CN102180780A - Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle - Google Patents
Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102180780A CN102180780A CN2011100530428A CN201110053042A CN102180780A CN 102180780 A CN102180780 A CN 102180780A CN 2011100530428 A CN2011100530428 A CN 2011100530428A CN 201110053042 A CN201110053042 A CN 201110053042A CN 102180780 A CN102180780 A CN 102180780A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- alkyl
- phenyl
- substituted phenyl
- och
- indanone
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Abstract
本发明涉及通式(1)的化合物或其药用可接受的盐、酯、酰胺或前药作为淀粉样蛋白沉积物与神经纤维缠结的显像剂和聚集抑制剂的用途,以及用于显像的标记化合物的制备方法,并涉及向淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结输送该类化合物的方法。该类化合物作为用于检测体内或组织淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结的显像剂时,需使用合适的放射性同位素或适用于磁共振检测的造影剂对其进行标记。该化合物尤其用于诊断和治疗包括阿尔茨海默病在内的患有淀粉样蛋白沉积和神经纤维缠结疾病的患者。
The present invention relates to the use of a compound of general formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, amide or prodrug thereof as an imaging agent and an aggregation inhibitor for amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles, and for Methods for the preparation of marker compounds for imaging, and methods of delivering such compounds to amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles. When such compounds are used as imaging agents for detecting amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in vivo or in tissues, they need to be labeled with appropriate radioactive isotopes or contrast agents suitable for magnetic resonance detection. The compounds are especially useful in the diagnosis and treatment of patients suffering from amyloid deposition and neurofibrillary tangle diseases, including Alzheimer's disease.
Description
发明领域field of invention
本发明涉及新的生物活性化合物及其用途,及使用放射性同位素或磁共振造影剂标记的化合物进行诊断和治疗的方法,同时涉及标记化合物的制备方法。The present invention relates to a new biologically active compound and its application, a method for diagnosis and treatment using a radioactive isotope or magnetic resonance contrast agent-labeled compound, and a preparation method for the labeled compound.
背景技术Background technique
阿尔茨海默氏病(Alzheimer’s Disease,AD)是一种隐匿发病并进行性加重的神经退行性疾病,主要临床表现为认知功能减退、不可逆的记忆缺失、定向力障碍和语言功能障碍等。脑组织尸检证实有大量的由淀粉样蛋白-β(Aβ)肽聚集而形成的老年斑(Senile plaques,SPs)和许多由高度磷酸化的tau蛋白的细丝形成的神经纤维缠结(neurofibrillary tangles,NFTs),以及神经元和突触的丢失等,本发明中提到的淀粉样沉积物包括但不限于老年斑。Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease with insidious onset and progressive aggravation. The main clinical manifestations are cognitive decline, irreversible memory loss, disorientation and language dysfunction. Brain tissue autopsy confirmed a large number of senile plaques (Senile plaques, SPs) formed by amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide aggregation and many neurofibrillary tangles (neurofibrillary tangles) formed by filaments of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, NFTs), and the loss of neurons and synapses, etc., the amyloid deposits mentioned in the present invention include but are not limited to senile plaques.
淀粉样蛋白沉积物构成的老年斑和神经纤维缠结作为AD的两个标志物,也是临床尸检或活检诊断AD的金标准。目前,淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结的检测方法主要包括活组织检查和尸检材料的组织学分析等。这两种方法都有明显的缺陷:活组织检查有较大的创伤和风险,尸检仅能用于死后诊断等。因此,一种简单有效且非侵入性的在患者脑中检测并定量淀粉样蛋白沉积物的方法将对相关疾病尤其是阿尔茨海默病的诊断和治疗很有用。Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles composed of amyloid deposits, as two markers of AD, are also the gold standard for diagnosis of AD by clinical autopsy or biopsy. Currently, methods for the detection of amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles mainly include biopsy and histological analysis of autopsy material. These two methods have obvious defects: biopsy has greater trauma and risk, and autopsy can only be used for postmortem diagnosis. Therefore, a simple, effective and non-invasive method to detect and quantify amyloid deposits in patient brains would be useful for the diagnosis and treatment of related diseases, especially Alzheimer's disease.
由于脑内的淀粉样蛋白沉积物与正常脑组织具有许多相同的物理性质(例如密度和水分含量),因此这些沉积物在体内难以直接成像。以前试图使用磁共振成像(MRI)和计算机X线断层摄影术(CT)对淀粉样蛋白沉积物直接成像(不使用探针)的研究,效果都难以令人满意或者仅在某些有利条件下才能检测到淀粉样蛋白沉积物。Because amyloid deposits in the brain share many of the same physical properties (such as density and water content) with normal brain tissue, these deposits are difficult to directly image in vivo. Previous attempts to image amyloid deposits directly (without probes) using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) have been unsatisfactory or only under certain favorable conditions to detect amyloid deposits.
过去一些经典的荧光染料,如刚果红(Congo Red,CR)、硫黄素S(Thioflavin S,ThS)等都能在体外高度特异性地结合淀粉样蛋白沉积物(老年斑)和神经纤维缠结。如果将这些高亲和力的配体改造并使用放射性同位素或磁共振造影剂标记,若这些标记好的配体能顺利进入脑组织,那就可以采用正电子发射体层摄影 术(PET)、单光子发射计算体层摄影术(SPECT)或磁共振成像(MRI)技术来对AD患者老年斑进行分布、定量等在体可视化检测,从而提高诊断的准确性,同时也可以为抗Aβ的药物的研究和治疗提供直观的评价,从而为早期诊断打下基础。Some classic fluorescent dyes in the past, such as Congo Red (CR), Thioflavin S (ThS), etc., can bind amyloid deposits (senile plaques) and neurofibrillary tangles with high specificity in vitro. If these high-affinity ligands are engineered and labeled with radioisotopes or magnetic resonance contrast agents, and if these labeled ligands can enter brain tissue smoothly, then positron emission tomography (PET), single photon Emission computed tomography (SPECT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology can be used to visually detect the distribution and quantification of senile plaques in AD patients, so as to improve the accuracy of diagnosis, and it can also be used for the research and development of anti-Aβ drugs. Treatment provides intuitive evaluation, thereby laying the foundation for early diagnosis.
检测活体脑内的Aβ淀粉样蛋白沉积物的配体必需能顺利穿过血脑屏障(Blood-Brain-Barrier,BBB)。刚果红、硫黄素S和硫黄素T等由于分子较大或带有电荷而难以通过血脑屏障。使用具有相对小的分子大小(与刚果红相比)的配体可以提高脑摄取并增加亲脂性。目前比较有潜力的几个配体,大都是基于刚果红、硫黄素T、硫黄素S)的结构改造,例如[11C]PIB(Mathis,Wang et al.2003.46:2740-54;Wang,Klunk et al.2004.24:55-62;Klunk,Lopresti et al.2005.25:10598-606.),[123I]IBOX(Zhuang,Kung et al.2001.28:887-94.),[123I]IMPY(Kung,Hou et al.2002.956:202-10;Zhuang,Kung et al.2003.46:237-43.;Cai,Chin et al.2004.47:2208-18.;Newberg,Wintering etal.2006.47:748-54.),[18F]FDDNP(Agdeppa,Kepe et al.2001.21:RC189.;Shoghi-Jadid,Small et al.2002.10:24-35.;Nordberg 2004.3:519-27.),[11C]SB-13(Verhoeff,Wilson et al.2004.12:584-595.;Ono,Wilson et al.2003.30:565-571.;Zhang,Oya et al.2005.48:5980-8.)[11C]-BF-227(Okamura,Suemoto et al.2005.25:10857-62;Kudo,Okamura et al.2007.48:553-61.),其中[18F]FDDNP,[11C]PIB,[11C]SB-13,[11C]-BF-227,都已经用AD患者和年龄匹配的正常老年人利用正电子发射体层摄影术(PET)做了一些临床研究。(Shoghi-Jadid,Small et al.2002.10:24-35.;Klunk,W.E.,H.Engler,et al.(2004).55(3):306-19.;Verhoeff,N.P.L.G.,A.A.Wilson,etal.(2004).12(6):584-595.;Kudo,Okamura et al.2007.48:553-61.;Nordberg,A.2007.20:398-402.)。Ligands for detecting Aβ amyloid deposits in living brains must be able to pass through the blood-brain barrier (Blood-Brain-Barrier, BBB) smoothly. Congo red, Thioflavin S, and Thioflavin T are difficult to pass through the blood-brain barrier due to their large size or charge. Using a ligand with a relatively small molecular size (compared to Congo red) can enhance brain uptake and increase lipophilicity. At present, several potential ligands are mostly based on structural modification of Congo red, Thioflavin T, and Thioflavin S), such as [ 11 C]PIB (Mathis, Wang et al.2003.46: 2740-54; Wang, Klunk et al.2004.24:55-62; Klunk, Lopresti et al.25:10598-606.), [ 123 I]IBOX (Zhuang, Kung et al.28:887-94.), [ 123 I]IMPY (Kung , Hou et al.2002.956:202-10; Zhuang, Kung et al.2003.46:237-43.; Cai, Chin et al.2004.47:2208-18.; Newberg, Wintering et al.2006.47:748-54.), [ 18 F]FDDNP (Agdeppa, Kepe et al.21: RC189.; Shoghi-Jadid, Small et al. 2002.10: 24-35.; Nordberg 2004.3: 519-27.), [ 11 C]SB-13 (Verhoeff , Wilson et al.2004.12:584-595.; Ono, Wilson et al.2003.30:565-571.; Zhang, Oya et al.2005.48:5980-8.) [ 11 C]-BF-227 (Okamura, Suemoto et al.2005.25:10857-62; Kudo, Okamura et al.2007.48:553-61.), where [ 18 F]FDDNP, [ 11 C]PIB, [ 11 C]SB-13, [ 11 C]-BF -227, both have been studied clinically using positron emission tomography (PET) in AD patients and age-matched normal elderly. (Shoghi-Jadid, Small et al. 2002.10: 24-35.; Klunk, WE, H. Engler, et al. (2004). 55(3): 306-19.; Verhoeff, NPLG, AAWilson, et al. ( 2004). 12(6): 584-595.; Kudo, Okamura et al. 2007. 48: 553-61.; Nordberg, A. 2007. 20: 398-402.).
目前已有的靶向配体按照与Aβ淀粉样蛋白沉积物结合位点的不同主要分为以下几类:The existing targeting ligands are mainly divided into the following categories according to the different binding sites with Aβ amyloid deposits:
1.刚果红和柯胺G的类似物1. Analogs of Congo Red and Chrysamine G
使用与刚果红结构类似的柯胺G(Chrysamine G)及其衍生物,如X-34、ISB、BSB、IMSB、FSB也能有效地结合Aβ。但进一步研究表明,柯胺G的疏水性虽有所增加,但脑吸收也比较低。把柯胺G进行结构修饰制备了X-34、BSB、ISB、IMSB。放射性碘标记的ISB和IMSB脑吸收仍比硫黄素-T衍生物低,可能是其结构中的羧基影响了通过血脑屏障的能力。Chrysamine G and its derivatives, such as X-34, ISB, BSB, IMSB, and FSB, which are similar in structure to Congo red, can also effectively bind Aβ. However, further studies have shown that although the hydrophobicity of Chrysamine G has increased, the brain absorption is also relatively low. X-34, BSB, ISB and IMSB were prepared by modifying the structure of Chrysamine G. The brain uptake of radioactive iodine-labeled ISB and IMSB is still lower than that of thioflavin-T derivatives, which may be due to the carboxyl group in its structure affecting the ability to pass through the blood-brain barrier.
2.苯并噻唑类(硫黄素T类似物)和茋类2. Benzothiazoles (thioflavin T analogues) and stilbenes
为了提高硫黄素T的脑通透性,对其进行分子结构改造,得到几种衍生物,如TZDM、IBOX、IMPY、6-OH-BTA-1。其中,[125I]TZDM、[125I]IBOX虽能结合淀粉样蛋白,但正常小鼠脑清除较慢,表明可能在体内存在较高程度的非特异性结合。[11C]6-OH-BTA-1(PIB)是一种效果很好的AD分子探针材料,对于正常小鼠脑具有高的脑吸收和快速的脑清除,PIB的人体试验表明和正常人脑相比AD病人的脑有高吸收。In order to improve the brain permeability of Thioflavin T, its molecular structure was modified to obtain several derivatives, such as TZDM, IBOX, IMPY, and 6-OH-BTA-1. Among them, although [ 125 I]TZDM and [ 125 I]IBOX can bind amyloid, they are cleared slowly in the brain of normal mice, indicating that there may be a high degree of non-specific binding in vivo. [ 11 C]6-OH-BTA-1 (PIB) is a very effective molecular probe material for AD. It has high brain uptake and rapid brain clearance for normal mouse brain. The human brain has a higher uptake than that of AD patients.
茋类的[11C]SB-13在检测老年斑时显示出潜力,它具有中等的亲脂性,对于正常小鼠脑皮层有较高的初始脑吸收和快速脑清除。以半衰期更长的氟同位素18F标记,研究表明这类化合物也是很有潜力的老年斑影像剂。[ 11 C]SB-13 of the stilbene class shows potential in detecting senile plaques, it has moderate lipophilicity, and has high initial brain uptake and rapid brain clearance for normal mouse cerebral cortex. Labeled with 18 F, a fluorine isotope with a longer half-life, studies have shown that this type of compound is also a potential age spot imaging agent.
3.FDDNP类3. FDDNP class
将非甾体类抗炎药萘普生和布洛芬进行结构改造,得到了一个中性亲脂的荧光染料DDNP,再以氟标记为18FDDNP。这种放射性配体的PET结果显示能结合老年斑和神经元纤维缠结,而且亲脂性高,易于通过血脑屏障。临床研究表明,AD 病人的PET显像显示18FDDNP的浓集和18FDG低代谢的位置一致,而正常对照组无浓集。18FDDNP的不足是从正常脑区的清除较慢。The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs naproxen and ibuprofen were structurally modified to obtain a neutral lipophilic fluorescent dye DDNP, which was then labeled with fluorine as 18 FDDNP. The PET results of this radioligand show that it can bind to senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, and has high lipophilicity, which makes it easy to pass through the blood-brain barrier. Clinical studies have shown that the PET imaging of AD patients shows that the concentration of 18 FDDNP is consistent with the position of hypometabolism of 18 FDG, while the normal control group has no concentration. 18 FDDNP deficiency is slower to clear from normal brain regions.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提供了茚酮类衍生物通式1-33中的化合物作为淀粉样蛋白聚合物和神经纤维缠结的显像剂和抑制剂的用途,以及用于显像的标记化合物的制备方法,并涉及向淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结输送该类化合物的方法。该类化合物尤其用于诊断、评价和治疗包括阿尔茨海默病在内的患有淀粉样蛋白聚集和神经纤维缠结疾病的患者。The present invention provides the use of compounds in the general formula 1-33 of indanone derivatives as imaging agents and inhibitors of amyloid polymers and neurofibrillary tangles, as well as a preparation method of the labeled compound for imaging, It also relates to methods of delivering such compounds to amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles. Such compounds are especially useful in the diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of patients suffering from amyloid aggregation and neurofibrillary tangle diseases, including Alzheimer's disease.
通式1-33中的新颖化合物或其药用可接受的盐、酯、酰胺或前药:Novel compounds of general formula 1-33 or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, amides or prodrugs thereof:
式中,In the formula,
R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、R6、R7、R8独立地表示氢、氚、卤素、-OH、-NH2、NHRa、NRaRb、-COOH、COORa、-NO2、-OC1-C12烷基、C1-C12烷基、-CF3、-CN、-OCH2-苯基、-OCH2取代苯基、-O-苯基、-O-取代苯基、-CH=CH-苯基、-CH=CH-取代苯基、-O(CH2)mNRaRb、-CO-NRaRb或NHCO-Ra、-Sn(烷基)3、99mTc络合物、123I、125I、131I、11C、13N、15O、18F、 22Na、52Fe、64Cu、68Ga、76Br、82Rb、18F(C1-5)烷基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]氨基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]烷基氨基其中Ra和Rb独立地表示氢、C1-6烷基或-(CH2)m-苯基,m为1-5;R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , and R 8 independently represent hydrogen, tritium, halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , NHR a , NR a R b , -COOH, COOR a , -NO 2 , -OC 1 -C 12 alkyl, C 1 -C 12 alkyl, -CF 3 , -CN, -OCH 2 -phenyl, -OCH 2 substituted phenyl, -O-phenyl , -O-substituted phenyl, -CH=CH-phenyl, -CH=CH-substituted phenyl, -O(CH 2 ) m NR a R b , -CO-NR a R b or NHCO-R a , -Sn(alkyl) 3 , 99 mTc complex , 123 I, 125 I, 131 I, 11 C, 13 N, 15 O, 18 F, 22 Na, 52 Fe, 64 Cu, 68 Ga, 76 Br, 82 Rb, 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]amino, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]alkylamino wherein R a and R b are independent Ground represents hydrogen, C 1-6 alkyl or -(CH 2 ) m -phenyl, m is 1-5;
n为0-5;n is 0-5;
X1、X2、X3、X4独立的表示C、O、S、N;X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , X 4 independently represent C, O, S, N;
中 独立地表示为单键、双键或三键; middle independently represented as a single bond, double bond or triple bond;
X’表示氢、氚、卤素、99mTc络合物、123I、125I、131I、11C、13N、15O、18F、22Na、52Fe、 64Cu、68Ga、76Br、82Rb、18F(C1-5)烷基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]氨基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]烷基氨基、Sn(烷基)3;X' represents hydrogen, tritium, halogen, 99 mTc complex, 123 I, 125 I, 131 I, 11 C, 13 N, 15 O, 18 F, 22 Na, 52 Fe, 64 Cu, 68 Ga, 76 Br , 82 Rb, 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]amino, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]alkylamino, Sn(alkyl) 3 ;
Q表示取代的或非取代的芳环或者杂环;Q represents a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic or heterocyclic ring;
B、D独立表示为C、N、O;B and D are independently expressed as C, N, O;
A表示C、O、S、N;A means C, O, S, N;
Z1表示氢、氚、卤素、-OH、-NH2、-NHRa、-NRaRb、-COOH、-COORa、-NO2、-OC1-12烷基、C1-12烷基、-CF3、-CN、-OCH2-苯基、-OCH2取代苯基、-O-苯基、-O-取代苯基、-CH=CH-苯基、-CH=CH-取代苯基、-O(CH2)mNRaRb、-CONRaRb或NHCORa、Sn(烷基)3、99mTc络合物、123I、125I、131I、11C、13N、15O、18F、22Na、52Fe、64Cu、68Ga、 76Br、82Rb、18F(C1-5)烷基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]氨基、[18F(C1-5)烷基]烷基氨基;其中Ra和Rb独立地表示氢、C1-6烷基或-(CH2)m-苯基、m为1-5。Z 1 represents hydrogen, tritium, halogen, -OH, -NH 2 , -NHR a , -NR a R b , -COOH, -COOR a , -NO 2 , -OC 1-12 alkyl, C 1-12 alkane -CF3, -CN, -OCH 2 -phenyl, -OCH 2 substituted phenyl, -O-phenyl, -O-substituted phenyl, -CH=CH-phenyl, -CH=CH-substituted phenyl group, -O(CH 2 ) m NR a R b , -CONR a R b or NHCOR a , Sn(alkyl) 3 , 99 mTc complex, 123 I, 125 I, 131 I, 11 C, 13 N , 15 O, 18 F, 22 Na, 52 Fe, 64 Cu, 68 Ga, 76 Br, 82 Rb, 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]amino, [ 18 F(C 1-5 )alkyl]alkylamino; wherein R a and R b independently represent hydrogen, C 1-6 alkyl or -(CH 2 ) m -phenyl, and m is 1-5.
本发明还提供了诊断组合物,它包括一种放射性标记或磁共振造影剂的通式1-33的化合物和一种药用可接受的载体、赋型剂或稀释剂。The present invention also provides a diagnostic composition comprising a compound of formula 1-33 as a radiolabel or magnetic resonance contrast agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, excipient or diluent.
本发明还提供了该诊断组合物作为淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结的显像剂的用途和使用方法,使用方法包括将可检测量的通式1-33的标记化合物或其药用可接受的盐、酯、酰胺或前药引入到哺乳动物或患者体内,过一定的时间待其与蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结结合,然后使用对应仪器进行显像。The present invention also provides the use and method of using the diagnostic composition as an imaging agent for amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles. Acceptable salts, esters, amides or prodrugs are introduced into mammals or patients, and after a certain period of time, they are combined with protein deposits and neurofibrillary tangles, and then imaged using corresponding instruments.
本发明还提供了通式1-33的化合物作为淀粉样蛋白沉积物和神经纤维缠结的聚集抑制剂的用途和使用方法,使用方法包括在一段时间内给予哺乳动物或患者一种抑制量的通式1-33的化合物或一种药用可接受的盐、酯、酰胺或前药。The present invention also provides the use and method of use of the compound of general formula 1-33 as an aggregation inhibitor of amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles, the method of use comprising administering to a mammal or a patient an inhibitory amount of A compound of general formula 1-33 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, amide or prodrug.
当本发明通式1-33的化合物作为在体显像剂时,必须使用合适的放射性同位素或者适用于磁共振检测的造影剂对其进行标记。When the compound of the general formula 1-33 of the present invention is used as an in vivo imaging agent, it must be labeled with a suitable radioactive isotope or a contrast agent suitable for magnetic resonance detection.
对于放射性药物成像而言,可以标记的成像基团可能基于两类同位素。常用于单光子发射计算体层摄影术(SPECT)的例如99mTc(T1/2=6小时;140KeV)和 123I(T1/2=13小时;159KeV),或者常用于正电子发射体层摄影术(PET)的,例如 11C(T1/2=20分钟;511KeV)和18F(T1/2=110分钟;511KeV)等。For radiopharmaceutical imaging, the imaging moieties that can be labeled may be based on two classes of isotopes. Commonly used in single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) such as 99 mTc (T 1/2 = 6 hours; 140 KeV) and 123 I (T 1/2 = 13 hours; 159 KeV), or commonly used in positron emitters For tomography (PET), for example, 11 C (T 1/2 = 20 minutes; 511KeV) and 18 F (T 1/2 = 110 minutes; 511KeV) and the like.
通式1-33的药用标记化合物通常是药用组合物的一部分并且通过本领域技术人员公知的方法施于组织或患者。例如,该化合物可以经口腔、静脉内、肌内、皮下、直肠、脑池内、阴道内、腹腔内、膀胱内、局部(粉剂、软膏或滴剂)或作为颊用或鼻用喷剂等给药方式进行给药。A pharmaceutically acceptable marker compound of general formula 1-33 is usually part of a pharmaceutical composition and administered to a tissue or patient by methods well known to those skilled in the art. For example, the compound can be administered orally, intravenously, intramuscularly, subcutaneously, rectally, intracisternally, intravaginally, intraperitoneally, intravesically, topically (powder, ointment or drops), or as a buccal or nasal spray, etc. Drug administration.
将标记化合物给药于患者可采用全身或局部给药途径。例如,标记化合物可以以传输于患者全身的方式给药。也可将标记化合物给药于特定器官或感兴趣的组织。例如,将脑中的淀粉样沉积物定位和定量,以诊断或追踪阿尔茨海默病的 发病进程。Administration of a labeled compound to a patient may be by systemic or local routes of administration. For example, a labeled compound can be administered in a system that is delivered throughout the body of the patient. Labeled compounds may also be administered to specific organs or tissues of interest. For example, localizing and quantifying amyloid deposits in the brain to diagnose or track the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
通式1-33的化合物如果可以与金属形成稳定的螯合物,若由此形成的螯合物作为放射性或磁共振成像诊断剂足够稳定,则其本身可以立即给药或者贮藏直到其使用。如果需要的话,该诊断剂可以含有任意添加剂如pH控制剂(例如,酸、碱、缓冲剂)、稳定剂(例如,维生素C)或等渗剂(例如,氯化钠)。Compounds of general formula 1-33, if they can form stable chelates with metals, and if the chelates thus formed are sufficiently stable as radiological or magnetic resonance imaging diagnostic agents, can be administered as such or stored until their use. The diagnostic agent may contain optional additives such as pH control agents (eg, acids, bases, buffers), stabilizers (eg, vitamin C) or isotonic agents (eg, sodium chloride), if necessary.
除了在阿尔茨海默病中作为病理特征之外,淀粉样蛋白沉积物还和以下疾病有关:瘙痒病(Scrapie)、Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease(CJD克雅(氏)病)、库鲁病(Kuru disease)、Down氏综合征、II型糖尿病胰岛瘤、甲状腺的骨髓癌、自发性骨髓瘤、地中海热病、淀粉样蛋白多发性神经病、淀粉样蛋白心肌病、全身性老年淀粉样蛋白病、Muckle-Wells综合征、具有淀粉样变的遗传性脑出血、分离的心房性淀粉样蛋白、包涵体肌炎和肌肉萎缩病中的β2-淀粉样蛋白沉积物等。In addition to being a pathological feature in Alzheimer's disease, amyloid deposits are also associated with the following diseases: Scrapie, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease), Kuru disease disease), Down's syndrome, type II diabetic insulinoma, bone marrow carcinoma of the thyroid, idiopathic myeloma, Mediterranean fever, amyloid polyneuropathy, amyloid cardiomyopathy, systemic senile amyloid disease, Muckle - Wells syndrome, hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis, isolated atrial amyloid, inclusion body myositis, and beta2-amyloid deposits in muscular dystrophy, among others.
除了在阿尔茨海默病中的作为病理特征之外,神经纤维缠结还和以下疾病有关:In addition to being a pathological feature in Alzheimer's disease, neurofibrillary tangles have been associated with:
匹克氏病、皮质基底节变性、额颞叶痴呆、额颞叶变性、进行性核上性麻痹、慢性创伤性脑病(拳击痴呆)、额颞痴呆症、Lytico-Bodig疾病、缠结为主型痴呆、神经节神经胶质瘤、神经节细胞瘤、脑膜血管瘤病、亚急性硬化性全脑炎、铅性脑病、结节性硬化症等。Pick's disease, corticobasal degeneration, frontotemporal dementia, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, progressive supranuclear palsy, chronic traumatic encephalopathy (dementia pugilistica), frontotemporal dementia, Lytico-Bodig disease, tangle predominance Dementia, ganglioglioma, gangliocytoma, meningeal angiomatosis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, lead encephalopathy, tuberous sclerosis, etc.
在本发明中作为本身或另一基团的部分使用的术语“烷基”指至多8个碳、优选6个碳、更优选1-4个碳的直链和支链基团,如甲基、乙基、丙基。The term "alkyl" as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to straight and branched chain groups of up to 8 carbons, preferably 6 carbons, more preferably 1-4 carbons, such as methyl , ethyl, propyl.
在本发明中作为本身或另一基团的部分使用的术语″一烷基胺″指被一个以上定义的烷基取代的氨基。The term "monoalkylamine" as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to an amino group substituted with one alkyl group as defined above.
在本发明中作为本身或另一基团的部分使用的术语″二烷基胺″指被两个以上定义的烷基取代的氨基。The term "dialkylamine" as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to an amino group substituted with two or more defined alkyl groups.
在本发明中作为本身或另一基团的部分使用的术语“卤”或“卤素”指氟、氯、溴、或碘。The term "halo" or "halogen" as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine.
在本发明中作为本身或另一基团的部分使用的术语″芳环″指在环部分含有6-12个碳、优选在环部分含有6-10个碳的单环或双环芳香基因,例如苯基、萘基或四氢萘基。The term "aromatic ring" as used herein by itself or as part of another group refers to a monocyclic or bicyclic aromatic group containing 6-12 carbons in the ring portion, preferably 6-10 carbons in the ring portion, e.g. Phenyl, naphthyl or tetrahydronaphthyl.
本发明所用的术语杂环除了其中指明以外,代表可以是饱和或不饱和的稳定的5至7元单环系统,且它由碳原子和1-3个选自以下的杂原子组成N、O和S,且其中该氮和硫杂原子可以任选被氧化。特别有用的是含有一个与一个氧或硫结合的氮或者两个氮杂原子的环。这些杂环基团的实例包括哌啶基、吡咯基、吡咯烷基、咪唑基、咪唑啉基、咪唑烷基、吡啶基、吡嗪基、嘧啶基、噁唑基、噁唑烷基、异噁唑基、异噁唑烷基、噻唑基、噻唑烷基、异噻唑基、高哌啶基、高哌嗪基、哒嗪基、吡唑基和吡唑烷基,最优选硫杂吗啉基、哌嗪基和吗啉基。The term heterocycle used in the present invention, unless otherwise specified, represents a stable 5- to 7-membered monocyclic ring system which may be saturated or unsaturated, and which consists of carbon atoms and 1-3 heteroatoms selected from N, O and S, and wherein the nitrogen and sulfur heteroatoms can be optionally oxidized. Particularly useful are rings containing one nitrogen or two nitrogen heteroatoms bonded to an oxygen or sulfur. Examples of such heterocyclic groups include piperidinyl, pyrrolyl, pyrrolidinyl, imidazolyl, imidazolinyl, imidazolidinyl, pyridinyl, pyrazinyl, pyrimidinyl, oxazolyl, oxazolidinyl, iso Oxazolyl, isoxazolidinyl, thiazolyl, thiazolidinyl, isothiazolyl, homopiperidinyl, homopiperazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrazolyl and pyrazolidinyl, most preferably thiamorpholine group, piperazinyl and morpholinyl.
本发明所用的术语″杂原子″意指氧原子(″O″)、硫原子(″S″)或氮原子(″N″)。可以认识到当杂原子为氮时,它可以形成NRaRb部分,其中Ra和Rb彼此独立地为氢或C1-4烷基、C2-4氨基烷基、C1-4卤代烷基。The term "heteroatom" as used herein means an oxygen atom ("O"), a sulfur atom ("S") or a nitrogen atom ("N"). It is recognized that when the heteroatom is nitrogen, it can form an NR a R b moiety, wherein R a and R b independently of each other are hydrogen or C 1-4 alkyl, C 2-4 aminoalkyl, C 1-4 Haloalkyl.
附图说明:Description of drawings:
图1.茚酮类衍生物D8L能结合AD人脑切片上的老年斑。四张邻近的AD人脑切片(6μm厚AD人脑石蜡切片)分别被染色:A.阳性对照刚果红(CR),B.阳性对照硫磺素S(ThS),C.D8L,D.阴性空白对照(溶剂空白对照)。3个实心箭头所指的为地标,空心箭头所指的是老年斑。A2为A1图中白色方框内的区域放大后的图片。Bar=100μm。Figure 1. Indanone derivative D8L can bind to senile plaques on AD human brain slices. Four adjacent AD human brain sections (paraffin sections of 6 μm thick AD human brain) were stained separately: A. Positive control Congo red (CR), B. Positive control Thioflavin S (ThS), C. D8L, D. Negative blank Control (solvent blank control). The three solid arrows point to landmarks, and the hollow arrows point to senile plaques. A2 is the enlarged picture of the area inside the white box in A1. Bar = 100 μm.
图2.茚酮类衍生物D8L能结合AD人脑切片上的神经纤维缠结。四张邻近的AD人脑切片(6μm厚AD人脑石蜡切片)分别被染色:A.阳性对照刚果红(CR),B.阳性对照硫磺素S(ThS),C.D8L,D.阴性空白对照(溶剂空白对照)。两个实心箭头所指的为地标,空心箭头所指的是神经纤维缠结。每列中3,4,5分别是同一张切片在三个荧光通道下激发(DAPI、CY3、GFP)的照片,A6、B6、C6、D6分别为A4、B5、C5、D5图中白色方框内区域放大后的图片。Bar=100μm。Figure 2. Indanone derivative D8L can bind to neurofibrillary tangles on AD human brain slices. Four adjacent AD human brain sections (paraffin sections of 6 μm thick AD human brain) were stained separately: A. Positive control Congo red (CR), B. Positive control Thioflavin S (ThS), C. D8L, D. Negative blank Control (solvent blank control). The two solid arrows point to landmarks, and the hollow arrows point to neurofibrillary tangles. 3, 4, and 5 in each column are photos of the same slice excited under three fluorescent channels (DAPI, CY3, GFP), and A6, B6, C6, and D6 are the white squares in A4, B5, C5, and D5, respectively. A magnified image of the area inside the frame. Bar = 100 μm.
图3.放射性125I标记的茚酮类衍生物[125I]D8j和[125I]D8L使用AD人脑石蜡切片做的体外放射自显影的结果。a1和a1-2是同一个AD病人,c1和c2是两个老年正常对照。A、B、C水平横排分别代表阳性对照[125I]IMPY、[125I]D8j和[125I]D8L的放射自显影结果。实心白色箭头显示的是组织切片有褶皱的部分以及部分石蜡残留造成的异常信号。A排的四张照片显示在AD病人的脑片上有很多老年斑(A-a1 and A-a1-2),而正常的老年对照(A-c1 and A-c2)的脑片上只有零星的几个斑块。和A排的阳性对照[125I]IMPY一样,B、C排的数据显示能被[125I]IMPY标记的老年斑也能被[125I]D8j和[125I]D8L标记出来。Figure 3. The results of in vitro autoradiography of radioactive 125 I-labeled indanone derivatives [ 125 I]D8j and [ 125 I]D8L using paraffin sections of AD human brain. a1 and a1-2 are the same AD patient, c1 and c2 are two elderly normal controls. Horizontal rows A, B, and C represent the autoradiographic results of positive controls [ 125 I]IMPY, [ 125 I]D8j, and [ 125 I]D8L, respectively. The solid white arrows show the wrinkled part of the tissue section and the abnormal signal caused by some paraffin residues. The four photos in row A show that there are many senile plaques (A-a1 and A-a1-2) on the brain slices of AD patients, but only a few sporadic ones on the brain slices of normal aged controls (A-c1 and A-c2) plaque. Like the positive control [ 125 I]IMPY in row A, the data in rows B and C show that senile plaques that can be labeled by [ 125 I]IMPY can also be labeled by [ 125 I]D8j and [ 125 I]D8L.
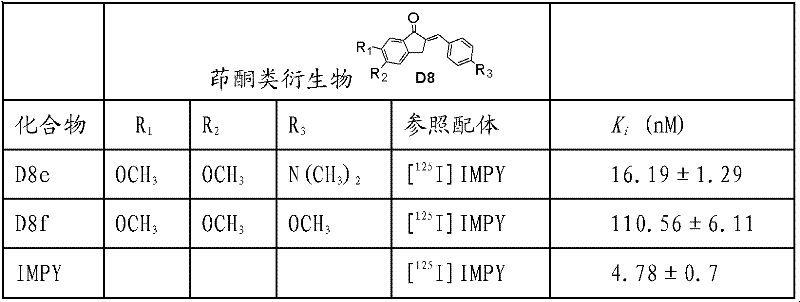
表1.茚酮类衍生物D8e和D8f使用AD人脑匀浆做的竞争结合后的Ki值。Table 1. Ki values after competitive binding of indanone derivatives D8e and D8f using AD human brain homogenate.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
实施例一:放射性同位素的标记方法示例Example 1: Example of labeling method of radioactive isotope
1.11C标记(如下反应式所示):1. 11 C labeling (shown in the following reaction formula):
在3mL V形瓶中,1mg(0.0036mmol)化合物2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-羟基-1-茚酮溶于400μL DMSO,加入10mg干KOH,涡旋5min。[11C]CH3I以30mL/min鼓泡通过溶液,在95℃加热反应5min。然后,反应产物用半制备HPLC纯化,Prodigy ODS柱,洗脱剂为70%乙腈/30%三乙胺磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2),收集含11C标记的放射性化合物。In a 3 mL V-shaped flask, 1 mg (0.0036 mmol) of compound 2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-hydroxy-1-indanone was dissolved in 400 μL DMSO, 10 mg dry KOH was added, and vortexed for 5 min. [ 11 C]CH 3 I was bubbled through the solution at 30 mL/min, and the reaction was heated at 95° C. for 5 min. Then, the reaction product was purified by semi-preparative HPLC, Prodigy ODS column, the eluent was 70% acetonitrile/30% triethylamine phosphate buffer (pH7.2), and the 11 C-labeled radioactive compound was collected.
2.125I标记(如下反应式所示):2. 125 I labeling (as shown in the following reaction formula):
依次称取化合物2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-溴-1-茚酮400mg(1.17mmol)、双三丁基锡4.0g(7.02mmol)和四三苯基膦合钯Pd(PPh3)4135mg(0.12mmol),加入8mL二氧六环和2mLEt3N,在氮气保护下加热回流反应16h。减压除去溶剂,上硅胶柱,以石油醚∶乙酸乙酯8/1过柱,收集相应组分,得产物2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-三丁基锡基-1-茚酮(26%)。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.82(d,1H,J=7.5Hz),7.68-7.64(m,2H),7.62-7.59(d,2H,J=9.0Hz),7.52(d,1H,J=7.5Hz),6.75-6.72(d,2H,J=9.0Hz),3.99(s,2H),3.04(s,6H),1.61-1.51(m,6H),1.41-1.29(m,6H),1.14-1.08(m,6H),0.90(t,9H,J=7.2Hz).5-SnBu3-G964 IR(cm-1):2955,2925,1687,1624,1595,1453,1091,882.ESI-MS:[M+H]+528.28.Sequentially weigh the compound 2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-bromo-1-indanone 400mg (1.17mmol), bistributyltin 4.0g (7.02mmol) and tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 135mg (0.12mmol), add 8mL dioxane and 2mL Et 3 N, and heat to reflux reaction for 16h under the protection of nitrogen. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure, put on a silica gel column, pass through the column with petroleum ether: ethyl acetate 8/1, collect the corresponding components, and obtain the product 2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-tributyltin- 1-Indanone (26%). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.82(d, 1H, J=7.5Hz), 7.68-7.64(m, 2H), 7.62-7.59(d, 2H, J=9.0Hz), 7.52(d, 1H , J=7.5Hz), 6.75-6.72(d, 2H, J=9.0Hz), 3.99(s, 2H), 3.04(s, 6H), 1.61-1.51(m, 6H), 1.41-1.29(m, 6H), 1.14-1.08 (m, 6H), 0.90 (t, 9H, J=7.2Hz). 5-SnBu3-G964 IR (cm -1 ): 2955, 2925, 1687, 1624, 1595, 1453, 1091, 882.ESI-MS: [M+H] + 528.28.
在室温下,向含有三丁基锡前体化合物的乙醇溶液(100μg/50μL EtOH)、1.5mCi[125I]NaI(活性2200Ci/mmol)、100μL 1N HCl的混合液中加入50μL 3%H2O2,反应10min。加入NaHSO3淬灭反应。反应混合液以碳酸钠溶液中和,再 以乙酸乙酯萃取。萃取物通过无水硫酸钠柱干燥,N2吹干。放射性配体用HPLC纯化,Cosmosil C18柱,流动相为乙腈∶水(2/3),流速1.0mL/min。纯化后的放射性标记物于-20℃保存。At room temperature, add 50 μL 3% H 2 O 2 to a mixture containing tributyltin precursor compound in ethanol (100 μg/50 μL EtOH), 1.5 mCi [ 125 I]NaI (activity 2200 Ci/mmol), 100 μL 1N HCl , react for 10min. The reaction was quenched by adding NaHSO 3 . The reaction mixture was neutralized with sodium carbonate solution, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was dried through anhydrous sodium sulfate column and blown dry under N2 . The radioligand was purified by HPLC with a Cosmosil C18 column, the mobile phase was acetonitrile: water (2/3), and the flow rate was 1.0 mL/min. The purified radiolabel was stored at -20°C.
3.18F标记(如下反应式所示):3. 18 F labeling (shown in the following reaction formula):
在圆底烧瓶中依次加入(E)-2-(4-甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮309mg(1mmol)、2-溴乙醇137mg(1.1mmol)、碳酸钾207mg(1.5mmol)和DMF10mL,回流反应15h。减压除去溶剂,过硅胶柱,以二氯甲烷∶甲醇10/1洗脱。收集相应组分,得产物。Add (E)-2-(4-methylamino-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone 309 mg (1 mmol), 2-bromoethanol 137 mg (1.1 mmol), potassium carbonate 207mg (1.5mmol) and DMF10mL, reflux for 15h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and passed through a silica gel column, eluting with dichloromethane:methanol 10/1. Collect the corresponding components to obtain the product.
称取177mg(0.5mmol)(E)-2-(4-N-甲基,N-羟乙基氨基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮溶于15mL无水吡啶,冷至0℃,在搅拌下加入137mg(0.72mmol)对甲苯磺酰氯,保持0℃反应2h,再室温反应1h。减压除去吡啶,加入15mL水,以15mL二氯甲烷萃取二次,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥。过硅胶柱,以氯仿∶甲醇20/1洗脱。收集相应组分,得产物。Weigh 177mg (0.5mmol) of (E)-2-(4-N-methyl, N-hydroxyethylamino-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone and dissolve it in 15mL Anhydrous pyridine, cooled to 0°C, added 137 mg (0.72 mmol) p-toluenesulfonyl chloride under stirring, kept at 0°C for 2 hours, and then reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. Pyridine was removed under reduced pressure, 15 mL of water was added, extracted twice with 15 mL of dichloromethane, the organic phases were combined and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Pass through a silica gel column and elute with chloroform:methanol 20/1. Collect the corresponding components to obtain the product.
取对甲苯磺酰前体4mg溶于0.2mLDMSO加入含有已干燥的18F活性物,120℃加热反应4min。加入2mL水,1mL乙酸乙酯萃取二次,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥。使用氩气吹扫去溶剂,残余物溶于乙腈,用HPLC纯化。色谱条件:Hamilton PRP-1 column(7.0×305mm,10μm);CH3CN/dimethylglutarate buffer(5mM,pH 7)=9/1;flow rate=2mL/min)。Dissolve 4 mg of p-toluenesulfonyl precursor in 0.2 mL DMSO and add the dried 18 F active substance, and heat at 120°C for 4 min. Add 2 mL of water, extract twice with 1 mL of ethyl acetate, combine the organic phases, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was purged with argon and the residue was dissolved in acetonitrile and purified by HPLC. Chromatographic conditions: Hamilton PRP-1 column (7.0×305 mm, 10 μm); CH 3 CN/dimethylglutarate buffer (5 mM, pH 7)=9/1; flow rate=2 mL/min).
实施例二:配合物的设计示例Embodiment 2: Design example of complexes
1.配体示例:1. Ligand example:
如上结构式(1-4)所示的配体结构中,在苯环上构建了多齿配位点,这个配位点可位于苯环的其他位置,也可移至与茚酮相连的苯环上。在这个多齿的配位区域,可用碳碳双键或三键代替单键,也可将双键还原为单键。其中的杂原子可为O、N、S、P。In the ligand structure shown in the above structural formula (1-4), a multi-dentate coordination site is constructed on the benzene ring. This coordination site can be located at other positions of the benzene ring, and can also be moved to the benzene ring connected to indanone superior. In this multidentate coordination region, single bonds can be replaced by carbon-carbon double bonds or triple bonds, and double bonds can also be reduced to single bonds. The heteroatoms therein can be O, N, S, P.
铁磁性络合物设计示例(如下反应式所示)Design example of ferromagnetic complex (shown in the following reaction formula)
以上面的配体1为例,制备Mn络合物(如下反应式所示)Taking the above ligand 1 as an example, prepare the Mn complex (as shown in the following reaction formula)
在20mL DMF中,加入溴代乙醇375mg(3mmol)、(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二氨基-1-茚酮293mg(1mmol)和碳酸钾276mg(2mmol),在100℃下反应4h。然后减压除去溶剂,水洗,以乙酸乙酯萃取,无水硫酸钠干燥。硅胶柱色谱分离,以氯仿/甲醇(10∶1)洗脱,得棕红色固体。In 20mL DMF, add bromoethanol 375mg (3mmol), (E)-2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5,6-diamino-1-indanone 293mg (1mmol) and carbonic acid Potassium 276mg (2mmol), reacted at 100°C for 4h. Then the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, washed with water, extracted with ethyl acetate, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Silica gel column chromatography and eluting with chloroform/methanol (10:1) gave a brown-red solid.
在含上述配体50mg(0.13mmol)和10mL甲醇的溶液中,加入醋酸锰30mg(0.14mmol),室温搅拌1h。然后,加入氢氧化钠210mg(5.2mmol),搅拌过夜。加入30mL水,以25mL苯萃取3次,合并有机相。有机相再以 水洗后,无水硫酸钠干燥。过滤,除去溶剂,浓缩,过柱。以石油醚/乙酸乙酯(3∶2)洗脱,收集相应组分,即可得目标络合物。In a solution containing 50 mg (0.13 mmol) of the above-mentioned ligand and 10 mL of methanol, 30 mg (0.14 mmol) of manganese acetate was added, and stirred at room temperature for 1 h. Then, 210 mg (5.2 mmol) of sodium hydroxide was added, followed by stirring overnight. Add 30 mL of water, extract 3 times with 25 mL of benzene, and combine the organic phases. The organic phase was washed with water and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Filter, remove the solvent, concentrate and pass through the column. The target complex was obtained by eluting with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (3:2), and collecting the corresponding components.
实施例三:Embodiment three:
以茚酮为原料的系列衍生物的合成方法,其中D8a-c,D8e-h,D8l和D8m可以很容易通过碱催化获得,操作简单,产率高。D8d可通过D8c在SnCl2 2H2O催化下还原得到,D8h和D8j与(Bu3Sn)2在Pd(PPh3)4催化下、三乙胺中回流可得到三丁基锡取代产物D8i和D8k。D8i和碘在THF中反应,可得碘代产物D8j。反应过程如下反应式所示:A method for synthesizing a series of derivatives using indanone as a raw material, wherein D8a-c, D8e-h, D8l and D8m can be easily obtained by base catalysis, and the operation is simple and the yield is high. D8d can be obtained by reducing D8c under the catalysis of SnCl2 2H2O, and D8h and D8j can be refluxed with (Bu3Sn)2 under the catalysis of Pd(PPh3)4 in triethylamine to obtain tributyltin substituted products D8i and D8k. D8i reacts with iodine in THF to obtain iodo product D8j. The reaction process is shown in the following reaction formula:
(E)-2-苯亚甲基-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8a)。称取5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮192mg(1mmol)和苯甲醛106mg(1mmol)溶于10mL乙醇,在搅拌下滴加10%NaOH水溶液2.2mL,室温搅拌过夜,析出大量黄色沉淀。抽滤,滤饼以乙醇重结晶(产率86%)。(E)-2-苯亚甲基-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(E)-2-benzylidene-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone(D8a).1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.66-7.64(m,2H),7.59(s,1H),7.46-7.43(m,2H),7.40-7.37(m,1H),7.33(s,1H),6.98(s,1H),4.00(s,3H),3.96(s,2H),3.95(s,3H).13CNMR(CDCl3):δ193.3,155.6,149.8,145.1,135.7,135.6,132.6,131.2,130.7,129.5,129.2,129.1,129.0,107.3,105.2,56.5,56.3,32.3.HRMS:calcd for C18H16O3 280.1099,found 280.1092([M]+).IR(cm-1):3002,2938, 2835,1688,1631,1587,1501,1305,1255,1223,1128,1095,774。 (E)-2-Benzylidene-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8a). Weigh 192 mg (1 mmol) of 5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone and 106 mg (1 mmol) of benzaldehyde in 10 mL of ethanol, add 2.2 mL of 10% NaOH aqueous solution dropwise under stirring, stir overnight at room temperature, and precipitate a large amount of yellow precipitation. After suction filtration, the filter cake was recrystallized from ethanol (yield 86%). (E)-2-benzylidene-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (E)-2-benzylidene-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8a). 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.66-7.64(m, 2H), 7.59(s, 1H), 7.46-7.43(m, 2H), 7.40-7.37(m, 1H), 7.33(s, 1H), 6.98(s, 1H), 4.00(s, 3H), 3.96(s, 2H), 3.95(s, 3H). 13 CNMR(CDCl 3 ): δ193.3, 155.6, 149.8, 145.1, 135.7, 135.6, 132.6, 131.2, 130.7 , 129.5, 129.2, 129.1, 129.0, 107.3, 105.2, 56.5, 56.3, 32.3. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 16 O 3 280.1099, found 280.1092([M] + ).IR(cm -1 ): 3002, 2938 , 2835, 1688, 1631, 1587, 1501, 1305, 1255, 1223, 1128, 1095, 774.
实施例四:Embodiment four:
(E)-2-(4-溴-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8b,产率82%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8b。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.57-7.55(m,2H),7.49-7.47(m,3H),7.30(s,1H),6.96(s,1H),3.99(s,3H),3.94(s,3H),3.89(s,2H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.0,155.7,149.8,144.9,136.2,134.6,132.3,132.2,132.0,131.9,131.8,131.1,123.9,107.2,105.2,56.5,56.3,32.3.HRMS:calcd for C18H15 79BrO3 358.0205,found 358.0203([M]+),calcd for C18H15 81BrO3 360.0184,found 360.0175([M+2]+).IR(cm-1):3003,2938,2834,1690,1632,1585,1500,1309,1128,1090,1007,796。 (E)-2-(4-Bromo-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8b, 82% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8b was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.57-7.55 (m, 2H), 7.49-7.47 (m, 3H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 3.99 (s, 3H), 3.94 (s, 3H), 3.89 (s, 2H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ193.0, 155.7, 149.8, 144.9, 136.2, 134.6, 132.3, 132.2, 132.0, 131.9, 131.8, 131.1, 123.9, 107.2 , 105.2, 56.5, 56.3, 32.3. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 15 79 BrO 3 358.0205, found 358.0203 ([M] + ), calcd for C 18 H 15 81 BrO 3 360.0184, found 360.0175 ([M+2] + ).IR(cm −1 ): 3003, 2938, 2834, 1690, 1632, 1585, 1500, 1309, 1128, 1090, 1007, 796.
实施例五:Embodiment five:
(E)-2-(4-硝基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8c,产率89%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8c。1H-NMR(CDCl3):δ8.31(d,2H,J=8.7Hz),7.79(d,2H,J=8.7Hz),7.61(s,1H),7.36(s,1H),7.00(s,1H),4.02(s,3H),4.01(s,2H),3.96(s,3H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ192.3,156.1,150.0,147.6,144.8,141.9,139.3,130.8,129.4,124.1,107.2,105.3,56.4,56.2,32.1.HRMS:calcd for C18H15NO5 325.0950,found 325.0947([M]+).IR(cm-1):3077,2944,2866,1682,1631,1516,1502,1341,1310,1095,1002,850。 (E)-2-(4-Nitro-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8c, 89% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8c was synthesized. 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ8.31(d, 2H, J=8.7Hz), 7.79(d, 2H, J=8.7Hz), 7.61(s, 1H), 7.36(s, 1H), 7.00 (s, 1H), 4.02 (s, 3H), 4.01 (s, 2H), 3.96 (s, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ192.3, 156.1, 150.0, 147.6, 144.8, 141.9, 139.3 , 130.8, 129.4, 124.1, 107.2, 105.3, 56.4, 56.2, 32.1. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 15 NO 5 325.0950, found 325.0947 ([M] + ).IR(cm -1 ): 3077, 2944, 2866 , 1682, 1631, 1516, 1502, 1341, 1310, 1095, 1002, 850.
实施例六:Embodiment six:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8e,80%)。用和 D8a类似的方法,合成了D8e。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.59-7.57(m,3H),7.34(s,1H),6.98(s,1H),6.75-6.73(m,2H),3.99(s,3H),3.95(s,3H),3.92(s,2H),3.05(s,6H).IR(cm-1):2923,1676,1596,1524,1303,1122,1001,817.13C NMR(CDCl3):δ32.3,40.1,56.1,56.2,104.9,107.1,111.9,123.3,130.5,131.6,132.4,133.4,144.3,149.3,150.9,154.6,193.4.HRMS:cacldfor C20H21NO3 323.1521,found 323.1513([M]+)。(E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8e, 80%). In a similar manner to D8a, D8e was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.59-7.57 (m, 3H), 7.34 (s, 1H), 6.98 (s, 1H), 6.75-6.73 (m, 2H), 3.99 (s, 3H), 3.95 (s, 3H), 3.92 (s, 2H), 3.05 (s, 6H). IR (cm-1): 2923, 1676, 1596, 1524, 1303, 1122, 1001, 817. 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ) : δ32.3, 40.1, 56.1, 56.2, 104.9, 107.1, 111.9, 123.3, 130.5, 131.6, 132.4, 133.4, 144.3, 149.3, 150.9, 154.6, 193.4. HRMS: cacldfor C 20 H 21 NO 3 323f.15 ([M] + ).
实施例七:Embodiment seven:
(E)-2-(4-甲氧基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8f,78%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8f。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.63-7.62(m,2H),7.57(s,1H),7.35(s,1H),6.99-6.97(m,3H),3.99(s,3H),3.95-3.94(m,5H),3.87(s,3H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ32.2,55.4,56.2,56.3,105.0,107.2,114.4,128.3,131.2,132.3,133.1,144.7,149.5,155.2,160.6,193.3.HRMS:cacld for C19H18O4 310.1205,found 310.1202([M]+).IR(cm-1):2941,2834,1685,1605,1504,1299,1258,1091,820。 (E)-2-(4-Methoxy-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8f, 78%). In a similar manner to D8a, D8f was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.63-7.62 (m, 2H), 7.57 (s, 1H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 6.99-6.97 (m, 3H), 3.99 (s, 3H), 3.95 -3.94 (m, 5H), 3.87 (s, 3H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ32.2, 55.4, 56.2, 56.3, 105.0, 107.2, 114.4, 128.3, 131.2, 132.3, 133.1, 144.7, 149.5 , 155.2, 160.6, 193.3. HRMS: cacld for C 19 H 18 O 4 310.1205, found 310.1202 ([M] + ). IR (cm -1 ): 2941, 2834, 1685, 1605, 1504, 1299, 1258, 1091 , 820.
实施例八:Embodiment eight:
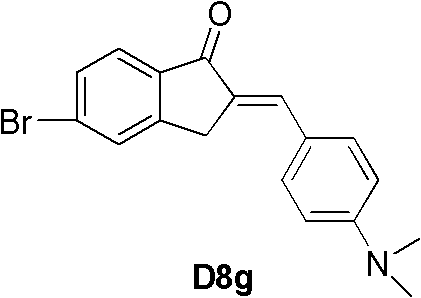
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-溴-1-茚酮(D8g,产率75%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8g。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.75-7.64(m,3H),7.58-7.53(m,3H),6.74-6.71(m,2H),3.95(s,2H),3.05(s,6H). 13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.0,151.3,151.0,137.7,135.7,132.9,130.9,129.2,128.9,128.6,125.2,122.8,111.9,40.0,32.4.HRMS:calcd for C18H16 79BrNO341.0415,found 341.0417([M]+),calcd for C18H16 81BrNO 343.0395,found343.0392([M+2]+).IR(cm-1):2919,1683,1592,1526,1444,1316,1113,960,882。 (E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-bromo-1-indanone (D8g, 75% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8g was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.75-7.64(m, 3H), 7.58-7.53(m, 3H), 6.74-6.71(m, 2H), 3.95(s, 2H), 3.05(s, 6H) . 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ193.0, 151.3, 151.0, 137.7, 135.7, 132.9, 130.9, 129.2, 128.9, 128.6, 125.2, 122.8, 111.9, 40.0, 32.4. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 16 79 BrNO341.0415, found 341.0417([M] + ), calcd for C 18 H 16 81 BrNO 343.0395, found343.0392([M+2] + ).IR(cm -1 ): 2919, 1683, 1592, 1526, 1444, 1316, 1113, 960, 882.
实施例九:Embodiment nine:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-6-溴-1-茚酮(D8h,产率81%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8h。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ8.00(s,1H),7.67-7.64(m,2H),7.57(d,2H,J=8.8Hz),7.41(d,1H,J=8.0Hz),6.72(d,2H,J=8.8Hz),3.91(s,2H),3.06(s,6H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.0,151.5,148.0,140.9,136.6,136.2,133.2,129.4,127.7,127.2,123.0,121.8,112.0,40.3,32.6.HRMS:calcd for C18H16 79BrNO 341.0415,found341.0409([M]+),calcd for C18H16 81BrNO 343.0395,found 343.0387([M+2]+).IR(cm-1):2893,1681,1589,1523,1462,1363,1188,1169,1115,810。 (E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-6-bromo-1-indanone (D8h, 81% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8h was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ8.00 (s, 1H), 7.67-7.64 (m, 2H), 7.57 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.41 (d, 1H, J=8.0Hz), 6.72 (d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 3.91 (s, 2H), 3.06 (s, 6H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ193.0, 151.5, 148.0, 140.9, 136.6, 136.2, 133.2, 129.4, 127.7, 127.2, 123.0, 121.8, 112.0, 40.3, 32.6. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 16 79 BrNO 341.0415, found 341.0409 ([M] + ), calcd for C 18 H 16 81 BrNO 343.03743, found 3 ([M+2] + ).IR(cm −1 ): 2893, 1681, 1589, 1523, 1462, 1363, 1188, 1169, 1115, 810.
实施例十:Embodiment ten:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-6-碘-1-茚酮(D8L,产率76%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8L。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ8.20(s,1H),7.85-7.83(m,1H),7.63(s,1H),7.55(d,2H,J=8.8Hz),7.30-7.26(m,1H),6.71(d,2H,J=8.8Hz),3.88(s,2H),3.05(s,6H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ192.9,151.5,148.7,142.3,141.1,136.1,133.3,133.1,129.1,128.0,123.0,112.1,92.9,40.3,32.6.HRMS:calcd for C18H16INO 389.0277,found389.0279([M]+).IR(cm-1):2851,1678,1585,1522,1362,1308,1263,1187,1116,809。 (E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-6-iodo-1-indanone (D8L, 76% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8L was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ8.20(s, 1H), 7.85-7.83(m, 1H), 7.63(s, 1H), 7.55(d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 7.30-7.26(m , 1H), 6.71(d, 2H, J=8.8Hz), 3.88(s, 2H), 3.05(s, 6H). 13 C NMR(CDCl 3 ): δ192.9, 151.5, 148.7, 142.3, 141.1, 136.1, 133.3, 133.1, 129.1, 128.0, 123.0, 112.1, 92.9, 40.3, 32.6. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 16 INO 389.0277, found 389.0279([M] + ).IR(cm -1 ): 2851, 1678, 1585, 1522, 1362, 1308, 1263, 1187, 1116, 809.
实施例十一:Embodiment eleven:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8m, 产率85%)。用和D8a类似的方法,合成了D8m。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.83(d,1H,J=8.4Hz),7.59-7.56(m,3H),6.99(s,1H),6.96-6.92(dd,1H,J=8.4Hz,1.8Hz),6.74(d,2H,J=8.7Hz),3.95(s,2H),3.90(s,3H),3.05(s,6H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.0,164.7,152.2,151.0,133.7,132.5,132.1,130.4,125.7,123.3,114.8,111.9,109.7,55.6,40.1,32.8。 (E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-methoxy-1-indanone (D8m, 85% yield). In a similar manner to D8a, D8m was synthesized. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.83(d, 1H, J=8.4Hz), 7.59-7.56(m, 3H), 6.99(s, 1H), 6.96-6.92(dd, 1H, J=8.4Hz , 1.8Hz), 6.74(d, 2H, J=8.7Hz), 3.95(s, 2H), 3.90(s, 3H), 3.05(s, 6H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ193.0, 164.7, 152.2, 151.0, 133.7, 132.5, 132.1, 130.4, 125.7, 123.3, 114.8, 111.9, 109.7, 55.6, 40.1, 32.8.
实施例十二:Embodiment 12:
(E)-2-(4-氨基-苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8d)的合成:称取200mg(0.61mmol)2-(4-硝基苯亚甲基)-5,6-二甲氧基-1-茚酮(D8c)溶于25mL乙醇,在氮气保护下,加入695mg SnCl2·2H2O(3.08mmol),加热回流反应4h。冷至室温,加入1MNaOH调节pH至弱碱性。以50mL乙酸乙酯萃取,水相再以乙酸乙酯萃取二次,合并有机相,有机相水洗后,无水硫酸钠干燥。过滤,减压除去溶剂,得粗品。过硅胶柱,以石油醚∶乙酸乙酯2/1洗脱,收集相应组分,得目标产物(产率56%)。1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.52-7.48(m,3H),7.34(s,1H),6.97(s,1H),6.74-6.71(m,2H),3.99(s,3H),3.94(s,3H),3.91(s,2H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.6,149.6,147.8,144.7,133.2,132.7,115.3,107.3,105.1,56.4,56.3,32.5.HRMS:calcd for C18H17NO3295.1208,found 295.1201([M]+).IR(cm-1):3427,3348,2929,1671,1578,1499,1304,1130,1099,1004,819。 Synthesis of (E)-2-(4-amino-benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8d): Weigh 200mg (0.61mmol) 2-(4-nitro Benzylidene)-5,6-dimethoxy-1-indanone (D8c) was dissolved in 25mL of ethanol, under the protection of nitrogen, 695mg of SnCl 2 ·2H 2 O (3.08mmol) was added, and heated to reflux for 4h. After cooling to room temperature, 1M NaOH was added to adjust the pH to slightly alkaline. Extract with 50 mL of ethyl acetate, extract the aqueous phase twice with ethyl acetate, combine the organic phases, wash the organic phase with water, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After filtration, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product. After passing through a silica gel column and eluting with petroleum ether:
实施例十三:Embodiment thirteen:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-三丁基锡基-1-茚酮(D8i).依次称取化合物D8g 400mg(1.17mmol)、双三丁基锡4.0g(7.02mmol)和四三苯基膦合钯Pd(PPh3)4135mg(0.12mmol),加入10mLEt3N,在氮气保护下加热回流反应16h。减压除去溶剂,上硅胶柱,以石油醚∶乙酸乙酯8/1过柱,收集相应组分,得产物D8i 176mg(产率26%)。 (E)-2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-tributyltin base-1-indanone (D8i). Weigh compound D8g 400mg (1.17mmol), bistributyltin 4.0g ( 7.02mmol) and tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 135mg (0.12mmol), add 10mL Et 3 N, and heat to reflux for 16h under the protection of nitrogen. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, put on a silica gel column, passed through the column with petroleum ether: ethyl acetate 8/1, and collected the corresponding components to obtain 176 mg of product D8i (yield 26%).
1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.82(d,1H,J=7.5Hz),7.68-7.64(m,2H),7.62-7.59(d,2H,J=9.0Hz),7.52(d,1H,J=7.5Hz),6.75-6.72(d,2H,J=9.0Hz),3.99(s,2H),3.04(s,6H),1.61-1.51(m,6H),1.41-1.29(m,6H),1.14-1.08(m,6H),0.90(t,9H,J=7.2Hz).5-SnBu3-G964IR(cm-1):2955,2925,1687,1624,1595,1453,1091,882.ESI-MS:[M+H]+528.28。 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.82(d, 1H, J=7.5Hz), 7.68-7.64(m, 2H), 7.62-7.59(d, 2H, J=9.0Hz), 7.52(d, 1H , J=7.5Hz), 6.75-6.72(d, 2H, J=9.0Hz), 3.99(s, 2H), 3.04(s, 6H), 1.61-1.51(m, 6H), 1.41-1.29(m, 6H), 1.14-1.08(m, 6H), 0.90(t, 9H, J=7.2Hz).5-SnBu3-G964IR(cm -1 ): 2955, 2925, 1687, 1624, 1595, 1453, 1091, 882 .ESI-MS: [M+H] + 528.28.
实施例十四:Embodiment 14:
用和D8i类似的方法合成化合物(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-6-三丁基锡基-1-茚酮(D8k).1H-NMR(CDCl3):δ8.01(s,1H),7.66-7.58(m,4H),7.53-7.50(m,1H),6.75-6.72(m,2H),3.97(s,2H),3.04(s,6H),1.58-1.49(m,6H),1.37-1.30(m,6H),1.13-1.07(m,6H),0.89(t,9H,J=7.2Hz).IR(cm-1):2925,1735,1686,1596,1524,1458,1109,882。 Compound (E)-2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-6-tributyltinyl-1-indanone (D8k) was synthesized by a method similar to D8i. 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ8.01(s, 1H), 7.66-7.58(m, 4H), 7.53-7.50(m, 1H), 6.75-6.72(m, 2H), 3.97(s, 2H), 3.04(s, 6H), 1.58-1.49(m, 6H), 1.37-1.30(m, 6H), 1.13-1.07(m, 6H), 0.89(t, 9H, J=7.2Hz).IR(cm -1 ): 2925, 1735, 1686, 1596, 1524, 1458, 1109, 882.
实施例十五:Embodiment fifteen:
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-碘-1-茚酮(D8j).称取化合物D8i 75mg(0.14mmol)溶于3mL THF,冰浴,53mg I2(0.20mmol)溶于2mL THF滴加入上述体系,滴加完毕后,体系在0℃继续反应1h,然后加入5mL饱和NaHSO3溶液淬灭反应。加入5mL饱和Na2CO3溶液中和后,10mL乙酸乙酯萃取三次,合并有机相,无水硫酸钠干燥。过滤,减压除去溶剂,过硅胶柱,以石油醚∶乙酸乙酯6/1洗脱,收集相应组分,旋干,得棕色固体D8j(42mg,产率52%)。(E)-2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-iodo-1-indanone (D8j). Weigh compound D8i 75mg (0.14mmol) and dissolve in 3mL THF, ice bath, 53mg I 2 (0.20mmol) dissolved in 2mL THF was added dropwise to the above system. After the dropwise addition, the system continued to react at 0°C for 1h, and then 5mL saturated NaHSO 3 solution was added to quench the reaction. After adding 5 mL of saturated Na 2 CO 3 solution for neutralization, 10 mL of ethyl acetate was used to extract three times, and the organic phases were combined and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After filtration, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, passed through a silica gel column, and eluted with petroleum ether: ethyl acetate 6/1, the corresponding components were collected and spin-dried to obtain D8j as a brown solid (42 mg, yield 52%).
1H NMR(CDCl3):δ7.95(s,1H),7.77(m,1H),7.66(s,1H),7.62-7.58(m,3H),6.78(d,2H,J=7.8Hz),3.96(s,2H),3.07(s,6H).13C NMR(CDCl3):δ193.6,151.1,138.4,137.0,135.9,135.5,133.1,125.5,112.4,101.9,40.5,32.4.HRMS:calcd for C18H16INO 389.0277,found 389.0271([M]+).IR(cm-1):2898,1682,1590,1525,1312,1111,959,810。 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ7.95(s, 1H), 7.77(m, 1H), 7.66(s, 1H), 7.62-7.58(m, 3H), 6.78(d, 2H, J=7.8Hz ), 3.96(s, 2H), 3.07(s, 6H). 13 C NMR (CDCl 3 ): δ193.6, 151.1, 138.4, 137.0, 135.9, 135.5, 133.1, 125.5, 112.4, 101.9, 40.5, 32.4. HRMS: calcd for C 18 H 16 INO 389.0277, found 389.0271 ([M] + ). IR (cm −1 ): 2898, 1682, 1590, 1525, 1312, 1111, 959, 810.
实施例十六:Embodiment sixteen:
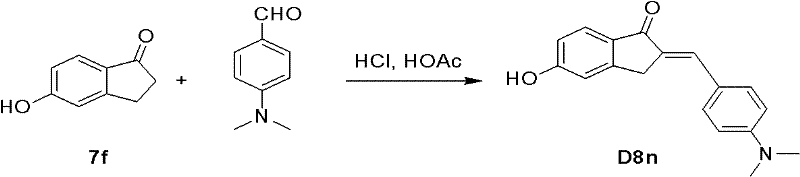
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-羟基-1-茚酮(D8n).如示意图8所示,在10mL圆底烧瓶中,依次加入5-羟基-1-茚酮200mg(1.35mmol)、冰醋酸2.2mL、浓盐酸0.38mL,室温搅拌10min后,加入4-二甲氨基苯甲醛201mg(1.35mmol),室温搅拌2h,放置2天。加入饱和碳酸钠溶液中和至碱性,析出大量沉淀,过滤得棕色固体。粗品经硅胶柱色谱纯化,以二氯甲烷∶甲醇20/1洗脱,得产物D8n(产率65%).1H NMR(DMSO-d6)δ7.58-7.53(m,3H),7.29(s,1H),6.87(s,1H),6.80-6.75(m,4H),3.88(s,2H),3.0(s,6H)。 (E)-2-(4-Dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-hydroxy-1-indanone (D8n). As shown in Scheme 8, in a 10mL round bottom flask, add 5-hydroxy- 200 mg (1.35 mmol) of 1-indanone, 2.2 mL of glacial acetic acid, and 0.38 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid were stirred at room temperature for 10 minutes, then 201 mg (1.35 mmol) of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde was added, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and left for 2 days. Add saturated sodium carbonate solution to neutralize to alkaline, precipitate a large amount of precipitate, and filter to obtain a brown solid. The crude product was purified by silica gel column chromatography, eluting with dichloromethane:methanol 20/1, to obtain the product D8n (65% yield). 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ) δ7.58-7.53 (m, 3H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 6.87 (s, 1H), 6.80-6.75 (m, 4H), 3.88 (s, 2H), 3.0 (s, 6H).
(E)-2-(4-二甲氨基-苯亚甲基)-5-羟基-1-茚酮的合成Synthesis of (E)-2-(4-dimethylamino-benzylidene)-5-hydroxy-1-indanone
实施例十七:茚酮类衍生物D8L的AD人脑石蜡切片对比染色Example 17: Contrastive staining of AD human brain paraffin sections of indenone derivatives D8L
使用本领域的经典方法,对连续的AD人脑石蜡切片进行对比染色,步骤如下:Using the classical method in this field, carry out comparative staining to the consecutive paraffin sections of AD human brain, the steps are as follows:
1.脱蜡致水1. Dewaxing to water
2.高锰酸钾(0.25%,PBS配制)溶液处理20分钟(待切片出现棕色),偏重亚硫酸钾(1.0%,PBS配制)和草酸(1.0%,PBS配制)的混合溶液处理切片直到棕色褪去(大致1-6分钟,待切片的棕色褪去再处理30秒即可)3.0.3% Trioton X-100处理切片20分钟。2. Potassium permanganate (0.25%, prepared in PBS) solution was treated for 20 minutes (until the section appeared brown), and a mixed solution of potassium metabisulfite (1.0%, prepared in PBS) and oxalic acid (1.0%, prepared in PBS) was used to treat the section until Brown fading (approximately 1-6 minutes, after the browning of the slices fades, it can be processed for 30 seconds) 3.0.3% Trioton X-100 treats the slices for 20 minutes.
4.组化笔画图,将茚酮类衍生物之一D8L对应的切片和ThioflavinS、Congo red对应的切片分别进行染色,步骤分别如下:4. Histochemical pen drawing, staining the slices corresponding to D8L, one of the indanone derivatives, and the slices corresponding to ThioflavinS and Congo red, respectively, and the steps are as follows:
茚酮类衍生物D8L的染色:(上接第4步)Staining of indanone derivatives D8L: (continued from step 4)
5.D8L的工作液滴染,37度湿盒中1h。5. D8L working liquid drop dyeing, 1h in 37 degree humidity box.
6.70%乙醇15分钟,PBS 10分钟2次。6. 70% ethanol for 15 minutes, PBS for 10 minutes twice.
7.70%甘油封片,4度保存。7. 70% glycerol for sealing and storage at 4 degrees.
硫黄素S染色的步骤:(上接第4步)Steps for Thioflavin S staining: (continued from Step 4)
5.硫黄素S(ThioflavinS,0.5g%in PBS),染色20分钟。5. Thioflavin S (ThioflavinS, 0.5g% in PBS), staining for 20 minutes.
6.70%乙醇分化10分钟,PBS 5分钟。6. Differentiate in 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, PBS for 5 minutes.
7.80%甘油封片。7. 80% glycerol for mounting.
刚果红染色的步骤:(上接第4步)Congo red staining steps: (continued from step 4)
5.刚果红(Congo Red,0.5g%,50%乙醇配制),染色10分钟。5. Congo Red (Congo Red, 0.5g%, 50% ethanol preparation), staining for 10 minutes.
6.0.2%KOH(80%乙醇配制)分化,大约15秒。6. 0.2% KOH (80% ethanol preparation) differentiation, about 15 seconds.
7.80%甘油封片。7. 80% glycerol for mounting.
实施例十八:使用AD脑匀浆做竞争结合试验(Ki测定,结果如下表1所示)使用本领域的经典方法,使用AD病人死后的脑组织匀浆做竞争结合实验,将BSA(PBS配制),已知的阳性对照放射性配体(125IMPY),AD及对照的脑组织匀浆,待测的配体(配制10个梯度浓度)进行分装混匀,依次加入到硼硅玻璃试管中,恒温37度孵育2h,然后用ZT-II型多头细胞样品收集器通过Whatman GF/B滤纸(1%的聚乙烯亚胺溶液浸泡过的)经真空过滤将结合和游离的放射性配体分离,用50mM的PBS溶液洗3次,然后用γ计数器测量膜上计数,将试验的结果使用Graphpad5.0软件,进行非线性回归分析,由此计算Ki值。取值是3个独立试验的平均取值±SEM,每个试验重复一次。Embodiment 18: Use AD brain homogenate to do competition binding test (Ki determination, the results are shown in Table 1 below). Using the classic method in this field, use postmortem brain tissue homogenate of AD patients to do competition binding test, and BSA ( prepared in PBS), the known positive control radioactive ligand ( 125 IMPY), AD and control brain tissue homogenate, the ligand to be tested (prepared 10 gradient concentrations) were aliquoted and mixed, and then added to borosilicate glass In the test tube, incubate at a constant temperature of 37 degrees for 2 hours, and then vacuum filter the bound and free radioligands through Whatman GF/B filter paper (soaked in 1% polyethyleneimine solution) with a ZT-II multi-head cell sample collector Separate and wash with 50mM PBS solution for 3 times, then measure the count on the membrane with a gamma counter, use Graphpad5.0 software for the test results, and perform nonlinear regression analysis to calculate the Ki value. Values are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments, with each experiment repeated once.
表1Table 1
实施例十九:使用AD人脑切片做放射自显影Example 19: Autoradiography using AD human brain slices
使用本领域的经典方法,使用连续的AD人脑组织切片做放射自显影实验。先将6μm厚度石蜡人脑切片脱蜡至水,配制125I标记的茚酮类衍生物的[125I]D8j和[125I]D8L(放射性配体),将组织上加500ul配制好的125I标记的放射性配体工 作液,37度水浴锅内孵育2h。吸去组织切片上的热配体溶液,0.01M PBS处理2次,各5min。再根据不同待测化合物的性质选择不同的分化条件,以125IMPY为例,分化条件为溶于40%乙醇的饱和Li2CO3 2min,40%乙醇2min,再用0.01M PBS洗,ddH2O冲洗30秒,通风橱内放置30min晾干。晾干后的组织切片在暗室中置于暗匣中压上X光胶片曝光。曝光一定时间后,在暗室中取出X光胶片进行显影和定影,处理好的胶片使用扫描仪进行扫描。Autoradiography experiments were performed using serial AD human brain tissue sections using classical methods in the field. First dewax paraffin human brain slices with a thickness of 6 μm to water, prepare [ 125 I]D8j and [ 125 I]D8L ( radioactive ligands) of 125 I-labeled indanone derivatives, and add 500ul of the prepared 125 I-labeled radioligand working solution, incubated in a 37-degree water bath for 2 hours. The hot ligand solution on the tissue slices was sucked off, and treated with 0.01M PBS twice, each for 5 minutes. Then choose different differentiation conditions according to the properties of different compounds to be tested. Taking 125 IMPY as an example, the differentiation conditions are saturated Li 2 CO 3 dissolved in 40% ethanol for 2 minutes, 40% ethanol for 2 minutes, then washed with 0.01M PBS, and rinsed with ddH2O 30 seconds, placed in a fume hood for 30 minutes to dry. The dried tissue sections were placed in a cassette in a darkroom and exposed to X-ray film. After exposure for a certain period of time, the X-ray film is taken out in the darkroom for development and fixing, and the processed film is scanned with a scanner.
Claims (17)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011100530428A CN102180780A (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2011-03-07 | Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011100530428A CN102180780A (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2011-03-07 | Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102180780A true CN102180780A (en) | 2011-09-14 |
Family
ID=44567097
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011100530428A Pending CN102180780A (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2011-03-07 | Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN102180780A (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102584774A (en) * | 2011-12-22 | 2012-07-18 | 合肥工业大学 | Xanthenone derivative and application thereof |
| US9266886B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2016-02-23 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| CN105585614A (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2016-05-18 | 中国科学技术大学 | Angiopeptides and their derivatives for amyloid imaging |
| US9481674B1 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-11-01 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9663515B2 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2017-05-30 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9796710B2 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2017-10-24 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9845308B2 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2017-12-19 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Isoindoline inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10301261B2 (en) | 2015-08-05 | 2019-05-28 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Substituted indoles as modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US10829481B2 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2020-11-10 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Benzimidazole derivatives as modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US10913739B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2021-02-09 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, LLC (121374) | Inhibitors of RORγ |
| US11008340B2 (en) | 2015-11-20 | 2021-05-18 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US11186573B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2021-11-30 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Inhibitors of ROR gamma |
-
2011
- 2011-03-07 CN CN2011100530428A patent/CN102180780A/en active Pending
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| MOHAMED ASHRAF ALI ET AL.: "Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel 5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-2-indenyl-3,4-substituted phenyl methanone analogues", 《BIOORGANIC & MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS》 * |
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102584774A (en) * | 2011-12-22 | 2012-07-18 | 合肥工业大学 | Xanthenone derivative and application thereof |
| US10047085B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2018-08-14 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9266886B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2016-02-23 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10807980B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2020-10-20 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US11535614B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2022-12-27 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9624217B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2017-04-18 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10399976B2 (en) | 2014-02-03 | 2019-09-03 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9796710B2 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2017-10-24 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10087184B2 (en) | 2014-10-14 | 2018-10-02 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of RORγ |
| CN105585614B (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2019-06-07 | 中国科学技术大学 | Vascular peptides and derivatives thereof for amyloid imaging |
| CN105585614A (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2016-05-18 | 中国科学技术大学 | Angiopeptides and their derivatives for amyloid imaging |
| US9845308B2 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2017-12-19 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Isoindoline inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US11001583B2 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2021-05-11 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US9663515B2 (en) | 2014-11-05 | 2017-05-30 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10301261B2 (en) | 2015-08-05 | 2019-05-28 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Substituted indoles as modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US10829448B2 (en) | 2015-08-05 | 2020-11-10 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Substituted benzoimidazoles as modulators of ROR-γ |
| US11008340B2 (en) | 2015-11-20 | 2021-05-18 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US10829481B2 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2020-11-10 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Benzimidazole derivatives as modulators of ROR-gamma |
| US9481674B1 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2016-11-01 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Dihydropyrrolopyridine inhibitors of ROR-gamma |
| US10913739B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2021-02-09 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, LLC (121374) | Inhibitors of RORγ |
| US11186573B2 (en) | 2017-07-24 | 2021-11-30 | Vitae Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Inhibitors of ROR gamma |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102180780A (en) | Indenone derivative and applications thereof as developing agent and aggregation inhibitor of amyloid protein deposit and neurofibrillary tangle | |
| JP5719903B2 (en) | Imaging agents for detecting neurological disorders | |
| TWI245764B (en) | Amyloid plaque aggregation inhibitors and diagnostic imaging agents | |
| EP1999109B1 (en) | Styrylpyridine derivatives and their use for binding and imaging amyloid plaques | |
| Ono et al. | Aurones serve as probes of β-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease | |
| EP2365974B1 (en) | Fluorinated benzothiazole derivatives, preparation method thereof and imaging agent for diagnosing altzheimer's disease using the same | |
| AU2002258915A1 (en) | Amyloid plaque aggregation inhibitors and diagnostic imaging agents | |
| JP2010524965A (en) | Diphenyl-heteroaryl derivatives and their use for binding to amyloid plaques and imaging | |
| Matsumura et al. | Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel styryl benzimidazole derivatives as probes for imaging of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease | |
| BRPI0808503A2 (en) | COMPOUND AND USE OF A COMPOUND | |
| Fuchigami et al. | Synthesis and evaluation of ethyleneoxylated and allyloxylated chalcone derivatives for imaging of amyloid β plaques by SPECT | |
| Wang et al. | 99mTc-labeled-2-arylbenzoxazole derivatives as potential Aβ imaging probes for single-photon emission computed tomography | |
| CN102557969A (en) | Cyclic ketone derivatives and applications thereof as developers and aggregation inhibitors of amyloid protein sediments and neurofibrillary tangles | |
| KR20110045023A (en) | Novel benzofuran suitable as precursor of compounds useful for imaging amyloid deposits | |
| CN102558091B (en) | Benzothiazole derivative and application thereof | |
| US7737183B2 (en) | β-amyloid and neurofibrillary tangle imaging agents | |
| Ono et al. | Synthesis and biological evaluation of (E)-3-styrylpyridine derivatives as amyloid imaging agents for Alzheimer's disease | |
| Fuchigami et al. | Synthesis and biological evaluation of radioiodinated quinacrine-based derivatives for SPECT imaging of Aβ plaques | |
| CN102584774B (en) | Xanthenone derivative and application thereof | |
| CN108047145B (en) | 2-Arylquinoxaline compounds with affinity for Tau protein and preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP5954737B2 (en) | Radioactive fluorine-labeled quinoxaline compound | |
| JPWO2008068974A1 (en) | Diagnostic composition containing aurone derivatives | |
| CN101293864B (en) | A compound having affinity with brain Aβ plaques and its preparation method and application | |
| JP2010520275A (en) | Novel 2-heteroaryl substituted indole 695 | |
| AU2002350751A1 (en) | Compounds which can be used to diagnose and monitor diseases associated with the formation of amyloid protein fibrils |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |
Application publication date: 20110914 |