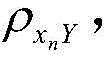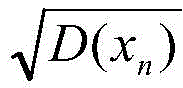CN113642779A - ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion - Google Patents
ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113642779A CN113642779A CN202110829782.XA CN202110829782A CN113642779A CN 113642779 A CN113642779 A CN 113642779A CN 202110829782 A CN202110829782 A CN 202110829782A CN 113642779 A CN113642779 A CN 113642779A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- sample
- residual
- matrix
- space
- dimension
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 22
- 238000010219 correlation analysis Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 claims description 53
- 208000037170 Delayed Emergence from Anesthesia Diseases 0.000 claims description 49
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000011176 pooling Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 9
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 abstract description 7
- 230000003449 preventive effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 5
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004880 explosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003862 health status Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000644 propagated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/04—Forecasting or optimisation specially adapted for administrative or management purposes, e.g. linear programming or "cutting stock problem"
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/21—Design or setup of recognition systems or techniques; Extraction of features in feature space; Blind source separation
- G06F18/214—Generating training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/25—Fusion techniques
- G06F18/253—Fusion techniques of extracted features
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/084—Backpropagation, e.g. using gradient descent
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,首先对系统设备中各传感器采集的数据信息进行相关性分析,过滤与寿命关联程度较低的特征变量,确定影响系统寿命的高关联度特征变量;然后利用ISOMAP算法融合高关联度特征变量,得到融合特征变量,有效的集成传感器信息;针对融合特征变量,和系统对应时刻的剩余寿命构成剩余寿命预测总样本集,最后建立预测模型并预测剩余寿命,得到系统剩余寿命预测结果。本发明对工业领域中的设备寿命进行准确预测,及时提示工作人员对设备进行预防性维护。
The invention discloses a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in a ResNet50 network based on feature fusion. First, correlation analysis is performed on data information collected by various sensors in the system equipment, and feature variables with a low degree of correlation with the life are filtered to determine the impact on the life of the system. Then use the ISOMAP algorithm to fuse the highly correlated feature variables to obtain the fused feature variables, effectively integrating sensor information; for the fused feature variables, and the remaining life at the corresponding moment of the system constitute the total remaining life prediction sample set, and finally Establish a prediction model and predict the remaining life, and obtain the prediction result of the system's remaining life. The invention accurately predicts the service life of the equipment in the industrial field, and prompts the staff to perform preventive maintenance on the equipment in time.
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明属于智能制造系统的监测与维护技术领域,具体涉及一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of monitoring and maintenance of an intelligent manufacturing system, in particular to a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in a ResNet50 network based on feature fusion.
背景技术Background technique
预测与健康管理(Prognostic and Health Management,PHM)技术在现代工业中至关重要,并已广泛应用于民用航空、汽车和制造业。随着时间的累积,由于设备在受到内部因素和各种外部因素(如磨损、外部冲击、负载、运行环境)的影响下,其性能及健康状态将会呈现不同程度的退化趋势,不断累积最终导致设备发生故障,造成无法估量的经济损失与安全事故等。剩余使用寿命(RUL)预测是现代工业领域预测健康管理(PHM)技术中最重要的组成部分之一,它的定义是从当前时刻的使用寿命到该寿命结束的长度。为了提高系统的安全性与可靠性,降低维修成本,需要确保在最佳时期对设备进行维护,定期更换零件,防止故障的累积最终造成的设备失效。对设备各部件传感器数据进行监测,准确的预测设备处于某时刻的剩余使用寿命,便可找到适当的时机对设备进行预防性维护,减少设备的停机时间,节约成本。Prognostic and Health Management (PHM) technology is crucial in modern industry and has been widely used in civil aviation, automotive and manufacturing. With the accumulation of time, due to the influence of internal factors and various external factors (such as wear, external impact, load, operating environment), the performance and health status of the equipment will show different degrees of degradation trend, and the accumulation will eventually Cause equipment failure, resulting in immeasurable economic losses and safety accidents. Remaining useful life (RUL) prediction is one of the most important components of Predictive Health Management (PHM) technology in modern industry, and it is defined as the length of useful life from the current moment to the end of that life. In order to improve the safety and reliability of the system and reduce the maintenance cost, it is necessary to ensure that the equipment is maintained at the best time, and the parts are replaced regularly to prevent the equipment failure caused by the accumulation of faults. By monitoring the sensor data of each component of the equipment and accurately predicting the remaining service life of the equipment at a certain time, it is possible to find an appropriate time to perform preventive maintenance on the equipment, reduce equipment downtime and save costs.
由于对系统剩余使用寿命的预测主要基于多传感器收集到的大量监测数据,来评估系统整体的退化状态,及时对系统做出维护。单个传感器特征不足以准确判断系统的健康状态,因此需要多种特征。但特征过多会造成信息冗余,增大计算负担。于是过滤与寿命关联度低的特征并对其余多传感器特征进行融合,以获得更好的健康指标,提高预测方法的准确性,使预防性维护更加及时有效。针对剩余寿命预测研究中,特征过多导致维数爆炸从而使得计算效率低下的问题,提出一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,该方法不仅能够增强对剩余寿命预测研究的信心,对于该学科和行业的进步起着关键性的作用。Since the prediction of the remaining service life of the system is mainly based on a large amount of monitoring data collected by multiple sensors, the overall degradation status of the system is evaluated and the system is maintained in time. A single sensor feature is not enough to accurately judge the health of a system, so multiple features are needed. However, too many features will cause information redundancy and increase the computational burden. Therefore, the features with low correlation with lifespan are filtered and the remaining multi-sensor features are fused to obtain better health indicators, improve the accuracy of prediction methods, and make preventive maintenance more timely and effective. Aiming at the problem that too many features lead to dimensionality explosion in the research of remaining life prediction, which leads to low computational efficiency, a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in the ResNet50 network based on feature fusion is proposed, which can not only enhance the confidence in the research on remaining life prediction , plays a key role in the advancement of the discipline and industry.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的是提供一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,对工业领域中的设备寿命进行准确预测,及时提示工作人员对设备进行预防性维护。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in the ResNet50 network based on feature fusion, which can accurately predict the life of the equipment in the industrial field and prompt the staff to perform preventive maintenance on the equipment in time.
本发明所采用的技术方案是,一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,具体按照以下步骤实施:The technical solution adopted by the present invention is a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in the ResNet50 network based on feature fusion, which is specifically implemented according to the following steps:
步骤1、对系统设备中各传感器采集的数据信息进行相关性分析,过滤与寿命关联程度较低的特征变量,确定影响系统寿命的高关联度特征变量;
步骤2、对所述步骤1得到的高关联度特征变量进行特征融合:利用ISOMAP算法融合步骤1中的高关联度特征变量,得到融合特征变量,有效的集成传感器信息;
步骤3、构建数据集构造策略:针对步骤2中得到的融合特征变量,和系统对应时刻的剩余寿命构成剩余寿命预测总样本集,并将其分为训练集与测试集;
步骤4:建立预测模型并预测剩余寿命:将步骤3中得到的剩余寿命预测总样本集的训练集作为深度残差网络Resnet50的输入训练该预测网络,利用训练好的网络对测试样本进行预测,得到系统剩余寿命预测结果。Step 4: Establish a prediction model and predict the remaining life: use the training set of the total remaining life prediction sample set obtained in
本发明的特点还在于,The present invention is also characterized in that,
步骤1具体如下:
步骤1.1、对系统设备中传感器采集的数据信息进行编号,n表示为传感器的序号,xn为第n个传感器的监测数据信息,监测数据X表示为其中,为系统中i时刻第n个传感器的监测数据信息,i=1,2,...,t,该系统的剩余寿命Y表示为Y={yi},其中,yi为系统对应i时刻的剩余寿命;Step 1.1. Number the data information collected by the sensors in the system equipment, n is the serial number of the sensor, x n is the monitoring data information of the nth sensor, and the monitoring data X is expressed as in, is the monitoring data information of the nth sensor at time i in the system, i=1,2,...,t, the remaining life Y of the system is expressed as Y={y i }, where y i is the time corresponding to the system i remaining life;
步骤1.2、利用相关性分析计算相关系数 Step 1.2, use correlation analysis to calculate the correlation coefficient
其中,Cov(xn,Y)为监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y之间的协方差,和分别为监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y的标准差;Among them, Cov(x n , Y) is the covariance between the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y, and are the standard deviation of the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y respectively;
步骤1.3、计算监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y的Pearson相关系数具体如下:Step 1.3. Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y details as follows:
相关系数范围: Correlation coefficient scope:
保留结果超过0.8以上的高关联度特征变量。Retain the highly correlated feature variables whose results exceed 0.8.
步骤2具体如下:
步骤2.1、选取邻域,构造邻域图G:近邻参数设置为k,将步骤1.3保留的高关联度特征变量构造样本集D={x1,x2,...,xm},m是原始d维空间的样本集D中样本点的个数,在样本集D={x1,x2,...,xm}中任意选取某两个数据点xh与xj,其中,h,j是样本集D中选取的两个数据点的编号,h,j∈1,2,3...m,第一个数据点xh与近邻参数k间距离设为欧氏距离,另一个数据点xj是xh最近的近邻参数k个点之一时,表示它们相近邻,邻域图G有边,即邻域图G构造完毕;Step 2.1. Select a neighborhood and construct a neighborhood graph G: set the nearest neighbor parameter to k, and construct a sample set D={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m }, m is the number of sample points in the sample set D of the original d-dimensional space, and two data points x h and x j are arbitrarily selected in the sample set D={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m }, where , h, j are the numbers of the two data points selected in the sample set D, h, j∈1,2,3...m, the distance between the first data point x h and the neighbor parameter k is set as the Euclidean distance , when another data point x j is one of the k points of the nearest neighbor parameters of x h , it means that they are adjacent, and the neighborhood graph G has edges, that is, the neighborhood graph G is constructed;
步骤2.2、计算最短路径距离矩阵:若邻域图G上两点xh、xj存在边连接时,定义样本点xh与xj之间的最短路径为dG(xh,xj)=d(xh,xj);否则dG(xh,xj)=∞,其中,d(xh,xj)为数据点xh与xj的欧氏距离;Step 2.2. Calculate the shortest path distance matrix: If there are edge connections between two points x h and x j on the neighborhood graph G, define the shortest path between the sample points x h and x j as d G (x h , x j ) =d(x h , x j ); otherwise d G (x h , x j )=∞, where d(x h , x j ) is the Euclidean distance between data points x h and x j ;
对l∈1,2,3...m,有:For l∈1,2,3...m, we have:
dG(xh,xj)=min{dG(xh,xj),dG(xh,xl)+dG(xl,xj)} (3)d G (x h ,x j )=min{d G (x h ,x j ),d G (x h ,x l )+d G (x l ,x j )} (3)
其中,xl是样本集D中新的样本点,dG(xh,xl)表示样本点xh与xl之间的最短路径,dG(xl,xj)表示样本点xl与xj之间的最短路径,dG(xh,xj)表示样本点xh与xj之间的最短路径;Among them, x l is a new sample point in the sample set D, d G (x h ,x l ) represents the shortest path between the sample points x h and x l , d G (x l ,x j ) represents the sample point x The shortest path between l and x j , d G (x h ,x j ) represents the shortest path between sample points x h and x j ;
基于此,即可确定最短路径距离矩阵为其中,m是d维原始空间的样本集D中样本点的个数,h,j,l是样本集D中选取的三个数据点的编号,h,j,l∈1,2,3...m;Based on this, the shortest path distance matrix can be determined as Among them, m is the number of sample points in the sample set D of the d-dimensional original space, h, j, l are the numbers of the three data points selected in the sample set D, h, j, l ∈ 1, 2, 3. ..m;
步骤2.3、通过对d维原始空间降维,构造d'维新样本空间,并且使得d'维新样本空间与d维原始空间中的距离保持不变,求取降维后样本的内积矩阵B:令B=ZTZ∈Rm×m,其中,d是原始空间的维数,d'是新样本空间的维数,Z为d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示,R为实数集;Step 2.3. Construct a new d'-dimensional sample space by reducing the dimension of the d-dimensional original space, and keep the distance between the d'-dimensional new sample space and the d-dimensional original space unchanged, and obtain the inner product matrix B of the samples after dimensionality reduction: Let B=Z T Z∈R m×m , where d is the dimension of the original space, d' is the dimension of the new sample space, Z is the matrix representation of the d-dimensional original space embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space, and R is set of real numbers;
构造新样本空间后,d'<d,且任意两个样本在d'维新样本空间中的欧氏距离等于d维原始空间中的距离,即:After constructing the new sample space, d'<d, and the Euclidean distance of any two samples in the new sample space of dimension d' is equal to the distance in the original space of dimension d, namely:
||zh-zj||=disthj (4)||z h -z j ||=dist hj (4)
其中,zh,zj分别表示样本点xh,xj在d'维新样本空间中的欧氏距离,disthj表示样本点xh和xj在d维原始空间中的距离;Among them, z h , z j represent the Euclidean distance of the sample points x h , x j in the d'-dimensional new sample space, respectively, and dist hj represents the distance between the sample points x h and x j in the d-dimensional original space;
将式(4)展开并对等号两端求平方得:Expand Equation (4) and square both sides of the equal sign to get:
bhh与bjj以此类推,则有: b hh and b jj and so on, there are:
其中,bhj为内积矩阵B中第h行j列的元素,bhh与bjj以此类推,disthj表示样本点xh和xj在d维原始空间的距离,disth·、dist·j及dist··以此类推;Among them, b hj is the element of the hth row and j column in the inner product matrix B, b hh and b jj and so on, dist hj represents the distance between the sample points x h and x j in the d-dimensional original space, dist h , dist ·j and dist · and so on;
通过求得bhj,bhh,bjj等内积矩阵B中的元素可得内积矩阵B;The inner product matrix B can be obtained by obtaining the elements in the inner product matrix B such as b hj , b hh , b jj ;
步骤2.4、对最短路径距离矩阵DG构造d维嵌入,最终得到样本通过d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示Z∈Rd′×m;Step 2.4, construct a d-dimensional embedding for the shortest path distance matrix D G , and finally obtain the matrix representation Z∈R d′×m in which the samples are embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space through the d-dimensional original space;
由步骤2.3求得的内积矩阵B通过特征分解获得特征值矩阵和特征向量矩阵,即:The inner product matrix B obtained in step 2.3 obtains the eigenvalue matrix and the eigenvector matrix through eigendecomposition, namely:
B=VΛVT (8)B=VΛV T (8)
其中,Λ=diag(λ1,λ2,...,λd)为特征值构成的对角矩阵,λ1≥λ2≥...≥λd,λ1,λ2,...,λd为分解获得的特征值,V为对应的特征向量矩阵。Among them, Λ=diag(λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ d ) is a diagonal matrix composed of eigenvalues, λ 1 ≥λ 2 ≥...≥λ d , λ 1 ,λ 2 ,... , λ d is the eigenvalue obtained by decomposition, and V is the corresponding eigenvector matrix.
则d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示Z的计算公式为:计算Z的结果后可得到矩阵表示为:此时的结果便是融合后的特征变量;Then the matrix representation Z of the d-dimensional original space embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space is calculated as: After calculating the result of Z, the matrix can be obtained as: result at this time is the feature variable after fusion;
其中,有d*个非零特征值,为特征值构成的对角矩阵,特征值V*为对应的特征向量矩阵;为d'维新样本空间中i时刻第m'个样本点的融合特征变量,m'是d'维新样本空间中样本点的个数。where, there are d * non-zero eigenvalues, is a diagonal matrix of eigenvalues, eigenvalues V * is the corresponding eigenvector matrix; is the fusion feature variable of the m'th sample point at time i in the d'-dimensional sample space, where m' is the number of sample points in the d'-dimensional sample space.
步骤3具体如下:
步骤3.1、构造样本集:将步骤2中得到的融合后的特征变量和系统剩余寿命Y={yi}重构为剩余寿命预测样本集 分别为重构的剩余寿命预测样本集中的特征变量,并按照7:3的比例划分为训练集和验证集,其中,yi为系统对应i时刻的剩余寿命;Step 3.1. Construct a sample set: combine the fused feature variables obtained in
步骤3.2、构造子训练集和子测试集:将步骤3.1中划分好的训练集再次按照7:3的比例划分为子训练集和子测试集;Step 3.2, construct sub-training set and sub-test set: divide the training set divided in step 3.1 into sub-training set and sub-test set according to the ratio of 7:3 again;
步骤3.3、构造总训练集和总测试集:将步骤3.2得到的子训练集中的特征变量按照列堆叠的形式合并为总训练集,同时,对应步骤3.2中子训练集的合并顺序,将子测试集中的特征变量以列堆叠的形式合并为总测试集,最终形成由总训练集、总测试集和步骤3.1得到的验证集构成的剩余寿命预测总样本集。Step 3.3. Construct the total training set and the total test set: Combine the feature variables in the sub-training set obtained in step 3.2 into the total training set in the form of column stacking. The feature variables in the set are merged into the total test set in the form of column stacking, and finally the total remaining life prediction sample set consisting of the total training set, the total test set and the validation set obtained in step 3.1 is formed.
步骤4具体如下:
步骤4.1、构建50层深度残差网络ResNet50:深度残差网络ResNet50由3部分组成,分别为卷积池化部分、4个残差块部分、池化展平部分,残差块部分有两个基本的结构,分别为恒等残差块和卷积残差块;Step 4.1. Build a 50-layer deep residual network ResNet50: The deep residual network ResNet50 consists of three parts, namely the convolution pooling part, the four residual block parts, and the pooling and flattening part. There are two residual block parts. The basic structure is the identity residual block and the convolution residual block;
步骤4.2、特征提取:将步骤3中得到的剩余寿命预测总样本集的训练集作为深度残差网络Resnet50的输入,采用一维卷积核对训练集进行特征提取,并对提取的卷积特征进行最大值池化,以获得池化特征;Step 4.2. Feature extraction: The training set of the total remaining life prediction sample set obtained in
步骤4.3、残差块的特征提取:将池化特征作为残差块的输入,深度残差网络Resnet50的残差块由以下四部分组成:一个卷积残差块和两个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和三个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和五个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和两个恒等残差块,上述四个残差块按照顺序连接组成为残差网络核心部分;Step 4.3. Feature extraction of residual block: The pooled feature is used as the input of the residual block. The residual block of the deep residual network Resnet50 consists of the following four parts: a convolution residual block and two identity residual blocks , one convolutional residual block and three identity residual blocks, one convolutional residual block and five identity residual blocks, one convolutional residual block and two identity residual blocks, the above four residual blocks The difference blocks are sequentially connected to form the core part of the residual network;
步骤4.4、建立预测模型:经平均池化层整合残差块的输出,再通过展平层获得预测模型;Step 4.4, establish a prediction model: integrate the output of the residual block through the average pooling layer, and then obtain the prediction model through the flattening layer;
步骤4.5、得到剩余寿命预测结果:将测试集输入预测模型中,得到剩余寿命预测结果,每进行一次预测得到输出的预测结果,将该预测结果和系统采集的剩余寿命真实数据之间的误差反向传播给深度残差网络Resnet50,并对网络中的各参数进行调优,当网络的误差小于0.05时,说明网络收敛,利用训练好的网络对测试样本进行预测,最终得到系统剩余寿命预测结果,实现系统的剩余寿命的准确预测。Step 4.5. Obtain the remaining life prediction result: Input the test set into the prediction model to obtain the remaining life prediction result. Each time a prediction is performed, the output prediction result is obtained, and the error between the prediction result and the real data of the remaining life collected by the system is reversed. It is propagated to the deep residual network Resnet50, and the parameters in the network are adjusted. When the error of the network is less than 0.05, it means that the network has converged. The trained network is used to predict the test samples, and finally the prediction result of the remaining life of the system is obtained. , to achieve accurate prediction of the remaining life of the system.
本发明的有益效果是,一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,通过相关性分析的方法排除影响系统设备寿命的低关联度特征,利用ISOMAP算法对高关联度特征进行融合,有效的集成传感器信息,并且消除传感器之间的耦合性。将ISOMAP算法和深度残差网络Resnet50结合,使融合后的传感器特征信息作为深度残差网络Resnet50的输入训练该预测网络,学习各特征之间的隐层关系,构建剩余寿命预测模型,实现了剩余寿命的预测。通过实验仿真验证了所提方法在剩余寿命预测方面的准确性和高效性。The beneficial effect of the present invention is that, a method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in the ResNet50 network based on feature fusion, eliminates the low correlation degree features affecting the life of the system equipment through the method of correlation analysis, and uses the ISOMAP algorithm to fuse the high correlation degree features, Effectively integrate sensor information and eliminate coupling between sensors. Combining the ISOMAP algorithm and the deep residual network Resnet50, the fused sensor feature information is used as the input of the deep residual network Resnet50 to train the prediction network, learn the hidden layer relationship between each feature, and build the remaining life prediction model. Prediction of lifespan. The accuracy and efficiency of the proposed method in remaining life prediction are verified by experimental simulation.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法总体流程图;Fig. 1 is the overall flow chart of the residual life prediction method of ResNet50 network key equipment based on feature fusion of the present invention;
图2为本发明中传感器特征变量相关性分析结果图;Fig. 2 is a graph showing the results of correlation analysis of sensor characteristic variables in the present invention;
图3为本发明中采用ISOMAP算法进行特征融合流程图;Fig. 3 adopts ISOMAP algorithm to carry out feature fusion flow chart in the present invention;
图4为本发明中深度残差网络ResNet50整体结构图;Fig. 4 is the overall structure diagram of the deep residual network ResNet50 in the present invention;
图5为本发明中深度残差网络ResNet50预测过程流程图;5 is a flowchart of the prediction process of the deep residual network ResNet50 in the present invention;
图6为本发明预测结果图。FIG. 6 is a graph of the prediction result of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和具体实施方式对本发明进行详细说明。The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
本发明一种基于特征融合的ResNet50网络关键设备剩余寿命预测方法,流程图如图1所示,具体按照以下步骤实施:A method for predicting the remaining life of key equipment in the ResNet50 network based on feature fusion of the present invention, the flowchart is shown in Figure 1, and is specifically implemented according to the following steps:
步骤1、保留影响系统设备运行时长的高关联度特征变量:对系统设备中各传感器采集的数据信息进行相关性分析,过滤与寿命关联程度较低的特征变量,确定影响系统寿命的高关联度特征变量;
结合图2~图5,步骤1具体如下:With reference to Figures 2 to 5,
步骤1.1、对系统设备中传感器采集的数据信息进行编号,n表示为传感器的序号,xn为第n个传感器的监测数据信息,监测数据X表示为其中,为系统中i时刻第n个传感器的监测数据信息,i=1,2,...,t,该系统的剩余寿命Y表示为Y={yi},其中,yi为系统对应i时刻的剩余寿命;Step 1.1. Number the data information collected by the sensors in the system equipment, n is the serial number of the sensor, x n is the monitoring data information of the nth sensor, and the monitoring data X is expressed as in, is the monitoring data information of the nth sensor at time i in the system, i=1,2,...,t, the remaining life Y of the system is expressed as Y={y i }, where y i is the time corresponding to the system i remaining life;
步骤1.2、利用相关性分析计算相关系数 Step 1.2, use correlation analysis to calculate the correlation coefficient
其中,Cov(xn,Y)为监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y之间的协方差,和分别为监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y的标准差;Among them, Cov(x n , Y) is the covariance between the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y, and are the standard deviation of the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y respectively;
步骤1.3、计算监测数据信息xn和剩余寿命Y的Pearson相关系数具体如下:Step 1.3. Calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between the monitoring data information x n and the remaining life Y details as follows:
相关系数范围: Correlation coefficient scope:
保留结果超过0.8以上的高关联度特征变量。Retain the highly correlated feature variables whose results exceed 0.8.
步骤2、对所述步骤1得到的高关联度特征变量进行特征融合:利用ISOMAP算法融合步骤1中的高关联度特征变量,得到融合特征变量,有效的集成传感器信息;
步骤2具体如下:
步骤2.1、选取邻域,构造邻域图G:近邻参数设置为k,将步骤1.3保留的高关联度特征变量构造样本集D={x1,x2,...,xm},m是原始d维空间的样本集D中样本点的个数,在样本集D={x1,x2,...,xm}中任意选取某两个数据点xh与xj,其中,h,j是样本集D中选取的两个数据点的编号,h,j∈1,2,3...m,第一个数据点xh与近邻参数k间距离设为欧氏距离,另一个数据点xj是xh最近的近邻参数k个点之一时,表示它们相近邻,邻域图G有边,即邻域图G构造完毕;Step 2.1. Select a neighborhood and construct a neighborhood graph G: set the nearest neighbor parameter to k, and construct a sample set D={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m }, m is the number of sample points in the sample set D of the original d-dimensional space, and two data points x h and x j are arbitrarily selected in the sample set D={x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x m }, where , h, j are the numbers of the two data points selected in the sample set D, h, j∈1,2,3...m, the distance between the first data point x h and the neighbor parameter k is set as the Euclidean distance , when another data point x j is one of the k points of the nearest neighbor parameters of x h , it means that they are adjacent, and the neighborhood graph G has edges, that is, the neighborhood graph G is constructed;
步骤2.2、计算最短路径距离矩阵:若邻域图G上两点xh、xj存在边连接时,定义样本点xh与xj之间的最短路径为dG(xh,xj)=d(xh,xj);否则dG(xh,xj)=∞,其中,d(xh,xj)为数据点xh与xj的欧氏距离;Step 2.2. Calculate the shortest path distance matrix: If there are edge connections between two points x h and x j on the neighborhood graph G, define the shortest path between the sample points x h and x j as d G (x h , x j ) =d(x h , x j ); otherwise d G (x h , x j )=∞, where d(x h , x j ) is the Euclidean distance between data points x h and x j ;
对l∈1,2,3...m,有:For l∈1,2,3...m, we have:
dG(xh,xj)=min{dG(xh,xj),dG(xh,xl)+dG(xl,xj)} (3)d G (x h ,x j )=min{d G (x h ,x j ),d G (x h ,x l )+d G (x l ,x j )} (3)
其中,xl是样本集D中新的样本点,dG(xh,xl)表示样本点xh与xl之间的最短路径,dG(xl,xj)表示样本点xl与xj之间的最短路径,dG(xh,xj)表示样本点xh与xj之间的最短路径;Among them, x l is a new sample point in the sample set D, d G (x h ,x l ) represents the shortest path between the sample points x h and x l , d G (x l ,x j ) represents the sample point x The shortest path between l and x j , d G (x h ,x j ) represents the shortest path between sample points x h and x j ;
基于此,即可确定最短路径距离矩阵为其中,m是d维原始空间的样本集D中样本点的个数,h,j,l是样本集D中选取的三个数据点的编号,h,j,l∈1,2,3...m;Based on this, the shortest path distance matrix can be determined as Among them, m is the number of sample points in the sample set D of the d-dimensional original space, h, j, l are the numbers of the three data points selected in the sample set D, h, j, l ∈ 1, 2, 3. ..m;
步骤2.3、通过对d维原始空间降维,构造d'维新样本空间,并且使得d'维新样本空间与d维原始空间中的距离保持不变,求取降维后样本的内积矩阵B:令B=ZTZ∈Rm×m,其中,d是原始空间的维数,d'是新样本空间的维数,Z为d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示,R为实数集;Step 2.3. Construct a new d'-dimensional sample space by reducing the dimension of the d-dimensional original space, and keep the distance between the d'-dimensional new sample space and the d-dimensional original space unchanged, and obtain the inner product matrix B of the samples after dimensionality reduction: Let B=Z T Z∈R m×m , where d is the dimension of the original space, d' is the dimension of the new sample space, Z is the matrix representation of the d-dimensional original space embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space, and R is set of real numbers;
构造新样本空间后,d'<d,且任意两个样本在d'维新样本空间中的欧氏距离等于d维原始空间中的距离,即:After constructing the new sample space, d'<d, and the Euclidean distance of any two samples in the new sample space of dimension d' is equal to the distance in the original space of dimension d, namely:
||zh-zj||=disthj (4)||z h -z j ||=dist hj (4)
其中,zh,zj分别表示样本点xh,xj在d'维新样本空间中的欧氏距离,disthj表示样本点xh和xj在d维原始空间中的距离;Among them, z h , z j represent the Euclidean distance of the sample points x h , x j in the d'-dimensional new sample space, respectively, and dist hj represents the distance between the sample points x h and x j in the d-dimensional original space;
将式(4)展开并对等号两端求平方得:Expand Equation (4) and square both sides of the equal sign to get:
bhh与bjj以此类推,则有: b hh and b jj and so on, there are:
其中,bhj为内积矩阵B中第h行j列的元素,bhh与bjj以此类推,disthj表示样本点xh和xj在d维原始空间的距离,disth·、dist·j及dist··以此类推;Among them, b hj is the element of the hth row and j column in the inner product matrix B, b hh and b jj and so on, dist hj represents the distance between the sample points x h and x j in the d-dimensional original space, dist h , dist ·j and dist · and so on;
通过求得bhj,bhh,bjj等内积矩阵B中的元素可得内积矩阵B;The inner product matrix B can be obtained by obtaining the elements in the inner product matrix B such as b hj , b hh , b jj ;
步骤2.4、对最短路径距离矩阵DG构造d维嵌入,最终得到样本通过d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示Z∈Rd′×m;Step 2.4, construct a d-dimensional embedding for the shortest path distance matrix D G , and finally obtain the matrix representation Z∈R d′×m in which the samples are embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space through the d-dimensional original space;
由步骤2.3求得的内积矩阵B通过特征分解获得特征值矩阵和特征向量矩阵,即:The inner product matrix B obtained in step 2.3 obtains the eigenvalue matrix and the eigenvector matrix through eigendecomposition, namely:
B=VΛVT (8)B=VΛV T (8)
其中,Λ=diag(λ1,λ2,...,λd)为特征值构成的对角矩阵,λ1≥λ2≥...≥λd,λ1,λ2,...,λd为分解获得的特征值,V为对应的特征向量矩阵。Among them, Λ=diag(λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ d ) is a diagonal matrix composed of eigenvalues, λ 1 ≥λ 2 ≥...≥λ d , λ 1 ,λ 2 ,... , λ d is the eigenvalue obtained by decomposition, and V is the corresponding eigenvector matrix.
则d维原始空间嵌入d'维新样本空间的矩阵表示Z的计算公式为:计算Z的结果后可得到矩阵表示为:此时的结果便是融合后的特征变量;Then the matrix representation Z of the d-dimensional original space embedded in the d'-dimensional new sample space is calculated as: After calculating the result of Z, the matrix can be obtained as: result at this time is the feature variable after fusion;
其中,有d*个非零特征值,为特征值构成的对角矩阵,特征值V*为对应的特征向量矩阵;为d'维新样本空间中i时刻第m'个样本点的融合特征变量,m'是d'维新样本空间中样本点的个数。where, there are d * non-zero eigenvalues, is a diagonal matrix of eigenvalues, eigenvalues V * is the corresponding eigenvector matrix; is the fusion feature variable of the m'th sample point at time i in the d'-dimensional sample space, where m' is the number of sample points in the d'-dimensional sample space.
步骤3、构建数据集构造策略:针对步骤2中得到的融合特征变量,和系统对应时刻的剩余寿命构成剩余寿命预测总样本集,并将其分为训练集与测试集;
步骤3具体如下:
步骤3.1、构造样本集:将步骤2中得到的融合后的特征变量和系统剩余寿命Y={yi}重构为剩余寿命预测样本集 分别为重构的剩余寿命预测样本集中的特征变量,并按照7:3的比例划分为训练集和验证集,其中,yi为系统对应i时刻的剩余寿命;Step 3.1. Construct a sample set: combine the fused feature variables obtained in
步骤3.2、构造子训练集和子测试集:将步骤3.1中划分好的训练集再次按照7:3的比例划分为子训练集和子测试集;Step 3.2, construct sub-training set and sub-test set: divide the training set divided in step 3.1 into sub-training set and sub-test set according to the ratio of 7:3 again;
步骤3.3、构造总训练集和总测试集:将步骤3.2得到的子训练集中的特征变量按照列堆叠的形式合并为总训练集,同时,对应步骤3.2中子训练集的合并顺序,将子测试集中的特征变量以列堆叠的形式合并为总测试集,最终形成由总训练集、总测试集和步骤3.1得到的验证集构成的剩余寿命预测总样本集。Step 3.3. Construct the total training set and the total test set: Combine the feature variables in the sub-training set obtained in step 3.2 into the total training set in the form of column stacking. The feature variables in the set are merged into the total test set in the form of column stacking, and finally the total remaining life prediction sample set consisting of the total training set, the total test set and the validation set obtained in step 3.1 is formed.
步骤4:建立预测模型并预测剩余寿命:将步骤3中得到的剩余寿命预测总样本集的训练集作为深度残差网络Resnet50的输入训练该预测网络,利用训练好的网络对测试样本进行预测,得到系统剩余寿命预测结果,,及时提示工作人员对设备整体进行预防性维护。Step 4: Establish a prediction model and predict the remaining life: use the training set of the total remaining life prediction sample set obtained in
步骤4具体如下:
步骤4.1、构建50层深度残差网络ResNet50:深度残差网络ResNet50由3部分组成,分别为卷积池化部分、4个残差块部分、池化展平部分,残差块部分有两个基本的结构,分别为恒等残差块和卷积残差块;整体结构如图4所示。两种残差块的不同点在于捷径连接处有无卷积层,作用是解决维度不匹配的问题。Step 4.1. Build a 50-layer deep residual network ResNet50: The deep residual network ResNet50 consists of three parts, namely the convolution pooling part, the four residual block parts, and the pooling and flattening part. There are two residual block parts. The basic structure is the identity residual block and the convolution residual block respectively; the overall structure is shown in Figure 4. The difference between the two residual blocks is whether there is a convolution layer at the shortcut connection, which is used to solve the problem of dimension mismatch.
步骤4.2、特征提取:将步骤3中得到的剩余寿命预测总样本集的训练集作为深度残差网络Resnet50的输入,采用一维卷积核对训练集进行特征提取,并对提取的卷积特征进行最大值池化,以获得池化特征;Step 4.2. Feature extraction: The training set of the total remaining life prediction sample set obtained in
步骤4.3、残差块的特征提取:将池化特征作为残差块的输入,深度残差网络Resnet50的残差块由以下四部分组成:一个卷积残差块和两个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和三个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和五个恒等残差块、一个卷积残差块和两个恒等残差块,上述四个残差块按照顺序连接组成为残差网络核心部分,随着网络层数的加深,经由残差块特有的捷径连接,将残差结果逼近于0,减少输入的损失;Step 4.3. Feature extraction of residual block: The pooled feature is used as the input of the residual block. The residual block of the deep residual network Resnet50 consists of the following four parts: a convolution residual block and two identity residual blocks , one convolutional residual block and three identity residual blocks, one convolutional residual block and five identity residual blocks, one convolutional residual block and two identity residual blocks, the above four residual blocks The difference blocks are sequentially connected to form the core part of the residual network. With the deepening of the number of network layers, the residual results are approached to 0 through the unique shortcut connection of the residual blocks to reduce the loss of input;
步骤4.4、建立预测模型:经平均池化层整合残差块的输出,再通过展平层获得预测模型;Step 4.4, establish a prediction model: integrate the output of the residual block through the average pooling layer, and then obtain the prediction model through the flattening layer;
步骤4.5、得到剩余寿命预测结果:将测试集输入预测模型中,得到剩余寿命预测结果,具体的寿命预测流程见图5所示。每进行一次预测得到输出的预测结果,将该预测结果和系统采集的剩余寿命真实数据之间的误差反向传播给深度残差网络Resnet50,并对网络中的各参数进行调优,当网络的误差小于0.05时,说明网络收敛,利用训练好的网络对测试样本进行预测,最终得到系统剩余寿命预测结果,实现系统的剩余寿命的准确预测。Step 4.5. Obtain the remaining life prediction result: Input the test set into the prediction model to obtain the remaining life prediction result. The specific life prediction process is shown in Figure 5. Each time a prediction is made to obtain the output prediction result, the error between the prediction result and the real data of the remaining life collected by the system is back-propagated to the deep residual network Resnet50, and the parameters in the network are adjusted. When the error is less than 0.05, it means that the network has converged, and the trained network is used to predict the test sample, and finally the prediction result of the remaining life of the system is obtained, so as to realize the accurate prediction of the remaining life of the system.
实施例Example
本次实验以涡轮发动机系统为研究对象,共收集了21个传感器在四种故障模式下的样本数据,以一种故障模式的数据集为例(100台发动机共20631个样本数据),随机选取第17台发动机数据(共276个寿命周期数据)。经过相关性分析与ISOMAP特征融合后,保留相关系数超过0.8的4个特征变量。将前200个寿命周期数据作为总训练集,将后76个寿命周期数据作为总测试集。基于以上数据,采用本发明的方法进行多变量剩余寿命预测,为了更加清晰地描述实验结果,将仿真结果可视化,结果见图6。通过观察图6可知,所提模型的预测结果与实际数据误差较小,效果较好。This experiment takes the turbine engine system as the research object, and collects the sample data of 21 sensors under four failure modes. Taking the data set of one failure mode as an example (100 engines have a total of 20,631 sample data), randomly selected 17th engine data (276 life cycle data in total). After correlation analysis and ISOMAP feature fusion, the correlation coefficient is retained 4 feature variables over 0.8. Take the first 200 life cycle data as the total training set and the last 76 life cycle data as the total test set. Based on the above data, the method of the present invention is used for multivariate remaining life prediction. In order to describe the experimental results more clearly, the simulation results are visualized, and the results are shown in Figure 6 . By observing Figure 6, it can be seen that the prediction result of the proposed model has a small error with the actual data, and the effect is better.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110829782.XA CN113642779A (en) | 2021-07-22 | 2021-07-22 | ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110829782.XA CN113642779A (en) | 2021-07-22 | 2021-07-22 | ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113642779A true CN113642779A (en) | 2021-11-12 |
Family
ID=78418030
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110829782.XA Pending CN113642779A (en) | 2021-07-22 | 2021-07-22 | ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113642779A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114399440A (en) * | 2022-01-13 | 2022-04-26 | 马上消费金融股份有限公司 | Image processing method, image processing network training method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN114398825A (en) * | 2021-12-30 | 2022-04-26 | 燕山大学 | A method for predicting the remaining life of cutting tools for complex and variable working conditions |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20190114511A1 (en) * | 2017-10-16 | 2019-04-18 | Illumina, Inc. | Deep Learning-Based Techniques for Training Deep Convolutional Neural Networks |
| CN109726517A (en) * | 2019-01-31 | 2019-05-07 | 西安理工大学 | A prediction method of equipment remaining life based on multivariate correlation data |
| CN109855875A (en) * | 2019-01-15 | 2019-06-07 | 沈阳化工大学 | A kind of rolling bearing operational reliability prediction technique |
| CN110046409A (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2019-07-23 | 西安交通大学 | A kind of components of steam turbine health state evaluation method based on ResNet |
| CN110096500A (en) * | 2019-05-07 | 2019-08-06 | 上海海洋大学 | A kind of visual analysis method and system towards ocean multidimensional data |
| CN110378870A (en) * | 2019-06-06 | 2019-10-25 | 西安交通大学 | A kind of turbine blade erosion degree method of discrimination based on ResNet-GRU network |
| US20200210826A1 (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-07-02 | Northeastern University | Intelligent analysis system using magnetic flux leakage data in pipeline inner inspection |
| WO2020191800A1 (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2020-10-01 | 东北大学 | Method for predicting remaining service life of lithium-ion battery employing wde-optimized lstm network |
| CN112598144A (en) * | 2020-12-31 | 2021-04-02 | 西安理工大学 | CNN-LSTM burst fault early warning method based on correlation analysis |
-
2021
- 2021-07-22 CN CN202110829782.XA patent/CN113642779A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20190114511A1 (en) * | 2017-10-16 | 2019-04-18 | Illumina, Inc. | Deep Learning-Based Techniques for Training Deep Convolutional Neural Networks |
| US20200210826A1 (en) * | 2018-12-29 | 2020-07-02 | Northeastern University | Intelligent analysis system using magnetic flux leakage data in pipeline inner inspection |
| CN109855875A (en) * | 2019-01-15 | 2019-06-07 | 沈阳化工大学 | A kind of rolling bearing operational reliability prediction technique |
| CN109726517A (en) * | 2019-01-31 | 2019-05-07 | 西安理工大学 | A prediction method of equipment remaining life based on multivariate correlation data |
| WO2020191800A1 (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2020-10-01 | 东北大学 | Method for predicting remaining service life of lithium-ion battery employing wde-optimized lstm network |
| CN110046409A (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2019-07-23 | 西安交通大学 | A kind of components of steam turbine health state evaluation method based on ResNet |
| CN110096500A (en) * | 2019-05-07 | 2019-08-06 | 上海海洋大学 | A kind of visual analysis method and system towards ocean multidimensional data |
| CN110378870A (en) * | 2019-06-06 | 2019-10-25 | 西安交通大学 | A kind of turbine blade erosion degree method of discrimination based on ResNet-GRU network |
| CN112598144A (en) * | 2020-12-31 | 2021-04-02 | 西安理工大学 | CNN-LSTM burst fault early warning method based on correlation analysis |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| 彭鸿博;蒋雄伟;: "基于相关向量机的发动机剩余寿命预测", 科学技术与工程 * |
| 胡伟健;樊杰;杜永兴;李宝山;李灵芳;杨颜博;: "基于深度残差网络的番茄细粒度病症识别", 内蒙古科技大学学报 * |
| 邓玲;陕振;马连志;: "基于数据筛选的硬盘剩余使用寿命预测方法", 计算机工程与设计 * |
| 闵宇航: "基于深度残差网络ResNet-50的绿萝状态识别系统", 科学技术创新 * |
| 魏永合;刘炜;杨艳君;苏君金;: "基于LLE及其改进距离算法的轴承故障诊断模型", 组合机床与自动化加工技术 * |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114398825A (en) * | 2021-12-30 | 2022-04-26 | 燕山大学 | A method for predicting the remaining life of cutting tools for complex and variable working conditions |
| CN114398825B (en) * | 2021-12-30 | 2024-08-02 | 燕山大学 | Method for predicting residual life of cutting tool facing complex and variable working conditions |
| CN114399440A (en) * | 2022-01-13 | 2022-04-26 | 马上消费金融股份有限公司 | Image processing method, image processing network training method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN114399440B (en) * | 2022-01-13 | 2022-12-13 | 马上消费金融股份有限公司 | Image processing method, image processing network training method and device and electronic equipment |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109522600B (en) | Complex equipment residual service life prediction method based on combined deep neural network | |
| CN109446187B (en) | Health status monitoring method of complex equipment based on attention mechanism and neural network | |
| CN111273623B (en) | Fault diagnosis method based on Stacked LSTM | |
| CN102175282B (en) | Method for diagnosing fault of centrifugal air compressor based on information fusion | |
| CN111008363B (en) | Multivariable causal-driven complex electromechanical system service safety situation evaluation method | |
| CN112580263A (en) | Turbofan engine residual service life prediction method based on space-time feature fusion | |
| CN110895814B (en) | Aero-engine hole-finding image damage segmentation method based on context coding network | |
| CN107941537A (en) | A kind of mechanical equipment health state evaluation method | |
| CN106447039A (en) | Non-supervision feature extraction method based on self-coding neural network | |
| CN107505837A (en) | A kind of semi-supervised neural network model and the soft-measuring modeling method based on the model | |
| CN108363382A (en) | A kind of complex equipment fault diagnosis method and system | |
| CN108764601A (en) | A kind of monitoring structural health conditions abnormal data diagnostic method based on computer vision and depth learning technology | |
| CN109213753B (en) | Industrial system monitoring data recovery method based on online PCA | |
| CN108153982B (en) | Prediction method of after-repair performance of aero-engine based on stacked autoencoder deep learning network | |
| CN112598144A (en) | CNN-LSTM burst fault early warning method based on correlation analysis | |
| CN111860775B (en) | Ship fault real-time diagnosis method based on CNN and RNN fusion | |
| CN113642779A (en) | ResNet50 network key equipment residual life prediction method based on feature fusion | |
| CN113157732A (en) | Underground scraper fault diagnosis method based on PSO-BP neural network | |
| CN115757813A (en) | A Method for Predicting the Remaining Life of Equipment Based on Fault Time Series Knowledge Graph | |
| CN117349786B (en) | Evidence fusion transformer fault diagnosis method based on data equalization | |
| CN113255584A (en) | Fault diagnosis and monitoring system based on edge calculation | |
| CN113485261B (en) | A Soft Sensing Modeling Method Based on CAEs-ACNN | |
| CN115901232A (en) | Electromagnetic directional valve service life prediction method based on flow signal | |
| CN113159225B (en) | A Multivariate Industrial Process Fault Classification Method | |
| CN115182910A (en) | Multi-fault diagnosis method and device for hydraulic system based on fully convolutional network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |
Application publication date: 20211112 |
|
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |