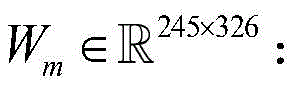CN109934815B - A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints - Google Patents
A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN109934815B CN109934815B CN201910202771.1A CN201910202771A CN109934815B CN 109934815 B CN109934815 B CN 109934815B CN 201910202771 A CN201910202771 A CN 201910202771A CN 109934815 B CN109934815 B CN 109934815B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- tensor
- target
- image
- background
- objective function
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 58
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003190 augmentative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010606 normalization Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 11
- 101100012902 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) FIG2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000007 visual effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 101100233916 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) KAR5 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000513 principal component analysis Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241001270131 Agaricus moelleri Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 101000827703 Homo sapiens Polyphosphoinositide phosphatase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100023591 Polyphosphoinositide phosphatase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241001085205 Prenanthella exigua Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004880 explosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004424 eye movement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003331 infrared imaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004321 preservation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000779 smoke Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
技术领域Technical Field
本发明涉及红外图像处理及目标检测领域,尤其是一种结合ATV约束的张量恢复红外弱小目标检测方法。The invention relates to the field of infrared image processing and target detection, and in particular to a tensor recovery infrared dim small target detection method combined with ATV constraints.
背景技术Background Art
红外成像技术具有非接触性、捕捉细节能力强等特点,并且不受烟、雾等障碍物的影响实现昼夜的连续远距离目标的探测;红外搜索与跟踪IRST(Infrared search andtrack)系统在军事、民用等领域得到广泛应用其中,红外弱小目标检测技术作为IRST系统的一个基本功能,在红外搜索、红外预警、远距离目标检测中具有重要意义。但是,由于在红外波段中,目标的纹理、结构信息缺乏,同时远距离、复杂背景、各种杂波的影响,红外目标经常呈斑点或点状,甚至淹没在背景中,这就造成了红外弱小目标检测极其困难。Infrared imaging technology has the characteristics of non-contact and strong ability to capture details. It is not affected by obstacles such as smoke and fog, and can detect long-distance targets continuously during the day and night. Infrared search and tracking IRST (Infrared search and track) systems are widely used in military and civilian fields. Among them, infrared weak target detection technology, as a basic function of IRST system, is of great significance in infrared search, infrared early warning, and long-distance target detection. However, due to the lack of texture and structural information of the target in the infrared band, and the influence of long distance, complex background, and various clutter, infrared targets often appear as spots or dots, or even submerged in the background, which makes infrared weak target detection extremely difficult.
红外弱小目标检测技术分为两大类:基于单帧的弱小目标检测技术和基于多帧的弱小目标检测技术,但是由于基于多帧的检测技术需要联合多帧捕获目标的运动轨迹,排除噪声的干扰,因此需要极大的计算量和存储量,对硬件要求高,实际工程中应用很少。目前,常用的基于单帧的检测方法分为以下三类:Infrared small target detection technology is divided into two categories: single-frame based small target detection technology and multi-frame based small target detection technology. However, since multi-frame based detection technology needs to capture the target's motion trajectory by combining multiple frames and eliminate noise interference, it requires a huge amount of calculation and storage, and has high hardware requirements, so it is rarely used in actual projects. At present, the commonly used single-frame based detection methods are divided into the following three categories:
(1)背景抑制:背景抑制类方法基于红外图像中背景一致性的假设,采用滤波器对红外图像的背景进行预测,然后再从原图中减去背景,最后进行阈值分割以此检测弱小目标。最大中值滤波、最大均值滤波、顶帽变换、二维最小均方滤波等均属于背景抑制的范畴。尽管这类方法实现简单,但是由于噪声并不符合一致性的假设,背景抑制的方法极易受噪声杂波的影响,导致大部分低信噪比的红外图像的抑制效果很差。(1) Background suppression: Background suppression methods are based on the assumption of background consistency in infrared images. They use filters to predict the background of infrared images, then subtract the background from the original image, and finally perform threshold segmentation to detect weak targets. Maximum median filtering, maximum mean filtering, top hat transformation, two-dimensional minimum mean square filtering, etc. all belong to the category of background suppression. Although this type of method is simple to implement, since the noise does not meet the consistency assumption, the background suppression method is easily affected by noise clutter, resulting in poor suppression effect for most low signal-to-noise ratio infrared images.
(2)视觉显著性:人类视觉系统HVS(Human Visual System)涉及对比度、视觉注意和眼动三种机制,其中涉及最多的为对比度机制即假设红外图像中,目标是最显著的对象。比如,高斯差分滤波器利用两个不同的高斯滤波器计算显著性图,并对目标进行检测和识别;基于局部对比的方法,利用包含目标的小邻域局部对比度高,而不包含的目标的背景区域局部对比度低的特点,通过计算局部对比度图,突出目标,抑制背景,达到检测的目的。当红外图像符合视觉显著性假设时,这类方法可以得到优异的效果,但是,在实际应用场景下,这一假设很难满足,比如显著性的虚警源的存在时,误检问题难以克服,造成准确率低。(2) Visual saliency: The human visual system (HVS) involves three mechanisms: contrast, visual attention, and eye movement. The most involved mechanism is the contrast mechanism, which assumes that the target is the most salient object in the infrared image. For example, the Gaussian difference filter uses two different Gaussian filters to calculate the saliency map and detect and identify the target; the local contrast-based method uses the characteristics that the local contrast of the small neighborhood containing the target is high, while the local contrast of the background area that does not contain the target is low. By calculating the local contrast map, the target is highlighted and the background is suppressed to achieve the purpose of detection. When the infrared image meets the visual saliency hypothesis, this type of method can achieve excellent results. However, in actual application scenarios, this assumption is difficult to meet. For example, when there is a significant false alarm source, the false detection problem is difficult to overcome, resulting in low accuracy.
(3)目标背景分离:这一类方法利用的是红外图像背景的非局部自相关性以及目标的稀疏性,把目标检测问题转换为优化问题;其又可细分为基于超完备字典、低秩表示的方法和基于低秩背景与稀疏目标复原的方法。第一种方法需要提前由高斯强度模型构造不同目标尺寸和形状的超完备字典,构造目标字典的过程繁琐,检测结果受字典影响大,并且如果目标尺寸和形状变化较大时,高斯强度模型将不再适用;第二种方法借助块图像模型IPI(Infrared Patch-Image)模型可以得到低秩的原始块图像,再借助目标稀疏的特性,通过优化目标函数,同时恢复出背景和目标图像,最后得到检测结果;第二种方法效果极佳,但是存在以下两个问题:一、由于强边缘、部分噪声、虚警源也具有稀疏的特点,其会降低检测的准确率;二、由于目标函数优化的过程需要迭代,难以达到实时性。(3) Target-background separation: This type of method uses the non-local autocorrelation of the infrared image background and the sparsity of the target to convert the target detection problem into an optimization problem. It can be further divided into methods based on super-complete dictionaries and low-rank representations and methods based on low-rank background and sparse target restoration. The first method requires the construction of a super-complete dictionary of different target sizes and shapes by the Gaussian intensity model in advance. The process of constructing the target dictionary is cumbersome, and the detection results are greatly affected by the dictionary. In addition, if the target size and shape change greatly, the Gaussian intensity model will no longer be applicable. The second method uses the block image model IPI (Infrared Patch-Image) model to obtain the low-rank original block image, and then uses the sparse characteristics of the target to optimize the objective function to simultaneously restore the background and target images, and finally obtain the detection result. The second method has excellent results, but there are two problems: First, since strong edges, some noise, and false alarm sources are also sparse, it will reduce the accuracy of detection; second, since the objective function optimization process requires iteration, it is difficult to achieve real-time performance.
在当今这个信息爆炸的时代,数据的维度不再局限于一维和二维,处理的难度也日益增大,张量则是用来表示多维信息的方式;实际上,张量是多维数组的泛概念,比如一维数组通常称之为向量,二维数组通常称之为矩阵。鲁棒主成分分析(Robust PrincipleComponent Analysis,RPCA)克服了鲁棒主成分分析易受异常点影响的缺点,更加稳健,目前已广泛应用于图像补全、图像去噪和人脸识别等领域;但RPCA只能直接用于处理二维矩阵,若要处理高维数据,需先把高维数据转换为二维数据,处理完成后再转换至高维空间。这一过程不仅繁杂,而且完全破坏数据的内在结构,且效率低下。为了能更加灵活地处理高维数据,基于张量的技术逐渐发展起来,其中,张量恢复(Tensor Recovery)能利用更多的数据信息(结构、颜色、时间等),在稀疏低秩分解上比RPCA表现更好。张量鲁棒主成分分析(Tensor RPCA,TRPCA)为张量恢复技术中的一种关键技术,是RPCA的高阶扩展,由Goldfarb和Qin两人提出。假定给定一个已知张量并且已知可分解为:In today's era of information explosion, the dimension of data is no longer limited to one-dimensional and two-dimensional, and the difficulty of processing is increasing. Tensors are used to represent multidimensional information. In fact, tensors are a general concept of multidimensional arrays. For example, one-dimensional arrays are usually called vectors, and two-dimensional arrays are usually called matrices. Robust principal component analysis (RPCA) overcomes the shortcomings of robust principal component analysis that is easily affected by outliers and is more robust. It has been widely used in image completion, image denoising, and face recognition. However, RPCA can only be used directly to process two-dimensional matrices. If high-dimensional data is to be processed, the high-dimensional data must first be converted into two-dimensional data, and then converted to high-dimensional space after processing. This process is not only complicated, but also completely destroys the internal structure of the data and is inefficient. In order to process high-dimensional data more flexibly, tensor-based technologies have gradually developed. Among them, tensor recovery can utilize more data information (structure, color, time, etc.) and performs better than RPCA in sparse low-rank decomposition. Tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis (TRPCA) is a key technology in tensor recovery technology. It is a high-order extension of RPCA and was proposed by Goldfarb and Qin. Assume that a known tensor And it is known Can be decomposed into:
其中,为低秩张量,ε为稀疏张量,根据求解和ε的问题就是一个张量恢复问题。in, is a low-rank tensor, ε is a sparse tensor, according to Solution The problem with ε is a tensor recovery problem.
全变分(Total Variation,TV)模型是一种著名的偏微分方程去噪模型,由于图像细节部分和噪声有很大的相似性,所以在图像去噪的同时,很难保护细节部分。Osher等人在1992年提出了全变分的思想,该模型能在去噪的同时有效的保护图像边缘。TV被证明能够保留图像的重要边缘和边角,在需要对图像不连续部分进行精确估计时,经常将其作为正则项。换句话说,TV代表了给定图像的平滑度,它也广泛用于图像分解,它可以将图像分解为两部分:一部分是不相关的随机图案,另一部分是锐边和分段光滑分量。通过最小化图像的TV,图像光滑的内表面将被保留,同时保持清晰的边缘。TV模型包括各向同性全变分(Isotropic Total Variation,ITV)以及各向异性全变分(Anisotropic TotalVariation,ATV),但是由于ATV的边缘保持能力优于ITV,因此,ATV被越来越多地应用到图像去噪、图像重建等领域。在不失一般性假设的前提下,给定一幅图X,ATV定义如下:The total variation (TV) model is a well-known partial differential equation denoising model. Since the image details and noise are very similar, it is difficult to protect the details while denoising the image. Osher et al. proposed the idea of total variation in 1992. This model can effectively protect the image edges while denoising. TV has been proven to be able to preserve important edges and corners of the image. It is often used as a regular term when accurate estimation of discontinuous parts of the image is required. In other words, TV represents the smoothness of a given image. It is also widely used in image decomposition. It can decompose the image into two parts: one is an unrelated random pattern, and the other is a sharp edge and piecewise smooth component. By minimizing the TV of the image, the smooth inner surface of the image will be preserved while maintaining clear edges. The TV model includes isotropic total variation (ITV) and anisotropic total variation (ATV). However, since ATV has better edge preservation ability than ITV, ATV is increasingly used in image denoising, image reconstruction and other fields. Without loss of generality, given a graph X, ATV is defined as follows:
其中,和分别表示水平和垂直的二维有限差分算子。in, and denote the horizontal and vertical two-dimensional finite difference operators respectively.
为了提高红外弱小目标检测能力,考虑到传统的红外弱小目标检测方法只考虑了图像的局部特点,而优化类方法只考虑了图像的非局部自相关特性,现有文献提出RIPT(Reweighted Infrared Patch-Tensor Model)模型,即在块张量模型的基础上,同时结合红外图像的局部与非局部特性来构建目标函数,并利用交替方向乘子法(AlternatingDirection Method of Multipliers,ADMM)来对目标函数进行求解。在大部分情况下,RIPT有更好的背景抑制和目标增强能力,但是RIPT所采用的张量核范数为核范数和SNN(Sum ofNuclear Norms),文献《A new convex relaxation for tensor completion》指出SNN并不是张量秩的最优凸近似,核范数当中赋予所有的奇异值相同的权重,而在实际的场景中,目标内容和噪声的奇异值是不同的,因此RIPT会造成局部最优解,增大目标图像中虚警率。同时,RIPT中的局部结构权重在突出背景边缘的同时也突出了目标的边缘,导致检测结果的目标形状减小,甚至会出现检测不到目标的情况。因此,需要一种红外弱小目标检测方法结合张量恢复和ATV克服以上问题。In order to improve the detection capability of infrared dim small targets, considering that the traditional infrared dim small target detection method only considers the local characteristics of the image, and the optimization method only considers the non-local autocorrelation characteristics of the image, the existing literature proposes the RIPT (Reweighted Infrared Patch-Tensor Model) model, that is, on the basis of the block tensor model, the local and non-local characteristics of the infrared image are combined to construct the objective function, and the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) is used to solve the objective function. In most cases, RIPT has better background suppression and target enhancement capabilities, but the tensor nuclear norm used by RIPT is the nuclear norm and SNN (Sum of Nuclear Norms). The literature "A new convex relaxation for tensor completion" points out that SNN is not the optimal convex approximation of the tensor rank. The nuclear norm gives all singular values the same weight, but in actual scenes, the singular values of the target content and noise are different, so RIPT will cause a local optimal solution and increase the false alarm rate in the target image. At the same time, the local structure weight in RIPT While highlighting the background edge, the target edge is also highlighted, resulting in a reduction in the target shape of the detection result, or even failure to detect the target. Therefore, an infrared dim target detection method combining tensor recovery and ATV is needed to overcome the above problems.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明的目的在于:本发明提供了一种结合ATV约束的张量恢复红外弱小目标检测方法,克服现有方法易受背景边缘和噪声的影响导致红外弱小目标检测中虚警率高的问题和核范数引起的局部最优性问题,提高目标检测和背景抑制能力,提高目标检测的准确率。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a tensor recovery infrared small target detection method combined with ATV constraints, which overcomes the problem that the existing method is easily affected by background edges and noise, resulting in a high false alarm rate in infrared small target detection and the local optimality problem caused by the nuclear norm, improves target detection and background suppression capabilities, and improves the accuracy of target detection.
本发明采用的技术方案如下:The technical solution adopted by the present invention is as follows:
一种结合ATV约束的张量恢复红外弱小目标检测方法,包括如下步骤:A tensor recovery infrared small target detection method combined with ATV constraints includes the following steps:
步骤1:构建原始图像的三阶张量;Step 1: Construct the third-order tensor of the original image;
步骤2:提取原始图像的先验信息,构建先验信息权重张量;Step 2: Extract the prior information of the original image and construct the prior information weight tensor;
步骤3:利用张量logDet函数和张量l1范数,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数,将三阶张量和先验信息权重张量输入目标函数,利用ADMM求解目标函数获取背景张量和目标张量;Step 3: Use the tensor logDet function and tensor l 1 norm, combined with the ATV constraint, to construct the objective function, input the third-order tensor and the prior information weight tensor into the objective function, and use ADMM to solve the objective function to obtain the background tensor and target tensor;
步骤4:根据背景张量和目标张量重构背景图像和目标图像;Step 4: Reconstruct the background image and the target image according to the background tensor and the target tensor;
步骤5:对目标图像进行自适应阈值分割确定目标的位置,输出目标检测结果。Step 5: Perform adaptive threshold segmentation on the target image to determine the location of the target and output the target detection result.
优选地,所述步骤1包括如下步骤:Preferably,
步骤1.1:获取原始图像其中,m和n分别表示图像的长和宽;Step 1.1: Get the original image Among them, m and n represent the length and width of the image respectively;
步骤1.2:采用大小为p×p的滑动窗口w、按步长为s遍历原始图像D;Step 1.2: Use a sliding window w of size p×p and traverse the original image D with a step size of s;
步骤1.3:将每次滑动窗口w中的图像小块作为一个正面切片,滑动q次后组建三阶张量 Step 1.3: Take the image block in each sliding window w as a front slice, and form a third-order tensor after sliding q times
优选地,所述步骤2包括如下步骤:Preferably,
步骤2.1:定义原始图像D的结构张量Jρ定义如下:Step 2.1: Define the structure tensor of the original image D Jρ is defined as follows:
其中,Kρ表示方差ρ的高斯核函数,*表示卷积运算,Dσ表示对原始图像进行方差为σ(>0)的高斯平滑滤波,表示克罗内克积,表示求梯度,表示Dσ沿x方向的梯度,表示Dσ沿y方向的梯度,J11替代J12替代Kρ*IxIy,J21替代Kρ*IxIy,J22替代 Among them, K ρ represents the Gaussian kernel function with variance ρ, * represents the convolution operation, and D σ represents the Gaussian smoothing filter with variance σ (>0) on the original image. represents the Kronecker product, represents the gradient, represents the gradient of Dσ along the x direction, represents the gradient of Dσ along the y direction, J 11 replaces J 12 replaces K ρ *I x I y , J 21 replaces K ρ *I x I y , J 22 replaces
步骤2.2:计算Jρ的特征值矩阵和计算如下:Step 2.2: Calculate the eigenvalue matrix of J ρ and The calculation is as follows:
步骤2.3:计算与目标相关的先验信息矩阵 Step 2.3: Calculate the prior information matrix related to the target
其中,⊙表示哈达马积;Among them, ⊙ represents the Hadamard product;
步骤2.4:计算与背景相关的先验信息矩阵 Step 2.4: Calculate the prior information matrix related to the background
Wm=max(λ1,λ2);W m =max(λ 1 ,λ 2 );
步骤2.5:根据得到的Wcs和Wm计算先验信息矩阵 Step 2.5: Calculate the prior information matrix based on the obtained W cs and W m
Wp=Wcs*Wm;W p =W cs *W m ;
对Wp作如下的归一化:Normalize W p as follows:
其中,wmin和wmax分别表示Wp的最小值和最大值;Wherein, w min and w max represent the minimum and maximum values of W p respectively;
步骤2.6:根据归一化的先验信息矩阵Wp构建先验信息权重张量构建方法为:采用大小为p×p的滑动窗口w遍历Wp,把每次滑动窗口w中的图像小块作为一个正面切片,滑动q次后,构成一个三阶张量即先验信息权重张量 Step 2.6: Construct the prior information weight tensor based on the normalized prior information matrix W p The construction method is: use a sliding window w of size p×p to traverse W p , and take the image block in each sliding window w as a front slice. After sliding q times, a third-order tensor, namely the prior information weight tensor, is constructed.
优选地,所述步骤3中构建目标函数包括如下步骤:Preferably, constructing the objective function in step 3 comprises the following steps:
步骤a1:三阶张量包括低秩张量和稀疏张量为分离低秩张量和稀疏张量将张量logDet函数作为低秩张量的正则化项,张量l1范数作为稀疏张量的正则化项,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数,公式如下:Step a1: Third-order tensor Including low-rank tensors and sparse tensors To separate low-rank tensors and sparse tensors The tensor logDet function is used as the regularization term of the low-rank tensor, the tensor l 1 norm is used as the regularization term of the sparse tensor, and the objective function is constructed in combination with the ATV constraint. The formula is as follows:
其中,η>0表示一个很小的正则化常数,λ和β表示平衡系数,logDet(·)表示张量的logDet函数,且有表示,表示的第i(1≤i≤p)个奇异值是沿第三维做离散傅里叶变换所得到的张量的第l个正面切片,下文的l表示相同的含义),||·||1表示张量l1范数(即张量中所有元素的奇异值之和),||·||HTV表示各向异性全变分约束,它的定义为其中 和分别表示水平和垂直的二维有限差分算子;Among them, η>0 represents a small regularization constant, λ and β represent balance coefficients, logDet(·) represents the logDet function of the tensor, and express, express The i-th (1≤i≤p) singular value of yes The lth positive slice of the tensor obtained by discrete Fourier transform along the third dimension, l has the same meaning below), ||·|| 1 represents the l 1 norm of the tensor (that is, the sum of the singular values of all elements in the tensor), and ||·|| HTV represents the anisotropic total variation constraint, which is defined as in and denote the horizontal and vertical two-dimensional finite difference operators respectively;
步骤a2:令表示稀疏权重张量,根据稀疏权重和先验信息权重张量定义权重张量公式如下:Step a2: Let Represents a sparse weight tensor, which defines a weight tensor based on sparse weights and prior information weight tensors The formula is as follows:
其中,c和ξ表示大于0的正数,./表示两个张量之间对应的元素相除;Among them, c and ξ represent positive numbers greater than 0, and ./ represents the division of corresponding elements between two tensors;
步骤a3:引入替代变量改写原目标函数如下:Step a3: Introducing substitution variables Rewrite the original objective function as follows:
则可得改写后目标函数的增广拉格朗日方程如下:Then the augmented Lagrangian equation of the rewritten objective function is as follows:
其中,和表示拉格朗日乘子,μ表示非负的惩罚因子,⊙表示哈达马积,<·>表示内积运算,||·||F表示Frobenius范数。in, and represents the Lagrange multiplier, μ represents a non-negative penalty factor, ⊙ represents the Hadamard product, <·> represents the inner product operation, and ||·|| F represents the Frobenius norm.
优选地,所述步骤3中将三阶张量和先验信息权重张量输入目标函数,利用ADMM求解目标函数包括如下步骤:Preferably, in step 3, the third-order tensor and the prior information weight tensor are input into the objective function, and solving the objective function using ADMM includes the following steps:
步骤b1:将由原图构建的三阶张量输入待求解的目标函数;Step b1: The third-order tensor constructed from the original image Input the objective function to be solved;
步骤b2:初始化增广拉格朗日方程参数,令迭代次数k=0,最大迭代次数为kmax;Step b2: Initialize the parameters of the augmented Lagrangian equation, set the number of iterations k = 0, and the maximum number of iterations is kmax;
步骤b3:在第k+1次迭代中,固定更新计算公式如下:Step b3: In the k+1th iteration, fix renew The calculation formula is as follows:
其中,Sτ(·)表示软阈值收缩算子,Sτ(x)=sgn(x)max(|x|-τ,0);Where S τ (·) represents the soft threshold shrinkage operator, S τ (x) = sgn(x)max(|x|-τ,0);
步骤b4:固定更新计算公式如下:Step b4: Fixing renew The calculation formula is as follows:
其中, 为的奇异值分解,为f-对角张量,并且这里,和分别表示和沿第三维做离散傅里叶变换得到的结果,表示在第k次迭代中,的第l个正面切片的第i个奇异值;in, for The singular value decomposition of is an f-diagonal tensor, and here, and Respectively and The result of discrete Fourier transform along the third dimension is: Indicates that in the kth iteration, The i-th singular value of the l-th positive slice of ;
步骤b5:固定更新如下:Step b5: Fixing renew as follows:
要求解上式,可把上式分为q个子问题来求解,子问题如下:To solve the above equation, we can divide it into q sub-problems to solve. The sub-problems are as follows:
此问题可由快速的迭代阈值收缩算法(Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm,FISTA)求解;This problem can be solved by the Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm (FISTA);
步骤b6:固定更新如下:Step b6: Fixing renew as follows:
步骤b7:固定更新和如下:Step b7: Fixing renew and as follows:
步骤b8:更新μk+1=ρμk,其中,ρ表示增长系数,ρ≥1;Step b8: Update μ k+1 =ρμ k , where ρ represents the growth coefficient, ρ≥1;
步骤b9:迭代次数k=k+1;Step b9: number of iterations k=k+1;
步骤b10:判断k是否大于kmax,若是,则停止迭代,转到步骤b11;若否,则满足以下条件时停止迭代,并转到步骤b11:Step b10: Determine whether k is greater than kmax . If so, stop the iteration and go to step b11. If not, stop the iteration and go to step b11 when the following conditions are met:
若迭代停止条件未满足,且迭代次数未到最大值,则转到步骤b3;If the iteration stop condition is not met and the number of iterations has not reached the maximum value, go to step b3;
步骤b11:求出最优解,输出背景张量和目标张量 Step b11: Find the optimal solution and output the background tensor and the target tensor
优选地,所述步骤4的具体步骤为:对于输入的背景张量按顺序取出的q个正面切片并依次重构获取背景图对于输入的目标张量按顺序取出的q个正面切片并依次重构获取目标图 Preferably, the specific steps of step 4 are: for the input background tensor Take out in order q frontal slices of And reconstruct the background image in sequence For the input target tensor Take out in order q frontal slices of And reconstruct the target graph in turn
综上所述,由于采用了上述技术方案,本发明的有益效果是:In summary, due to the adoption of the above technical solution, the beneficial effects of the present invention are:
1.本发明考虑到不同大小的奇异值的重要程度不同,本发明采用非凸的logDet函数来对张量秩进行约束,赋予不同奇异值不同的权重,加上函数的非凸性质,更加贴近张量真实的秩,解决了现有方法中由于采用赋予奇异值相同权重的核范数而导致的局部最优解,从而使得目标检测准确性低的问题,提高了目标检测和背景抑制的能力;1. Taking into account the different importance of singular values of different sizes, the present invention uses a non-convex logDet function to constrain the tensor rank, assigning different weights to different singular values. Combined with the non-convex nature of the function, it is closer to the true rank of the tensor, and solves the problem of low target detection accuracy caused by the local optimal solution in the existing method due to the use of the nuclear norm that assigns the same weight to the singular values, thereby improving the capabilities of target detection and background suppression;
2.本发明由于实际场景复杂多变,引入ATV专门对背景边缘的约束,ATV能够描述背景的内部平滑性和清晰性,与图像的梯度(高频成分)紧密相关,而边缘为高频成分,通过引入ATV正则项,可以更好地描述背景中的边缘,抑制目标分量中的稀疏边缘成分,解决了现有方法难以抑制具有稀疏性质的高亮边缘,而导致分离的目标中含有边缘噪声的问题,提高在非光滑和非均匀场景中的检测能力;2. Due to the complexity and changeability of actual scenes, the present invention introduces ATV to specifically constrain the background edge. ATV can describe the internal smoothness and clarity of the background, which is closely related to the gradient (high-frequency component) of the image. The edge is a high-frequency component. By introducing the ATV regularization term, the edge in the background can be better described, and the sparse edge components in the target component can be suppressed. This solves the problem that the existing method is difficult to suppress the highlight edge with sparse properties, resulting in edge noise in the separated target, and improves the detection capability in non-smooth and non-uniform scenes;
3.本发明同时利用与背景相关和与目标相关的先验信息,通过利用更加突显目标的权重,增加目标约束能力,同时把先验作为正则项的一部分被加入到了目标函数当中,使得目标函数要达到最优的条件更强,缩小了可行域的范围,提高了达到最优解的速度,加快算法收敛速度的同时提高了算法的鲁棒性;3. The present invention simultaneously utilizes prior information related to the background and the target, and increases the target constraint capability by utilizing a weight that highlights the target more. At the same time, the prior is added to the objective function as a part of the regular term, so that the objective function has stronger conditions to achieve the optimal solution, narrows the scope of the feasible domain, increases the speed of reaching the optimal solution, accelerates the convergence speed of the algorithm, and improves the robustness of the algorithm;
4.本发明把传统的红外弱小目标检测问题转化为求解张量恢复问题,不用提取任何特征便可自适应地分离出目标和背景,本发明的可适用性更广。4. The present invention transforms the traditional infrared dim target detection problem into a tensor recovery problem, and can adaptively separate the target and the background without extracting any features. The present invention has wider applicability.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例的技术方案,下面将对实施例中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,应当理解,以下附图仅示出了本发明的某些实施例,因此不应被看作是对范围的限定,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他相关的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention, the drawings required for use in the embodiments are briefly introduced below. It should be understood that the following drawings only show certain embodiments of the present invention and therefore should not be regarded as limiting the scope. For ordinary technicians in this field, other related drawings can be obtained based on these drawings without creative work.
图1为本发明的流程图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart of the present invention;
图2为本发明一幅含有弱小目标的红外图像;FIG2 is an infrared image of a small target according to the present invention;
图3为本发明由图2构建的三阶张量;FIG3 is a third-order tensor constructed from FIG2 according to the present invention;
图4为本发明由图2计算出的先验信息图以及先验信息张量;FIG4 is a priori information graph and a priori information tensor calculated by the present invention from FIG2;
图5为本发明由图3分离出的目标张量;FIG5 is a target tensor separated from FIG3 according to the present invention;
图6为本发明由图3分离出的背景张量;FIG6 is a background tensor separated from FIG3 according to the present invention;
图7为本发明由图5和图6重构的目标图像和背景图像;FIG7 is a target image and a background image reconstructed from FIG5 and FIG6 according to the present invention;
图8为本发明图2以及图5中的目标图像的灰度三维分布图;FIG8 is a three-dimensional grayscale distribution diagram of the target image in FIG2 and FIG5 of the present invention;
图9为本发明由图5中的目标图像经自适应阈值分割得到检测结果;FIG9 is a detection result obtained by adaptive threshold segmentation of the target image in FIG5 according to the present invention;
图10为LoG方法对图2的检测结果图及三维灰度图;FIG10 is a detection result diagram and a three-dimensional grayscale diagram of FIG2 using the LoG method;
图11为RLCM方法对图2的检测结果图以及三维灰度图;FIG11 is a diagram showing the detection result of FIG2 using the RLCM method and a three-dimensional grayscale diagram;
图12为IPI方法对图2的检测结果图以及三维灰度图;FIG12 is a diagram showing the detection result of FIG2 using the IPI method and a three-dimensional grayscale image;
图13为NIPPS方法对图2的检测结果图以及三维灰度图;FIG13 is a diagram showing the detection result of FIG2 using the NIPPS method and a three-dimensional grayscale image;
图14为RIPT方法对图2的检测结果图以及三维灰度图;FIG14 is a detection result diagram and a three-dimensional grayscale diagram of FIG2 using the RIPT method;
图15为RIPT方法与本发明先验信息示意图。FIG. 15 is a schematic diagram of the RIPT method and the prior information of the present invention.
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明,即所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。通常在此处附图中描述和示出的本发明实施例的组件可以以各种不同的配置来布置和设计。In order to make the purpose, technical scheme and advantages of the present invention more clearly understood, the present invention is further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention and are not used to limit the present invention, that is, the embodiments described are only part of the embodiments of the present invention, rather than all of the embodiments. The components of the embodiments of the present invention described and shown in the drawings herein can be arranged and designed in various different configurations.
因此,以下对在附图中提供的本发明的实施例的详细描述并非旨在限制要求保护的本发明的范围,而是仅仅表示本发明的选定实施例。基于本发明的实施例,本领域技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。Therefore, the following detailed description of the embodiments of the present invention provided in the accompanying drawings is not intended to limit the scope of the invention claimed for protection, but merely represents selected embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art without making creative work are within the scope of protection of the present invention.
需要说明的是,术语“第一”和“第二”等之类的关系术语仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的情况下,由语句“包括一个……”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备中还存在另外的相同要素。It should be noted that relational terms such as "first" and "second" are used only to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, and do not necessarily require or imply any such actual relationship or order between these entities or operations. Moreover, the terms "include", "comprise" or any other variants thereof are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion, so that a process, method, article or device including a series of elements includes not only those elements, but also other elements not explicitly listed, or also includes elements inherent to such process, method, article or device. In the absence of further restrictions, the elements defined by the sentence "comprise a ..." do not exclude the existence of other identical elements in the process, method, article or device including the elements.
以下结合实施例对本发明的特征和性能作进一步的详细描述。The features and performance of the present invention are further described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments.
实施例1Example 1
如图1-15所示,一种结合ATV约束的张量恢复红外弱小目标检测方法,包括如下步骤:As shown in FIG1-15, a tensor recovery infrared small target detection method combined with ATV constraints includes the following steps:
步骤1:构建原始图像的三阶张量;Step 1: Construct the third-order tensor of the original image;
步骤2:提取原始图像的先验信息,构建先验信息权重张量;Step 2: Extract the prior information of the original image and construct the prior information weight tensor;
步骤3:利用张量logDet函数和张量l1范数,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数,将三阶张量和先验信息权重张量输入目标函数,利用ADMM求解目标函数获取背景张量和目标张量;Step 3: Use the tensor logDet function and tensor l 1 norm, combined with the ATV constraint, to construct the objective function, input the third-order tensor and the prior information weight tensor into the objective function, and use ADMM to solve the objective function to obtain the background tensor and target tensor;
步骤4:根据背景张量和目标张量重构背景图像和目标图像;Step 4: Reconstruct the background image and the target image according to the background tensor and the target tensor;
步骤5:对目标图像进行自适应阈值分割确定目标的位置,输出目标检测结果。Step 5: Perform adaptive threshold segmentation on the target image to determine the location of the target and output the target detection result.
为提高弱小目标检测的准确率,需要克服核范数引起的局部最优性问题和图像中背景边缘和噪声对检测的影响,将张量logDet函数作为低秩张量的正则项,张量l1范数作为稀疏张量的正则项构建张量恢复目标函数,赋予不同奇异值不同的权重,加上函数的非凸性质,更加贴近张量真实的秩,解决了现有方法中采用赋予奇异值相同权重的核范数而导致局部最优解的问题;结合ATV,更好地描述背景中的边缘,抑制目标分量中的稀疏边缘成分;达到了提高目标检测和背景抑制能力,提高红外弱小目标检测准确率。In order to improve the accuracy of small target detection, it is necessary to overcome the local optimality problem caused by the nuclear norm and the influence of background edges and noise in the image on detection. The tensor logDet function is used as the regularization term of the low-rank tensor, and the tensor l 1 norm is used as the regularization term of the sparse tensor to construct the tensor recovery objective function. Different singular values are assigned different weights. Combined with the non-convex nature of the function, it is closer to the true rank of the tensor, and the problem of local optimal solution caused by the use of the nuclear norm that assigns the same weight to singular values in the existing method is solved; combined with ATV, the edges in the background are better described, and the sparse edge components in the target component are suppressed; the target detection and background suppression capabilities are improved, and the accuracy of infrared small target detection is improved.
根据附图进行效果分析:图2表示的是一幅背景复杂的红外图像,除了弱小目标之外,还有亮度很高的白色虚警源;图3是经过步骤1由原始图像构建的三阶张量图4是由步骤2提取到的先验信息以及对应的先验信息权重张量图5是经过步骤3分离得到的背景张量和目标张量图6是由步骤4重构的背景图像B与目标图像T;图7是原始图像D与目标图像T对应的灰度三维分布,可以看出,分离出的目标图像很好地压制了背景,除去小目标处,其余位置的背景的灰度均为0;图8是最终的检测结果;图9-图14是几种其他的方法(依次是LoG、RLCM、IPI、NIPPS和RIPT)对图2中小目标的检测结果(未阈值分割),以及对应的灰度三维分布图,可以看到,LoG和IPI(图10和图12)这两种方法对背景边缘和噪声极其敏感,RLCM和NIPPS(图11和图13)中,除去目标以外,还残留较多噪声,虚警率偏高,目标有不同程度的缩小,而RIPT(图14)则未检测到目标。综上,本申请背景抑制能力强,噪声极其小,无失真,目标检测的效果极佳,目标检测准确度大大提高。The effect analysis is carried out according to the attached figures: Figure 2 shows an infrared image with a complex background. In addition to the weak target, there is also a bright white false alarm source; Figure 3 is the third-order tensor constructed from the original image after
实施例2Example 2
基于实施例1,细化本申请的步骤,详细记载解决技术问题采用的技术手段:利用张量logDet函数和张量l1范数,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数,将三阶张量和先验信息权重张量输入目标函数,利用ADMM求解目标函数获取背景张量和目标张量。Based on Example 1, the steps of this application are refined and the technical means used to solve the technical problems are recorded in detail: the objective function is constructed by using the tensor logDet function and the tensor l 1 norm, combined with the ATV constraint, the third-order tensor and the prior information weight tensor are input into the objective function, and the objective function is solved by ADMM to obtain the background tensor and the target tensor.
步骤1包括如下步骤:
步骤1.1:获取待处理的红外图像D∈Rm×n,大小为245×326;Step 1.1: Get the infrared image D∈R m×n to be processed, with a size of 245×326;
步骤1.2:采用大小为40×40的滑动窗口w、按步长为40遍历原始图像D,把每次滑动窗口w中大小为40×40的矩阵作为一个正面切片;Step 1.2: Use a sliding window w of
步骤1.3:根据窗口滑动次数(本实施例为63)重复步骤1.2直至遍历完成,将所有正面切片组成新的三阶张量 Step 1.3: Repeat step 1.2 according to the number of window sliding times (63 in this example) until the traversal is completed, and form all the front slices into a new third-order tensor
如图2所示,表示的是一幅背景复杂的红外图像,除了弱小目标之外,还有亮度很高的白色虚警源;如图3所示,表示经过步骤1由原始图像构建的三阶张量 As shown in Figure 2, it shows an infrared image with a complex background. In addition to the weak target, there is also a white false alarm source with high brightness. As shown in Figure 3, it shows the third-order tensor constructed from the original image in
步骤2:提取原始图像的先验信息,构建先验信息权重张量;Step 2: Extract the prior information of the original image and construct the prior information weight tensor;
步骤3包括如下步骤:Step 3 includes the following steps:
步骤3.1:利用张量logDet函数,张量l1范数,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数;Step 3.1: Use the tensor logDet function, tensor l 1 norm, and ATV constraints to construct the objective function;
步骤3.2:将三阶张量和先验信息权重张量输入目标函数,利用ADMM求解目标函数,解出背景张量和目标张量 Step 3.2: Convert the third-order tensor and the prior information weight tensor Input the objective function, use ADMM to solve the objective function, and solve the background tensor and the target tensor
步骤3.1包括如下步骤:Step 3.1 includes the following steps:
步骤3.1.1:三阶张量包括低秩张量和稀疏张量为分离低秩张量和稀疏张量将张量logDet函数作为低秩张量的正则化项,张量l1范数作为稀疏张量的正则化项,结合ATV约束,构建目标函数,公式如下:Step 3.1.1: Third-order tensor Including low-rank tensors and sparse tensors To separate low-rank tensors and sparse tensors The tensor logDet function is used as the regularization term of the low-rank tensor, the tensor l 1 norm is used as the regularization term of the sparse tensor, and the objective function is constructed in combination with the ATV constraint. The formula is as follows:
其中,η>0表示一个很小的正则化常数,λ和β表示平衡系数,logDet(·)表示张量的logDet函数,且有表示,表示的第i(1≤i≤40)个奇异值是沿第三维做离散傅里叶变换所得到的张量的第l个正面切片,下文的l表示相同的含义),||·||1表示张量l1范数(即张量中所有元素的奇异值之和),||·||HTV表示各向异性全变分约束,它的定义为其中 和分别表示水平和垂直的二维有限差分算子;Among them, η>0 represents a small regularization constant, λ and β represent balance coefficients, logDet(·) represents the logDet function of the tensor, and express, express The i-th (1≤i≤40) singular value of yes The lth positive slice of the tensor obtained by discrete Fourier transform along the third dimension, l has the same meaning below), ||·|| 1 represents the l 1 norm of the tensor (that is, the sum of the singular values of all elements in the tensor), and ||·|| HTV represents the anisotropic total variation constraint, which is defined as in and denote the horizontal and vertical two-dimensional finite difference operators respectively;
步骤3.1.2:令表示稀疏权重张量,则有Step 3.1.2: Order represents a sparse weight tensor, then
其中,c和ξ表示大于0的正数,则最终的权重张量的定义如下:Among them, c and ξ represent positive numbers greater than 0, so the final weight tensor is defined as follows:
其中,./表示两个张量之间对应的元素相除;Among them, ./ represents the division of corresponding elements between two tensors;
步骤3.1.3:引入替代变量改写原目标函数如下:Step 3.1.3: Introducing alternative variables Rewrite the original objective function as follows:
则可得改写后目标函数的增广拉格朗日方程如下:Then the augmented Lagrangian equation of the rewritten objective function is as follows:
其中,和表示拉格朗日乘子,μ表示非负的惩罚因子,⊙表示哈达马积,<·>表示内积运算,||·||F表示Frobenius范数。in, and represents the Lagrange multiplier, μ represents a non-negative penalty factor, ⊙ represents the Hadamard product, <·> represents the inner product operation, and ||·|| F represents the Frobenius norm.
步骤3.2包括如下步骤:Step 3.2 includes the following steps:
步骤3.2.1:将由原图构建的三阶张量输入待求解的目标函数;Step 3.2.1: The third-order tensor constructed from the original image Input the objective function to be solved;
步骤3.2.2:初始化增广拉格朗日方程参数,令迭代次数k=0,最大迭代次数为kmax=500,ρ=1.05,μ0=0.001,c=1,ξ=0.01,η=0.2,β=0.5;Step 3.2.2: Initialize the parameters of the augmented Lagrangian equation, set the number of iterations k = 0, the maximum number of iterations is kmax = 500, ρ = 1.05, μ0 = 0.001, c=1, ξ=0.01, η=0.2, β=0.5;
步骤3.2.3:在第k+1次迭代中,固定更新计算公式如下:Step 3.2.3: In the k+1th iteration, fix renew The calculation formula is as follows:
其中,Sτ()表示软阈值收缩算子,Sτ(x)=sgn(x)max(|x|-τ,0);Wherein, S τ () represents the soft threshold shrinkage operator, S τ (x) = sgn(x)max(|x|-τ,0);
步骤3.2.4:固定更新计算公式如下:Step 3.2.4: Fixation renew The calculation formula is as follows:
其中, 为的奇异值分解,为f-对角张量,并且这里,和分别表示和沿第三维做离散傅里叶变换得到的结果,表示在第k次迭代中,的第l个正面切片的第i个奇异值;in, for The singular value decomposition of is an f-diagonal tensor, and here, and Respectively and The result of discrete Fourier transform along the third dimension is: Indicates that in the kth iteration, The i-th singular value of the l-th positive slice of ;
步骤3.2.5:固定更新如下:Step 3.2.5: Fixation renew as follows:
要求解上式,可把上式分为q个子问题来求解,子问题如下:To solve the above equation, we can divide it into q sub-problems to solve. The sub-problems are as follows:
此问题可由快速的迭代阈值收缩算法(Fast Iterative Shrinkage-ThresholdingAlgorithm,FISTA)求解;This problem can be solved by the Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm (FISTA);
步骤3.2.6:固定更新如下:Step 3.2.6: Fixation renew as follows:
步骤3.2.7:固定更新和如下:Step 3.2.7: Fixation renew and as follows:
步骤3.2.8:更新μk+1=ρμk,其中,ρ表示增长系数,ρ≥1;Step 3.2.8: Update μ k+1 =ρμ k , where ρ represents the growth coefficient, ρ ≥ 1;
步骤3.2.9:迭代次数k=k+1;Step 3.2.9: Iteration number k = k + 1;
步骤3.2.10:判断k是否大于kmax,若是,则停止迭代,转到步骤3.2.11;若否,则满足以下条件时停止迭代,并转到步骤3.2.11:Step 3.2.10: Determine whether k is greater than k max . If so, stop the iteration and go to step 3.2.11. If not, stop the iteration and go to step 3.2.11 when the following conditions are met:
若迭代停止条件未满足,且迭代次数未到最大值,则转到步骤3.2.3;If the iteration stop condition is not met and the number of iterations has not reached the maximum value, go to step 3.2.3;
步骤3.2.11:求出最优解,输出背景张量和目标张量输出的带*的符号表示最优解,在迭代收敛后得到的B和T的解即分离出的目标张量和背景张量。Step 3.2.11: Find the optimal solution and output the background tensor and the target tensor The output symbol with * represents the optimal solution. The solutions of B and T obtained after iterative convergence are the separated target tensor and background tensor.
步骤4的具体步骤为:对于输入的背景张量按顺序取出的63个正面切片并依次重构获取背景图对于输入的目标张量按顺序取出的63个正面切片并依次重构获取目标图 The specific steps of step 4 are: for the input background tensor Take out in order 63 frontal slices And reconstruct the background image in sequence For the input target tensor Take out in order 63 frontal slices And reconstruct the target graph in sequence
步骤5的具体步骤为:对目标图像T进行自适应阈值分割,阈值Th=m+c*σ,其中,m表示目标图像T中所有灰度的均值,σ表示目标图像T中所有灰度的标准差,c=5,分割完成获取目标检测结果。The specific steps of step 5 are: perform adaptive threshold segmentation on the target image T, the threshold Th = m + c * σ, where m represents the mean of all grayscales in the target image T, σ represents the standard deviation of all grayscales in the target image T, c = 5, and the segmentation is completed to obtain the target detection result.
如图7所示,通过本发明的方法将背景图像经过计算和处理获取最终的目标图像,完全抑制背景,无噪声,无失真;采用比SNN近似低秩能力更强的非凸的logDet函数来约束背景,ATV能够描述背景的内部平滑性和清晰性,与图像的梯度(高频成分)紧密相关,而边缘为高频成分,通过引入ATV正则项,可以更好地描述背景中的边缘,抑制目标分量中的稀疏边缘成分,解决了现有方法难以抑制具有稀疏性质的高亮边缘,而导致分离的目标中含有边缘噪声的问题,提高在非光滑和非均匀场景中的检测能力,从而提高目标检测准确性。As shown in Figure 7, the background image is calculated and processed by the method of the present invention to obtain the final target image, which completely suppresses the background, is noise-free, and has no distortion. A non-convex logDet function with stronger low-rank approximation ability than SNN is used to constrain the background. ATV can describe the internal smoothness and clarity of the background, which is closely related to the gradient (high-frequency component) of the image. The edge is a high-frequency component. By introducing the ATV regularization term, the edge in the background can be better described, and the sparse edge components in the target component can be suppressed. This solves the problem that the existing method is difficult to suppress highlighted edges with sparse properties, resulting in edge noise in the separated target, and improves the detection capability in non-smooth and non-uniform scenes, thereby improving the accuracy of target detection.
实施例3Example 3
基于实施例1,本实施例细化步骤2,提取原始图像的先验信息,构建先验信息权重张量,利用与背景、与目标相关的先验信息,保证目标不失真,加快了算法的收敛速度,也提高对算法的鲁棒性。Based on Example 1, this example refines
步骤2包括如下步骤:
步骤2.1:定义原始图像D的结构张量Jρ定义如下:Step 2.1: Define the structure tensor of the original image D Jρ is defined as follows:
其中,Kρ表示方差2的高斯核函数,*表示卷积运算,Dσ表示对原图进行方差为9的高斯平滑滤波,表示克罗内克积,表示求梯度,表示Dσ沿x方向的梯度,表示Dσ沿y方向的梯度,J11替代J12替代Kρ*IxIy,J21替代Kρ*IxIy,J22替代 Among them, K ρ represents the Gaussian kernel function with
步骤2.2:计算Jρ的特征值矩阵和计算如下:Step 2.2: Calculate the eigenvalue matrix of J ρ and The calculation is as follows:
步骤2.3:计算与目标相关的先验信息矩阵 Step 2.3: Calculate the prior information matrix related to the target
其中,⊙表示哈达马积;Among them, ⊙ represents the Hadamard product;
步骤2.4:计算与背景相关的先验信息矩阵 Step 2.4: Calculate the prior information matrix related to the background
Wm=max(λ1,λ2);W m =max(λ 1 ,λ 2 );
步骤2.5:根据得到的Wcs和Wm的计算先验信息矩阵 Step 2.5: Calculate the prior information matrix based on the obtained W cs and W m
Wp=Wcs*Wm;W p =W cs *W m ;
对Wp作如下的归一化:Normalize W p as follows:
其中,wmin和wmax分别表示Wp的最小值和最大值;Wherein, w min and w max represent the minimum and maximum values of W p respectively;
步骤2.6:根据归一化的先验信息矩阵Wp构建先验信息权重张量构建方法为:采用大小为40×40的滑动窗口w遍历Wp,把每次滑动窗口w中的图像小块作为一个正面切片,滑动63次后构成一个三阶张量 Step 2.6: Construct the prior information weight tensor based on the normalized prior information matrix W p The construction method is: use a sliding window w of
如图15所示,(a)为RIPT中得到的先验信息图,(b)为本方法所得先验信息图,通过观察两幅图可以发现,本发明的先验信息图只突出目标,而RIPT在突出目标边缘的同时也突出了边缘;因此本发明通过利用更加突显目标的权重,增强了目标约束能力;利用与背景相关和与目标相关的先验信息,把先验作为正则项的一部分被加入到了目标函数当中,使得目标函数要达到最优的条件更强,缩小了可行域的范围,提高了达到最优解的速度,加快算法收敛速度的同时提高了算法的鲁棒性。As shown in Figure 15, (a) is the prior information graph obtained in RIPT, and (b) is the prior information graph obtained by this method. By observing the two figures, it can be found that the prior information graph of the present invention only highlights the target, while RIPT highlights the edge while highlighting the edge of the target; therefore, the present invention enhances the target constraint ability by utilizing weights that highlight the target more; utilizing the background-related and target-related prior information, the prior is added to the objective function as part of the regularization term, so that the objective function has stronger conditions for reaching the optimal solution, narrows the scope of the feasible domain, increases the speed of reaching the optimal solution, accelerates the convergence speed of the algorithm, and improves the robustness of the algorithm.
以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention and is not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent substitutions and improvements made within the spirit and principles of the present invention should be included in the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910202771.1A CN109934815B (en) | 2019-03-18 | 2019-03-18 | A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910202771.1A CN109934815B (en) | 2019-03-18 | 2019-03-18 | A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN109934815A CN109934815A (en) | 2019-06-25 |
| CN109934815B true CN109934815B (en) | 2023-04-14 |
Family
ID=66987341
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910202771.1A Active CN109934815B (en) | 2019-03-18 | 2019-03-18 | A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN109934815B (en) |
Families Citing this family (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110619624B (en) * | 2019-08-22 | 2022-03-01 | 深圳大学 | Image decomposition method and device |
| CN110969638B (en) * | 2019-11-12 | 2023-09-29 | 桂林电子科技大学 | A tensor-based background subtraction method and system |
| CN110992342B (en) * | 2019-12-05 | 2023-04-18 | 电子科技大学 | SPCP infrared small target detection method based on 3DATV constraint |
| CN111191547A (en) * | 2019-12-23 | 2020-05-22 | 中电健康云科技有限公司 | Medical waste online screening method based on hyperspectral deconvolution and unmixing |
| CN111738926B (en) * | 2020-01-17 | 2024-10-15 | 西安万宏电子科技有限公司 | Method for restoring image |
| CN112305548B (en) * | 2020-10-28 | 2022-08-19 | 西北工业大学 | Real-time detection method for moving small target in active sonar echo map |
| CN112946636B (en) * | 2021-01-13 | 2023-06-20 | 电子科技大学 | A Multi-Frequency Near-Field Millimeter Wave Sparse Image Reconstruction Method |
| CN113256585B (en) * | 2021-05-24 | 2022-11-11 | 北京理工大学 | Real-time detection method for small infrared video moving target based on space-time tensor decomposition |
| CN113409261B (en) * | 2021-06-13 | 2024-05-14 | 西北工业大学 | Hyperspectral anomaly detection method based on spatial spectrum feature joint constraint |
| CN113393402B (en) * | 2021-06-25 | 2022-09-13 | 广东工业大学 | Method for restoring image background based on tensor ring decomposition |
| CN113421279B (en) * | 2021-07-07 | 2023-03-31 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | Infrared weak and small target detection method based on weighted nuclear norm minimization |
| CN113450413B (en) * | 2021-07-19 | 2022-09-27 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Ship target detection method based on GF4 single-frame image |
| CN114782789B (en) * | 2022-02-14 | 2025-03-21 | 中国科学院空天信息创新研究院 | Time-sensitive small target detection method and device for infrared scene based on space-time tensor |
| CN114742720B (en) * | 2022-03-16 | 2023-03-14 | 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳) | Tensor completion method, tensor completion device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN114882231B (en) * | 2022-05-25 | 2024-12-10 | 南京邮电大学 | A method for infrared small target detection based on multi-angle prior analysis |
| CN114898117B (en) * | 2022-05-25 | 2025-02-11 | 南京邮电大学 | A target detection method for sequential infrared images based on equalized structure and texture representation |
| CN115205696B (en) * | 2022-05-30 | 2024-11-05 | 电子科技大学 | Infrared imaging false alarm source and target cooperative modeling and detection method |
| CN115184889B (en) * | 2022-06-07 | 2025-11-14 | 北京理工大学 | A Ground Penetrating Radar Clutter Suppression Method Based on Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition and Total Variation |
| CN115345902A (en) * | 2022-07-20 | 2022-11-15 | 上海卫星工程研究所 | Infrared image dim target detection tracking method and system based on machine learning |
| CN115100415B (en) * | 2022-08-04 | 2024-12-31 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Infrared small target detection method, device and storage medium in complex noise scene |
| CN116485834B (en) * | 2023-05-11 | 2025-11-21 | 中国人民解放军火箭军工程大学 | Method, device, equipment and medium for detecting infrared dim target |
| CN116883447A (en) * | 2023-05-15 | 2023-10-13 | 电子科技大学 | Infrared image target and background separation method and system based on space-time tensor decomposition |
| CN116777847A (en) * | 2023-05-31 | 2023-09-19 | 电子科技大学 | Non-singular value decomposition detection method for infrared weak and small target |
| CN118733852B (en) * | 2024-09-02 | 2024-12-13 | 威海润蓝水处理设备有限公司 | Visualization system and method for whole production process of MVR scraper crystallizer |
| CN120747042B (en) * | 2025-08-19 | 2025-11-07 | 陕西凝远新材料科技股份有限公司 | Autoclaved aerated concrete plate surface flatness evaluation method |
Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1169071A (en) * | 1996-02-27 | 1997-12-31 | 佳能株式会社 | Billing device, communication device and communication system |
| CN1194541A (en) * | 1997-03-25 | 1998-09-30 | 三星电子株式会社 | Design Method of NTSC Band-Stop Filter and Receiver Using the Filter |
| CN101604383A (en) * | 2009-07-24 | 2009-12-16 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A Maritime Target Detection Method Based on Infrared Image |
| CN103020897A (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2013-04-03 | 香港应用科技研究院有限公司 | Apparatus, system and method for super-resolution reconstruction of single-frame image based on multi-blocks |
| CN103605122A (en) * | 2013-12-04 | 2014-02-26 | 西安电子科技大学 | Receiving-transmitting type robust dimensionality-reducing self-adaptive beam forming method of coherent MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar |
| CN105913448A (en) * | 2016-05-25 | 2016-08-31 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Hyperspectral image target detection method based on tensor matched subspace |
| CN106097321A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-11-09 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of polarization high spectrum image object detection method based on tensor representation |
| CN106250873A (en) * | 2016-08-16 | 2016-12-21 | 四川大学 | Extracting of Moving Object and device |
| CN106610483A (en) * | 2016-11-11 | 2017-05-03 | 长江大学 | MIMO radar angle estimation algorithm based on tensor space and spectral peak search |
| CN107038436A (en) * | 2017-05-24 | 2017-08-11 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of high spectrum image object detection method based on tensor Spectral match filter |
| CN108710851A (en) * | 2018-05-21 | 2018-10-26 | 闽南师范大学 | seismic signal random noise attenuation method, terminal device and storage medium |
| CN109215025A (en) * | 2018-09-25 | 2019-01-15 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of method for detecting infrared puniness target approaching minimization based on non-convex order |
| CN109325446A (en) * | 2018-09-19 | 2019-02-12 | 电子科技大学 | An infrared weak and small target detection method based on weighted truncation kernel norm |
| CN109447073A (en) * | 2018-11-08 | 2019-03-08 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of method for detecting infrared puniness target based on tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7471975B2 (en) * | 2004-09-22 | 2008-12-30 | The Research Foundation Of State University Of New York | Optical tensor imaging |
| US9082164B2 (en) * | 2008-04-04 | 2015-07-14 | Lina Jamil Karam | Automatic cell migration and proliferation analysis |
-
2019
- 2019-03-18 CN CN201910202771.1A patent/CN109934815B/en active Active
Patent Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1169071A (en) * | 1996-02-27 | 1997-12-31 | 佳能株式会社 | Billing device, communication device and communication system |
| CN1194541A (en) * | 1997-03-25 | 1998-09-30 | 三星电子株式会社 | Design Method of NTSC Band-Stop Filter and Receiver Using the Filter |
| CN101604383A (en) * | 2009-07-24 | 2009-12-16 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A Maritime Target Detection Method Based on Infrared Image |
| CN103020897A (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2013-04-03 | 香港应用科技研究院有限公司 | Apparatus, system and method for super-resolution reconstruction of single-frame image based on multi-blocks |
| CN103605122A (en) * | 2013-12-04 | 2014-02-26 | 西安电子科技大学 | Receiving-transmitting type robust dimensionality-reducing self-adaptive beam forming method of coherent MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar |
| CN105913448A (en) * | 2016-05-25 | 2016-08-31 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Hyperspectral image target detection method based on tensor matched subspace |
| CN106097321A (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2016-11-09 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of polarization high spectrum image object detection method based on tensor representation |
| CN106250873A (en) * | 2016-08-16 | 2016-12-21 | 四川大学 | Extracting of Moving Object and device |
| CN106610483A (en) * | 2016-11-11 | 2017-05-03 | 长江大学 | MIMO radar angle estimation algorithm based on tensor space and spectral peak search |
| CN107038436A (en) * | 2017-05-24 | 2017-08-11 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A kind of high spectrum image object detection method based on tensor Spectral match filter |
| CN108710851A (en) * | 2018-05-21 | 2018-10-26 | 闽南师范大学 | seismic signal random noise attenuation method, terminal device and storage medium |
| CN109325446A (en) * | 2018-09-19 | 2019-02-12 | 电子科技大学 | An infrared weak and small target detection method based on weighted truncation kernel norm |
| CN109215025A (en) * | 2018-09-25 | 2019-01-15 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of method for detecting infrared puniness target approaching minimization based on non-convex order |
| CN109447073A (en) * | 2018-11-08 | 2019-03-08 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of method for detecting infrared puniness target based on tensor Robust Principal Component Analysis |
Non-Patent Citations (5)
| Title |
|---|
| Tensor Completion for Estimating Missing Values in Visual Data;J. Liu;《IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence》;20131231;第208-220页 * |
| 图像自适应中基于形变控制的细缝剪裁方法;张琳等;《信号处理》;20151225(第12期);第82-87页 * |
| 基于小波和SVR的红外弱小目标检测方法;荣健等;《西南交通大学学报》;20081015(第05期);第5-10页 * |
| 多传感器分布式检测系统的跨层优化设计;刘向阳等;《半导体光电》;20160815(第04期);第105-112+116页 * |
| 面向目标检测的稀疏表示方法研究进展;高仕博等;《电子学报》;20150215(第02期);第114-126页 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109934815A (en) | 2019-06-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109934815B (en) | A Tensor Restoration Infrared Weak Small Target Detection Method Combined with ATV Constraints | |
| CN109447073B (en) | An infrared weak and small target detection method based on tensor robust principal component analysis | |
| CN110992342B (en) | SPCP infrared small target detection method based on 3DATV constraint | |
| Rejeesh et al. | MOTF: Multi-objective Optimal Trilateral Filtering based partial moving frame algorithm for image denoising | |
| Ye et al. | Dynamic texture based smoke detection using Surfacelet transform and HMT model | |
| CN114897741B (en) | Image blind deblurring method based on depth residual Fourier transform | |
| CN110188614B (en) | A Finger Vein Denoising Method Based on Skin Crack Segmentation with NLM Filtering | |
| CN108830818B (en) | Rapid multi-focus image fusion method | |
| CN110796625B (en) | Image compressed sensing reconstruction method based on group sparse representation and weighted total variation | |
| CN109934178A (en) | A Kronecker-Based Sparse Representation-Based Method for Infrared Small and Small Target Detection | |
| CN105046664B (en) | A kind of image de-noising method based on adaptive EPLL algorithms | |
| CN109215025B (en) | Infrared weak and small target detection method based on non-convex rank approach minimization | |
| CN108198147A (en) | A kind of method based on the multi-source image fusion denoising for differentiating dictionary learning | |
| CN114820352A (en) | Hyperspectral image denoising method and device and storage medium | |
| Guo et al. | Infrared and visible image fusion based on saliency and fast guided filtering | |
| Hu | Variable lighting face recognition using discrete wavelet transform | |
| Wang et al. | Latent representation learning model for multi-band images fusion via low-rank and sparse embedding | |
| CN111814682A (en) | Face living body detection method and device | |
| Deng | Guided wavelet shrinkage for edge-aware smoothing | |
| CN112085683A (en) | A depth map reliability detection method in saliency detection | |
| CN119850467A (en) | Polarized image defogging method based on double-iteration regular separation | |
| Wang et al. | Fusion of infrared and visible images based on fuzzy logic and guided filtering | |
| CN116777847A (en) | Non-singular value decomposition detection method for infrared weak and small target | |
| Guo et al. | Event-driven multimodal fusion for image motion deblurring | |
| Baiju et al. | L 1/2 regularized joint low rank and sparse recovery technique for illumination map estimation in low light image enhancement |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |