JP3644472B2 - Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map - Google Patents
Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3644472B2 JP3644472B2 JP18693997A JP18693997A JP3644472B2 JP 3644472 B2 JP3644472 B2 JP 3644472B2 JP 18693997 A JP18693997 A JP 18693997A JP 18693997 A JP18693997 A JP 18693997A JP 3644472 B2 JP3644472 B2 JP 3644472B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- building
- information
- displayed
- shape map
- screen
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Instructional Devices (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、座標列により建造物の形状を表示した建造物形状地図上において設定した建造物の表示形態を変化させて、当該施設を識別できるようにした建造物形状地図による情報案内装置及び情報案内方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
地図を表示して地図上から種々の案内を行う場合、従来、目的とする施設等の建造物に対して旗印、丸印等のマークを付したり、建造物の外形表示により目的地点を表示して案内を行っている。例えば、東京駅を出発地としてサンシャインビルまで経路案内する場合、名称入力、電話入力等でサンシャインビルを目的地点として設定すると、その周辺の地図が表示され、サンシャインビルの建物の位置に目的地点であることを示す旗印や丸印が付加され、或いはサンシャインビルの建物の外形が表示されてそこに至るまでの経路が探索され、これに沿ってナビゲーションが行われる。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、旗印、丸印等の統一したマークで目的地点を表示したのでは、その地点がどのような地点であるのか、目的の施設がどのような施設であるのか一目で判別するのは容易ではなく、利用者にとっては不便であった。
【0004】
また、平面地図で目的となる建造物を特定しようとすると、特に市街地等複数のビルが乱立する地域においては、平面における形状が似通ったものが多く、特定することが困難であることもある。また、目的となる建造物は見つけ出せたとしても、その建物内で目的とする施設、入居者の場所までは特定できない。特に、建造物が高層である場合にはどの階に目的となる施設があり、入居者がいるのか分かり難い。
【0005】
本発明は上記課題を解決するためのもので、目的の建造物の表示形態を他の建造物と変化させたり、立体表示させることにより、目的とする建造物を容易に認識可能にすることを目的とする。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の建造物形状地図による情報案内装置は、建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報を記憶する記憶手段と、該記憶手段に記憶された建造物形状地図情報に基づいて建造物形状地図を表示する建造物形状地図表示制御手段と、該表示された建造物形状地図上の建造物を指定する建造物指定手段と、該建造物指定手段により指定された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する立体表示制御手段と、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する選択手段とを備え、前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする。
また、本発明は、建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報を記憶する記憶手段と、ジャンルを選択するジャンル選択手段と、該ジャンル選択手段により選択されたジャンルに基づいて建造物を検索する建造物検索手段と、該建造物検索手段により検索された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する立体表示制御手段と、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する選択手段とを備え、前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする。
【0007】
また、本発明は、建造物形状地図を表示する情報案内装置を用いて案内する方法において、建造物形状地図表示制御手段により、記憶手段に記憶された建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報に基づいて建造物形状地図を表示する段階、建造物指定手段により、前記建造物形状地図表示制御手段で表示された建造物形状地図上の建造物を指定する段階、表示処理手段により、前記建造物指定手段で指定された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する段階、立体表示制御手段により、記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する段階、選択手段により、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する段階を備え、前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする。
また、本発明は、建造物形状地図を表示する情報案内装置を用いて案内する方法において、ジャンル選択手段によりジャンルを選択する段階、建造物検索手段により、ジャンル選択手段で選択されたジャンルに基づいて、記憶手段に記憶された建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報から建造物を検索する段階、表示処理手段により、建造物検索手段で検索された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、立体表示制御手段により、前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する段階、選択手段により、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する段階を備え、前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする。
【0008】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の1形態を図面を参照しつつ説明する。
図1は本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置の実施の1形態を示す図、図2は本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置による形状地図の表示案内処理を説明するための図、図3は建造物形状地図のデータ構造の例を示す図である。
【0009】
図1において、記憶装置100は、建築物(一般家屋、事務室用建造物、マンション、消防署、デパート、病院、駅等)、施設(塔、公園、遊園地、運動場等)、橋、道路その他各種の所謂建造物の形状を描画し表示するための建造物形状地図のデータ100a、目的地点の表示形態を変化させて認識し易くするための表示形態変更データ100bを記憶したものであり、さらに道路地図のデータ、建造物形状地図のデータ等を記憶したものであってもよい。建造物形状地図のデータ100aは、建造物の形状を描画し表示するための複数の座標値からなる座標列、その建造物の名称、番地(住所)、その建造物に属する各種情報、例えば種別、高さ、構成(入居者)、さらにその電話番号等の情報を有する。表示形態変更データ100bは、後述する建造物形状地図において地点設定がされたときに、設定された建造物がマンション、個人宅、施設等の何れであるかの種別や面積等に応じて表示形態を変更するためのデータ(例えば、種別や面積に応じた異なるマーク等のデータ)、建造物の高さ方向、階も表示可能なデータ等からなっている。
【0010】
中央処理装置200は、記憶装置100から表示範囲の建造物形状地図のデータを読み出して建造物の種別や高さ、その他の詳細情報(構成の規模等)から、座標列に基づき建造物の形状地図を描画表示し、その表示した建造物形状地図上で建造物が選択されると、記憶装置100から表示形態変更データを読みだしてその建造物の表示形態を変化させて強調表示したり、立体表示し、その建造物に属する情報や周辺情報を検索し案内出力したり、逆に建造物に属する情報から建造物を中心とする形状地図を表示するものである。形状表示処理部200aは、例えば建造物の種別や高さ、構成の規模に基づいて建造物形状地図を描画し、また形状地図の上に、主要な形状物の名称を描画し表示する処理を行うものである。表示形態変更表示処理部200bは、建造物の種別、面積等に応じて異なるマークを選択表示したり、また、立体表示処理等を行って描画し表示するものである。検索案内処理部200cは、建造物に関する各種の情報、例えば建造物内に入居する会社や事務所、店舗等の名称のリスト、電話番号、その建造物の周辺に存在する同様の情報(周辺情報)を検索し案内したり、電話番号や名称から建造物を検索し形状地図で案内したりするものである。出力装置300は、中央処理装置200による建造物形状地図や、案内情報出力を表示するディスプレイ、印刷出力するプリンタ等である。入力指示装置400は、建造物形状地図の出力範囲(地域)、地図上の建造物のエリア、建造物に関する情報案内、周辺情報の検索等の選択、指示を入力するものであり、例えば出力装置300のディスプレイ画面に組み合わせたタッチパネル、ジョイスティックやマウス等のポインティングデバイス、リモコンが用いられる。
【0011】
中央処理装置200では、図2に示すように例えば選択された縮尺の道路地図を表示している状態で、建造物形状地図が選択されると(ステップS1)、まず、形状地図の表示処理を実行し(ステップS2)、その形状地図の上に建造物名称の表示処理を実行する(ステップS3)。その後、建造物に属する情報、例えばビルであれば、そのビル内に入居している店舗や事務所等、入居者の具体的な名称や業種、業務内容、電話番号等の情報に関して建造物形状地図による検索案内処理を実行する(ステップS5)。建造物の形状は、一般家屋やビル、その他の建築物であれば、その平面形状になり、公園や道路であればその平面地形になる。
【0012】
地図データ記憶装置100に記憶する建造物形状地図のデータ構造は、例えば図3(A)に示すように建造物のデータ数Nの次にN個の各建造物のデータが記憶される。そして、各建造物のデータは、建造物の名称、番地(住所)、種別、建造物の形状、高さ、詳細の各情報からなる。名称は、建造物であればその名前、個人の家屋であればその居住者名、施設であればその施設名、道路であれば「中央通り」、「国道1号」のように道路種別や通り名であり、番地(住所)は、その建造物の番地である。建造物の形状は、形状を表す座標数nとその座標値(x0 ,y0 )、(x1 ,y1 )、………、(xn-1 ,yn-1 )であり、種別は、一般の家屋、マンション、事務室用建造物、公共施設、道路、公園等の情報である。高さは、階数や高さ(m)の情報である。そして詳細は、例えば貸室用建造物であれば各入居者に関する情報であり、名称数mと各入居者について、名称、電話番号、部屋番号、入居階数、分類(レストラン、コンビニ、……等の業種、事業内容)に関する情報である。したがって、図3(B)に示すように建造物の形状に関する情報として座標値を順に読み出して線で結び描画し表示することによって、例えばビルや家屋の平面形状や公園の地形を出力することができる。
【0013】
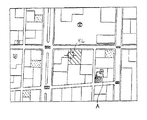
次に、目的地点の表示形態の変更処理について図4により説明する。目的地点の表示形態の変更は、建造物形状地図において、設定された目的地点に対して行われる。建造物形状地図は、前述したように建造物形状地図のデータに形状データとして記憶された座標列を順に読み出して線で結ぶことにより描画し表示するものであり、例えば、図5(a)に示すような道路地図に対して図5(b)に示すように建造物形状が表示される。
【0014】
この建造物形状地図のデータは必ずしもあらゆる地域に対して準備されているとは限らない。そこで、目的地点を、座標や電話番号により入力すると、入力したx,y座標を検索し、当該座標が建造物形状地図のある範囲か否か検索する(ステップS11〜S13)。建造物形状地図のある範囲であれば、建造物形状地図を表示し(S14)、建造物形状地図のある範囲でなければ従来の道路地図を表示する(S15)。そして、画面上でカーソルを移動し、カーソルが停止した地点の位置を検出し地点設定が行われる(S16〜S19)。建造物形状地図が表示されている場合は、入力した(x,y)座標に該当する建造物形状を検索し、検索した建造物の形状の種別、面積を判断し(S20〜S21)、表示形態を決定する(S22)。従来の道路地図を表示した場合には、地点設定後、表示形態を決定する。
【0015】
例えば、建造物形状地図が表示されている場合の表示形態について、マーク表示を例にとって図6、図7により説明する。
図6はマーク選択条件テーブルの1例を示し、例えば、階数が1階、2階、3〜5階、6階以上という条件に対してマークNo.a〜dを対応させ、また、個人名や電話番号等の名称数0〜1、2、3〜10、11以上に対してマークNo.a〜dを対応させ、面積(m2 )0〜150、151〜250、251〜600、601〜1200、1201以上に対してマークNo.a〜eを対応させる。
【0016】
マークNo.a〜eは、例えば、図7に示すようなマークテーブルでマークが登録されており、それぞれ個人宅平屋、個人宅2階建、アパート、マンション、別荘を意味するものとして登録されている。
【0017】
したがって、検索した建造物の種類を判断し、例えば階数が3〜5階であればマーク選択条件テーブルを参照してマークNo.cが分かり、これにより図7のマークテーブルを参照してアパートを示すマークが呼び出されて表示される。また、検索した建造物の名称数が11以上であればマーク選択条件テーブルよりマークNo.dが分かり、マークテーブルを参照してマンションを示すマークが表示される。また、検索した建造物の面積が1201m2 以上であれば、マーク選択条件テーブルよりマークNo.eが分かり、マークテーブルを参照して別荘のマークが表示される。
【0018】
また、設定された建造物のみを表示して、他の建造物(ビル、家、工場等の建築物)の形状を形状地図表示上から消去する構成をとることにより、道路、川、線路等の土地に関する建造物と目的地点のみの表示となり、目的地点が強調されて表示されるとともに、道路、川、線路等は表示されているので目的地点の位置関係が明瞭に把握可能となる。
【0019】
また、カーソルの位置を検出し、地点が設定された時には、該当する建造物を検索して、建造物の平面区画から中央処理装置により選択された立体形状のマークを表示させることにより、あたかも、その地点に建造物が建てられたかのように表示処理することにより、該当する建造物をより認識しやすくすることができる。
【0020】
また、マーク表示に限らず、図8のAとして示すように、該当する建造物を立体表示することにより認識し易くするようにしてもよい。
【0021】
次に、建造物形状地図を利用した検索・案内について説明する。図9は建造物形状地図による検索案内処理を説明するための図、図10は建造物形状地図による建造物選択操作時の画面の例を示す図、図11は情報表示画面の例を示す図、図12は建造物形状地図による情報の案内画面の例を示す図、図13は建造物の周辺情報検索のリスト表示画面の例を示す図、図14はジャンル検索画面の例を示す図である。
【0022】
上記のようにして表示された建造物形状地図を利用すると、図3で説明したデータに基づきその建造物だけでなく、その周辺の情報についても検索することができ、さらに、各建造物内の情報の案内を行うことができる。例えば建造物形状地図では、その中央に図10に示すような○に十の字のカーソルが表示され、入力指示手段から、建造物選択の指示を入力することによって、その建造物が選択される。したがって、検索・案内処理では、図9に示すようにこの建造物選択があるのを待ち(ステップS41)、建造物選択があると、図10に示すように目的地や通過点、メモリ、インフォメーション、周辺情報検索の各モードの選択肢を表示する(ステップS42)。目的地や通過点、メモリは、後述する車両用ナビゲーション装置に本発明を組み込んだ場合に、経路探索のための地点設定に使うものであり、ここでは説明を省略し、以下、インフォメーション、周辺情報検索の各モードに限って説明する。
【0023】
そこで、選択キーがインフォメーションか、周辺情報検索かを調べ(ステップS43)、図10に示すようにインフォメーションの欄が選択された場合には、該当する建造物データの詳細情報の名称数と各名称を読み込んで五十音順に名称のリストを作成し、それらの情報を図11に示すように表示する(ステップS44)。そして、その中の名称欄の1つ、例えば図11に示すようにアイウエ株式会社が選択されると(ステップS45)、建造物データから番地(住所)、その選択された名称、電話番号、分類等を読み込んで図12に示すようにアイウエ株式会社の名称と電話番号と住所を表示する(ステップS46)。なお、この画面に表示された戻り、目的地、通過点、メモリは操作キーであり、このような他の操作キーが選択されると、割り込みによりそれぞれの処理を実行する。また、名称欄の選択以外の指示の場合にも、同様にその指示に対応する他の処理を割り込み実行する。
【0024】
ステップS43において、周辺情報検索の欄が選択された場合には、まず、図13に示すように周辺情報の検索範囲を特定するために「繊維・織物の製造、販売」、「繊維・織物の染色、デザイン」、……等のジャンルリスト(分類のリスト)を表示する(ステップS47)。そして、ある分類欄が選択されると(ステップS48)、その選択された分類をデータの詳細情報から検索し、選択されている建造物との距離を求め(ステップS49)、検索された所定距離以内の名称を距離の短い順にソートし、図14に示すようにそのジャンル名と件数、そして検索された各名称と検索地点からの距離のリストを表示する(ステップS50)。この名称欄の1つが選択されると(ステップS51)、図12の場合と同様に建造物データから番地(住所)、その選択された名称、電話番号、分類等を読み込んでこれらを表示する(ステップS52)。ここで、戻りのキーが入力されると、この建造物を中心とする周辺の建造物形状地図を表示する。勿論、図示しない他のキーを用いて建造物形状地図を表示したり、道路地図等他の地図に切り換えるようにしてもよい。ステップS48において分類欄の選択以外の指示、ステップS51において名称欄の選択以外の指示の場合には、その指示に対応する他の処理を割り込み実行する。
【0025】
次に、建造物を立体表示する例について説明する。
図15は、入力指示手段で選択した建物の形状を3次元表示する検索・案内処理フローを説明する図である。
図9の場合と同様に、入力指示手段からの建造物選択があるのを待ち(ステップ61)、建造物選択があると、図10に示したように、目的地や通過点、メモリ、インフォメーション、周辺情報検索の各モードの選択肢を表示する(ステップ62)。次いで、選択キーがインフォメーションか、周辺検索かを調べ(ステップ63)、周辺検索が選択された場合には、図9のステップ47の処理にジャンプして同様の処理がなされる。
【0026】
次に、選択された建造物が高さ情報を有していて、テナントが複数ある場合を示す図16を参照しながら説明する。
図16(a)はインフォメーションを選択した画面を示しており、建造物形状地図上に選択肢が表示されており、インフォメーションの選択で、該当する建造物データの詳細情報の名称数と各名称を読み込み名称のリストを作成して図16(b)に示すように画面分割して表示する(ステップ64)。次いで、リスト表示はそのままの状態で、図16(c)に示すように、建造物形状を3次元表示し(ステップ65)、次いで、リスト中のカーソル位置の建造物の階を強調表示する(ステップ66)。このとき、リスト項目をカーソルで選択することにより、図16(d)に示すように、選択項目の階が強調表示される。次いで、名称欄の選択があると、図16(f)に示すように、建造物データの番地、選択された名称、電話番号、分類、店のジャンル、業種等の詳細情報等を読み込んで表示する(ステップ67、ステップ68)。また、図16(f)の状態において、リターンキーを操作すると、図16(e)の画面に戻る。また、建造物の階の階調表示をカーソルの上下操作により移動させることができ、リストには現在階調表示さている階に含まれるテナント或いは個人宅等が表示される。
【0027】
また、テナントが1つの場合を図17を参照して説明すると、図17(a)でインフォメーションを選択すると、建造物データの詳細情報の名称数と各名称を読み込んで名称のリストを作成し、画面分割して表示する処理が行われる。この場合、テナントが1つなので、図17(b)に示すように、その名称、電話番号、住所等が表示される。次いで、リスト表示はそのままの状態で、図17(c)に示すように、建造物形状を3次元表示し、建造物の2階(テナント階)を強調表示する。なお、建造物の3次元表示方法については、例えば、特開平9ー62179号に示される方法を用いる。
なお、高さ情報がない場合には、当然、3次元表示は行われないが、その他の処理は同様である。
【0028】
図18は電話番号や名称入力で選択した建物の形状を3次元表示する検索・案内処理フローを説明する図である。
電話番号或いは名称(50音)で目的地点を入力すると、該当する地点データが検索される(ステップ71、ステップ72)。この検索で建造物形状のデータがあれば、建造物形状を3次元表示する(ステップ73、ステップ74)。次いで、図16で説明したと同様に、リスト中のカーソル位置の建造物の階を強調表示した後、入力地点の詳細情報を表示する。
【0029】
なお、上記の例においては、名称のリストを画面分割して表示するようにしたが、画面分割せずに、リストを地図表示に重ねて別ウインドウで表示するようにしてもよい。また、上記の例においては、詳細情報のリストの項目をカーソルで選択することにより、選択項目の階を強調表示するようにしたが、逆に、立体表示された建物の階をカーソルで選択して強調表示し、選択されている階に含まれるテナントをリスト表示してその中から選択するようにしてもよい。また、強調表示の方法としては、太線表示、塗りつぶし表示、色分け表示、点滅表示等適宜採用すればよい。また、立体表示で階を強調表示するとともに、文字で強調表示した階数を表示してもよい。
【0030】
次に、図19〜図21により3次元表示処理の例について説明する。
【0031】
図19は建造物の3次元表示処理フローの例を示す図、図20は建造物形状地図、図21はフロアの高さを一定にして建造物を立体表示する例を示す図、図22は建造物の高さを一定にしてフロアの高さを可変にして表示する例を示す図、図23は図22の表示方法を説明する図である。
図19において、建造物形状地図データから建造物の高さを検索し(ステップ81)、検索した高さが、一定の表示縮尺で画面内で表示可能か否か判断する(ステップ82)。画面内で表示可能であれば1階あたりの高さを固定して建造物を立体化し(ステップ83)、次いで、平面地図を傾けて建造物を立体表示する(ステップ85、ステップ86)。例えば、図20に示すような市街の平面地図において、選択された建造物を図21に示すように1階あたりの高さを固定して平面地図を傾けて立体表示する。図21(a)は1階建ての場合、図21(b)は2階建ての場合を示しており、該当する階が強調表示されている。
【0032】
また、図19のステップ82において、画面内で表現できない場合には、建造物の高さは最大値で固定し、1階あたりの高さを変更し(ステップ84)、同様に平面地図を傾けて立体表示する。例えば、図22(a)は20階建て、図22(b)は40階建ての場合であり、該当する階(図22(a)は8階、図22(b)は19階)が強調表示されている。この表示方法は、図23に示すように、建物の高さhが所定以上の場合には、高さhを破線で示す設定枠の高さl1 に一致させ、建物の表示幅は設定枠の幅l2 内におさまるように表示する。この場合は、設定枠に収まるような表示縮尺で表示したことになる。
【0033】
なお、建造物を3次元表示する方法は、上記の例に限定されるものではなく、上から見下ろした鳥瞰表示や建物を水平方向に倒して横方向から見ることができるような表示としてもよい。また、表示縮尺は、一定縮尺でもよいが、一定縮尺で表示すると、建物の大きさにより見づらい場合があるので、建物の高さに応じて見やすい大きさとなるように表示縮尺を変えるようにしてもよい。また、建物の部分のみを拡大表示するようにしてもよいし、建造物形状地図は残しつつ別枠で建物を拡大表示するようにしてもよい。
【0034】
本発明の建造物形状地図による情報案内装置を利用すると、建造物形状地図から、その建造物の中に入居する会社や事務所、店舗、各種機関等の情報、さらには、その個別の会社の電話番号等を調べることができ、また、その建造物から一定の範囲内にある様々な会社や店舗、各種機関等を検索してリストアップし、その建造物を調べることができる。逆に、電話番号や名称を入力して、その名称、電話番号を図3に示した地図データの名称、詳細情報の名称や電話番号から検索することによって、その建造物を中心とする建造物形状地図を表示することも容易に行える。したがって、名称や分類に関する情報と大体の地域は判るが、建造物が判らない場合に、その建造物、例えば入居しているビルを検索することができ、また、あるビルに入居しているテナントを案内することもできるので、これを車両用ナビゲーション装置の地点設定等に利用すると、都市部での地点設定が容易になるというメリットがある。さらに、建造物の1つとして道路を対象とした場合、道路に関する情報としてパーキングメータの有無を提供できるようにすれば、車で行動する際の駐車に関する情報を提供することもできる。以下に、本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置を利用することのできる車両用ナビゲーション装置の構成例を説明する。
【0035】
図24は本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置を組み込んだ車両用ナビゲーション装置の1実施例構成を示す図である。
【0036】
本発明に係る車両用ナビゲーション装置は、図24に示すように経路案内に関する情報を入出力する入出力装置1、自車両の現在位置に関する情報を検出する現在位置検出装置2、経路の算出に必要なナビゲーション用データや経路案内に必要な表示/音声の案内データとプログラム(アプリケーション及び/又はOS)等が記録されている情報記憶装置3、経路探索処理や経路案内に必要な表示/音声案内処理を行うと共に、システム全体の制御を行う中央処理装置4から構成されている。そして、入出力装置1に図1の入力指示装置400と出力装置300が組み込まれ、情報記憶装置3に図1の記憶装置100が組み込まれ、中央処理装置4に図1の中央処理装置200が組み込まれている。まず、それぞれの構成について説明する。
【0037】
入出力装置1は、目的地を入力したり、運転者が必要な時に案内情報を音声および/または画面により出力できるように、運転者の意志によりナビゲーション処理を中央処理装置4に指示すると共に、処理後のデータなどをプリント出力する機能を備えている。その機能を実現するための手段として、入力部には、目的地を電話番号や地図上の座標などにて入力したり、経路案内をリクエストしたりするタッチスイッチ11や操作スイッチを有する。勿論、リモートコントローラ等の入力装置でもよい。また、出力部には、入力データを画面表示したり、運転者のリクエストに応じ自動的に経路案内を画面で表示するディスプレイ12、中央処理装置4で処理したデータや情報記憶装置3に格納されたデータをプリント出力するプリンタ13および経路案内を音声で出力するスピーカ16などを備えている。
【0038】
ここで、音声入力を可能にするための音声認識装置やICカードや磁気カードに記録されたデータを読み取るための記録カード読み取り装置を付加することもできる。また、ナビゲーションに必要なデータを蓄積し、運転者の要求により通信回線を介して情報提供する情報センターや、予め地図データや目的地データなどの運転者固有のデータが記憶されている手帳型電子装置などの情報源との間でデータのやりとりを行うためのデータ通信装置を付加することもできる。
【0039】
ディスプレイ12は、カラーCRTやカラー液晶表示器により構成されており、中央処理装置4が処理する地図データや案内データに基づく経路設定画面、区間図画面、交差点図画面などナビゲーションに必要なすべての画面をカラー表示出力すると共に、本画面に経路案内の設定および経路誘導中の案内や画面の切り換え操作を行うためのボタンが表示される。特に、通過交差点名などの通過交差点情報は、随時、区間図画面にポップアップでカラー表示される。
【0040】
このディスプレイ12は、運転席近傍のインストルメントパネル内に設けられており、運転者は区間図を見ることにより自車両の現在地を確認し、またこれからの経路についての情報を得ることができる。また、ディスプレイ12には機能ボタンの表示に対応してタッチスイッチ11が設けられており、ボタンをタッチすることにより入力される信号に基づいて上記の操作が実行されるように構成されている。このボタンとタッチスイッチなどから構成される入力信号発生手段は入力部を構成するものであるが、ここではその詳細な説明を省略する。
【0041】
現在位置検出手段2は、車両の現在位置衛星航法システム(GPS)を利用して情報を入手するGPS受信装置21と、FM多重放送、電波ビーコン、光ビーコン等を利用して情報を入手するためのVICS情報受信装置22と、携帯電話、パソコン等を利用することにより、情報センター(例えばATIS)や他車両と情報を双方向に通信するためのデータ送受信装置23と、車両の進行方位を、例えば地磁気を利用することにより絶対方位で検出する絶対方位センサ24と、車両の進行方位を、例えばステアリングセンサ、ジャイロセンサを利用することにより相対方位で検出する相対方位センサ25と、例えば車輪の回転数から車両の走行距離を検出する距離センサ26とから構成され、車両の走行に関する情報である例えば道路情報、交通情報を送受信したり、車両の現在位置に関する情報を検出したり、さらに現在位置に関する情報を送受信したりする装置である。
【0042】
情報記憶装置3は、ナビゲーション用のプログラム及びデータを記憶した外部記憶装置で、例えば磁気テープ、磁気ディスク、プロッピィディスク、CD−ROM、DVD、光ディスク、ICカード等からなっている。プログラムは、経路探索などの処理を行うためのプログラム、本実施例記載のフローチャートに示される処理プログラムや経路案内に必要な表示出力制御、音声案内に必要な音声出力制御を行うためのプログラム及びそれに必要なデータ、さらには経路案内及び地図表示に必要な表示情報データが格納されている。また、データは、地図データ、探索データ、案内データ、マップマッチングデータ、目的地データ、登録地点データ、道路データ、ジャンル別データ、ランドマークデータ等のファイルからなり、ナビゲーション装置に必要なすべてのデータが記憶されている。この地図データに経路案内のための道路地図や建造物形状地図とともに本発明の建造物形状地図のデータを含んでいる。なお、本発明は、CD−ROMにはデータのみ格納し、プログラムは中央処理装置に格納するタイプのものにも適用可能である。
【0043】
中央処理装置4は、種々の演算処理を実行するCPU40、情報記憶装置3のCD−ROMからプログラムを読み込んで格納するフラッシュメモリ41、フラッシュメモリ41のプログラムチェック、更新処理を行うプログラム(プログラム読み込み手段)を格納したROM42、設定された目的地の地点座標、道路名コードNo.等の探索された経路案内情報や演算処理中のデータを一時的に格納するRAM43、ディスプレイへの画面表示に使用する画像データが記憶された画像メモリ44、CPU40からの表示出力制御信号に基づいて画像メモリ44から画像データを取り出し、画像処理を施してディスプレイに出力する画像プロセッサ45、CPUからの音声出力制御信号に基づいて情報記憶装置3から読み出した音声、フレーズ、1つにまとまった文章、音等を合成してアナログ信号に変換してスピーカ16に出力する音声プロセッサ46、通信による入出力データのやり取りを行う通信インタフェース47および現在位置検出装置2のセンサ信号を取り込むためのセンサ入力インタフェース48、内部ダイアグ情報に日付や時間を記入するための時計49などを備えている。ここで、経路案内は画面表示と音声出力で行い、音声出力の有無は、運転者が選択できるように構成されている。
【0044】
なお、前記した更新処理を行うプログラムを外部記憶装置に格納しておいてもよい。
本発明に係るプログラム、その他ナビゲーションを実行するためのプログラムは全て外部記憶媒体であるCD−ROMに格納されてもよいし、それらプログラムの一部または全てが本体側のROM42に格納されていてもよい。
【0045】
また、本発明における機能が実現されるためのプログラムの全部又は一部、及びデータの全部又は一部を情報センタや他の車両からデータ送受信部23を介して受信し、ナビゲーション装置内の記録媒体であるフラッシュメモリ41やRAM43に記憶させるようにしてもよい。
【0046】
この外部記憶媒体に記憶されたデータやプログラムが外部信号としてナビゲーション装置本体の中央処理装置に入力されて演算処理されることにより、種々のナビゲーション機能が実現される。
【0047】
本発明に係るナビゲーション装置は、上記のように外部記憶装置のCD−ROMからプログラムを読み込むための比較的大容量のフラッシュメモリ41、CDの立ち上げ処理を行うプログラム(プログラム読み込み手段)を格納した小容量のROM42を内蔵する。フラッシュメモリ41は、電源が切断しても記憶情報が保持される、つまり不揮発性の記憶手段である。そして、CDの立ち上げ処理として、プログラム読み込み手段であるROM42のプログラムを起動してフラッシュメモリ41に格納したプログラムチェックを行い、情報記憶装置3のCD−ROMのディスク管理情報等を読み込む。プログラムのローディング処理(更新処理)は、この情報とフラッシュメモリ41の状態から判断して行われる。
【0048】
なお、本発明は、上記の実施例に限定されるものではなく、種々の変形が可能である。例えば上記の実施例では、建造物の名称として説明したが、これには町名その他の地区名も含めてもよい。全ての名称について処理するように説明したが、予め地図上に表示する優先度や表示の有無の情報を設定し、或いは名称に付加しておき、その情報に基づき名称を表示するように処理してもよいし、名称数が所定数以上のもの、所定高さ以上のものを対象として処理してもよい。また、xyの座標列を建造物の形状を表すデータとしたが、高さ方向の座標値(z)をも併せて3次元の座標データとして持ち、平面図で表す場合にはxyの座標列のみを用い、例えば斜め上から見た図やパースのような3次元形状図で表す場合にはxyzの座標列を用いるようにしてもよい。さらに、本発明は、車両用ナビゲーション装置に組み込むことにより、より親切な地点案内を行うことができるものであるが、単に市街地や観光地等の案内のみに用い、その情報をプリント出力してサービスを行うようにしてもよいことをいうまでもない。
【0049】
【発明の効果】
以上の説明から明らかなように、本発明によれば目的とする建造物を特定することが容易となり、その建造物に含まれる施設を選択した場合にも、それらがどの階にあるのかを容易に知ることができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置の実施の1形態を示す図である。
【図2】 本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置による形状地図の表示案内処理を説明するための図である。
【図3】 建造物形状地図のデータ構造の例を示す図である。
【図4】 本発明の表示形態変更処理を説明するための図である。
【図5】 建造物形状地図の例を説明するための図である。
【図6】 マーク選択条件テーブルを示す図である。
【図7】 マークテーブルを示す図である。
【図8】 立体表示の例を説明するための図である。
【図9】 建造物形状地図による検索案内処理を説明する図である。
【図10】 建造物形状地図による建造物選択操作時の画面の例を示す図である。
【図11】 情報表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図12】 建造物形状地図による情報の案内画面の例を示す図である。
【図13】 建造物の周辺情報検索のリスト表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図14】 ジャンル検索画面の例を示す図である。
【図15】 入力指示手段で選択した建物の形状を3次元表示する検索・案内処理フローを説明する図である。
【図16】 選択された建造物が高さ情報を有していて、テナントが複数ある場合の検索画面を示す図である。
【図17】 選択された建造物が高さ情報を有していて、テナントが1つの場合の検索画面を示す図である。
【図18】 電話番号/名称入力で選択した建物の形状を3次元表示する検索・案内処理フローを説明する図である。
【図19】 建造物の3次元表示処理フローの例を示す図である。
【図20】 建造物形状地図を示す図である。
【図21】 フロアの高さを一定にして建造物を立体表示する例を示す図である。
【図22】 建造物の高さを一定にしてフロアの高さを可変にして表示する例を示す図である。
【図23】 図22の表示方法を説明する図である。
【図24】 本発明に係る建造物形状地図による情報案内装置を組み込んだ車両用ナビゲーション装置の1実施例構成を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
100…記憶装置、200…中央処理装置、300…出力装置、400…入力装置。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an information guide device and information using a building shape map that can identify the facility by changing the display form of the building set on the building shape map displaying the shape of the building by a coordinate sequence. It relates to the guidance method.
[0002]
[Prior art]
When displaying various types of information on the map and displaying the map, conventionally, the target facility is marked with a flag or circle, or the destination is displayed by displaying the building outline. And give guidance. For example, when route guidance is made from Tokyo Station to the Sunshine Building, if the Sunshine Building is set as a destination by entering a name, telephone input, etc., a map of the surrounding area will be displayed, and the location of the Sunshine Building will be displayed at the destination. A flag mark or a circle mark indicating that there is, or an outline of the building of the sunshine building is displayed, and a route to that point is searched, and navigation is performed along this route.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, if the destination point is displayed with a unified mark such as a flag or a circle, it is not easy to determine at a glance what the point is and what the target facility is. It was inconvenient for users.
[0004]
In addition, when trying to identify a target building on a planar map, it is often difficult to identify, especially in an area where a plurality of buildings, such as an urban area, are prosperous, having a similar shape on the plane. Even if the target building can be found, the target facility and resident location in the building cannot be specified. In particular, if the building is a high-rise building, it is difficult to tell which floor has the target facility and there are residents.
[0005]
The present invention is for solving the above-mentioned problem, and makes it possible to easily recognize a target building by changing the display form of the target building from another building or by displaying it three-dimensionally. Objective.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The information guide device using a building shape map according to the present invention stores a building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing a shape for each building, height information, and detailed information, and is stored in the storage unit. A building shape map display control means for displaying a building shape map based on the building shape map information, a building designation means for designating a building on the displayed building shape map, and the building designation The name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the building designated by the means, and the name list of the facility read out is created, and the name list is divided into one screen and the name list on the other side. Display processing means for displaying a building shape map including the building designated on the screen, and the building displayed on the other screen by the display processing means based on the height information stored in the storage means 3D display Display control means and selection means for selecting a facility name from the name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means, and the stereoscopic display control means includes the facility selected by the selection means. The whole floor is highlighted in the three-dimensionally displayed building.
Further, the present invention provides a storage means for storing building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing a shape for each building, height information, and detailed information, a genre selection means for selecting a genre, and the genre selection means. The building search means for searching for a building based on the genre selected by the above, and the name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the building searched by the building search means. A display processing means for creating a name list of facilities, dividing the screen into a name list on one screen, and displaying a building shape map including the building designated on the other screen, and stored in the storage means Based on the height information, a stereoscopic display control means for stereoscopically displaying the building displayed on the other screen by the display processing means, and a name list displayed on the one screen by the display processing means And selecting means for selecting the name of the facility, the stereoscopic display control means may be highlighted in a building the overall floor is the stereoscopic display said selected by the selection means facilities exist.
[0007]
Further, the present invention provides a method for guiding using an information guide device for displaying a building shape map, wherein the building shape map display control means uses a coordinate sequence representing a shape for each building stored in the storage means, Displaying the building shape map based on the building shape map information having the depth information and the detailed information, and building on the building shape map displayed by the building shape map display control means by the building designation means In the step of designating the object, the display processing means reads out the names of the facilities included in the building from the detailed information of the building designated by the building designating means, and creates a facility name list read out. Dividing the screen and displaying the name list on one screen and the building shape map including the building designated on the other screen, based on the height information stored in the storage means by the stereoscopic display control means. Z The three-dimensional display of the building displayed on the other screen, and the step of selecting the facility name from the name list displayed on the one screen by the display processing means by the selection means, The means highlights the entire floor where the facility selected by the selection means is present in the three-dimensionally displayed building.
According to the present invention, in the method of guiding using the information guide device for displaying the building shape map, the step of selecting the genre by the genre selecting unit, the genre selected by the genre selecting unit by the building searching unit, A step of searching for a building from a building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing the shape, height information, and detailed information stored for each building stored in the storage unit; The name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the searched building, and the name list of the facility is read out. The name list is divided into one screen and the name list is displayed on the other screen. Based on the height information stored in the storage means by the display processing means for displaying the building shape map including the designated building and the stereoscopic display control means, the display processing means The three-dimensional display control means comprises a step of three-dimensionally displaying the building displayed on the other screen, and a step of selecting a facility name from the name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means by the selection means. The whole floor on which the facility selected by the selection means exists is highlighted in the three-dimensionally displayed building.
[0008]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an embodiment of an information guide device using a building shape map according to the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining display guidance processing of a shape map by the information guide device using a building shape map according to the present invention. FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the data structure of a building shape map.
[0009]
In FIG. 1, the
[0010]
The
[0011]
In the
[0012]
As for the data structure of the building shape map stored in the map
[0013]
Next, the change process of the display format of the destination point will be described with reference to FIG. The display format of the destination point is changed with respect to the set destination point in the building shape map. The building shape map is drawn and displayed by sequentially reading out the coordinate sequence stored as shape data in the building shape map data and connecting them with lines as described above. For example, FIG. A building shape is displayed on the road map as shown in FIG. 5B.
[0014]
This building shape map data is not necessarily prepared for every region. Therefore, when the destination point is input by coordinates or a telephone number, the input x and y coordinates are searched, and it is searched whether or not the coordinates are within a certain range of the building shape map (steps S11 to S13). If the building shape map is within a certain range, the building shape map is displayed (S14), and if it is not within the building shape map, a conventional road map is displayed (S15). Then, the cursor is moved on the screen, the position of the point where the cursor stops is detected, and the point is set (S16 to S19). When the building shape map is displayed, the building shape corresponding to the input (x, y) coordinates is searched, the type and area of the searched building shape are determined (S20 to S21), and displayed. The form is determined (S22). When a conventional road map is displayed, the display form is determined after setting the points.
[0015]
For example, a display form when a building shape map is displayed will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 and 7 taking mark display as an example.
FIG. 6 shows an example of the mark selection condition table. For example, the mark No. a to d, and mark numbers “0”, “1”, “2”, “3” to “10”, and 11 or more names such as personal names and telephone numbers a to d correspond to each other (m 2 ) 0 to 150, 151 to 250, 251 to 600, 601 to 1200, 1201 or more, the mark No. a to e are made to correspond.
[0016]
Mark No. For example, marks a to e are registered in a mark table as shown in FIG. 7, and are registered to mean a private house, a two-storied house, an apartment, a condominium, and a villa, respectively.
[0017]
Therefore, the type of the searched building is determined. For example, if the number of floors is 3 to 5, the mark No. As a result, the mark indicating the apartment is called up and displayed with reference to the mark table of FIG. If the number of searched building names is 11 or more, the mark No. is selected from the mark selection condition table. d is known, and a mark indicating the apartment is displayed with reference to the mark table. In addition, the area of the searched building is 1201m 2 If it is above, the mark No. e is known and the mark of the villa is displayed with reference to the mark table.
[0018]
In addition, by displaying only the set buildings, and deleting the shape of other buildings (buildings, houses, factories, etc.) from the shape map display, roads, rivers, tracks, etc. Only the buildings and destination points related to the land are displayed, the destination points are highlighted and displayed, and the roads, rivers, tracks, etc. are displayed, so the positional relationship between the destination points can be clearly understood.
[0019]
In addition, when the position of the cursor is detected and the point is set, the corresponding building is searched, and the three-dimensional shape mark selected by the central processing unit from the plane section of the building is displayed. By performing display processing as if a building was built at that point, the corresponding building can be more easily recognized.
[0020]
Not only the mark display but also the corresponding building may be easily recognized by three-dimensional display as shown as A in FIG.
[0021]
Next, search / guidance using a building shape map will be described. FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining search guidance processing using a building shape map, FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a screen during a building selection operation using a building shape map, and FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of an information display screen. FIG. 12 is a diagram showing an example of an information guidance screen by a building shape map, FIG. 13 is a diagram showing an example of a list display screen for peripheral information search of a building, and FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an example of a genre search screen. is there.
[0022]
By using the building shape map displayed as described above, it is possible to search not only for the building based on the data described in FIG. Information can be provided. For example, in a building shape map, a crossed-out cursor is displayed at the center as shown in FIG. 10, and the building is selected by inputting a building selection instruction from the input instruction means. . Therefore, in the search / guidance process, the system waits for this building selection as shown in FIG. 9 (step S41), and if there is a building selection, the destination, passing point, memory, information as shown in FIG. Then, options for each mode of the peripheral information search are displayed (step S42). The destination, passing point, and memory are used for setting a point for route search when the present invention is incorporated in a vehicle navigation device to be described later, and will not be described here. Only the search modes will be described.
[0023]
Therefore, it is checked whether the selection key is information or peripheral information search (step S43), and when the information column is selected as shown in FIG. 10, the number of names of detailed information and the names of the corresponding building data. Are created in alphabetical order and their information is displayed as shown in FIG. 11 (step S44). Then, when one of the name fields in the list, for example, Aiue Corporation is selected as shown in FIG. 11 (step S45), the address (address) from the building data, the selected name, telephone number, classification Etc. are read and the name, telephone number and address of Aiue Corporation are displayed as shown in FIG. 12 (step S46). The return, destination, passing point, and memory displayed on this screen are operation keys, and when such other operation keys are selected, the respective processes are executed by interruption. In the case of an instruction other than the selection of the name column, other processing corresponding to the instruction is similarly interrupted and executed.
[0024]
When the peripheral information search field is selected in step S43, first, as shown in FIG. 13, in order to specify the search range of the peripheral information, “manufacture and sale of fiber / textile”, “fiber / textile A genre list (classification list) such as “dyeing, design”,... Is displayed (step S47). When a certain category field is selected (step S48), the selected category is searched from the detailed information of the data, the distance from the selected building is obtained (step S49), and the predetermined distance searched. Names within are sorted in ascending order of distance, and as shown in FIG. 14, a list of the genre names and the number of cases, and each searched name and distance from the search point is displayed (step S50). When one of the name fields is selected (step S51), the address (address), the selected name, telephone number, classification, etc. are read from the building data and displayed, as in FIG. Step S52). Here, when a return key is inputted, a building shape map around the building is displayed. Of course, the building shape map may be displayed using another key (not shown) or may be switched to another map such as a road map. In the case of an instruction other than the selection of the classification field in step S48 and an instruction other than the selection of the name field in step S51, other processing corresponding to the instruction is interrupted and executed.
[0025]
Next, an example of stereoscopic display of a building will be described.
FIG. 15 is a diagram for explaining a search / guidance processing flow for three-dimensionally displaying the shape of the building selected by the input instruction means.
As in the case of FIG. 9, it waits for the building selection from the input instruction means (step 61). If there is a building selection, as shown in FIG. 10, the destination, passing point, memory, information Then, the selection of each mode of the peripheral information search is displayed (step 62). Next, it is checked whether the selection key is information or peripheral search (step 63). If peripheral search is selected, the processing jumps to the processing of
[0026]
Next, a description will be given with reference to FIG. 16 showing a case where the selected building has height information and there are a plurality of tenants.
FIG. 16 (a) shows a screen in which information is selected, and options are displayed on the building shape map. By selecting information, the number of names of detailed information of the corresponding building data and each name are read. A list of names is created and divided into screens and displayed as shown in FIG. 16B (step 64). Next, with the list displayed as it is, as shown in FIG. 16C, the building shape is three-dimensionally displayed (step 65), and then the building floor at the cursor position in the list is highlighted ( Step 66). At this time, by selecting the list item with the cursor, the floor of the selected item is highlighted as shown in FIG. Next, when the name column is selected, as shown in FIG. 16 (f), detailed information such as the address of the building data, the selected name, the telephone number, the classification, the genre of the store, the type of business, etc. is read and displayed (
[0027]
Further, a case where there is one tenant will be described with reference to FIG. 17. When information is selected in FIG. 17A, the number of names of detailed information of building data and each name are read to create a list of names. A process of splitting and displaying the screen is performed. In this case, since there is one tenant, the name, telephone number, address, etc. are displayed as shown in FIG. Next, with the list displayed as it is, as shown in FIG. 17C, the building shape is three-dimensionally displayed, and the second floor (tenant floor) of the building is highlighted. In addition, about the three-dimensional display method of a building, the method shown by Unexamined-Japanese-Patent No. 9-62179 is used, for example.
If there is no height information, the 3D display is naturally not performed, but the other processes are the same.
[0028]
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining a search / guidance processing flow for three-dimensionally displaying the shape of a building selected by inputting a telephone number or name.
When a destination point is input by telephone number or name (50 sounds), the corresponding point data is searched (steps 71 and 72). If there is building shape data in this search, the building shape is three-dimensionally displayed (
[0029]
In the above example, the list of names is divided and displayed on the screen. However, the list may be displayed in a separate window on the map display without dividing the screen. In the above example, the floor of the selected item is highlighted by selecting the item in the detailed information list with the cursor. Conversely, the floor of the three-dimensional building is selected with the cursor. The tenants included in the selected floor may be displayed in a list and selected from the list. As a highlighting method, bold line display, filled display, color-coded display, blinking display, or the like may be employed as appropriate. Further, the floor may be highlighted with a three-dimensional display, and the number of floors highlighted with characters may be displayed.
[0030]
Next, an example of a three-dimensional display process will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0031]
FIG. 19 is a diagram showing an example of a three-dimensional display processing flow of a building, FIG. 20 is a building shape map, FIG. 21 is a diagram showing an example of three-dimensional display of a building with a constant floor height, and FIG. FIG. 23 is a diagram illustrating an example in which the height of the building is made constant and the floor height is variable, and FIG. 23 is a diagram illustrating the display method of FIG.
In FIG. 19, the height of the building is searched from the building shape map data (step 81), and it is determined whether or not the searched height can be displayed on the screen at a constant display scale (step 82). If display is possible within the screen, the height per floor is fixed and the building is three-dimensionalized (step 83), and then the plan map is tilted to three-dimensionally display the building (
[0032]
In addition, in
[0033]
In addition, the method of displaying a building three-dimensionally is not limited to the above example, but may be a bird's-eye view viewed from above or a display that allows the building to be viewed horizontally from the horizontal direction. . The display scale may be a constant scale, but if displayed at a constant scale, it may be difficult to see depending on the size of the building, so the display scale may be changed so that it is easy to see according to the height of the building. Good. Further, only the building portion may be enlarged and displayed, or the building may be enlarged and displayed in a separate frame while leaving the building shape map.
[0034]
By using the information guide device by the building shape map of the present invention, information on companies, offices, stores, various institutions, etc. that move into the building from the building shape map, and further, A telephone number or the like can be checked, and various companies, stores, various institutions, etc. within a certain range from the building can be searched and listed to check the building. On the other hand, by entering a telephone number or name and searching for the name and telephone number from the map data name and detailed information name and telephone number shown in FIG. It is easy to display a shape map. Therefore, if you know the name and classification information and the general area, but you do not know the building, you can search for the building, for example, the occupying building, and the tenant occupying a certain building. Since this can be used for setting the point of the vehicle navigation device, there is a merit that it becomes easy to set the point in an urban area. Furthermore, when a road is targeted as one of the buildings, information on parking when acting by car can be provided if the presence or absence of a parking meter can be provided as information on the road. Below, the structural example of the navigation apparatus for vehicles which can utilize the information guidance apparatus by the building shape map which concerns on this invention is demonstrated.
[0035]
FIG. 24 is a diagram showing a configuration of one embodiment of a vehicle navigation device incorporating an information guide device based on a building shape map according to the present invention.
[0036]
As shown in FIG. 24, the vehicle navigation apparatus according to the present invention is necessary for the input /
[0037]
The input /
[0038]
Here, a voice recognition device for enabling voice input and a recording card reading device for reading data recorded on an IC card or a magnetic card may be added. In addition, an information center that accumulates data necessary for navigation and provides information via a communication line at the request of the driver, or a notebook electronic device that stores driver-specific data such as map data and destination data in advance. A data communication device for exchanging data with an information source such as a device can also be added.
[0039]
The
[0040]
The
[0041]
The current position detecting means 2 obtains information using a
[0042]
The
[0043]
The
[0044]
Note that a program for performing the above-described update processing may be stored in an external storage device.
The program according to the present invention and other programs for executing navigation may all be stored in a CD-ROM which is an external storage medium, or a part or all of these programs may be stored in the
[0045]
Also, the recording medium in the navigation device receives all or part of the program for realizing the functions of the present invention and all or part of the data from the information center or other vehicle via the data transmission /
[0046]
Various navigation functions are realized by inputting data and programs stored in the external storage medium as external signals to the central processing unit of the navigation apparatus main body and performing arithmetic processing.
[0047]
The navigation device according to the present invention stores a relatively large-
[0048]
In addition, this invention is not limited to said Example, A various deformation | transformation is possible. For example, in the above embodiment, the name of the building has been described, but this may include a town name or other district name. Although all the names have been processed, priority information to be displayed on the map and information on presence / absence of display are set in advance, or added to the name, and the name is displayed based on the information. Alternatively, processing may be performed on a target whose number of names is equal to or greater than a predetermined number or a predetermined height. In addition, although the xy coordinate sequence is data representing the shape of the building, the coordinate value (z) in the height direction is also included as three-dimensional coordinate data, and when represented in a plan view, the xy coordinate sequence For example, in the case of representing in a three-dimensional shape diagram such as a perspective view or a perspective view, an xyz coordinate sequence may be used. Furthermore, the present invention can provide more friendly point guidance by incorporating it into a vehicle navigation device. However, the present invention is used only for guidance in urban areas, sightseeing spots, etc., and the information is printed out for service. It goes without saying that you may be allowed to do.
[0049]
【The invention's effect】
As is clear from the above description, according to the present invention, it becomes easy to specify a target building, and even when a facility included in the building is selected, it is easy to determine which floor they are on. To know.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an embodiment of an information guide device using a building shape map according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining shape map display guidance processing by an information guidance device for building shape maps according to the present invention;
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example of a data structure of a building shape map.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a display form changing process according to the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining an example of a building shape map;
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a mark selection condition table.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a mark table.
FIG. 8 is a diagram for describing an example of stereoscopic display.
FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining search guidance processing using a building shape map;
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing an example of a screen at the time of a building selection operation using a building shape map.
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of an information display screen.
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of an information guidance screen using a building shape map;
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing an example of a list display screen for searching surrounding information of a building.
FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating an example of a genre search screen.
FIG. 15 is a diagram for explaining a search / guidance processing flow for three-dimensionally displaying the shape of the building selected by the input instruction means;
FIG. 16 is a diagram showing a search screen when a selected building has height information and there are a plurality of tenants.
FIG. 17 is a diagram showing a search screen when a selected building has height information and there is one tenant.
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining a search / guidance process flow for three-dimensionally displaying the shape of a building selected by telephone number / name input.
FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating an example of a three-dimensional display processing flow of a building.
FIG. 20 is a diagram showing a building shape map.
FIG. 21 is a diagram illustrating an example in which a building is three-dimensionally displayed with a constant floor height.
FIG. 22 is a diagram showing an example in which the height of the building is made constant and the height of the floor is made variable to display.
23 is a diagram for explaining the display method of FIG.
FIG. 24 is a diagram showing a configuration of one embodiment of a vehicle navigation device incorporating an information guide device based on a building shape map according to the present invention.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (9)
該記憶手段に記憶された建造物形状地図情報に基づいて建造物形状地図を表示する建造物形状地図表示制御手段と、
該表示された建造物形状地図上の建造物を指定する建造物指定手段と、
該建造物指定手段により指定された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する立体表示制御手段と、
前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する選択手段とを備え、
前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする建造物形状地図による情報案内装置。Storage means for storing building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing a shape for each building, height information, and detailed information;
A building shape map display control means for displaying a building shape map based on the building shape map information stored in the storage means;
A building designating means for designating a building on the displayed building shape map;
The name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the building designated by the building designating means, and the name list of the facility read out is created, and the name list is divided into one screen. Display processing means for displaying a building shape map including the building designated on the other screen,
3D display control means for stereoscopically displaying the building displayed on the other screen by the display processing means based on the height information stored in the storage means;
Selecting means for selecting a facility name from a name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means;
The three-dimensional display control means highlights the entire floor on which the facility selected by the selection means is present in the three-dimensionally displayed building, and is an information guide device using a building shape map.
ジャンルを選択するジャンル選択手段と、
該ジャンル選択手段により選択されたジャンルに基づいて建造物を検索する建造物検索手段と、
該建造物検索手段により検索された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、
前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する立体表示制御手段と、
前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する選択手段とを備え、
前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする建造物形状地図による情報案内装置。Storage means for storing building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing a shape for each building, height information, and detailed information;
Genre selection means for selecting a genre,
A building search means for searching for a building based on the genre selected by the genre selection means;
The name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the building searched by the building search means to create a read facility name list, and the name list is divided into one screen. Display processing means for displaying a building shape map including the building designated on the other screen,
3D display control means for stereoscopically displaying the building displayed on the other screen by the display processing means based on the height information stored in the storage means;
Selecting means for selecting a facility name from a name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means;
The three-dimensional display control means highlights the entire floor on which the facility selected by the selection means is present in the three-dimensionally displayed building, and is an information guide device using a building shape map.
建造物形状地図表示制御手段により、記憶手段に記憶された建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報に基づいて建造物形状地図を表示する段階、
建造物指定手段により、前記建造物形状地図表示制御手段で表示された建造物形状地図上の建造物を指定する段階、
表示処理手段により、前記建造物指定手段で指定された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する段階、
立体表示制御手段により、記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する段階、
選択手段により、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する段階を備え、
前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする建造物形状地図による情報案内方法。In a method of guiding using an information guide device that displays a building shape map,
The building shape map display control means displays the building shape map based on the building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing the shape, height information, and detailed information for each building stored in the storage means. ,
Designating a building on the building shape map displayed by the building shape map display control means by a building designating means;
The display processing means reads out the names of the facilities included in the building from the detailed information of the building specified by the building specifying means, creates a read facility name list, Displaying the name list on the screen of, and the building shape map containing the building specified on the other screen ,
A step of stereoscopically displaying the building displayed on the other screen based on the height information stored in the storage means by the stereoscopic display control means;
Selecting a facility name from a name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means by the selection means;
The three-dimensional display control means highlights the entire floor where the facility selected by the selection means is present in the three-dimensionally displayed building, and is an information guidance method using a building shape map.
ジャンル選択手段によりジャンルを選択する段階、
建造物検索手段により、ジャンル選択手段で選択されたジャンルに基づいて、記憶手段に記憶された建造物毎に形状を表す座標列、高さ情報、詳細情報とを有する建造物形状地図情報から建造物を検索する段階、
表示処理手段により、建造物検索手段で検索された建造物の前記詳細情報から該建造物に含まれる施設の名称を読み出して読み出された施設の名称リストを作成し、画面分割して一方の画面に名称リストを、他方の画面に指定された建造物を含む建造物形状地図を表示する表示処理手段と、
立体表示制御手段により、前記記憶手段に記憶された高さ情報に基づいて、前記表示処理手段により他方の画面に表示された建造物を立体表示する段階、
選択手段により、前記表示処理手段により一方の画面に表示された名称リストから施設の名称を選択する段階を備え、
前記立体表示制御手段は、前記選択手段により選択された施設が存在する階全体を前記立体表示された建造物において強調表示することを特徴とする建造物形状地図による情報案内方法。In a method of guiding using an information guide device that displays a building shape map,
Selecting a genre by genre selection means,
Based on the genre selected by the genre selection means by the building search means, the building is constructed from the building shape map information having a coordinate sequence representing the shape, height information, and detailed information for each building stored in the storage means. Searching for things,
By the display processing means, the name of the facility included in the building is read out from the detailed information of the building searched by the building searching means, a read facility name list is created, and the screen is divided into one Display processing means for displaying a name list on the screen and a building shape map including the building designated on the other screen;
A three-dimensional display control means for three-dimensionally displaying the building displayed on the other screen by the display processing means based on the height information stored in the storage means;
Selecting a facility name from a name list displayed on one screen by the display processing means by the selection means;
The three-dimensional display control means highlights the entire floor where the facility selected by the selection means is present in the three-dimensionally displayed building, and is an information guidance method using a building shape map.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18693997A JP3644472B2 (en) | 1997-07-11 | 1997-07-11 | Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18693997A JP3644472B2 (en) | 1997-07-11 | 1997-07-11 | Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004354368A Division JP4334000B2 (en) | 2004-12-07 | 2004-12-07 | Information guide device by building shape map |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH1130952A JPH1130952A (en) | 1999-02-02 |
| JP3644472B2 true JP3644472B2 (en) | 2005-04-27 |
Family
ID=16197373
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18693997A Expired - Lifetime JP3644472B2 (en) | 1997-07-11 | 1997-07-11 | Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3644472B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (32)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4114772A1 (en) * | 1991-05-06 | 1992-11-12 | Kaufmann Klaus | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR PROMOTING AN ELECTRICALLY POLARIZED MOLECULE AT LEAST CONTAINING MEDIUM |
| JP2000242166A (en) * | 1999-02-23 | 2000-09-08 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Three-dimensional map display device |
| JP4134423B2 (en) * | 1999-02-24 | 2008-08-20 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | Vehicle information display device and recording medium of the device |
| JP3648091B2 (en) * | 1999-03-23 | 2005-05-18 | アルパイン株式会社 | Navigation method |
| JP4254979B2 (en) * | 1999-04-14 | 2009-04-15 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Navigation device |
| JP2001092889A (en) * | 1999-09-22 | 2001-04-06 | Hitachi Information Systems Ltd | Visiting care schedule creation support system and method, and recording medium on which processing program is recorded |
| JP3967046B2 (en) * | 1999-09-24 | 2007-08-29 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | Location search output device by telephone number and recording medium |
| JP2002168637A (en) * | 2000-11-30 | 2002-06-14 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Navigation system |
| JP2002229992A (en) * | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-16 | Fujitsu Ltd | Server apparatus for spatial information service, method for providing spatial information service, and billing processing apparatus and method for spatial information service |
| JP2002229991A (en) * | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-16 | Fujitsu Ltd | Server, user terminal, information providing service system, and information providing service method |
| JP2002267464A (en) * | 2001-03-08 | 2002-09-18 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Navigation system |
| US7076741B2 (en) * | 2001-03-16 | 2006-07-11 | Alpine Electronics, Inc. | Point-of-interest icon and point-of-interest mark display method |
| JP3892741B2 (en) * | 2002-02-21 | 2007-03-14 | アルパイン株式会社 | Navigation device |
| JP2003307428A (en) * | 2002-04-16 | 2003-10-31 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Navigation apparatus |
| JP4010183B2 (en) * | 2002-05-17 | 2007-11-21 | ソニー株式会社 | Map display system, map display method, and program |
| JP2004004262A (en) * | 2002-05-31 | 2004-01-08 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Method for displaying stores in facilities in map display system |
| JP2004040445A (en) | 2002-07-03 | 2004-02-05 | Sharp Corp | Portable equipment having 3d display function and 3d transformation program |
| KR20040037794A (en) * | 2002-10-30 | 2004-05-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Apparatus and method for displaying stories in navigation system |
| JP2004317222A (en) * | 2003-04-15 | 2004-11-11 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Navigation device, and display method of landmark in the navigation device |
| JP4116492B2 (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2008-07-09 | 株式会社富士通エフサス | Parking lot utilization rate improvement method and system |
| JP4201673B2 (en) * | 2003-09-03 | 2008-12-24 | シャープ株式会社 | Content display device, content display method, program, and recording medium |
| JP2005201919A (en) * | 2004-01-13 | 2005-07-28 | Nec Toshiba Space Systems Ltd | Building information guide apparatus and method |
| JP4528004B2 (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2010-08-18 | アルパイン株式会社 | Building information display device |
| JP4062270B2 (en) * | 2004-03-17 | 2008-03-19 | Kddi株式会社 | Integrated display program for location objects in map content |
| JP2006058193A (en) * | 2004-08-23 | 2006-03-02 | Sony Corp | Navigation apparatus, and its control method, control program of navigation apparatus, and service providing method of navigation apparatus |
| JP4841897B2 (en) * | 2005-08-29 | 2011-12-21 | アルパイン株式会社 | Navigation device |
| JP2007234057A (en) * | 2007-05-18 | 2007-09-13 | Fujitsu Ltd | server |
| US8825387B2 (en) * | 2008-07-25 | 2014-09-02 | Navteq B.V. | Positioning open area maps |
| JP5899524B2 (en) * | 2010-12-16 | 2016-04-06 | 株式会社ユピテル | Automotive electronics |
| JP6138641B2 (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2017-05-31 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | MAP INFORMATION DISPLAY DEVICE, MAP INFORMATION DISPLAY METHOD, AND MAP INFORMATION DISPLAY PROGRAM |
| JP6317849B1 (en) * | 2017-03-24 | 2018-04-25 | 株式会社オーガスタス | User interface method for parking selection |
| JP7128392B2 (en) * | 2018-12-11 | 2022-08-31 | 株式会社ユピテル | Automotive electronics |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0394376A (en) * | 1989-09-07 | 1991-04-19 | Canon Inc | Method for retrieving data base |
| JPH0799450B2 (en) * | 1989-09-11 | 1995-10-25 | 晴彦 洲嵜 | Map and its manufacturing method |
| JP3212113B2 (en) * | 1990-11-07 | 2001-09-25 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Map information display method and device |
| JP2865856B2 (en) * | 1990-11-30 | 1999-03-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | How to display map / drawing information |
| JP3474022B2 (en) * | 1995-04-20 | 2003-12-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Map display device, map display method, arithmetic processing unit for map display device, and navigation system |
| JPH09159481A (en) * | 1995-10-04 | 1997-06-20 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | Map display device, navigation apparatus and medium with stored computer program for processing of map information |
-
1997
- 1997-07-11 JP JP18693997A patent/JP3644472B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH1130952A (en) | 1999-02-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3644472B2 (en) | Information guide apparatus and information guide method by building shape map | |
| US5890088A (en) | Information guidance system based on structure configuration map | |
| KR100267542B1 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP2840062B2 (en) | Information guidance device having building information | |
| JP3228191B2 (en) | Navigation device and storage medium | |
| JPH10332405A (en) | Car navigation system provided with re-searching function, and its storage medium | |
| JP2807447B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP4334000B2 (en) | Information guide device by building shape map | |
| JPH10153950A (en) | Map display device | |
| JPH10333562A (en) | Guiding device by building shape map and recording medium for guiding device | |
| JP3019007B2 (en) | Vehicle navigation device with re-search function and guidance method | |
| JP2982716B2 (en) | Building shape map display device and storage medium therefor | |
| JP2843023B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP4238439B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP3307530B2 (en) | Guidance device | |
| JP3822063B2 (en) | Guide device | |
| JP3770325B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP3238080B2 (en) | Information guidance device and storage medium using building shape map | |
| JP2840063B2 (en) | Information guidance device by building shape map | |
| JP3173370B2 (en) | Guidance device by building shape map | |
| JP3173371B2 (en) | Guidance device by building shape map | |
| JPH09210696A (en) | Car navigation system and location registering method | |
| JP3760996B2 (en) | Building shape map display device | |
| JPH11352878A (en) | Building information guide device and its memory medium | |
| JPH10333565A (en) | Information guiding device by building shape map and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20031208 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20031226 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040220 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20041008 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041207 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20050112 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20050125 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090210 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090210 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100210 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110210 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120210 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130210 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140210 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |