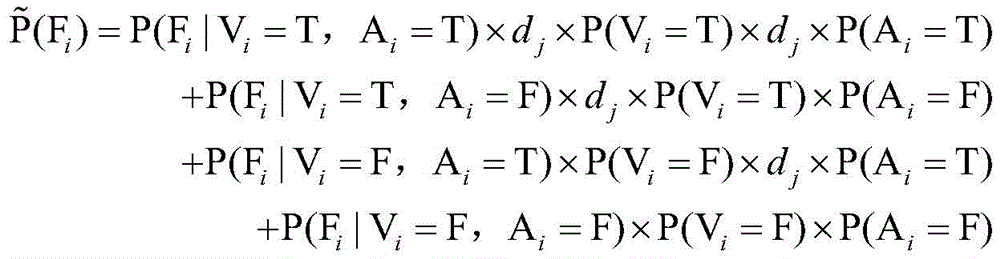CN113434866B - Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies - Google Patents
Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113434866B CN113434866B CN202110737559.2A CN202110737559A CN113434866B CN 113434866 B CN113434866 B CN 113434866B CN 202110737559 A CN202110737559 A CN 202110737559A CN 113434866 B CN113434866 B CN 113434866B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- instrument
- safety
- attack
- security
- probability
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 238000011158 quantitative evaluation Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 5
- 238000013210 evaluation model Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 230000001364 causal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000011002 quantification Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 claims 3
- 238000013139 quantization Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000037361 pathway Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000012938 design process Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004445 quantitative analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011217 control strategy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/50—Monitoring users, programs or devices to maintain the integrity of platforms, e.g. of processors, firmware or operating systems
- G06F21/57—Certifying or maintaining trusted computer platforms, e.g. secure boots or power-downs, version controls, system software checks, secure updates or assessing vulnerabilities
- G06F21/577—Assessing vulnerabilities and evaluating computer system security
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/18—Complex mathematical operations for evaluating statistical data, e.g. average values, frequency distributions, probability functions, regression analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/20—Design optimisation, verification or simulation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0639—Performance analysis of employees; Performance analysis of enterprise or organisation operations
- G06Q10/06393—Score-carding, benchmarking or key performance indicator [KPI] analysis
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明属于仪表安全防护领域,更具体地,涉及一种仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的统一风险量化评估方法。The invention belongs to the field of instrument safety protection, and more particularly relates to a unified risk quantitative assessment method for instrument function safety and information safety strategy.
背景技术Background technique
随着微型计算机技术和网络通信技术的快速发展,具有测量、运算、控制、执行、通信、诊断等功能的智能仪表在工业控制系统现场设备中得到了广泛运用。然而,相比于传统仪表,智能仪表给生产运行带来极大便利的同时,也面临着功能失效因素不断增多和信息攻击加速渗透等威胁。因此,智能仪表存在功能安全和信息安全防护的迫切需求。如何在功能安全和信息安全防护需求下对仪表安全防护策略进行有效的统一量化评估,从而给后期部署仪表功能安全和信息安全防护策略提供理论指导是目前需要解决的一大难题。With the rapid development of microcomputer technology and network communication technology, intelligent instruments with functions such as measurement, calculation, control, execution, communication, and diagnosis have been widely used in field devices of industrial control systems. However, compared with traditional instruments, smart instruments bring great convenience to production and operation, but also face threats such as increasing functional failure factors and accelerated penetration of information attacks. Therefore, there is an urgent need for functional safety and information security protection of smart meters. How to carry out an effective and unified quantitative assessment of instrument security protection strategies under the requirements of functional safety and information security protection, so as to provide theoretical guidance for the later deployment of instrument functional safety and information security protection strategies is a major problem to be solved at present.
现阶段仪表功能安全和信息安全策略有独立的有效性评估方法,而不同的安全标准缺乏对安全策略的统一评估方法和指标。现有技术中有对功能安全策略的目标和功能进行了定性描述,还由对信息安全策略所缓解的漏洞以及目前存在的问题等方面进行定性评估。上述方法都是通过定性方法对安全防护策略进行评估描述,缺乏准确性,目前尚没有一种评估方法能定量评估仪表的安全风险。At present, there are independent effectiveness evaluation methods for instrument functional safety and information security policies, while different safety standards lack unified evaluation methods and indicators for safety policies. In the prior art, the objectives and functions of the functional security strategy are qualitatively described, and the vulnerabilities mitigated by the information security strategy and the existing problems are also qualitatively evaluated. The above methods all use qualitative methods to evaluate and describe the safety protection strategy, which lacks accuracy. At present, there is no evaluation method that can quantitatively evaluate the safety risk of the instrument.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对现有技术的以上缺陷或改进需求,本发明提供了一种仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的统一风险量化评估方法,其目的在于基于风险的角度通过定量方法对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行统一评估,相比于目前的定性方法,提高了准确性。In view of the above defects or improvement requirements of the prior art, the present invention provides a unified risk quantitative assessment method for instrument function safety and information security strategy, the purpose of which is to carry out quantitative method for instrument function safety and information security strategy based on the perspective of risk. Unified assessment, which improves accuracy compared to current qualitative methods.
为实现上述目的,本发明提供了一种仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的统一风险量化评估方法,所述方法具体包括以下步骤:In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a unified risk quantitative assessment method for instrument functional safety and information security strategy, and the method specifically includes the following steps:
(1)查询仪表信息安全漏洞,分析攻击者会采取的攻击路径,建立攻击树;(1) Query instrument information security vulnerabilities, analyze the attack paths that attackers will take, and establish attack trees;
(2)分析仪表功能模块脆弱性,推演功能失效过程,建立故障树;(2) Analyze the vulnerability of instrument function modules, deduce the function failure process, and establish a fault tree;
(3)根据信息安全事件和功能失效事件之间的关联性,基于攻击树和故障树建立仪表一体化因果失效模型;(3) According to the correlation between information security events and functional failure events, establish a causal failure model of instrument integration based on attack tree and fault tree;
(4)从实施攻击的概率和漏洞被利用的概率量化仪表功能模块的失效概率;(4) Quantify the failure probability of the instrument function module from the probability of the attack and the probability of the vulnerability being exploited;
(5)从安全功能、策略关联、安全等级以及安全目标的角度对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行安全属性分析;(5) Analyze the security attributes of instrument function security and information security policy from the perspective of security functions, policy associations, security levels and security objectives;
(6)在仪表一体化因果失效模型中添加安全属性关联的防护节点,建立安全策略的评价模型;(6) Add protection nodes associated with safety attributes in the causal failure model of instrument integration to establish an evaluation model for safety strategies;
(7)结合仪表各功能模块资产,根据风险量化公式对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行量化评估。(7) Combined with the assets of each functional module of the instrument, according to the risk quantification formula, quantitatively evaluate the instrument functional safety and information security strategy.
进一步地,所述步骤(4)具体包括:Further, the step (4) specifically includes:
(41)实施攻击的概率为:(41) The probability of implementing an attack is:
其中,Ai表示任意一个攻击节点,即攻击者发起的攻击事件;P(Ai)表示攻击节点发生的概率;costAi表示发起攻击事件所需的成本;表示发起攻击事件的难易程度;detAi表示攻击事件可能被发现的等级;Wcost表示攻击成本参数的权重;Wdiff表示攻击难度参数的权重;Wdet表示被发现的可能性参数的权重,且Wcost+Wdiff+Wdet=1;表示攻击成本参数的效用值;表示攻击难度参数的效用值;表示攻击被发现可能性参数的效用值;Among them, A i represents any attack node, that is, the attack event initiated by the attacker; P(Ai) represents the probability of the attack node occurring; cost Ai represents the cost required to initiate the attack event; Indicates the difficulty of initiating an attack event; det Ai represents the level at which the attack event may be discovered; W cost represents the weight of the attack cost parameter; W diff represents the weight of the attack difficulty parameter; W det represents the weight of the possibility of being discovered, and W cost + W diff + W det =1; represents the utility value of the attack cost parameter; Indicates the utility value of the attack difficulty parameter; The utility value of the parameter representing the probability of an attack being discovered;
漏洞被利用的概率=攻击途径得分×攻击复杂度得分×认证得分×((机密性影响得分×机密性权重)+(完整性×完整性权重)+(可用性×可用性权重));The probability of vulnerability being exploited = attack route score × attack complexity score × authentication score × ((confidentiality impact score × confidentiality weight) + (integrity × integrity weight) + (availability × availability weight));
(42)将实施攻击的概率和漏洞被利用的概率结合仪表一体化因果失效模型,量化仪表各功能模块的失效概率:(42) Combine the probability of attacking and the probability of exploiting vulnerabilities with the integrated causal failure model of the instrument to quantify the failure probability of each functional module of the instrument:
P(Fi)=P(Fi|Vi=T,Ai=T)×P(Vi=T)×P(Ai=T)+P(Fi|Vi=T,Ai=F)×P(Vi=T)×P(Ai=F)+P(Fi|Vi=F,Ai=T)×P(Vi=F)×P(Ai=T)+P(Fi|Vi=F,Ai=F)×P(Vi=F)×P(Ai=F)P(F i )=P(F i |V i =T,A i =T)×P(V i =T)×P(A i =T)+P(Fi |V i = T,A i =F)×P(V i =T)×P(A i =F)+P(Fi |V i =F,A i =T)×P(V i =F)×P(A i = T )+P(F i |V i =F, A i =F)×P(V i =F)×P(A i =F)
其中,P(Fi)为智能仪表功能模块Fi失效概率,P(Fi|Vi,Ai)表示智能仪表功能模块失效条件概率,P(Vi=T)表示漏洞节点被利用概率,P(Vi=F)表示漏洞节点未被利用概率,P(Ai=T)表示攻击节点发生概率,P(Ai=F)表示攻击节点未发生概率。Among them, P(F i ) is the failure probability of the smart meter function module F i , P(F i |V i ,A i ) represents the failure condition probability of the smart meter function module, and P(V i =T) represents the exploited probability of the vulnerable node , P(V i =F) represents the probability that the vulnerability node is not exploited, P(A i =T) represents the probability that the attack node occurs, and P(A i =F) represents the probability that the attack node does not occur.
进一步地,所述步骤(5)具体包括:Further, the step (5) specifically includes:
(51)基于步骤(1)和步骤(2)中仪表信息安全漏洞和仪表功能模块脆弱性,查询安全标准,选择适用于仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略;(51) Based on the instrument information security vulnerabilities and instrument functional module vulnerabilities in steps (1) and (2), query the security standards, and select functional security policies and information security policies applicable to the instrument;
(52)根据安全标准中对仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略的定性描述,结合安全策略的安全功能、策略关联和安全目标属性,分析安全策略能够缓解的信息安全漏洞和功能模块脆弱性;(52) According to the qualitative description of the instrument's functional security strategy and information security strategy in the security standard, combined with the security function, strategy association and security target attributes of the security strategy, analyze the information security vulnerabilities and functional module vulnerabilities that the security strategy can alleviate;
根据安全策略的安全等级属性,对安全策略进行分级,确定策略实施效果。According to the security level attribute of the security policy, the security policy is graded to determine the effect of the policy implementation.
进一步地,所述步骤(6)具体包括:Further, the step (6) specifically includes:
(61)根据仪表安全策略实施够缓解的仪表功能模块安全漏洞,在仪表一体化因果失效模型中连接攻击节点和漏洞节点的逻辑门后,以及功能失效节点后添加防护节点;(61) Implement the security vulnerability of the instrument function module that can be mitigated according to the instrument security policy, and add a protection node after connecting the logic gate of the attack node and the vulnerability node in the instrument integrated causal failure model, and after the function failure node;
(62)根据仪表安全策略的等级,对关联防护节点设置不同的防护系数,建立仪表安全策略评价模型。(62) According to the level of the instrument security strategy, set different protection coefficients for the associated protection nodes, and establish the instrument security strategy evaluation model.
进一步地,所述步骤(7)具体包括:Further, the step (7) specifically includes:
(71)对安全相关功能模块资产进行重要性交互打分,安全相关功能模块资产包括仪表传感与检测、数据处理与控制、电输出与驱动、网络通信;(71) The importance of security-related functional module assets is interactively scored. Security-related functional module assets include instrument sensing and detection, data processing and control, electrical output and drive, and network communication;
(72)结合安全策略实施后通过仪表安全策略评价模型得到的仪表各安全相关功能模块失效概率,运用量化公式对仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略进行量化评估;(72) Combined with the failure probability of each safety-related functional module of the instrument obtained through the instrument security strategy evaluation model after the implementation of the security strategy, the quantitative formula is used to quantitatively evaluate the functional safety strategy and information security strategy of the instrument;
量化公式为:The quantification formula is:
其中,ΔR为安全策略实施前后仪表风险变化值,Wi为基于交互打分的仪表各功能模块的价值分数;Among them, ΔR is the change value of the instrument risk before and after the implementation of the security policy, and Wi is the value score of each functional module of the instrument based on the interactive scoring;
实施功能安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing functional safety policy The calculation formula is:
实施信息安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing information security policy The calculation formula is:
其中,dj为能够缓解仪表安全漏洞对应安全策略的关联防护节点的防护系数。Among them, d j is the protection coefficient of the associated protection node that can alleviate the security policy corresponding to the instrument security vulnerability.
另一方面,本申请还实现了一种仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的统一风险量化评估系统,所述系统包括以下部分:On the other hand, the present application also implements a unified risk quantitative assessment system for instrument functional safety and information security strategy, the system includes the following parts:
第一模块,用于查询仪表信息安全漏洞,分析攻击者会采取的攻击路径,建立攻击树;The first module is used to query instrument information security vulnerabilities, analyze the attack paths that attackers will take, and establish an attack tree;
第二模块,用于分析仪表功能模块脆弱性,推演功能失效过程,建立故障树;The second module is used to analyze the vulnerability of the instrument function module, deduce the function failure process, and establish a fault tree;
第三模块,用于根据信息安全事件和功能失效事件之间的关联性,基于攻击树和故障树建立仪表一体化因果失效模型;The third module is used to establish an instrument-integrated causal failure model based on the attack tree and fault tree according to the correlation between information security events and functional failure events;
第四模块,用于从实施攻击的概率和漏洞被利用的概率量化仪表功能模块的失效概率;The fourth module is used to quantify the failure probability of the instrument function module from the probability of the attack and the probability of the vulnerability being exploited;
第五模块,用于从安全功能、策略关联、安全等级以及安全目标的角度对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行安全属性分析;The fifth module is used to analyze the security attributes of instrument functional security and information security policies from the perspective of security functions, policy associations, security levels and security objectives;
第六模块,用于在仪表一体化因果失效模型中添加安全属性关联的防护节点,建立安全策略的评价模型;The sixth module is used to add protection nodes associated with safety attributes in the instrument integrated causal failure model to establish an evaluation model of safety policies;
第七模块,用于结合仪表各功能模块资产,根据风险量化公式对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行量化评估。The seventh module is used to quantitatively evaluate the functional safety of the instrument and the information security strategy according to the risk quantification formula in combination with the assets of each functional module of the instrument.
进一步地,所述第四模块具体包括:Further, the fourth module specifically includes:
第一单元,用于分析实施攻击的概率,具体为:The first unit is used to analyze the probability of implementing an attack, specifically:
其中,Ai表示任意一个攻击节点,即攻击者发起的攻击事件;P(Ai)表示攻击节点发生的概率;costAi表示发起攻击事件所需的成本;表示发起攻击事件的难易程度;detAi表示攻击事件可能被发现的等级;Wcost表示攻击成本参数的权重;Wdiff表示攻击难度参数的权重;Wdet表示被发现的可能性参数的权重,且Wcost+Wdiff+Wdet=1;表示攻击成本参数的效用值;表示攻击难度参数的效用值;表示攻击被发现可能性参数的效用值;Among them, A i represents any attack node, that is, the attack event initiated by the attacker; P(Ai) represents the probability of the attack node occurring; cost Ai represents the cost required to initiate the attack event; Indicates the difficulty of launching an attack event; det Ai represents the level at which the attack event may be discovered; W cost represents the weight of the attack cost parameter; W diff represents the weight of the attack difficulty parameter; W det represents the weight of the possibility of being discovered, and W cost + W diff + W det =1; represents the utility value of the attack cost parameter; Indicates the utility value of the attack difficulty parameter; The utility value of the parameter representing the probability of an attack being discovered;
漏洞被利用的概率=攻击途径得分×攻击复杂度得分×认证得分×((机密性影响得分×机密性权重)+(完整性×完整性权重)+(可用性×可用性权重));The probability of vulnerability being exploited = attack route score × attack complexity score × authentication score × ((confidentiality impact score × confidentiality weight) + (integrity × integrity weight) + (availability × availability weight));
第二单元,用于将实施攻击的概率和漏洞被利用的概率结合仪表一体化因果失效模型,量化仪表各功能模块的失效概率:The second unit is used to quantify the failure probability of each functional module of the instrument by combining the probability of the attack and the probability of the vulnerability being exploited with the integrated causal failure model of the instrument:
P(Fi)=P(Fi|Vi=T,Ai=T)×P(Vi=T)×P(Ai=T)+P(Fi|Vi=T,Ai=F)×P(Vi=T)×P(Ai=F)+P(Fi|Vi=F,Ai=T)×P(Vi=F)×P(Ai=T)+P(Fi|Vi=F,Ai=F)×P(Vi=F)×P(Ai=F)P(F i )=P(F i |V i =T,A i =T)×P(V i =T)×P(A i =T)+P(Fi |V i = T,A i =F)×P(V i =T)×P(A i =F)+P(Fi |V i =F,A i =T)×P(V i =F)×P(A i = T )+P(F i |V i =F, A i =F)×P(V i =F)×P(A i =F)
其中,P(Fi)为智能仪表功能模块Fi失效概率,P(Fi|Vi,Ai)表示智能仪表功能模块失效条件概率,P(Vi=T)表示漏洞节点被利用概率,P(Vi=F)表示漏洞节点未被利用概率,P(Ai=T)表示攻击节点发生概率,P(Ai=F)表示攻击节点未发生概率。Among them, P(F i ) is the failure probability of the smart meter function module F i , P(F i |V i ,A i ) represents the failure condition probability of the smart meter function module, and P(V i =T) represents the exploited probability of the vulnerable node , P(V i =F) represents the probability that the vulnerability node is not exploited, P(A i =T) represents the probability that the attack node occurs, and P(A i =F) represents the probability that the attack node does not occur.
进一步地,所述第五模块具体包括:Further, the fifth module specifically includes:
查询模块,用于基于第一模块和第二模块中仪表信息安全漏洞和仪表功能模块脆弱性,查询安全标准,选择适用于仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略;The query module is used for querying the security standard based on the instrument information security vulnerability and the vulnerability of the instrument function module in the first module and the second module, and selecting the functional security policy and information security policy applicable to the instrument;
分析单元,用于根据安全标准中对仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略的定性描述,结合安全策略的安全功能、策略关联和安全目标属性,分析安全策略能够缓解的信息安全漏洞和功能模块脆弱性;The analysis unit is used to analyze the information security vulnerabilities and functional module vulnerabilities that can be mitigated by the security strategy according to the qualitative description of the functional security strategy and information security strategy of the instrument in the security standard, combined with the security function, strategy association and security target attributes of the security strategy. sex;
根据安全策略的安全等级属性,对安全策略进行分级,确定策略实施效果。According to the security level attribute of the security policy, the security policy is graded to determine the effect of the policy implementation.
进一步地,所述第六模块具体包括:Further, the sixth module specifically includes:
防护添加单元,用于根据仪表安全策略实施够缓解的仪表功能模块安全漏洞,在仪表一体化因果失效模型中连接攻击节点和漏洞节点的逻辑门后,以及功能失效节点后添加防护节点;The protection adding unit is used to implement the security vulnerability of the instrument function module that can be mitigated according to the instrument security policy, and add a protection node after the logic gate connecting the attack node and the vulnerability node in the instrument integrated causal failure model, and after the function failure node;
评价模型建立单元,用于根据仪表安全策略的等级,对关联防护节点设置不同的防护系数,建立仪表安全策略评价模型。The evaluation model establishment unit is used to set different protection coefficients for the associated protection nodes according to the level of the instrument security strategy, and establish an instrument security strategy evaluation model.
进一步地,所述第七模块具体包括:Further, the seventh module specifically includes:
重要性打分单元,用于对安全相关功能模块资产进行重要性交互打分,安全相关功能模块资产包括仪表传感与检测、数据处理与控制、电输出与驱动、网络通信;The importance scoring unit is used to interactively score the importance of security-related functional module assets. The security-related functional module assets include instrument sensing and detection, data processing and control, electrical output and drive, and network communication;
量化评估单元,用于结合安全策略实施后通过仪表安全策略评价模型得到的仪表各安全相关功能模块失效概率,运用量化公式对仪表的功能安全策略和信息安全策略进行量化评估;The quantitative evaluation unit is used to quantitatively evaluate the functional safety strategy and information security strategy of the instrument by using the quantitative formula in combination with the failure probability of each safety-related functional module of the instrument obtained through the instrument security strategy evaluation model after the implementation of the security strategy;
量化公式为:The quantification formula is:
其中,ΔR为安全策略实施前后仪表风险变化值,Wi为基于交互打分的仪表各功能模块的价值分数;Among them, ΔR is the change value of the instrument risk before and after the implementation of the security policy, and Wi is the value score of each functional module of the instrument based on the interactive scoring;
实施功能安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing functional safety policy The calculation formula is:
实施信息安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing information security policy The calculation formula is:
其中,dj为能够缓解仪表安全漏洞对应安全策略的关联防护节点的防护系数。Among them, d j is the protection coefficient of the associated protection node that can alleviate the security policy corresponding to the instrument security vulnerability.
总体而言,通过本发明所构思的以上技术方案与现有技术相比,具有以下有益效果:In general, compared with the prior art, the above technical solutions conceived by the present invention have the following beneficial effects:
(1)本发明提出的上述仪表功能安全和信息安全策略统一风险量化评估方法,克服了传统安全标准中对功能安全和信息安全策略定性描述的局限性,能够有效分析仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的实施效果;(1) The above-mentioned unified risk quantitative assessment method for instrument functional safety and information security strategy proposed by the present invention overcomes the limitation of qualitative description of functional safety and information security strategy in traditional security standards, and can effectively analyze instrument functional safety and information security strategy implementation effect;
(2)本发明首先根据仪表功能安全和信息安全策略的安全目标、安全功能以及策略关联属性分析仪表安全策略能够缓解的仪表功能模块漏洞,然后根据仪表安全策略的安全等级属性分析安全策略实施效果,最后将安全属性关联到安全策略评价模型中的防护节点,为仪表功能安全策略和信息安全策略基于统一尺度分析提供了可能;(2) The present invention first analyzes the instrument function module loopholes that can be alleviated by the instrument security strategy according to the security objectives, security functions and policy associated attributes of the instrument function security and information security strategy, and then analyzes the security strategy implementation effect according to the security level attribute of the instrument security strategy. Finally, the security attributes are associated with the protection nodes in the security policy evaluation model, which provides the possibility for the analysis of the instrument function security policy and the information security policy based on a unified scale;
(3)本发明从风险的角度对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行统一量化评估,相比于定性方法,提高了准确性以及为安全策略的部署提供了一定的理论依据。(3) The present invention performs a unified quantitative assessment on instrument function safety and information security strategy from the perspective of risk. Compared with qualitative methods, the accuracy is improved and a certain theoretical basis is provided for the deployment of security strategies.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明方法的流程示意图;Fig. 1 is the schematic flow sheet of the method of the present invention;
图2是本发明实施例中仪表攻击树示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of an instrument attack tree in an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例中仪表故障树示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of an instrument fault tree in an embodiment of the present invention;
图4是本发明实施例中仪表一体化因果失效模型示意图;4 is a schematic diagram of a causal failure model of instrument integration in an embodiment of the present invention;
图5是本发明中仪表功能安全和信息安全策略属性提取分析流程示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of the extraction and analysis process flow of instrument function safety and information safety policy attributes in the present invention;
图6是本发明中仪表功能安全和信息安全策略评价模型示意图。FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the evaluation model of instrument function safety and information safety policy in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。此外,下面所描述的本发明各个实施方式中所涉及到的技术特征只要彼此之间未构成冲突就可以相互组合。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not conflict with each other.
本发明提供了一种仪表功能安全和信息安全策略统一风险量化评估方法,其流程如图1所示,包括如下步骤:The present invention provides a unified risk quantification assessment method for instrument function safety and information security strategy, the process of which is shown in FIG. 1 and includes the following steps:
步骤1:查询仪表信息安全漏洞,分析攻击者可能采取的攻击路径,建立攻击树。Step 1: Query instrument information security vulnerabilities, analyze possible attack paths taken by attackers, and establish attack trees.
步骤1.1:通过执行漏洞扫描或查询信息安全漏洞库,获得仪表安全漏洞列表,然后根据仪表安全漏洞列表,结合已知的攻击策略,分析所有可能的攻击场景。Step 1.1: Obtain the list of instrument security vulnerabilities by performing vulnerability scanning or querying the information security vulnerability database, and then analyze all possible attack scenarios based on the list of instrument security vulnerabilities and combined with known attack strategies.
查询信息安全漏洞库,找到仪表常见信息安全漏洞CNVD-2021-07490,CNVD-2021-17406,CNVD-2020-10538,攻击者可利用这些漏洞发起拒绝服务攻击,导致网络通信接口功能模块失效;可以借助通用的便携式手操器或者仪表管理通信软件的组态、校验管理、调试等功能,通过调试接口等,对智能仪表的固件或操作系统进行篡改,甚至注入恶意代码,导致智能仪表数据处理与控制模块功能失效;攻击者还可通过未授权的外部设备或者通信组态软件接入智能仪表时,可以实现对智能仪表量程的恶意篡改、零点漂移、停止工作等操作。Query the information security vulnerability database and find the common information security vulnerabilities CNVD-2021-07490, CNVD-2021-17406, CNVD-2020-10538 of the instrument. Attackers can use these vulnerabilities to launch denial of service attacks, resulting in the failure of the network communication interface function module; With the help of the configuration, verification management, debugging and other functions of the general portable handheld terminal or the instrument management communication software, the firmware or operating system of the smart instrument is tampered with through the debugging interface, etc., and even malicious code is injected, resulting in the data processing of the smart instrument. The function of the control module is invalid; when an attacker can also access the smart meter through unauthorized external devices or communication configuration software, he can maliciously tamper with the range of the smart meter, zero drift, and stop working.
步骤1.2:将攻击事件节点和漏洞节点作为叶子节点,分析通过利用漏洞发动信息攻击可能导致的功能失效事件,并将功能失效事件作为根节点,自底向上建立攻击树。攻击树如图2所示。Step 1.2: Take the attack event node and the vulnerability node as leaf nodes, analyze the function failure event that may be caused by launching an information attack by exploiting the vulnerability, and use the function failure event as the root node to build an attack tree from bottom to top. The attack tree is shown in Figure 2.
步骤2:分析仪表功能模块脆弱性,推演功能失效过程,建立故障树。Step 2: Analyze the vulnerability of instrument function modules, deduce the function failure process, and establish a fault tree.
步骤2.1:结合过程潜在失效模式及后果分析表或咨询现场工程人员,分析仪表各安全相关功能模块的脆弱性,确定仪表常见失效的功能模块,过程潜在失效模式及后果分析表参见表1所示。Step 2.1: Combine the process potential failure mode and consequence analysis table or consult on-site engineering personnel, analyze the vulnerability of each safety-related functional module of the instrument, and determine the common failure function modules of the instrument. The process potential failure mode and consequence analysis table is shown in Table 1. .
表1Table 1
步骤2.2:将仪表某个功能模块失效事件作为顶层事件节点,结合仪表工作运行原理,将引起顶层事件发生的功能模块失效事件作为基本事件节点,通过逻辑门和有向边将顶层事件节点和基本事件节点连接起来,自顶向下建立故障树。Step 2.2: Take the failure event of a certain functional module of the instrument as the top-level event node. Combined with the working principle of the instrument, the functional module failure event that caused the top-level event is taken as the basic event node, and the top-level event node and the basic event node are connected by logic gates and directed edges Event nodes are connected to build a fault tree from top to bottom.
智能仪表的输入信号要经过开关量输入通道电路或模拟量输入通道电路进行变换、放大、整形、补偿等处理。对于模拟量信号,需经A/D转换器转换成数字信号,再通过接口送入微控制器。由微控制器对输入数据进行加工处理、计算分析等一系列工作,通过接口送至显示器或打印机,也可输出开关量信号或经模拟量通道的D/A转换器转换成模拟量信号,还可通过串行接口(例如RS-232等)实现数据通信,完成更复杂的测量、控制任务。因此一旦传感检测模块或者数据处理与控制模块功能失效,输出驱动模块以及网络通信模块也将失效。基于上述失效场景,自顶向下建立故障树,故障树如图3所示。The input signal of the smart instrument should be transformed, amplified, shaped, compensated, etc. through the switch input channel circuit or the analog input channel circuit. For the analog signal, it needs to be converted into a digital signal by the A/D converter, and then sent to the microcontroller through the interface. The input data is processed, calculated and analyzed by the microcontroller, and sent to the display or printer through the interface. It can also output the switch signal or convert it into an analog signal through the D/A converter of the analog channel. Data communication can be achieved through serial interfaces (such as RS-232, etc.) to complete more complex measurement and control tasks. Therefore, once the function of the sensing detection module or the data processing and control module fails, the output driving module and the network communication module will also fail. Based on the above failure scenarios, a fault tree is established from top to bottom, as shown in Figure 3.
步骤3:分析故障树的基本事件节点和攻击树的攻击目标节点之间是否存在相同节点,一旦存在相同节点,将相同的故障树基本节点作为攻击目标,添加攻击路径,得到仪表一体化因果失效模型。仪表一体化因果失效模型如图4所示。Step 3: Analyze whether the same node exists between the basic event node of the fault tree and the attack target node of the attack tree. Once the same node exists, take the same basic node of the fault tree as the attack target, add the attack path, and obtain the causal failure of instrument integration Model. The causal failure model of instrument integration is shown in Figure 4.
步骤4:从实施攻击的可能性和漏洞被利用可能性等角度分析仪表功能模块失效事件发生的可能性。Step 4: Analyze the possibility of instrument function module failure events from the perspectives of the possibility of implementing attacks and the possibility of exploiting vulnerabilities.
步骤4.1:从攻击成本、攻击难度以及攻击被发现的可能性分析发起攻击的可能性,通过CVSS漏洞评分标准分析漏洞被利用的可能性。Step 4.1: Analyze the possibility of launching an attack from the attack cost, attack difficulty, and possibility of being discovered, and analyze the possibility of exploiting the vulnerability through the CVSS vulnerability scoring standard.
考虑攻击者发起攻击的可能性跟攻击成本、攻击难度以及攻击被发现的可能性有关,在计算攻击节点的可能性时,给每个攻击节点赋予这三个属性值。运用多属性效用理论,将以上属性转换成其实现目标的效用值。则计算攻击者发起攻击可能性的公式如下:Considering that the possibility of an attacker launching an attack is related to the cost of the attack, the difficulty of the attack, and the possibility of the attack being discovered, when calculating the possibility of attacking a node, assign these three attribute values to each attacking node. Using the multi-attribute utility theory, the above attributes are converted into their utility values for achieving their goals. The formula for calculating the probability of an attacker launching an attack is as follows:
其中:Ai表示任意一个攻击节点,即攻击者发起的攻击事件;P(Ai)表示攻击节点发生的概率;表示发起攻击事件所需的成本;表示发起攻击事件的难易程度;detAi表示攻击事件可能被发现的等级。Wcost表示攻击成本参数的权重;Wdiff表示攻击难度参数的权重;Wdet表示估计被发现的可能性参数的权重,且这三个权重系数之和为1。表示攻击成本参数的效用值;表示攻击难度参数的效用值;表示攻击被发现可能性参数的效用值。Among them: A i represents any attack node, that is, the attack event initiated by the attacker; P(A i ) represents the probability of the attack node occurring; Indicates the cost of launching an attack event; Indicates the difficulty of launching an attack event; det Ai indicates the level at which an attack event may be discovered. W cost represents the weight of the attack cost parameter; W diff represents the weight of the attack difficulty parameter; W det represents the weight of the estimated probability of being discovered, and the sum of these three weight coefficients is 1. represents the utility value of the attack cost parameter; Indicates the utility value of the attack difficulty parameter; Indicates the utility value of the attack detection probability parameter.
通过公式(1)求解攻击事件发生的概率P(Ai)涉及到三个属性,因此需要制定相应的评分标准对它们进行评价。本发明采用的等级评分标准参见表2所示。Finding the probability P(A i ) of an attack event by formula (1) involves three attributes, so it is necessary to formulate corresponding scoring standards to evaluate them. See Table 2 for the grading criteria used in the present invention.
表2Table 2
为了计算攻击者发起攻击事件的概率,需要计算效用值 通过分析可知,diffAi、与 成反比例关系。为了计算,三组之间的对应关系均取为U(x)=1/x。运用式(1)即可求出攻击事件发生的概率P(Ai)。In order to calculate the probability of an attacker launching an attack event, the utility value needs to be calculated From the analysis, it can be seen that diff Ai , and inversely proportional. For calculation, the correspondence between the three groups is taken as U(x)=1/x. Using formula (1), the probability P(A i ) of the attack event can be obtained.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System(CVSS),即“通用漏洞评分系统”,是一个“行业公开标准,其被设计用来评测漏洞的严重程度,主要目的是帮助人们建立衡量漏洞严重程度的标准,便于分析漏洞的严重程度。本发明通过CVSS计算仪表信息安全漏洞被利用的可能性。CVSS包括基本得分,临时得分和环境得分这三个要素,这里仅需考虑基本得分,基本得分评价指标参见表3。Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), the "Common Vulnerability Scoring System", is an "industry open standard, which is designed to evaluate the severity of vulnerabilities. The main purpose is to help people establish a standard for measuring the severity of vulnerabilities and facilitate the analysis of vulnerabilities. The present invention calculates the possibility of exploiting instrument information security loopholes through CVSS. CVSS includes three elements: basic score, temporary score and environmental score. Only the basic score is considered here, and the basic score evaluation index is shown in Table 3.
表3table 3
基本得分=攻击途径得分*攻击复杂度得分*认证得分*((机密性影响得分*机密性权重)+(完整性*完整性权重)+(可用性*可用性权重))Basic Score = Attack Path Score * Attack Complexity Score * Authentication Score * ((Confidentiality Impact Score * Confidentiality Weight) + (Integrity * Integrity Weight) + (Availability * Availability Weight))
步骤4.2:分析历史数据或咨询现场工程人员分析仪表各功能模块失效的条件概率,结合公式(1)中的攻击者发动攻击的概率和漏洞被利用的概率,得到仪表各功能模块的失效概率。Step 4.2: Analyze historical data or consult on-site engineers to analyze the conditional probability of failure of each functional module of the instrument, and obtain the failure probability of each functional module of the instrument by combining the probability of attackers launching attacks and the probability of exploiting vulnerabilities in formula (1).
步骤5:从安全功能、策略关联、安全等级、安全目标等角度对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行安全属性特征量化分析。安全策略的属性分析量化流程示意图参见图5所示。Step 5: From the perspectives of security functions, policy associations, security levels, security objectives, etc., perform quantitative analysis of security attributes and characteristics on instrument functional security and information security policies. See Figure 5 for a schematic diagram of the attribute analysis and quantification process of the security policy.
步骤5.1:根据步骤1和步骤2得到的仪表常见信息安全漏洞和功能模块失效机理,通过查询相关安全标准,选择适用于仪表的功能失效控制策略和信息安全防护策略。Step 5.1: According to the common information security vulnerabilities of the instrument and the failure mechanism of functional modules obtained in
智能仪表作为现场物理层的设备,面临的信息安全威胁主要包括DOS攻击,未知设备的接入,篡改等,本发明根据IEC62443信息安全标准选取了访问控制、入侵检测、日志管理、权限控制、身份验证策略,考虑仪表主要通过传感与检测、数据处理与控制、电输出与驱动以及网络通信接口功能模块实现仪表的采集、运算、输出以及通信功能,一旦某功能模块失效,将极大影响仪表作用价值。本发明根据IEC61508选取了微处理器单元诊断、采集诊断、输出诊断、时序和逻辑监视以及多重化技术策略。As an on-site physical layer device, the information security threats faced by smart meters mainly include DOS attacks, access to unknown devices, tampering, etc. The present invention selects access control, intrusion detection, log management, authority control, and identity The verification strategy considers that the instrument mainly realizes the acquisition, calculation, output and communication functions of the instrument through the function modules of sensing and detection, data processing and control, electrical output and drive, and network communication interface. Once a functional module fails, it will greatly affect the instrument. effect value. According to IEC61508, the present invention selects microprocessor unit diagnosis, acquisition diagnosis, output diagnosis, timing and logic monitoring, and multiple technical strategies.
步骤5.2:根据相关安全标准中对仪表的功能安全和信息安全策略的定性描述,根据仪表安全策略的安全功能、策略关联、安全目标属性,分析安全策略能够缓解的仪表功能模块安全漏洞以及安全策略实施效果。Step 5.2: According to the qualitative description of the functional safety and information security policies of the instrument in the relevant security standards, and according to the security functions, policy associations, and security target attributes of the instrument security policy, analyze the instrument function module security vulnerabilities and security policies that can be mitigated by the security policy Implementation Effect.
以权限控制为例,权限控制是保护工业控制系统及其关键资产不受意外破坏的第一步。权限控制决定相关角色应该被允许进入或离开一个系统的过程。一旦确定了这些信息,就可以实施纵深防御访问控制措施,以验证只有经过授权的人员和设备才能真正访问工业控制系统。因此权限控制能够缓解未知设备接入漏洞。相比于传统的权限控制,基于角色的权限控制通过基于用户角色或工作职责的访问克服了动态环境中难以及时更新角色权限的问题,具有更好的漏洞防护效果。Taking access control as an example, access control is the first step in protecting industrial control systems and their critical assets from accidental damage. Permission control determines the process by which relevant roles should be allowed to enter or leave a system. Once this information is identified, defense-in-depth access controls can be implemented to verify that only authorized personnel and equipment can actually access the industrial control system. Therefore, permission control can mitigate unknown device access vulnerabilities. Compared with traditional permission control, role-based permission control overcomes the difficulty of timely updating role permissions in dynamic environments through access based on user roles or job responsibilities, and has better vulnerability protection effects.
步骤6:在因果失效模型中添加安全属性关联的防护节点,建立安全策略的评价模型。Step 6: Add protection nodes associated with security attributes in the causal failure model to establish an evaluation model of security policies.
步骤6.1:根据仪表安全策略实施能够缓解的仪表功能模块安全漏洞,在仪表一体化因果失效模型中连接攻击节点和漏洞节点的逻辑门后以及功能失效节点后添加防护节点。Step 6.1: Implement the security vulnerabilities of the instrument function module that can be mitigated according to the instrument security policy, and add a protection node after the logic gate connecting the attack node and the vulnerability node and after the function failure node in the instrument integrated causal failure model.
根据步骤五分析得出信息安全策略实施能够缓解的漏洞,在相应的攻击路径中添加防护节点,根据步骤五分析得出的功能安全策略实施能够缓解的功能模块脆弱性,在相应的失效路径中添加防护节点。仪表功能安全和信息安全策略关联防护节点参见表4所示。According to the analysis in step 5, the vulnerabilities that can be mitigated by the implementation of the information security policy are obtained, and protection nodes are added to the corresponding attack paths. Add a guard node. The protection nodes associated with the instrument functional safety and information security policies are shown in Table 4.
表4Table 4
步骤6.2:根据仪表安全策略的实施效果,对防护节点设置不同的防护系数,建立仪表安全策略评价模型。Step 6.2: According to the implementation effect of the instrument security strategy, set different protection coefficients for the protection nodes, and establish the instrument security strategy evaluation model.
对于功能安全和信息安全策略安全等级属性,本发明设置了两种不同等级,安全策略等级属性表参见表5所示。For functional safety and information security policy security level attributes, the present invention sets two different levels, and the security policy level attribute table is shown in Table 5.
表5table 5
基于上述步骤,建立仪表安全策略评价模型。仪表安全策略评价模型中各节点的含义参见表6所示。Based on the above steps, an instrument security policy evaluation model is established. The meaning of each node in the instrument security policy evaluation model is shown in Table 6.
表6Table 6
步骤7:结合仪表各功能模块资产,根据风险量化公式对仪表功能安全和信息安全策略进行量化评估。Step 7: Combined with the assets of each functional module of the instrument, quantify the functional safety of the instrument and the information security strategy according to the risk quantification formula.
步骤7.1:考虑仪表传感与检测、数据处理与控制、电输出与驱动、网络通信等安全相关功能模块资产,根据功能模块的重要性进行专家打分;Step 7.1: Consider the security-related functional module assets such as instrument sensing and detection, data processing and control, electrical output and drive, network communication, etc., and score experts according to the importance of the functional modules;
步骤7.2:结合安全策略实施前后仪表各功能模块失效概率的变化值ΔP(Fi),运用量化公式对仪表的功能安全和信息安全策略进行量化评估。Step 7.2: Combine the change value ΔP(F i ) of the failure probability of each functional module of the instrument before and after the implementation of the security strategy, and use the quantitative formula to quantitatively evaluate the functional safety and information security strategy of the instrument.
其中,ΔR为安全策略实施前后仪表风险变化值,n为仪表安全相关功能模块数量,Wi为基于专家打分的仪表各功能模块的价值分数。Among them, ΔR is the change value of the instrument risk before and after the implementation of the security policy, n is the number of instrument safety-related functional modules, and Wi is the value score of each functional module of the instrument based on expert scoring.
通过分析历史数据或咨询现场工程人员获得F1,F2,F3节点的条件概率P(F1|A1,V1),P(F2|A2,V2),P(F3|F1,F2),P(F4|F1,A3,V3),结合攻击事件节点A1,A2,A3的发生概率P(A1),P(A2),P(A3),以及漏洞节点的发生概率P(V1),P(V2),P(V3)。进而能够计算出各功能模块失效概率P(F1),P(F2),P(F3),P(F4)。Obtain the conditional probabilities P(F 1 |A 1 ,V 1 ), P(F 2 |A 2 ,V 2 ), P(F 3 of F 1 , F 2 , F 3 nodes by analyzing historical data or consulting field engineers |F 1 , F 2 ), P(F 4 |F 1 , A 3 , V 3 ), combined with the probability of occurrence of attack event nodes A 1 , A 2 , A 3 P(A 1 ), P(A 2 ), P(A 3 ), and the probability of occurrence of vulnerable nodes P(V 1 ), P(V 2 ), and P(V 3 ). Furthermore, the failure probabilities P(F 1 ), P(F 2 ), P(F 3 ), and P(F 4 ) of each functional module can be calculated.
通过实施安全策略,在安全防护节点的作用下,得到新的攻击事件节点发生概率新的漏洞节点的发生概率进而得到各功能模块失效事故新的概率结合功能模块的价值分数Wi,i=1,2,3,4,最终得到风险变化值公式By implementing security policies, under the action of security protection nodes, the probability of occurrence of new attack event nodes is obtained The probability of occurrence of new vulnerability nodes Then, the new probability of failure accident of each functional module is obtained. Combined with the value score W i of the functional module, i=1, 2, 3, 4, the risk change value formula is finally obtained
根据公式(3)计算出的各安全策略实施前后的风险值的变化,对仪表的功能安全和信息安全策略进行量化评估。According to the change of the risk value before and after the implementation of each security policy calculated by formula (3), the functional safety and information security policy of the instrument are quantitatively evaluated.
实施功能安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing functional safety policy The calculation formula is:
实施信息安全策略后的功能模块失效概率计算公式为:Failure probability of functional modules after implementing information security policy The calculation formula is:
dj为能够缓解仪表安全漏洞对应安全策略的关联防护节点的防护系数。d j is the protection coefficient of the associated protection node that can alleviate the security policy corresponding to the instrument security vulnerability.
以上内容本领域的技术人员容易理解,以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。Those skilled in the art can easily understand the above content, the above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention, any modification, equivalent replacement and improvement made within the spirit and principle of the present invention etc., should be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110737559.2A CN113434866B (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2021-06-30 | Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110737559.2A CN113434866B (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2021-06-30 | Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113434866A CN113434866A (en) | 2021-09-24 |
| CN113434866B true CN113434866B (en) | 2022-05-20 |
Family
ID=77758371
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110737559.2A Active CN113434866B (en) | 2021-06-30 | 2021-06-30 | Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113434866B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114666115B (en) * | 2022-03-15 | 2023-02-24 | 中国科学院信息工程研究所 | Integrated risk attack tree generation method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN114844953A (en) * | 2022-05-12 | 2022-08-02 | 机械工业仪器仪表综合技术经济研究所 | Petrochemical device instrument automatic control equipment safety monitoring system based on industrial internet |
| CN115801334B (en) * | 2022-10-27 | 2024-05-14 | 华中科技大学 | Intelligent instrument function safety and information safety strategy fusion method and system |
| CN115811425B (en) * | 2022-11-18 | 2024-04-16 | 中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所 | Two-safety integrated instrument risk iterative design method |
| CN116227914A (en) * | 2022-12-14 | 2023-06-06 | 广州大学 | Function and information security comprehensive risk assessment method combining fault tree/attack and defense tree |
| CN117749529B (en) * | 2024-02-19 | 2024-06-21 | 中汽智联技术有限公司 | Method for searching full attack path |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105045251A (en) * | 2015-05-27 | 2015-11-11 | 华中科技大学 | Demand analysis and integration method for function safety and information safety of industrial control system |
| CN105631698A (en) * | 2014-11-24 | 2016-06-01 | 奥多比公司 | Risk quantification for policy deployment |
| EP3282668A1 (en) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-14 | Tata Consultancy Services Limited | Comprehensive risk assessment in a heterogeneous dynamic network |
| CN108183897A (en) * | 2017-12-28 | 2018-06-19 | 南京林业大学 | A kind of information physical emerging system safety risk estimating method |
| CN108833416A (en) * | 2018-06-21 | 2018-11-16 | 北京市劳动保护科学研究所 | A SCADA system information security risk assessment method and system |
| CN109117637A (en) * | 2018-07-03 | 2019-01-01 | 北京航空航天大学 | Intelligent network connection information of vehicles security incident probability of happening appraisal procedure and system based on Attack Tree |
| US10868825B1 (en) * | 2018-08-14 | 2020-12-15 | Architecture Technology Corporation | Cybersecurity and threat assessment platform for computing environments |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7774293B2 (en) * | 2005-03-17 | 2010-08-10 | University Of Maryland | System and methods for assessing risk using hybrid causal logic |
| US11206278B2 (en) * | 2019-01-29 | 2021-12-21 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Risk-informed autonomous adaptive cyber controllers |
-
2021
- 2021-06-30 CN CN202110737559.2A patent/CN113434866B/en active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105631698A (en) * | 2014-11-24 | 2016-06-01 | 奥多比公司 | Risk quantification for policy deployment |
| CN105045251A (en) * | 2015-05-27 | 2015-11-11 | 华中科技大学 | Demand analysis and integration method for function safety and information safety of industrial control system |
| EP3282668A1 (en) * | 2016-08-12 | 2018-02-14 | Tata Consultancy Services Limited | Comprehensive risk assessment in a heterogeneous dynamic network |
| CN108183897A (en) * | 2017-12-28 | 2018-06-19 | 南京林业大学 | A kind of information physical emerging system safety risk estimating method |
| CN108833416A (en) * | 2018-06-21 | 2018-11-16 | 北京市劳动保护科学研究所 | A SCADA system information security risk assessment method and system |
| CN109117637A (en) * | 2018-07-03 | 2019-01-01 | 北京航空航天大学 | Intelligent network connection information of vehicles security incident probability of happening appraisal procedure and system based on Attack Tree |
| US10868825B1 (en) * | 2018-08-14 | 2020-12-15 | Architecture Technology Corporation | Cybersecurity and threat assessment platform for computing environments |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 基于状态时间的故障树的信息物理融合系统风险建模;徐丙凤 等;《计算机科学》;20190531;全文 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113434866A (en) | 2021-09-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113434866B (en) | Unified risk quantitative evaluation method for instrument function safety and information safety strategies | |
| Kandias et al. | An insider threat prediction model | |
| Ou et al. | Quantitative security risk assessment of enterprise networks | |
| US20090099885A1 (en) | Method for risk analysis using information asset modelling | |
| CN104125217A (en) | A real-time risk assessment method for cloud data centers based on host log analysis | |
| CN117478433B (en) | Network and information security dynamic early warning system | |
| Zalewski et al. | Threat modeling for security assessment in cyberphysical systems | |
| KR102590081B1 (en) | Security compliance automation method | |
| CN118295765B (en) | Cloud security monitoring method and system based on virtual environment situation assessment | |
| CN106790211B (en) | A kind of Mathematical Statistical System and method for predicting malware infection | |
| CN116915515B (en) | Access security control method and system for industrial control network | |
| CN108805453A (en) | A kind of Network Abnormal safety evaluation method in power distribution network CPS based on AHP | |
| Min et al. | The Detection and Defense Mechanism for SQL Injection Attack Based on Web Application | |
| Kai et al. | Development of qualification of security status suitable for cloud computing system | |
| Maynard et al. | Using Application Layer Metrics to Detect Advanced SCADA Attacks. | |
| Hou et al. | Zero-day vulnerability inspired hazard assessment for autonomous driving vehicles | |
| CN114372269A (en) | Risk assessment method based on system network topological structure | |
| Slamet et al. | Campus hybrid intrusion detection system using snort and c4. 5 algorithm | |
| Hussain et al. | Verifiable Sustainability in Data Centers | |
| Wang et al. | A framework for security quantification of networked machines | |
| Möller | Cybersecurity in Cyber-Physical Systems | |
| Wei et al. | Research on Multidimensional Information Security Assessment Based on Big Data | |
| Alzubi et al. | Threats, Security and Safety of Cyber-Physical Systems in Construction Industry | |
| Yang et al. | Novel Attack Tree Analysis Scheme to Assess the Security Risks on the Cloud Platform | |
| Ye et al. | Exploring Automated Defense Technology of Artificial Intelligence in Network Security |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |