CN107911414B - Data access system - Google Patents
Data access system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN107911414B CN107911414B CN201710982909.5A CN201710982909A CN107911414B CN 107911414 B CN107911414 B CN 107911414B CN 201710982909 A CN201710982909 A CN 201710982909A CN 107911414 B CN107911414 B CN 107911414B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data access
- network
- address information
- switch
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/10—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network
- H04L67/1097—Protocols in which an application is distributed across nodes in the network for distributed storage of data in networks, e.g. transport arrangements for network file system [NFS], storage area networks [SAN] or network attached storage [NAS]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/0604—Improving or facilitating administration, e.g. storage management
- G06F3/0607—Improving or facilitating administration, e.g. storage management by facilitating the process of upgrading existing storage systems, e.g. for improving compatibility between host and storage device
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0655—Vertical data movement, i.e. input-output transfer; data movement between one or more hosts and one or more storage devices
- G06F3/0658—Controller construction arrangements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/067—Distributed or networked storage systems, e.g. storage area networks [SAN], network attached storage [NAS]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
- Multi Processors (AREA)
Abstract
The invention discloses a data access system, which comprises at least one data access module and a network switch. The data access module comprises at least one storage unit, a switching chip and a main control unit. The storage unit stores data of the data access system. The exchange chip stores a first address information table which contains address information corresponding to the storage unit. The main control unit comprises a network controller and two network interfaces. The network switch is coupled with the data access module. The network switch sends a data access request received from the remote client to the network controller through the two network interfaces, the network controller generates a data access instruction containing access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access instruction to the switching chip, the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, and then the storage unit executes data access with the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of data access, in particular to a data access system.
Background
Generally, the high-density storage system currently on the market is mainly a storage system based on SAS interface, and the access to the storage system is realized through a Central Processing Unit (CPU) of a motherboard. However, such a system has a slow access speed, and thus, the system has insufficient performance for a storage server system requiring a timely response.
In addition, the host of the conventional storage system needs to be connected to the storage system by a cable (cable), which causes waste in component usage and high power consumption and cost. Therefore, there is still room for improvement in the design of the storage system.
Disclosure of Invention
The present invention is directed to a data access system, which solves the problems of insufficient storage performance, waste of components, high power consumption and high cost in the prior art.
To solve the above problems, an embodiment of the present invention provides a data access system, which includes at least one data access module and a network switch. The at least one data access module comprises at least one storage unit, a switching chip and a main control unit. At least one memory cell stores data of the data access system. The switching chip is coupled to the at least one storage unit and stores a first address information table, wherein the first address information table includes address information corresponding to the at least one storage unit. The main control unit is coupled with the exchange chip and comprises a network controller and two network interfaces. The network switch is coupled with the data access module. The network switch sends a data access request received from the remote client to the network controller through the two network interfaces, the network controller generates a data access instruction containing access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access instruction to the switching chip, the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, and then the at least one storage unit executes data access with the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch.
After the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, the at least one storage unit provides the stored data to the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch, or acquires and stores the data transmitted from the remote client.
The network switch stores a second address information table which contains address information corresponding to the data access module, and the step of sending a data access request received from a remote client to the network controller through the two network interfaces comprises the step of sending the data access request to the network controller of the corresponding data access module by the network switch according to the data access request and the second address information table.
Wherein the data access system further comprises a bandwidth extension interface. The bandwidth expansion interface is coupled with the switching chip and the network controller to increase the bandwidth of data transmission between the switching chip and the network controller.
The bandwidth expansion interface is an interface of PCIE x 16.
Wherein the data access system further comprises a backplane. The two network interfaces are arranged on the back plate.
The at least one storage unit is a solid state disk.
The two network interfaces are respectively network interface controller interfaces, and the switching chip is a PCIE exchanger.
The switching chip is coupled to the at least one memory unit in series.
The switching chip is coupled to the at least one memory unit in parallel.
According to the technical scheme of the invention, the data access request received from the remote client is sent to the network controller through the two network interfaces by the network switch. Then, the network controller generates a data access instruction containing access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access instruction to the switching chip. And then, after the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, the at least one storage unit executes data access with the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch. Therefore, the main control unit does not need to read the data stored in the storage unit to the memory first, but directly exchanges the data in the storage unit with the network controller of the main control unit so as to meet more service requests in real time, and the system efficiency is higher.
Drawings
The accompanying drawings, which are included to provide a further understanding of the invention and are incorporated in and constitute a part of this application, illustrate embodiment(s) of the invention and together with the description serve to explain the invention without limiting the invention. In the drawings:
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a data access system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a coupling relationship between a memory unit and a switch chip according to an embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 3 is a block diagram of another data access system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
Detailed Description
In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more apparent, the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
In the embodiments listed below, the same or similar elements or components will be denoted by the same reference numerals.
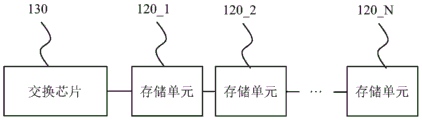
Fig. 1 is a block diagram of a data access system according to an embodiment of the present invention. The data access system 100 includes data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M and a network switch 160, wherein M is a positive integer greater than 0. For convenience of description, the data access module 110_1 is taken as an example for description in the present embodiment, and fig. 1 only illustrates the internal components and the connection relationship of the data access module 110_1, and the connection relationship and the corresponding implementation manner of the internal components and the internal components of the remaining data access modules 110_2 to 110_ M can refer to the data access module 110_ 1.
The data access module 110_1 includes memory units 120_1 to 120_ N, a switch chip 130 and a main control unit 140, wherein N is a positive integer greater than 0. The memory units 120_1 to 120_ N store data of the data access system 100. In the embodiment, the storage units 120_1 to 120_ N are solid state disks.
The switching chip 130 is coupled to the memory units 120_1 to 120_ N and stores a first address information table. The first address information table includes address information corresponding to the storage units 120_1 to 120_ N, and the first address information table can be pre-stored in the switch chip 130 by a user. In this embodiment, when N is equal to 1, which means that there are 1 memory cells, for example, the memory cell 120_1, the switch chip is coupled to the memory cell 120_ 1. When N is greater than or equal to 2, it means that there are a plurality of memory units, such as memory units 120_ 1-120 _ N, and the memory units 120_ 1-120 _ N are coupled to the switch chip 130 in parallel, as shown in FIG. 1. However, the embodiment is not limited thereto, and in another embodiment, when N is greater than or equal to 2, which means that there are a plurality of memory units, such as the memory units 120_1 to 120_ N, the memory units 120_1 to 120_ N are coupled to the switch chip 130 in series, as shown in fig. 2.
The main control unit 140 is coupled to the switch chip 130, and the main control unit 140 includes a network controller 141 and two network interfaces 142 and 143. The two network interfaces 142 and 143 are network interface controller interfaces, respectively, and the switch chip 130 is a PCIE switch. Network switch 160 is coupled to data access module 110_ 1.
In this embodiment, when a user sends a data access request to the network switch 160 through the remote client 180, the network switch 160 sends the data access request received from the remote client 180 to the network controller 141 through the two network interfaces 142 and 143. Then, the network controller 141 generates a data access command including access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access command to the switch chip 130. Then, the switch chip 130 finds the memory cell (e.g., the memory cell 120_1) corresponding to the access address according to the first address information table, so as to send the data access instruction to the memory cell 120_1 corresponding to the access address information. Then, when the storage unit 120_1 performs data access with the remote client 180 through the switch chip 130, the network controller 141, the two network interfaces 142 and 143, and the network switch 160. For the remaining embodiments of the memory cells 120_2 to 120_ N, reference may be made to the embodiment of the memory cell 120_1, and thus, the description thereof is omitted.
Therefore, the main control unit 140 does not need to read the data stored in the storage units 120_2 to 120_ N to the memory of the main control unit 140 first, but the data in the storage units 120_2 to 120_ N is directly exchanged with the network controller 141 of the main control unit 140, so that the processor (CPU) of the server is in an off-load state, and does not need to process specific data exchange, so as to satisfy more service requests in time, and thus the system efficiency is higher.
Further, after the switch chip 130 sends the data access instruction to the storage unit 120_1 corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, the storage unit 120_1 provides the stored data to the remote client 180 through the switch chip 130, the network controller 141, the two network interfaces 142 and 143, and the network switch 160, or obtains and stores the data transmitted from the remote client 180.
In addition, the network switch 160 stores a second address information table, wherein the second address information table includes address information corresponding to the data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M. That is, when the user sends a data access request to the network switch 160 through the remote client 180, the network switch 160 finds a data access module, such as the data access module 110_1, corresponding to the data access request and the second address information table according to the data access request and the second address information table. Then, the network switch 160 sends the data access request to the network controller 141 of the data access module 110_1 through the two network interfaces 142 and 143 of the data access module 110_ 1. The embodiments of the other data access modules 110_2 to 110_ M can refer to the embodiment of the data access module 110_1, and thus are not described herein again.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram of another data access system according to an embodiment of the present invention. The data access system 300 includes data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M and a network switch 160, wherein M is a positive integer greater than 0. The data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M respectively include memory units 120_1 to 120_ N, a switch chip 130, a main control unit 140 and a bandwidth extension interface 310, wherein N is a positive integer greater than 0. The data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M, the network switch 160, the storage units 120_1 to 120_ N, the switch chip 130 and the main control unit 140 are the same as or similar to the data access modules 110_1 to 110_ M, the network switch 160, the storage units 120_1 to 120_ N, the switch chip 130 and the main control unit 140 of fig. 1, and reference may be made to the description of the embodiment of fig. 1, so that no further description is provided herein.
In addition, in FIG. 3, the memory units 120_1 to 120_ N and the switching chip 130 are coupled in parallel. However, the embodiment is not limited thereto, when N is greater than or equal to 2, which means that there are a plurality of memory cells, the memory cells 120_1 to 120_ N are coupled to the switch chip 130 in series, as shown in fig. 2.
In addition, the main control unit 140 includes a network controller 141 and two network interfaces 142 and 143. The network controller 141 and the two network interfaces 142 and 143 are also the same as or similar to the network controller 141 and the two network interfaces 142 and 143 of fig. 1, and reference may be made to the description of the embodiment of fig. 1, so that no further description is provided herein.
The bandwidth expansion interface 310 couples the switch chip 130 and the network controller 141 to increase the bandwidth of data transmission between the switch chip 130 and the network controller 141. In this embodiment, the bandwidth extension interface 310 is an interface of PCIE x 16. Therefore, the uplink bandwidth of the system can reach 32GB/S (256Gb/S), and the requirement of high-speed data calculation and access can be met, so that the convenience in use is improved.
Further, each of the data access systems 110_1 to 110_ M further includes a backplane 220. The two network interfaces 142 and 143 are disposed on the backplane 220.
In summary, according to the technical solution of the present invention, the network switch sends the data access request received from the remote client to the network controller through the two network interfaces. Then, the network controller generates a data access instruction containing access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access instruction to the switching chip. And then, after the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, the at least one storage unit executes data access with the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch. Therefore, the main control unit does not need to read the data stored in the storage unit to the memory firstly, but directly exchanges the data in the storage unit with the network controller of the main control unit, so that the processor of the server is in a dismounting state without processing specific data exchange, more service requests are met in real time, the system efficiency is higher, and the convenience in use is further improved.
The above description is only an example of the present invention, and is not intended to limit the present invention, and it is obvious to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the present invention. Any modification, equivalent replacement, or improvement made within the spirit and principle of the present invention should be included in the scope of the claims of the present invention.
Claims (10)
1. A data access system, comprising:
at least one data access module, comprising:
at least one storage unit for storing data of the data access system;
a switching chip, coupled to the at least one memory cell, for storing a first address information table, where the first address information table includes address information corresponding to the at least one memory cell;
a main control unit coupled to the switch chip and including a network controller and two network interfaces;
a network switch coupled to the data access module;
the network switch sends a data access request received from a remote client to the network controller through the two network interfaces, the network controller generates a data access instruction containing access address information according to the data access request and sends the data access instruction to the switching chip, the switching chip sends the data access instruction to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, and then the at least one storage unit executes data access with the remote client through the switching chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch.
2. The data access system of claim 1, wherein after the switch chip sends the data access command to the at least one storage unit corresponding to the access address information according to the first address information table, the at least one storage unit provides the stored data to a remote client through the switch chip, the network controller, the two network interfaces and the network switch, or obtains and stores the data transmitted from the remote client.
3. The data access system of claim 1, wherein the network switch stores a second address information table containing address information corresponding to the data access module, and wherein the step of the network switch sending a data access request received from a remote client to the network controller via the two network interfaces comprises the network switch sending the data access request to the network controller corresponding to the data access module according to the data access request and the second address information table.
4. The data access system of claim 1, further comprising: and the bandwidth expansion interface is coupled with the switching chip and the network controller so as to increase the bandwidth of data transmission between the switching chip and the network controller.
5. The data access system of claim 4, wherein the bandwidth extension interface is a PCIE x16 interface.
6. The data access system of claim 1, further comprising: the two network interfaces are arranged on the back plate.
7. The data access system of claim 1, wherein the at least one storage unit is a solid state drive.
8. The data access system of claim 1, wherein the two network interfaces are network interface controller interfaces, respectively, and the switch chip is a PCIE switch.
9. The data access system of claim 1, wherein the at least one memory cell is a plurality of memory cells, and the plurality of memory cells are coupled in series with the switch chip.
10. The data access system of claim 1, wherein the at least one memory unit is multiple, and the multiple memory units are coupled in parallel with the switch chip.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710982909.5A CN107911414B (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2017-10-20 | Data access system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710982909.5A CN107911414B (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2017-10-20 | Data access system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN107911414A CN107911414A (en) | 2018-04-13 |
| CN107911414B true CN107911414B (en) | 2020-10-20 |
Family
ID=61841616
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710982909.5A Active CN107911414B (en) | 2017-10-20 | 2017-10-20 | Data access system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN107911414B (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102890621A (en) * | 2011-07-22 | 2013-01-23 | 弗森-艾奥公司 | Apparatus, system and method for determining a configuration parameter for solid-state storage media |
| CN104111907A (en) * | 2014-06-27 | 2014-10-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for accessing NVMe storage device and NVMe storage device |
| CN105556930A (en) * | 2013-06-26 | 2016-05-04 | 科内克斯实验室公司 | NVM EXPRESS controller for remote memory access |
| CN106155959A (en) * | 2015-05-11 | 2016-11-23 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Data transmission method and data transmission system |
| CN107170474A (en) * | 2016-03-07 | 2017-09-15 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Expandable memory cartridge, computer-implemented method, and computer-readable storage device |
-
2017
- 2017-10-20 CN CN201710982909.5A patent/CN107911414B/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102890621A (en) * | 2011-07-22 | 2013-01-23 | 弗森-艾奥公司 | Apparatus, system and method for determining a configuration parameter for solid-state storage media |
| CN105556930A (en) * | 2013-06-26 | 2016-05-04 | 科内克斯实验室公司 | NVM EXPRESS controller for remote memory access |
| CN104111907A (en) * | 2014-06-27 | 2014-10-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for accessing NVMe storage device and NVMe storage device |
| CN106155959A (en) * | 2015-05-11 | 2016-11-23 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Data transmission method and data transmission system |
| CN107170474A (en) * | 2016-03-07 | 2017-09-15 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Expandable memory cartridge, computer-implemented method, and computer-readable storage device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107911414A (en) | 2018-04-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108062285B (en) | NVMe storage device and method for accessing same | |
| CN102063274B (en) | Storage array, storage system and data access method | |
| US6421742B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for emulating an input/output unit when transferring data over a network | |
| CN101477511B (en) | Method and apparatus for sharing memory medium between multiple operating systems | |
| US20180225254A1 (en) | Network communications using pooled memory in rack-scale architecture | |
| CN107992436A (en) | A kind of NVMe data read-write methods and NVMe equipment | |
| CN114546913B (en) | Method and device for high-speed data interaction between multiple hosts based on PCIE interface | |
| CN103907088A (en) | Method and apparatus for scalable low latency solid state drive interface | |
| US10951741B2 (en) | Computer device and method for reading or writing data by computer device | |
| US7774514B2 (en) | Method of transmitting data between storage virtualization controllers and storage virtualization controller designed to implement the method | |
| CN106844249B (en) | RAID storage system and method based on RapidIO bus | |
| CN102065071A (en) | Storage equipment supporting multi-transport protocol | |
| CN111190749A (en) | Server and method for data exchange between BMC and BIOS | |
| WO2024179298A1 (en) | Cross-cabinet server memory pooling method, apparatus and device, server, and medium | |
| CN102843435A (en) | Access and response method and access and response system of storing medium in cluster system | |
| CN1331070C (en) | Method and equipment of data communication | |
| US9116881B2 (en) | Routing switch apparatus, network switch system, and routing switching method | |
| US8065401B2 (en) | Systems and methods for frame ordering in wide port SAS connections | |
| CN114238156A (en) | Processing system and method of operating a processing system | |
| CN107911414B (en) | Data access system | |
| CN116601616A (en) | Data processing device, method and related equipment | |
| CN107408071A (en) | A kind of memory pool access method, device and system | |
| CN105511990A (en) | Novel dual-redundancy storage control node architecture based on fusion architecture | |
| CN104035529A (en) | Ice storage server | |
| CN104035524B (en) | A kind of cold storage server |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |