKDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XLHYAEBESNFTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chloro-3-fluorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Cl)C(F)=C1 XLHYAEBESNFTCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WXNZTHHGJRFXKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chlorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 WXNZTHHGJRFXKQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CVNOWLNNPYYEOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-cyanophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(C#N)C=C1 CVNOWLNNPYYEOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVVRCYWZTJLJSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-dimethylaminophenol Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 JVVRCYWZTJLJSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000549 4-dimethylaminophenol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-dimethylaminopyridine Substances CN(C)C1=CC=NC=C1 VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BOJLCKCCKQMGKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-ethylhexan-3-ol Chemical group CCC(O)C(CC)CC BOJLCKCCKQMGKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RHMPLDJJXGPMEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-fluorophenol Chemical group OC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 RHMPLDJJXGPMEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MNVMYTVDDOXZLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxyguaiacol Natural products COC1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1 MNVMYTVDDOXZLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WVYWICLMDOOCFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-2-pentanol Chemical group CC(C)CC(C)O WVYWICLMDOOCFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ISDBWOPVZKNQDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-phenylbenzaldehyde Chemical group C1=CC(C=O)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ISDBWOPVZKNQDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTXINXDGSUFPNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-tert-butylbenzaldehyde Chemical group CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(C=O)C=C1 OTXINXDGSUFPNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ORPHLVJBJOCHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 403-19-0 Chemical group OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1F ORPHLVJBJOCHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ONQOZTFAOFZDFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(2-chlorophenyl)furan-2-carbaldehyde Chemical group ClC1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=C(C=O)O1 ONQOZTFAOFZDFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QBYRUURYXPVDAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(2-nitrophenyl)furan-2-carbaldehyde Chemical group [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=C(C=O)O1 QBYRUURYXPVDAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IRPVABHDSJVBNZ-RTHVDDQRSA-N 5-[1-(cyclopropylmethyl)-5-[(1R,5S)-3-(oxetan-3-yl)-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-6-yl]pyrazol-3-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(C(F)(F)F)C(N)=NC=C1C1=NN(CC2CC2)C(C2[C@@H]3CN(C[C@@H]32)C2COC2)=C1 IRPVABHDSJVBNZ-RTHVDDQRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BECHPBVVELWRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]furan-2-carbaldehyde Chemical group FC(F)(F)C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=C(C=O)O1 BECHPBVVELWRBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LWAQTCWTCCNHJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-acetyl-2-hydroxybenzamide Chemical group CC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C(C(N)=O)=C1 LWAQTCWTCCNHJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZBIBQNVRTVLOHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-aminonaphthalen-1-ol Chemical group C1=CC=C2C(N)=CC=CC2=C1O ZBIBQNVRTVLOHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006043 5-hexenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- KCBWAFJCKVKYHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-(4-cyclopropyl-6-methoxypyrimidin-5-yl)-1-[[4-[1-propan-2-yl-4-(trifluoromethyl)imidazol-2-yl]phenyl]methyl]pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine Chemical compound C1(CC1)C1=NC=NC(=C1C1=NC=C2C(=N1)N(N=C2)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C=1N(C=C(N=1)C(F)(F)F)C(C)C)OC KCBWAFJCKVKYHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HUMZENGQNOATEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-chloro-4-hydroxycoumarin Chemical compound C1=CC(Cl)=CC2=C1OC(=O)C=C2O HUMZENGQNOATEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JWZFCOOWAQHCBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-ethyloctan-3-ol Chemical group CCC(O)CCC(CC)CC JWZFCOOWAQHCBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OVZCGYYCEKAVIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-methyl-4-(trifluoromethylsulfonylmethyl)chromen-2-one Chemical compound O1C(=O)C=C(CS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F)C2=CC(C)=CC=C21 OVZCGYYCEKAVIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-{[2-carboxy-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(phosphanyloxy)oxan-3-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-3-phosphanyloxane-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound O1C(C(O)=O)C(P)C(O)C(O)C1OC1C(C(O)=O)OC(OP)C(O)C1O FHVDTGUDJYJELY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CYJRNFFLTBEQSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(3-methyl-1-benzothiophen-5-yl)-N-(4-methylsulfonylpyridin-3-yl)quinoxalin-6-amine Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)C1=C(C=NC=C1)NC=1C=C2N=CC=NC2=C(C=1)C=1C=CC2=C(C(=CS2)C)C=1 CYJRNFFLTBEQSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TXSBSDLVHXCOIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-(oxolan-3-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C12=NC(N)=CC=C2C=CC=C1OCC1CCOC1 TXSBSDLVHXCOIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZKOBEHNFUIUBDX-OCCSQVGLSA-N 8-[(1s,5s)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1C(C)(C)C[C@H](C)C[C@@H]1OC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 ZKOBEHNFUIUBDX-OCCSQVGLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWVXPWWPAAGTBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)methoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1COC1=CC=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C12 BWVXPWWPAAGTBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZDVPLVAZUCNXKZ-NSHDSACASA-N 8-[(2s)-4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(O[C@H](CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 ZDVPLVAZUCNXKZ-NSHDSACASA-N 0.000 description 1
- HJLUBPZTSWCEGL-KRWDZBQOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound O1CCOC2=CC(CN3CC[C@@H](C3)OC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=C21 HJLUBPZTSWCEGL-KRWDZBQOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BTZMZCMCFFBTBB-INIZCTEOSA-N 8-[(3s)-1-[(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]oxyquinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C([C@@H](C1)OC2=CC=CC3=CC=C(N=C32)N)CN1CC1=CC=CC=C1F BTZMZCMCFFBTBB-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HZGLMGHXWHPWQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxypropoxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C1=C(N)N=C2C(OCCCOC3=CC=CC4=CC=C(N=C43)N)=CC=CC2=C1 HZGLMGHXWHPWQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DOPJJBLAOOPGNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(3-methoxyphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(OCCCC(C)OC=2C3=NC(N)=CC=C3C=CC=2)=C1 DOPJJBLAOOPGNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DJTNYWWNUJNXTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-chlorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 DJTNYWWNUJNXTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PXXARWYRZBSPKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-fluorophenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 PXXARWYRZBSPKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XEEKNPUUDKTEKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[5-(4-imidazol-1-ylphenoxy)pentan-2-yloxy]quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound C=1C=CC2=CC=C(N)N=C2C=1OC(C)CCCOC(C=C1)=CC=C1N1C=CN=C1 XEEKNPUUDKTEKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bicarbonate Chemical compound OC([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M Butyrate Chemical compound CCCC([O-])=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyric acid Natural products CCCC(O)=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Carbonate Chemical compound [O-]C([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N Deuterated methanol Chemical compound [2H]OC([2H])([2H])[2H] OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWLUMTFWVZZZND-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dibenzylamine Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1CNCC1=CC=CC=C1 BWLUMTFWVZZZND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicyclohexylamine Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC1CCCCC1 XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GYCKQBWUSACYIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl salicylate Chemical group CCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O GYCKQBWUSACYIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCN PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GISRWBROCYNDME-PELMWDNLSA-N F[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](NC1=O)COC1=NC=CC2=CC(=C(C=C12)OC)C(=O)N)C Chemical compound F[C@H]1[C@H]([C@H](NC1=O)COC1=NC=CC2=CC(=C(C=C12)OC)C(=O)N)C GISRWBROCYNDME-PELMWDNLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004606 Fillers/Extenders Substances 0.000 description 1
- UIOFUWFRIANQPC-JKIFEVAISA-N Floxacillin Chemical group N([C@@H]1C(N2[C@H](C(C)(C)S[C@@H]21)C(O)=O)=O)C(=O)C1=C(C)ON=C1C1=C(F)C=CC=C1Cl UIOFUWFRIANQPC-JKIFEVAISA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Formate Chemical compound [O-]C=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005526 G1 to G0 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000034826 Genetic Predisposition to Disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 101500028288 Homo sapiens Melanin-concentrating hormone Proteins 0.000 description 1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012359 Methanesulfonyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241001529936 Murinae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 1
- AYCPARAPKDAOEN-LJQANCHMSA-N N-[(1S)-2-(dimethylamino)-1-phenylethyl]-6,6-dimethyl-3-[(2-methyl-4-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidinyl)amino]-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrazole-5-carboxamide Chemical compound C1([C@H](NC(=O)N2C(C=3NN=C(NC=4C=5SC=CC=5N=C(C)N=4)C=3C2)(C)C)CN(C)C)=CC=CC=C1 AYCPARAPKDAOEN-LJQANCHMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007832 Na2SO4 Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000003797 Neuropeptides Human genes 0.000 description 1
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IDRGFNPZDVBSSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N OCCN1CCN(CC1)c1ccc(Nc2ncc3cccc(-c4cccc(NC(=O)C=C)c4)c3n2)c(F)c1F Chemical compound OCCN1CCN(CC1)c1ccc(Nc2ncc3cccc(-c4cccc(NC(=O)C=C)c4)c3n2)c(F)c1F IDRGFNPZDVBSSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 1
- SKZKKFZAGNVIMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Salicilamide Chemical group NC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O SKZKKFZAGNVIMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LUSZGTFNYDARNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sesamol Natural products OC1=CC=C2OCOC2=C1 LUSZGTFNYDARNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bisulfite Chemical compound [Na+].OS([O-])=O DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- OKJPEAGHQZHRQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triiodomethane Natural products IC(I)I OKJPEAGHQZHRQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LXRZVMYMQHNYJB-UNXOBOICSA-N [(1R,2S,4R)-4-[[5-[4-[(1R)-7-chloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-1-yl]-5-methylthiophene-2-carbonyl]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2-hydroxycyclopentyl]methyl sulfamate Chemical compound CC1=C(C=C(S1)C(=O)C1=C(N[C@H]2C[C@H](O)[C@@H](COS(N)(=O)=O)C2)N=CN=C1)[C@@H]1NCCC2=C1C=C(Cl)C=C2 LXRZVMYMQHNYJB-UNXOBOICSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BXEHKCUWIODEDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methanol Chemical group OCC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 BXEHKCUWIODEDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWVAOONFBYYRHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N [4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]methanol Chemical compound OCC1=CC=C(CO)C=C1 BWVAOONFBYYRHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001539 acetonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(=O)C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- QOMNQGZXFYNBNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetyloxymethyl 2-[2-[2-[5-[3-(acetyloxymethoxy)-2,7-difluoro-6-oxoxanthen-9-yl]-2-[bis[2-(acetyloxymethoxy)-2-oxoethyl]amino]phenoxy]ethoxy]-n-[2-(acetyloxymethoxy)-2-oxoethyl]-4-methylanilino]acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OCOC(=O)CN(CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O)C1=CC=C(C)C=C1OCCOC1=CC(C2=C3C=C(F)C(=O)C=C3OC3=CC(OCOC(C)=O)=C(F)C=C32)=CC=C1N(CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O)CC(=O)OCOC(C)=O QOMNQGZXFYNBNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000641 acridinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-L adipate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCCCC([O-])=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 210000001789 adipocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000556 agonist Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001299 aldehydes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940072056 alginate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000001348 alkyl chlorides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- AWUCVROLDVIAJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-glycerophosphate Natural products OCC(O)COP(O)(O)=O AWUCVROLDVIAJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940024606 amino acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000019270 ammonium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000003042 antagnostic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002178 anthracenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000036528 appetite Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019789 appetite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003125 aqueous solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004104 aryloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- YCOXTKKNXUZSKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N as-o-xylenol Natural products CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1C YCOXTKKNXUZSKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940009098 aspartate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- METKIMKYRPQLGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N atenolol Chemical compound CC(C)NCC(O)COC1=CC=C(CC(N)=O)C=C1 METKIMKYRPQLGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003725 azepanyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002393 azetidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004069 aziridinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003828 azulenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- JUHORIMYRDESRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzathine Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1CNCCNCC1=CC=CC=C1 JUHORIMYRDESRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940077388 benzenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000003785 benzimidazolyl group Chemical group N1=C(NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940050390 benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000928 benzodioxinyl group Chemical group O1C(=COC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004619 benzopyranyl group Chemical group O1C(C=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001164 benzothiazolyl group Chemical group S1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004196 benzothienyl group Chemical group S1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004600 benzothiopyranyl group Chemical group S1C(C=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003354 benzotriazolyl group Chemical group N1N=NC2=C1C=CC=C2* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004541 benzoxazolyl group Chemical group O1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003236 benzoyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- PUJDIJCNWFYVJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl carbamate Chemical compound NC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 PUJDIJCNWFYVJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XMIIGOLPHOKFCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-phenylpropanoic acid Natural products OC(=O)CCC1=CC=CC=C1 XMIIGOLPHOKFCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229950011260 betanaphthol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GPRLTFBKWDERLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N bicyclo[2.2.2]octane Chemical group C1CC2CCC1CC2 GPRLTFBKWDERLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SHOMMGQAMRXRRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane Chemical group C1C2CC1CCC2 SHOMMGQAMRXRRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GNTFBMAGLFYMMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N bicyclo[3.2.2]nonane Chemical group C1CC2CCC1CCC2 GNTFBMAGLFYMMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WNTGVOIBBXFMLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane Chemical group C1CCC2CCCC1C2 WNTGVOIBBXFMLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KVLCIHRZDOKRLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N bicyclo[4.2.1]nonane Chemical group C1C2CCC1CCCC2 KVLCIHRZDOKRLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002988 biodegradable polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004621 biodegradable polymer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- SIPUZPBQZHNSDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(2-methylpropyl)aluminum Chemical compound CC(C)C[Al]CC(C)C SIPUZPBQZHNSDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000036772 blood pressure Effects 0.000 description 1
- UWTDFICHZKXYAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N boron;oxolane Chemical compound [B].C1CCOC1 UWTDFICHZKXYAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001649 bromium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000005587 bubbling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006172 buffering agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 230000003185 calcium uptake Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019577 caloric intake Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1CC2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)CC1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003917 carbamoyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 125000000609 carbazolyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004623 carbolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011089 carbon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002057 carboxymethyl group Chemical group [H]OC(=O)C([H])([H])[*] 0.000 description 1
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- DBDXTIAEVFSDNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N chembl2148101 Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=NO1 DBDXTIAEVFSDNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- WBLIXGSTEMXDSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloromethane Chemical compound Cl[CH2] WBLIXGSTEMXDSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004218 chloromethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])(Cl)* 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000259 cinnolinyl group Chemical group N1=NC(=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940001468 citrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000010549 co-Evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- KTHXBEHDVMTNOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclobutanol Chemical group OC1CCC1 KTHXBEHDVMTNOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001995 cyclobutyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- WPOPOPFNZYPKAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclobutylmethanol Chemical group OCC1CCC1 WPOPOPFNZYPKAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QCRFMSUKWRQZEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N cycloheptanol Chemical group OC1CCCCCC1 QCRFMSUKWRQZEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000582 cycloheptyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-PTQBSOBMSA-N cyclohexanol Chemical group O[13CH]1CCCCC1 HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-PTQBSOBMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000113 cyclohexyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- VSSAZBXXNIABDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexylmethanol Chemical group OCC1CCCCC1 VSSAZBXXNIABDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000640 cyclooctyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- SNRCKKQHDUIRIY-UHFFFAOYSA-L cyclopenta-1,4-dien-1-yl(diphenyl)phosphane;dichloromethane;dichloropalladium;iron(2+) Chemical compound [Fe+2].ClCCl.Cl[Pd]Cl.C1=C[CH-]C(P(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1.C1=C[CH-]C(P(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1 SNRCKKQHDUIRIY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- XCIXKGXIYUWCLL-HOSYLAQJSA-N cyclopentanol Chemical group O[13CH]1CCCC1 XCIXKGXIYUWCLL-HOSYLAQJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001511 cyclopentyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- ISQVBYGGNVVVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclopentylmethanol Chemical group OCC1CCCC1 ISQVBYGGNVVVHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001559 cyclopropyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- QWBBPBRQALCEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N di-methylphenol Natural products CC1=CC=CC(O)=C1C QWBBPBRQALCEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002576 diazepinyl group Chemical group N1N=C(C=CC=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- 235000005911 diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000037213 diet Effects 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-BQYQJAHWSA-N diethyl azodicarboxylate Substances CCOC(=O)\N=N\C(=O)OCC FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-BQYQJAHWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylamine Chemical compound CCNCC HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NCBFTYFOPLPRBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethyl azodicarboxylate Substances COC(=O)N=NC(=O)OC NCBFTYFOPLPRBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000003292 diminished effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000000532 dioxanyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000005883 dithianyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003438 dodecyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001804 emulsifying effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037149 energy metabolism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002148 esters Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001301 ethoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003754 ethoxycarbonyl group Chemical group C(=O)(OCC)* 0.000 description 1
- ZGYXABNSOOACGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoate Chemical group CCOC(=O)C1=CC(C)=CC=C1O ZGYXABNSOOACGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IIEWJVIFRVWJOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl cyclohexane Natural products CCC1CCCCC1 IIEWJVIFRVWJOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl n-ethoxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)N=NC(=O)OCC FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940005667 ethyl salicylate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000006125 ethylsulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004705 ethylthio group Chemical group C(C)S* 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003818 flash chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003983 fluorenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001035 gastrointestinal tract Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195712 glutamate Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001963 growth medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001867 guaiacol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005802 health problem Effects 0.000 description 1
- MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-N heptanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(O)=O MNWFXJYAOYHMED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(O)=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003707 hexyloxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- 229940088597 hormone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000005556 hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003840 hydrochlorides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M hydrogensulfate Chemical compound OS([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000000687 hydroquinonyl group Chemical group C1(O)=C(C=C(O)C=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-M hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-] XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 1
- 230000001639 hypophagic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002632 imidazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002636 imidazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 1
- PEHSSTUGJUBZBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N indan-5-ol Chemical group OC1=CC=C2CCCC2=C1 PEHSSTUGJUBZBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003392 indanyl group Chemical group C1(CCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003453 indazolyl group Chemical group N1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003454 indenyl group Chemical group C1(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003406 indolizinyl group Chemical group C=1(C=CN2C=CC=CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001041 indolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000007972 injectable composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004694 iodide salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodomethane Chemical compound IC INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SUMDYPCJJOFFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N isethionic acid Chemical compound OCCS(O)(=O)=O SUMDYPCJJOFFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001977 isobenzofuranyl group Chemical group C=1(OC=C2C=CC=CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005990 isobenzothienyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229940035429 isobutyl alcohol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000904 isoindolyl group Chemical group C=1(NC=C2C=CC=CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001972 isopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- CSNXUYRHPXGSJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoquinolin-5-ol Chemical group N1=CC=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=C1 CSNXUYRHPXGSJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002183 isoquinolinyl group Chemical group C1(=NC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004628 isothiazolidinyl group Chemical group S1N(CCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005969 isothiazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001786 isothiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003965 isoxazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003971 isoxazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000842 isoxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 210000003140 lateral ventricle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 102000005861 leptin receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010019813 leptin receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006194 liquid suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-M lithium bromide Inorganic materials [Li+].[Br-] AMXOYNBUYSYVKV-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- DLEDOFVPSDKWEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N lithium butane Chemical compound [Li+].CCC[CH2-] DLEDOFVPSDKWEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000011068 loading method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108020004999 messenger RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000004060 metabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000037323 metabolic rate Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CS(Cl)(=O)=O QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001160 methoxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC(*)=O 0.000 description 1
- 125000004184 methoxymethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LLGVQUKFXIDBNH-JTQLQIEISA-N methyl (2s)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)propanoate Chemical group COC(=O)[C@@H](NC)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 LLGVQUKFXIDBNH-JTQLQIEISA-N 0.000 description 1
- NCBFTYFOPLPRBX-AATRIKPKSA-N methyl (ne)-n-methoxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound COC(=O)\N=N\C(=O)OC NCBFTYFOPLPRBX-AATRIKPKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XGDZEDRBLVIUMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetate Chemical group COC(=O)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 XGDZEDRBLVIUMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002816 methylsulfanyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S[*] 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003068 molecular probe Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002757 morpholinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001421 myristyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- UQEIFYRRSNJVDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N n,n-dibenzyl-2-phenylethanamine Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1CN(CC=1C=CC=CC=1)CCC1=CC=CC=C1 UQEIFYRRSNJVDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PHWISQNXPLXQRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N n,n-dimethylcarbamothioyl chloride Chemical compound CN(C)C(Cl)=S PHWISQNXPLXQRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LLEOJFPMCGJKOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropanamide Chemical compound C1=C(NC(=O)C(C)(C)C)N=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=C1 LLEOJFPMCGJKOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MNBOFLCSNXJHFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[[5-(2-chlorophenyl)furan-2-yl]methyl]-8-(4,4-dimethylpentan-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine Chemical compound N1=C2C(OC(CC(C)(C)C)C)=CC=CC2=CC=C1NCC(O1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1Cl MNBOFLCSNXJHFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003136 n-heptyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001280 n-hexyl group Chemical group C(CCCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001038 naphthoyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)C(=O)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004593 naphthyridinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CN=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001971 neopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011664 nicotinic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 231100000344 non-irritating Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- UMRZSTCPUPJPOJ-KNVOCYPGSA-N norbornane Chemical group C1C[C@H]2CC[C@@H]1C2 UMRZSTCPUPJPOJ-KNVOCYPGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000013116 obese mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001956 orexigenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002524 organometallic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005963 oxadiazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005882 oxadiazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001715 oxadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000160 oxazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005968 oxazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002971 oxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- PCPUMGYALMOCHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxolan-3-ylmethanol Chemical group OCC1CCOC1 PCPUMGYALMOCHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWMVAQHMFFZQGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N p-Hydroxybenzyl acetone Natural products CC(=O)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 VWMVAQHMFFZQGD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NKTOLZVEWDHZMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N p-cumyl phenol Natural products CC1=CC=C(C)C(O)=C1 NKTOLZVEWDHZMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIBWKRNGBLPSSY-UHFFFAOYSA-L palladium(II) chloride Chemical compound Cl[Pd]Cl PIBWKRNGBLPSSY-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- QNGNSVIICDLXHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N para-ethylbenzaldehyde Natural products CCC1=CC=C(C=O)C=C1 QNGNSVIICDLXHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960005489 paracetamol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000006340 pentafluoro ethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)C(F)(F)* 0.000 description 1
- 239000000813 peptide hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- JRKICGRDRMAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-L peroxydisulfate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=O JRKICGRDRMAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011422 pharmacological therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000001791 phenazinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000001484 phenothiazinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2SC3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001644 phenoxazinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2OC3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004592 phthalazinyl group Chemical group C1(=NN=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940075930 picrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- OXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-M picrate anion Chemical compound [O-]C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O OXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000004193 piperazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003386 piperidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229950010765 pivalate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- IUGYQRQAERSCNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pivalic acid Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C(O)=O IUGYQRQAERSCNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001992 poloxamer 407 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000166 polytrimethylene carbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002953 preparative HPLC Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003138 primary alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- DBABZHXKTCFAPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N probenecid Chemical compound CCCN(CCC)S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1 DBABZHXKTCFAPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003081 probenecid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- MFDFERRIHVXMIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N procaine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1 MFDFERRIHVXMIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004919 procaine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 1
- MTTKOBXFUGIESR-UHFFFAOYSA-N prop-1-ene-1,3-diol Chemical compound OCC=CO MTTKOBXFUGIESR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OCAAZRFBJBEVPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N prop-2-enyl carbamate Chemical compound NC(=O)OCC=C OCAAZRFBJBEVPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-2-yl n-propan-2-yloxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CC(C)OC(=O)N=NC(=O)OC(C)C VVWRJUBEIPHGQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QLNJFJADRCOGBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N propionamide Chemical compound CCC(N)=O QLNJFJADRCOGBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000004309 pyranyl group Chemical group O1C(C=CC=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003373 pyrazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003072 pyrazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002755 pyrazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002098 pyridazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000714 pyrimidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- LHGVFZTZFXWLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrocatechol monomethyl ether Natural products COC1=CC=CC=C1O LHGVFZTZFXWLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000719 pyrrolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001422 pyrrolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000168 pyrrolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002294 quinazolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- XCRPPAPDRUBKRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinolin-7-ol Chemical group C1=CC=NC2=CC(O)=CC=C21 XCRPPAPDRUBKRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AQLYZDRHNHZHIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinoline-2,6-diol Chemical group N1C(=O)C=CC2=CC(O)=CC=C21 AQLYZDRHNHZHIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZXZKYYHTWHJHFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinoline-2,8-diol Chemical group C1=CC(=O)NC2=C1C=CC=C2O ZXZKYYHTWHJHFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002943 quinolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001567 quinoxalinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=NC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- NJGBTKGETPDVIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N raspberry ketone Chemical group CC(=O)CCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 NJGBTKGETPDVIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000664 rectum Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000241 respiratory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003340 retarding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960000581 salicylamide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 150000003335 secondary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000276 sedentary effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- XIIOFHFUYBLOLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N selpercatinib Chemical compound OC(COC=1C=C(C=2N(C=1)N=CC=2C#N)C=1C=NC(=CC=1)N1CC2N(C(C1)C2)CC=1C=NC(=CC=1)OC)(C)C XIIOFHFUYBLOLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N simurosertib Chemical compound N1N=CC(C=2SC=3C(=O)NC(=NC=3C=2)[C@H]2N3CCC(CC3)C2)=C1C XGVXKJKTISMIOW-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWUCVROLDVIAJX-GSVOUGTGSA-N sn-glycerol 3-phosphate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O AWUCVROLDVIAJX-GSVOUGTGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WBHQBSYUUJJSRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium bisulfate Chemical compound [Na+].OS([O-])(=O)=O WBHQBSYUUJJSRZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229910000342 sodium bisulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012279 sodium borohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000033 sodium borohydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012321 sodium triacetoxyborohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 230000003381 solubilizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000000891 standard diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000004079 stearyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000003206 sterilizing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000638 stimulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PXQLVRUNWNTZOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfanyl Chemical compound [SH] PXQLVRUNWNTZOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003457 sulfones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000472 sulfonyl group Chemical group *S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 150000003462 sulfoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000829 suppository Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000375 suspending agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010189 synthetic method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006188 syrup Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000020357 syrup Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000003718 tetrahydrofuranyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003039 tetrahydroisoquinolinyl group Chemical group C1(NCCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001712 tetrahydronaphthyl group Chemical group C1(CCCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000147 tetrahydroquinolinyl group Chemical group N1(CCCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005958 tetrahydrothienyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005247 tetrazinyl group Chemical group N1=NN=NC(=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003831 tetrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005304 thiadiazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005305 thiadiazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001113 thiadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004627 thianthrenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2SC3=CC=CC=C3SC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001984 thiazolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002769 thiazolinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000335 thiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004568 thiomorpholinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- SLYPOVJCSQHITR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tioxolone Chemical group OC1=CC=C2SC(=O)OC2=C1 SLYPOVJCSQHITR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-M toluene-4-sulfonate Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000011269 treatment regimen Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004306 triazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001425 triazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ITMCEJHCFYSIIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N triflic acid Chemical group OS(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F ITMCEJHCFYSIIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000005455 trithianyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 208000001072 type 2 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- ZDPHROOEEOARMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N undecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZDPHROOEEOARMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000001834 xanthenyl group Chemical group C1=CC=CC=2OC3=CC=CC=C3C(C12)* 0.000 description 1
- PVURAUIMVICLOH-UHFFFAOYSA-M zinc;cyclohexane;bromide Chemical group Br[Zn+].C1CC[CH-]CC1 PVURAUIMVICLOH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- QZPAOOQIWZQBDH-UHFFFAOYSA-M zinc;heptane;bromide Chemical group Br[Zn+].CCCC[CH-]CC QZPAOOQIWZQBDH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- OQVKRKNQBLNDDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M zinc;hexane;bromide Chemical group Br[Zn+].CCCC[CH-]C OQVKRKNQBLNDDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D215/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems
- C07D215/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D215/16—Heterocyclic compounds containing quinoline or hydrogenated quinoline ring systems having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D215/38—Nitrogen atoms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D405/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D411/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having oxygen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D411/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having oxygen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D411/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having oxygen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D413/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the antagonism of the effects of melanin- concentrating hormone (MCH) through the melanin concentrating hormone receptor which is useful for the prevention or treatment of eating disorders, weight gain, obesity, abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders.
- MCH melanin- concentrating hormone
- Obesity is a major cause and contributor to health problems such as type II diabetes, coronary heart disease, increased incidence of certain forms of cancer, and respiratory complications. It is a disease that is increasing at an alarming rate due to increased availability of high-fat diets, genetic susceptibility, and a more sedentary way of life in modern society. Obesity can be defined as weight gain resulting from a mismatch of energy intake and energy expenditure. Food intake and energy metabolism are regulated, in part, by the interaction of neuropeptides and their receptors. Recently, the role that the hormone leptin plays in controlling appetite has been elucidated. Leptin is a peptide hormone produced by fat cells, regulating both food intake and and metabolism by acting on leptin receptors in the hypothalamus.
- MCH Melanin-concentrating hormone
- MCH is a cyclic 19 amino acid neuropeptide expressed in the zona incerta and lateral hypothalamus in response to both energy restriction and leptin deficiency.
- MCH is known to stimulate feeding when injected into the lateral ventricle of rats and the mRNA for MCH is upregulated in the hypothalamus of genetically obese mice (ob/ob) and in fasted control and ob/ob animals.
- Mice lacking MCH are hypophagic and lean with increased metabolic rate, whereas animals over-expressing MCH gain excess weight on both standard and high fat diets.
- GPCR G-protein coupled receptor
- Li is a bond or is a member selected from the group consisting of-C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, and -S(O) 2 -;
- Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B -, and R R ⁇ Ncarbonyl;
- R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R 7 L 2 R 6 -, RAS
- a method of treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- a method for treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- a method for treating treating abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- the present invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) in combination with a pharmaceutically suitable carrier.
- alkenyl refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon containing from 2 to 10 carbons and containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond formed by the removal of two hydrogens.
- Representative examples of alkenyl include, but are not limited to, ethenyl, 2-propenyl, 2-methyl-2 -propenyl, 3-butenyl, 4-pentenyl, 5- hexenyl, 2-heptenyl, 2-methyl-l-heptenyl, and 3-decenyl.
- alkoxy refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an oxygen atom.
- Representative examples of alkoxy include, but are not limited to, methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, 2- ⁇ ropoxy, butoxy, tert- butoxy, pentyloxy, and hexyloxy.
- alkoxyalkyl refers to an alkoxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of alkoxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, tert-butoxymethyl, 2- ethoxy ethyl, 2-methoxy ethyl, and methoxymethyl.
- alkoxycarbonyl refers to an alkoxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of alkoxycarbonyl include, but are not limited to, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, and tert-butoxycarbonyl.
- alkoxycarbonylalkyl refers to an alkoxycarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of alkoxycarbonylalkyl include, but are not limited to, 3 -methoxy carbonylpropyl, 4-ethoxycarbonylbutyl, and 2-tert-butoxycarbonylethyl.
- alkyl refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon containing from 1 to 10 carbon atoms.
- alkyl include, but are not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, iso-butyl, tert-butyl, n- pentyl, isopentyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl, 3-methylhexyl, 2,2-dimethylpentyl, 2,3- dimethylpentyl, n-heptyl, n-octyl, n-nonyl, and n-decyl.
- alkylcarbonyl refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of alkylcarbonyl include, but are not limited to, acetyl, 1- oxopropyl, 2,2-dimethyl-l-oxopropyl, 1-oxobutyl, and 1-oxopentyl.
- alkylcarbonylalkyl refers to an alkylcarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- alkylcarbonylalkyl include, but are not limited to, 2- oxopropyl, 3,3 ⁇ dimethyl-2-oxopropyl, 3-oxobutyl, and 3-oxopentyl.
- alkylcarbonyloxy refers to an alkylcarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an oxygen atom.
- alkylcarbonyloxy include, but are not limited to, acetyloxy, ethylcarbonyloxy, and tert-butylcarbonyloxy.
- alkylsulfonyl refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a sulfonyl group, as defined herein.
- alkylsulfonyl include, but are not limited to, methylsulfonyl and ethylsulfonyl.
- alkylthio refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a sulfur atom.
- Representative examples of alkylthio include, but are not limited, methylsulfanyl, ethylsulfanyl, tert-butylsulfanyl, and hexylsulfanyl.
- alkynyl refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon group containing from 2 to 10 carbon atoms and containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
- Representative examples of alkynyl include, but are not limited, to acetylenyl, 1- propynyl, 2-propynyl, 3-butynyl, 2-pentynyl, and 1-butynyl.
- aryl refers to a monocyclic-ring system, or a bicyclic- or a tricyclic- fused ring system wherein one or more of the fused rings are aromatic.
- Representative examples of aryl include, but are not limited to, anthracenyl, azulenyl, fluorenyl, indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, phenyl, and tetrahydronaphthyl.
- aryl groups of this invention can be substituted with 1, 2, or 3 substituents independently selected from alkenyl, alkoxy, alkoxyalkyl, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonylalkyl, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl, alkylcarbonylalkyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylsulfonyl, alkylthio, alkynyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, cyano, cyanoalkyl.
- Re and R D are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl.
- arylalkoxy refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkoxy group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of arylalkoxy include, but are not limited to, 2-phenylethoxy, 3- naphth-2-ylpropoxy, and 5-phenylpentyloxy.
- arylalkyl refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of arylalkyl include, but are not limited to, benzyl, 2-phenylethyl, 3-phenylpropyl, and 2-naphth-2-ylethyl.
- arylcarbonyl refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of arylcarbonyl include, but are not limited to, benzoyl and naphthoyl.
- carbonyl refers to a -C(O)- group.
- carboxyalkyl refers to a carboxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of carboxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, carboxymethyl, 2- carboxy ethyl, and 3-carboxypropyl.
- cyano refers to a -CN group.
- cyanoalkyl refers to a cyano group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of cyanoalkyl include, but are not limited to, cyanomethyl, 2- cyanoethyl, and 3-cyanopropyl.
- cycloalkyl refers to a monocyclic, bicyclic, or tricyclic ring system.
- Monocyclic ring systems are exemplified by a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon group containing from 3 to 8 carbon atoms. Examples of monocyclic ring systems include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, and cyclooctyl.
- Bicyclic ring systems are exemplified by a bridged monocyclic ring system in which two non-adjacent carbon atoms of the monocyclic ring are linked by an alkylene bridge of between one and three additional carbon atoms.
- bicyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane, bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, bicyclo[3.2.2]nonane, bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, and bicyclo[4.2.1]nonane.
- Tricyclic ring systems are exemplified by a bicyclic ring system in which two non-adjacent carbon atoms of the bicyclic ring are linked by a bond or an alkylene bridge of between one and three carbon atoms.
- tricyclic-ring systems include, but are not limited to, tricyclo[3.3.1.0 3 ' 7 ]nonane and tricyclo[3.3.1.1 3,7 ]decane (adamantane).
- haloalkyl refers to at least one halogen, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of haloalkyl include, but are not limited to, chloromethyl, 2- fluoroethyl, trifluoromethyl, pentafluoroethyl, and 2-chloro-3-fluoropentyl.
- heterocycle or “heterocyclic,” as used herein, refers to a monocyclic, bicyclic, or tricyclic ring system.
- Monocyclic ring systems are exemplified by any 3- or 4- membered ring containing a heteroatom independently selected from oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur; or a 5-, 6- or 7-membered ring containing one, two or three heteroatoms wherein the heteroatoms are independently selected from nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur.
- the 5-membered ring has from 0-2 double bonds and the 6- and 7-membered ring have from 0-3 double bonds.
- monocyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, azetidinyl, azepanyl, aziridinyl, diazepinyl, 1,3-dioxolanyl, dioxanyl, dithianyl, furyl, imidazolyl, imidazolinyl, imidazolidinyl, isothiazolyl, isothiazolinyl, isothiazolidinyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, isoxazolidinyl, morpholinyl, oxadiazolyl, oxadiazolinyl, oxadiazolidinyl, oxazolyl, oxazolinyl, oxazolidinyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, pyranyl, pyrazinyl, pyrazolyl, pyrazolinyl, pyrazolidinyl, pyridinyl,
- Bicyclic ring systems are exemplified by any of the above monocyclic ring systems fused to an aryl group as defined herein, a cycloalkyl group as defined herein, or another monocyclic ring system.
- Representative examples of bicyclic ring systems include but are not limited to, for example, benzimidazolyl, benzodioxinyl, benzothiazolyl, benzothienyl, benzotriazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzofiiranyl, benzopyranyl, benzothiopyranyl, cinnolinyl, indazolyl, indolyl, 2,3-dihydroindolyl, indolizinyl, naphthyridinyl, isobenzofuranyl, isobenzothienyl, isoindolyl, isoquinolinyl, phthalazinyl, 4H-pyrido[l,2- ⁇ ]pyrimidin-4
- Tricyclic rings systems are exemplified by any of the above bicyclic ring systems fused to an aryl group as defined herein, a cycloalkyl group as defined herein, or a monocyclic ring system.
- Representative examples of tricyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, acridinyl, carbazolyl, carbolinyl, dibenzo[b,d]furanyl, dibenzo[b,d]thienyl, naphtho[2,3- bjfuran, naphtho[2,3-b]thienyl, phenazinyl, phenothiazinyl, phenoxazinyl, thianthrenyl, thioxanthenyl and xanthenyl.
- heterocycles of this invention can be substituted with 1, 2,or 3 substituents independently selected from alkenyl, alkoxy, alkoxyalkyl, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonylalkyl, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl, alkylcarbonylalkyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylsulfonyl, alkylthio, alkynyl, aryl, arylalkoxy, arylalkyl, arylcarbonyl, aryloxy, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, cyano, cyanoalkyl, formyl, halogen, haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, mercapto, nitro, phenyl, and RcR ⁇ N-, RcR ⁇ Ncarbonyl, RcR ⁇ Nalkyl, wherein Re and R ⁇ are defined herein.
- heterocyclealkyl refers to a heterocycle, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- Representative examples of heterocyclealkyl include, but are not limited to, pyridin-3- ylmethyl and 2-pyrimidin-2-ylpropyl and the like.
- hydroxy refers to an -O ⁇ group.
- hydroxyalkyl refers to a hydroxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of hydroxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, 2-hydroxyethyl, 2- hydroxypropyl, 3-hydroxybutyl and the like.
- mercapto refers to a -SH group.
- RAR B N- refers to both R A and R B appended to the parent molecular moiety through a -N- group.
- nitro refers to a -NO 2 group.
- RAR B Nalkyl refers to a R A R B N group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular ' moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- R A R- B Ncarbonyl refers to a A R B N group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein.
- R A S refers to a A group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a -S- group, as defined herein.
- R A Salkyl refers to a R A S group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
- the present invention is directed to compounds of formula (I), wherein Rj, R , R 3 ,
- R4, R 5 , R , R B , and L are defined herein.
- the compounds of thepresent invention are useful for treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor.
- a method of treating or preventing disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administrering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- Li is a bond or is a member selected from the group consisting of -C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, and -S(0) -;
- R ⁇ is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R R B N-, and R RsNcarbonyl;
- R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R 7 L 2 R 6 - whom R A Salkyl
- R is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B N-, and RAR B Ncarbonyl;
- R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl;
- R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
- R ⁇ and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R ⁇ N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
- R A and R B are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen,
- a compound according to formula (la), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof wherein Li is-O-; Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B N- and R R B carbonyl; R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl; R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R4, and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R A and R B are each
- Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B N-, and R A R B Ncarbonyl
- R 2 is alkyl, wherein alkyl is C 6 or larger
- R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- R ⁇ and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B -, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- RA and R B are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen
- Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R R B N-, and R A R B Ncarbonyl
- R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkoxyalkyl, haloalkyl, R Salkyl, and R A R ⁇ Nalkyl
- R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- R t , and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- R t , and R 5 are each independently a member selected
- Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B N-, and R A R ⁇ Ncarbonyl
- R 2 is a member selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl and heterocycle
- R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RAR B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- R_ t , and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B N-, and alkylcarbonylNH-
- R A and R B are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy
- R t is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R B N-, and R A B Ncarbonyl;
- R is a member selected from the group consisting of arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R 7 L 2 R 6 -;
- R 3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy,
- R 4 , and R 5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, R A R B -, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
- R A and B are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
- a method for treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- a method for treating abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) in combination with a pharmaceutically suitable carrier.
- Specific compounds of formula (I) include, but are not limited to:
- the present compounds can exist as therapeutically suitable salts.
- therapeutically suitable salt refers to salts or zwitterions of the compounds which are water or oil-soluble or dispersible, suitable for treatment of disorders without undue toxicity, irritation, and allergic response, commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio, and effective for their intended use.
- the salts can be prepared during the final isolation and purification of the compounds or separately by reacting an amino group of the compounds with a suitable acid.
- Representative salts include acetate, adipate, alginate, citrate, aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulfate, butyrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, digluconate, glycerophosphate, hemisulfate, heptanoate, hexanoate, formate, isethionate, fumarate, lactate, maleate, methanesulfonate, naphthylenesulfonate, nicotinate, oxalate, pamoate, pectinate, persulfate, 3-phenylpropionate, picrate, oxalate, maleate, pivalate, propionate, succinate, tartrate, trichloroacetic, trifluoroacetic, glutamate, para-toluenesulfonate, undecanoate, hydrochloric, hydrobromic, sulfuric, phosphoric, and the like.
- the amino groups of the compounds can also be quaternized with alkyl chlorides, bromides, and iodides such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, lauryl, myristyl, stearyl, and the like.
- the present invention contemplates pharmaceutically suitable salts formed at the nitrogen attached to 2-amino group of formula (I), when R t is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R A R ⁇ N.
- Basic addition salts can be prepared during the final isolation and purification of the present compounds by reaction of a carboxyl group with a suitable base such as the hydroxide, carbonate, or bicarbonate of a metal cation such as lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, or aluminum, or an organic primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
- a suitable base such as the hydroxide, carbonate, or bicarbonate of a metal cation such as lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, or aluminum, or an organic primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
- the present compounds can also exist as therapeutically suitable prodrugs.
- therapeutically suitable prodrug refers to those prodrugs or zwitterions which are suitable for use in contact with the tissues of patients without undue toxicity, irritation, and allergic response, are commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio, and are effective for their intended use.
- prodrug refers to compounds which are rapidly transformed in vivo to the parent compounds of formula (I) for example, by hydrolysis in blood.
- Asymmetric centers can exist in the present compounds. Individual stereoisomers of the compounds are prepared by synthesis from chiral starting materials or by preparation of racemic mixtures and separation by conversion to a mixture of diastereomers followed by separation or recrystallization, chromatographic techniques, or direct separation of the enantiomers on chiral chromatographic columns. Starting materials of particular stereochemistry are either commercially available or are made by the methods described hereinbelow and resolved by techniques well-known in the art. Geometric isomers can exist in the present compounds The invention contemplates the various geometric isomers and mixtures thereof resulting from the disposal of substituents around a carbon-carbon double bond, a cycloalkyl group, or a heterocycloalkyl group. Substituents around a carbon-carbon double bond are designated as being of Z or E configuration and substituents around a cycloalkyl or heterocycloalkyl are designated as being of cis or trans configuration.
- compositions of the present compounds comprise an effective amount of the same formulated with one or more therapeutically suitable excipients.
- therapeutically suitable excipient represents a non-toxic, solid, semi-solid or liquid filler, diluent, encapsulating material, or formulation auxiliary of any type.
- therapeutically suitable excipients include sugars; cellulose and derivatives thereof; oils; glycols; solutions; buffering, coloring, releasing, coating, sweetening, flavoring, and perfuming agents; and the like.
- These therapeutic compositions can be administered parenterally, intracisternally, orally, rectally, or intraperitoneally.
- Liquid dosage forms for oral administration of the present compounds comprise formulations of the same as emulsions, microemulsions, solutions, suspensions, syrups, and elixirs.
- the liquid dosage forms can contain diluents and/or solubilizing or emulsifying agents.
- the oral compositions can include wetting, emulsifying, sweetening, flavoring, and perfuming agents.
- injectable preparations of the present compounds comprise sterile, injectable, aqueous and oleaginous solutions, suspensions or emulsions, any of which can be optionally formulated with parenterally suitable diluents, dispersing, wetting, or suspending agents.
- injectable preparations can be sterilized by filtration through a bacterial-retaining filter or formulated with sterilizing agents which dissolve or disperse in the injectable media.
- Antagonism of the effects of MCH through the MCH receptor by the compounds of the present invention can be delayed by using a liquid suspension of crystalline or amorphous material with poor water solubility.
- the rate of absorption of the compounds depends upon their rate of dissolution which, in turn, depends on their crystallinity. Delayed absorption of a parenterally administered compound can be accomplished by dissolving or suspending the compound in oil.
- injectable depot forms of the compounds can also be prepared by microencapsulating the same in biodegradable polymers.
- Solid dosage forms for oral administration of the present compounds include capsules, tablets, pills, powders, and granules.
- the compound is mixed with at least one inert, therapeutically suitable excipient such as a carrier, filler, extender, disintegrating agent, solution retarding agent, wetting agent, absorbent, or lubricant.
- the excipient can also contain buffering agents.
- Suppositories for rectal administration can be prepared by mixing the compounds with a suitable non-irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperature but fluid in the rectum.
- the present compounds can be micro-encapsulated with one or more of the excipients discussed previously.
- the solid dosage forms of tablets, dragees, capsules, pills, and granules can be prepared with coatings and shells such as enteric and release-controlling.
- the compounds can be mixed with at least one inert diluent and can optionally comprise tableting lubricants and aids.
- Capsules can also optionally contain opacifying agents which delay release of the compounds in a desired part of the intestinal tract.
- Transdermal patches have the added advantage of providing controlled delivery of the present compounds to the body.
- dosage forms are prepared by dissolving or dispensing the compounds in the proper medium.
- Absorption enhancers can also be used to increase the flux of the compounds across the skin, and the rate of absorption can be controlled by providing a rate controlling membrane or by dispersing the compounds in a polymer matrix or gel.
- Disorders caused or exacerbated by MCH are treated or prevented in a patient by administering to the patient, a therapeutically effective amount of compound of the present invention in such an amount and for such time as is necessary to achieve the desired result.
- terapéuticaally effective amount refers to a sufficient amount of a compound to effectively emeliorate disorders mediated by MCH, by antagonizing the effect of MCH through the MCH receptor at a reasonable benefit/risk ratio applicable to any medical treatment.
- the specific therapeutically effective dose level for any particular patient will depend upon a variety of factors including the disorder being treated and the severity of the disorder; the activity of the compound employed; the specific composition employed; the age, body weight, general health, sex, and diet of the patient; the time of administration, route of administration, rate of excretion; the duration of the treatment; and drugs used in combination or coincidental therapy.
- the total daily dose of the present compounds in single or divided doses can be in amounts, for example, from 0.01 to 50 mg/kg body weight or more usually from 0.1 to 25 mg/kg body weight.
- treatment regimens comprise administration to a patient in need of such treatment from about 10 mg to about 1000 mg of the compounds per day in single or multiple doses.
- MCHR melanin concentrating hormone receptor
- the assays are performed as follows. HEK293 cells expressing the murine MCHR are plated overnight at 50,000 cells/well in 96-well plates. The following day, culture medium is removed and replaced with 100 ⁇ l/well of D-PBS (+glucose and sodium pyruvate) containing 2.5 ⁇ M Fluo-4AM (Molecular Probes), 0.01% Pluronic F-127 and 2.5 mM probenecid. Cells are loaded with the Fluo-4 dye for at least one hour at room temp. After loading, the cells are washed gently to remove extracellular dye and 100 ⁇ l of D-PBS (+glucose and sodium pyruvate) is added to each well. Test compounds are prepared at 40 ⁇ M in 4% DMSO.
- the cell plate is placed in the FLIPRTM and 50 ⁇ l/well of test compound is delivered.
- the calcium signal is followed for 3 minutes to assay for potential agonist activity by the test compounds.
- 50 ⁇ l/well of 12 nM human MCH in D-PBS containing 0.1% BSA
- the ligand-induced calcium signal is followed for an additional 3 minutes.
- fTC MCH-induced fluorescence in the presence of test compound
- fMCH MCH-induced fluorescence in the absence of test compound
- fB Baseline fluorescence.
- the compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence at a dose of 10 ⁇ M.
- compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence in a range of about 75 to about 100% inhibition of MCH at a dose of 10 ⁇ M. More preferably compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence in a range of about 90 to about 100% inhibition of MCH at a dose of 10 ⁇ M.
- the compounds of the present invention are useful in treating disorders that are mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor, such as obesity.
- m-CPBA meta-chloroperoxy-benzoic acid
- DMF for N,N- dimethylformamide
- DMSO for dimethylsulfoxide
- ED AC for l-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)- 3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
- HOBT for 1 -hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate
- NMP for N- methylpyrrolidinone
- THF for tetrahydrofuran
- TFA trifluoroacetic acid
- Pd(dppf)Cl 2 for (diphenylphospino)ferrocenyl palladium chloride.
- compounds of formula 1 can be reacted with m-CPBA followed by a reaction with phosphorous oxychloride to provide compounds of formula 2.
- the reaction of compound of formula 1 with m-CPBA are generally carried out in solvents such as but not limited to chloroform, dichloromethane, benzene and the like and are generally done at 25 °C for 20 minutes.
- the further reaction with phosphorous oxychloride are generally carried out in solvents such as but not limited to chloroform, dichloromethane, benzene and the like and are generally done at 100 °C for 15 minutes.
- Compounds of formula 2 can then be reacted with amines of formula 3 in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 4.
- Typical bases used in the reaction include but are not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and typical solvents include but not limited to tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and the like.
- bases such as sodium hydride in solvents such as but not limited to DMF may be utilized in the transformation.
- compounds of general formula 5 can be reacted with aldehydes of general formula 6 in the presence of a reducing agent such as but not limited to sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride and sodium triacetoxyborohydride in solvents such as but not limited to THF and the like to provide compounds of formula 4.
- a reducing agent such as but not limited to sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride and sodium triacetoxyborohydride in solvents such as but not limited to THF and the like to provide compounds of formula 4.
- Reactions are performed at temperatures ranging from 25 to 80 °C and are generally complete between 5 and 96 hours.
- compounds of general formula 5 can be reacted with compounds of formula 7 (wherein X is halogen) in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 4.
- the reactions are typically carried out at 60 °C in solvents including but not limited to acetonitrile, DMF, THF and the like, and reactions are generally complete within 6-18 hours.
- compounds of formula 5 wherein L is selected from the group consisting of-O-, -S-, or a covalent bond
- compounds of formula 8 wherein Ri is alkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, heterocycle and heterocyclealkyl in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 9.
- Typical bases include but are not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like. Reactions are typically carried out at 25 °C for 1-10 hours.
- Compounds of formula 9 can be reacted with an excess of butyl lithium at -78 °C for 4 hours in solvents including but not limited to THF followed by the reaction with compounds of formula K), wherein R 3 is alkyl, to provide compounds of formula 11.
- Compounds of formula 11 can be reacted with reagents commonly known to those skilled in the art which are useful for the hydrolysis of amides to provide compounds of formula 12.
- Such reagents and conditions useful for the hydrolysis of amides include but are not limited to sodium or potassium hydroxide in aqueous solvent mixtures such as but not limited to aqueous isopropanol and aqueous tetrahydrofuran and the like. Reactions may or may not need to be heated to 50-70 °C for 1-10 hours.
- compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of formula 14 in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like to provide compounds of formula L5.
- a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like.
- Typical reaction conditions may involve heating to 50 °C in such solvents that include but are not limited to acetonitrile, THF and DMF.
- sodium hydride in DMF may be utilized for this transformation.
- compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of formula 8 in the presence of triphenylphosphine and a dialkyl azodicarboxylate such as but not limited to dimethyl azodicarboxylate, diethyl azodicarboxylate, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate and dicyclohexyl azodicarboxylate at 0 °C in solvents such as but not limited to THF, diethyl ether and the like to provide compounds of formula 20.
- triphenylphosphine and a dialkyl azodicarboxylate such as but not limited to dimethyl azodicarboxylate, diethyl azodicarboxylate, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate and dicyclohexyl azodicarboxylate at 0 °C in solvents such as but not limited to THF, diethyl ether and the like to provide compounds of formula 20.
- compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride and a base to provide compounds of formula 24.
- Typical reactions utilize bases such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like and are carried out in solvents including but not limited to THF and dichloromethane and are generally done at 0 °C.
- organozinc reagents represented by the formula R 2 ZnX (wherein R 2 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, and X represents a halogen) in the presence of Pd(dppf)Cl 2 to provide compounds of formula 25.
- organozinc reagents represented by the formula R 2 ZnX (wherein R 2 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocycleoxyalkyl, and X represents a halogen) in the presence of Pd(dppf)Cl 2 to provide compounds of formula 25.
- compounds of formula 24 can be reacted with carbon dioxide in the presence of Pd(dppf)Cl 2 and a base in methanol to provide compounds of formula 26.
- Compounds of formula 26 can be reacted with compounds of formula R'M (wherein R' is alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, cycloalkyl; and M is lithium or magnesium bromide) to provide compounds of formula 27.
- Compounds of formula 27 can be reacted with compounds of formula R 2 X, (wherein R 2 is previously described in formula (I), but is not hydrogen; and X is halogen) and a base to provide compounds of formula 28.
- Typical bases utilized in the transformation of compounds of formula 27 to compounds of formula 28 include but are not limited to sodium hydride in DMF and potassium hydroxide in dimethyl sulfoxide.
- compounds of formula 30 can be reacted with methanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, N-methylmorpholine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to dichloromethane and THF to provide compounds of general formula 30 A.
- a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, N-methylmorpholine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to dichloromethane and THF
- compounds of general formula 30 A can be reacted with alcohols of formula 18 in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to THF, acetonitrile and the like to provide compounds of general formula 3L
- compounds of formula 26 can also be converted to compounds of formula 32 through hydrolysis of the ester functionality to provide the carboxylic acid which can be converted to the amide 32 through methods commonly known to those skilled in the art.
- the conversion of the amide 32 to compounds of formula 33 by the addition of organometallic reagents wherein R 2 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, and M is magnesium bromide is well known to those skilled in the art.
- compounds of formula 1 _ can be reacted with sodium hydride in solvents such as but not limited to THF and DMF followed be a reaction with dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride to provide compounds of formula 34.
- Compounds of formula 32 can then be heated to provide compounds of formula 35.
- Compounds of formula 35 can be reacted with potassium hydroxide to hydrolyze the carbamoyl functionality followed by a reaction with R 2 X with a base to provide compounds of formula 36.
- Compounds of formula 36 can be reacted with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid to provide either the compounds of formula 37, wherein n is either 1 or 2.
- the product of the oxidation with m-CPBA to provide sulfone or the sulfoxide has been established in the literature and is known to those skilled in the art.
- compounds of general formula 13 can be reacted with heterocycles of general formula 38 using the same conditions described in Scheme 7 to provide compounds of general formula 39, wherein P is a nitrogen protecting group such as but not limited to acetyl, benzyl, tert-butoxycarbamate, benzylcarbamate and allylcarbamate.
- P is a nitrogen protecting group such as but not limited to acetyl, benzyl, tert-butoxycarbamate, benzylcarbamate and allylcarbamate.
- Compounds of general formula 39 can be reacted under conditions known to those skilled in the art to remove nitrogen protecting groups to provide compounds of general formula 40.
- the nitrogen protecting groups used in the compounds described within are specific to the protecting group used for each example and can be found in the description in Greenes "Protecting groups in Organic Chemistry" 3 rd ed. 1999, Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- a typical protecting group used in these examples described within is tert-butoxycarbonyl which can be removed by the reaction with either 4N HCl in dioxane or trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane.
- Compounds of general formula 40 can be reacted with compounds of general formula 41, wherein R 7 , L 2 are defined in formula (I), r is 1, 2, or 3 and X is halogen with a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to THF, acetonitrile and the like to provide compounds of general formula 42.
- compounds of general formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of general formula 43 wherein LG is a leaving group such as but not limited to mesyl, triflic, or halogen, in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like under heating conditions to provide compounds of general formula 39.
- Typical conditions for this reaction include heating the reaction mixture to 65 °C in solvents such as but not limited to THF or acetonitrile for 12 to 24 hours.
- Compounds of general formula 39 can then be reacted under conditions described in Scheme 15 to provide compounds of general formula 42.
- Example 1 8-isopropox ⁇ quinolin-2-amine
- a reaction vessel of the PE Biosystems Solaris 530TM Organic Synthesizer was charged with PS-PPh resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 176 mg, 4.2 equiv for reactions involving a secondary alcohol; 88 mg, 2.1 equiv for reactions involving a primary alcohol), and purged by passing a stream of N 2 for 45 seconds.
- THF was added to the vessel and the resultant suspension was shaken for 15 min. Then, a solution of DBAD (0.50 mL; 46 mg/mL; 1.6 equiv) in anhydr.
- Example 2 8-(cyclobutyloxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclobutanol for isopropylalcohol.
- J H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.94 (d, IH), 7.27 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, IH), 4.82 (m, IH), 2.48 (m, 4H), 1.95 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 215 [M+H] + .
- Example 4 8-(cyclopentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclopentanol for isopropylalcohol.
- X H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, IH), 7.04 (d, IH), 4.94 (m, IH), 2.13 (m, 2H), 1.97 (m, 4H), 1.64 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 229 [M+H] + .
- Example 7 8-( 1 -ethy lpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-pentanol for isopropylalcohol. ! H NMR (500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.34 (m, IH), 1.93 (m, 2H), 1.79 (m, 2H), 0.99 (t, 6H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 231 [M+H] + .
- Example 8 8-(2-methoxy-l-methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting l-methoxy-2-propanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.76 (m, IH), 3.93 (dd, IH), 3.60 (dd, IH), 3.41 (s, 3H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 233 [M+H] + .
- Example 10 8-((3-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methylcyclopentanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.05 (m, 2H), 4.97 (m, 0.6H), 4.90 (m, 0.4H), 2.40 (m, IH), 2.26 (m, 1.6H), 1.93-2.16 (m, 1.8H), 1.81 (m, 0.4H), 1.70 (m, 0.4H), 1.57 (m, 0.4H), 1.46 (m, 0.8H), 1.17 (m, 0.6H), 1.10 (d, 1.2H), 1.03 (d, 1.8H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 243 [M+H] + .
- Example 12 8-(2-ethoxy- 1 -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting l-ethoxy-2-propanol for isopropylalcohol.
- Example 13 8-((3-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methylcyclohexanol for isopropylalcohol. Mixture of isomers.
- Example 16 8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.19 (d, IH), 7.15 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 2.30 (dd, IH), 1.49 (dd, IH), 1.39 (d, 3H), 0.96 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 259 [M+H] + .
- Example 17 8-(2-ethyl- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-ethyl-2-pentanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.61 (m, IH), 1.82 (m, IH), 1.66 (m, IH), 1.54 (m, 2H), 1.39 (d, 3H), 1.32 (m, IH), 0.94 (t, 3H), 0.89 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 259 [M+H] + .
- Example 19 8-propo ⁇ yquinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-propanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDCI3 ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.13 (t, 2H), 2.01 (m, 2H), 1.09 (t, 3H); MS (DCI ⁇ NH3) m z 203 [M+H] + .
- Example 20 8-butoxyquinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-butanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.17 (t, 2H), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.53 (m, 2H), 0.99 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H] + .
- Example 22 8-(cyclobutylmethoxy)quinolin-2 -amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclobutylmethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.07 (m, 2H), 4.16 (d, 2H), 3.05 (m, IH), 2.25 (m, 2H), 1.78-2.07 (m, 4H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 229 [M+H] + .
- Example 24 8-(pentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-pentanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.16 (t, 2H), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.43 (m, 4H), 0.93 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 231 [M+H] + .
- Example 25 8-(2-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-methyl-l-butanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.91 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 1.61 (m, IH), 1.34 (m, IH), 1.09 (d, 3H), 0.97 (t, 3H); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m/z 231 [M+H] + .
- Example 27 8-(2-(methylthio)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-(methylthio)ethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.34 (t, 2H), 3.13 (t, 2H), 2.22 (s, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 235 [M+H] + .
- Example 28 8-(cyclopentylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclopentylmethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 2 H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.20 (d, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.04 (d, 2H), 2.65 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.64 (m, 4H), 1.30 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m/z 243 [M+H] + .
- Example 29 8-(tetrahydrofuran-3-ylmethoxy)qu ⁇ nolm-2-amme
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting tetrahydro-3-furanmethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.99 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.25 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.09 (m, 2H), 3.96 (m, 2H), 3.78 (m, 2H), 3.11 (m, IH), 2.28 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 245
- Example 31 8-(3,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3,3-dimethylbutanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.23 (t, 2H), 1.99 (t, 2H), 1.01 (s, 9H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 245 [M+H] + .
- Example 33 8-(cyclohexylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclohexylmethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- Example 34 8-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methoxy-3-methyl-l-butanol for isopropylalcohol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.28 (t, 2H), 3.23 (s, 3H), 2.30 (t, 2H), 1.27 (s, 6H); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m z 261 [M+H] + .
- Example 35 8-(2-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-cyclohexylethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDCI 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.20 (d, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.21 (t, 2H), 1.94 (m, 2H), 1.78 (m, 2H), 1.71 (m, 2H), 1.65 (m, IH), 1.51 (m, IH), 1.12-1.34 (m, 3H), 1.02 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 271 [M+H] + .
- Example 36 8-((lS,4R)-bicyclo[2.2.11hept-2-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-norbornanemethanol for isopropylalcohol.
- Example 37 8-((l-ethylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- a reaction vessel of the PE Biosystems Solaris 530TM Organic Synthesizer was charged with 230 mg PS-PPh 3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 5.50 equiv), and purged by passing a stream of N 2 for 45 seconds.
- THF was added to the vessel and the resultant suspension was shaken for 15 min.
- a solution of DBAD (0.50 mL; 46 mg/mL; 1.6 equiv) in anhydr.
- Example 38 8-(((l R)- 1 -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (2S)-butan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol.
- l R NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.38-4.58 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 217 [M+H] + .
- Example 40 8-(l-ethyl-2-methylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 41 8-((( 1 R,2S)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting trans-2-methylcyclohexanol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.13 (m. 3H), 4.59 (m, IH), 2.15 (m, IH), 1.99 (m, 2H), 1.68 (m, 3H), 1.53 (m, IH), 1.38 (m, 2H), 1.04 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 257 [M+H] + .
- Example 44 8-(3-ethoxy-l-ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-ethoxypentan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. !
- Example 48 8-(l,2-diethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 4-ethylhexan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.47 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.61-1.82 (m, 3H), 1.50 (m, 2H), 1.29 (m, IH), 0.98 (m, 6H), 0.86 ( , 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 273 [M+H] + .
- Example 50 8-(l,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 4-methylpentan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.3 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.67 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.83 (m, IH), 1.53 (m, IH), 1.41 (d, 3H), 0.96 (d, 3H), 0.92 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 245 [M+H] + .
- Example 53 8-(( 1 -isopropylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 2-methylheptan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, IH), 7.17 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.28 (m, IH), 2.19 (m, IH), 1.98 (m, IH), 1.68 (m, IH), 1.46 (m, IH), 1.31 (m, 3H), 1.01 (m, 6H), 0.86 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 273 [M+H] + .
- Example 54 8-(l-benzylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-phenylbutan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol.
- 2 H NMR 500 MHz, CDCI3 ⁇ ppm 7.86 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, 2H), 7.16 (m, 3H), 6.99 (m, IH), 6.88 (d, IH), 4.59 ( , IH), 3.27 (dd, IH), 2.99 (dd, IH), 1.73-1.97 (m, 2H), 1.02 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 293
- Example 55 8-( 1 -(4-fluorophenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-(4-fluorophenyl)ethanol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.92 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.14 (m, 2H), 7.01 (m, 3H), 6.94 (m, IH), 5.50 (q, IH), 1.84 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 283 [M+H] + .
- Example 57 8-( 1 -methyl-2-phenylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 58 8-(((l S)-l -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (R)-(-)-2-butanol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.11 (m, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.51 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.76 (m, IH), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 217 [M+H] + .
- Example 59 8-(2,3 -dihydro- 1 H-inden-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 2-indanol for heptan-3-ol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.49 (m, 3H), 7.31 (m, 2H), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.11 (d, IH), 5.51 (m, IH), 3.59 (d, IH), 3.55 (d, IH), 3.28 (d, IH), 3.24 (d, IH); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m/z 277 [M+H] + .
- Example 61 8-(2-(l-naphthyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 62 8-(( 1 -ethyl-4-methylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- a 7.5 mL conical microwave vessel (Personal Chemistry) equipped with a septum cap and a magnetic stirring bar was charged with PS-PPh 3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 140 mg, 4.40 equiv), 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (15.0 mg, 0.0960 mmol) and DBAD (69 mg, 3.2 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N 2 for 45 seconds.
- Anhydr. THF 1.5 mL was added and contents of the vessel were stirred for 10 min.
- Example 64 8-(((lR,5S)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 62 substituting cis-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexanol for 6-methyl-3-heptanol.
- Example 65 8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh 3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 100 mg, 2.2 equiv), 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (22 mg, 0.14 mmol) and DBAD (51 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3 mL) was added and the contents of the vial were shaken for 5 min. Then, a solution of benzyl alcohol (1.25 equiv) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 8 h.
- PS-PPh 3 resin Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 100 mg, 2.2 equiv
- 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline 22 mg, 0.14 mmol
- DBAD 51 mg, 1.6 equiv
- the suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (2.5, 3.5 and 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo.
- the resulting crude product was then dissolved in a mixture of DCM (1 mL), thf (1 mL) and MeOH (3 mL) and the solution was added to MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 0.5 g). The resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 1.5 h. The supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed with DCM (2 mL), MeOH (2 mL), THF (2 mL) and DCM (2 mL).
- the washed resin was treated with 2 N NH 3 in MeOH (4 mL) at room temperature for 1 h. The supernatant was collected and the resin was washed with MeOH (3 mL) and DCM (3 mL). The washes were combined with the collected supernatant. The NH 3 /MeOH treatment and washes were then repeated. The filtrate and the washes were combined with previously collected and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC.
- Example 66 8-((3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting 3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl alcohol for benzyl alcohol.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.88 (d, IH), 7.78 (s, IH), 7.72 (d, IH), 7.56 (d, IH), 7.48 (t, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.12 (t, IH), 6.96 (m, IH), 6.78 (d, IH), 5.42 (s, 2H); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m/z 319 [M+H] + .
- Example 69 8-(((3R)- 1 -benzylpyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting (S)-l-benzyl-3-pyrrolidinol for benzyl alcohol.
- Example 71 8-((l,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 72 8-((( 1 R)- 1 -phenylethyl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting (S)-(-)-l-phenylethanol for benzyl alcohol.
- l B NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.32 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, IH), 7.13 (dd, IH), 7.01 (t, IH), 6.84 (dd, IH), 6.76 (m, IH), 5.51 (m, IH), 1.82 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 265 [M+H] + .
- Example 77 3 ((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propan- 1 -ol
- the reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature and stirring was maintained for 8 h. Then, 0.652 g (2 equiv) of PPh 3 was added, the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and 0.431 g (1.5 equiv) of DBAD in 15 mL THF was added dropwise over 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The solution was evaporated in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in DMA (25 mL) and MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 4.5 g) was added. The resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 12 h.
- the supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed with DMA (2x20 mL), MeOH (2x20 mL) and DMA (20 mL).
- the washed resin was treated with a mixture of 2 N NH 3 in MeOH (15 mL) and DMA (5 mL) at room temperature for 1 h.
- the solution was drained and the basic wash was repeated two more times. Filtered solutions were combined.
- PS-PPh 3 resin Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 60 mg, 2.4 equiv
- DBAD 28 mg, 1.6 equiv
- the suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (3x3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo.
- the residue was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 6 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo.
- the residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC.
- Example 80 8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 81 6-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 2,6-quinolinediol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine.
- Example 82 4-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 2-aminoquinolin-4-ol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine.
- Example 83 8-(3-phenoxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 84 8-(3-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 3,5-dichlorophenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine.
- 1HNMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.99 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.24 (m, IH), 7.14 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 6.86 (m, IH), 6.82 (m, 2H), 4.35 (m, 4H), 2.49 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 363 [M+H] + .
- Example 85A 8-( 1 -Methyl-but-3 -enyloxy)-quinolin-2-ylamine To a 100 mL round bottom flask equipped with a stirring bar, under N 2 , was added
- Example 85B 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan- 1 -ol To a 100 mL round bottom flask containing 1.33 g (5.83 mmol) of 8-(l-methyl-but-
- Example 88 8-(4-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting 3,5-dichlorophenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine.
- Example 90 8-(l-methyl-4-(quinolin-7-yloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amme
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting 7-hydroxyquinoline for 8-hydroxyquinaldine.
- HNMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 8.99 (br d, IH), 8.61 (d, IH), 7.88 (d, IH), 7.83 (d, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.65 (dd, IH), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.01 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.22-4.42 (m, 2H), 2.19 (m, 2H), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH 3 ) m z 373 [M+H] + .
- Example 92 methyl 3 -((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate
- PS-PPh 3 resin Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 120 mg, 4.4 equiv
- a solution of methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate (0.41 mL, 0.30 mM) in anhydr.
- THF DMA for phenols not soluble in THF
- DBAD 0.50 mL; 60 mg/mL
- Example 93 8-( 1 -methyl-4-(3 ,4,5-trimethylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 3,4,5-trimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 94 methyl 0-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)-L-tyrosinate
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl methyl L-tyrosinate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 95 8-( 1 -methyl-4-(2-naphthyloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-naphthol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 96 l-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-3-methylphenyl)ethanone
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting l-(4-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl)ethanone for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 97 8-(l-methyl-4-(4-propylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-propylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, 3H), 6.74 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.00 (m, 2H), 2.49 (t, 2H), 2.20 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 3H), 1.59 (m, 2H), 1.46 (d, 3H), 0.91 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 365 [M+H] + .
- Example 100 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Exampl 92 substituting 2-hydroxybenzonitrile for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 101 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting salicylamide for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- 1H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO- d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 7.76 (dd, IH), 7.35-7.58 (m, 6H), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.01 (m, IH), 4.87 (m, IH), 4.18 (m, 2H), 1.84-2.05 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 366 [M+H] + .
- Example 102 8-(l-methyl-4-(2-methyl-5-nitrophenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- X H NMR 500 MHz, CDC1 3 ) ⁇ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.68 (dd, IH), 7.59 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.01 (d, IH), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.15 (m, IH), 4.08 (m, IH), 2.25 (m, IH), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.12 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 2H), 1.49 (d, 3H); MS (DCI7NH 3 ) m/z 382 [M+H] + .
- Example 103 8-(4-((5-amino- 1 -naphthyl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 5-amino-l-naphthol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 108 ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methylbenzoate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 109 8-(4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-bromo-2-fluorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 110 N-(3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)urea
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting N-(3-hydroxyphenyI)urea for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 111 4-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)butan-2-one
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-one for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 112 ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting ethyl salicylate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- H NMR 500 MHz, CDCI3 ⁇ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.71 (dd, IH), 7.40 (m, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.16 (m, 2H), 7.00 (d, IH),
- Example 113 methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methoxybenzoate
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 114 8-(4-(4-amino-2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-amino-2-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 118 8-(4-(l,r-biphenyl-3-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting l,l'-biphenyl-3-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 120 8-(4-(2-ethoxy-5-(( 1 E)-prop- 1 -enyl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 121 methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-4-methoxybenzoate
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 122 8-(4-(2-benzylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-benzylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 123 8-(4-(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-fluoro-4-nitrophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 128 8-(4-((2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-l-benzofuran-7-yl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,2-dimethy 1-2,3 -dihydro- l-benzofuran-7-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 129 8 (4-(2-isoxazol-5 -ylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 130 6-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)- 1 ,3 -benzoxathiol-2-one
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92substituting 6-hydroxy- 1 ,3 -benzoxathiol-2-one for methyl 3 -hydroxybenzoate .
- Example 131 8-(4-(2-methoxy-4-propylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-allyl-2-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 132 8-(4-(2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-3-(triflouromethyl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 135 8-(l-methyl-4-(4-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting o-cresol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- l U NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 3H), 7.40 (m, 2H), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, IH), 6.74 (m, IH), 4.83 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 2.22 (m, 3H), 1.76-2.08 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 337 [M+H] + .
- Example 138 8-(4-(3 -mefhoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz,
- Example 139 8-(4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 140 8-(4-(2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-flourophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 142 8-f 4-f 4-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 143 8-(4-(2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 144 8-(4-(3 -chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 146 8-(4-(2-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 147 8-(4-(3 -bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-bromophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 148 8-(4-(4-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-bromophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 149 3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-cyanophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 151 8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 152 8-(l-methyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-(triflouromethyl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- J H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-de) ⁇ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, 2H), 4.76-4.96 (m, IH), 4.13 (m, 2H), 1.80-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 391 [M+H] + .
- Example 153 8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-(triflouromethoxy)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H).
- Example 154 8-(4-(2,3 -dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,3-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. ! H NMR (500 MHz,
- Example 155 8-(4-(2,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,4-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !
- Example 157 8-(4-(3 ,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3,4-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 160 8-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 161 8-(4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,4-dichlorophenol for methyl 3 -hydroxybenzoate.
- H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 8.36 (m, IH), 7.31-7.58 (m, 5H), 6.95-7.24 (m, 2H), 4.74-5.11 (m, IH), 3.84-4.11 ( , 2H), 1.80-2.14 (m, 4H), 1.41 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m z 392 [M+H] + .
- Example 162 8-(4-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine .
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,5-dichlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- 'H NMR 500 MHz, DMSO-de) ⁇ ppm 8.36 (m, IH), 7.42 (m, 4H), 7.16 (m, 2H), 6.95 (m, IH), 4.79-5.07 (m, IH), 4.16 (m, 2H), 1.73-2.10 (m, 4H), 1.41 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 392 [M+H] + .
- Example 164 8-(4-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- reaction mixture was cooled in an ice bath and a solution of 4.76 g (0.75 equiv) of DBAD in 25 mL of anhydr. THF was added dropwise over 15 minutes. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature, and stirring was maintained for an additional 6 h. The reaction mixture was then evaporated in vacuo and the resulting residue dissolved in 150 mL of EtOAc. The solution was washed with 2 N HCl (3 x 400 mL). The aqueous layers were combined and basified with 10 N
- Example 166 N-propyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine To a 4 mL scintillation vial was added a stir bar and the title compound from Example 16 (15.0 mg, 0.058 mmol). To this was added 0.42 mL of a 1 :1
- Example 167 ⁇ D 20 +107°.
- 1H NMR 300 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ⁇ ppm 7.83 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, 2H), 6.76 (m, IH), 6.18-6.38 (m, 2H), 4.72 (m, IH), 1.85 (m, IH), 1.47 (m, IH), 1.24 (m, 3H), 0.84-1.04 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 259 [M+H .
- Example 168 ⁇ ⁇ D 20 -111°.
- 1H NMR 300 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) ⁇ ppm 7.83 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, 2H), 6.76 (m, IH), 6.18-6.38 (m, 2H), 4.72 (m, IH), 1.85 (m, IH), 1.47 (m, IH), 1.24 (m, 3H), 0.84-1.04 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 259 [M+H] + .
- Example 169 N-((5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 166 substituting 5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-furaldehyde for propionaldehyde.
- Example 170 N-((5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 166 substituting 5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furaldehyde for propionaldehyde.
- Example 172 8-hexylquinolin-2-amine A solution of 2-amino-8-trifluoromethanesulfonylquinoline (50.0 mg, 0.171 mmol) in THF (1.0 mL) was degassed by bubbling N through the solution under vacuum for 5 min. The solution was added to a glass screw-top tube containing Pd(dppf) Cl 2 -CH 2 Cl 2 (13.9 mg, 0.1 equiv). Argon was then bubbled through the mixture for 1 minute, and 1-hexylzinc bromide (1.0 mL, 1 M in THF) was added. The tube was quickly sealed and placed in a heater/shaker at 65 °C for 20 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, filtered through a 0.45 ⁇ m filter, and concentrated. The residue was dissolved in 1 : 1
- Example 173 8-( 1 -methylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting 1-methylpentylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide.
- J H NMR 300 MHz, DMSO-de) ⁇ 9.20 (br s, IH), 8.45 (br s, IH), 8.37 (d, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.70 (d, IH), 7.49 (br s, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 1.71-1.67 (m, 3H), 1.28-1.14 (m, 4H), 0.82 (d, 3H), 0.74 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 228 [M] + .
- Example 174 8-( 1 -ethylbutyl)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting 1-ethylbutylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide.
- Example 175 8-( 1 -ethylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting 1-ethylpentylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide.
- Example 178 8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 179 8-(3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yloxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- PS-PPI13 resin Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 200 mg, 4 equiv
- 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline 100 mg, 5 equiv
- Anhydr. THF (3.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 3 min.
- 1,3-propanenediol (10 mg, 0.13 mmol) was added to the vial followed by DBAD (66 mg, 2 equiv) and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 15 min. Then additional DBAD (33 mg, 1 equiv) was added and the mixture was agitated for additional 15 min. The last addition of DBAD was repeated and the mixture was agitated for 6 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with DMA (6 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in DMA (10 mL) and MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 4.5 g) was added.
- the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 12 h.
- the supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed with DMA (10 mL), MeOH (10 mL) and DMA 00 mL) and MeOH (10 mL).
- the washed resin was treated with a mixture of 2 N NH 3 in MeOH (15 mL) and DMA (5 mL) at room temperature for 1 h.
- the solution was drained and the basic wash was repeated two more times.
- the filtered solutions were combined.
- the resin was washed with MeOH (10 mL), DMA (10 mL), MeOH (10 mL), DMA (10 mL) and MeOH (10 mL).
- the washes were combined with the previously collected solutions and evaporated in vacuo.
- Example 180 8-((2E)-but-2-enyloxy)quinolin-2 -amine
- 1.51 mL of 3-chloro-l-butene (15.0 mmol) was added in one portion, and the mixture was heated to 65 °C in an oil bath. After 48 h, the solvent was evaporated and the residue dissolved in EtOAc and washed with H 2 0. The combined aqueous layers were back-extracted with EtOAc.
- Example 181 A 2,2-dimethyl-N-(8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)propanamide To a 20 mL scintillation vial was added a stir bar, the title compound from Example 16 (161 mg , 0.624 mmol) and 1.5 mL of THF. To the resultant solution was added Et 3 ⁇ (0.174 mL, 2 equiv) and trirnethylacetylchloride (93 ⁇ L, 1.2 equiv). The solution was allowed to stir overnight, after which time the mixture placed directly on a silica column and eluted with EtOAc/hexanes to afford the title compound.
- Example 18 IB 2,2-dimethyl-N-(3-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)qumolin-2-yl)propanamide
- a 50 mL three-neck flask with a stir bar was charged with the title compound from Example 181 A (270 mg, 0.790 mmol) and 3 mL of THF.
- the flask was cooled to 0 °C in an ice bath and 0.9 mL of a 2.5 M solution of n-BuLi in THF was added slowly via syringe.
- the resultant solution was allowed to stir at 0 °C for 4 h, and then cooled to -78 °C.
- Example 181C 3-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- a 20 mL glass tube was charged with the title compound from Example 181B(57.0 mg, 0.160 mmol), 1.5 mL of MeOH and sodium methoxide (26.0 mg, 3 equiv.).
- the tube was sealed and heated to 70 °C in an oil bath for 12 h.
- the reaction mixture was then allowed to cool to room temperature and was then quenched with saturated aqueous NH 4 C1.
- the mixture was diluted with Et 2 0 and partitioned, the aqueous layer was washed with Et 2 O.
- the ethereal layers were combined, dried, and filtered.
- Example 183 A 3-((8-(l ,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)amino)propan-l -ol
- the resulting solution was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (220 °C for 25 min; 300 W). After cooling to room temperature, the contents were directly loaded on a silica gel column and eluted with EtOAc/hexanes to afford the title compound.
- Example 183B N-(3 -((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)-8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
- PS-PPI1 3 resin Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 46 mg, 2.2 equiv
- DBAD DBAD
- Example 184 8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-4-methylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate.
- a 4 dram scintillation vial was charged with 135 mg (0.509 mmol) of Example 195, l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde (92.0 mg, 0.613 mmol), and macroporous sodium cyanoborohydride resin (400 mg, 2.55 mmol/g, 2 equiv).
- a solution of 1:1 MeOH/dichloroethane with 1% AcOH was added (3 mL) and the reaction vessel shaken for approximately 16 hours. After this time the resin was filtered off and the solvents evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 1 : 1 MeOH/DMSO and purified on a reverse-phase HPLC column to afford the title compound.
- Example 189 8-(((3S)-l-(2-fluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
- Example 190 8-(((3S)- 1 -( 1 , 1 '-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 4-biphenylcarboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde.
- Example 191 8-(((3S)-l-((3 -methyl- 1 -benzothien-2-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 3-methylbenzo(B)thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5- carbaldehyde.
- Example 194 tgrt-butyl 8-((3S)-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-ylcarbamate
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting (3 S)-hydroxy-pyrrolidine-l -carboxylic acid-tert-butyl ester for methyl 3- hydroxybenzoate.
- Example 195 8-((3S)-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine To a 4 dram vial containing Example 194 (300 mg, 0.608 mmol) was added 3 mL of a 4 M solution of HCl in dioxane. The mixture was allowed to sit for 60 min and then the solvent was evaporated to afford the HCl salt of the title compound. !
- Example 197 8-(((3S)- 1 -(2,3-dihydro- 1 ,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting l,4-benzodioxan-6-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde.
- Example 199 8-(((3S ⁇ -l-(3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)py ⁇ olidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 3-(triflouromethyl)benzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde.
- Example 200 8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-difluoro-l,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 2,2-diflouro-l,3-benzodioxolo-5-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5- carbaldehyde.
- Example 202 N-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)-8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6- ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting l,4-benzodioxan-6-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde.
- a 250 mL round bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and a pressure equalizing dropping funnel was charged with 5.20 g (29.5 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-6-methyl- chromen-2-one.
- the flask was purged with nitrogen and a solution of NEt 3 (8.3 mL) in DCM (60 mL) was added.
- the resulting solution was cooled to -10 °C and trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride (10.0 g; 1.2 eq) was added dropwise to the flask over 5 min.
- the resulting mixture was kept at -10 °C for 2 h then diluted with 130 mL of 1:1 mixture of ether/hexanes.
- Example 203 B 4-((3-hydroxypropyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one
- a 7.5 L conical microwave reaction vessel (Personal Chemistry) was charged with the title compound from Example 203 A (0.030 g, 0.097 mol) and purged with N 2 . Then a solution of 3-amino-propan-l-ol (0.075 mL, 10 eq.) in a mixture of acetonitrile (2 mL) and triethylamine (0.2 mL) was added. The resulting solution was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (150 °C for 180 s; 300 W). The reaction mixture was then evaporated in vacuo.
- Example 204 A Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid 6-chloro-2-oxo-2H-chromen-yl ester
- the title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 203 A substituting 4-hydroxy-6-methyl-chromen-2-one for 4-hydroxy-6-chloro-chromen-2- one.
- 1H NMR 300 MHz, MeOD-d 4 ) ⁇ 6.56 (s, IH), 7.26 (s, IH), 7.38 (d, IH, d), 7.64 (d, IH); MS (DCI/NH 3 ) m/z 329 [M+H] + .
- Example 204 C 4-r3-(2-amino-quinolin-8-yloxy)-propylamino1-6-chIoro-chromen-2-one The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention is related to compounds of formula (I), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, which antagonize the effects of melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) through the melanin concentrating hormone receptor and are useful for the prevention or treatment of eating disorders, weight gain and obesity.
Description
2-Aminoquinolines as Melanin Concentrating Hormone Receptor Antagonists
Field of the Invention The present invention relates to the antagonism of the effects of melanin- concentrating hormone (MCH) through the melanin concentrating hormone receptor which is useful for the prevention or treatment of eating disorders, weight gain, obesity, abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders.
Background of the Invention
Obesity is a major cause and contributor to health problems such as type II diabetes, coronary heart disease, increased incidence of certain forms of cancer, and respiratory complications. It is a disease that is increasing at an alarming rate due to increased availability of high-fat diets, genetic susceptibility, and a more sedentary way of life in modern society. Obesity can be defined as weight gain resulting from a mismatch of energy intake and energy expenditure. Food intake and energy metabolism are regulated, in part, by the interaction of neuropeptides and their receptors. Recently, the role that the hormone leptin plays in controlling appetite has been elucidated. Leptin is a peptide hormone produced by fat cells, regulating both food intake and and metabolism by acting on leptin receptors in the hypothalamus. Increased fat stores leads to increased secretion of leptin, resulting in a signal to the hypothalamus to decrease food intake, whereas decreases in adiposity result in lower leptin levels and a stimulation of food intake. Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) has been identified as an orexigenic peptide that counterbalances the activity of leptin.
MCH is a cyclic 19 amino acid neuropeptide expressed in the zona incerta and lateral hypothalamus in response to both energy restriction and leptin deficiency. MCH is known to stimulate feeding when injected into the lateral ventricle of rats and the mRNA for MCH is upregulated in the hypothalamus of genetically obese mice (ob/ob) and in fasted control and ob/ob animals. Mice lacking MCH are hypophagic and lean with increased metabolic rate, whereas animals over-expressing MCH gain excess weight on both standard and high fat diets. An orphan G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) was recently identified as a receptor for MCH.
Although there exists current pharmacologic therapies used to treat obesity, none of the current therapies achieve the U.S. Food and Drug Administration criteria for benefit measured by a 5% difference in mean weight loss, as weight loss efficacy is diminished by reduction of patient adherence to pharmacological therapy due to side effects of the drugs. Some of the side effects associated with current therapies include increased heart rate and
blood pressure, and uncontrolled excretion of fat in stools. Thus, there exists a medical need for agents capable of preventing or treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity, that at the same time, have improved efficacy and safety.
Summary of the Invention The present invention is directed to compound of formula (I),
(I), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Li is a bond or is a member selected from the group consisting of-C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, and -S(O)2-; Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARB -, and R RβNcarbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R7L2R6-, RASalkyl, and RARβNalkyl; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R^ and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RA B -, and alkylcarbonylNH-; 5 and R7 -ire each independently a member selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycle; RA and Rβ are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle; L2 is -(CH2)mX(CH2)„-; X is a member selected from the group consisting of — C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, -S(O)2- or is a covalent bond; m is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4; n is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4; provided that if i) any of R3, R , or R5 is alkyl or alkoxy, or if ii) L is a bond and R is either alkyl or alkoxy; then R] must be other than hydrogen.
According to one embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a method of treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I). According to another embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a method for treating treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I). According to another embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a method for treating treating abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders comprising administering a therapeutically
effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
According to still another embodiment, the present invention is directed to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) in combination with a pharmaceutically suitable carrier.
Detailed Description of the Invention
Definitions As used throughout this specification and the appended claims, the following terms have the following meanings:
The term "alkenyl," as used herein, refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon containing from 2 to 10 carbons and containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond formed by the removal of two hydrogens. Representative examples of alkenyl include, but are not limited to, ethenyl, 2-propenyl, 2-methyl-2 -propenyl, 3-butenyl, 4-pentenyl, 5- hexenyl, 2-heptenyl, 2-methyl-l-heptenyl, and 3-decenyl.
The term "alkoxy," as used herein, refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an oxygen atom. Representative examples of alkoxy include, but are not limited to, methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, 2-ρropoxy, butoxy, tert- butoxy, pentyloxy, and hexyloxy.
The term "alkoxyalkyl," as used herein, refers to an alkoxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of alkoxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, tert-butoxymethyl, 2- ethoxy ethyl, 2-methoxy ethyl, and methoxymethyl.
The term "alkoxycarbonyl," as used herein, refers to an alkoxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of alkoxycarbonyl include, but are not limited to, methoxycarbonyl, ethoxycarbonyl, and tert-butoxycarbonyl.
The term "alkoxycarbonylalkyl," as used herein, refers to an alkoxycarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of alkoxycarbonylalkyl include, but are not limited to, 3 -methoxy carbonylpropyl, 4-ethoxycarbonylbutyl, and 2-tert-butoxycarbonylethyl. The term "alkyl," as used herein, refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon containing from 1 to 10 carbon atoms. Representative examples of alkyl include, but are not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, iso-butyl, tert-butyl, n- pentyl, isopentyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl, 3-methylhexyl, 2,2-dimethylpentyl, 2,3- dimethylpentyl, n-heptyl, n-octyl, n-nonyl, and n-decyl. The term "alkylcarbonyl," as used herein, refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of alkylcarbonyl include, but are not limited to, acetyl, 1- oxopropyl, 2,2-dimethyl-l-oxopropyl, 1-oxobutyl, and 1-oxopentyl.
The term "alkylcarbonylalkyl," as used herein, refers to an alkylcarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of alkylcarbonylalkyl include, but are not limited to, 2- oxopropyl, 3,3~dimethyl-2-oxopropyl, 3-oxobutyl, and 3-oxopentyl. The term "alkylcarbonyloxy," as used herein, refers to an alkylcarbonyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an oxygen atom. Representative examples of alkylcarbonyloxy include, but are not limited to, acetyloxy, ethylcarbonyloxy, and tert-butylcarbonyloxy.
The term "alkylsulfonyl," as used herein, refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a sulfonyl group, as defined herein.
Representative examples of alkylsulfonyl include, but are not limited to, methylsulfonyl and ethylsulfonyl.
The term "alkylthio," as used herein, refers to an alkyl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a sulfur atom. Representative examples of alkylthio include, but are not limited, methylsulfanyl, ethylsulfanyl, tert-butylsulfanyl, and hexylsulfanyl.
The term "alkynyl," as used herein, refers to a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon group containing from 2 to 10 carbon atoms and containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. Representative examples of alkynyl include, but are not limited, to acetylenyl, 1- propynyl, 2-propynyl, 3-butynyl, 2-pentynyl, and 1-butynyl.
The term "aryl," as used herein, refers to a monocyclic-ring system, or a bicyclic- or a tricyclic- fused ring system wherein one or more of the fused rings are aromatic. Representative examples of aryl include, but are not limited to, anthracenyl, azulenyl, fluorenyl, indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, phenyl, and tetrahydronaphthyl. The aryl groups of this invention can be substituted with 1, 2, or 3 substituents independently selected from alkenyl, alkoxy, alkoxyalkyl, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonylalkyl, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl, alkylcarbonylalkyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylsulfonyl, alkylthio, alkynyl, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, cyano, cyanoalkyl. formyl, halogen, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, mercapto, nitro, phenyl and -NRCRD wherein Re and RD are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl.
The term "arylalkoxy," as used herein, refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkoxy group, as defined herein. Representative examples of arylalkoxy include, but are not limited to, 2-phenylethoxy, 3- naphth-2-ylpropoxy, and 5-phenylpentyloxy.
The term "arylalkyl," as used herein, refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of arylalkyl include, but are not limited to, benzyl, 2-phenylethyl, 3-phenylpropyl, and 2-naphth-2-ylethyl.
The term "arylcarbonyl," as used herein, refers to an aryl group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of arylcarbonyl include, but are not limited to, benzoyl and naphthoyl. The term "carbonyl," as used herein, refers to a -C(O)- group.
The term "carboxy," as used herein, refers to a -CO2H group.
The term "carboxyalkyl," as used herein, refers to a carboxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of carboxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, carboxymethyl, 2- carboxy ethyl, and 3-carboxypropyl.
The term "cyano," as used herein, refers to a -CN group.
The term "cyanoalkyl," as used herein, refers to a cyano group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of cyanoalkyl include, but are not limited to, cyanomethyl, 2- cyanoethyl, and 3-cyanopropyl.
The term "cycloalkyl," as used herein, refers to a monocyclic, bicyclic, or tricyclic ring system. Monocyclic ring systems are exemplified by a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon group containing from 3 to 8 carbon atoms. Examples of monocyclic ring systems include cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl, and cyclooctyl. Bicyclic ring systems are exemplified by a bridged monocyclic ring system in which two non-adjacent carbon atoms of the monocyclic ring are linked by an alkylene bridge of between one and three additional carbon atoms. Representative examples of bicyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane, bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, bicyclo[3.2.2]nonane, bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, and bicyclo[4.2.1]nonane. Tricyclic ring systems are exemplified by a bicyclic ring system in which two non-adjacent carbon atoms of the bicyclic ring are linked by a bond or an alkylene bridge of between one and three carbon atoms. Representative examples of tricyclic-ring systems include, but are not limited to, tricyclo[3.3.1.03'7]nonane and tricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane (adamantane).
The term "formyl," as used herein, refers to a -C(0)H group. The term "halo" or "halogen," as used herein, refers to -CI, -Br, -I or -F.
The term "haloalkyl," as used herein, refers to at least one halogen, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of haloalkyl include, but are not limited to, chloromethyl, 2- fluoroethyl, trifluoromethyl, pentafluoroethyl, and 2-chloro-3-fluoropentyl. The term "heterocycle" or "heterocyclic," as used herein, refers to a monocyclic, bicyclic, or tricyclic ring system. Monocyclic ring systems are exemplified by any 3- or 4- membered ring containing a heteroatom independently selected from oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur; or a 5-, 6- or 7-membered ring containing one, two or three heteroatoms wherein the heteroatoms are independently selected from nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur. The 5-membered
ring has from 0-2 double bonds and the 6- and 7-membered ring have from 0-3 double bonds. Representative examples of monocyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, azetidinyl, azepanyl, aziridinyl, diazepinyl, 1,3-dioxolanyl, dioxanyl, dithianyl, furyl, imidazolyl, imidazolinyl, imidazolidinyl, isothiazolyl, isothiazolinyl, isothiazolidinyl, isoxazolyl, isoxazolinyl, isoxazolidinyl, morpholinyl, oxadiazolyl, oxadiazolinyl, oxadiazolidinyl, oxazolyl, oxazolinyl, oxazolidinyl, piperazinyl, piperidinyl, pyranyl, pyrazinyl, pyrazolyl, pyrazolinyl, pyrazolidinyl, pyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolinyl, pyrrolidinyl, tetrahydrofuranyl, tetrahydrothienyl, tetrazinyl, tetrazolyl, thiadiazolyl, thiadiazolinyl, thiadiazolidinyl, thiazolyl, thiazolinyl, thiazolidinyl, thienyl, thiomorpholinyl, 1,1-dioxidothiomorpholinyl (thiomorpholine sulfone), thiopyranyl, triazinyl, triazolyl, and trithianyl. Bicyclic ring systems are exemplified by any of the above monocyclic ring systems fused to an aryl group as defined herein, a cycloalkyl group as defined herein, or another monocyclic ring system. Representative examples of bicyclic ring systems include but are not limited to, for example, benzimidazolyl, benzodioxinyl, benzothiazolyl, benzothienyl, benzotriazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzofiiranyl, benzopyranyl, benzothiopyranyl, cinnolinyl, indazolyl, indolyl, 2,3-dihydroindolyl, indolizinyl, naphthyridinyl, isobenzofuranyl, isobenzothienyl, isoindolyl, isoquinolinyl, phthalazinyl, 4H-pyrido[l,2-α]pyrimidin-4-one, pyranopyridinyl, quinolinyl, quinolizinyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, tetrahydroisoquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl, and thiopyranopyridinyl. Tricyclic rings systems are exemplified by any of the above bicyclic ring systems fused to an aryl group as defined herein, a cycloalkyl group as defined herein, or a monocyclic ring system. Representative examples of tricyclic ring systems include, but are not limited to, acridinyl, carbazolyl, carbolinyl, dibenzo[b,d]furanyl, dibenzo[b,d]thienyl, naphtho[2,3- bjfuran, naphtho[2,3-b]thienyl, phenazinyl, phenothiazinyl, phenoxazinyl, thianthrenyl, thioxanthenyl and xanthenyl.
According to the present invention, heterocycles of this invention can be substituted with 1, 2,or 3 substituents independently selected from alkenyl, alkoxy, alkoxyalkyl, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonylalkyl, alkyl, alkylcarbonyl, alkylcarbonylalkyl, alkylcarbonyloxy, alkylsulfonyl, alkylthio, alkynyl, aryl, arylalkoxy, arylalkyl, arylcarbonyl, aryloxy, carboxy, carboxyalkyl, cyano, cyanoalkyl, formyl, halogen, haloalkyl, hydroxy, hydroxyalkyl, mercapto, nitro, phenyl, and RcRβN-, RcRβNcarbonyl, RcRβNalkyl, wherein Re and Rβ are defined herein.
The term "heterocyclealkyl," as used herein, refers to a heterocycle, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. Representative examples of heterocyclealkyl include, but are not limited to, pyridin-3- ylmethyl and 2-pyrimidin-2-ylpropyl and the like.
The term "hydroxy," as used herein, refers to an -OΗ group. The term "hydroxyalkyl," as used herein, refers to a hydroxy group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
Representative examples of hydroxyalkyl include, but are not limited to, 2-hydroxyethyl, 2- hydroxypropyl, 3-hydroxybutyl and the like.
The term "mercapto," as used herein, refers to a -SH group.
The term "RARBN-," as used herein, refers to both RA and RB appended to the parent molecular moiety through a -N- group.
The term "nitro," as used herein, refers to a -NO2 group.
The term "RARBNalkyl," as used herein, refers to a RARBN group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular' moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein.
The term "RAR-BNcarbonyl," as used herein, refers to a ARBN group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a carbonyl group, as defined herein.
The term "RAS," as used herein, refers to a A group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through a -S- group, as defined herein.
The term "RASalkyl," as used herein, refers to a RAS group, as defined herein, appended to the parent molecular moiety through an alkyl group, as defined herein. The present invention is directed to compounds of formula (I), wherein Rj, R , R3,
R4, R5, R , RB, and L are defined herein. The compounds of thepresent invention are useful for treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor.
According to one embodiment of the present invention there is provided a method of treating or preventing disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administrering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
According to the principle embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound of formula (I),
(I), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Li is a bond or is a member selected from the group consisting of -C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, and -S(0) -; RΪ is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R RBN-, and R RsNcarbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R7L2R6-„ RASalkyl, and RARBNalkyl; R is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARβN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; Rt, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARβN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R6 and R7 are each independently a member
selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycle; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle; L2 is -(CH2)mX(CH2)n-; X is a member selected from the group consisting of- C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, -S(0)2- or is a covalent bond; m is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4; n is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4; provided that if i) any of R3, R4, or R5 is alkyl or alkoxy, or if ii) L is a bond and R2 is either alkyl or alkoxy; then Ri must be other than hydrogen.
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (la),
da), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein L] is-O-; R is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARBNcarbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R^ and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARβN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle; with the following provisions that if any of R3, R4, or R5 is alkyl or alkoxy, or if R2 is alkyl, wherein alkyl is C5 or smaller; then R\ must be other then hydrogen.
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (la), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Li is-O-; Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN- and R RB carbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R4, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (lb),
(lb), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein L] is-O-; Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARBNcarbonyl; R2 is alkyl, wherein alkyl is C6 or larger; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R^ and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARB -, and alkylcarbonylNH-; and RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (Ic),
(Ic), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Lt is-O-; Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, R RBN-, and RARBNcarbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkoxyalkyl, haloalkyl, R Salkyl, and RARβNalkyl; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; Rt, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (Id),
or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Lj is-O-; Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARβNcarbonyl; R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl and heterocycle; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R_t, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle. According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a compound according to formula (Ie),
(Ie), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein L] is-O-; Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RA BNcarbonyl; R is a member selected from the group consisting of arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R7L2R6-; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy,
RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R4, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARB -, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and B are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle. According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a method of treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a method for treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a method for treating abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I). According to another embodiment of the present invention there is provided a
pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) in combination with a pharmaceutically suitable carrier. Specific compounds of formula (I) include, but are not limited to:
8-isopropoxyquinolin-2-amine; 8-(cyclobutyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-sec-butoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-(cyclopentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l,2-dimethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(l-ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-methoxy- 1 -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(cyclohexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((3-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(2-ethoxy-l -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((3-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((4-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(cycloheptyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(2-ethyl- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-ethoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-propoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-butoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-isobutoxyquinolin-2-amine; 8-(cyclobutylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-cyclopropylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(pentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2--vmine; 8-(2-(methylthio)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(cyclopentylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(tetrahydrofuran-3-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(hexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(3,3,3-trifluoropropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(cyclohexylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((lS,4R)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
-((l-ethylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR)- 1 -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -( 1 -cyclohexylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-ethyl-2-methylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR,2S)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((l S)- 1 ,2-dimethylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-(methoxymethyl)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(3 -ethoxy- 1 -ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((( 1 R)- 1 ,2-dimethylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((l S)-2 -methyl- 1 -phenylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR,2S)-2-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -( 1 ,2-diethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l,4-diethylhexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR,2R)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l-isopropylbut-3-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l-isopropylpentyI)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-benzylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-(4-fluorophenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-methyl-2-phenylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((l S)-l -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(2,3-dihydro- 1 H-inden-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(3-methoxybutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(2-(l -naphthyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l-ethyl-4-methylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lS,5S)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR,5 S)-3 ,3 ,5 -trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((2,4-dimethylbenzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((3 S)- 1 -benzylpyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((3R)- 1 -benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l-benzylpiperidin-4-yI)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((l ,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(((lR)-l-phenylethyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; -( 1 -(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(2-(l-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(2-(2-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)-quinolin-2-amine;
8-((4-(((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)methyl)benzyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine;
3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propan-l-ol;
8-(3-((2-memylquinolm-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-(quinolin-8-yloxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(3 -((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol;
6-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol;
4-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-phenoxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan-l -ol;
8-(l-methyl-4-((2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 , 5 -dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine ;
8-(4-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(l-methyl-4-(quinolin-7-yloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetamide; methyl 3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yI)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate;
8-(l-methyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; methyl 0-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)-L-tyrosinate; 8-(l-methyl-4-(2-naphthyloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; l-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-3-methylphenyl)ethanone;
8-(l-methyl-4-(4-propylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3-isopropylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-chloro-3-fluorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile;
2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide;
8-(l-methyl-4-(2-methyl-5-nitrophenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((5-amino-l-naphthyl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 -anilinophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methoxyphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((4-methoxy- 1 -naphthyl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine ; methyl (4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetate; ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methylbenzoate;
8-(4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; N-(3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)urea;
4-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)butan-2-one; ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate; methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methoxybenzoate;
8-(4-(4-amino-2-chlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
1 -(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)propan- 1 -one;
8-(4-(3-(diethylamino)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8 -(4-( 1 , 1' -biphenyl-3 -yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-ethoxy-5-((l E)-prop- 1 -enyl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-4-methoxybenzoate;
8-(4-(2-benzylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 5-acetyl-2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide;
8-(4-(2,3 -dihydro- 1 H-inden-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-(lH-imidazol-l-yl)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(dibenzo[b,d]furan-2-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((2,2-dimethyl-2,3 -dihydro- 1 -benzofuran-7-yl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine;
8-(4-(2-isoxazol-5-ylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
6-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-l,3-benzoxathiol-2-one;
8-(4-(2-methoxy-4-propylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-chloro-3 -(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(l-methyl-4-(2-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(l-methyl-4-(3-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-methyl-4-(4-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-chloro-5-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenol; 8-(4-(3 -methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(4-(2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8 -(4-(3 -fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-fluorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3-chlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)qumolin-2 -amine;
8-(4-(2-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 -bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(4-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile;
4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile;
8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(l-methyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2,3-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(3 ,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 ,5-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(l ,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)-l -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)-l -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3-isopropyl-5-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
N-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-propyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((lR)-l,3,3-trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((( 1 S)- 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-((5-(2-(trifluorome l)phenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3- trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-((5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; Ν-((5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-hexylquinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-methylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l -ethylbutyl)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l -ethylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine; 8-cyclohexylquinolin-2-amine;
8-((5-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)-N-methylquinolin-2-amine;
8-((2E)-but-2-enyloxy)quinolin-2-amine; 3-methyl-8-(l ,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
2-(((8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)amino)carbonyl)benzyl benzoate;
Ν-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine;
8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2-(benzyloxy)phenoxy)-l -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(l,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -(2-fluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -( 1 , 1 '-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -((3 -methyl- 1 -benzothien-2-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-
amine;
8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-6-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3- yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; tert-butyl (3 S)-3 -((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pyrrolidine- 1 -carboxylate; 8-((3 S)-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -(4-tert-butylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2- amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-difluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((3 S)-l-(3 -(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine ;
8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-difluoro-l,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin- 2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,4-dimethylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)-8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-dihydro-l,4- benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one; and
4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-chloro-2H-chromen-2-one.
The present compounds can exist as therapeutically suitable salts. The term "therapeutically suitable salt," refers to salts or zwitterions of the compounds which are water or oil-soluble or dispersible, suitable for treatment of disorders without undue toxicity, irritation, and allergic response, commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio, and effective for their intended use. The salts can be prepared during the final isolation and purification of the compounds or separately by reacting an amino group of the compounds with a suitable acid. Representative salts include acetate, adipate, alginate, citrate, aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulfate, butyrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, digluconate, glycerophosphate, hemisulfate, heptanoate, hexanoate, formate, isethionate, fumarate, lactate, maleate, methanesulfonate, naphthylenesulfonate, nicotinate, oxalate, pamoate, pectinate, persulfate, 3-phenylpropionate, picrate, oxalate, maleate, pivalate, propionate, succinate, tartrate, trichloroacetic, trifluoroacetic, glutamate, para-toluenesulfonate, undecanoate, hydrochloric, hydrobromic, sulfuric, phosphoric, and the like. The amino groups of the compounds can also be quaternized with alkyl chlorides, bromides, and iodides such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, lauryl, myristyl, stearyl, and the like. The present invention contemplates pharmaceutically suitable salts formed at the nitrogen attached to 2-amino group of formula (I), when Rt is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARβN.
Basic addition salts can be prepared during the final isolation and purification of the present compounds by reaction of a carboxyl group with a suitable base such as the hydroxide, carbonate, or bicarbonate of a metal cation such as lithium, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, or aluminum, or an organic primary, secondary, or tertiary amine.
Quaternary amine salts derived from methylamine, dimethylamine, trimethylamine, triethylamine, diethylamine, ethylamine, tributlyamine, pyridine, N,N-dimethylaniline, N- methylpiperidine, N-methylmorpholine, dicyclohexylamine, procaine, dibenzylamine, N,N- dibenzylphenethylamine, 1-ephenamine, and N,N'-dibenzylethylenediamine, ethylenediamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, piperidine, piperazine, and the like, are contemplated as being within the scope of the present invention.
The present compounds can also exist as therapeutically suitable prodrugs. The term "therapeutically suitable prodrug," refers to those prodrugs or zwitterions which are suitable for use in contact with the tissues of patients without undue toxicity, irritation, and allergic response, are commensurate with a reasonable benefit/risk ratio, and are effective for their intended use. The term "prodrug," refers to compounds which are rapidly transformed in vivo to the parent compounds of formula (I) for example, by hydrolysis in blood.
Asymmetric centers can exist in the present compounds. Individual stereoisomers of the compounds are prepared by synthesis from chiral starting materials or by preparation of racemic mixtures and separation by conversion to a mixture of diastereomers followed by separation or recrystallization, chromatographic techniques, or direct separation of the enantiomers on chiral chromatographic columns. Starting materials of particular stereochemistry are either commercially available or are made by the methods described hereinbelow and resolved by techniques well-known in the art. Geometric isomers can exist in the present compounds The invention contemplates the various geometric isomers and mixtures thereof resulting from the disposal of substituents around a carbon-carbon double bond, a cycloalkyl group, or a heterocycloalkyl group. Substituents around a carbon-carbon double bond are designated as being of Z or E configuration and substituents around a cycloalkyl or heterocycloalkyl are designated as being of cis or trans configuration.
Therapeutic compositions of the present compounds comprise an effective amount of the same formulated with one or more therapeutically suitable excipients. The term "therapeutically suitable excipient," as used herein, represents a non-toxic, solid, semi-solid or liquid filler, diluent, encapsulating material, or formulation auxiliary of any type. Examples of therapeutically suitable excipients include sugars; cellulose and derivatives thereof; oils; glycols; solutions; buffering, coloring, releasing, coating, sweetening, flavoring, and perfuming agents; and the like. These therapeutic compositions can be administered parenterally, intracisternally, orally, rectally, or intraperitoneally.
Liquid dosage forms for oral administration of the present compounds comprise formulations of the same as emulsions, microemulsions, solutions, suspensions, syrups, and elixirs. In addition to the compounds, the liquid dosage forms can contain diluents and/or solubilizing or emulsifying agents. Besides inert diluents, the oral compositions can include wetting, emulsifying, sweetening, flavoring, and perfuming agents. Injectable preparations of the present compounds comprise sterile, injectable, aqueous and
oleaginous solutions, suspensions or emulsions, any of which can be optionally formulated with parenterally suitable diluents, dispersing, wetting, or suspending agents. These injectable preparations can be sterilized by filtration through a bacterial-retaining filter or formulated with sterilizing agents which dissolve or disperse in the injectable media. Antagonism of the effects of MCH through the MCH receptor by the compounds of the present invention can be delayed by using a liquid suspension of crystalline or amorphous material with poor water solubility. The rate of absorption of the compounds depends upon their rate of dissolution which, in turn, depends on their crystallinity. Delayed absorption of a parenterally administered compound can be accomplished by dissolving or suspending the compound in oil. Injectable depot forms of the compounds can also be prepared by microencapsulating the same in biodegradable polymers. Depending upon the ratio of compound to polymer and the nature of the polymer employed, the rate of release can be controlled. Depot injectable formulations are also prepared by entrapping the compounds in liposomes or microemulsions which are compatible with body tissues. Solid dosage forms for oral administration of the present compounds include capsules, tablets, pills, powders, and granules. In such forms, the compound is mixed with at least one inert, therapeutically suitable excipient such as a carrier, filler, extender, disintegrating agent, solution retarding agent, wetting agent, absorbent, or lubricant. With capsules, tablets, and pills, the excipient can also contain buffering agents. Suppositories for rectal administration can be prepared by mixing the compounds with a suitable non-irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperature but fluid in the rectum.
The present compounds can be micro-encapsulated with one or more of the excipients discussed previously. The solid dosage forms of tablets, dragees, capsules, pills, and granules can be prepared with coatings and shells such as enteric and release-controlling. In these forms, the compounds can be mixed with at least one inert diluent and can optionally comprise tableting lubricants and aids. Capsules can also optionally contain opacifying agents which delay release of the compounds in a desired part of the intestinal tract.
Transdermal patches have the added advantage of providing controlled delivery of the present compounds to the body. Such dosage forms are prepared by dissolving or dispensing the compounds in the proper medium. Absorption enhancers can also be used to increase the flux of the compounds across the skin, and the rate of absorption can be controlled by providing a rate controlling membrane or by dispersing the compounds in a polymer matrix or gel. Disorders caused or exacerbated by MCH are treated or prevented in a patient by administering to the patient, a therapeutically effective amount of compound of the present invention in such an amount and for such time as is necessary to achieve the desired result. The term "therapeutically effective amount," refers to a sufficient amount of a compound to effectively emeliorate disorders mediated by MCH, by antagonizing the effect of MCH
through the MCH receptor at a reasonable benefit/risk ratio applicable to any medical treatment. The specific therapeutically effective dose level for any particular patient will depend upon a variety of factors including the disorder being treated and the severity of the disorder; the activity of the compound employed; the specific composition employed; the age, body weight, general health, sex, and diet of the patient; the time of administration, route of administration, rate of excretion; the duration of the treatment; and drugs used in combination or coincidental therapy.
The total daily dose of the present compounds in single or divided doses can be in amounts, for example, from 0.01 to 50 mg/kg body weight or more usually from 0.1 to 25 mg/kg body weight. In general, treatment regimens comprise administration to a patient in need of such treatment from about 10 mg to about 1000 mg of the compounds per day in single or multiple doses.
Determination of Biological Activity Assay for release of intracellular calcium:
Activation of the melanin concentrating hormone receptor (MCHR) by MCH induces the release of Ca"^ from intracellular stores. This intracellular calcium release is measured using a fluorometric imaging plate reader (FLIPR™, Molecular Devices Corp.) in conjunction with the Ca^-sensitive dye Fluo-4. Release of CsX from intracellular stores causes an increase in fluorescence of the dye that is proportional to Ca++ concentration.
Briefly, the assays are performed as follows. HEK293 cells expressing the murine MCHR are plated overnight at 50,000 cells/well in 96-well plates. The following day, culture medium is removed and replaced with 100 μl/well of D-PBS (+glucose and sodium pyruvate) containing 2.5 μM Fluo-4AM (Molecular Probes), 0.01% Pluronic F-127 and 2.5 mM probenecid. Cells are loaded with the Fluo-4 dye for at least one hour at room temp. After loading, the cells are washed gently to remove extracellular dye and 100 μl of D-PBS (+glucose and sodium pyruvate) is added to each well. Test compounds are prepared at 40 μM in 4% DMSO. The cell plate is placed in the FLIPR™ and 50 μl/well of test compound is delivered. The calcium signal is followed for 3 minutes to assay for potential agonist activity by the test compounds. Then 50 μl/well of 12 nM human MCH (in D-PBS containing 0.1% BSA) is added and the ligand-induced calcium signal is followed for an additional 3 minutes. Antagonist activity as determined by the test compounds ability to inhibit MHC induced Ca flux is calculated as % inhibition as described by the following formula: % inhibition = [1 - ((fTC - ffi) ÷ (fMCH - £B))] x 100. fTC = MCH-induced fluorescence in the presence of test compound; fMCH = MCH-induced fluorescence in the absence of test compound; fB = Baseline fluorescence.
MCH (3 nM) usually elicits a response of 30,000 - 40,000 relative fluorescence units (RFU)
with a baseline of ~1000 RFU. Fluo-4 fluorescence is measured at 488 nm, with an exposure of 0.40 sec. and F-stop = 2.0 and the laser set at 0.40-0.60 W constant light output.
The compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence at a dose of 10 μM. Preferably compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence in a range of about 75 to about 100% inhibition of MCH at a dose of 10 μM. More preferably compounds of the present invention inhibit MCH induced fluorescence in a range of about 90 to about 100% inhibition of MCH at a dose of 10 μM.
As antagonists of MCH action upon the MCH receptor, therefore, the compounds of the present invention are useful in treating disorders that are mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor, such as obesity.
Synthetic Methods
Abbreviations which have been used in the descriptions of the scheme and the examples that follow are: m-CPBA for meta-chloroperoxy-benzoic acid; DMF for N,N- dimethylformamide; DMSO for dimethylsulfoxide; ED AC for l-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)- 3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride; HOBT for 1 -hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate; NMP for N- methylpyrrolidinone; THF for tetrahydrofuran; TFA for trifluoroacetic acid; and Pd(dppf)Cl2 for (diphenylphospino)ferrocenyl palladium chloride.
The compounds and processes of the present invention will be better understood in connection with the following synthetic schemes which together illustrate the methods by which the compounds of the invention may be prepared. The synthesis of compounds of formula (I) wherein the groups Rj, R2, R , t, R5, and L are as defined above unless otherwise noted below, are exemplified below.
As shown in Scheme 1, compounds of formula 1 can be reacted with m-CPBA followed by a reaction with phosphorous oxychloride to provide compounds of formula 2. The reaction of compound of formula 1 with m-CPBA are generally carried out in solvents such as but not limited to chloroform, dichloromethane, benzene and the like and are generally done at 25 °C for 20 minutes. The further reaction with phosphorous oxychloride are generally carried out in solvents such as but not limited to chloroform, dichloromethane, benzene and the like and are generally done at 100 °C for 15 minutes. Compounds of formula 2 can then be reacted with amines of formula 3 in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 4. Typical bases used in the reaction include but are not limited to
triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and typical solvents include but not limited to tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and the like. Alternatively, bases such as sodium hydride in solvents such as but not limited to DMF may be utilized in the transformation.
Scheme 2
As shown in Scheme 2, compounds of general formula 5 can be reacted with aldehydes of general formula 6 in the presence of a reducing agent such as but not limited to sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride and sodium triacetoxyborohydride in solvents such as but not limited to THF and the like to provide compounds of formula 4. Reactions are performed at temperatures ranging from 25 to 80 °C and are generally complete between 5 and 96 hours.
Scheme 3
As shown in Scheme 3, compounds of general formula 5 can be reacted with compounds of formula 7 (wherein X is halogen) in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 4. The reactions are typically carried out at 60 °C in solvents including but not limited to acetonitrile, DMF, THF and the like, and reactions are generally complete within 6-18 hours.
Scheme4
As shown in Scheme 4, compounds of formula 5 wherein L is selected from the group consisting of-O-, -S-, or a covalent bond, can be reacted with compounds of formula 8 wherein Ri is alkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, heterocycle and heterocyclealkyl in the presence of a base to provide compounds of formula 9. Typical bases include but are not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like. Reactions are typically carried out at 25 °C for 1-10 hours. Compounds of formula 9 can be reacted with an excess of butyl lithium at -78 °C for 4 hours in solvents including but not limited to THF followed by the reaction with compounds of formula K), wherein R3 is alkyl, to provide compounds of formula 11. Compounds of formula 11 can be reacted with reagents commonly known to those skilled in the art which are useful for the hydrolysis of amides to provide compounds of formula 12. Such reagents and conditions useful for the hydrolysis of amides include but are not limited to sodium or potassium hydroxide in aqueous solvent mixtures such as but not limited to aqueous isopropanol and aqueous tetrahydrofuran and the like. Reactions may or may not need to be heated to 50-70 °C for 1-10 hours.
Scheme 5
As shown in Scheme 5, compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of formula 14 in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like to provide compounds of formula L5. Typical reaction conditions may involve heating to 50 °C in such solvents that include but are not limited to acetonitrile, THF and DMF. Alternatively, sodium hydride in DMF may be utilized for this transformation.
As shown in Scheme 6, compounds of formula 13 can be reacted under the same conditions as described in Scheme 5 with compounds of formula 16 (wherein n is between 0 and 3) to provide compounds of formula 17. Compounds of formula 17 can be further reacted under the same conditions with compounds of formula 18 to provide compounds of formula 19.
Scheme 7
As shown in Scheme 7, compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of formula 8 in the presence of triphenylphosphine and a dialkyl azodicarboxylate such as but not limited to dimethyl azodicarboxylate, diethyl azodicarboxylate, diisopropyl azodicarboxylate and dicyclohexyl azodicarboxylate at 0 °C in solvents such as but not limited to THF, diethyl ether and the like to provide compounds of formula 20.
Scheme 8
As shown in Scheme 8, compounds of formula can be reacted under the same conditions as described in Scheme 7 with compounds of formula 21 to provide compounds of formula 22. Compounds of formula 22 can be further reacted under the same conditions with compounds of formula 1_3 or with compounds of formula j_8 to provide compounds of formula 23.
Scheme 9
As shown in Scheme 9, compounds of formula 13 can be reacted with trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride and a base to provide compounds of formula 24. Typical reactions utilize bases such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like and are carried out in solvents including but not limited to THF and dichloromethane and are generally done at 0 °C. Compounds of formula 24 can be reacted with organozinc reagents represented by the formula R2ZnX (wherein R2 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, and X represents a halogen) in the presence of Pd(dppf)Cl2 to provide compounds of formula 25.
As shown in Scheme 10, compounds of formula 24 can be reacted with carbon dioxide in the presence of Pd(dppf)Cl2 and a base in methanol to provide compounds of formula 26. Compounds of formula 26 can be reacted with compounds of formula R'M (wherein R' is alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, cycloalkyl; and M is lithium or magnesium bromide) to provide compounds of formula 27. Compounds of formula 27 can be reacted with compounds of formula R2X, (wherein R2 is previously described in formula (I), but is not hydrogen; and X is halogen) and a base to provide compounds of formula 28. Typical bases utilized in the transformation of compounds of formula 27 to compounds of formula 28 include but are not limited to sodium hydride in DMF and potassium hydroxide in dimethyl sulfoxide.
As shown in Scheme 11, compounds of formula 29 can be reacted with Dibal-H in THF at 0 °C to provide compounds of formula 30. Compounds of formula 30 can be reacted with compounds of formula R2X using conditions described in Scheme 10 to provide compounds of formula 31.
Scheme 12
Alternatively, compounds of formula 30 can be reacted with methanesulfonyl chloride in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, N-methylmorpholine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to dichloromethane and THF to provide compounds of general formula 30 A. Compounds of formula 30 A can be reacted with alcohols of formula 18 in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to THF, acetonitrile and the like to provide compounds of general formula 3L
Scheme 13
As shown in scheme 13, compounds of formula 26 can also be converted to compounds of formula 32 through hydrolysis of the ester functionality to provide the carboxylic acid which can be converted to the amide 32 through methods commonly known to those skilled in the art. The conversion of the amide 32 to compounds of formula 33 by the addition of organometallic reagents wherein R2 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, and M is magnesium bromide is well known to those skilled in the art.
Scheme 14
As shown in scheme 14, compounds of formula 1 _ can be reacted with sodium hydride in solvents such as but not limited to THF and DMF followed be a reaction with dimethylthiocarbamoyl chloride to provide compounds of formula 34. Compounds of formula 32 can then be heated to provide compounds of formula 35. Compounds of formula 35 can be reacted with potassium hydroxide to hydrolyze the carbamoyl functionality followed by a reaction with R2X with a base to provide compounds of formula 36.
Compounds of formula 36 can be reacted with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid to provide either the compounds of formula 37, wherein n is either 1 or 2. The product of the oxidation with m-CPBA to provide sulfone or the sulfoxide has been established in the literature and is known to those skilled in the art.
Scheme 15
As shown in Scheme 15, compounds of general formula 13 can be reacted with heterocycles of general formula 38 using the same conditions described in Scheme 7 to provide compounds of general formula 39, wherein P is a nitrogen protecting group such as but not limited to acetyl, benzyl, tert-butoxycarbamate, benzylcarbamate and allylcarbamate. Compounds of general formula 39 can be reacted under conditions known to those skilled in the art to remove nitrogen protecting groups to provide compounds of general formula 40. The nitrogen protecting groups used in the compounds described within are specific to the protecting group used for each example and can be found in the description in Greenes "Protecting groups in Organic Chemistry" 3rd ed. 1999, Wiley & Sons, Inc. A typical protecting group used in these examples described within is tert-butoxycarbonyl which can be removed by the reaction with either 4N HCl in dioxane or trifluoroacetic acid in dichloromethane. Compounds of general formula 40 can be reacted with compounds of general formula 41, wherein R7, L2 are defined in formula (I), r is 1, 2, or 3 and X is halogen with a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like in solvents such as but not limited to THF, acetonitrile and the like to provide compounds of general formula 42.
Scheme 16
Scheme 15 42
Alternatively, compounds of general formula 13 can be reacted with compounds of general formula 43 wherein LG is a leaving group such as but not limited to mesyl, triflic, or halogen, in the presence of a base such as but not limited to triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine and the like under heating conditions to provide compounds of general formula 39. Typical conditions for this reaction include heating the reaction mixture to 65 °C in solvents such as but not limited to THF or acetonitrile for 12 to 24 hours. Compounds of general formula 39 can then be reacted under conditions described in Scheme 15 to provide compounds of general formula 42.
The present invention will now be described in connection with certain embodiments which are not intended to limit its scope. On the contrary, the present invention covers all alternatives, modifications, and equivalents as can be included within the scope of the claims. Thus, the following examples, which include preferred embodiments, will illustrate the preferred practice of the present invention, it being understood that the examples are for the purposes of illustration of certain preferred embodiments.
Compounds of the invention were named by ACD/ChemSketch version 5.01 (developed by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) or were given names which appeared to be consistent with ACD nomenclature.
Experimentals
Example 1 8-isopropoxγquinolin-2-amine A reaction vessel of the PE Biosystems Solaris 530™ Organic Synthesizer was charged with PS-PPh resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 176 mg, 4.2 equiv for reactions involving a secondary alcohol; 88 mg, 2.1 equiv for reactions involving a primary alcohol), and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. A solution of 2-amino-8- hydroxyquinoline (1.50 mL; 13.3 mg/mL) in anhydr. THF was added to the vessel and the resultant suspension was shaken for 15 min. Then, a solution of DBAD (0.50 mL; 46 mg/mL; 1.6 equiv) in anhydr. THF was added and the contents of the flask were shaken for 10 min. A solution of isopropylalcohol (0.105 mL, 0.300 mM; 1.25 equiv) in anhydr. THF was then added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 4 h. After this time for reactions involving secondary alcohols, the addition of DBAD and the alcohol
was repeated and the agitation of all reactions was maintained for an additional 6 h. The resultant suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (2.5, 3.5 and 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude product was then treated with 4.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 4 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 : 1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, IH), 7.08 (d, IH), 4.78 (m, IH), 1.49 (d, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 203 [M+H]+.
Example 2 8-(cyclobutyloxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclobutanol for isopropylalcohol. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.94 (d, IH), 7.27 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, IH), 4.82 (m, IH), 2.48 (m, 4H), 1.95 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 215 [M+H]+.
Example 3 8-sec-butoxyquinolin-2 -amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-butanol 1 for isopropylalcohol. lU NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.11 (m, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.38-4.58 (m, IH), 2.00 ( ,
IH), 1.73 (m, IH), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H]+.
Example 4 8-(cyclopentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclopentanol for isopropylalcohol. XH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, IH), 7.04 (d, IH), 4.94 (m, IH), 2.13 (m, 2H), 1.97 (m, 4H), 1.64 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 229 [M+H]+.
Example 5
8-(l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-pentanol 1 for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.19 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.08 (d, IH), 4.60 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.69
(m, IH), 1.51 (m, IH), 1.42 (d, 3H), 1.41 (m, IH), 0.94 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 6
8-( 1 ,2-dimethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methyl-2-butanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 7.11 (m, 2H), 4.34 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 1.38 (d, 3H), 1.05 (d, 3H), 1.01 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 7 8-( 1 -ethy lpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-pentanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.34 (m, IH), 1.93 (m, 2H), 1.79 (m, 2H), 0.99 (t, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 8 8-(2-methoxy-l-methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting l-methoxy-2-propanol for isopropylalcohol. H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.76 (m, IH), 3.93 (dd, IH), 3.60 (dd, IH), 3.41 (s, 3H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 233 [M+H]+.
Example 9 8-(cyclohexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclohexanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.42 (m, IH), 2.10 (m, 2H), 1.90 (m, 2H), 1.76 (m, 2H), 1.62 (m, IH), 1.26-1.47 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 243 [M+H]+.
Example 10 8-((3-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1
substituting 3-methylcyclopentanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.05 (m, 2H), 4.97 (m, 0.6H), 4.90 (m, 0.4H), 2.40 (m, IH), 2.26 (m, 1.6H), 1.93-2.16 (m, 1.8H), 1.81 (m, 0.4H), 1.70 (m, 0.4H), 1.57 (m, 0.4H), 1.46 (m, 0.8H), 1.17 (m, 0.6H), 1.10 (d, 1.2H), 1.03 (d, 1.8H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 243 [M+H]+.
Example 11
8-((2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-methylcyclohexanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm
7.92 (d, IH), 7.28 (d, IH), 7.13 (m, 3H), 4.60 (m, 0.25H), 3.99 (td, 0.75H), 1.91-2.18 (m,
2.25H), 1.85 (m, 1.5H), 1.49-1.77 (m, 2.25H), 1.24-1.47 (m, 2.5H), 1.13 (m, 0.75H), 1.04 (d,
2.25H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 12 8-(2-ethoxy- 1 -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting l-ethoxy-2-propanol for isopropylalcohol. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.23 (d, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.76 (m, IH), 3.92 (dd, IH), 3.64 (dd, IH), 3.57 (m, 2H), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.15 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 247 [M+H]+.
Example 13 8-((3-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methylcyclohexanol for isopropylalcohol. Mixture of isomers. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (m, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, 3H), 4.79 (m, 0.45H), 4.41 (m, 0.55H), 2.11 (m, 2.45H), 1.90 (m, IH), 1.75 (m, 0.45H), 1.28-1.70 (m, 4.1H), 1.06 (m, 0.55H), 0.97 (d, 1.65H), 0.96 (m, 0.45H), 0.92 (d, 1.35H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 14
8-((4-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 4-methylcyclohexanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (m, IH), 7.29 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.62 (m, 0.6H), 4.37 (m, 0.4H), 2.16
(m, 2H), 1.67-1.88 (m, 2.6H), 1.45-1.66 (m, 3.4H), 1.06 (m,"θ"6H), o ( ,"O. ri oM(d, 1.8H), 0.93 (m, 1.2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 15
8-(cycloheptyloxy)quinolin-2-amme The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cycloheptanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC1 ) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.17 (d, IH), 7.07 (m, 2H), 4.60 (m, IH), 2.08 (m, 4H), 1.82 (m, 2H), 1.63 (m, 4H), 1.46 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 16 8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.19 (d, IH), 7.15 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 2.30 (dd, IH), 1.49 (dd, IH), 1.39 (d, 3H), 0.96 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 259 [M+H]+.
Example 17 8-(2-ethyl- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-ethyl-2-pentanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.61 (m, IH), 1.82 (m, IH), 1.66 (m, IH), 1.54 (m, 2H), 1.39 (d, 3H), 1.32 (m, IH), 0.94 (t, 3H), 0.89 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 259 [M+H]+.
Example 18
8-ethoxyquinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 ethanol for isopropylalcohol. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.25 (q, 2H), 1.58 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 189 [M+H]+.
Example 19 8-propoχyquinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1
substituting 1-propanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.13 (t, 2H), 2.01 (m, 2H), 1.09 (t, 3H); MS (DCIΛNH3) m z 203 [M+H]+.
Example 20 8-butoxyquinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-butanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, IH), 4.17 (t, 2H), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.53 (m, 2H), 0.99 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H]+.
Example 21 8-isobutoxyquinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting isobutyl alcohol for isopropylalcohol. LH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 3.92 (d, 2H), 2.37 (m, IH), 1.09 (d, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H]+.
Example 22 8-(cyclobutylmethoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclobutylmethanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.07 (m, 2H), 4.16 (d, 2H), 3.05 (m, IH), 2.25 (m, 2H), 1.78-2.07 (m, 4H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 229 [M+H]+.
Example 23
8-(2-cyclopropylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-cyclopropyletlιanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.22 (d, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.25 (t, 2H), 1.88 (m, 2H), 0.93 (m, IH), 0.48 (m, 2H), 0.15 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 229 [M+H]+.
Example 24 8-(pentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-pentanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.16 (t, 2H), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.43 (m, 4H), 0.93 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 25 8-(2-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-methyl-l-butanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.91 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 1.61 (m, IH), 1.34 (m, IH), 1.09 (d, 3H), 0.97 (t, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 26
8-(3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine , The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting isoamylalcohol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.20 (t, 2H), 1.88 (m, 3H), 0.98 (d, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+Hf.
Example 27 8-(2-(methylthio)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-(methylthio)ethanol for isopropylalcohol. H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.34 (t, 2H), 3.13 (t, 2H), 2.22 (s, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 235 [M+H]+.
Example 28 8-(cyclopentylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclopentylmethanol for isopropylalcohol. 2H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.20 (d, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.04 (d, 2H), 2.65 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.64 (m, 4H), 1.30 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 243 [M+H]+.
Example 29
8-(tetrahydrofuran-3-ylmethoxy)quιnolm-2-amme The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting tetrahydro-3-furanmethanol for isopropylalcohol. ]H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.99 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.25 (d, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.09 (m, 2H), 3.96 (m, 2H), 3.78 (m, 2H), 3.11 (m, IH), 2.28 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 245
Example 30 8-(hexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 1-hexanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.16 (t, 2H), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.49 (m, 2H), 1.35 (m, 4H), 0.91 (m, 3H); MS (DCI H3) m/z 245 [M+H]+.
Example 31 8-(3,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3,3-dimethylbutanol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.23 (t, 2H), 1.99 (t, 2H), 1.01 (s, 9H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 245 [M+H]+.
Example 32
8-(3,3,3-trifluoropropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3,3,3-trifluoropropan-l-ol for isopropylalcohol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.03 (d, IH), 7.36 (t, IH), 7.31 (m, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.01 (d, IH), 4.39 (t, 2H), 3.05 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 33 8-(cyclohexylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting cyclohexylmethanol for isopropylalcohol. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.99 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.04 (d, IH), 3.96 (d, 2H), 2.14 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.73 (m, 3H), 1.37 (m, 2H), 1.22 (m, IH), 1.05 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3)
m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 34 8-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 3-methoxy-3-methyl-l-butanol for isopropylalcohol. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.28 (t, 2H), 3.23 (s, 3H), 2.30 (t, 2H), 1.27 (s, 6H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 261 [M+H]+.
Example 35 8-(2-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-cyclohexylethanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.20 (d, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.21 (t, 2H), 1.94 (m, 2H), 1.78 (m, 2H), 1.71 (m, 2H), 1.65 (m, IH), 1.51 (m, IH), 1.12-1.34 (m, 3H), 1.02 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 271 [M+H]+.
Example 36 8-((lS,4R)-bicyclo[2.2.11hept-2-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 1 substituting 2-norbornanemethanol for isopropylalcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (m, IH), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.10 (m, 1.3H), 3.98 (t, 0.35H), 3.83 (m, 0.35H), 2.64 (m, 0.7H), 2.57 (m, 0.7H), 2.31 (m, 0.35H), 2.24 (m, 1.3H), 1.92 (m, 0.70H), 1.28-1.64 (m, 4.9H), 1.17 (m, 1.65H), 0.76 (m, 0.7H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 269 [M+H]+.
Example 37 8-((l-ethylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine A reaction vessel of the PE Biosystems Solaris 530™ Organic Synthesizer was charged with 230 mg PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 5.50 equiv), and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. A solution of 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (1.200 mL; 16.6 mg/mL; 0.125 mmol) in anhydr. THF was added to the vessel and the resultant suspension was shaken for 15 min. Then, a solution of DBAD (0.50 mL; 46 mg/mL; 1.6 equiv) in anhydr. THF was added and the contents of the flask were shaken for 10 min. A
solution of heptan-3-ol (0.400 mL, 0.400 mM; 1.25 equiv) in anhydr. THF was then added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 2 h. Then a solution of
DBAD (0.38 mL; 46 mg/mL; 1.6 equiv) in anhydr. THF was added. After 10 minutes of shaking a solution of heptan-3-ol (0.400 mL, 0.400 mM; 1.25 equiv) in anhydr. THF was added and the reaction mixture was shaken for 2 h. The last addition of DBAD was then repeated and the reaction mixture was shaken for an additional 4 h. The resultant suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (2.5, 3.5 and 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude product was then treated with
6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 4 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 : 1 mixture of
DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz,
CDC13) δ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.11 (m, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.38 (m,
IH), 1.92 (m, 2H), 1.76 (m, 2H), 1.45 (m, IH), 1.34 (m, 3H), 0.98 (t, 3H), 0.88 (t, 3H); MS
(DCI/NH3) m/z 259 [M+H]+.
Example 38 8-(((l R)- 1 -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (2S)-butan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. lR NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.38-4.58 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H]+.
Example 39
8-( 1 -cyclohexylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amme The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 1-cyclohexylpropan-l-ol for heptan-3-ol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.27 (t, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.23 ( , IH), 1.91 (m, 3H), 1.58-1.84 (m, 5H), 1.03-1.34 (m, 5H), 0.94 (t, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 285 [M+H]+.
Example 40 8-(l-ethyl-2-methylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting 2-methylpentan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 4.23 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 1.96 (m, IH), 1.63-1.84 (m, IH), 0.80-1.12 (m, 9H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 245 [M+H]+.
Example 41 8-((( 1 R,2S)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting trans-2-methylcyclohexanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.13 (m. 3H), 4.59 (m, IH), 2.15 (m, IH), 1.99 (m, 2H), 1.68 (m, 3H), 1.53 (m, IH), 1.38 (m, 2H), 1.04 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 42
8-(((l S)-l ,2-dimethylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (2R)-3-methylbutan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, 2H), 4.34 (m, IH), 2.22 (m, IH), 1.38 (d, 3H), 1.05 (d, 3H), 1.01 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 43 8-(l-(methoxymethyl)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting l-methoxybutan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.56 (m, IH), 3.88 (dd, IH), 3.64 (dd, IH), 3.37 (s, 3H), 1.74-1.95 (m, 2H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 247 [M+H]+.
Example 44 8-(3-ethoxy-l-ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-ethoxypentan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.24 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.68 (m, IH), 3.55 (m, 2H), 3.46 (m, IH), 3.33 (m, IH), 2.20 (m, IH), 1.95 (m, 2H), 1.78 (m, IH), 1.13 (t, 3H), 0.97 (t, 3H); MS (DC17NH3) m/z 275 [M+H]+.
Example 45
8-(((lR)-l,2-dimethylpropyl)oχy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (2S)-3-methylbutan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.07 (m, 2H), 4.32 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 1.38 (d,
3H), 1.05 (d, 3H), 1.01 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 231 [M+H]+.
Example 46 8-((flS)-2-methyl-l-phenylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (lR)-2-methyl-l-phenylpropan-l-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.79 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 2H), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.09 (dd, IH), 6.96 (t, IH), 6.80 (dd, IH), 6.72 (d, IH), 4.93 (d, IH), 2.40 ( , IH), 1.22 (d, 3H), 0.92 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 293 [M+H]+.
Example 47
8-(((lR,2S)-2-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting trans-2-methylcyclopentanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, IH), 7.07 (d, IH), 4.81 (m, IH), 2.21
(m, IH), 2.07 (m, 2H), 1.87 (m, 3H), 1.61 (m, IH), 1.12 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 243
Example 48 8-(l,2-diethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 4-ethylhexan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.47 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.61-1.82 (m, 3H), 1.50 (m, 2H), 1.29 (m, IH), 0.98 (m, 6H), 0.86 ( , 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 273 [M+H]+.
Example 49
8-(( 1 ,4-diethylhexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 6-ethyloctan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.38 (m, IH), 1.78-1.99 (m, 3H), 1.72 (m, IH), 1.40 (m, IH), 1.28 (m, 5H), 1.18 (m, IH), 0.99 (t, IH), 0.79 (m, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 301 [M+H]+.
Example 50
8-(l,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 4-methylpentan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.3 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.67 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.83 (m, IH), 1.53 (m, IH), 1.41 (d, 3H), 0.96 (d, 3H), 0.92 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 245 [M+H]+.
Example 51 8-((( 1 R,2R)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting cis-2-methylcyclohexanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH) 7.07 (d, IH), 3.99 (m, IH), 2.11 (m, 2H), 1.86 (m, 2H), 1.69 (m, IH), 1.56 (m, IH), 1.36 (m, 2H), 1.13 (m, IH), 1.03 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 257 [M+H]+.
Example 52
8-((l-isopropylbut-3-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting 2-methylhex-5-en-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm
7.89 (d, IH), 7.20 (in, 2H), 7.08 (d, IH), 6.96 (m, IH), 5.90 (m, IH), 5.12 (dd, IH), 4.99 (d,
IH), 4.31 (m, IH), 2.69 (m, IH), 2.51 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 1.06 (d, 3H), 1.02 (d, 3H); MS
(DCI/NH3) m/z 257 [M+H .
Example 53 8-(( 1 -isopropylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 2-methylheptan-3-ol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, IH), 7.17 (m, IH), 7.08 (m, 2H), 4.28 (m, IH), 2.19 (m, IH), 1.98 (m, IH), 1.68 (m, IH), 1.46 (m, IH), 1.31 (m, 3H), 1.01 (m, 6H), 0.86 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 273 [M+H]+.
Example 54 8-(l-benzylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-phenylbutan-2-ol for heptan-3-ol. 2H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.86
(d, IH), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, 2H), 7.16 (m, 3H), 6.99 (m, IH), 6.88 (d, IH), 4.59 ( , IH), 3.27 (dd, IH), 2.99 (dd, IH), 1.73-1.97 (m, 2H), 1.02 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 293
Example 55 8-( 1 -(4-fluorophenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting l-(4-fluorophenyl)ethanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.92 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.14 (m, 2H), 7.01 (m, 3H), 6.94 (m, IH), 5.50 (q, IH), 1.84 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 283 [M+H]+.
Example 56 8-(l-cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 1-cyclohexylethanol for heptan-3-ol. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.34 (m, IH), 2.02 (m, IH), 1.92 (m, IH), 1.83 (m, IH), 1.71 (m, 3H), 1.39 (d, 3H), 1.28 (m, 2H), 1.16 (m, IH), 1.03 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 271 [M+H]+.
Example 57 8-( 1 -methyl-2-phenylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting l-phenyl-2-propanol for heptan-3-ol. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.28 (m, 5H), 7.17 (m, 2H), 7.07 (m, 2H), 4.80 (m, IH), 3.39 (dd, IH), 2.99 (dd, IH), 1.45 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 279 [M+H]+.
Example 58 8-(((l S)-l -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting (R)-(-)-2-butanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.11 (m, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 4.51 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.76 (m, IH), 1.43 (d, 3H), 1.01 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 217 [M+H]+.
Example 59 8-(2,3 -dihydro- 1 H-inden-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 2-indanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.49 (m, 3H), 7.31 (m, 2H), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.11 (d, IH), 5.51 (m, IH), 3.59 (d, IH), 3.55 (d, IH), 3.28 (d, IH), 3.24 (d, IH); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 277 [M+H]+.
Example 60 8-(3-methoxybutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 37 substituting 3 -methoxy- 1-butanol for heptan-3-ol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.98 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 4.34 (m, IH), 4.25 (m, IH), 3.70 (m, IH), 3.32 (s, 3H), 2.30 (m, IH), 2.06 (m, IH), 1.24 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 247 [M+H]+.
Example 61 8-(2-(l-naphthyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
37 substituting 1-naphthaleneethanol for heptan-3-ol. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.16 (m, IH), 7.98 (d, IH), 7.86 (m, IH), 7.74 (m, IH), 7.50 (m, 3H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.23 (m, 2H), 7.07 (d, IH), 7.02 (dd, IH), 4.48 (d, 2H), 3.86 (d, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 315 [M+H]+.
Example 62 8-(( 1 -ethyl-4-methylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine A 7.5 mL conical microwave vessel (Personal Chemistry) equipped with a septum cap and a magnetic stirring bar was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 140 mg, 4.40 equiv), 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (15.0 mg, 0.0960 mmol) and DBAD (69 mg, 3.2 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (1.5 mL) was added and contents of the vessel were stirred for 10 min. Then, neat 6-methyl-3- heptanol (4 equiv) was added to the vessel and the resulting suspension was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (150 °C for 330s; 300 W). The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with THF (3x3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 4 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The
residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1:1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.05. (br d, IH), 4.37 (m, IH), 1.91 (m, 2H), 1.78 (m, 2H), 1.55 (m, IH), 1.35 (m, IH), 1.24 (m, IH), 0.98 (t, 3H), 0.87 (m, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 273 [M+H]+.
Example 63
8-((( 1 S ,5 S)-3 ,3 ,5 -trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
62 substituting trans-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexanol for 6-methyl-3-heptanol. 1H NMR (500
MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (br d, IH), 7.28 (d, IH), 7.17 (d, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.05 (br d,
IH), 4.61 (m, IH), 2.15 (m, IH), 1.88 (m, IH), 1.73 (m, IH), 1.56 (m, IH), 1.39 (m, IH),
1.31 (m, IH), 1.02 (m, 6H), 0.96 (d, 3H), 0.91 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 285 [M+H]+.
Example 64 8-(((lR,5S)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 62 substituting cis-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexanol for 6-methyl-3-heptanol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.11 (d, IH), 7.04 (br d, IH), 4.84 (m, IH), 2.52 (m, IH), 2.22 (m, IH), 1.99 (m, IH), 1.52 (m, IH), 1.33 (dd, IH), 1.27 (m, IH), 0.98 (d, 3H), 0.94 (s, 3H), 0.90 (m, IH), 0.88 (s, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 285 [M+H]+.
Example 65 8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 100 mg, 2.2 equiv), 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (22 mg, 0.14 mmol) and DBAD (51 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3 mL) was added and the contents of the vial were shaken for 5 min. Then, a solution of benzyl alcohol (1.25 equiv) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 8 h. The suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (2.5, 3.5 and 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude product was then dissolved in a mixture of DCM (1 mL), thf (1 mL) and MeOH (3 mL) and the solution was added to MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 0.5 g). The resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 1.5 h. The supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed
with DCM (2 mL), MeOH (2 mL), THF (2 mL) and DCM (2 mL). The washed resin was treated with 2 N NH3 in MeOH (4 mL) at room temperature for 1 h. The supernatant was collected and the resin was washed with MeOH (3 mL) and DCM (3 mL). The washes were combined with the collected supernatant. The NH3/MeOH treatment and washes were then repeated. The filtrate and the washes were combined with previously collected and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.50 (m, 2H), 7.37 (m, 2H), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.20 (dd, IH), 7.08 (t, IH), 6.95 (dd, IH), 6.68 (d, IH), 5.38 (s, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 251 [M+H]+.
Example 66 8-((3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting 3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl alcohol for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.88 (d, IH), 7.78 (s, IH), 7.72 (d, IH), 7.56 (d, IH), 7.48 (t, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.12 (t, IH), 6.96 (m, IH), 6.78 (d, IH), 5.42 (s, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 319 [M+H]+.
Example 67
8-((2,4-dimethylbenzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting 2,4-dimethylbenzyl alcohol for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.80 (d, IH), 7.33 (d, IH), 7.19 (dd, IH), 7.11 (t, IH), 7.02 (br s, IH), 6.98 (m, 2H), 6.57 (d, IH), 5.24 (s, 2H), 2.37 (s, 3H), 2.32 (s, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 279 [M+H]+.
Example 68 8-(((3S)-l-benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
62 substituting (R)-l-benzyl-3-pyrroIidinol for benzyl alcohol. ]H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.37 (m, 2H), 7.32 (m, 2H), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.20 (dd, IH), 7.14 (t, IH), 6.90 (dd, IH), 6.72 (d, IH), 5.08 (m, IH), 3.87 (d, IH), 3.80 (d, IH), 3.28 (dd, IH), 3.07 (dd, IH), 2.95 (m, IH), 2.83 (m, IH), 2.38 (m, IH), 2.24 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 320 [M+H]+.
Example 69 8-(((3R)- 1 -benzylpyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting (S)-l-benzyl-3-pyrrolidinol for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.37 (m, 2H), 7.32 (m, 2H), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.20 (dd, IH), 7.14 (t, IH), 6.90 (dd, IH), 6.72 (d, IH), 5.08 (m, IH), 3.87 (d, IH), 3.80 (d, IH), 3.28 (dd, IH), 3.07 (dd, IH), 2.95 (m, IH), 2.83 (m, IH), 2.38 (m, IH), 2.24 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 320
Example 70 8-((l-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oχy)quinolin-2 -amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting l-benzyl-4-hydroxypiperidine for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.84 (d, IH), 7.33 (m, 5H), 7.22 (dd, IH), 7.15 (t, IH), 7.04 (dd, IH), 6.72 (d, IH), 4.54 (m, IH), 3.69 (s, 2H), 3.00 (m, 2H), 2.47 (m, 2H), 2.16 (m, 2H), 2.06 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 334 [M+H]+.
Example 71 8-((l,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
65 substituting 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-ol for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.85 (m, IH), 7.18 (m, 2H), 7.01 (dd, IH), 6.74 (m, IH), 5.16 (m, IH), 4.55 (m, IH), 2.19 (m, 2H), 2.04 (m, IH), 1.72 (m, IH), 1.66 (s, 3H), 1.55 (s, 3H), 1.44 (d, 3H); MS
(DCI/NH3) m/z 271 [M+H]+.
Example 72 8-((( 1 R)- 1 -phenylethyl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting (S)-(-)-l-phenylethanol for benzyl alcohol. lB NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.32 (m, 2H), 7.23 (m, IH), 7.13 (dd, IH), 7.01 (t, IH), 6.84 (dd, IH), 6.76 (m, IH), 5.51 (m, IH), 1.82 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 265 [M+H]+.
Example 73
8-(l-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting α-methyl-4-trifluoromethylbenzyl alcohol for benzyl alcohol. !H NMR (500
MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.85 (d, IH), 7.60 (m, 4H), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.02 (t, IH), 6.82 (m, IH), 6.75 (d, IH), 5.61 (q, IH), 1.81 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 333 [M+H]+.
Example 74
8-(2-( 1 -methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 65 substituting l-methyl-2-pyrrolidineethanol for benzyl alcohol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.85 (d, IH), 7.23 (dd, IH), 7.17 (t, IH), 7.03 (m, IH), 6.75 (d, IH), 4.35 (m, IH), 4.21 (m, IH), 3.50 (m, IH), 3.02 (m, IH), 2.59 (s, 3H), 2.53 (m, 2H), 2.17 (m, 2H), 1.98 (m, IH), 1.84 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 272 [M+H]+.
Example 75 8-(2-(2-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)-quinolin-2-amine
A 20 mL scintillation vial equipped with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 132 mg, 4.2 equiv) 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (151 mg, 10 equiv) and DBAD (70 mg, 3.2 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (2.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 5 min. Then, a solution of diethylene glycol (10 mg, 0.094 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added to the vial and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 8 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with DMA (6 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting solid was washed with EtOAc (2.5 mL) DMF (3.0 mL) and hexanes (50 mL in a few portions) and dried under high vacuum at room temperature for 12 h to afford the product. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.06 (d, 2H), 7.34 (t, 2H), 7.29 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, 2H), 7.06 (d, 2H), 4.36 (m, 4H), 4.08 (m, 4H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 391 [M+H]+.
Example 76
8-((4-(((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)methyl)benzyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL scintillation vial equipped with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPb.3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 132 mg, 4.2 equiv) 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (151 mg, 10 equiv) and DBAD (70 mg, 3.2 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (2.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 5 min. Then, a solution of 1,4-benzenedimethanol (10 mg, 0.072 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added to the vial and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 8 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with DMA (6 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting solid was washed with
EtOAc (2.5 mL) and hexanes (50 mL in a few portions) and dried under high vacuum at room temperature for 12 h to afford the product. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.14 (d, 2H), 7.52 (br s, 4H), 7.46 (t, 2H), 7.33 (m, 2H), 7.08 (m, 2H), 7.07 (d, 2H), 5.18 (s, 4H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 423 [M+H]+.
Example 77 3 -((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propan- 1 -ol A 100 mL round bottom flask equipped with a stirring bar and a pressure equalized dropping funnel, under N2, was charged with 0.652 g (2 equiv) PPh3, 0.200 g (1.25 mmol) of 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline and 10 mL of anhydr. THF. After stirring for 10 min, 1.8 mL of 1,3-propanediol (20 equiv) was added in one portion. The reaction mixture was then cooled to 0 °C and 0.43 g (1.5 equiv) of DBAD in 15 mL THF was added dropwise over 10 minutes. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature and stirring was maintained for 8 h. Then, 0.652 g (2 equiv) of PPh3 was added, the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and 0.431 g (1.5 equiv) of DBAD in 15 mL THF was added dropwise over 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. The solution was evaporated in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in DMA (25 mL) and MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 4.5 g) was added. The resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 12 h. The supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed with DMA (2x20 mL), MeOH (2x20 mL) and DMA (20 mL). The washed resin was treated with a mixture of 2 N NH3 in MeOH (15 mL) and DMA (5 mL) at room temperature for 1 h. The solution was drained and the basic wash was repeated two more times. Filtered solutions were combined. The resin was washed with MeOH (20 mL), DMA (20 mL), MeOH (20 mL), DMA (20 mL) and MeOH (20 mL). The washes were combined with the previously collected solutions and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude material was purified by silica gel column chromatography (20:1 EtOAc/MeOH + 2% TEA) to afford the title compound. 2H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.87 (d, IH), 7.29 (dd, IH), 7.17 (t, IH), 7.12 (dd, IH), 6.72 (d, IH), 4.34 (t, 2H), 3.99 (t, 2H), 2.12 (m, 2H), MS (DCI NH3) m z 219 [M+H]+.
Example 78 8-(3-((2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 L scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh resin
(Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 60 mg, 2.4 equiv), 8-hydroxyquinaldine (1.5 equiv) and DBAD (28 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3 mL) was added and the contents of the vial were shaken for 5 min. Then, a solution of 3-((2- aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propan-l-ol (16.7 mg/mL; 1.0 mL, 0.077 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1
mL) was added and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 8 h. Then, PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 60 mg, 2.4 equiv) and DBAD (28 mg, 1.6 equiv) were added and the mixture was agitated at room temperature for additional 6 h. The suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (3x3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 6 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.60 (d, IH), 7.90 (d, IH), 7.69 (t, IH), 7.65 (d, IH), 7.53 (d, IH), 7.46 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.24 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 4.65 (br t, 2H), 4.48 (br t, 2H), 3.10 (s, 3H), 2.64 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 360 [M+H]+.
Example 79 8-(3-(quinolin-8-yloxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 8-hydroxyquinoline for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. XH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.93 (m, IH), 8.50 (br d, IH), 8.37 (d, IH), 7.67 (dd, IH), 7.59 (m, 2H), 7.49 (m, 2H), 7.40 (t, IH), 7.33 (dd, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 4.57 (br t, 2H), 4.50 (br t, 2H), 2.50 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 346 [M+H]+.
Example 80 8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
78 substituting 2,8-quinolinediol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1HNMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.88 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.42 (m, IH), 7.23 (dd, IH), 7.10 (m, 3H), 6.52 (d, IH), 4.59 (t, 2H), 4.35 (t, 2H), 2.45 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 362 [M+H]+.
Example 81 6-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 2,6-quinolinediol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. XH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.80 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.22 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, 2H), 6.48 (d, IH), 4.45 (t, 2H), 4.27 (t, 2H), 2.33 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 362 [M+H]+.
Example 82
4-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 2-aminoquinolin-4-ol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.96 (m, IH), 7.76 (m, IH), 7.61 (d, IH), 7.50 (m, 2H), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.44 (m, IH), 4.55 (m, 4H), 2.54 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 361 [M+H]+.
Example 83 8-(3-phenoxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
78 substituting phenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.28 (m, 2H), 7.13 (d, IH), 6.93 (m, 3H), 4.44 (t, 2H), 4.24 (t, 2H), 2.34 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 295 [M+H]+.
Example 84 8-(3-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 78 substituting 3,5-dichlorophenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1HNMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.99 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.24 (m, IH), 7.14 (m, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 6.86 (m, IH), 6.82 (m, 2H), 4.35 (m, 4H), 2.49 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 363 [M+H]+.
Example 85 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan- 1 -ol
Example 85A 8-( 1 -Methyl-but-3 -enyloxy)-quinolin-2-ylamine To a 100 mL round bottom flask equipped with a stirring bar, under N2, was added
6.25 g (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 2 equiv) of PS-PPh3 resin followed by 35 mL of anhydr. THF. After stirring for 30 min, 1.5 g (9.38 mmol) of 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline was added, followed by 1.16 mL (1.7 equiv) of 4-penten-2-ol. The reaction mixture was then cooled to 0 °C and 2.70 g (1.25 equiv) of DBAD was added in two portions. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature and stirring was maintained for 12 h. Then, 0.40 mL (0.5 equiv) of 4-penten-2-ol, 1.26 g (4.81 mmol) of PPh3, and 1.5 g (0.7 equiv) of DBAD were added and stirring was maintained for an additional 12 h. The supernatant was then decanted and the resin was washed several times with CHC13 and MeOH. The supernatant and the washes were combined, filtered through a layer of Celite®,
and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in a 50% tfa/CH2Cl2 (10 mL) and left overnight at room temperature. The resulting solution was then diluted with CHzCl2 (30 mL) and slowly quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3. The organic layer was separated and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting residue was dissolved in a 3:1 mixture of MeOH/DMSO and purified by preparative HPLC. The homogeneous fractions were combined, evaporated in vacuo, re-dissolved in EtOAc and free-based with saturated aqueous NaHCO3. The organic layer was separated, dried over anhydr. Na2SO , and evaporated in vacuo to afford 8- (l-methyl-but-3-enyloxy)-quinolin-2-ylamine. H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.22 (m, 2H), 7.03 (m, IH), 6.74 (d, IH), 6.37 (s, 2H), 5.79-6.02 (m, IH), 5.00-5.21 (m, 2H), 4.68 (m, IH), 2.35 (m, 2H), 1.28 (d, 3H), MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 229 [M+H]+.
Example 85B 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan- 1 -ol To a 100 mL round bottom flask containing 1.33 g (5.83 mmol) of 8-(l-methyl-but-
3-enyloxy)-quinolin-2-ylamine was added 30 mL of a IM solution of BH3/THF via syringe. Following the addition, the flask was fitted with a reflux condenser and the solution heated to reflux under N2 for 6 h. The reaction mixture was then allowed to cool to room temperature and the volatiles were removed in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in Et2O. Following the addition of 2.25 g (56.2 mmol) of solid NaOH, the mixture was placed in an ice bath. The flask was then fitted with a dropping funnel and 10 mL of 20% aqueous H2O2 was added dropwise with stirring. The funnel was then replaced with a reflux condenser and the mixture heated to reflux with stirring overnight. The resulting suspension was allowed to cool to room temperature and was filtered through a fritted funnel. The ethereal layer was separated, washed thoroughly with 1 M NaHSO4, dried over anhydr. Na2S04 and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude material was purified by silica gel column chromatography (5- 25% MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.82 (d, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, IH), 6.97 (m, IH), 6.73 (d, IH), 6.33 (s, IH), 4.62 (m, IH), 4.46 (m, IH), 3.44 (m, 2H), 1.76 (m, IH), 1.59 (m, 3H), 1.27 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 247 [M+H]+.
Example 86 8-(l-methyl-4-((2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh3 resin
(Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 90 mg, 4.4 equiv), 8-hydroxyquinaldine (1.5 equiv) and DBAD (22 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3 mL) was added and the contents of the vial were shaken for 5 min. Then, a solution of 4-((2- aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan-l-ol (15.0 mg/mL; 1.0 mL, 0.061 mmol)) in anhydr. THF (1
mL) was added and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 6 h. Following this, DBAD (22 mg, 1.6 equiv) was added and the mixture was agitated at room temperature for additional 12 h. The suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (3x3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 6 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1:1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.61 (d, IH), 7.89 (d, IH), 7.66 (m, 2H), 7.52 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, 3H), 7.15 (m, 2H), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.31 (m, 2H), 3.09 (s, 3H), 2.36 (m, 2H), 2.05 (m, 2H), 1.44 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 388 [M+H]+.
Example 87 8-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
86 substituting 2-aminoquinolin-8-ol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.99 (m, 2H), 7.33 (m, 3H), 7.22 (m, 2H), 7.14 (m, 2H), 7.08 (m, IH), 4.69 (m, IH), 4.23 (m, 2H), 1.88 (m, 4H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 389 [M+H]+.
Example 88 8-(4-(3,5-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting 3,5-dichlorophenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.21 (dd, IH), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.84 (m, IH), 6.64 (m, 2H), 4.68 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.95 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 391 [M+H]+.
Example 89
8-(4-(2-methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting 2-methoxyphenol for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.02 (d, IH), 6.86 (m, 4H), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.06 (m, 2H), 3.80 (m, 3H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.02 (m, 3H), 1.45 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 353 [M+H]+.
Example 90
8-(l-methyl-4-(quinolin-7-yloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amme The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting 7-hydroxyquinoline for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. HNMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.99 (br d, IH), 8.61 (d, IH), 7.88 (d, IH), 7.83 (d, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.65 (dd, IH), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.01 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.22-4.42 (m, 2H), 2.19 (m, 2H), 2.00 (m, 2H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m z 373 [M+H]+.
Example 91 N-(4-((4-((2-ammoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetamide
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 86 substituting acetaminophen for 8-hydroxyquinaldine. H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.90 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, 3H), 7.11 (m, IH), 6.95 (d, IH), 6.61 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.91 (m, IH), 2.14 (s, 3H), 2.08 (m, IH), 1.95 (m, 3H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 380 [M+H]+.
Example 92 methyl 3 -((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate A reaction vessel of the PE Biosystems Solaris 530™ Organic Synthesizer was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 120 mg, 4.4 equiv), and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. A solution of methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate (0.41 mL, 0.30 mM) in anhydr. THF (DMA for phenols not soluble in THF) was added to the vessel and the resultant suspension was shaken for 15 min. Then, a solution of DBAD (0.50 mL; 60 mg/mL) in anhydr. THF was added and the contents of the flask were shaken for 10 min. A solution of 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan-l-ol (1.50 mL; 13.3 mg/mL) in anhydr. THF was then added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 3 h. The addition of DBAD and the phenol was then repeated and the agitation maintained for an additional 3 h. The addition of DBAD was then repeated one more time and the agitation was maintained for an additional 6 h. The resultant suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (2.5, 3.5 and 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude product was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 12 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo.
The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1:1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC.
XH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.56 (m, IH), 7.46 (m, IH), 7.29 (m, 2H),
7.19 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.00 (m, 2H), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.11 (m, IH), 4.04 (m, IH), 3.89 (s,
3H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DC17NH3) m z 381 [M+H]+.
Example 93 8-( 1 -methyl-4-(3 ,4,5-trimethylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 3,4,5-trimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.92 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.98 (d, IH), 6.48 (s, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.01 (m, IH), 3.95 (m, IH), 2.20 (s, 6H), 2.19 (m, IH), 2.06 (s, 3H), 1.95 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 365 [M+H]+.
Example 94 methyl 0-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)-L-tyrosinate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl methyl L-tyrosinate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.09 (d, 2H), 6.84 (d, 2H), 4.85 (m, IH), 4.23 (t, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 3.68 (s, 3H), 3.01 (m, 2H), 1.80-2.04 (m, 4H), 1.39 (d, 3H); MS (DCI H3) m/z 424 [M+H]+.
Example 95 8-( 1 -methyl-4-(2-naphthyloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-naphthol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.83 (d, IH), 7.70 (m, 2H), 7.61 (d, IH), 7.40 (m, IH), 7.30 (m, 2H), 7.12 (m, 2H), 7.06 (m, IH), 6.97 (dd, IH), 6.86 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.20 (m, IH), 4.11 (m, IH), 2.24 (m, IH), 2.05 (m. 3H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 373 [M+H]+.
Example 96 l-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-3-methylphenyl)ethanone The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting l-(4-hydroxy-3-methylphenyl)ethanone for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.74 (dd, IH), 7.67 (m, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.95 (d, IH), 6.80 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.17 (m, IH), 4.07 (m, IH), 2.51 (s, 3H), 2.19 (m, IH), 2.10 (s, 3H), 2.04 (m, 3H), 1.49 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 379 [M+H]+.
Example 97 8-(l-methyl-4-(4-propylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-propylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, 3H), 6.74 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.00 (m, 2H), 2.49 (t, 2H), 2.20 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 3H), 1.59 (m, 2H), 1.46 (d, 3H), 0.91 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 365 [M+H]+.
Example 98
8 -(4-(3 -isopropylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-isopropylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.14 (m, 2H), 7.01 (d, IH), 6.78 (m, IH), 6.72 (m, IH), 6.66 (m, IH), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.02 (m, 2H), 2.83 (t, IH), 2.21 (m, IH),
1.88-2.10 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H), 1.22 (d, 3H), 1.21 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 365 [M+H]+.
Example 99 8-(4-(4-chloro-3 -fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-chloro-3-fluorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.31 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, 2H), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.55 (m, 2H), 4.69 (m, IH), 4.04 (m, IH), 3.95 (m, IH), 2.19 (m, IH), 1.87-2.09 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 375 [M+H]+.
Example 100 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Exampl 92 substituting 2-hydroxybenzonitrile for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.46 (m, 2H), 7.33 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, 2H), 6.96 (m, 2H), 6.91 (m, IH), 4.78 (m, IH), 4.22 (m, IH), 4.12 (m, IH), 2.23 (m, IH), 1.96-2.18 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DC1YNH3) m/z 348 [M+H]+.
Example 101 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting salicylamide for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 7.76 (dd, IH), 7.35-7.58 (m, 6H), 7.10 (d, IH), 7.01 (m, IH), 4.87 (m, IH), 4.18 (m, 2H), 1.84-2.05 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 366 [M+H]+.
Example 102 8-(l-methyl-4-(2-methyl-5-nitrophenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. XH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.96 (d, IH), 7.68 (dd, IH), 7.59 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.21 (m, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.01 (d, IH), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.15 (m, IH), 4.08 (m, IH), 2.25 (m, IH), 2.21 (s, 3H), 2.12 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 2H), 1.49 (d, 3H); MS (DCI7NH3) m/z 382 [M+H]+.
Example 103 8-(4-((5-amino- 1 -naphthyl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 5-amino-l-naphthol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !HNMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d5) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.56 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.39 (m, 2H), 7.27 (t, IH), 7.17 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.87 (d, IH), 6.80 (d, IH), 4.92 (m, IH), 4.17 (m, 2H), 2.04 (m, 4H), 1.45 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 388 [M+H]+.
Example 104
8-(4-(3 -anilinophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-anilinophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.91 (d, IH), 7.26 (m, 3H), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, IH), 7.07 (m, 3H), 6.94 (d, IH), 6.91 (m, IH), 6.60 (m, IH), 6.52 (t, IH), 6.37 (m, IH), 4.69 (m, IH), 4.03 (m, IH), 3.96 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 1.96 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 414 [M+H]+.
Example 105 8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methoxyphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-4-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 7.15 (d, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.85
(m, 2H), 6.70 (dd, IH), 4.76 (m, IH), 4.07 (m, IH), 4.01 (m, IH), 3.73 (s,' 3H), 2.2Ϊ(m, IH), 2.00 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 387 [M+H]+.
Example 106
8-(4-((4-methoxy- 1 -naphthyl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-methoxy-l-naphthol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 8.13 (m, IH), 8.02 (m, IH), 7.82 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, IH), 7.37 (m, IH), 7.18 (t, IH), 7.07 (m, 2H), 6.92 (d, IH), 6.65 (m, 2H), 4.76 (m, IH), 4.21 (m, IH), 4.12 (m, IH), 3.92 (s, 3H), 2.24 (m, IH), 2.10 (m, 3H), 1.51 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 403 [M+H]+.
Example 107 methyl (4-((4-((2-aminoquinolιn-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetate
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl (4-hydroxyphenyl)acetate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H MR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, 3H), 6.98 (d, IH), 6.76 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.04 (m, IH), 3.97 (m, IH), 3.68 (s, 3H), 3.53 (s, 2H), 2.17 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 4H), 1.47 (d, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 395 [M+H]+.
Example 108 ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methylbenzoate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting ethyl 2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzoate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.51 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.17 (m, 3H), 7.00 (d, IH), 6.83 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.29 (m, 2H), 4.10 (m, IH), 4.04 (m, IH), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.19 ( , IH), 2.02 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H), 1.34 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 409 [M+H]+.
Example 109 8-(4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-bromo-2-fluorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. ]H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.95 (d, IH), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, 3H), 6.98 (d, IH), 6.81 (m, IH), 4.72 (m, IH), 4.13 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.03 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 419/421 [M+H]+.
Example 110 N-(3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)urea The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting N-(3-hydroxyphenyI)urea for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.42 (m, IH), 7.17 (t, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.06 (t, IH), 6.77 (dd, IH), 6.42 (dd, IH), 4.86 (m, IH), 3.97 (m, 2H), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.88 (m, 3H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 381 [M+H]+.
Example 111 4-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)butan-2-one The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-one for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. lH NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.19 (d, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.03 (m, 2H), 6.98 (m, IH), 6.74 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 2.80 (t, 2H), 2.70 (t, 2H), 2.19 (m, IH), 2.12 (s, 3H), 1.95 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 393 [M+H]+.
Example 112 ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting ethyl salicylate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.71 (dd, IH), 7.40 (m, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.16 (m, 2H), 7.00 (d, IH),
6.94 (d, IH), 6.90 (td, IH), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.30 (m, 2H), 4.14 (m, IH), 4.08 (m, IH), 2.20 (m, IH), 1.93-2.15 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H), 1.34 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 395 [M+H]+.
Example 113 methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methoxybenzoate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.25 (d, IH), 7.17 (dd, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 6.99 (m, 2H), 6.89 (d, IH), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.09 (m, IH), 4.03 (m, IH), 3.82 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 2.18 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 411 [M+H]+.
Example 114 8-(4-(4-amino-2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-amino-2-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 6.96 (d, IH), 6.90 (d, IH), 6.75 (dd, IH), 4.88 (m, IH), 4.00 (m, 2H), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.88 (m, 3H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 372 [M+H]+.
Example 115
1 -(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)ρentyl)oxy)phenyl)propan- 1 -one The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting l-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-l-one for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.86 (m, 2H), 7.30 (t, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.97 (d, IH), 6.82 (m, 2H), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.14 (m, IH), 4.06 (m, IH), 2.92 (q, 2H), 2.22 (m, IH), 2.07 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 2H), 1.47 (d, 3H), 1.20 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 379 [M+Hf.
Example 116
8-(4-(3 -(diethylamino)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-(diethylamino)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.21 (dd, IH), 7.15 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 6.90 (m, 2H), 6.74 (m, IH), 4.69 (m, IH), 4.11 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 3.49 (m, 4H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.08 (m, IH), 1.93 (m, 2H), 1.46 (d, 3H), 1.11 (t, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 394 [M+H]+.
Example 117
8-(4-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting isoquinolin-5-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 9.43 (s, IH), 8.36 (d, IH), 8.26 (d, IH), 7.89 (d, IH), 7.74 (t, IH), 7.68 (d, IH), 7.29 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, 2H), 6.93 (d, IH), 4.77 (m, IH), 4.43 (m, IH), 4.28 (m, IH), 2.06-2.34 (m, 4H), 1.51 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 374 [M+H]+.
Example 118
8-(4-(l,r-biphenyl-3-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting l,l'-biphenyl-3-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.90 (d, IH), 7.54 (m, 2H), 7.41 (m, 2H), 7.30 (m, 3H), 7.13 (m, 3H), 7.02 (t, IH), 6.98 (d, IH), 6.81 (dd, IH), 4.72 (m, IH), 4.12 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 399 [M+H]+.
Example 119 8-(4-(2-fluoro-5 -methylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-fluoro-5-methylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.15 (d, IH), 7.00 (d, IH), 6.86 (dd, IH), 6.74 (dd, IH), 6.61 (m, IH), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.11 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, IH), 2.26 (s, 3H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 355 [M+H]+.
Example 120 8-(4-(2-ethoxy-5-(( 1 E)-prop- 1 -enyl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2-ethoxy-5-[(lE)-prop-l-enyl]phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.27 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, 2H), 7.01 (d, IH), 6.88 (d, IH), 6.75 (m, 2H), 6.28 (dd, IH), 6.06 (m, IH), 4.77 (m, IH), 4.06 (m, 4H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.84 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H), 1.36 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 407 [M+H]+.
Example 121 methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-4-methoxybenzoate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting methyl 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.92 (d, IH), 7.75 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.16 (m, 2H), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.45 (d, IH), 6.41 (dd, IH), 4.77 (m, IH), 4.15 (m, IH), 4.06 (m, IH), 3.81 (s, 3H), 3.78 (s, 3H), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.05 (m, 3H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 411 [M+H]+.
Example 122 8-(4-(2-benzylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2-benzylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ ppm 7.91 (d, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.17 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, 4H), 7.07 (d, IH), 7.02 (dd, IH), 6.98 (d, IH), 6.82 (m, 2H), 4.62 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 3.87 (m, 2H), 2.10 (m, IH), 2.00 (m, IH), 1.88 (m, 2H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 413 [M+H]+.
Example 123 8-(4-(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-fluoro-4-nitrophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.98 (m, 2H), 7.84 (dd, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, IH), 6.94 (d, IH), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.31 (m, IH), 4.20 (m, IH), 2.11-2.31 ( , 2H), 2.04 (m, 2H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 386 [M+H]+.
Example 124 5-acetyl-2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 5-acetyl-2-hydroxybenzamide for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.66 (d, IH), 8.06 (dd, IH), 7.96 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.04 (d, IH), 6.97 (d, IH), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.38 (m, IH), 4.26 (m, IH), 2.58 (s, 3H), 2.24 (m, 2H), 1.92-2.13 (m, 2H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 408 [M+H]+.
Example 125
8-(4-(2,3-dihydro-lH-inden-5-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting indan-5-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.28 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.03 (d, IH), 7.00 (d, IH), 6.70 (d, IH), 6.60 (dd, IH), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.00 (m, 2H), 2.82 (m, 4H), 2.19 (m, IH), 1.88-2.09 (m, 5H), 1.46 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 363 [M+H]+.
Example 126 8-(4-(4-( 1 H-imidazol- 1 -yl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-(lH-imidazol-l-yl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.89 (s, IH), 7.93 (d, IH), 7.45 (s, IH), 7.38 (s, IH), 7.32 (m, 3H), 7.20
(dd, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 6.96 (m, 2H), 4.69 (m, IH), 4.21 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, IH), 2.23 (m, IH), 2.12 (m, IH), 1.94 (m, 2H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 389 [M+H]+.
Example 127
8-(4-(dibenzorb,d1furan-2-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting dibenzo[b,d]furan-2-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.86 (m, IH), 7.79 (d, IH), 7.51 (m, IH), 7.42 (m, IH), 7.34 (d, IH), 7.28 (m, 3H), 7.11 (d, 2H), 6.90 (dd, IH), 6.84 (d, IH), 4.74 (m, IH), 4.20 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, IH), 2.23 (m, IH), 2.04 (m, 3H), 1.49 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 413 [M+H]+.
Example 128 8-(4-((2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-l-benzofuran-7-yl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,2-dimethy 1-2,3 -dihydro- l-benzofuran-7-ol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1HNMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.94 (d, IH), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.18 ( , IH), 7.14 (d, IH), 7.02 (d, IH), 6.72 (m, 3H), 4.72 (m, IH), 4.11 (m, 2H), 2.99 (s, 2H), 2.19 (m, IH), 1.97 (m, 3H), 1.47 (s, 3H), 1.47 (s, 3H), 1.44 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 393 [M+H]+.
Example 129 8 -(4-(2-isoxazol-5 -ylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2-isoxazol-5-ylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. JH NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 8.20 (d, IH), 7.92 (d, IH), 7.86 (dd, IH), 7.34 (m, IH), 7.23 (t, IH), 7.16 (dd, IH), 7.05 (d, IH), 6.97 (m, 3H), 6.68 (d, IH), 4.71 (m, IH), 4.26 (m, IH), 4.15 (m, IH), 1.98-2.26 (m, 4H), 1.48 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 390 [M+H]+.
Example 130 6-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)- 1 ,3 -benzoxathiol-2-one The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92substituting 6-hydroxy- 1 ,3 -benzoxathiol-2-one for methyl 3 -hydroxybenzoate . ] H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.97 (d, IH), 7.32 (t, IH), 7.21 (dd, IH), 7.17 (d, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 6.95 (d, IH), 6.74 (dd, IH), 6.71 (d, IH), 4.70 (m, IH), 4.09 (m, IH), 4.00 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 397 [M+H]+.
Example 131 8-(4-(2-methoxy-4-propylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-allyl-2-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, 2H), 7.01 (d, IH), 6.79 (m, IH), 6.66 (m, 2H), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 2.50 (m, 2H), 2.21 (m, IH), 1.99 (m, 3H), 1.61 (m, 2H), 1.45 (d, 3H), 0.92 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 395 [M+H]+.
Example 132 8-(4-(2-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-3-(triflouromethyl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d5) δ ppm 8.35 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 4H), 7.39 (m, 2H), 7.12 (d, IH), 4.89 (m, IH), 4.20 (m, 2H), 1.83-2.08 (m, 4H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 426 [M+H]+.
Example 133
8-(l-methyl-4-(2-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting o-cresol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H), 7.39 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, 3H), 6.87 (d, IH), 6.76 (m, IH), 4.89 (m, IH), 4.02 (m, 2H), 2.06 (m, 3H), 1.82-2.04 (m, 4H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z
Example 134 8-(l-methyl-4-(3-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting w.-cresol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. ]H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.40 (m, IH), 7.10 (m, 2H), 6.70 (d, IH), 6.64 (m, 2H), 4.86 (m, IH), 3.97 (m, 2H), 2.22 (m, 3H), 2.00 (m, IH), 1.87 (m, 3H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 337 [M+H]+.
Example 135
8-(l-methyl-4-(4-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting o-cresol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. lU NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 3H), 7.40 (m, 2H), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, IH), 6.74 (m, IH), 4.83 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 2.22 (m, 3H), 1.76-2.08 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 337 [M+H]+.
Example 136 8-(4-(2-chloro-5 -methylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-4-methylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.21 (d, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.91 (m, IH), 6.72 (m, IH), 4.89 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, 2H), 2.26 (m, 3H), 1.94 (m, 4H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 371 [M+H]+.
Example 137 4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenol The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting hydroquinone for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- D6) δ ppm 8.38 (m, 1 H), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.40 (m, 1 H), 7.14 (m, 1 H), 6.69 (m, 2H), 6.62 (m, 2H), 4.85 (m, 1 H), 3.90 (m, 2H), 3.69 (m, 1 H), 1.96 (m, 1 H), 1.83 (m, 3 H), 1.39 (m, 3 H) ; MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 339 [M+H]+.
Example 138 8-(4-(3 -mefhoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz,
DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.13 (m, 2H), 6.47 (m, 2H), 6.38 (m, IH), 4.84 (m, IH), 4.01 (m, 2H), 3.69 (m, 3H), 1.78-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z
Example 139 8-(4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 4-methoxyphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.13 (d, IH), 6.78 (m, 4H), 4.84 (m, IH), 3.97 (m, 2H), 3.68 (m, 3H), 1.73-2.07 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 353 [M+H]+.
Example 140 8-(4-(2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-flourophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. *H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d5) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.12 (m, 4H), 6.89 (m, IH), 4.86 (m, IH), 4.09 (m, 2H), 1.73-2.10 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 341 [M+H]+.
Example 141 8-(4-(3 -fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-flourophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- de) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.70 (m, 3H), 4.65-4.94 (m, IH), 3.90-4.14 (m, 2H), 1.73-2.07 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 341 [M+H]+.
Example 142 8-f 4-f 4-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 4-flourophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. JH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.05 (m, 2H), 6.71-6.94 (m, 2H), 4.87 (m, IH), 3.85-4.13 (m, 2H), 1.71-2.08 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 341 [M+Hf.
Example 143 8-(4-(2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- de) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.27 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, 2H), 6.92 (m, 2H), 4.77-5.00 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, 2H), 1.78-2.12 (m, 4H), 1.41 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 358 [M+H]+.
Example 144 8-(4-(3 -chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.37 (m, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, IH), 6.93 (m, 2H), 6.82 (m, IH), 4.73-4.94 (m, IH), 3.79,-4.12 (m, 2H), 1.69-2.07 (m, 4H), 1.40 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3)
Example 145
8-(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-chlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1HNMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.27 (m, 2H), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.88 (m, 2H), 4.88 (m, IH), 3.89-4.15 (m, 2H), 1.68-2.06 ( , 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 358 [M+H]+.
Example 146 8-(4-(2-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2-bromophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.50 (m, 3H), 7.40 (m, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.13 (d, IH), 7.08 (m, IH), 6.84 (m, IH), 4.89 (m, IH), 4.12 (m, 2H), 1.76-2.10 (m, 4H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 402 [M+H]+.
Example 147 8-(4-(3 -bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-bromophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.08 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, IH), 6.87 (m, IH), 4.86 (m, IH), 4.05 (m, 2H), 1.74-2.07 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 402 [M+H]+.
Example 148 8-(4-(4-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 4-bromophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. Η NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.45 (m, 5H), 7.13 (m, IH), 6.83 (m, 2H), 4.86 (m, IH), 4.03 (m, 2H), 1.73-2.10 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 402 [M+H]+.
Example 149 3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-cyanophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.47 (m, 2H), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.35 (m, IH), 7.31 (m, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 4.87 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, 2H), 1.78-2.07 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 348 [M+H]+.
Example 150
4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-cyanophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.70 (m, 2H), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.00 (m, 2H), 4.84 (m, IH), 4.12 (m, 2H), 1.74-2.05 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H) ; MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 348 [M+H]+.
Example 151 8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 3-(triflouromethyl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. JH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 3H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.25 (m, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, 2H), 4.86 (m, IH), 3.96-4.17 (m, 2H), 1.79-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.41 (d, 3H) ; MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 391 [M+H]+.
Example 152 8-(l-methyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 4-(triflouromethyl)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. JH NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.12 (d, IH), 7.02 (m, 2H), 4.76-4.96 (m, IH), 4.13 (m, 2H), 1.80-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 391 [M+H]+.
Example 153 8-(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-(triflouromethoxy)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. ]H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.48 (m, 2H). 7.38 (m, 2H), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.91 (m, 2H), 6.81 (m, IH), 4.75-4.97 (m, IH), 3.94-4.18 (m, 2H), 1.78-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.40 (d, 3H) ; MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 407 [M+H]+.
Example 154 8-(4-(2,3 -dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,3-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz,
DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.35 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.98 (m, IH), 6.70 (m, 2H), 4.89 (m, IH), 3.88-4.08 (m, 2H), 2.18 (m, 3H), 2.01 (m, IH), 1.96 (m, 3H), 1.88 (m, 3H), 1.42 (d, 3H) ; MS (DCIZNH3) m/z 351 [M+H]+.
Example 155 8-(4-(2,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,4-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.35 (d, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.12 (d, IH), 6.89 (m, 2H), 6.75 (m, IH), 4.77- 4.98 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 2.18 (m, 3H), 1.99 (m, 4H), 1.88 (m, 3H), 1.41 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 351 [M+H]+.
Example 156
8-(4-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,5-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.35 (d, IH), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.11 (d, IH), 6.92 (d, IH), 6.70 (m, IH), 6.58 (m, IH), 4.88 (m, IH), 3.99 (m, 2H), 2.24 (m, 3H), 1.80-2.04 (m, 7H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DC17NH3) m/z 351 [M+H]+.
Example 157 8-(4-(3 ,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3,4-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.37 (m, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.13 (m, IH), 6.96 (m, IH), 6.57 (m, 2H), 4.82 (m, IH), 3.76-4.05 (m, 2H), 2.11 (m, 6H), 1.73-2.02 (m, 4H), 1.38 ( , 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 351 [M+H]+.
Example 158
8-(4-(3,5-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3,5-dimethylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H MR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (m, IH), 7.31-7.52 (m, 3H), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.53 (m, IH), 6.27-6.47 (m, 2H), 4.67-4.98 (m, IH), 3.88-4.10 (m, 2H), 2.16 (m, 6H), 1.73-2.06 (m, 4H), 1.41 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 351 [M+H]+.
Example 159 , 8-(4-( 1 ,3 -benzodioxol-5 -yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting sesamol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.39 (m, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.10 (m, IH), 6.72 (m, IH), 6.49 (m, IH), 6.26 (m, IH), 5.93 (m, 2H), 4.64-4.96 (m, IH), 3.76-4.01 (m, 2H), 1.74-2.03 (m, 4H), 1.39 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 367 [M+H]+.
Example 160 8-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2,3-dichlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.37 (m, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.28 (m, IH), 7.12 (m, 3H), 4.91 (m, IH), 4.00-4.26 (m, 2H), 1.71-2.08 (m, 4H), 1.42 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 392 [M+H]+.
Example 161 8-(4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 2,4-dichlorophenol for methyl 3 -hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (m, IH), 7.31-7.58 (m, 5H), 6.95-7.24 (m, 2H), 4.74-5.11 (m, IH), 3.84-4.11 ( , 2H), 1.80-2.14 (m, 4H), 1.41 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 392 [M+H]+.
Example 162 8-(4-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine . The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2,5-dichlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 'H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.36 (m, IH), 7.42 (m, 4H), 7.16 (m, 2H), 6.95 (m, IH), 4.79-5.07 (m, IH), 4.16 (m, 2H), 1.73-2.10 (m, 4H), 1.41 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 392 [M+H]+.
Example 163 8-(4-(3 -isopropyl-5-methylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 3-isopropyl-5-methylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.36 (m, IH), 7.45 (m, 3H), 7.12 (m, IH), 6.59 (m, IH), 6.48 ( , 2H), 4.72-4.93 (m, IH), 3.83-4.05 (m, 2H), 2.75 (m, IH), 2.21 (m, 3H), 1.75-2.05 (m, 4H), 1.37 (m, 3H), 1.12 (m, 6H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 379 [M+H]+.
Example 164 8-(4-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
92 substituting 3,4-dichlorophenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. *H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (m, IH), 7.44 (m, 3H), 7.11 (m, 2H), 6.88 (m, 2H), 4.86 (m, IH), 4.10 (m, 2H), 1.71-2.03 (m, 4H), 1.40 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 392 [M+H]+.
Example 165 N-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
Example 165 A
8-(l,3.3-trimethylbutoxy)quinoline A 250 mL round bottom flask equipped with a pressure equalizing dropping funnel, stirring bar and N2 outlet was charged with 4.00 g (27.6 mmol) of 8-hydroxyquinoline, 21.7
g (3 equiv) of PPh3 and 80 mL of anhydr. THF. After stirring for 5 min, 4.91 mL (1.25 equiv) of 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentanol was added. The reaction mixture was then cooled in an ice bath and a solution of 9.52 g (1.5 equiv) of DBAD in 50 mL of anhydr. THF was added dropwise over 30 minutes. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature, and stirring was maintained for an additional 6 h. Then, an additional 2.46 mL (0.62 equiv) of the alcohol was added, the reaction mixture was cooled in an ice bath and a solution of 4.76 g (0.75 equiv) of DBAD in 25 mL of anhydr. THF was added dropwise over 15 minutes. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature, and stirring was maintained for an additional 12 h. An additional 10.9 g (1.5 equiv) of PPh3 was added, followed by 2.46 mL (0.62 equiv) of the alcohol. The reaction mixture was cooled in an ice bath and a solution of 4.76 g (0.75 equiv) of DBAD in 25 mL of anhydr. THF was added dropwise over 15 minutes. The reaction was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature, and stirring was maintained for an additional 6 h. The reaction mixture was then evaporated in vacuo and the resulting residue dissolved in 150 mL of EtOAc. The solution was washed with 2 N HCl (3 x 400 mL). The aqueous layers were combined and basified with 10 N
NaOH to pH 14. The resulting solution was extracted with EtOAc (3 x 150 mL), the organic layers were combined, dried over anhydr. Na2SO4 and evaporated in vacuo. The crude material was purified by silica gel column chromatography (10% EtOAc/hexanes + 2% TEA) to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.95 (dd, IH), 8.10 (dd, IH), 7.40 (m, 3H), 7.09 (br d, IH), 4.79 (m, IH), 2.20 (dd, IH), 1.57 (m, IH), 1.46 (d, 3H), 0.98 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 244 [M+H]+.
Example 165B 2-Chloro-8-(l ,3 ,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinoline
To a 100 L round bottom flask charged with 2 mL of CH2C12, 0.500 g (2.07 mmol) of 8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinoline was slowly added with gentle heating in order to dissolve the material. To this was added 1.8 equiv m-CPBA (50-70% by weight) in three portions. After stirring for 30 min, the dense solution became a brown solid. The solid was dissolved in 25 mL EtOAc and the resulting solution was washed with 10% aqueous
NaHSO3, saturated aqueous NaHC03, and the organic layer evaporated in vacuo. After co- evaporation with toluene, the residue was dissolved in POCI3 (5 mL) and the flask fitted with a reflux condenser. The reaction flask was then placed in an oil bath that had been preheated to 95 °C for 15 min. After cooling to room temperature, the solution was concentrated down to a red oil, which was then dissolved in CH2C12 and washed with saturated aqueous
NaHCO3 until the aqueous layers became basic. The organic layer was evaporated in vacuo and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (EtOAc/hexanes) to afford the title compound. H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.37 (d, IH), 7.55 (m, 3H), 7.34 (m, IH), 4.70-4.93 (m, IH), 1.90 (dd, IH), 1.53 (dd, IH), 1.30 (d, 3H), 0.94 (s, 9H); MS
(DCI NH3) m/z 277 [M+H] +
Example 165C N-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
A 7.5 mL conical microwave vessel (Personal Chemistry) equipped with a septum cap and a magnetic stirring bar was charged with 0.25 g (0.90 mmol) of 2-Chloro-8-(l,3,3- trimethylbutoxy)quinoline, NEt3 (1.26 mL) and NMP (1.26 mL). The resulting suspension was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (220 °C for 25 min; 300 W). Upon cooling, the residue was dissolved in a 3:1 hexanes/CH2Cl2 mixture (10 mL) and washed with H2O. The organic layer was evaporated in vacuo and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (5-15% MeOH/CH2Cl2) to afford the title compound. 1H NMR
(500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 6.67-7.79 (m, 5H), 4.87 (m, IH), 3.11 (m, 3H), 2.03 (m, IH),
1.56 (m, IH), 1.30 (m, 3H), 0.89 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 273 [M+H]+.
Example 166 N-propyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine To a 4 mL scintillation vial was added a stir bar and the title compound from Example 16 (15.0 mg, 0.058 mmol). To this was added 0.42 mL of a 1 :1
MeOH/ClCH2CH2Cl mixture followed by MP -cyanoborohydride resin (84 mg, 3.7 equiv Argonaut Technologies, Inc.) and 40 μL (10 equiv) of propionaldehyde. The reaction vessel was placed in an oil bath that had been preheated to 80 °C and the contents were allowed to stir overnight. Upon cooling to room temperature, the suspension was filtered and the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo. The crude material was purified by reverse phase HPLC to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 8.06 (d, IH), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.17 (m, 2H), 6.90 (d, IH), 4.54-4.81 (m, IH), 3.38 (m, 2H), 2.38 (m, IH), 1.80 (m, IH), 1.50 (m, 2H), 1.39 (d, 3H), 1.03 (t, 3H), 0.96 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 301 [M+H]+.
Example 167
8-((( 1 R)- 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
Example 168 8-(((l S)-l ,3,3-trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
100 mg of the title compound from Example 16 (3.88 mmol) were dissolved in 100 mL EtOH, loaded on a preparative column with chiral stationary phase (Chiralcel OD; 4.6 x 250 mm, flow = 1.0 mL/min, detection: UV210 nm), and eluted with hexanes/EtOH. The two enantiomeric compounds were collected at 7.2 min and 12.8 min, respectively
(dextrorotatory, assumed R; levorotatory, assumed S). The solvents were evaporated to afford the title products.
Example 167 {α}D 20 = +107°. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.83 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, 2H), 6.76 (m, IH), 6.18-6.38 (m, 2H), 4.72 (m, IH), 1.85 (m, IH), 1.47 (m, IH), 1.24 (m, 3H), 0.84-1.04 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 259 [M+H .
Example 168 { }D 20 = -111°. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.83 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.03 (m, 2H), 6.76 (m, IH), 6.18-6.38 (m, 2H), 4.72 (m, IH), 1.85 (m, IH), 1.47 (m, IH), 1.24 (m, 3H), 0.84-1.04 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 259 [M+H]+.
Example 169 N-((5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 166 substituting 5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-furaldehyde for propionaldehyde. H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.68-7.94 (m, 5H), 7.42-7.66 (m, 4H), 6.67-6.89 (m, 2H), 4.79-5.05 (m, 3H), 1.96 (m, IH), 1.56 (m, IH), 1.31 (m, 3H), 0.92 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 483 [M+H]+.
Example 170 N-((5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 166 substituting 5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furaldehyde for propionaldehyde. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 7.83 (m, 2H), 7.71 (m, 2H), 7.40-7.63 (m, 5H), 6.95 (m, IH), 6.70 (m, IH), 4.74-5.02 (m, 3H), 1.99 (m, IH), 1.58 (m, IH), 1.31 (m, 3H), 0.76-0.99 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 460 [M+H]+.
Example 171
N-((5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-( 1 ,3 ,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 166 substituting 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-furaldehyde for propionaldehyde. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CHC13) δ ppm 8.11 (m, IH), 7.78 (m, IH), 7.41 (rα, IH), 7.33 (m, 2H), 7.19 (m, 4H), 7.04 (m, IH), 6.48 (m, IH), 4.59-4.80 (m, 3H), 2.39 (m, IH), 1.50 (m, IH), 1.37 (m, 3H), 0.96 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/ H3) m/z 407 [M+H]+.
Example 172 8 -hexylquinolin-2-amine
Example 172A
8-trifluoromethylsulfonylquinoline-2 -amine To an oven-dried 500 mL round bottom flask was added of 2-amino-8- hydroxyquinoline (5.04 g, 31.5 mmol). The system was evacuated and purged with N2 three times, then charged with THF (70.0 mL) and pyridine (23.0 mL, 8 equiv). The solution was cooled to -30 °C in an isopropyl alcohol/dry ice bath, and triflic anhydride (14.9 mL, 2.8 equiv) was added dropwise over 50 min. The reaction mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature under N . After 2 h, the crude mixture was filtered through a pad of Celite, which was subsequently washed with THF (100 mL). The resulting solution was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in EtOAc (100 mL). This solution was washed with 1 M ammonium chloride (4 x 100 mL), saturated aqueous NaHC03, (4 x 100 mL), and brine (2 x 100 mL). The organic phase was concentrated, and the residue was purified by flash chromatography (20% EtOAc/hexane) to afford the title compound. MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 293 [M]+, 160.
Example 172 8-hexylquinolin-2-amine A solution of 2-amino-8-trifluoromethanesulfonylquinoline (50.0 mg, 0.171 mmol) in THF (1.0 mL) was degassed by bubbling N through the solution under vacuum for 5 min. The solution was added to a glass screw-top tube containing Pd(dppf) Cl2-CH2Cl2 (13.9 mg, 0.1 equiv). Argon was then bubbled through the mixture for 1 minute, and 1-hexylzinc bromide (1.0 mL, 1 M in THF) was added. The tube was quickly sealed and placed in a heater/shaker at 65 °C for 20 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and concentrated. The residue was dissolved in 1 : 1
DMSO/MeOH, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and purified by reverse phase HPLC. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.10 (br s, IH), 8.36 (br s, IH), 8.23 (br s, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.63 (d, IH), 7.43 (br s, IH), 7.10 (d, IH), 1.41-1.25 (m, 10H), 0.86 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z228 [M]+.
Example 173 8-( 1 -methylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
172 substituting 1-methylpentylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide. JH NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) δ 9.20 (br s, IH), 8.45 (br s, IH), 8.37 (d, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.70 (d, IH), 7.49 (br s, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 1.71-1.67 (m, 3H), 1.28-1.14 (m, 4H), 0.82 (d, 3H), 0.74 (t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 228 [M]+.
Example 174 8-( 1 -ethylbutyl)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting 1-ethylbutylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) δ 9.20 (br s, IH), 8.40 (br s, IH), 8.37 (br s, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.69 (d, IH), 7.49 (br s, IH), 7.12 (d, IH), 1.79-1.62 (m, 3H), 1.28-1.18 (m, 4H), 0.81 (t, 3H), 0.74'(t, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 228 [M .
Example 175 8-( 1 -ethylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting 1-ethylpentylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) δ 9.15 (br s, IH), 8.37 (br s, IH), 8.20 (br s, IH), 7.77 (d, IH), 7.67 (d, IH), 7.48 (br s, IH), 7.08 (d, IH), 1.81-1.62 (m, 3H), 1.21-1.15 (m, 6H), 0.79 (t, 3H), 0.73 (t, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 242 [M]+.
Example 176
8-cyclohexylquinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 172 substituting cyclohexylzinc bromide for 1-hexylzinc bromide. !H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 9.10 (br s, IH), 8.36 (br s, IH), 8.23 (br s, IH), 7.75 (d, IH), 7.67 (br s, IH), 7.45 (d, IH), 7.09 (br s, IH), 1.80 (m, IH), 1.60-1.48 (m, 8H), 1.35-1.28 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 226 [M]+.
Example 177 8-((S-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine
A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 132 mg, 4.2 equiv) 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (154 mg, 10 equiv) and DBAD (70 mg, 3.2 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N for 45 seconds.
Anhydr. THF (2.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 5 min. Then, a solution of 1,5-pentanediol (10 mg, 0.094 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added to the vial and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 8 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with DMA (6 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting oily residue was dissolved in 50 mL of EtOAc and washed with aqueous NH3. The solution was then evaporated in vacuo and the residue was dissolved in 3.0 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. *H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.95 (d, 2H), 7.27 (m, 2H), 7.21 (m, 2H), 7.14 (d, 2H), 7.05 (m, 2H), 4.20 (m, 4H), 2.04 (m, 4H), 1.94 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 389 [M+H]+.
Example 178 8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
177 substituting 1,3-butanediol for 1,5-pentanediol. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.31 (m, 2H), 7.41 (m, 3H), 7.32 (m, 3H), 7.10 (m, 2H), 5.15 (m, IH), 4.46 (m, 2H), 2.41 (m, 2H), 1.46 (m, 3H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 375 [M+H]+.
Example 179 8-(3-(2-aminoquinolin-8-yloxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPI13 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 200 mg, 4 equiv) 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (100 mg, 5 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 3 min. Then, 1,3-propanenediol (10 mg, 0.13 mmol) was added to the vial followed by DBAD (66 mg, 2 equiv) and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 15 min. Then additional DBAD (33 mg, 1 equiv) was added and the mixture was agitated for additional 15 min. The last addition of DBAD was repeated and the mixture was agitated for 6 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with DMA (6 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in DMA (10 mL) and MP-TsOH resin (Argonaut Technologies, Inc., 4.5 g) was added. The resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 12 h. The supernatant was subsequently drained and the resin was washed with DMA (10 mL), MeOH (10 mL) and DMA 00 mL) and MeOH (10 mL). The washed resin was treated with a mixture of 2 N NH3 in MeOH (15 mL) and DMA (5 mL) at room temperature for 1 h. The solution was drained and the basic wash was repeated two more times. The filtered solutions were combined. The resin was washed with MeOH (10
mL), DMA (10 mL), MeOH (10 mL), DMA (10 mL) and MeOH (10 mL). The washes were combined with the previously collected solutions and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1:1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse- phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ ppm 8.00 (d, 2H), 7.26 (m, 2H), 7.18 (m, 4H), 6.89 (d, 2H), 4.46 (m, 4H), 2.53 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 361 [M+H]+.
Example 180 8-((2E)-but-2-enyloxy)quinolin-2 -amine A 250 mL round bottom flask was charged with 2.00 g (12.5 mmol) of 2-amino-8- hydroxyquinoline, 3.46 g (25.0 mmol), of 2CO3 and 63 mL of anhydr ethanol. Following the dissolution of 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline, 1.51 mL of 3-chloro-l-butene (15.0 mmol) was added in one portion, and the mixture was heated to 65 °C in an oil bath. After 48 h, the solvent was evaporated and the residue dissolved in EtOAc and washed with H20. The combined aqueous layers were back-extracted with EtOAc. The organic layers were then pooled, dried, and filtered. The residue was then purified by column chromatography (SiO2; EtOAc/hexanes with 0.1% Et3N). The resultant material was then re-crystallized from Et20 to afford the title compound. lK NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.82 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 7.00 (m, 2H), 6.73 (m, IH), 6.39 (m, 2H), 5.67-5.98 (m, 2H), 4.44-4.67 (m, 2H), 1.74 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 215 [M+H]+.
Example 181 3 -methyl-8-(l ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
Example 181 A 2,2-dimethyl-N-(8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)propanamide To a 20 mL scintillation vial was added a stir bar, the title compound from Example 16 (161 mg , 0.624 mmol) and 1.5 mL of THF. To the resultant solution was added Et3Ν (0.174 mL, 2 equiv) and trirnethylacetylchloride (93 μL, 1.2 equiv). The solution was allowed to stir overnight, after which time the mixture placed directly on a silica column and eluted with EtOAc/hexanes to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de) ppm 8.27 (m, IH), 7.96-8.18 (m, IH), 7.42 (m, 2H), 7.21 (m, IH), 4.64-4.90 (m, IH), 1.90 (m, IH), 1.53 (m, IH), 1.31 (m, 12H), 0.83-1.05 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 343 [M+H]+.
Example 18 IB
2,2-dimethyl-N-(3-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)qumolin-2-yl)propanamide A 50 mL three-neck flask with a stir bar was charged with the title compound from Example 181 A (270 mg, 0.790 mmol) and 3 mL of THF. The flask was cooled to 0 °C in an ice bath and 0.9 mL of a 2.5 M solution of n-BuLi in THF was added slowly via syringe. The resultant solution was allowed to stir at 0 °C for 4 h, and then cooled to -78 °C. After 5 min at this temperature iodomethane (74.0 μL, 1.5 equiv.) was added slowly and the mixture was allowed to slowly warm to room temperature. After stirring overnight, the reaction was quenched with water and extracted with Et2O. The ethereal layers were combined and washed with saturated aqueous ΝH C1, dried, and evaporated. The residue was then purified by silica gel chromatography EtOAc/hexanes) to afford the title compound. !H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δppm 8.08 (m, IH), 7.44 (m, 2H), 7.17 (m, IH), 4.69-5.03 (m, IH), 2.27 (m, 3H), 1.73-1.95 (m, IH), 1.44-1.65 (m, IH), 1.29 (m, 3H), 1.27 (m, 9H), 0.95 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 357 [M+H]+.
Example 181C 3-methyl-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL glass tube was charged with the title compound from Example 181B(57.0 mg, 0.160 mmol), 1.5 mL of MeOH and sodium methoxide (26.0 mg, 3 equiv.). The tube was sealed and heated to 70 °C in an oil bath for 12 h. The reaction mixture was then allowed to cool to room temperature and was then quenched with saturated aqueous NH4C1. The mixture was diluted with Et20 and partitioned, the aqueous layer was washed with Et2O. The ethereal layers were combined, dried, and filtered. Evaporation of the solvent afforded a residue, which was purified by silica gel chromatography (MeOH/CH2Cl ) to afford the title product. 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.11 (s, IH), 7.35-7.49 (m, 2H), 7.16 (m, IH), 4.86 (m, IH), 2.26 (s, 3H), 1.86 (dd, IH), 1.52 (dd, IH), 1.27 (d, 3H), 0.97 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 273 [M+H]+.
Example 182
2-(((8-(l ,3 ,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)amino)carbonyl)benzyl benzoate To a 20 mL scintillation vial was added a stir bar, the title compound from Example 16 (100 mg, 0.388 mmol) and anhydr. THF (1.3 mL). To the resultant solution was added of Et3N (0.12 mL, 2.2 equiv), DMAP (5.0 mg, 1.06 equiv) and of 2- (benzoyloxymexhyl)benzoyl chloride (116 mg, 1.1 equiv). The solution was stirred overnight, after which time the mixture was placed directly on a silica gel column and eluted with EtOAc/hexanes to afford the title compound. JH NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 8.23 (m, IH), 8.16 (m, IH), 7.92 (m, 2H), 7.72 (m, IH), 7.55 (m, 4H), 7.38 (m, 4H), 7.24 (m, IH), 5.51 (s, 2H), 4.82 (m, IH), 1.88 (dd, IH), 1.49 (dd, IH), 1.34 (d, 3H), 0.92 (s, 9H); MS
(DCI/NH3) m/z 497 [M+H] +
Example 183 N-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine
Example 183 A 3-((8-(l ,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)amino)propan-l -ol A 7.5 mL conical microwave vessel (Personal Chemistry) equipped with a septum cap and a magnetic stirring bar was charged with the title compound from Example 165B (150 mg, 0.540 mmol) and 3-aminopropanol (0.825 mL, 20 equiv). The resulting solution was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (220 °C for 25 min; 300 W). After cooling to room temperature, the contents were directly loaded on a silica gel column and eluted with EtOAc/hexanes to afford the title compound. *H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.77 (m, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.02 (m, 3H), 6.70 (m, IH), 5.03 (m, IH), 4.64-4.86 (m, IH), 3.62 (m, IH), 3.43 (m, 3H), 1.91 (m, IH), 1.55-1.78 (m, 2H), 1.44 (m, IH), 1.23 (m, 3H), 0.96 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 317 [M+H]+.
Example 183B N-(3 -((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)-8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine A 20 mL scintillation vial with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPI13 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 46 mg, 2.2 equiv), the title compound from Example 183 A (10 mg, 0.03 mmol) and DBAD (12 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N2 for 45 seconds. Anhydr. THF (3 mL) was added and the contents of the vial were shaken for 5 min. Then, a solution of 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (11 mg, 0.07 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added and the resulting suspension was shaken at room temperature for 6 h. The suspension was filtered, and the resin washed with THF (three times 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was then treated with 6.0 mL of 4 M HCl in dioxane at room temperature for 12 h. The resulting solution was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCL3) δ ppm 8.04 (br d, IH), 7.92 (br d, IH), 7.29 (m, 2H), 7.16 (m, 4H), 7.01 (m, 2H), 4.71 (m. IH), 4.35 (m, 2H), 3.82-4.03 (m, 2H), 2.46 (m, 2H), 2.29 (m, IH), 1.51 (m, IH), 1.37 (d, 3H), 0.94 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 459 [M+H]+.
Example 184 8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-chloro-4-methylphenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.93 (d, IH), 7.29 (t, IH), 7.18 (m, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.94 (m, IH), 6.79 (d, IH), 4.77 (m, IH), 4.10 ( , IH), 4.03 (m, IH), 2.22 (s, 3H), 2.20 (m, IH), 2.03 (m, 3H), 1.47 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 371 [M+H]+.
Example 185
8-(4-(2-(benzyloxy)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting 2-(benzyloxy)phenol for methyl 3-hydroxybenzoate. !H NMR (500 MHz, CDCI3) δ ppm 7.91 (d, IH), 7.40 (m, 2H), 7.31 (m, 2H), 7.25 (m, IH), 7.20 (t, IH), 7.14 (dd, IH), 7.08 (m, IH), 6.99 (d, IH), 6.90 ( , 3H), 6.83 (m, IH), 5.06 (d, 2H), 4.73 (m, IH), 4.09 (m, 2H), 2.20 (m, IH), 2.01 (m, 3H), 1.42 (d, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 429 [M+H]+.
Example 188 8-(((3S)-l-(l,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine
A 4 dram scintillation vial was charged with 135 mg (0.509 mmol) of Example 195, l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde (92.0 mg, 0.613 mmol), and macroporous sodium cyanoborohydride resin (400 mg, 2.55 mmol/g, 2 equiv). A solution of 1:1 MeOH/dichloroethane with 1% AcOH was added (3 mL) and the reaction vessel shaken for approximately 16 hours. After this time the resin was filtered off and the solvents evaporated. The residue was dissolved in 1 : 1 MeOH/DMSO and purified on a reverse-phase HPLC column to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 7.81 (m, IH), 7.17 (m, IH), 7.02 (m, IH), 6.86 (m, 3H), 6.76 (m, 2H), 5.97 (m, 2H), 5.00 (m, IH), 3.56 (m, 2H), 2.88 (m, IH), 2.72 (m, 2H), 2.31 ( , 2H), 1.87 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 364 [M+H]+.
Example 189 8-(((3S)-l-(2-fluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
188 substituting 2-flourobenzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. 1HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.39 (m, IH), 7.58 (m, 2H), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.29 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, IH), 5.28-5.52 (m, IH), 4.34-4.67 (m, 2H), 3.80 (m, IH), 3.17 (m, 2H), 2.77 (m, IH), 2.21-2.45 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 338 [M+H]+.
Example 190 8-(((3S)- 1 -( 1 , 1 '-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 4-biphenylcarboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. H MR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.29 (m, IH), 7.70 ( , 4H), 7.59 (m, 2H), 7.49 (m, 3H), 7.37 (m, 3H), 7.12 (m, IH), 5.40 (m, IH), 4.43 (m, 2H), 3.79 (m, 2H), 3.63 (m, IH), 2.58 (m, IH), 2.37 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 396 [M+H]+.
Example 191 8-(((3S)-l-((3 -methyl- 1 -benzothien-2-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 3-methylbenzo(B)thiophene-2-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5- carbaldehyde. 1H MR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.22-8.44 (m, IH), 7.77 (m, IH), 7.40 (m, 5H), 7.11 (m, 2H), 5.28-5.59 (m, IH), 4.61-5.00 (m, 2H), 3.77-4.10 (m, IH), 3.21 (m, 2H), 2.69-2.96 (m, IH), 2.23-2.48 (m, 5H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 390 [M+H]+.
Example 193
8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-6-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3- yl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 2,2-dimethylchromane-6-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5- carbaldehyde. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.31 (m, IH), 7.51 (m, IH),
7.37 (m, 2H), 7.16 (m, 3H), 6.70 (m, IH), 5.37 (m, IH), 4.34 (m, 2H), 3.60 (m, 3H), 2.72 (m,
2H), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.40 (m, IH), 1.58-1.82 (m, 2H), 1.24 (m, 7H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 404
[M+H]+.
Example 194 tgrt-butyl 8-((3S)-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-ylcarbamate The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 92 substituting (3 S)-hydroxy-pyrrolidine-l -carboxylic acid-tert-butyl ester for methyl 3- hydroxybenzoate. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDC13) δ ppm 7.87 (m, IH), 7.22 (m, IH), 7.16 (m, IH), 6.96 (m, IH), 5.31 (s, IH), 5.10 (m, IH), 3.51-3.89 (m, 4H), 2.30-2.56 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH), 1.47 (s, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 330 [M+H]+.
Example 195 8-((3S)-pyrrolidin-3-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine To a 4 dram vial containing Example 194 (300 mg, 0.608 mmol) was added 3 mL of a 4 M solution of HCl in dioxane. The mixture was allowed to sit for 60 min and then the solvent was evaporated to afford the HCl salt of the title compound. !H NMR (300 MHz, d - MeOH) δ ppm 8.31 (m, IH), 7.46 (m, 3H), 7.07 (m, IH), 5.55 (m, IH), 3.82 (m, IH), 3.44- 3.71 (m, 3H), 2.41 (m, 2H); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 230 [M+H]+.
Example 196
8-(((3S)-l-(4-tert-butylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 4-tert-butylbenzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. !HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.31 (m, IH), 7.50 (m, IH), 7.43 (m, 4H), 7.37 (m, 2H), 7.12 (m, IH), 5.38 (m, IH), 3.54-3.84 (m, 3H), 3.38 (m, IH), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.36 (m, IH), 1.27 (m, 9H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 376 [M+H]+.
Example 197 8-(((3S)- 1 -(2,3-dihydro- 1 ,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting l,4-benzodioxan-6-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.29 (m, 1 H), 7.50 (m, IH), 7.36 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, IH), 7.02 (m, IH), 6.94 (m, IH), 6.85 (m, IH), 5.34 (m, IH), 4.25 (m, 6H), 3.48- 3.75 (m, 4H), 2.54 (m, IH), 2.36 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 378 [M+H]+.
Example 198 8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-difluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
188 substituting 2,3-diflourobenzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. ]HNMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.34 (m, IH), 7.50 (m, IH), 7.38 (m, 4H), 7.23 (m, IH), 7.14 (m, IH), 5.20-5.40 (m, IH), 4.17-4.38 (m, 2H), 3.61 (m, IH), 3.41 (m, 2H), 3.02-3.28 (m, IH), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.12-2.40 (m, IH); MS (DCI NH3) m/z 356 [M+H]+.
Example 199 8-(((3S^-l-(3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)pyιτolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
188 substituting 3-(triflouromethyl)benzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.33 (m, IH), 7.84 (m, IH), 7.75 (m, 2H), 7.63 (m, IH), 7.50 (m, IH), 7.36 (m, 2H), 7.11 (m, IH), 5.33 (m, IH), 4.37 (m, 2H), 3.64 (m, IH), 3.47 (m, 2H), 3.26 (m, IH), 2.58 (m, IH), 2.35 (m, IH) ; MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 388 [M+H]+.
Example 200 8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-difluoro-l,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 2,2-diflouro-l,3-benzodioxolo-5-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5- carbaldehyde. 1H NMR (300 MHz, MEOH) δ ppm 7.87 (m, IH), 7.26 (m, IH), 7.20 (m, IH), 7.15 (m, IH), 7.13 (m, IH), 7.09 (m, IH), 6.92 (m, IH), 6.81 (m, IH), 5.06 (m, IH), 3.71 (m, 2H), 3.13 (m, IH), 2.91 (m, IH), 2.82 (m, IH), 2.68 (m, IH), 2.39 (m, IH), 2.18 (m, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 364 [M+H]+.
Example 201
8-(((3S)-l-(2,4-dimethylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting 2,4-dimethylbenzaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-de, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.30 (m, IH), 7.49 (m, IH), 7.33 (m, 3H), 7.06 (m, 3H), 5.20-5.42 (m, IH), 4.16-4.38 (m, 2H), 3.44-3.75 (m, 5H), 2.55 (m, IH), 2.34 (m, 3H), 2.24 (m, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 348 [M+H]+.
Example 202 N-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)-8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6- ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 188 substituting l,4-benzodioxan-6-carboxaldehyde for l,3-benzodioxole-5-carbaldehyde. XHΝMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6, 90 °C) δ ppm 8.00 (m, 1 H), 7.41 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, 2H), 7.04 (m, 2H), 6.96 (m, 2H), 6.87 (m, 2), 6.77 (m, IH), 5.39 (m, IH), 4.57 (m, 2H), 4.34 (m, 2H), 4.21 (m, 10H), 3.38 (m, 2H), 2.13-2.44 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m z 526 [M+H]+.
Example 203
4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one
Example 203 A 6-methyl-4-(((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)methyl)-2H-chromen-2-one
A 250 mL round bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and a pressure equalizing dropping funnel was charged with 5.20 g (29.5 mmol) of 4-hydroxy-6-methyl- chromen-2-one. The flask was purged with nitrogen and a solution of NEt3 (8.3 mL) in DCM (60 mL) was added. The resulting solution was cooled to -10 °C and trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride (10.0 g; 1.2 eq) was added dropwise to the flask over 5 min. The resulting mixture was kept at -10 °C for 2 h then diluted with 130 mL of 1:1 mixture of ether/hexanes. The mixture was allowed to warm up to 0 °C and stirring was maintained for additional 10 min. The reaction mixture was then filtered through a short column of silica gel. Additional 100 mL of 1 : 1 mixture of ether hexanes and 50 mL of EtOAc were used to completely elute the product from the column. The volatiles were removed in vacuo to give 8.45 g (93%) of the title compound. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO- de) δ ppm ; MS (DCI/NH3) m z 309 [M+H]+.
Example 203 B 4-((3-hydroxypropyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one A 7.5 L conical microwave reaction vessel (Personal Chemistry) was charged with the title compound from Example 203 A (0.030 g, 0.097 mol) and purged with N2. Then a solution of 3-amino-propan-l-ol (0.075 mL, 10 eq.) in a mixture of acetonitrile (2 mL) and triethylamine (0.2 mL) was added. The resulting solution was irradiated in Personal Chemistry Smith Synthesizer (150 °C for 180 s; 300 W). The reaction mixture was then evaporated in vacuo. The resulting crude material was purified by silica gel column chromatography (ACN + 2% DIEA) to afford the title compound. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ ppm 7.86 (m, IH), 7.54 (m, IH), 7.39 (m, IH), 7.19 (m, IH), 5.12 (s, IH), 4.57 (m, IH), 3.52 (m, 2H), 2.38 (s, 3H), 1.80 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 234 [M+H .
Example 203 C 4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one
A 20 mL scintillation vial equipped with a septum cap was charged with PS-PPh3 resin (Aldrich Chemical Co., Inc, 130 mg, 2.2 equiv), 2-amino-8-hydroxyquinoline (31 mg, 2 equiv) and DBAD (36 mg, 1.6 equiv) and purged by passing a stream of N for 45 seconds.
Anhydrous THF (2.0 mL) was added and contents of the vial were agitated for 5 min. Then, a solution of the title compound from Example IB (22 mg, 0.094 mmol) in anhydr. THF (1 mL) was added to the vial and the resulting suspension was agitated at room temperature for 16 h. The suspension was then filtered, and the resin washed with THF (3 x 3.0 mL). The filtrate and washings were combined and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in 1.5 mL of a 1 :1 mixture of DMSO/MeOH and purified by preparative reverse-phase HPLC. !H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δ ppm 8.36 (d, IH), 7.82 (br s, IH), 7.43 (m, 3H), 7.30 (m, IH), 7.25 (d, IH), 7.06 (d, IH), 5.17 (s, IH), 4.49 (m, 2H), 3.71 (m, 2H), 2.47 (m, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 376 [M+H]+.
Example 204 4-[3-(2-amino-quinolin-8-yloxy)-propylaminol-6-chloro-chromen-2-one
Example 204 A Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid 6-chloro-2-oxo-2H-chromen-yl ester The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 203 A substituting 4-hydroxy-6-methyl-chromen-2-one for 4-hydroxy-6-chloro-chromen-2- one. 1H NMR (300 MHz, MeOD-d4) δ 6.56 (s, IH), 7.26 (s, IH), 7.38 (d, IH, d), 7.64 (d, IH); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 329 [M+H]+.
Example 204 B 6-chloro-4-((3-hydroxypropyl)amino)-2H-chromen-2-one
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example 203 B substituting trifluoromethanesulfonic acid 6-chloro-2-oxo--?H-chrornen-yl ester for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid 6-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-yl ester. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-de) δ ppm 8.22 (d, IH), 7.64 (m, 2H), 7.36 (d, IH), 5.19 (s, IH), 4.56 (m, IH), 3.52 (m, 2H), 1.79 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 254 [M+H]+.
Example 204 C 4-r3-(2-amino-quinolin-8-yloxy)-propylamino1-6-chIoro-chromen-2-one The title compound was prepared according to the procedure described in Example
203 C substituting 4-(3-hydroxy-propylamino)-6-chloro-chromen-2-one for 4-(3-hydroxy- propylamino)-6-methyl-chromen-2-one. 1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δ ppm 8.35 (br s, IH), 8.08 (m, IH), 7.49 (m, IH), 7.41 (m, 3H), 7.25 (d, IH), 7.18 (d, IH), 5.23 (s, IH), 4.49
(m, 2H), 3.72 (m, 2H), 2.48 (m, 2H); MS (DCI/NH3) m/z 396 [M+H] ' .
Claims
What is claimed is:
1. A compound according to formula (I),
(I), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein is a bond or is a member selected from the group consisting of-C(O)-, -O-, -S-, - S(O)-, and -S(0)2-;
RΪ is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARBNcarbonyl;
R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkoxy, alkenyl, alkoxyalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, haloalkyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R L2R6-„ RAS lkyl, and RARBNalkyl;
R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
R4, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; Re and R7 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl, and heterocycle;
RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle; L2 is -(CH2)mX(CH2)n-, X is a member selected from the group consisting of-C(O)-, -0-, -S-, -S(O)-, -
S(O)2- or is a covalent bond, m is O, 1, 2, 3, or 4; n is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4; and provided that if i) any of R3, t, or R5 is alkyl or alkoxy, or if ii) L is a bond and R2 is either alkyl or alkoxy; then R must be other than hydrogen.
(la), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein
Ri is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARβNcarbonyl; R is selected from the group consisting of alkyl, alkenyl; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; R4, and R5 are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
RA and RB are each independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle; provided that if i) any of R3, Rt, or R5 is alkyl or alkoxy, or if ii) L is a bond and R2 is either alkyl or alkoxy; then Rt must be other than hydrogen.
3. The compound according to claim 2, that is a member selected from the group consisting of
2-(((8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-yl)amino)carbonyl)benzyl benzoate;
N-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine;
4. A compound according to formula (lb),
(lb), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein
Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARB carbonyl;
R2 is alkyl, wherein alkyl is C6 or larger;
R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, ARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
R^ and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARB -, and alkylcarbonylNH-; and
RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
5. The compound according to claim 4, that is a member selected from the group consisting of
8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-ethyl- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(hexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(3 ,3 -dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(( 1 -ethylpenty l)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -ethyl-2-methylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l,2-diethylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-((l,4-diethylhexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(l ,3-dimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-((l-isopropylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((l-ethyl-4-methylpentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-methyl-8-( 1 ,3,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-propyl-8-(l ,3 ,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((l R)- 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((l S)- 1 ,3 ,3-trimethylbutyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; and
3-methyl-8-( 1 ,3 ,3 -trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine.
A compound according to formula (Ic),
(Ic), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein Li is-O-; Rt is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and
RARβNcarbonyl;
R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of alkoxyalkyl, haloalkyl, RASalkyl, and RARBNalkyl;
R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARβN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
R4, and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
7. The compound according to claim 6, that is a member selected from the group consisting of
8-(2-methoxy- 1 -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-ethoxy- 1 -methylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(3-methoxy-3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -(methoxymethyl)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3 -ethoxy- 1 -ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-methoxybutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3,3,3-trifluoropropoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(2-(methylthio)ethoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one; and
4-((3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propyl)amino)-6-chloro-2H-chromen-2-one.
8. A compound according to formula (Id),
(Id), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein
Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARBN-, and RARβNcarbonyl;
R2 is a member selected from the group consisting of aryl, cycloalkyl and heterocycle; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
R , and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting ot hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARB -, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
9. The compound according to claim 8, that is a member selected from the group consisting of
8-(cyclobutyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(cyclopentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(cyclohexyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((3-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((3-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((4-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(cycloheptyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((( 1 R,2S)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((lR,2S)-2-methylcyclopentyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2,3-dihydro-lH-inden-2-yloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((lS,5S)-3,3,5 -frimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((lR,5S)-3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(((3S)-l-benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3R)- 1 -benzylpyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((l-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(l,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((3S)-l-(2-fluorobenzyl)pyrrolidm-3-yl)oxy)quinoIin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -( 1 , 1 '-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -((3 -methyl- 1 -benzothien-2-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3 -yl)oxy)quinolin-2- amine;
8-(((3 S)- 1 -((2,2-dimethyl-3 ,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-6-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3 - yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; tert-butyl (3 S)-3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pyrrolidine- 1 -carboxylate;
8-((3 S)-pyrrolidin-3 -yloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(4-tert-butylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-dihydro-l,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2- amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,3-difluorobenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-((2,2-difluoro-l,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin- 2-amine;
8-(((3S)-l-(2,4-dimethylbenzyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quiriolin-2-amine; and N-(2,3 -dihydro-1 ,4-benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)-8-(((3 S)- 1 -(2,3 -dihydro- 1 ,4- benzodioxin-6-ylmethyl)pyrrolidin-3-yl)oxy)quinolin-2 -amine.
10. A compound according to formula (Ie),
(Ie), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, wherein
Ri is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, aryl, arylalkyl, arylalkoxy, arylcarbonyl, heterocycle, heterocyclealkyl, RARB -, and RARB c rbonyl;
R is a member selected from the group consisting of arylalkyl, aryloxyalkyl, cycloalkylalkyl, heterocyclealkyl, heterocycleoxyalkyl, heterocycleoxyalkoxyalkyl, R L2R6-; R3 is a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-;
R4., and R5 are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxy, hydroxy, cyano, halo, haloalkoxy, RARBN-, and alkylcarbonylNH-; RA and RB are each independently a member selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, aryl and heterocycle.
11. The compound according to claim 10, that is a member selected from the group consisting of 8-(((l S)-2-methyl-l-phenylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-benzylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-(4-fluorophenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -methyl-2-phenylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-(l-naphthyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(benzyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((3-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((2J4-dimethylbenzyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((( 1 R)-l -phenylethyl)oχy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; 8-((4-(((2--vminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)methyl)benzyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-phenoxypropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3 -(3 ,5 -dichlorophenoxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 ,5 -dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
S-(4-(2-methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
N-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetamide; methyl 3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate;
8-(l-methyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; methyl 0-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)-L-tyrosinate;
8-(l-methyl-4-(2-naphthyloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
1 -(4-((4-((2 -aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-3 -methylphenyl)ethanone; 8-( 1 -methyl-4-(4-propylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3-isopropylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(4-chloro-3 -fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolm-2-amine;
2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile;
2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide; 8-(l -methyl-4-(2-methyl-5-nitrophenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((5-amino-l-naphthyl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(3 -anilinophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-chloro-4-methoxyphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((4-methoxy- 1 -naphthyl)oxy)-l -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; methyl (4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)acetate; ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methylbenzoate;
8-(4-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-(3-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)urea;
4-(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)butan-2-one; ethyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzoate; methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-5-methoxybenzoate;
8-(4-(4-amino-2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
1 -(4-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenyl)propan- 1 -one;
8-(4-(3-(diethylamino)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(l , 1 '-biphenyl-3-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(4-(2-fluoro-5-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-ethoxy-5-((lE)-prop-l-enyl)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; methyl 2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-4-methoxybenzoate;
8-(4-(2-benzylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(4-(2-fluoro-4-nitrophenoxy)--l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
5-acetyl-2-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzamide;
8-(4-(2,3-dihydro- 1 H-inden-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-(4-(4-(lH-imidazol-l-yl)ρhenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(2-isoxazol-5-ylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
-(4-(2-methoxy-4-propylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2-chloro-3 -(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -( 1 -methyl-4-(2-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; -(l-methyl-4-(3-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-methyl-4-(4-methylphenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2-chloro-5-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)phenol; -(4-(3 -methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(4-methoxyphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2-fluorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; -(4-(3-fluorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; -(4-(4-fluorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; -(4-(2-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3 -chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine ; -(4-(4-chlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3-bromophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(4-bromophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile; -((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)benzonitrile; -(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethyl)ρhenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-methyl-4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(l-methyl-4-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,3-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,4-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3,4-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3,5-dimethylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3 -isopropyl-5-methylphenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(4-(3 ,4-dichlorophenoxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; -(4-(2-chloro-4-methylphenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2 -amine; ~(4-(2-(benzyloxy)phenoxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(cyclobutylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(2-cyclopropylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(cyclopentylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine; -(cyclohexylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-cyclohexyletnoxy)quιnolιn-z-amme;
8-((lS,4R)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-cyclohexylpropoxy)quinolin-2 -amine;
8-((( 1 R,2R)-2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-( 1 -cyclohexylethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(teμahydrofuran-3-ylmethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-( 1 -methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)ethoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3 -((2-methylquinolin- 8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-(quinolin-8-yloxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol;
6-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-ol;
4-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-methyl-4-((2-methylquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(l-methyl-4-(quinolin-7-yloxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(isoquinolin-5-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-(dibenzo[b,d]furan-2-yloxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(4-((2,2-dimethyl-2,3 -dihydro- 1 -benzofuran-7-yl)oxy)- 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2- amine; 6-((4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)- 1 ,3 -benzoxathiol-2-one;
8-(4-(l,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)-l-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-((5-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3- trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
N-((5-(2-nitrophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-μimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; Ν-((5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-furyl)methyl)-8-(l,3,3-trimethylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((5-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentyl)oxy)-quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)butoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propoxy)-N-methylquinolin-2-amine; and
8-(2-(2-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)ethoxy)ethoxy)-quinolin-2-amine.
12. Tlie following additional compounds
8-isopropoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-sec-butoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-( 1 ,2-dimethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-ethylpropoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-ethoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-propoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-butoxyquinolin-2-amine;
8-isobutoxyqumolm-2-amιne;
8-(pentyloxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(2-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(3-methylbutoxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-(((lR)-l-methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((l S)- 1 ,2-dimethylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((lR)-l,27dimethylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(((l S)- 1 -methylpropyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-((l -isopropylbut-3- enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-((l ,5-dimethylhex-4-enyl)oxy)quinolin-2-amine;
8-((2E)-but-2-enyloxy)quinolin-2-amine; 8-hexylquinolin-2-amine;
8-( 1 -methylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-ethylbutyl)quinolin-2-amine;
8-(l-ethylpentyl)quinolin-2-amine; 3-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)propan-l-ol; and 4-((2-aminoquinolin-8-yl)oxy)pentan- 1 -ol.
13. A method of treating disorders mediated by MCH through the MCH receptor comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
14. A method for treating eating disorders, weight gain and obesity comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
15. A method for treating abnormalities in reproduction and sexual behavior, thyroid hormone secretion, diuresis and water/electrolyte homeostasis, sensory processing, memory, sleeping, arousal, anxiety, depression, seizures, neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I).
16. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) in combination with a pharmaceutically suitable carrier.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17410902A | 2002-06-18 | 2002-06-18 | |
| US10/174,109 | 2002-06-18 | ||
| US10/460,139 | 2003-06-12 | ||
| US10/460,139 US6989392B2 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2003-06-12 | 2-Aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2003105850A1 true WO2003105850A1 (en) | 2003-12-24 |
Family
ID=29738989
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2003/018959 WO2003105850A1 (en) | 2002-06-18 | 2003-06-17 | 2-aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2003105850A1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009011336A1 (en) * | 2007-07-18 | 2009-01-22 | Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Quinoline compounds |
| US7803816B2 (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2010-09-28 | Hoffmann-La Roche Inc. | MCH receptor antagonists |
| US7884114B2 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2011-02-08 | Glaxo Group Limited | Compounds |
| EP2289891A3 (en) * | 2005-08-04 | 2011-04-27 | Palumed S.A. | Novel polyquinoline derivates and the therapeutic use thereof |
| WO2018031434A1 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Tlr7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| WO2021105497A1 (en) * | 2019-11-29 | 2021-06-03 | University Of Copenhagen | Small-molecule nadph oxidase 2 inhibitors |
| US11629134B2 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2023-04-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | TLR7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| CN116332918A (en) * | 2023-03-17 | 2023-06-27 | 遵义医科大学珠海校区 | Coumarin-quinoline derivative, and preparation method and application thereof |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000076984A2 (en) * | 1999-05-21 | 2000-12-21 | Biovitrum Ab | Novel compounds, their use and preparation |
| WO2001040217A1 (en) * | 1999-11-30 | 2001-06-07 | Pfizer Products Inc. | Novel benzoimidazole derivatives useful as antiproliferative agents |
-
2003
- 2003-06-17 WO PCT/US2003/018959 patent/WO2003105850A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2000076984A2 (en) * | 1999-05-21 | 2000-12-21 | Biovitrum Ab | Novel compounds, their use and preparation |
| WO2001040217A1 (en) * | 1999-11-30 | 2001-06-07 | Pfizer Products Inc. | Novel benzoimidazole derivatives useful as antiproliferative agents |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| GLENNON, RICHARD A. ET AL: "5-HT1 and 5-HT2: binding characteristics of some quipazine analogs", JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY (1986), 29(11), 2375-80, XP002093299 * |
| SAMPEI, NOBUYOSHI ET AL: "2-Aminoquinoline derivatives", SANKYO KENKYUSHO NEMPO (1964), 16, 42-8, XP001155335 * |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2289891A3 (en) * | 2005-08-04 | 2011-04-27 | Palumed S.A. | Novel polyquinoline derivates and the therapeutic use thereof |
| US7803816B2 (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2010-09-28 | Hoffmann-La Roche Inc. | MCH receptor antagonists |
| WO2009011336A1 (en) * | 2007-07-18 | 2009-01-22 | Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Quinoline compounds |
| US7884114B2 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2011-02-08 | Glaxo Group Limited | Compounds |
| US11629134B2 (en) | 2015-12-17 | 2023-04-18 | Merck Patent Gmbh | TLR7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| US11512069B2 (en) | 2016-08-08 | 2022-11-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | TLR7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| AU2017311047B2 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2021-07-22 | Merck Patent Gmbh | TLR7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| RU2758686C2 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2021-11-01 | Мерк Патент Гмбх | Tlr7/8 antagonists and their application |
| US10947214B2 (en) | 2016-08-08 | 2021-03-16 | Merck Patent Gmbh | TLR7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| WO2018031434A1 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2018-02-15 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Tlr7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| EP4198031A1 (en) * | 2016-08-08 | 2023-06-21 | Merck Patent GmbH | Tlr7/8 antagonists and uses thereof |
| WO2021105497A1 (en) * | 2019-11-29 | 2021-06-03 | University Of Copenhagen | Small-molecule nadph oxidase 2 inhibitors |
| CN116332918A (en) * | 2023-03-17 | 2023-06-27 | 遵义医科大学珠海校区 | Coumarin-quinoline derivative, and preparation method and application thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6989392B2 (en) | 2-Aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists | |
| ES2392200T3 (en) | Diaryl esters as opioid receptor antagonists | |
| JP5617919B2 (en) | Tetrahydrobenzothiophene compound | |
| CA2950952C (en) | Metabotropic glutamate receptor negative allosteric modulators (nams) and uses thereof | |
| US20060247439A1 (en) | Mchir antagonists | |
| MX2007011366A (en) | 1-benzylindole-2-carboxamide derivatives. | |
| CZ361392A3 (en) | Novel azaheterocyclylmethyl-chromans | |
| JP2007523139A (en) | Remedy | |
| WO2008059866A1 (en) | Novel 1,2-dihydroquinoline derivative having substituted phenylamino lower alkyl group and ester-introduced phenyl group as substituents | |
| CA2806821C (en) | Fused ring pyridine compound | |
| CA3085879A1 (en) | Substituted pyrrolidine amides ii | |
| CA3201443A1 (en) | Tetrahydroquinoline derivative and medicinal use thereof | |
| WO2003105850A1 (en) | 2-aminoquinolines as melanin concentrating hormone receptor antagonists | |
| JP4177435B2 (en) | Remedy | |
| US20070185079A1 (en) | Therapeutic agents I | |
| WO2005085212A1 (en) | Substituted pyrimidine derivative | |
| EP2261206A1 (en) | Indolinone compound | |
| AU644296B2 (en) | 2-(1-piperidyl)ethanol derivatives, their preparation and their therapeutic application | |
| CA2081256A1 (en) | Triazaspirodecanone-methylchromans | |
| CA2317515A1 (en) | Oxazole derivatives as serotonin-1a receptor agonists | |
| US20050209274A1 (en) | Antagonists of melanin concentrating hormone effects on the melanin concentrating hormone receptor | |
| RU2127732C1 (en) | Bis-phenylpiperazine nicotinic acid esters, method of their synthesis (variants), pharmaceutical composition, method of treatment of patients with central nervous system disorders | |
| JP2008544982A (en) | Thiophene-2-carboxamide derivatives as alpha 7 nicotinic receptor modulators | |
| WO2004080965A1 (en) | Neuropeptide ff receptor antagonist | |
| WO2019015640A1 (en) | Salt of azacyclic amide derivative, crystal form thereof and preparation method therefor and use thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): CA JP MX |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: JP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Country of ref document: JP |