CN111505291B - A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration - Google Patents
A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111505291B CN111505291B CN202010289352.9A CN202010289352A CN111505291B CN 111505291 B CN111505291 B CN 111505291B CN 202010289352 A CN202010289352 A CN 202010289352A CN 111505291 B CN111505291 B CN 111505291B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- serum
- enzyme
- giant
- adsorption
- interference
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 title claims abstract description 60
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 title claims abstract description 60
- 210000002966 serum Anatomy 0.000 title claims abstract description 53
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 23
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 108060003951 Immunoglobulin Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 102000018358 immunoglobulin Human genes 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 241000191967 Staphylococcus aureus Species 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 230000002779 inactivation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 claims description 12
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 claims description 12
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 claims description 12
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000001580 bacterial effect Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920001213 Polysorbate 20 Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000010486 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000256 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 102000002260 Alkaline Phosphatase Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 108020004774 Alkaline Phosphatase Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004382 Amylase Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 102000013142 Amylases Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 108010065511 Amylases Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- 102000004420 Creatine Kinase Human genes 0.000 claims description 3
- 108010042126 Creatine kinase Proteins 0.000 claims description 3
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000019418 amylase Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000000703 high-speed centrifugation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 108700023418 Amidases Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 241001052560 Thallis Species 0.000 claims 1
- 102000005922 amidase Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- 235000003704 aspartic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims 1
- OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-carboxyaspartic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)C(C(O)=O)C(O)=O OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 238000011534 incubation Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000108 ultra-filtration Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 239000011543 agarose gel Substances 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000001502 gel electrophoresis Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000009870 specific binding Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 229940072221 immunoglobulins Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- FRXSZNDVFUDTIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline Chemical compound N1CCCC2=CC(OC)=CC=C21 FRXSZNDVFUDTIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000282414 Homo sapiens Species 0.000 description 2
- 229940009098 aspartate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001962 electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 2
- WBQJTPDOGLYTBE-VIFPVBQESA-N 1-nitroso-L-tryptophan Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=CN(N=O)C2=C1 WBQJTPDOGLYTBE-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000057234 Acyl transferases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108700016155 Acyl transferases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000004625 Aspartate Aminotransferases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010003415 Aspartate Aminotransferases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000700199 Cavia porcellus Species 0.000 description 1
- 108010001857 Cell Surface Receptors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000282693 Cercopithecidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000006395 Globulins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010044091 Globulins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282898 Sus scrofa Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710120037 Toxin CcdB Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 235000014633 carbohydrates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001720 carbohydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cysteine Natural products SCC(N)C(O)=O XUJNEKJLAYXESH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000018417 cysteine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229930195712 glutamate Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 208000006454 hepatitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 231100000283 hepatitis Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000001114 immunoprecipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003734 kidney Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000002605 large molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 102000006240 membrane receptors Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000003340 mental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001184 polypeptide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000002035 prolonged effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013215 result calculation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 125000001493 tyrosinyl group Chemical group [H]OC1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])(N([H])[H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/573—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor for enzymes or isoenzymes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/68—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing involving proteins, peptides or amino acids
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N2333/00—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature
- G01N2333/195—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature from bacteria
- G01N2333/305—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature from bacteria from Micrococcaceae (F)
- G01N2333/31—Assays involving biological materials from specific organisms or of a specific nature from bacteria from Micrococcaceae (F) from Staphylococcus (G)
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/30—Against vector-borne diseases, e.g. mosquito-borne, fly-borne, tick-borne or waterborne diseases whose impact is exacerbated by climate change
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法,利用金黄色葡萄球菌表面的SpA与免疫球蛋白Fc段特异性结合的特性,可以去除“巨酶”对血清酶检测带来的干扰,对游离酶分子没有影响,同时,实验室只需要培养高表达SpA的Cowan I金葡菌,经过固定‑洗涤‑加热灭活几个步骤,可在4℃保存半年以上;与凝胶电泳、超滤、SpA琼脂糖凝胶颗粒吸附等方法比较起来,具有简便易行、经济快速、特异性强等特点,非常适合在临床上进行推广。The invention discloses a method for eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration. The specific binding characteristics of SpA on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus and the Fc segment of immunoglobulin can be used to remove the influence of "giant enzyme" on serum enzyme concentration. The interference caused by the detection has no effect on the free enzyme molecules. At the same time, the laboratory only needs to cultivate Cowan I S. aureus with high expression of SpA. After several steps of fixing-washing-heating inactivation, it can be stored at 4°C for more than half a year; Compared with gel electrophoresis, ultrafiltration, SpA agarose gel particle adsorption and other methods, it has the characteristics of simplicity, convenience, economy, speed, and strong specificity, and is very suitable for clinical promotion.
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种排除干扰的方法,特别涉及一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法,属于免疫沉淀技术领域。The invention relates to a method for eliminating interference, in particular to a method for eliminating interference caused by macrozyme molecules to detection of serum enzyme concentration, and belongs to the technical field of immunoprecipitation.
背景技术Background technique
巨酶是酶分子通过与血清免疫球蛋白(1型巨酶)结合或通过自身缔合(2型巨酶)导致分子量增加而在血液中循环的酶。血清中常见的巨酶包括巨肌酸激酶(Macro-CK)、巨淀粉酶(Macro-AMY)、巨碱性磷酸酶(Macro-ALP)、巨天冬氨酸转氨酶(macro-AST)等。由于酶分子与免疫球蛋白的结合,所形成的高分子量化合物不能够通过肾脏清除,半衰期延长,可导致假阳性升高。持续增加的酶含量往往引起疾病的误诊误治,给患者带来沉重的精神负担。最近,我们报道了一例确诊的巨酶病例,该病例在6前年发现血清AST升高,虽然患者没有其它的阳性发现,但6年来一直按照“肝炎”进行治疗。我们通过免疫球蛋白沉淀技术证实是由于巨AST导致的,从而避免了不必要的治疗,消除了患者的心理负担。相关的研究成果发表在了CCLM上(Clin Chem Lab Med.2020 Mar 26;58(4):e96-e99.)。Megazymes are enzyme molecules that circulate in the blood either by binding to serum immunoglobulins (type 1 megazyme) or by self-association (type 2 megazyme) resulting in an increase in molecular weight. Common giant enzymes in serum include giant creatine kinase (Macro-CK), giant amylase (Macro-AMY), giant alkaline phosphatase (Macro-ALP), giant aspartate aminotransferase (macro-AST) and so on. Due to the combination of enzyme molecules and immunoglobulins, the formed high-molecular-weight compounds cannot be cleared by the kidneys, and the half-life is prolonged, which can lead to increased false positives. The continuously increasing enzyme content often leads to misdiagnosis and mistreatment of diseases, which brings heavy mental burden to patients. Recently, we reported a confirmed case of macrozyme in which elevated serum AST was found 6 years ago, although the patient had no other positive findings, but had been treated as "hepatitis" for 6 years. We confirmed by immunoglobulin precipitation technique that it was caused by giant AST, thus avoiding unnecessary treatment and eliminating the psychological burden on patients. Related research results were published on CCLM (Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Mar 26; 58(4):e96-e99.).
研究报道,巨酶分子可以通过免疫球蛋白电泳、PEG沉淀、超滤等方法去除,但这些方法存在很多缺点,比如PEG同时会沉淀游离酶,免疫球蛋白电泳费时、成本高,超滤方法特异性差等。在我们报道的病例研究中,采用了商品化的蛋白A、蛋白G吸附血清中的免疫球蛋白,从而去除的巨酶的干扰。但同样由于成本较高,该方法不可能在临床中普及。因此迫切需要一种简单易行、低成本的方法,便于在临床上进行推广。Studies have reported that giant enzyme molecules can be removed by immunoglobulin electrophoresis, PEG precipitation, ultrafiltration and other methods, but these methods have many disadvantages, such as PEG will precipitate free enzymes at the same time, immunoglobulin electrophoresis is time-consuming and costly, and ultrafiltration methods are specific Poor sex and so on. In the case study we reported, commercialized protein A and protein G were used to adsorb immunoglobulin in serum, thereby removing the interference of macrozyme. However, due to the high cost, this method cannot be popularized in clinic. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a simple, low-cost method that is easy to promote clinically.
蛋白A(SpA)是几种金黄色葡萄球菌菌株产生的高度稳定的细胞表面受体。它由一条分子量为42kDa的多肽链组成,包含四个富含天冬氨酸和谷氨酸但不含半胱氨酸的重复域。它几乎不含碳水化合物,仅含有4个酪氨酸残基,不含色氨酸。蛋白A能够与多种物种(如人、猴子,兔子,猪,豚鼠)的免疫球蛋白(尤其是IgG)的Fc部分结合。已显示一种蛋白质A分子同时结合至少2个IgG分子。蛋白A结合人IgG亚类IgM,IgA和IgE的Fc部分和小鼠IgG1(弱),IgG2a和IgG2b分子。我们利用菌体表面高表达蛋白A的金黄色葡萄球菌CowanI作为载体,经过对固定和加热灭活等处理步骤,使之与血清中存在的巨酶分子相互作用,通过离心的方法进行分离,从而去除巨酶分子对血清酶检测带来的干扰。该方法简便易行,成本低,适合实验室的推广和普及,因此具有广阔的应用前景。Protein A (SpA) is a highly stable cell surface receptor produced by several strains of S. aureus. It consists of a polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of 42 kDa containing four repeat domains rich in aspartate and glutamate but not cysteine. It contains almost no carbohydrates, only 4 tyrosine residues, and no tryptophan. Protein A is capable of binding to the Fc portion of immunoglobulins (especially IgG) of various species (eg, human, monkey, rabbit, pig, guinea pig). One protein A molecule has been shown to bind at least 2 IgG molecules simultaneously. Protein A binds the Fc portion of human IgG subclasses IgM, IgA and IgE and mouse IgG1 (weak), IgG2a and IgG2b molecules. We use Staphylococcus aureus CowanI, which highly expresses protein A on the surface of the bacteria, as a carrier, and through the treatment steps of fixation and heat inactivation, make it interact with the giant enzyme molecule in the serum, and separate it by centrifugation, so that Remove the interference of giant enzyme molecules on serum enzyme detection. The method is simple and easy to implement, low in cost, suitable for promotion and popularization in laboratories, and thus has broad application prospects.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提出了一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法,解决了现有技术中提出的问题。The invention proposes a method for eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration, and solves the problems raised in the prior art.
为了解决上述技术问题,本发明提供了如下的技术方案:In order to solve the problems of the technologies described above, the present invention provides the following technical solutions:
本发明提供了一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法,所述排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的具体步骤如下:The present invention provides a method for eliminating the interference caused by macrozyme molecules to the detection of serum enzyme concentration. The specific steps for eliminating the interference caused by macrozyme molecules to the detection of serum enzyme concentration are as follows:
步骤一:Cowan I细菌准备Step 1: Cowan I bacteria preparation
(A1)、为使Cowan I细菌菌体表面的SpA分子更为稳定,首先利用2%福尔马林溶液进行固定,固定时间和条件为室温固定2小时;(A1), in order to make the SpA molecule on the surface of the Cowan I bacterial thalline more stable, at first utilize 2% formalin solution to fix, and the fixation time and condition are fixed at room temperature for 2 hours;
(A2)、将固定好的金葡菌放置在80℃水浴中进行灭活,由于SpA蛋白对热非常稳定,不会干扰SpA的结合活性,同时,灭活后的细菌可以长期保存;(A2), placing the fixed Staphylococcus aureus in an 80°C water bath for inactivation, because the SpA protein is very stable to heat, it will not interfere with the binding activity of SpA, and at the same time, the inactivated bacteria can be stored for a long time;
(A3)、采用含有0.5%tween 20的PBS溶液进行洗涤,可以去除菌体表面非共价结合的SpA蛋白,提高反应的特异性。(A3), using the PBS solution containing 0.5% tween 20 to wash, can remove the non-covalently bound SpA protein on the surface of the thalline, and improve the specificity of the reaction.
步骤二:血清吸附试验Step 2: Serum Adsorption Test
(B1)、抽取怀疑含有巨酶的患者空腹静脉血5ml,待血清自凝后离心,分离血清;(B1), extract 5ml of fasting venous blood from patients suspected of containing macrozyme, centrifuge after the serum autocoagulates, and separate the serum;
(B2)、将步骤一中的Cowan I菌液混匀,与血清按照1:1的比例进行混匀,置于37℃摇床(150rpm)孵育3小时,使菌体表面的SpA蛋白与免疫球蛋白Fc段充分结合成免疫复合物;(B2), mix the Cowan I bacteria solution in step 1, mix it with the serum at a ratio of 1:1, and incubate it on a shaker (150rpm) at 37°C for 3 hours, so that the SpA protein on the surface of the bacteria and the immune The Fc portion of the globulin is fully combined into an immune complex;
(B3)、通过高速离心的方式对免疫复合物进行分离,吸取上层分离血清进行酶浓度检测。(B3). The immune complex is separated by high-speed centrifugation, and the serum separated from the upper layer is drawn to detect the enzyme concentration.
步骤三:吸附前后血清酶浓度检测和结果计算Step 3: Serum enzyme concentration detection and result calculation before and after adsorption
(C1)、通过标准方法检测血清吸附前后的酶浓度;(C1), detect the enzyme concentration before and after serum adsorption by standard method;
(C2)、吸附后酶浓度校正:在酶和免疫球蛋白检测时,将吸附后检测到的浓度水平乘以稀释倍数,得到的数值与原始浓度的比值,即为回收率,相应的吸附率(%)计算方式为:100%-回收率%。(C2) Enzyme concentration correction after adsorption: When detecting enzymes and immunoglobulins, multiply the concentration level detected after adsorption by the dilution factor, and the ratio of the obtained value to the original concentration is the recovery rate, and the corresponding adsorption rate (%) calculation method is: 100%-recovery rate%.
(C3)、比较吸附前后血清酶的水平,以及回收率和吸附率,判断是否存在巨酶干扰现象;如吸附后酶水平处于正常参考区间,可以判断存在巨酶干扰,对检测报告进行结果更正。(C3), compare the serum enzyme levels before and after adsorption, as well as the recovery rate and adsorption rate, to determine whether there is macrozyme interference; if the enzyme level after adsorption is within the normal reference range, it can be judged that there is macrozyme interference, and the test report is corrected. .
作为本发明的一种优选技术方案,所利用的Cowan I菌株是高表达膜表面SpA的金黄色葡萄球菌。As a preferred technical solution of the present invention, the Cowan I bacterial strain utilized is Staphylococcus aureus highly expressing SpA on the membrane surface.
作为本发明的一种优选技术方案,对Cowan I金黄色葡萄球菌进行处理时,首先利用2%福尔马林溶液先行细胞固定;然后经洗涤后用80℃的水浴5分钟进行灭活。As a preferred technical scheme of the present invention, when Cowan I Staphylococcus aureus is processed, at first utilize 2% formalin solution to fix the cells first; then inactivate them in a water bath at 80° C. for 5 minutes after washing.
作为本发明的一种优选技术方案,本发明的方法适用于排除巨天冬氨酸酰基转移酶(Macro-AST)、巨肌酸激酶(Macro-CK)、巨淀粉酶(Macro-AMY)和巨碱性磷酸酶(Macro-ALP)造成的干扰。As a preferred technical scheme of the present invention, the method of the present invention is suitable for eliminating giant aspartate acyltransferase (Macro-AST), giant creatine kinase (Macro-CK), giant amylase (Macro-AMY) and Interference caused by giant alkaline phosphatase (Macro-ALP).
本发明所达到的有益效果是:本发明的一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法与现有技术相比,具有以下的有益效果:The beneficial effects achieved by the present invention are: compared with the prior art, a method for eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration has the following beneficial effects:
1、本发明的排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法利用金黄色葡萄球菌表面的SpA与免疫球蛋白Fc段特异性结合的特性,可以去除“巨酶”对血清酶检测带来的干扰,对游离酶分子没有影响,同时,实验室只需要培养高表达SpA的Cowan I金葡菌,经过固定-洗涤-加热灭活几个步骤,可在4℃保存半年以上。1. The method of the present invention that eliminates the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration utilizes the specific binding characteristics of SpA on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus and the Fc segment of immunoglobulin, and can remove the "giant enzyme" on the serum enzyme detection band. Interference from the outside has no effect on free enzyme molecules. At the same time, the laboratory only needs to cultivate Cowan I S. aureus with high expression of SpA. After several steps of fixation-washing-heating inactivation, it can be stored at 4°C for more than half a year.
2、本发明的排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法与凝胶电泳、超滤、SpA琼脂糖凝胶颗粒吸附等方法比较起来,具有简便易行、经济快速、特异性强等特点,非常适合在临床上进行推广。2. Compared with methods such as gel electrophoresis, ultrafiltration, and SpA agarose gel particle adsorption, the method of eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules to the detection of serum enzyme concentration is simple, easy to implement, economical, fast, and specific. And other characteristics, very suitable for clinical promotion.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下对本发明的优选实施例进行说明,应当理解,此处所描述的优选实施例仅用于说明和解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。Preferred embodiments of the present invention are described below, and it should be understood that the preferred embodiments described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention.
实施例1Example 1
本发明提供了一种排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法,利用CowanI金黄色葡萄球菌吸附血清中的“巨AST”,以排除其对血清游离AST检测的干扰,更为具体的步骤为:The present invention provides a method for eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration, using CowanI Staphylococcus aureus to absorb the "giant AST" in serum to eliminate its interference to the detection of serum free AST, more specifically The steps are:
步骤一:Cowan I细菌准备Step 1: Cowan I bacteria preparation
(A1)、将Cowan I接种于200ml LB液体培养基中,置于37℃摇床培养过夜;(A1), inoculate Cowan I in 200ml LB liquid medium, and place it in a shaker at 37°C for overnight culture;
(A2)、第二天将菌液离心(5000rpm,10分钟),收集细菌,PBS溶液洗涤2次;(A2), the next day, the bacteria solution was centrifuged (5000rpm, 10 minutes), the bacteria were collected, and washed twice with PBS solution;
(A3)细菌固定:将洗涤后的Cowan I金葡菌加入到含有1.5%福尔马林溶液,混匀,室温下固定2小时;(A3) Bacterial fixation: add the washed Cowan I Staphylococcus aureus to a solution containing 1.5% formalin, mix well, and fix at room temperature for 2 hours;
(A4)洗涤:PBS溶液洗涤,以去除溶液中的福尔马林,然后利用PBS配制成50%浓度的菌液;(A4) Washing: washing with PBS solution to remove formalin in the solution, and then using PBS to prepare a 50% bacterial solution;
(A5)灭活:将菌液倒入锥形瓶内(少于1.5cm高度),置于80℃水浴,水平摇动5min;(A5) Inactivation: Pour the bacterial solution into a conical flask (less than 1.5cm in height), place it in a water bath at 80°C, and shake it horizontally for 5 minutes;
(A6)、冰浴:将锥形瓶立即放置在冰上进行降温;(A6), ice bath: place the Erlenmeyer flask on ice immediately for cooling;
(A7)、洗涤:首先用含有0.5%tween 20的PBS溶液洗涤一次,再用不含tween 20的PBS洗涤;(A7), washing: first wash once with PBS solution containing 0.5% tween 20, then wash with PBS without tween 20;
(A8)、保存:洗涤后的菌液保存于4℃冰箱,用前需摇匀。(可保存半年)(A8) Storage: Store the washed bacterial solution in a refrigerator at 4°C and shake well before use. (can be stored for half a year)
步骤二:血清吸附试验Step 2: Serum Adsorption Test
(B1)、血清准备:抽取怀疑含有巨AST的患者空腹静脉血5ml,待血清自凝后离心,分离血清;(B1) Serum preparation: Take 5ml of fasting venous blood from patients suspected of containing giant AST, centrifuge after the serum autocoagulates, and separate the serum;
(B2)、将步骤一中的Cowan I菌液混匀,吸取500ul加入到EP管内,室温静置30分钟复温,然后加入患者血清500ul,混匀;(B2), mix the Cowan I bacterial solution in step 1, draw 500ul and add it in the EP tube, let stand at room temperature for 30 minutes to rewarm, then add 500ul of patient serum, and mix;
(B3)、置于37℃摇床(150rpm)孵育3小时;(B3), incubate on a shaker (150 rpm) at 37°C for 3 hours;
(B4)、离心:将上述EP管置于离心机中离心10分钟,转速为10000rpm,小心吸取上层血清500ul,加入到新的EP管,待测Ig和AST浓度。(B4), centrifugation: place the above EP tube in a centrifuge for 10 minutes at a speed of 10,000 rpm, carefully absorb 500ul of the upper serum, add it to a new EP tube, and test the Ig and AST concentrations.
步骤三:血清AST和免疫球蛋白浓度检测:Step 3: Detection of serum AST and immunoglobulin concentration:
(C1)、利用西门子BNProspec免疫比浊仪检测免疫球蛋白(IgM、IgG、IgA)浓度;(C1), using the Siemens BNProspec immunoturbidimeter to detect the concentration of immunoglobulins (IgM, IgG, IgA);
(C2)利用Roche cobas c701检测Cowan I吸附前后的AST浓度;(C2) Use Roche cobas c701 to detect the concentration of AST before and after Cowan I adsorption;
其中,检测试剂均为仪器配套试剂,按照标准操作规程进行。Among them, the detection reagents are all supporting reagents for the instrument, and are carried out in accordance with the standard operating procedures.
步骤四:结果计算Step 4: Calculation of Results
(D1)、吸附后酶浓度校正:在酶和免疫球蛋白检测时,因血清与Cowan I菌液按1:1进行混合,故将吸附后检测到的浓度水平乘以稀释倍数(此处为2),得到的数值与原始浓度的比值,即为回收率,相应的吸附率计算方式为:100%-回收率%。(D1), correction of enzyme concentration after adsorption: when detecting enzymes and immunoglobulins, since the serum and Cowan I bacterial solution are mixed at a ratio of 1:1, the concentration level detected after adsorption is multiplied by the dilution factor (here is 2) The ratio of the obtained value to the original concentration is the recovery rate, and the corresponding adsorption rate calculation method is: 100%-recovery rate%.
(D2)、结果:(D2), the result:
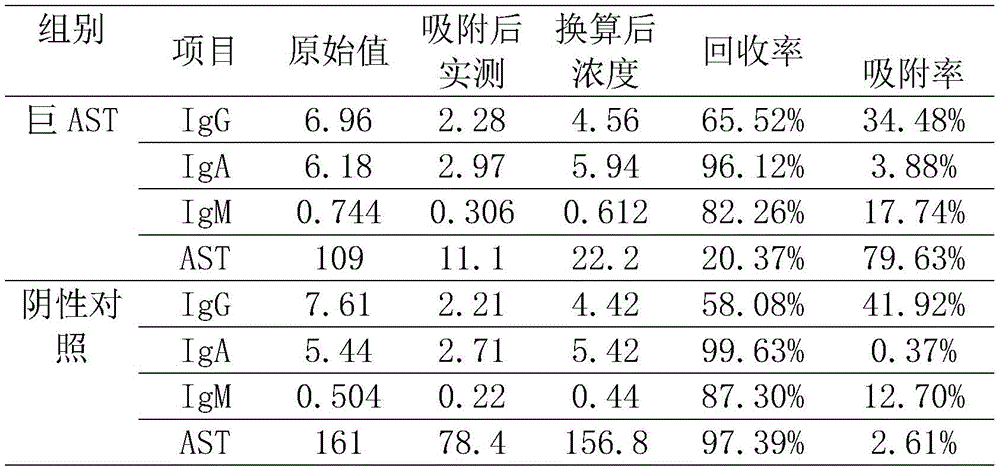
表1.Cowan I吸附前后血清免疫球蛋白和AST回收率Table 1. Recovery rate of serum immunoglobulin and AST before and after Cowan I adsorption
其中,Ig浓度单位为g/L,AST浓度单位为U/L。Wherein, the unit of Ig concentration is g/L, and the unit of AST concentration is U/L.
由表1结果显示:Cowan I对IgG吸附作用最强,巨AST和对照组吸附率分别为34.48%和41.92%,IgM吸附率低于IgG,分别为17.74%和12.7%。巨AST血清原始AST为109U/L,吸附后的换算浓度为22.2%,吸附率为79.63%,而对于对照血清,吸附前后的AST值分别为161U/L和156.8U/L,吸附率仅为2.61%。由此可见,巨AST组存在巨酶干扰现象,导致血清中AST的实测值明显增高,考虑到Cowan I细菌吸附免疫球蛋白并不能达到100%,实际血清中的AST浓度应小于22.2U/L,可按<22.2U/L进行结果报告,介于正常参考区间。The results in Table 1 show that: Cowan I has the strongest adsorption effect on IgG, the adsorption rates of giant AST and the control group are 34.48% and 41.92%, respectively, and the adsorption rates of IgM are lower than IgG, which are 17.74% and 12.7%, respectively. The original AST of giant AST serum was 109U/L, the converted concentration after adsorption was 22.2%, and the adsorption rate was 79.63%, while for the control serum, the AST values before and after adsorption were 161U/L and 156.8U/L, and the adsorption rate was only 2.61%. It can be seen that there is a phenomenon of giant enzyme interference in the giant AST group, which leads to a significant increase in the measured value of AST in the serum. Considering that the adsorption of immunoglobulin by Cowan I bacteria cannot reach 100%, the actual concentration of AST in the serum should be less than 22.2U/L , the results can be reported according to <22.2U/L, which is within the normal reference interval.
本发明的排除巨酶分子对血清酶浓度检测带来干扰的方法利用金黄色葡萄球菌表面的SpA与免疫球蛋白Fc段特异性结合的特性,可以去除“巨酶”对血清酶检测带来的干扰,对游离酶分子没有影响,同时,实验室只需要培养高表达SpA的Cowan I金葡菌,经过固定-洗涤-加热灭活几个步骤,可在4℃保存半年以上;与凝胶电泳、超滤、SpA琼脂糖凝胶颗粒吸附等方法比较起来,具有简便易行、经济快速、特异性强等特点,非常适合在临床上进行推广。The method for eliminating the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration utilizes the specific binding characteristics of SpA on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus and the Fc segment of immunoglobulins, and can remove the interference caused by "giant enzymes" on serum enzyme detection. Interference has no effect on free enzyme molecules. At the same time, the laboratory only needs to cultivate Cowan I Staphylococcus aureus with high expression of SpA. After several steps of fixation-washing-heating inactivation, it can be stored at 4°C for more than half a year; and gel electrophoresis Compared with other methods, such as ultrafiltration, SpA agarose gel particle adsorption, etc., they are simple, easy, economical, fast, and specific, and are very suitable for clinical promotion.
最后应说明的是:以上所述仅为本发明的优选实施例而已,并不用于限制本发明,尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,对于本领域的技术人员来说,其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换。凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所作的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。Finally, it should be noted that: the above is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention. Although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, for those skilled in the art, it still The technical solutions recorded in the foregoing embodiments may be modified, or some technical features thereof may be equivalently replaced. Any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289352.9A CN111505291B (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289352.9A CN111505291B (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111505291A CN111505291A (en) | 2020-08-07 |
| CN111505291B true CN111505291B (en) | 2023-04-25 |
Family
ID=71870883
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289352.9A Expired - Fee Related CN111505291B (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111505291B (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1723220A (en) * | 2003-11-13 | 2006-01-18 | 韩美药品工业株式会社 | Pharmaceutical composition containing immunoglobulin FC region as carrier |
| CN104792996A (en) * | 2014-01-20 | 2015-07-22 | 辽宁成大动物药业有限公司 | Rabies virus antibody (IgG) enzyme-linked immunoassay kit and detection method thereof |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7319015B2 (en) * | 2004-03-16 | 2008-01-15 | The Regents Of The University Of Michigan | Methods and compositions for using alveolar macrophage phospholipase A2 |
| US7521226B2 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2009-04-21 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | One-step enzymatic and amine detection technique |
| WO2006050177A2 (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-11 | The Regents Of The University Of Colorado | Antibodies that bind urokinase-type plasminogen activator and epitopes therefor |
| WO2007124105A2 (en) * | 2006-04-21 | 2007-11-01 | Nanobiosym, Inc. | Single-molecule platform for drug discovery: methods and apparatuses for drug discovery, including discovery of anticancer and antiviral agents |
-
2020
- 2020-04-14 CN CN202010289352.9A patent/CN111505291B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1723220A (en) * | 2003-11-13 | 2006-01-18 | 韩美药品工业株式会社 | Pharmaceutical composition containing immunoglobulin FC region as carrier |
| CN104792996A (en) * | 2014-01-20 | 2015-07-22 | 辽宁成大动物药业有限公司 | Rabies virus antibody (IgG) enzyme-linked immunoassay kit and detection method thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| Macroenzymes and their clinical significance;Turecky, L;《Bratislavske Lekarske Listy》;20041231;第260-263页 * |
| 巨分子酶在常规检验中的干扰因素及其鉴别方法;钟琴;《中外医学研究》;20110925(第27期);全文 * |
| 巨分子酶的临床意义;王爱华等;《现代检验医学杂志》;20070715(第04期);全文 * |
| 葡萄球菌蛋白A在病毒学诊断中的应用;解培英;《首都医科大学学报》;19851231(第02期);全文 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111505291A (en) | 2020-08-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Kobayashi et al. | Viral genotypes and response to interferon in patients with acute prolonged hepatitis B virus infection of adulthood in Japan | |
| CN111471103A (en) | Heterologous antibody of new coronavirus (2019-nCOV) and preparation method thereof | |
| CN109680026A (en) | The purifying of recombinant C A16 virus-like particle, the application in vaccine and vaccine | |
| CN103923900B (en) | Preparation and application of a bifunctional enzyme cross-linked enzyme aggregate for rice wine | |
| Biewenga | Complexes of lactate dehydrogenase and immunoglobulin G in human serum | |
| CN104181313B (en) | Factor IX quality-control product preparation method | |
| CN111505291B (en) | A method for excluding the interference of giant enzyme molecules on the detection of serum enzyme concentration | |
| CN116063467A (en) | Anti-H10 subtype avian influenza virus hemagglutinin protein monoclonal antibody 1F3 and its application in detection | |
| Schutte et al. | Effects of Anesthesia, Surgery and Inflammation Upon Host Defense Mechanisms: I. Effects Upon the Complement System | |
| Buezo et al. | Cryoglobulinemia and cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis with hepatitis C virus infection | |
| CN103233043A (en) | Tetrodotoxin-degrading extract liquid and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116068177A (en) | Direct immunofluorescence reagent, kit and application for detecting Cryptosporidium parvum | |
| Peters et al. | Serum immunoglobulin levels in Australia antigen positive and Australia antigen negative hepatitis | |
| CN107304230A (en) | A kind of anti-dog parvovirus refines antibody and preparation method thereof | |
| EP0068465A2 (en) | Non-A, non-B hepatitis-associated antibody conjugate, the use thereof and detection reagent | |
| Lorubbio et al. | Macro-aspartate aminotransferase in a healthy woman | |
| CN117305155B (en) | Method for inhibiting salmonella virulence factors | |
| CN103110943B (en) | Novel vaccine adjuvant capable of replacing aluminum hydroxide | |
| CN113801220B (en) | Rice fermentation acid composite antigen, rice fermentation acid antibody, preparation methods of rice fermentation acid composite antigen and rice fermentation acid antibody, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit | |
| Okamoto et al. | Molecular analysis of the interspousal transmission of hepatitis B virus in two Japanese patients who acquired fulminant hepatitis B after 50 and 49 years of marriage | |
| CN117568282A (en) | Hybridoma cell strain, and feline panleukopenia virus monoclonal antibody secreted by hybridoma cell strain and application of feline panleukopenia virus monoclonal antibody | |
| CN100383239C (en) | Method for extracting oxalate oxidase from wheat bran | |
| Morse et al. | Erythrokinetics and ferrokinetics of a viral-induced murine erythroblastosis | |
| NO821927L (en) | PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING PURE SURFACE ANTIGEN AGAINST HEPATITIS B, FROM PLASMA FROM HUMAN | |
| RU2159436C1 (en) | Method for determining functional state of immune system cellular link in the cases of thermal trauma |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |
Granted publication date: 20230425 |
|
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |