package-sync helps package repository maintainers keep their package files and settings in sync with a skeleton/template repository.
compares the contents of a package repo against a package skeleton repo, displaying out-of-sync files and other issues.
package-sync requires:
node v12+git
You can install this application using npm:
npm install package-sync-cli
./node_modules/.bin/package-sync analyze array-to-xmlor run using npx:
npx package-sync-cli analyze array-to-xml
# with a specific config file
npx package-sync-cli --config myconfig.yml analyze array-to-xmlEach release also has a standalone version released as an archive that can be extracted and run without the need for npm, npx, or git clone. See the latest release to download the most recent standalone version.
If you instead prefer to clone the repository, clone with git clone and then run:
npm install
npm run build:prod
./dist/package-sync --helpMake sure you've modified the configuration file dist/package-sync.yml, specifically the paths.packages and paths.templates settings.
If the directories don't exist, they will be created for you when you run package-sync.
You can use the placeholder {{__dirname}} in the values of either setting and it will be replaced with the directory that the config file is in.
Make sure to quote the yaml value if you use the
{{__dirname}}placeholder to ensure valid YAML.
To configure the github user/organization name packages are pulled from, set the config.packages.vendor key.
Not maintaining Spatie packages? make sure to customize the
config.packages.emailandconfig.packages.homepageproperties.
See the configuration file comments for more information on the various options.
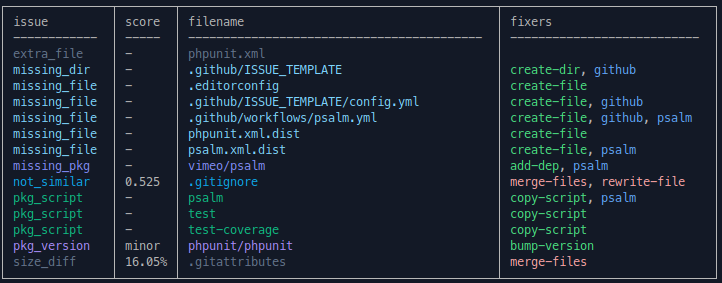
After running an analysis, you'll see a list of issues discovered with the package repository and the fixes available for each issue (not all issues have automated fixes available). Issues include out-of-sync files, missing composer dependencies, required version updates, missing files and more.
Analyze the spatie/array-to-xml package using the spatie/package-skeleton-php repository as a template:
./dist/package-sync analyze array-to-xmlFixers are color-coded:
green: considered safe to run without major file changesblue: 'multi' fixers run safe fixers on groups of related files (such as all psalm-related files, etc.)red: considered risky - these fixers make (possibly significant) modifications to existing files
The values in the score column indicate how similar the package copy of a file is to the skeleton's copy.
For decimal values, the closer to 1.0, the more similar the files are: 0.75 means the files are somewhat similar, and 0.89 means they are very similar.
Percentages indicate how different the files are: a value of 8.5% would mean the files are fairly similar, differing by only that much.
If an issue lists a filename but no value, the file only exists in either the skeleton or the package, but not both.
Dependency version issues list a score of major or minor, indicating the part of the semver version that needs to be upgraded.
Other issues not related to files, such as missing dependencies, do not have a score.
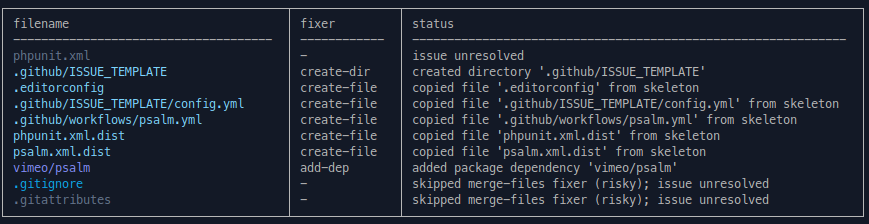
Issues are resolved by fixers, which are utilities that perform a various action, such as copying a missing file from the skeleton to the package repository. The available fixers for an issue are listed in the output of the analyze command.
If there are multiple fixers listed for an issue, the first one is used when running
fix.
Some fixers are considered "risky" - meaning they modify existing files. By default, these fixers will not run automatically when running the fix command. In order to permit risky fixers to run, you must call fix with the --risky flag.
You can apply all fixers to the discovered issues with the fix command.
You may specify both the fixer name and the --file flag to apply a fixer to the given file.
# fix all issues except for those with "risky" fixes
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml
# fix all issues
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml --risky
# only fix a specific file
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml --file psalm.xml.dist
# apply the 'psalm' fixer to only the specified filename
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml psalm --file psalm.xml.distFix only certian issue types:
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml missing_pkgRun a specific fixer by name:
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml psalmApply a specific fixer to a specific file:
./dist/package-sync fix array-to-xml psalm --file psalm.xml.dist| name | note | description |
|---|---|---|
add-dep |
adds a dependency to the package's composer.json file. | |
bump-version |
updates the version of a dependency in the package repository. | |
copy-script |
adds a missing composer script to the package's composer.json file. | |
create-dir |
creates a missing directory | |
create-file |
copies a file from the skeleton repository into the package repository. | |
github |
multi | recreates all missing directories and files under the '.github' directory. |
merge-files |
risky | merges the contents of both the skeleton and package versions of a file. |
overwrite-file |
risky | overwrite a file with the skeleton version to force an exact match. |
psalm |
multi | creates all missing psalm-related files and installs all psalm composer scripts and dependencies. |
rewrite-file |
risky | overwrites an existing file with a newer version from the skeleton. |
skip-dep |
skips the installation of a dependency. |
You can manually update your local copy of either a skeleton or package git repository. If the repository already exists locally, the pull-* commands will run git pull instead of git clone.
It's usually not necessary to run
pull-*commands manually
Repositories are cloned/updated automatically when running
analyzeorfix.
# pull an individual skeleton repo by name:
./dist/package-sync pull-template php
./dist/package-sync pull-template laravel
# or pull all skeleton repos:
./dist/package-sync pull-template# pull the spatie/array-to-xml package repo
./dist/package-sync pull-package array-to-xml
# pull spatie/laravel-sluggable
./dist/package-sync pull-package laravel-sluggable| Command | Aliases | Description |
|---|---|---|
analyze <packageName> |
a, an |
Compare a package against a template/skeleton repository |
fix <packageName> [type] |
-- | Fix a package's issues, optionally only fixing issues of the specified type |
fixers |
-- | List all fixers and their descriptions |
pull-template [name] |
pt |
Update/retrieve the named skeleton repository, or all if no name specified |
pull-package <name> |
pp |
Update/retrieve the named package repository |
package-sync uses Jest for unit tests. To run the test suite:
npm run testPlease see CHANGELOG for more information on what has changed recently.
Please see CONTRIBUTING for details.
Please review our security policy on how to report security vulnerabilities.
The MIT License (MIT). Please see License File for more information.