JAX-Fluids is a fully-differentiable CFD solver for 3D, compressible single-phase and two-phase flows. We developed this package with the intention to facilitate research at the intersection of ML and CFD. It is easy to use - running a simulation only requires a couple lines of code. Written entirely in JAX, the solver runs on CPU/GPU/TPU and enables automatic differentiation for end-to-end optimization of numerical models. JAX-Fluids is parallelized using JAX primitives and scales efficiently on state-of-the-art HPC clusters (tested on up to 512 NVIDIA A100 GPUs and on up to 2048 TPU-v3 cores).
To learn more about implementation details and details on numerical methods provided by JAX-Fluids, feel free to read our papers here and here. And also check out the documentation of JAX-Fluids.
Authors:
Correspondence via mail.
JAX-Fluids solves the Navier-Stokes-equations using the finite-volume-method on a Cartesian grid. The current version provides the following features:
- Explicit time stepping (Euler, RK2, RK3)
- High-order adaptive spatial reconstruction (WENO-3/5/7, WENO-CU6, WENO-3NN, TENO)
- Riemann solvers (Lax-Friedrichs, Rusanov, HLL, HLLC, Roe)
- Implicit turbulence sub-grid scale model ALDM
- Two-phase simulations via level-set method and diffuse-interface method
- Immersed solid boundaries via level-set method
- Positivity-preserving techniques
- Forcings for temperature, mass flow rate and kinetic energy spectrum
- Boundary conditions: Symmetry, Periodic, Wall, Dirichlet, Neumann
- CPU/GPU/TPU capability
- Parallel simulations on GPU & TPU
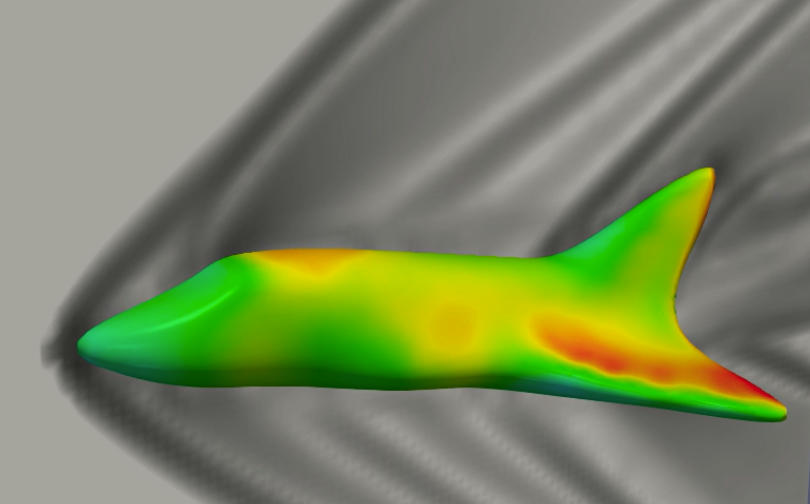
Space shuttle at Mach 2 - Immersed solid boundary method via level-set
Shock-bubble interaction with diffuse-interface method - approx. 800M cells on TPUv3-64
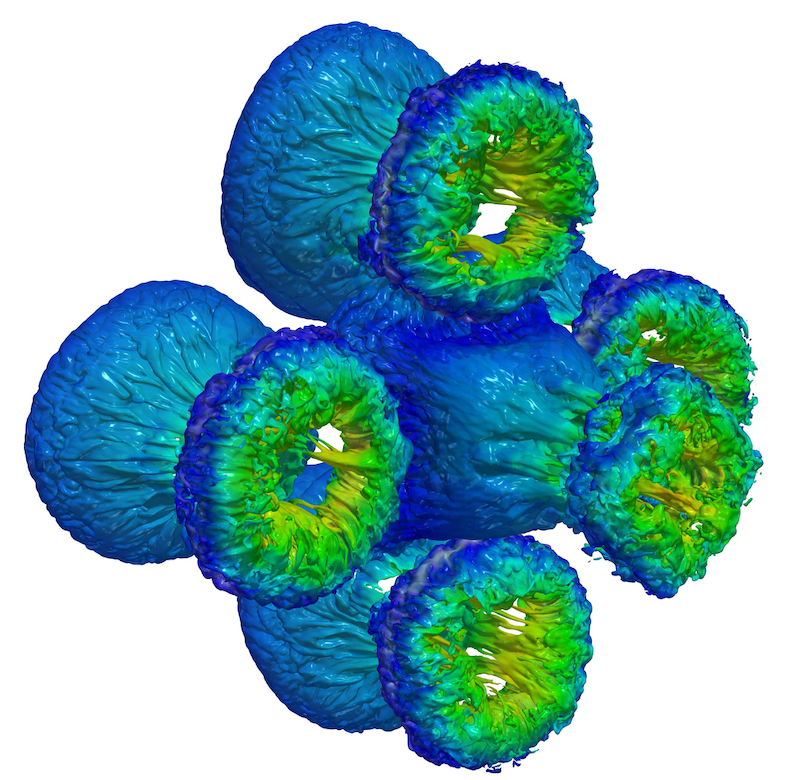
Shock-bubble interaction with level-set method - approx. 2B cells on TPUv3-256
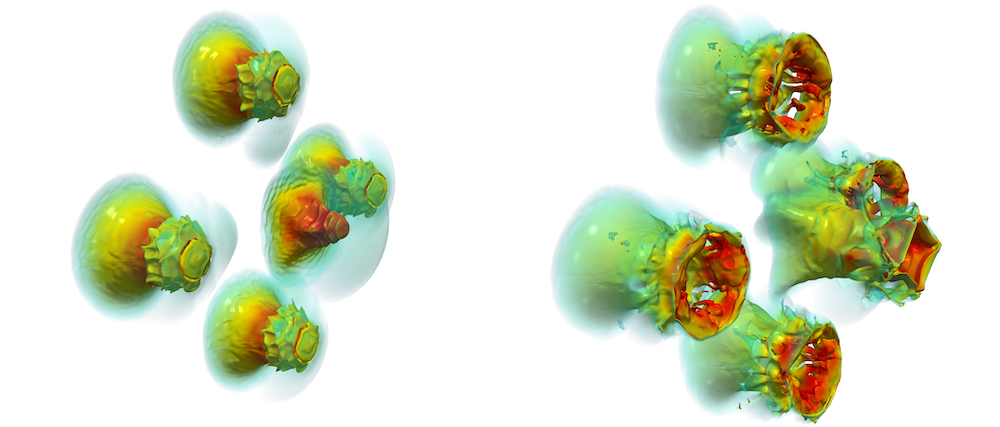
Shock-induced collapse of air bubbles in water (click link for video)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mt8HjZhm60U
Before installing JAX-Fluids, please ensure that you have an up-to-date version of pip.
pip install --upgrade pipTo install the CPU-only version of JAX-Fluids, you can run
pip install --upgrade "jax[cpu]"
git clone https://github.com/tumaer/JAXFLUIDS.git
cd JAXFLUIDS
pip install .Note: if you want to install JAX-Fluids in editable mode, e.g., for code development on your local machine, run
pip install -e .Note: if you want to use jaxlib on a Mac with M1 chip, check the discussion here.
If you want to install JAX-Fluids with CPU AND GPU support, you must first install JAX with GPU support. There are two ways to do this:
- installing CUDA & cuDNN via pip,
- installing CUDA & cuDNN by yourself.
See JAX installation for details.
We recommend installing CUDA & cuDNN using pip wheels:
pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda12]"
git clone https://github.com/tumaer/JAXFLUIDS.git
cd JAXFLUIDS
pip install -e .For more information on JAX on GPU please refer to the github of JAX
This github contains five jupyter-notebooks which will get you started quickly. They demonstrate how to run simple simulations like a 1D sod shock tube or a 2D air-helium shock-bubble interaction. Furthermore, they show how you can easily switch the numerical and/or case setup in order to, e.g., increase the order of the spatial reconstruction stencil or decrease the resolution of the simulation.
Check out the documentation of JAX-Fluids.
We gratefully acknowledge access to TPU compute resources granted by Google's TRC program.
JAX-Fluids 2.0: Towards HPC for Differentiable CFD of Compressible Two-phase Flows https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.05193
@article{bezgin2024jax,
title={JAX-Fluids 2.0: Towards HPC for Differentiable CFD of Compressible Two-phase Flows},
author={Bezgin, Deniz A and Buhendwa, Aaron B and Adams, Nikolaus A},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.05193},
year={2024}
}
JAX-Fluids: A fully-differentiable high-order computational fluid dynamics solver for compressible two-phase flows https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2022.108527
@article{BEZGIN2022108527,
title = {JAX-Fluids: A fully-differentiable high-order computational fluid dynamics solver for compressible two-phase flows},
journal = {Computer Physics Communications},
pages = {108527},
year = {2022},
issn = {0010-4655},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2022.108527},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010465522002466},
author = {Deniz A. Bezgin and Aaron B. Buhendwa and Nikolaus A. Adams},
keywords = {Computational fluid dynamics, Machine learning, Differential programming, Navier-Stokes equations, Level-set, Turbulence, Two-phase flows}
}
This project is licensed under the GNU General Public License v3 - see the LICENSE file or for details https://www.gnu.org/licenses/.