RU2337326C2 - Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) - Google Patents
Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2337326C2 RU2337326C2 RU2006122061/28A RU2006122061A RU2337326C2 RU 2337326 C2 RU2337326 C2 RU 2337326C2 RU 2006122061/28 A RU2006122061/28 A RU 2006122061/28A RU 2006122061 A RU2006122061 A RU 2006122061A RU 2337326 C2 RU2337326 C2 RU 2337326C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- valves
- output
- input
- outputs
- valve
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Sampling And Sample Adjustment (AREA)
- Automatic Analysis And Handling Materials Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к области дозирования жидкостей в технологический процесс и может быть использовано на обогатительных фабриках при флотации руд цветных металлов, в химической, металлургической и других отраслях промышленности.The invention relates to the field of dispensing liquids in the process and can be used in processing plants for flotation of non-ferrous metals, in the chemical, metallurgical and other industries.
Известно устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов ПРИ-1 [1], управляемое периодическим частотным сигналом, содержащее запорный клапан, приводимый в действие электромагнитом. Текущий расход реагента определяется временем открытого состояния клапана в течение периода, частотой срабатывания клапана и напором реагента на входе запорного клапана. Недостатком устройства [1] является низкая точность дозирования ввиду зависимости текущего расхода через клапан от изменения давления реагента на его входе.A known device for dispensing liquid reagents PRI-1 [1], controlled by a periodic frequency signal, containing a shut-off valve, actuated by an electromagnet. The current reagent flow rate is determined by the valve’s open state during the period, valve response rate and reagent pressure at the inlet of the shutoff valve. The disadvantage of the device [1] is the low metering accuracy due to the dependence of the current flow through the valve on the change in reagent pressure at its inlet.
Известно устройство для дозирования флотационных реагентов ПРМ-2 [2], содержащее мерный сосуд с мерной трубкой, соединенный входным патрубком с перекидным клапаном, управляемым электромагнитом, и выходным патрубком, являющимся выходом устройства. Мерный сосуд в устройстве [2] заполняется из расходного бака под напором, а сливается в технологический процесс самотеком, поэтому время слива реагента из мерного сосуда существенно больше времени наполнения мерного сосуда. Устройство [2] имеет низкую производительность.A device for dispensing flotation reagents PRM-2 [2], containing a measuring vessel with a measuring tube, connected by an inlet pipe with a flap valve controlled by an electromagnet, and an outlet pipe, which is the output of the device. The measuring vessel in the device [2] is filled from the supply tank under pressure, and merges into the process by gravity, therefore, the time of reagent discharge from the measuring vessel is significantly longer than the time of filling the measuring vessel. The device [2] has poor performance.
Прототипом предлагаемого изобретения является устройство [2].The prototype of the invention is a device [2].
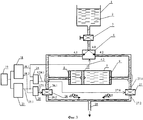
Предлагаемое устройство (вариант 1) изображено на фиг.1. На фиг.2 изображены эпюры сигналов в соответствующих точках устройства. На фиг.1 и 2 даны следующие обозначения:The proposed device (option 1) is shown in figure 1. Figure 2 shows the plot of the signals at the corresponding points of the device. Figure 1 and 2 are given the following notation:
1 - расходный бак,1 - supply tank
2 - жидкий реагент,2 - liquid reagent,
3 - регулируемый вентиль,3 - adjustable valve
4 - первый перекидной клапан [3],4 - the first changeover valve [3],
4.0 - вход устройства, вход/выход,4.0 - device input, input / output,
4.1 - первый вход/выход перекидного клапана,4.1 - the first input / output of the changeover valve,
4.2 - второй вход/выход первого перекидного клапана,4.2 - the second input / output of the first changeover valve,
4.3 - управляющий вход первого перекидного клапана,4.3 - control input of the first changeover valve,
5 - мерный сосуд,5 - measuring vessel,
6 - направление движения четных доз реагента,6 - direction of movement of even doses of the reagent,
7 - направление движения нечетных доз реагента,7 - direction of movement of odd doses of the reagent,
8 - первый торец мерного сосуда,8 - the first end of the measuring vessel,
9 - второй торец мерного сосуда,9 - the second end of the measuring vessel,
10 - свободно перемещаемый поршень,10 - freely movable piston,
11 - первое запорное устройство,11 - the first locking device
12 - второе запорное устройство,12 - second locking device
13 - первый вход/выход мерного сосуда,13 - the first input / output of the measuring vessel,
14 - второй вход/выход мерного сосуда,14 - the second input / output of the measuring vessel,
15 - второй перекидной клапан,15 - the second changeover valve
15.0 - выход устройства, вход/выход,15.0 - device output, input / output,
15.1 - первый вход/выход второго перекидного клапана,15.1 - the first input / output of the second changeover valve,
15.2 - второй вход/выход второго перекидного клапана,15.2 - the second input / output of the second changeover valve,
15.3 - управляющий вход второго перекидного клапана,15.3 - control input of the second changeover valve,
16 - первый узел соединения трубопроводов,16 is a first node connecting pipelines,
17 - второй узел соединения трубопроводов,17 - the second node connecting pipelines,
18 - генератор частоты,18 - frequency generator,
18.1 - прямой выход генератора частоты,18.1 - direct output of the frequency generator,
18.2 - инверсный выход генератора частоты,18.2 - inverse output of the frequency generator,
19 - задатчик,19 - setter,
19.1 - выход задатчика,19.1 - setpoint output,
20 - напряжение на управляющем входе первого перекидного клапана,20 - voltage at the control input of the first changeover valve,
21 - напряжение на управляющем входе второго перекидного клапана,21 - voltage at the control input of the second changeover valve,
22 - доза реагента, равная объему мерного сосуда.22 - dose of reagent equal to the volume of the measuring vessel.
Устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов (вариант 1) работает следующим образом. Реагент поступает на вход первого перекидного клапана 4, а выходит в технологический процесс из второго перекидного клапана 15, которые являются впускным и выпускным клапанами устройства соответственно. При открывании регулируемого вентиля 3 реагент 2 из напорного бака 1 поступает на вход 4.0 первого перекидного клапана 4. Для определенности положим, что в этот момент на управляющий вход 4.3 перекидного клапана 4 подан управляющий сигнал, обеспечивающий соединение входа 4.0 с первым входом/выходом 4.1 первого перекидного клапана. В этот момент на управляющий вход 15.3 второго перекидного клапана 15 поступает сигнал, обеспечивающий соединение выхода устройства 15.0 со вторым входом/выходом 15.2 второго перекидного клапана 15. Поэтому свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 в мерном сосуде перемещается от первого торца 8 мерной емкости 5 ко второму торцу 9 мерной емкости, а реагент поступает из входа устройства 4.0 на его выход 15.0 по входу/выходу 4.1 первого перекидного клапана 4, первый узел соединения трубопроводов 16, первый вход/выход 13 мерного сосуда, мерный сосуд 5, второй вход/выход 14 мерного сосуда, второй узел соединения трубопроводов 17, второй вход/выход 15.2 второго перекидного клапана 15. Когда свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 достигает второго торца 9 мерного сосуда 5, второе запорное устройство 12 перекрывает второй вход/выход 14 мерного сосуда 5, и проток реагента прекращается, а свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 остается в таком состоянии до изменения управляющих сигналов на управляющих входах 4.3 и 15.3 перекидных клапанов 4 и 15 на противоположные. После этого свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 проходит от второго торца 9 до первого торца 8 мерной емкости 5, а реагент поступает с входа устройства 4.0 на его выход 15.0 по цепи: второй вход/выход первого перекидного клапана 4, второй узел соединения трубопроводов 17, второй вход/выход 14 мерного сосуда 5, мерный сосуд 5, первый вход/выход 13 мерного сосуда 5, первый узел соединения трубопроводов 16, первый вход/выход 15.1 второго перекидного клапана 15. При достижении свободно перемещаемым поршнем 10 первого торца 8 мерной емкости 5 первое запорное устройство 11 перекрывает поток реагента на время до следующего изменения управляющих сигналов, подаваемых на управляющие входы 4.3 и 15.3 с выходов 18.1 и 18.2 генератора частоты 18. Далее цикл дозирования повторяется.A device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 1) works as follows. The reagent enters the input of the
Текущее значение расхода Qтек определяется выражением Qтек=2Vo·F, где Vo - объем мерного сосуда, F - частота генератора. Выходная частота 18.1 (18.2) генератора частоты 18 устанавливается сигналом с выхода 19.1 задатчика 19.The current value of the flow rate Qtec is determined by the expression Qtec = 2Vo · F, where Vo is the volume of the measuring vessel, F is the frequency of the generator. The output frequency 18.1 (18.2) of the
Таким образом, за каждый период Т на выход устройства поступают две дозы 22 реагента, при этом объем дозы равен объему Vo мерной емкости. Для уменьшения текущего расхода реагента изменяют частоту поступления доз 22 путем изменения выходного сигнала задатчика 19. Таким образом, за один период частоты генератора в технологический процесс поступает объем реагента 2Vo независимо от давления реагента на входе устройства.Thus, for each period T, two doses of
На фиг.3 (вариант 2) изображено устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов, в котором частота поступления уменьшенных доз в технологический процесс остается постоянной, но за период Т дозируется объем, равный 2Vo. На фиг.4 изображены сигналы на соответствующих выходах устройства и потоки Q реагента в трубопроводах устройства, а именно:Figure 3 (option 2) shows a device for dispensing liquid reagents, in which the frequency of receipt of reduced doses in the process remains constant, but for a period T a volume equal to 2Vo is dosed. Figure 4 shows the signals at the respective outputs of the device and the flow Q of the reagent in the pipelines of the device, namely:
23 - генератор широтно-импульсного сигнала,23 - pulse-width signal generator,
23.1 - выходной сигнал генератора широтно-импульсного сигнала,23.1 - output signal of the pulse width generator,
24 - первый логический элемент 2И,24 - the first logical element 2I,
24.1 - выходной сигнал первого логического элемента 24,24.1 - output signal of the
25 - второй логический элемент 2И,25 - the second logical element 2I,
25.1 - выходной сигнал второго логического элемента,25.1 - output signal of the second logic element,
26 - первый отсечной клапан,26 - the first shut-off valve
26.1 - вход первого отсечного клапана,26.1 - input of the first shut-off valve,
26.2 - выход первого отсечного клапана,26.2 - output of the first shut-off valve,
27 - второй отсечной клапан,27 - second shut-off valve,
27.0 - управляющий вход второго отсечного клапана,27.0 - control input of the second shut-off valve,
27.1 - вход второго отсечного клапана,27.1 - input of the second shut-off valve,
27.2 - выход второго отсечного клапана,27.2 - output of the second shut-off valve,
28 - выход устройства дозирования.28 - output device dispensing.
Устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов (вариант 2) работает следующим образом. Генератор частоты 18 и генератор широтно-импульсного сигнала 23, имеющий постоянную выходную частоту, управляющими входами подключены к выходу задатчика 19. Причем выходной сигнал задатчика 19, увеличивающий частоту генератора 18, пропорционально увеличивает длительность (ширину) импульса генератора широтно-импульсного сигнала 23.A device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 2) works as follows. The
Для определенности положим, что при поступлении напряжения на управляющий вход 4.3 первого перекидного клапана 4 его вход 4.0 соединяется с первой линией 4.1 первого перекидного клапана 4. Сигнал 18.1 является разрешающим для сигнала с выхода 23.1 генератора широтно-импульсного сигнала 23. Поэтому с выхода 24.1 логического элемента 24 поступают сигналы U23.1 на управляющий вход 27.0 отсечного клапана 27 и обеспечивают прохождение доз реагента ΔQ27 на выход 28 устройства дозирования. За время, меньшее или равное половине периода сигнала генератора частоты 18, свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 доходит до второго торца 9 мерного сосуда. По окончании управляющего сигнала на управляющем входе 4.3 вход 4.0 устройства соединяется со вторым входом/выходом 4.2 первого перекидного клапана 4. Одновременно появляется разрешающий сигнал с инверсного выхода 18.2, который поступает на вход второго логического элемента 2И 25. При этом первый отсечной клапан 26 под действием управляющего сигнала U25.1, поступающего на вход первого отсечного клапана 26, обеспечивает прохождение доз ΔQ26 реагента на выход 28 устройства. Далее цикл дозирования повторяется.For definiteness, we assume that when voltage is supplied to the control input 4.3 of the
Таким образом, устройство дозирования жидких реагентов обеспечивает поступление реагента с постоянной частотой в технологический процесс уменьшенными по сравнению с емкостью мерного сосуда дозами, что является одним из полезных свойств устройства для дозирования жидких реагентов.Thus, the device for dispensing liquid reagents ensures the flow of reagent with a constant frequency into the technological process in doses reduced in comparison with the capacity of the measuring vessel, which is one of the useful properties of the device for dispensing liquid reagents.
На фиг.5 изображено устройство для дозироваиия жидких реагентов (вариант 3), в котором фиксированные дозы объемом Vo поступают на второй вход/выход 4.2, являющийся выходом устройства, под давлением, определяемым давлением воздуха, подаваемого на первый вход/выход 15.1 второго перекидного клапана 15.Figure 5 shows a device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 3), in which fixed doses of volume Vo arrive at the second inlet / outlet 4.2, which is the outlet of the device, under pressure determined by the pressure of the air supplied to the first inlet / outlet 15.1 of the second changeover valve fifteen.
Устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов (вариант 3) работает следующим образом.A device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 3) works as follows.
При поступлении управляющего сигнала с прямого выхода генератора частоты 18 на управляющий вход 4.3 первого перекидного клапана 4 первый вход/выход первого перекидного клапана 4.1 соединяется с входом/выходом 4.0 первого перекидного клапана 4. Одновременно второй вход/выход 15.2 второго перекидного клапана 15 соединяется с входом/выходом 15.0 второго перекидного клапана, и свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 перемещается ко второму торцу 9 мерной емкости 5. По достижении свободно перемещаемым поршнем 10 торца 9 мерная емкость 5 наполняется реагентом, движение свободно перемещаемого поршня 10 прекращается, а доза реагента, равная емкости мерного сосуда 5, готова к пересылке ее в технологический процесс. При изменении управляющих сигналов на выходах 18.1 и 18,2 на противоположные первый 4 и второй 15 перекидные клапаны переходят в противоположные состояния. При этом вход/выход 4.0 первого перекидного клапана соединяется с вторым входом/выходом 4.2 первого перекидного клапана 4, а первый вход/выход 15.1 второго перекидного клапана 15 соединяется с линией 15.0 второго перекидного клапана 15 и свободно перемещаемый поршень 10 под давлением воздуха перемещается к первому торцу 8 мерной емкости 5, при этом на выход устройства под давлением поступает доза Q4.2, равная объему мерной емкости 5. Текущее значение расхода Отек. реагента определяется выражением Qтек=Vo·F. Далее цикл дозирования повторяется.Upon receipt of the control signal from the direct output of the
На фиг.7 изображено устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов (вариант 4) на базе нормально закрытых клапанов. В устройство введены нормально закрытые клапаны 29, 30, 31 и 32, соединенные по "мостовой схеме" (по аналогии с диодным "мостом" в электротехнике), образующие две диагонали AB и CD. Диагональ AB является входом/выходом устройства дозирования жидких реагентов, в диагональ CD подключены входы/выходы 13 и 14 мерного сосуда 5. Управляющие входы нормально закрытых клапанов 29, 32 и 30, 31 попарно соединены и подключены к прямому 18.1 и инверсному 18.2 выходам генератора частоты 18.Figure 7 shows a device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 4) based on normally closed valves. Normally closed
Устройство для дозирования жидких реагентов (вариант 4) работает следующим образом.A device for dispensing liquid reagents (option 4) works as follows.
Для определенности положим, что с прямого выхода генератора частоты 18 на объединенные управляющие входы 29.1 и 32.1 нормально закрытых клапанов 29 и 32 поступает управляющий сигнал, обеспечивающий открывание нормально закрытых клапанов 29 и 32. При этом реагент протекает с входа устройства по следующему пути: вход устройства А, нормально закрытый клапан 29, мерная емкость 5, нормально закрытый клапан 32, выход В устройства. По достижении свободно перемещаемым поршнем 10 второго торца 9 мерной емкости 5 истечение реагента на выходе В прекращается. При изменении управляющих сигналов на выходах 18.1 и 18.2 генератора частоты 18 на противоположные прохождение реагента на выход В устройства осуществляется по пути: вход А устройства дозирования, нормально закрытый клапан 31, мерный сосуд 5, нормально закрытый клапан 32, выход В устройства. Поступление реагента на выход В прекращается по достижении свободно перемещаемым поршнем 10 первого торца 8 мерной емкости 5. Далее цикл дозирования повторяется.For definiteness, we assume that from the direct output of the
Предлагаемое техническое решение является новым, так как включает совокупность новых существенных признаков с соответствующими связями между элементами, а именно: введены новые элементы и связи - первый и второй перекидные клапаны, мерный сосуд, оснащенный свободно перемещаемым поршнем, первое и второе запорные устройства, управляемый генератор широтно-импульсного сигнала, задатчик, два логических элемента 2И, причем входы перекидных клапанов подключены к выходам логических элементов 2И, введена связь второго перекидного клапана с источником воздуха под повышенным давлением, а также в один из вариантов устройства дозирования введена "мостовая" схема нормально закрытых клапанов и их связи с управляемым генератором частоты.The proposed technical solution is new, as it includes a set of new essential features with the corresponding connections between the elements, namely: new elements and connections are introduced - the first and second flapper valves, a measuring vessel equipped with a freely movable piston, the first and second locking devices, a controlled generator pulse-width signal, master, two logic elements 2I, and the inputs of the rocker valves connected to the outputs of the logic elements 2I, the connection of the second rocker valve with the source chnikom air under increased pressure, and in one embodiment of the dispensing device introduced "bridge" circuit, normally closed valves and their communication with the controlled frequency generator.
Указанная совокупность новых существенных признаков позволяет сделать изобретательский шаг и получить положительный эффект, заключающийся в расширении функциональных возможностей дозаторов жидких реагентов. Предлагаемое изобретение промышленно применимо для автоматического дозирования жидких реагентов при флотации руд цветных металлов, в других случаях дозирования жидких реагентов в химической и строительной отраслях промышленности.The specified set of new essential features allows you to take an inventive step and get a positive effect, which consists in expanding the functionality of the dispensers of liquid reagents. The present invention is industrially applicable for automatic dosing of liquid reagents during flotation of non-ferrous metal ores, in other cases, dosing of liquid reagents in the chemical and construction industries.
ЛитератураLiterature
1. Основы металлургии, том VI, Москва, изд."Металлургия", 1973 г., с.185.1. Fundamentals of Metallurgy, Volume VI, Moscow, Publishing House Metallurgy, 1973, p. 185.
2. Основы металлургии, том VI, Москва, изд. "Металлургия", 1973 г., с.182.2. Fundamentals of Metallurgy, Volume VI, Moscow, ed. Metallurgy, 1973, p. 182.
3. Каталог фирмы CAMOZZI, 2004-2005 г., с.2.02 /001.3. Catalog of the company CAMOZZI, 2004-2005, p. 02.02 / 001.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006122061/28A RU2337326C2 (en) | 2006-06-22 | 2006-06-22 | Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006122061/28A RU2337326C2 (en) | 2006-06-22 | 2006-06-22 | Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2006122061A RU2006122061A (en) | 2008-01-10 |
| RU2337326C2 true RU2337326C2 (en) | 2008-10-27 |
Family
ID=39019644
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2006122061/28A RU2337326C2 (en) | 2006-06-22 | 2006-06-22 | Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2337326C2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2473050C1 (en) * | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-20 | Оао "Союзцветметавтоматика" | Apparatus for feeding floatation agents |
| RU2664922C1 (en) * | 2017-10-06 | 2018-08-23 | Акционерное общество "Союзцветметавтоматика" | Reagent flow dosing and monitoring device |
| RU2685589C1 (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2019-04-22 | Чайна Юниверсити Оф Майнинг Энд Текнолоджи | Device for emulsification and controlled addition of flotation reagent |
-
2006
- 2006-06-22 RU RU2006122061/28A patent/RU2337326C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| Основы металлургии, T.VI, М.: Металлургия, 1973, с.182. * |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2473050C1 (en) * | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-20 | Оао "Союзцветметавтоматика" | Apparatus for feeding floatation agents |
| RU2685589C1 (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2019-04-22 | Чайна Юниверсити Оф Майнинг Энд Текнолоджи | Device for emulsification and controlled addition of flotation reagent |
| RU2664922C1 (en) * | 2017-10-06 | 2018-08-23 | Акционерное общество "Союзцветметавтоматика" | Reagent flow dosing and monitoring device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2006122061A (en) | 2008-01-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2006257205B2 (en) | Fluid flow controller | |
| RU2337326C2 (en) | Device for metering of liquid reagents (versions) | |
| CN109453545A (en) | The liquid dispensing device of Column eluate | |
| CN209287200U (en) | The liquid dispensing device of Column eluate | |
| RU2381415C1 (en) | Gas odorant automatic supply into pipeline method and equipment for its realisation | |
| CN102786018A (en) | Quantitative filling device and filling method thereof | |
| RU2664922C1 (en) | Reagent flow dosing and monitoring device | |
| CN202829551U (en) | Ration filling device | |
| JPS56166422A (en) | Fluid measuring apparatus | |
| CN110191772A (en) | The bonding agent feeding device and adhesive supply method of molding sand | |
| RU2018104327A (en) | LIQUID MIXING DEVICE | |
| CN207315760U (en) | A kind of novel hydraulic solenoid valve block based on miniature inserting valve technology | |
| CN207749582U (en) | Anti pollution water tank | |
| EP1515082B1 (en) | An arrangement for metering fluids, for instance for textile plants | |
| RU114072U1 (en) | WATER DISPOSABLE COLUMN DOSED WATER DISCHARGE | |
| US3653266A (en) | Dispenser valve for thick liquids or slurries | |
| RU2396516C1 (en) | Gas flow metre | |
| PL427446A1 (en) | Natural gas measuring and billing system | |
| CN216260048U (en) | PH detection device of electric drive membrane intelligence CIP system | |
| CN221951418U (en) | An intelligent control type high-precision ore dressing dosing machine | |
| RU2005139129A (en) | DEVICE FOR MEASURING THE EXPENDITURE OF LIQUID REAGENTS | |
| CN214332328U (en) | Homogeneous multi-path multi-point medicament precise injection device | |
| SU765785A1 (en) | Batchmeter-flowmeter | |
| RU2544258C2 (en) | Valve and system of gaseous medium flow measurement | |
| CN201568735U (en) | Atmospheric pressure balanced type quick switching valve |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20110623 |