JP2010199528A - ボンディングワイヤ - Google Patents
ボンディングワイヤInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010199528A JP2010199528A JP2009094065A JP2009094065A JP2010199528A JP 2010199528 A JP2010199528 A JP 2010199528A JP 2009094065 A JP2009094065 A JP 2009094065A JP 2009094065 A JP2009094065 A JP 2009094065A JP 2010199528 A JP2010199528 A JP 2010199528A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wire
- coating layer
- bonding
- copper
- bonding wire
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 53
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 239000011162 core material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000005496 tempering Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 abstract description 8
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 abstract description 8
- 238000007670 refining Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229910000510 noble metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010944 silver (metal) Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- QZPSXPBJTPJTSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N aqua regia Chemical compound Cl.O[N+]([O-])=O QZPSXPBJTPJTSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007772 electroless plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012776 electronic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010970 precious metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000682 scanning probe acoustic microscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007790 solid phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002345 surface coating layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013077 target material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/43—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/43—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/43—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/432—Mechanical processes
- H01L2224/4321—Pulling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/43—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/438—Post-treatment of the connector
- H01L2224/43848—Thermal treatments, e.g. annealing, controlled cooling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/4501—Shape
- H01L2224/45012—Cross-sectional shape
- H01L2224/45015—Cross-sectional shape being circular
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45144—Gold (Au) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45147—Copper (Cu) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45565—Single coating layer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45599—Material
- H01L2224/456—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45638—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45639—Silver (Ag) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45599—Material
- H01L2224/456—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45638—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45644—Gold (Au) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45599—Material
- H01L2224/456—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45663—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45664—Palladium (Pd) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45599—Material
- H01L2224/456—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45663—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45669—Platinum (Pt) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4554—Coating
- H01L2224/45599—Material
- H01L2224/456—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45663—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45673—Rhodium (Rh) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48091—Arched
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48095—Kinked
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/484—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/4847—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a wedge bond
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/74—Apparatus for manufacturing arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and for methods related thereto
- H01L2224/78—Apparatus for connecting with wire connectors
- H01L2224/7825—Means for applying energy, e.g. heating means
- H01L2224/783—Means for applying energy, e.g. heating means by means of pressure
- H01L2224/78301—Capillary
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/85009—Pre-treatment of the connector or the bonding area
- H01L2224/8503—Reshaping, e.g. forming the ball or the wedge of the wire connector
- H01L2224/85035—Reshaping, e.g. forming the ball or the wedge of the wire connector by heating means, e.g. "free-air-ball"
- H01L2224/85045—Reshaping, e.g. forming the ball or the wedge of the wire connector by heating means, e.g. "free-air-ball" using a corona discharge, e.g. electronic flame off [EFO]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/8512—Aligning
- H01L2224/85148—Aligning involving movement of a part of the bonding apparatus
- H01L2224/85169—Aligning involving movement of a part of the bonding apparatus being the upper part of the bonding apparatus, i.e. bonding head, e.g. capillary or wedge
- H01L2224/8518—Translational movements
- H01L2224/85181—Translational movements connecting first on the semiconductor or solid-state body, i.e. on-chip, regular stitch
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/852—Applying energy for connecting
- H01L2224/85201—Compression bonding
- H01L2224/85205—Ultrasonic bonding
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/74—Apparatus for manufacturing arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies
- H01L24/78—Apparatus for connecting with wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00011—Not relevant to the scope of the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00015—Technical content checked by a classifier the subject-matter covered by the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group, being disclosed as prior art
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01007—Nitrogen [N]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01014—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01015—Phosphorus [P]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01018—Argon [Ar]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01028—Nickel [Ni]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01046—Palladium [Pd]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01047—Silver [Ag]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01078—Platinum [Pt]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/012—Semiconductor purity grades
- H01L2924/01204—4N purity grades, i.e. 99.99%
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/102—Material of the semiconductor or solid state bodies
- H01L2924/1025—Semiconducting materials
- H01L2924/10251—Elemental semiconductors, i.e. Group IV
- H01L2924/10253—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/156—Material
- H01L2924/15786—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a non metallic, non metalloid inorganic material
- H01L2924/15787—Ceramics, e.g. crystalline carbides, nitrides or oxides
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/201—Temperature ranges
- H01L2924/20105—Temperature range 150 C=<T<200 C, 423.15 K =< T < 473.15K
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20751—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 10 microns less than 20 microns
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20752—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 20 microns less than 30 microns
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20753—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 30 microns less than 40 microns
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20754—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 40 microns less than 50 microns
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/20—Parameters
- H01L2924/207—Diameter ranges
- H01L2924/20755—Diameter ranges larger or equal to 50 microns less than 60 microns
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
Abstract
【解決手段】集積回路素子の電極aと回路配線基板の導体配線cをボールボンディング法によって接続するためのボンディングワイヤPである。99.99質量%以上の銅からなる芯材1の外周全面に金、白金、パラジウム、銀の1種以上からなる被覆層2を形成し、その被覆線に拡散熱処理を施して芯材1と被覆層2の密着性を高めた後、線径L:12μm以上50.8μm以下まで伸線し、さらに、引張伸びが8%以上となるように調質熱処理を行って、前記被覆層2の厚み0.04〜0.09μmのボンディングワイヤとする。この構成のボンディングワイヤは、電極と導体配線に十分な接合強度をもって接続され、低温度の高速作業の下でも、その作業がストップすることがない。
【選択図】図2
Description
1stボンドが形成されれば、キャピラリー10aは、一定高さまで上昇した後(同図(c))、導体配線cの真上まで移動する(同図(d)〜(e))。このとき、安定したループを形成するため、キャピラリー10aに特殊な動きをさせてワイヤPに「くせ」を付ける動作をする場合がある(同図(d)の鎖線から実線参照)。
その被覆金属(被覆層)2としては、金(Au)、白金(Pt)、パラジウム(Pd)、銀(Ag)、ニッケル(Ni)等が採用されている(特許文献1〜3)。
また、集積回路素子の電極aへの接続において、ボールbが下向き槍状(逆円錐状)になっていると、上記ボールbの電極aへの押付け時、そのボールbの尖鋭端によって電極aを損傷させる恐れがあるため、ボールbはできるだけ、真球であることが好ましい。そのボールbの真球度を高めるために、上記被覆層2の厚みtを芯線径の0.001以下としたり(特許文献1請求項1)、同じく被覆層2の厚みtを0.001〜0.2μmとしたり(特許文献3請求項1)、芯材1の銅よりも高融点の耐酸化金属で被覆層2を形成したりしている(特許文献2段落0014)。
さらに、有機基板をベースにしたBGA(Ball Grid Array)などでは加熱温度(ステージ温度)を高くすると、反りが発生してボンディング性が著しく悪化する。このため、上記ワイヤPと電極a又は導体配線cとの接合時の加熱温度(ステージ温度)を低く、例えば、150℃程度にしても、十分な接合強度を担保するための種々の工夫、例えば、熱処理後に伸線する加工等もされている(特許文献3段落0020、同0054等)。
また、線径Lの下限を12μm以上としたのは、12μm未満ではボンディング前にオペレータがワイヤPをキャピラリー10aに通すのが困難になり、作業性が悪くなるからである。
芯材1の銅純度を99.99質量%以上としたのは、銅の高導電性を担保するためである。
なお、ステージ温度:150℃程の低温度でのボールボンディングの時には、連続ボンディング性の実験結果からその厚みtを0.04μm以上、より好ましくは、その0.04μmを越えるものとする。ステージ温度を低くすると、ステッチボンド接合に要する加重が大きくなり、被覆層2の厚みtが0.02μm以上から0.04μm未満の範囲では芯材の銅が露出する度合いが大きくなり、連続ボンディング性が損なわれることがあるからである。
一方、被覆層2が厚いと、ボールbの硬度が高くなり、Siチップ(電極a)の損傷の可能性が高くなる。このため、後記実施例と比較例の実験結果から、被覆層2の厚みtは0.09μm以下とする。
つで形成しても良いが、2種以上の金属の多層とすることもできる。
この構成において、ステージ温度:150℃程の低温度でのボールボンディング用ボンディングワイヤにおいては、その被覆層の厚みtは0.04〜0.09μmとする。
上述のように、芯材1の銅よりも高融点の耐酸化金属で被覆層2を形成すれば、ボールbの真球度が増すことが確認されているが、本発明者は、その理由として、放電によって銅が溶融して真球となる時、その溶融部分が表面張力によって真上にワイヤを這い上がっていくが、被覆層2も溶融していると、その這い上がりが悪くなって、真球になりにくいためと考えた。このことは、0.02〜0.09μm厚の被覆層2であると、顕著に表れる。
また、パラジウムと白金では、パラジウムの方がボールbを真球にできる条件のマージン(限界)が広くなる。これは、パラジウムの融点が白金の融点に比べて銅の融点に近いためと考えられる。すなわち、被覆層2に白金を用いると、放電による銅の溶融後に白金が溶融するまでに時間差が生じるためである。被覆層2にパラジウムを用いれば、溶融の時間差は小さくなるため、より真球になりやすい。
また、被覆層2の厚みtを0.04μm以上とした場合、ステージ温度150℃でもマシントラブルが少なくなるが、特にパラジウムを被覆層2に採用し、被覆層2の厚みtを0.05μm以上とした時にはステージ温度をより低温の135℃としたときでもマシントラブルが起こらないことも確認されている。これは、パラジウム被覆層2の場合、上記のように、銅とパラジウムの溶融時間差が小さく、より真球になりやすいこととの相乗効果に基づくものと考える。
引張伸びを8%以上とするのは、ステッチボンド接合性を上げ、より安定したボンディング性を得るためである。
このとき、被覆層がパラジウムから成れば、芯材の銅純度を99.999質量%以上とし、その被覆層の厚みtを0.05〜0.09μmとすることができる。
すなわち、まず、銅純度99.99質量%の純銅(表1中:4N)と銅純度99.999質量%の純銅(表1中:5N)の0.2〜0.8mm径の銅線を用意し、その銅線に、Au、Pd、Pt及びAgの貴金属を電解メッキ法によって被覆し、その被覆線を巻き戻し、焼鈍炉を通したのち、再び巻き取り用リールで巻き取ることによって連続拡散熱処理を行った。焼鈍炉は炉長1mの炉芯管を有する電気炉を用い、炉芯管には窒素ガスを流した。その炉温度は500℃以上800℃以下として被覆線の温度を200〜500℃とし、その被覆線の走行速度は5〜60m/分とした。以上の拡散熱処理を施して銅線(芯材)1と被覆層2の密着性を高めた後、線径15〜50.8μmまで伸線し、さらに、引張伸びが8%以上となるように調質熱処理を行って、被覆層2の厚みt:0.001〜0.112μmのボンディングワイヤP(実施例1〜45及び比較例1〜13)を得た。表1中、2種の貴金属を示す例は、その2種の金属を同一厚で2重被覆したものである。
「被覆層(表面皮膜層)2の厚み」:
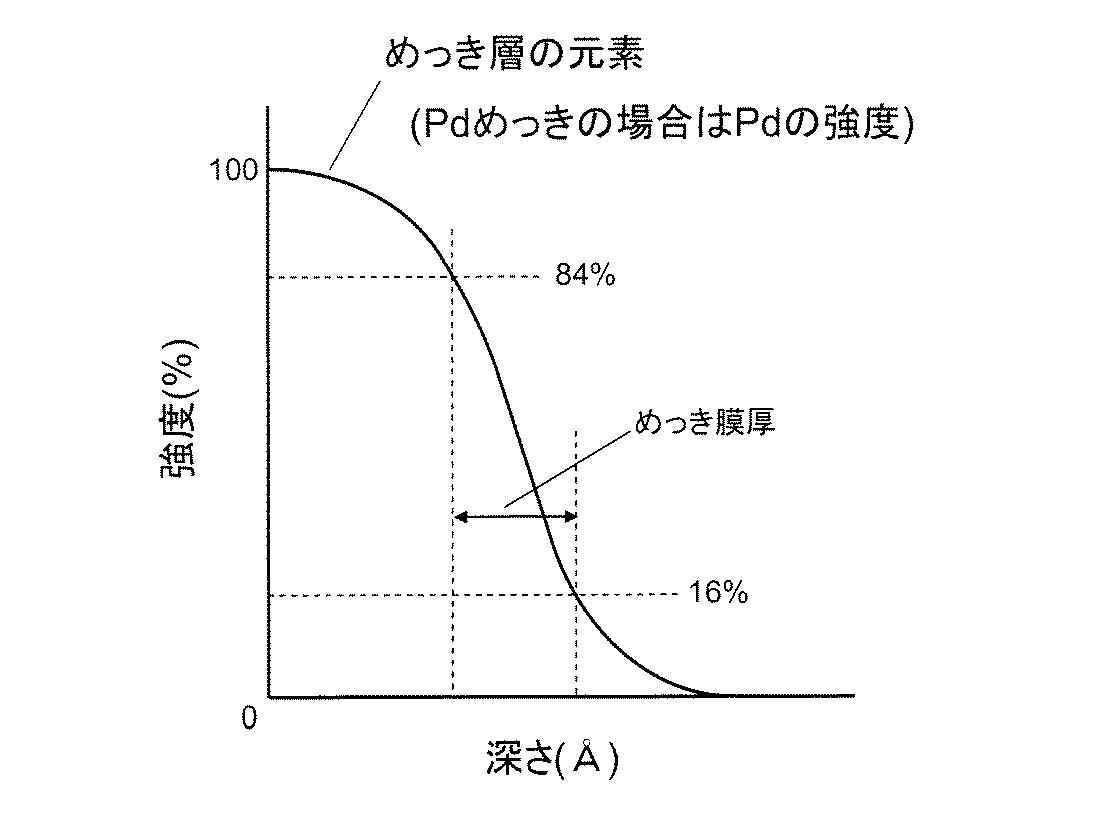
オージェ電子分光分析法にて測定した。Arで被覆層の表面からスパッタリングし、単位時間のスパッタリング毎にスペクトル測定を行った。深さ方向の単位はスパッタ時間とし、事前に測定しておいた標準試料SiO2のスパッタリングレートから、対象材の深さ方向の距離をSiO2換算にて算出した。被覆層については、図3の通り、対象被覆層元素のオージェピーク強度を縦軸、深さを横軸にとったグラフにおいて、オージェピーク強度が84%の位置から16%の位置までの距離を被覆層の厚みとした。
「芯材(銅)の純度」:
GDMS(グロー放電質量)分析にて全元素の濃度を測定してCu純度を決定した。
「連続ボンディング性」(1):
ボンディングマシンで10,000回の連続ボンディングを行い、マシンストップが発生しなければ「A」、1回のマシンストップが発生すれば「B」、2回以上のマシンストップが起これば「D」とした。このとき、ステージ温度が低くなれば、その連続ボンディングが困難になることから、200℃(±5℃)、150℃(±5℃)の2水準で行った。
「1st接合部のSiチップ損傷」(2):
ボンディング後、1stボール接合部直下のSiチップ損傷を評価するために、ボール接合部aおよび電極膜を王水で溶解し、Siチップのクラックを光顕とSEMで観察した。このとき、100個の接合部を観察して5μm以下の微小なピットが1個もしくはまったく見られない場合は「A」、5μm以下の微小なピットが2個以上認められる場合は実用上は有害でないため「B」、5μm以上のクラックが認められた場合は「D」とした。
「総合評価」:
(1)の評価が200℃・150℃ともにAであり、かつ(2)の評価がAのものを「A」、(1)の評価が200℃・150℃ともにAであり、かつ(2)の評価がBのものを「B」、(1)の評価が200℃ではAであり、150℃ではBのものを「C」とした。また、ひとつでもDのあるものについては実用上問題であるので「D」とした。
一方、被覆層厚tが0.09μmを越えると、ボールbが硬くなって、Siチップ(電極a)の損傷が認められるようになる(比較例3、6〜8、11、13)。
また、純銅5Nを使用し、被覆層厚tを0.04μm以上としたもの(実施例5、12、13、16、20、27、32、34、37、44、45)では、総合評価が「A」となって、ステージ温度が150℃程の低温度においても、連続ボンディング性が良好であってその連続ボンディング性の担保に有効であることが分る。特に、被覆層厚tが0.05μm以上では顕著である(実施例12、13、16)。
1 芯材
2 被覆層
a 集積回路素子の電極
b ボンディングボール
c 回路配線基板の導体配線
Claims (7)
- 集積回路素子の電極(a)と回路配線基板の導体配線(c)をボールボンディング法によって接続するための線径(L)12μm以上50.8μm以下のボンディングワイヤ(P)であって
、芯材(1)が純度99.99質量%以上の銅からなり、その芯材(1)の外周全面に、金、白金、パラジウム、銀の1種以上による厚み(t)0.02〜0.09μmの被覆層(2)を形成したことを特徴とするボンディングワイヤ。 - 上記被覆層(2)の厚み(t)が0.04〜0.09μmであることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のボンディングワイヤ。
- 上記被覆層(2)をその融点が上記銅の融点より高いパラジウム又は白金としたことを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載のボンディングワイヤ。
- 上記被覆層(2)をその融点が上記銅の融点より高いパラジウムとし、その厚み(t)が0.05〜0.09μmであることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のボンディングワイヤ。
- 上記芯材(1)の銅純度を99.999質量%以上としたことを特徴とする請求項1〜4の何れか1つに記載のボンディングワイヤ。
- 集積回路素子の電極(a)と回路配線基板の導体配線(c)をボールボンディング法によって接続するための請求項1〜4の何れか1つに記載のボンディングワイヤ(P)の製造方法であって、純度99.99質量%以上の銅からなる芯材(1)の外周全面に、金、白金、パラジウム、銀の1種以上による被覆層(2)を形成し、その被覆線を拡散熱処理して前記芯材(1)と被覆層(2)の密着性を高めた後、線径(L)12μm以上50.8μm以下まで伸線し、さらに、引張伸びが8%以上となるように調質熱処理を行ったことを特徴とするボンディングワイヤの製造方法。
- 上記芯材(1)の銅純度を99.999質量%以上とし、上記被覆層(2)がパラジウムから成ってその厚み(t)を0.05〜0.09μmとしたことを特徴とする請求項6に記載のボンディングワイヤの製造方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009094065A JP2010199528A (ja) | 2009-01-27 | 2009-04-08 | ボンディングワイヤ |
| PCT/JP2009/065735 WO2010087053A1 (ja) | 2009-01-27 | 2009-09-09 | ボンディングワイヤ |
| TW099102279A TW201037777A (en) | 2009-01-27 | 2010-01-27 | Bonding wire |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009015265 | 2009-01-27 | ||
| JP2009094065A JP2010199528A (ja) | 2009-01-27 | 2009-04-08 | ボンディングワイヤ |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010199528A true JP2010199528A (ja) | 2010-09-09 |
| JP2010199528A5 JP2010199528A5 (ja) | 2011-05-12 |
Family
ID=42395321
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009094065A Pending JP2010199528A (ja) | 2009-01-27 | 2009-04-08 | ボンディングワイヤ |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010199528A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW201037777A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010087053A1 (ja) |
Cited By (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014513439A (ja) * | 2011-05-03 | 2014-05-29 | テッセラ,インコーポレイテッド | 封止表面に至るワイヤボンドを有するパッケージ・オン・パッケージアセンブリ |
| US9391008B2 (en) | 2012-07-31 | 2016-07-12 | Invensas Corporation | Reconstituted wafer-level package DRAM |
| US9412714B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2016-08-09 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond support structure and microelectronic package including wire bonds therefrom |
| US9502390B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-11-22 | Invensas Corporation | BVA interposer |
| US9553076B2 (en) | 2010-07-19 | 2017-01-24 | Tessera, Inc. | Stackable molded microelectronic packages with area array unit connectors |
| US9570416B2 (en) | 2004-11-03 | 2017-02-14 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked packaging improvements |
| US9570382B2 (en) | 2010-07-19 | 2017-02-14 | Tessera, Inc. | Stackable molded microelectronic packages |
| US9583411B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2017-02-28 | Invensas Corporation | Fine pitch BVA using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US9601454B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2017-03-21 | Invensas Corporation | Method of forming a component having wire bonds and a stiffening layer |
| US9615456B2 (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2017-04-04 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic assembly for microelectronic packaging with bond elements to encapsulation surface |
| US9659848B1 (en) | 2015-11-18 | 2017-05-23 | Invensas Corporation | Stiffened wires for offset BVA |
| US9685365B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2017-06-20 | Invensas Corporation | Method of forming a wire bond having a free end |
| US9691679B2 (en) | 2012-02-24 | 2017-06-27 | Invensas Corporation | Method for package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| US9728527B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2017-08-08 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple bond via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US9735084B2 (en) | 2014-12-11 | 2017-08-15 | Invensas Corporation | Bond via array for thermal conductivity |
| US9761554B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2017-09-12 | Invensas Corporation | Ball bonding metal wire bond wires to metal pads |
| US9761558B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2017-09-12 | Invensas Corporation | Package-on-package assembly with wire bond vias |
| US9812402B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2017-11-07 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond wires for interference shielding |
| US9842745B2 (en) | 2012-02-17 | 2017-12-12 | Invensas Corporation | Heat spreading substrate with embedded interconnects |
| US9852969B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2017-12-26 | Invensas Corporation | Die stacks with one or more bond via arrays of wire bond wires and with one or more arrays of bump interconnects |
| US9888579B2 (en) | 2015-03-05 | 2018-02-06 | Invensas Corporation | Pressing of wire bond wire tips to provide bent-over tips |
| US9911718B2 (en) | 2015-11-17 | 2018-03-06 | Invensas Corporation | ‘RDL-First’ packaged microelectronic device for a package-on-package device |
| US9935075B2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2018-04-03 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bonding method and apparatus for electromagnetic interference shielding |
| US9953914B2 (en) | 2012-05-22 | 2018-04-24 | Invensas Corporation | Substrate-less stackable package with wire-bond interconnect |
| US9984901B2 (en) | 2005-12-23 | 2018-05-29 | Tessera, Inc. | Method for making a microelectronic assembly having conductive elements |
| US9984992B2 (en) | 2015-12-30 | 2018-05-29 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded wire bond wires for vertical integration with separate surface mount and wire bond mounting surfaces |
| US10008469B2 (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2018-06-26 | Invensas Corporation | Wafer-level packaging using wire bond wires in place of a redistribution layer |
| US10008477B2 (en) | 2013-09-16 | 2018-06-26 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic element with bond elements to encapsulation surface |
| US10026717B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2018-07-17 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple bond via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US10181457B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2019-01-15 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic package for wafer-level chip scale packaging with fan-out |
| CN109411591A (zh) * | 2018-09-14 | 2019-03-01 | 汕头市骏码凯撒有限公司 | 一种led封装用银合金线及其制作方法 |
| US10299368B2 (en) | 2016-12-21 | 2019-05-21 | Invensas Corporation | Surface integrated waveguides and circuit structures therefor |
| US10332854B2 (en) | 2015-10-23 | 2019-06-25 | Invensas Corporation | Anchoring structure of fine pitch bva |
| US10381326B2 (en) | 2014-05-28 | 2019-08-13 | Invensas Corporation | Structure and method for integrated circuits packaging with increased density |
| US10460958B2 (en) | 2013-08-07 | 2019-10-29 | Invensas Corporation | Method of manufacturing embedded packaging with preformed vias |
| US10490528B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2019-11-26 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded wire bond wires |
| JP2021093473A (ja) * | 2019-12-12 | 2021-06-17 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102130068B (zh) * | 2011-01-07 | 2012-09-05 | 四川威纳尔特种电子材料有限公司 | 一种表面有复合镀层的合金型键合丝 |
| JP4860004B1 (ja) * | 2011-02-28 | 2012-01-25 | タツタ電線株式会社 | ボンディングワイヤ及びその製造方法 |
| CN102324392B (zh) * | 2011-10-19 | 2013-03-27 | 广东佳博电子科技有限公司 | 一种防氧化的铜基键合丝的制备工艺 |
| CN103219246B (zh) * | 2013-03-01 | 2015-11-25 | 溧阳市虹翔机械制造有限公司 | 一种镀钯镀银的双镀层键合铜丝的制造方法 |
| CN103219247B (zh) * | 2013-03-01 | 2015-11-25 | 溧阳市虹翔机械制造有限公司 | 一种镀银键合铜丝的制造方法 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6297360A (ja) * | 1985-10-24 | 1987-05-06 | Mitsubishi Metal Corp | 半導体装置のボンデイングワイヤ用表面被覆高純度銅極細線 |
| JP2004064033A (ja) * | 2001-10-23 | 2004-02-26 | Sumitomo Electric Wintec Inc | ボンディングワイヤー |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6278863A (ja) * | 1985-09-30 | 1987-04-11 | Tanaka Denshi Kogyo Kk | 半導体素子のボンデイング用銅線 |
| JPH0786325A (ja) * | 1993-09-14 | 1995-03-31 | Hitachi Cable Ltd | 電子機器用銅線 |
| KR100717667B1 (ko) * | 2000-09-18 | 2007-05-11 | 신닛뽄세이테쯔 카부시키카이샤 | 반도체용 본딩 와이어 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP2003133361A (ja) * | 2001-10-23 | 2003-05-09 | Sumiden Magnet Wire Kk | ボンディングワイヤー |
-
2009
- 2009-04-08 JP JP2009094065A patent/JP2010199528A/ja active Pending
- 2009-09-09 WO PCT/JP2009/065735 patent/WO2010087053A1/ja active Application Filing
-
2010
- 2010-01-27 TW TW099102279A patent/TW201037777A/zh unknown
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6297360A (ja) * | 1985-10-24 | 1987-05-06 | Mitsubishi Metal Corp | 半導体装置のボンデイングワイヤ用表面被覆高純度銅極細線 |
| JP2004064033A (ja) * | 2001-10-23 | 2004-02-26 | Sumitomo Electric Wintec Inc | ボンディングワイヤー |
Cited By (66)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9570416B2 (en) | 2004-11-03 | 2017-02-14 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked packaging improvements |
| US9984901B2 (en) | 2005-12-23 | 2018-05-29 | Tessera, Inc. | Method for making a microelectronic assembly having conductive elements |
| US10128216B2 (en) | 2010-07-19 | 2018-11-13 | Tessera, Inc. | Stackable molded microelectronic packages |
| US9553076B2 (en) | 2010-07-19 | 2017-01-24 | Tessera, Inc. | Stackable molded microelectronic packages with area array unit connectors |
| US9570382B2 (en) | 2010-07-19 | 2017-02-14 | Tessera, Inc. | Stackable molded microelectronic packages |
| US10062661B2 (en) | 2011-05-03 | 2018-08-28 | Tessera, Inc. | Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| JP2017041643A (ja) * | 2011-05-03 | 2017-02-23 | テッセラ,インコーポレイテッド | 封止表面に至るワイヤボンドを有するパッケージ・オン・パッケージアセンブリ |
| US11424211B2 (en) | 2011-05-03 | 2022-08-23 | Tessera Llc | Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| JP2014513439A (ja) * | 2011-05-03 | 2014-05-29 | テッセラ,インコーポレイテッド | 封止表面に至るワイヤボンドを有するパッケージ・オン・パッケージアセンブリ |
| US9691731B2 (en) | 2011-05-03 | 2017-06-27 | Tessera, Inc. | Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| US10593643B2 (en) | 2011-05-03 | 2020-03-17 | Tessera, Inc. | Package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| US11735563B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2023-08-22 | Invensas Llc | Package-on-package assembly with wire bond vias |
| US10756049B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2020-08-25 | Invensas Corporation | Package-on-package assembly with wire bond vias |
| US11189595B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2021-11-30 | Invensas Corporation | Package-on-package assembly with wire bond vias |
| US9761558B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2017-09-12 | Invensas Corporation | Package-on-package assembly with wire bond vias |
| US9842745B2 (en) | 2012-02-17 | 2017-12-12 | Invensas Corporation | Heat spreading substrate with embedded interconnects |
| US9691679B2 (en) | 2012-02-24 | 2017-06-27 | Invensas Corporation | Method for package-on-package assembly with wire bonds to encapsulation surface |
| US10170412B2 (en) | 2012-05-22 | 2019-01-01 | Invensas Corporation | Substrate-less stackable package with wire-bond interconnect |
| US10510659B2 (en) | 2012-05-22 | 2019-12-17 | Invensas Corporation | Substrate-less stackable package with wire-bond interconnect |
| US9953914B2 (en) | 2012-05-22 | 2018-04-24 | Invensas Corporation | Substrate-less stackable package with wire-bond interconnect |
| US9917073B2 (en) | 2012-07-31 | 2018-03-13 | Invensas Corporation | Reconstituted wafer-level package dram with conductive interconnects formed in encapsulant at periphery of the package |
| US9391008B2 (en) | 2012-07-31 | 2016-07-12 | Invensas Corporation | Reconstituted wafer-level package DRAM |
| US10297582B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2019-05-21 | Invensas Corporation | BVA interposer |
| US9502390B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2016-11-22 | Invensas Corporation | BVA interposer |
| US9615456B2 (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2017-04-04 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic assembly for microelectronic packaging with bond elements to encapsulation surface |
| US9601454B2 (en) | 2013-02-01 | 2017-03-21 | Invensas Corporation | Method of forming a component having wire bonds and a stiffening layer |
| US10460958B2 (en) | 2013-08-07 | 2019-10-29 | Invensas Corporation | Method of manufacturing embedded packaging with preformed vias |
| US9685365B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2017-06-20 | Invensas Corporation | Method of forming a wire bond having a free end |
| US10008477B2 (en) | 2013-09-16 | 2018-06-26 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic element with bond elements to encapsulation surface |
| US10026717B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2018-07-17 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple bond via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US9728527B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2017-08-08 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple bond via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US10290613B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2019-05-14 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple bond via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US10629567B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2020-04-21 | Invensas Corporation | Multiple plated via arrays of different wire heights on same substrate |
| USRE49987E1 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2024-05-28 | Invensas Llc | Multiple plated via arrays of different wire heights on a same substrate |
| US9852969B2 (en) | 2013-11-22 | 2017-12-26 | Invensas Corporation | Die stacks with one or more bond via arrays of wire bond wires and with one or more arrays of bump interconnects |
| US11990382B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2024-05-21 | Adeia Semiconductor Technologies Llc | Fine pitch BVA using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US9583411B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2017-02-28 | Invensas Corporation | Fine pitch BVA using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US11404338B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2022-08-02 | Invensas Corporation | Fine pitch bva using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US9837330B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2017-12-05 | Invensas Corporation | Fine pitch BVA using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US10529636B2 (en) | 2014-01-17 | 2020-01-07 | Invensas Corporation | Fine pitch BVA using reconstituted wafer with area array accessible for testing |
| US10381326B2 (en) | 2014-05-28 | 2019-08-13 | Invensas Corporation | Structure and method for integrated circuits packaging with increased density |
| US9412714B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2016-08-09 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond support structure and microelectronic package including wire bonds therefrom |
| US9947641B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2018-04-17 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond support structure and microelectronic package including wire bonds therefrom |
| US9735084B2 (en) | 2014-12-11 | 2017-08-15 | Invensas Corporation | Bond via array for thermal conductivity |
| US9888579B2 (en) | 2015-03-05 | 2018-02-06 | Invensas Corporation | Pressing of wire bond wire tips to provide bent-over tips |
| US10806036B2 (en) | 2015-03-05 | 2020-10-13 | Invensas Corporation | Pressing of wire bond wire tips to provide bent-over tips |
| US10008469B2 (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2018-06-26 | Invensas Corporation | Wafer-level packaging using wire bond wires in place of a redistribution layer |
| US9761554B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2017-09-12 | Invensas Corporation | Ball bonding metal wire bond wires to metal pads |
| US10115678B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2018-10-30 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond wires for interference shielding |
| US10490528B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2019-11-26 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded wire bond wires |
| US9812402B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2017-11-07 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond wires for interference shielding |
| US10559537B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2020-02-11 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bond wires for interference shielding |
| US11462483B2 (en) | 2015-10-12 | 2022-10-04 | Invensas Llc | Wire bond wires for interference shielding |
| US10332854B2 (en) | 2015-10-23 | 2019-06-25 | Invensas Corporation | Anchoring structure of fine pitch bva |
| US10181457B2 (en) | 2015-10-26 | 2019-01-15 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic package for wafer-level chip scale packaging with fan-out |
| US9911718B2 (en) | 2015-11-17 | 2018-03-06 | Invensas Corporation | ‘RDL-First’ packaged microelectronic device for a package-on-package device |
| US10043779B2 (en) | 2015-11-17 | 2018-08-07 | Invensas Corporation | Packaged microelectronic device for a package-on-package device |
| US9659848B1 (en) | 2015-11-18 | 2017-05-23 | Invensas Corporation | Stiffened wires for offset BVA |
| US10325877B2 (en) | 2015-12-30 | 2019-06-18 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded wire bond wires for vertical integration with separate surface mount and wire bond mounting surfaces |
| US9984992B2 (en) | 2015-12-30 | 2018-05-29 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded wire bond wires for vertical integration with separate surface mount and wire bond mounting surfaces |
| US10658302B2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2020-05-19 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bonding method and apparatus for electromagnetic interference shielding |
| US9935075B2 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2018-04-03 | Invensas Corporation | Wire bonding method and apparatus for electromagnetic interference shielding |
| US10299368B2 (en) | 2016-12-21 | 2019-05-21 | Invensas Corporation | Surface integrated waveguides and circuit structures therefor |
| CN109411591A (zh) * | 2018-09-14 | 2019-03-01 | 汕头市骏码凯撒有限公司 | 一种led封装用银合金线及其制作方法 |
| JP2021093473A (ja) * | 2019-12-12 | 2021-06-17 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP7412998B2 (ja) | 2019-12-12 | 2024-01-15 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW201037777A (en) | 2010-10-16 |
| WO2010087053A1 (ja) | 2010-08-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2010087053A1 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5616739B2 (ja) | 複層銅ボンディングワイヤの接合構造 | |
| KR101707244B1 (ko) | 반도체용 본딩 와이어 | |
| JP5572121B2 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤの接合構造 | |
| WO2011129256A1 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP4672373B2 (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP2010245390A (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| KR101536554B1 (ko) | 본딩용 와이어 | |
| JP2011146754A5 (ja) | ||
| WO2013018238A1 (ja) | ボールボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5064577B2 (ja) | ボールボンディング用ワイヤ | |
| JP5671512B2 (ja) | ボンディング用ワイヤ | |
| JP2004014884A (ja) | ボンディングワイヤー | |
| JP2007012776A (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP4722671B2 (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP2006216929A (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5393614B2 (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP4860004B1 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ及びその製造方法 | |
| JP5591987B2 (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5996853B2 (ja) | ボールボンディング用ワイヤ | |
| JP2011222882A (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP2011249463A (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP5001455B1 (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2013042105A (ja) | ボンディングワイヤ | |
| JP2010245574A (ja) | 半導体装置用ボンディングワイヤ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20100701 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110325 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110325 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20110325 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20110407 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110412 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110510 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20110524 |