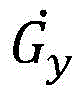Disclosure of Invention
The embodiment of the invention aims to provide a vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method and system based on driver body feeling, and aims to solve the technical problem that in the prior art, when a vehicle turns, the driver feels uncomfortable due to improper speed control in the automatic driving process, and the driving experience is influenced.
Therefore, the invention provides a vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver body feeling, which comprises the following steps:
when the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, acquiring the real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle;
comparing the real-time lateral acceleration with a pre-stored lateral acceleration threshold value, wherein the lateral acceleration threshold value is matched with physiological state parameters of the driver, and the physiological state parameters comprise height, weight, age and sex;
if the real-time lateral acceleration is greater than or equal to the lateral acceleration threshold, adjusting the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle until the real-time lateral acceleration is less than the lateral acceleration threshold.
Optionally, in the above vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver's body feeling, the lateral acceleration threshold is obtained through a lateral acceleration calibration test, where the lateral acceleration calibration test includes the following steps:
determining physiological state parameters of a subject participating in a calibration test;
acquiring the change process of the lateral acceleration value of the vehicle when the vehicle is in a turning state;
acquiring an electromyographic signal change process of the subject when a vehicle is in a turning state;
acquiring an experience result of the subject in the current calibration test process after the calibration test is finished;
and obtaining a lateral acceleration threshold value according to the change process of the lateral acceleration value, the change process of the electromyographic signal and the experience result, wherein the lateral acceleration threshold value corresponds to the current physiological state parameter.
Optionally, in the above vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver's body feeling, in the step of obtaining the electromyographic signal variation process of the subject when the vehicle is in a turning state:
the electromyographic signal is obtained by detecting an electromyographic signal of a measured muscle of a subject, wherein the measured muscle is located on a side of the subject opposite to a vehicle turning direction.
Optionally, in the above vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver's body feeling, the step of acquiring the electromyographic signal variation process of the subject when the vehicle is in a turning state includes:
collecting electromyographic signals of detected muscles of a subject as original electromyographic signal values in a set detection period according to a specific step length;
acquiring a root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period, and carrying out standardization processing on the root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period to obtain a characteristic value of the electromyographic signal in the detection period;
acquiring a process in which the characteristic value of the electromyogram signal changes with time as the electromyogram signal changing process.
Optionally, in the above vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver's body feeling, the step of obtaining a root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period, and normalizing the root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period to obtain a characteristic value of the electromyographic signal in the detection period includes:
filtering the original electromyographic signals in each detection period to filter interference values;
calculating the root mean square value of each detection period for the filtered original electromyographic signals:
wherein e (T) is an original electromyographic signal acquired in real time in a detection period, T is the detection period duration, [ (k-1) T, kT ] is the kth detection period, and tau is the sampling step length;
obtaining the root mean square value RMS of electromyographic signals of a subject in a static states;
The characteristic values of the myoelectric signal in each detection period are as follows: RMS (k) -RMSS。
Optionally, in the above vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver's body feeling, the step of obtaining a lateral acceleration threshold according to the change process of the lateral acceleration value, the change process of the electromyographic signal, and the experience result includes:
acquiring an average value of lateral acceleration in a set detection period;
corresponding the lateral acceleration average value and the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal in the same detection period one by one to obtain a relation fitting curve of the lateral acceleration average value and the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal;
determining a comfort threshold range and the comfort threshold range according to the experience result;
determining a curve point/segment in the fitted curve corresponding to the comfort threshold range, and selecting the maximum lateral acceleration in the curve point/segment as the lateral acceleration threshold.
Optionally, in the above method for adjusting intelligent steering of a vehicle based on driver's body feeling, in the step of obtaining a real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle when the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, the real-time lateral acceleration is obtained as follows:
acquiring a real-time steering wheel angle delta and a real-time running speed V of a vehicle;
the real-time lateral acceleration
Q is a speed coefficient, and the value of Q is related to the vehicle attribute and is obtained according to a historical experience value or through experimental measurement; i is a steering angle transmission ratio; l is the wheelbase.
Optionally, in the above method for adjusting intelligent steering of a vehicle based on driver's body feeling, if the real-time lateral acceleration is greater than or equal to the lateral acceleration threshold, the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle is adjusted until the real-time lateral acceleration is smaller than the lateral acceleration threshold, and the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle is adjusted by:
wherein G is
xIs the longitudinal acceleration; c
xyCalibrating model parameters; g
x_DCThe longitudinal component of the circular center acceleration which is the ideal change of the resultant acceleration;
is the derivative of the lateral acceleration and is,
the expression form of Laplace transform of the first-order inertia link is shown, wherein T is an inertia time constant. Description of the above formula, G
xAnd
the transmission between the two is first order inertial transmission.
The invention also provides a storage medium which is readable by a computer, wherein the storage medium stores program information, and the computer reads the program information and then executes any one of the above methods based on the driver's body feeling.
The invention also provides a vehicle intelligent steering adjusting system based on driver motion sensing, which is characterized by comprising at least one processor and at least one memory, wherein program information is stored in the at least one memory, and the at least one processor reads the program information and then executes any one of the vehicle intelligent steering adjusting methods based on driver motion sensing.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention at least comprises the following steps
Has the advantages that:
the embodiment of the invention provides a vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method and system based on driver motion sensing, wherein the method comprises the following steps: when the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, acquiring the real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle; comparing the real-time lateral acceleration with a pre-stored lateral acceleration threshold value, wherein the lateral acceleration threshold value is matched with the physiological state parameter of the driver; if the real-time lateral acceleration is greater than or equal to the lateral acceleration threshold, adjusting the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle until the real-time lateral acceleration is less than the lateral acceleration threshold. According to the scheme provided by the invention, the real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle in the turning process meets the condition that the lateral acceleration is smaller than the lateral acceleration threshold value in a mode of setting the lateral acceleration threshold value, so that the comfort level of a driver in the turning driving process of the vehicle can be improved, and the driving experience in the turning process is improved.
Detailed Description
The embodiments of the present invention will be further described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the description of the present invention, it should be noted that the terms "center", "upper", "lower", "left", "right", "vertical", "horizontal", "inner", "outer", etc., indicate orientations or positional relationships based on the orientations or positional relationships shown in the drawings, and are only for convenience of description of the present invention, and do not indicate or imply that the device or assembly referred to must have a specific orientation, be constructed and operated in a specific orientation, and thus, should not be construed as limiting the present invention. Furthermore, the terms "first," "second," and "third" are used for descriptive purposes only and are not to be construed as indicating or implying relative importance. Wherein the terms "first position" and "second position" are two different positions.
In the description of the present invention, it should be noted that, unless otherwise explicitly specified or limited, the terms "mounted," "connected," and "connected" are to be construed broadly, e.g., as meaning either a fixed connection, a removable connection, or an integral connection; can be mechanically or electrically connected; the two components can be directly connected or indirectly connected through an intermediate medium, and the two components can be communicated with each other. The specific meanings of the above terms in the present invention can be understood in specific cases to those skilled in the art.
Example 1
The embodiment provides a vehicle intelligent steering adjusting method based on driver motion sensing, which can be applied to an automatic driving system, an auxiliary driving system or a vehicle body control system of an intelligent vehicle, and as shown in fig. 1, the method comprises the following steps:
s101: when the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, acquiring the real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle; in the driving process of the intelligent vehicle, various types of sensors mounted on the vehicle can monitor the driving state of the vehicle in real time, so that whether the vehicle is in a turning state or not can be judged, for example, the straightness of a lane can be detected through a camera arranged on the vehicle, the lateral acceleration of the vehicle can be detected through a speed sensor arranged on the vehicle, the steering wheel angle can be detected through a sensor arranged on a steering wheel, and the like. When the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, the lateral acceleration of the vehicle is detected by a sensor provided on the vehicle.
S102: comparing the real-time lateral acceleration with a pre-stored lateral acceleration threshold value, wherein the lateral acceleration threshold value is matched with physiological state parameters of the driver, and the physiological state parameters comprise height, weight, age and sex; the relationship between the lateral acceleration threshold value and the physiological state parameter can be stored in an automatic driving system, an auxiliary driving system or a vehicle body control system, and can be stored in a table manner. It will be appreciated that the data stored in different vehicle models may vary due to the different vehicle models. Preferably, before this step is implemented, a step of receiving physiological state parameter information input by a driver can be further included. When the driver starts the vehicle, a dialog window can be popped up on the central control screen to ask the driver to input the real physiological state parameters of the driver, and after the physiological state parameter data are received, the physiological state parameter data can be compared with the data stored in the data table one by one to determine the matched lateral acceleration threshold. The lateral acceleration threshold is a threshold that can ensure a comfortable feeling for the driver, and is obtained by conducting a large number of experiments with subjects of different genders, heights, weights, ages, and driving ages before each vehicle leaves the factory.
S103: if the real-time lateral acceleration is greater than or equal to the lateral acceleration threshold, adjusting the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle until the real-time lateral acceleration is less than the lateral acceleration threshold. When the real-time lateral acceleration is larger than or equal to the lateral acceleration threshold value, which indicates that the driver may feel uncomfortable, the vehicle running speed can be automatically adjusted at the moment, so that the lateral acceleration is reduced, and the driving experience of the driver is improved. Since the lateral acceleration and the longitudinal acceleration have correlation and have a specific conversion relation with each other during the running process of the vehicle, the lateral acceleration of the vehicle can be simultaneously adjusted by adjusting the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle in the step, and the comfort of a driver is further improved.
In this embodiment, the lateral acceleration threshold is obtained through a lateral acceleration calibration test, where the lateral acceleration calibration test includes the following steps:
s201: determining physiological state parameters of a subject participating in a calibration test; a plurality of drivers are selected as test subjects to carry out a lateral acceleration calibration test, the sex, the height, the weight, the age and the driving age of the test subjects are uniformly distributed, and the lateral acceleration calibration test has no behaviors of fatigue, drinking and the like before the test. The embodiment adopts the electromyographic signals to reflect the physiological somatosensory feeling of the driver. Before the test, an electrode plate is pasted on each subject and the electromyographic signal transmission module is worn on the neck. In the experiment, the electromyographic signals are obtained by detecting the electromyographic signals of the tested muscles of the testee, wherein the tested muscles are positioned on the side of the testee opposite to the steering direction of the vehicle, because the muscle response on the side opposite to the steering direction of the vehicle is more obvious, the electromyographic signals of the muscles on the right side of the testee are selected for processing when the vehicle turns left, and the electromyographic signals of the muscles on the left side of the testee are selected for processing when the vehicle turns right. . Specifically, two muscles, the left and right sternocleidomastoid muscles, were tested per subject. Two electrodes were affixed to each muscle approximately 20mm apart using the principle of differential amplification. The reference electrode is affixed to the clavicle because there is a piece of skeletal muscle beneath the skin of the clavicle. A large number of tests are carried out in the calibration process, the lateral acceleration of each test is different and is distributed uniformly as much as possible, a U-turn route with different turning radius (20-35m) is selected in each test, and the bending speed is (30-60 km/h). In order to obtain better driving experience of the driver, the driver is required to turn to pass according to a comfortable and free driving state after entering a bend. In actual tests, the vehicle speed and the steering radius cannot be kept constant, so that a series of fluctuating lateral acceleration data is measured in each test. The test comprises the following steps:
s301: collecting electromyographic signals of detected muscles of a subject as original electromyographic signal values in a set detection period according to a specific step length; the set detection period can be selected to be 0.05 second, the step size can be selected to be 0.005 second, and the like.
S302: acquiring a root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period, and carrying out standardization processing on the root mean square value of the original electromyographic signal in each detection period to obtain a characteristic value of the electromyographic signal in the detection period; it includes:
the method comprises the following steps of filtering original electromyographic signals in each detection period to remove interference values, wherein the step is to remove the interference signals, band-pass filtering can be adopted for filtering, the upper limit and the lower limit of passband cut-off frequency are 30Hz and 120Hz, and the upper limit and the lower limit of stopband cut-off frequency are 20Hz and 130 Hz. Calculating the root mean square value of each detection period for the filtered original electromyographic signals:
wherein e (T) is an original electromyographic signal acquired in real time in a detection period, T is the detection period duration, [ (k-1) T, kT ] is the kth detection period, and tau is the sampling step length;
s303: obtaining the root mean square value RMS of electromyographic signals of a subject in a static statesThis process is the same as the acquisition in steps S301 and S302, except that the subject is in a static state.
S304: the characteristic values of the myoelectric signal in each detection period are as follows: RMS (k) -RMSS. After the normalization process is applied, errors due to differences in skin resistance between individuals can be filtered out.
S305: acquiring a process in which the characteristic value of the electromyogram signal changes with time as the electromyogram signal changing process.
S202: acquiring the change process of the lateral acceleration value of the vehicle when the vehicle is in a turning state;
s203: acquiring an electromyographic signal change process of the subject when a vehicle is in a turning state;
s204: acquiring an experience result of the subject in the current calibration test process after the calibration test is finished; the driving experience result can be given in real time in the calibration test process by the subject, the driving experience result and the time have corresponding relations, for example, scoring common subject selection can be provided, for example, the driving experience is divided into 5 grades, namely 1 uncomfortable, 2 uncomfortable, 3 common, 4 comfortable, 5 comfortable and the like.
S205: and obtaining a lateral acceleration threshold value according to the change process of the lateral acceleration value, the change process of the electromyographic signal and the experience result, wherein the lateral acceleration threshold value corresponds to the current physiological state parameter. The method specifically comprises the following steps:
s401: acquiring an average value of lateral acceleration in a set detection period; because the lateral acceleration fluctuates in each test steering process due to various practical factors, the average value of a series of lateral accelerations measured in each test process can be obtained, and the starting node and the ending node of the set period in the step are the same as the starting node and the ending node of the set detection period in the step S301.
S402: and (3) corresponding the lateral acceleration average value and the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal in the same detection period one by one to obtain a relation fitting curve of the lateral acceleration average value and the characteristic value of the electromyographic signal. The two curves are drawn in the same coordinate system, wherein the abscissa is time, and the ordinate is the lateral acceleration average value and the root mean square value of the normalized electromyographic signal respectively.
S403: determining a comfort threshold range and the comfort threshold range according to the experience result; as described above, the subject gives the driving experience result at any time during the calibration test, and the time given by the driving experience result and the driving experience score have a corresponding relationship. That is, the driving experience result, the average lateral acceleration value, and the root mean square value of the normalized electromyogram signal given by the subject can be obtained at the same time. If the driving experience result is also drawn under the same coordinate system, three curves can be obtained.
S404: determining a curve point/segment in the fitted curve corresponding to the comfort threshold range, and selecting the maximum lateral acceleration in the curve point/segment as the lateral acceleration threshold. Namely, determining all normalized electromyographic signal root mean square values corresponding to two more comfortable and comfortable grades of subjective evaluation of the subject, making a concentrated interval on a lateral acceleration curve, and selecting the maximum lateral acceleration value corresponding to the interval as an off-line lateral acceleration calibration threshold value. The above calibration test process provided by this embodiment can be summarized as the flow shown in fig. 2.
It will be appreciated that the lateral acceleration calibration test may be performed a number of times, for subjects with different physiological state parameters, for different cornering conditions, etc. And the calibration test can be carried out for multiple times under each condition, and the average value of the multiple tests can be obtained as the test result. Such tests can be performed for different vehicle types and can be stored in the control system of the vehicle after the test results are obtained. In the process of automatic driving or auxiliary driving of the vehicle, when the vehicle is detected to enter a turning state, the corresponding lateral acceleration threshold value can be directly extracted to adjust the speed of the vehicle, and the driving experience of a driver is ensured.
Further, in the step of acquiring the real-time lateral acceleration of the vehicle when the vehicle is detected to be in a turning state, the real-time lateral acceleration is acquired by: acquiring a real-time steering wheel angle delta and a real-time running speed V of a vehicle; the real-time lateral acceleration
Wherein Q is a speed coefficient, and i is a steering angle transmission ratio; l is the wheelbase. The value of Q is related to vehicle attributes, and is obtained from historical empirical values or through experimental measurements, specifically through a very simple centripetal acceleration (lateral acceleration) formula: a ═ V2The steering radius R is determined by the steering wheel angle delta, the wheel angle delta/i can be obtained by knowing the steering wheel angle through the steering system transmission ratio i, and then the triangle relation R is L/sin (delta/i), because the wheel angle is generally smaller sin (delta/i) and approximately equal to delta/i, the original formula can be verified, the formula is theoretical, the factors such as the tire slip angle and the like are also considered in practical application, a correction coefficient is needed to enable the result to be as close to the true value as possible, simple points can be selected according to different vehicle models through historical experience, and the simple points are repeatedMiscellaneous point can let the car turn to the driving with different speed of a motor vehicle in the experimental place, can carry out high accuracy location to the vehicle easily in the experimental environment, acquires the orbit and the speed of vehicle, calculates the camber of each subsection vehicle orbit and can reachs the turning radius of vehicle, according to a V turning radius2The lateral acceleration a is calculated by/R, so that in contrast to the calculation of the formula, a correction is made by means of a variable speed coefficient Q, noting that Q can be varied.
Preferably, the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle is adjusted by:
wherein G is
xIs the longitudinal acceleration; c
xySelecting through tests for calibrating model parameters; g
x_DCThe longitudinal component of the circular center acceleration of the ideal variation circle of the resultant acceleration is usually 0 in practical application.
Is the derivative of the lateral acceleration and is,
the method is an expression form of Laplace transform of a first-order inertia link, wherein T is an inertia time constant; sign denotes that the parameter is signed, positive numbers are signed, negative numbers are signed: description of the above formula, G
xAnd
the transmission between the two is first order inertial transmission. By adjusting G
xUntil the real-time lateral acceleration is less than the lateral acceleration threshold to meet an overbending comfort experience.
CxyCalibrating model parameters according to experience, and selecting one adaptive model according to the evaluation of the comfort level of a driverWhen the value is correct.
Through the scheme, in the automobile steering process, if the lateral acceleration exceeds the lateral acceleration threshold value, the system automatically applies a braking deceleration to the automobile to reduce the automobile speed, so that the lateral acceleration of the automobile is reduced, the lateral acceleration judging process is started again, and the steps are repeated until the real-time lateral acceleration is smaller than the lateral acceleration threshold value.
Example 2
The present embodiment provides a readable storage medium, where a computer program is stored in the storage medium, and the computer program is executed by a computer to implement the method for adjusting intelligent steering of a vehicle based on driver's body feeling in embodiment 1.
Example 3
The present embodiment provides a vehicle intelligent steering adjustment system based on driver's body feeling, as shown in fig. 3, including at least one processor 301 and at least one memory 302, where instruction information is stored in at least one of the memories 302, and after at least one of the processors 301 reads the program instruction, the vehicle intelligent steering adjustment method based on driver's body feeling in any one of embodiments 1 may be executed.
In addition, the vehicle intelligent steering adjustment system based on the driver's body feeling in the embodiment may further include various sensors disposed in the intelligent vehicle, and the system can receive detection signals sent by the various sensors, and determine the steering wheel angle, the driving speed, whether the vehicle turns, and the like according to the detection signals. When a lateral acceleration calibration test is carried out, a physiological information detector for detecting the electromyographic signals of the testee and the like are also used in the calibration process.
In addition, above-mentioned vehicle intelligence turns to governing system based on driver's body is felt can also include: an input device 303 and an output device 304. The processor 301, memory 302, input device 303, and output device 304 may be connected by a bus or other means. The vehicle intelligent steering adjusting system based on the driver motion sense can execute the method provided by the embodiment of the application, and has the corresponding functional modules and beneficial effects of the execution method. For technical details that are not described in detail in this example, reference is made to the method provided in example 1 of the present application.
Finally, it should be noted that: the above examples are only intended to illustrate the technical solution of the present invention, but not to limit it; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that: the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments may still be modified, or some technical features may be equivalently replaced; and such modifications or substitutions do not depart from the spirit and scope of the corresponding technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention.