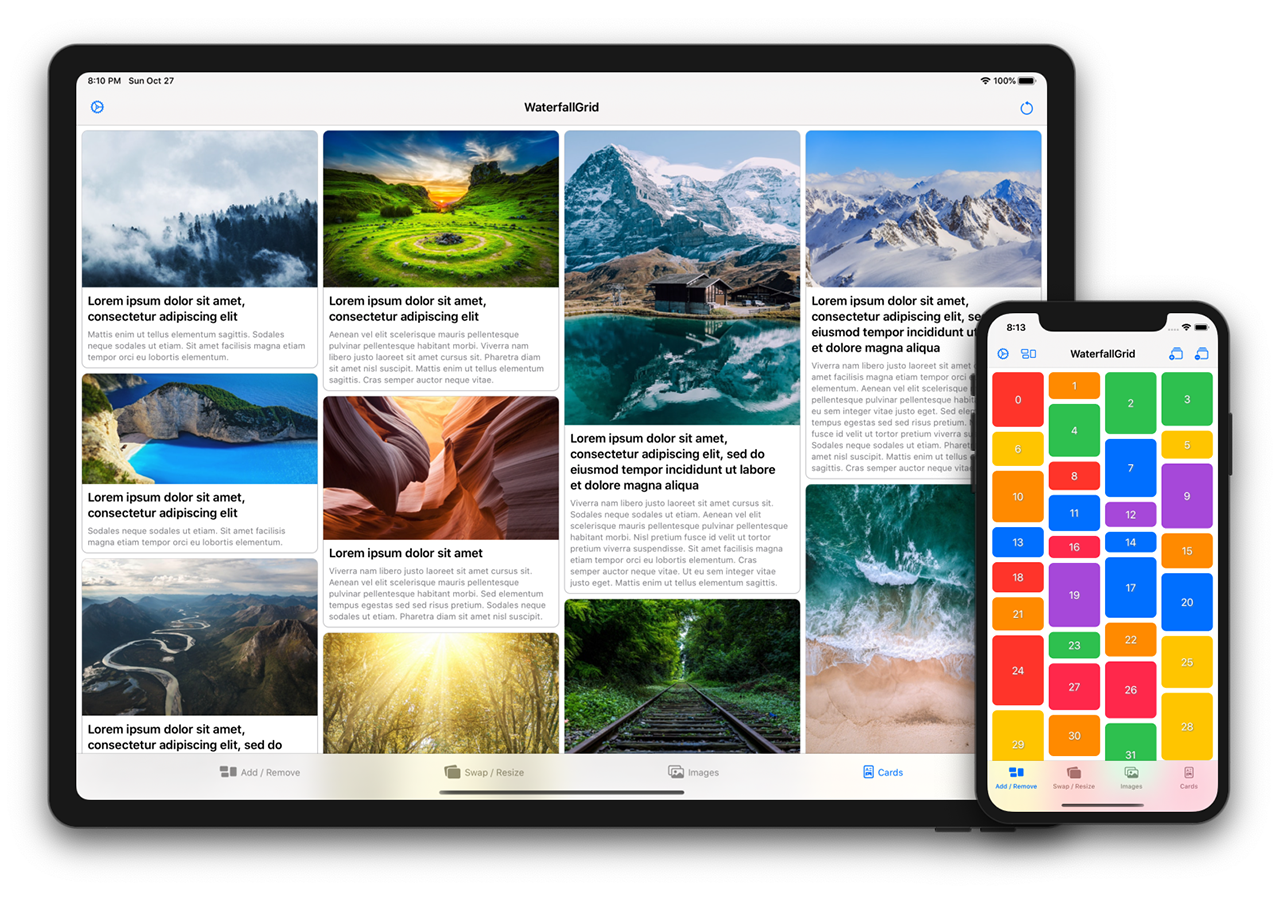
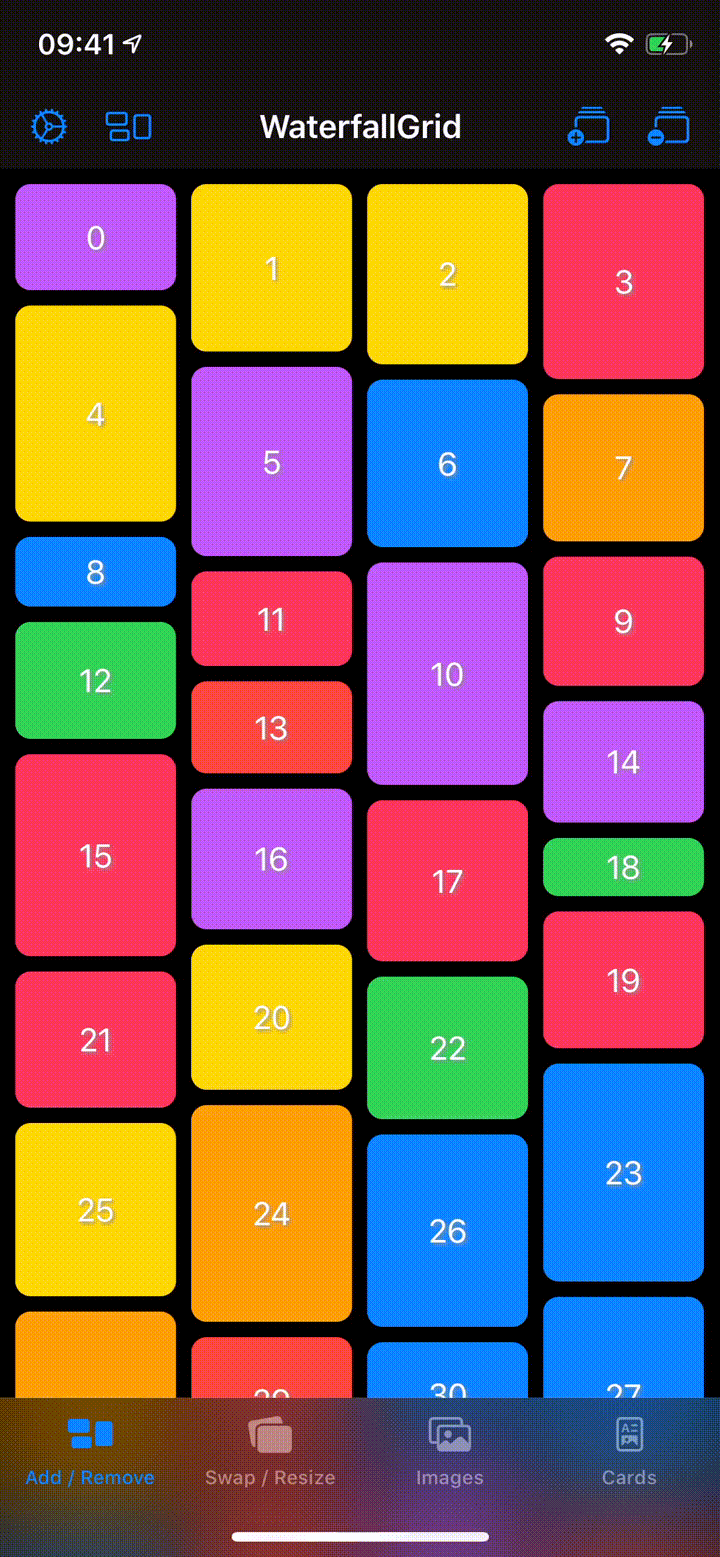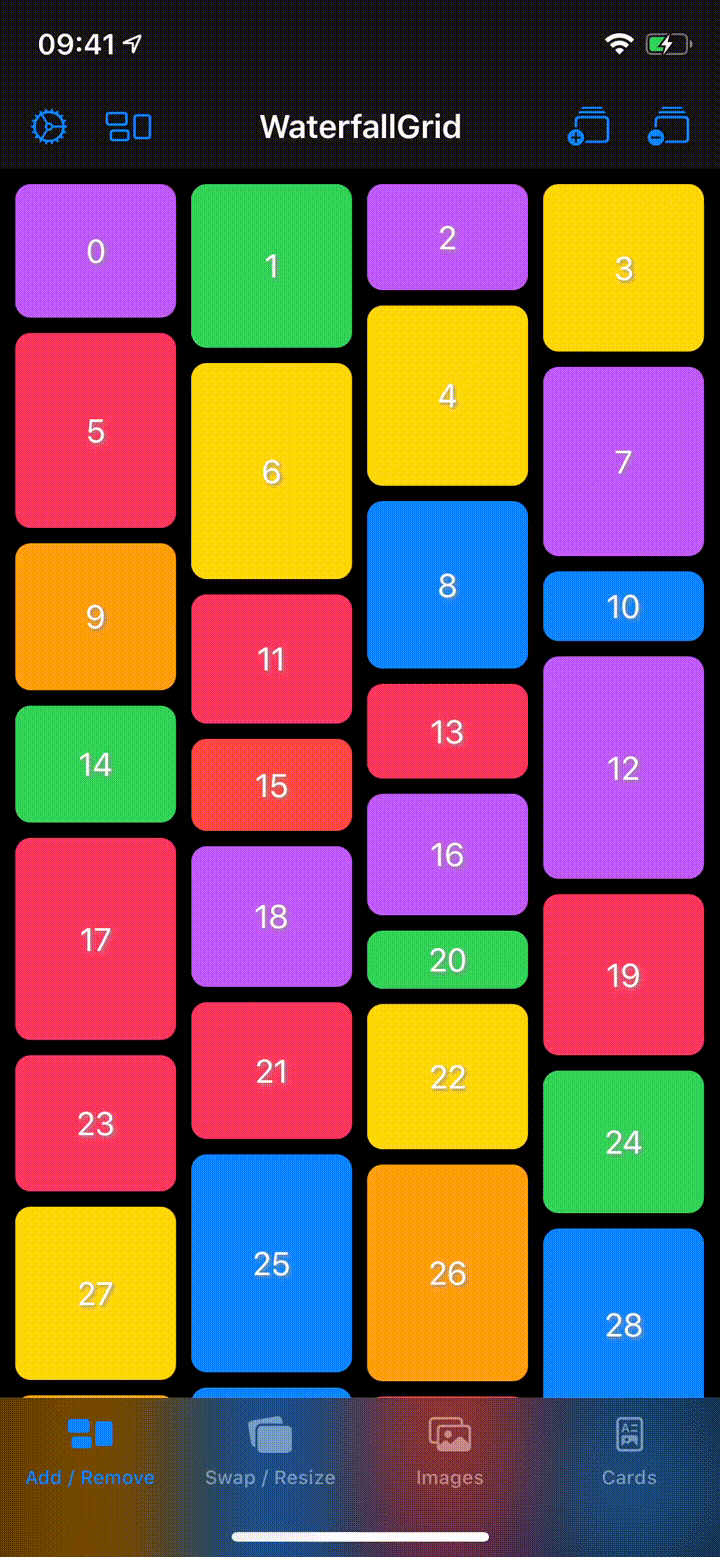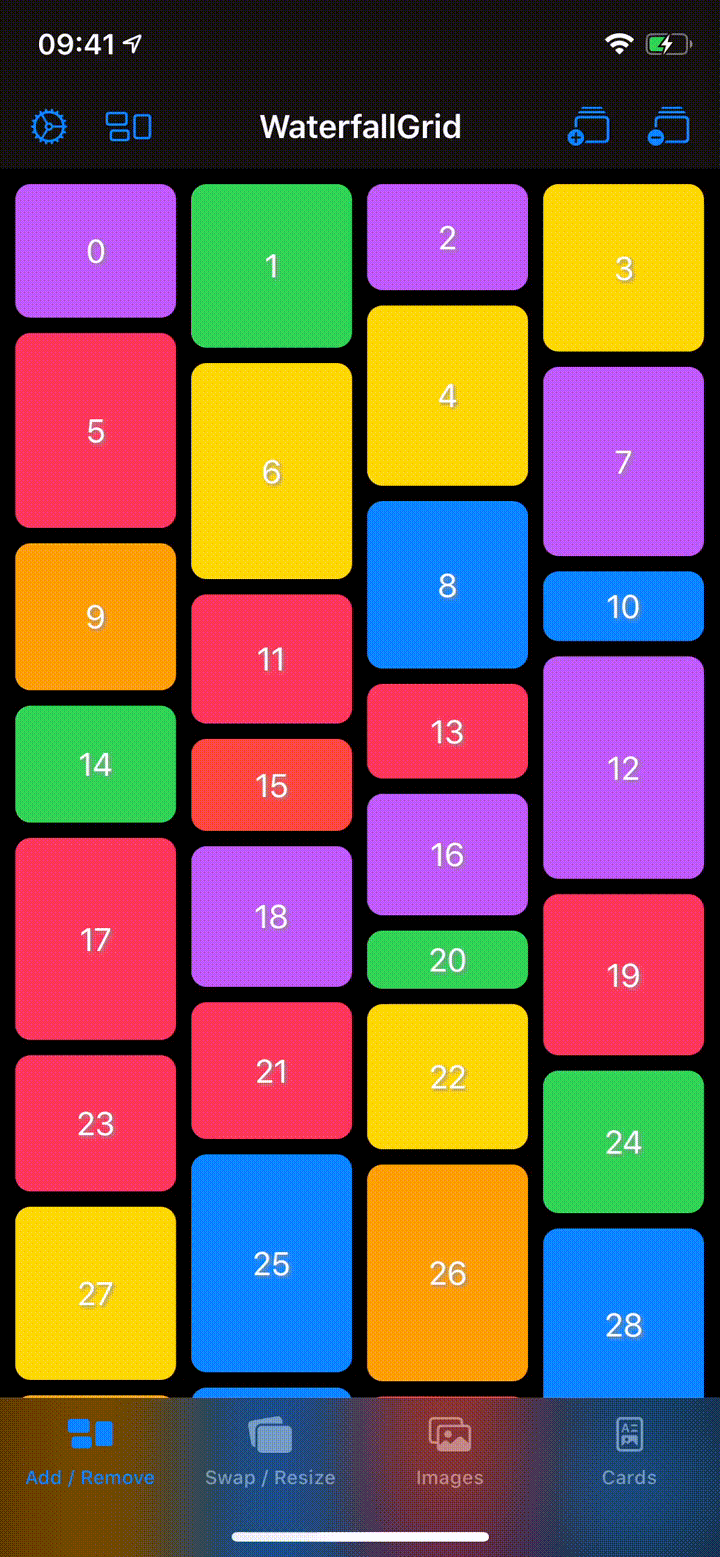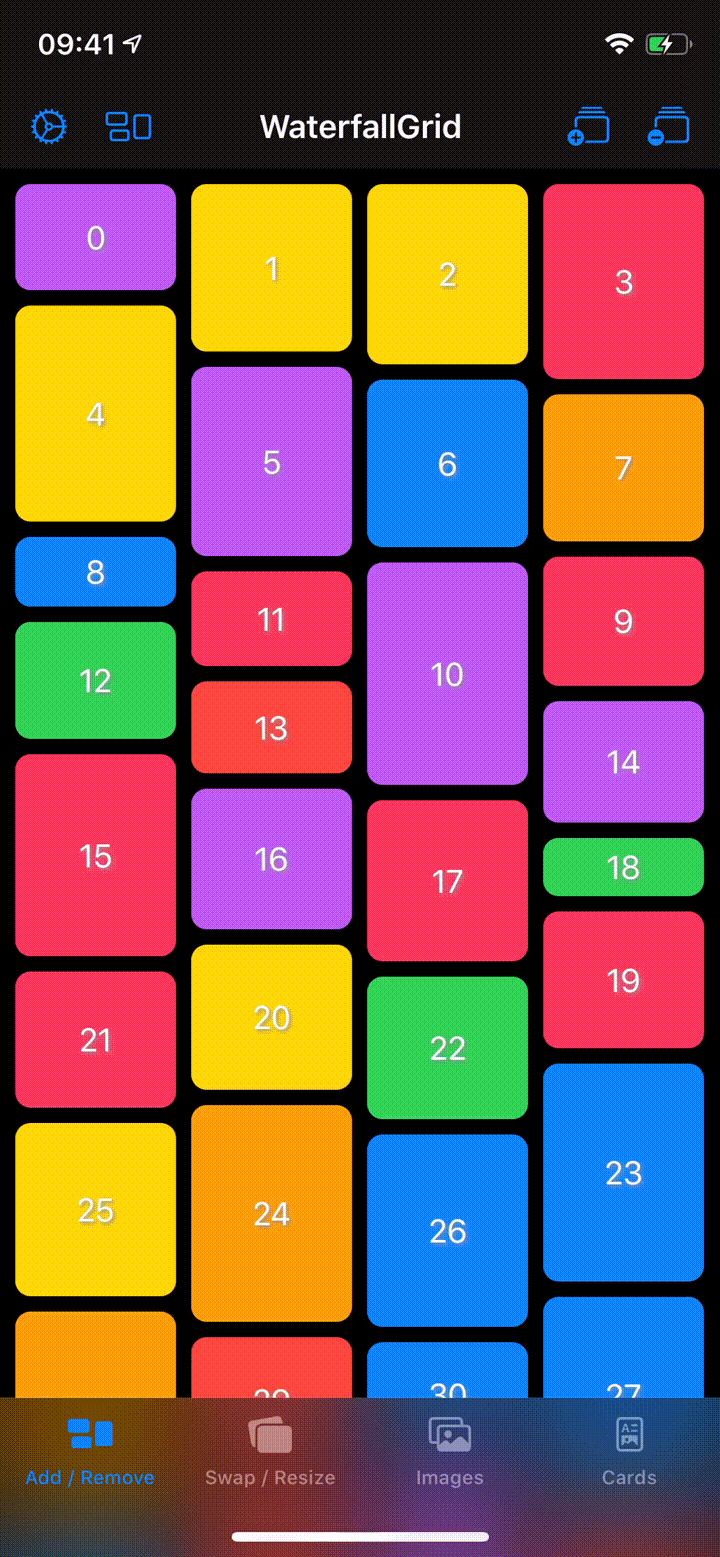
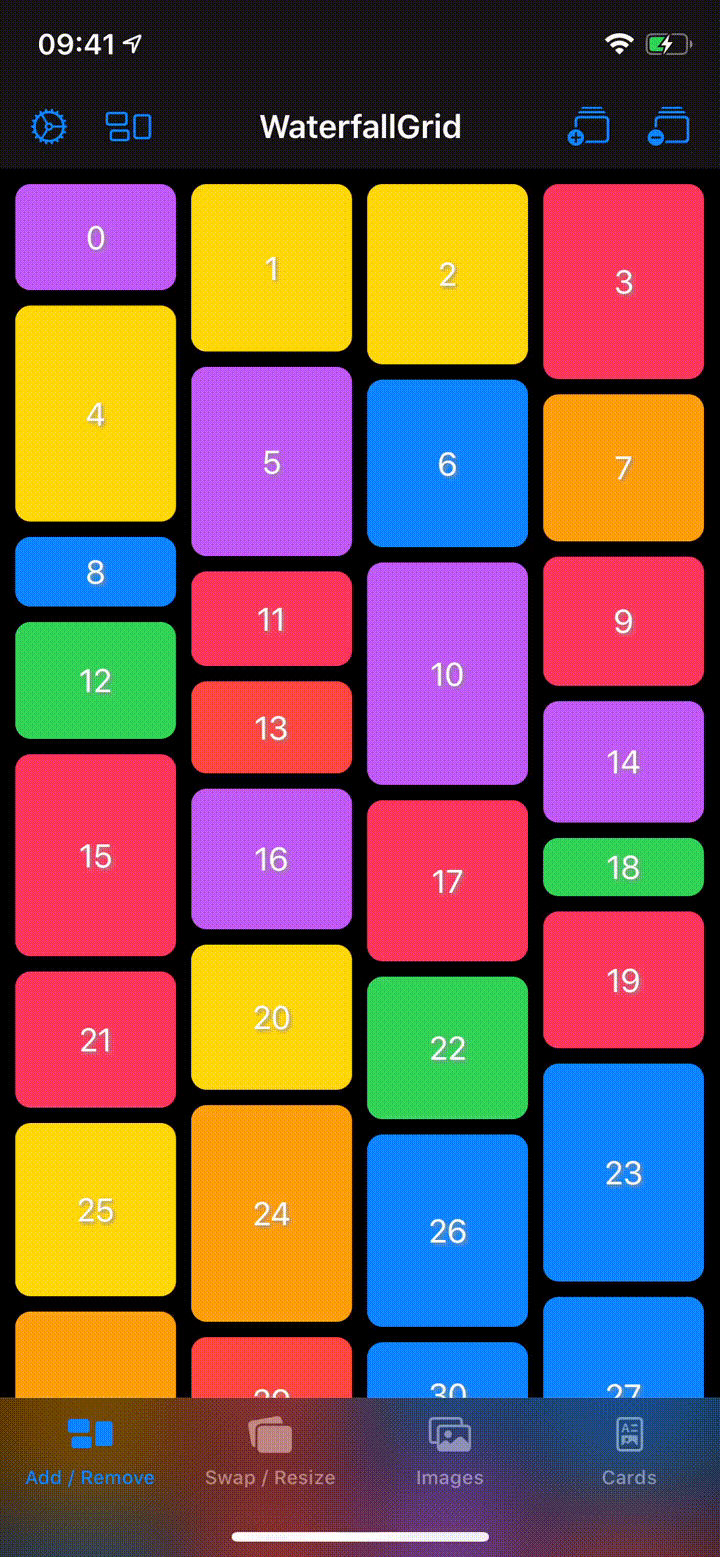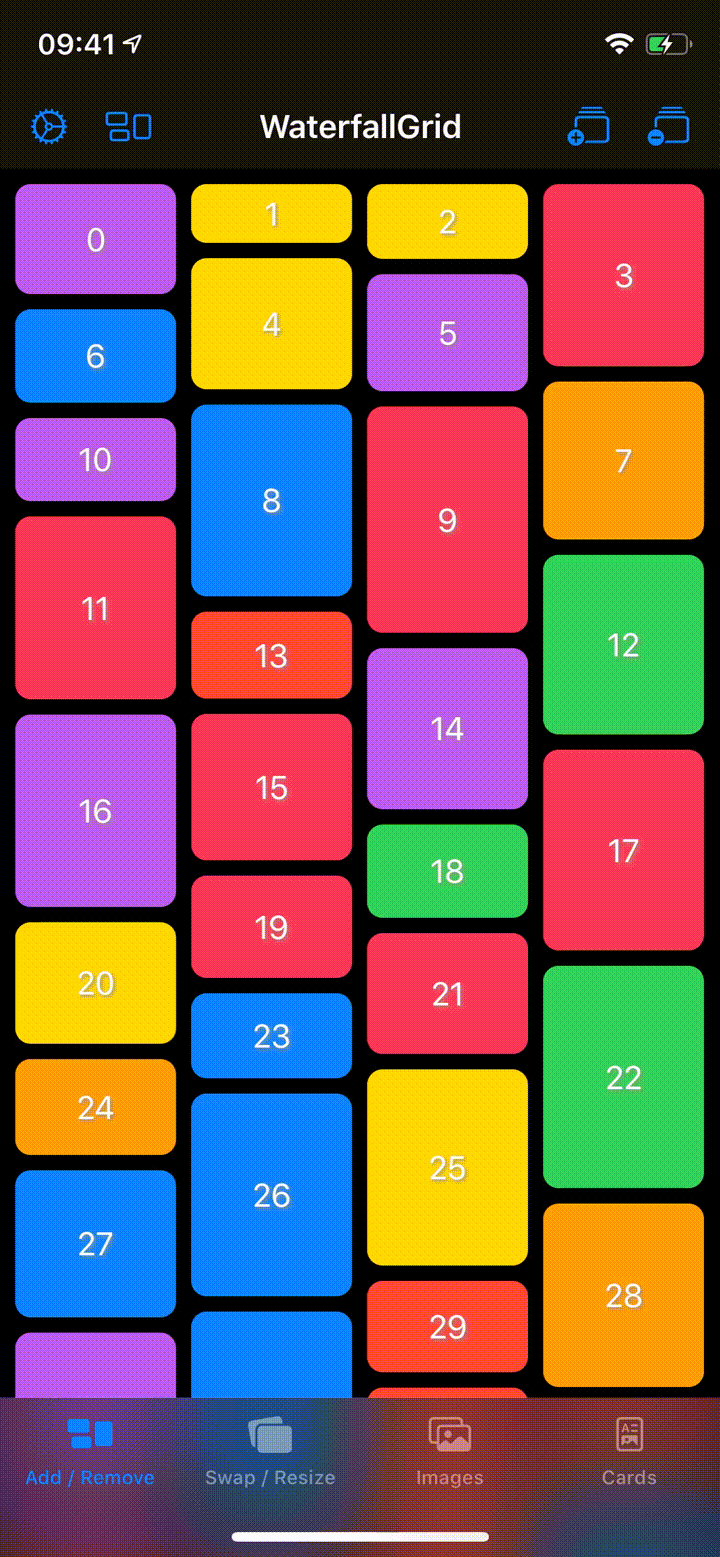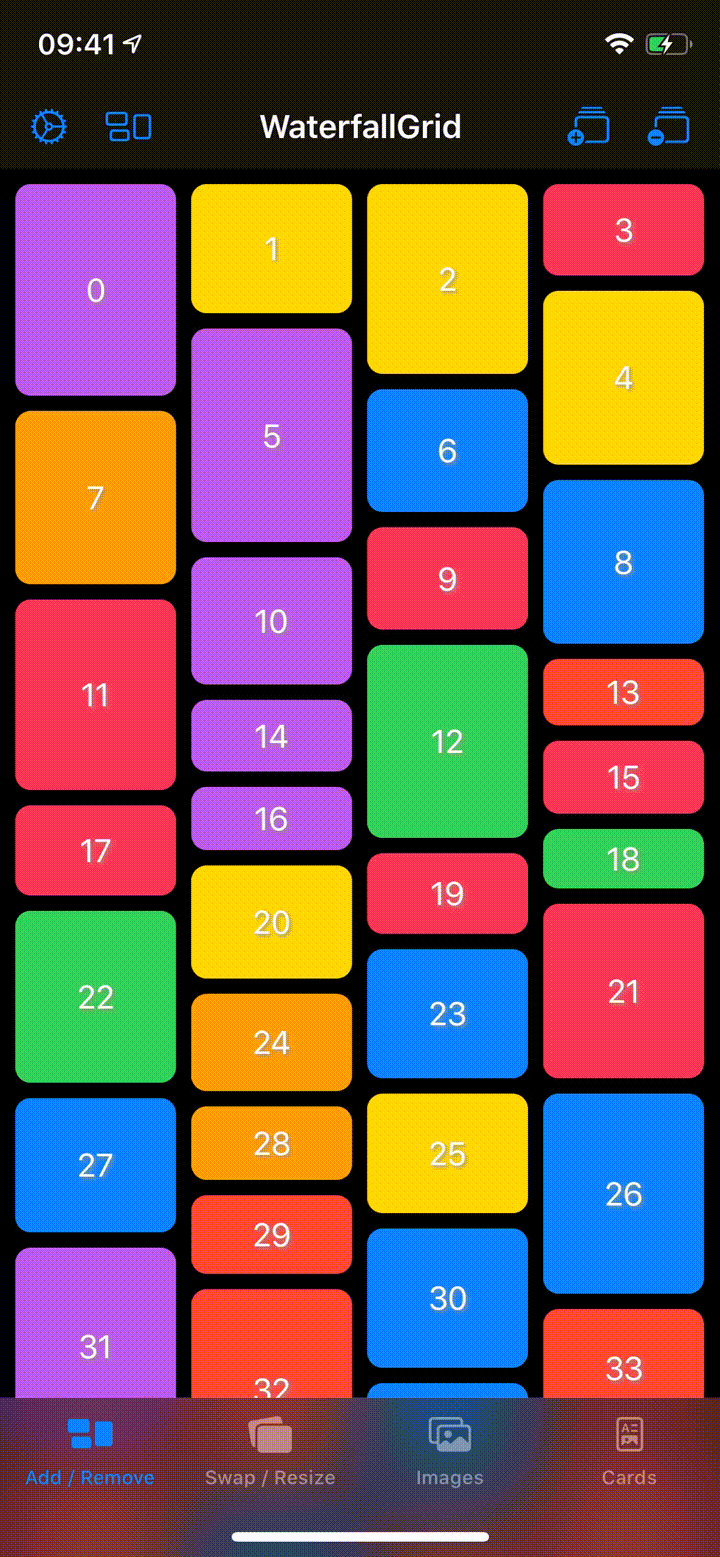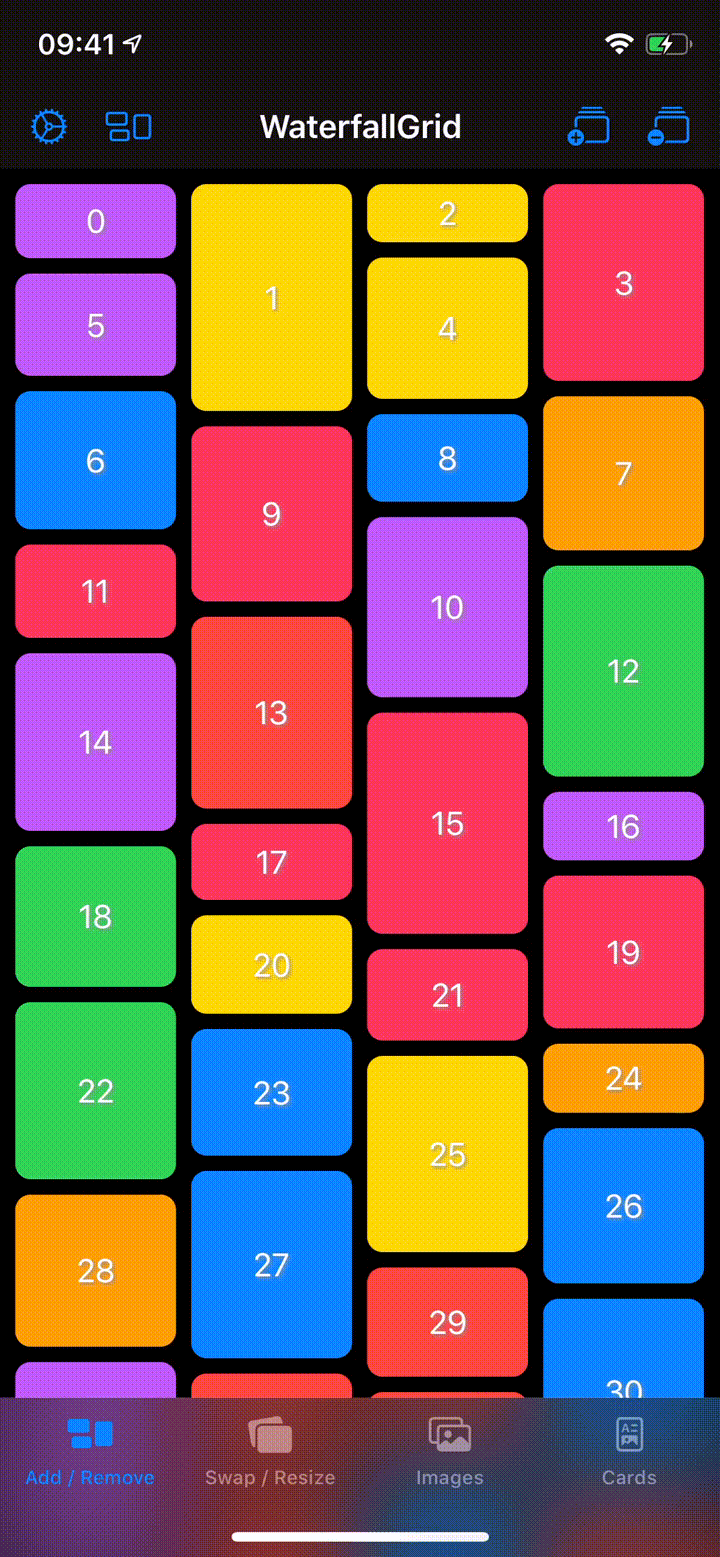
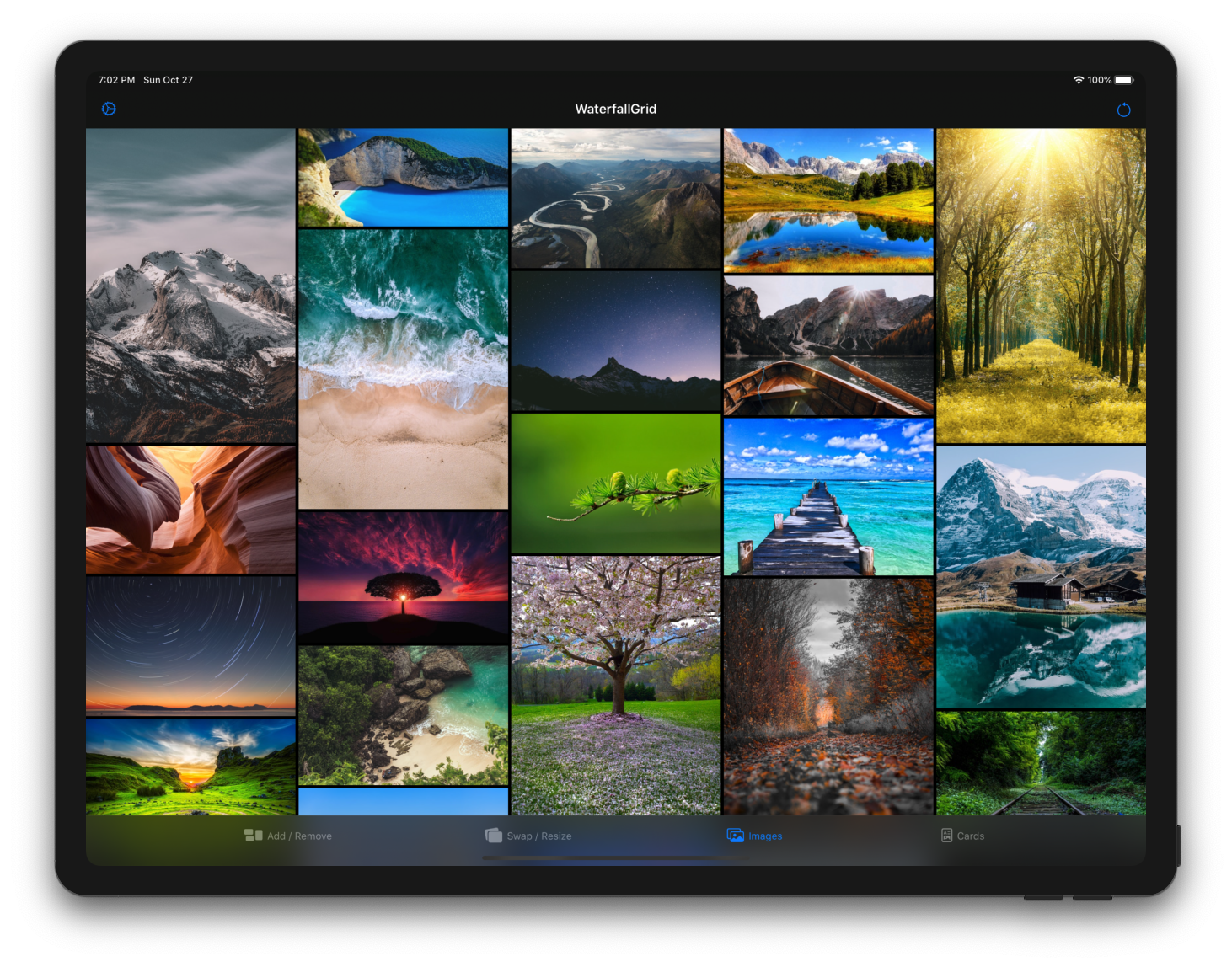
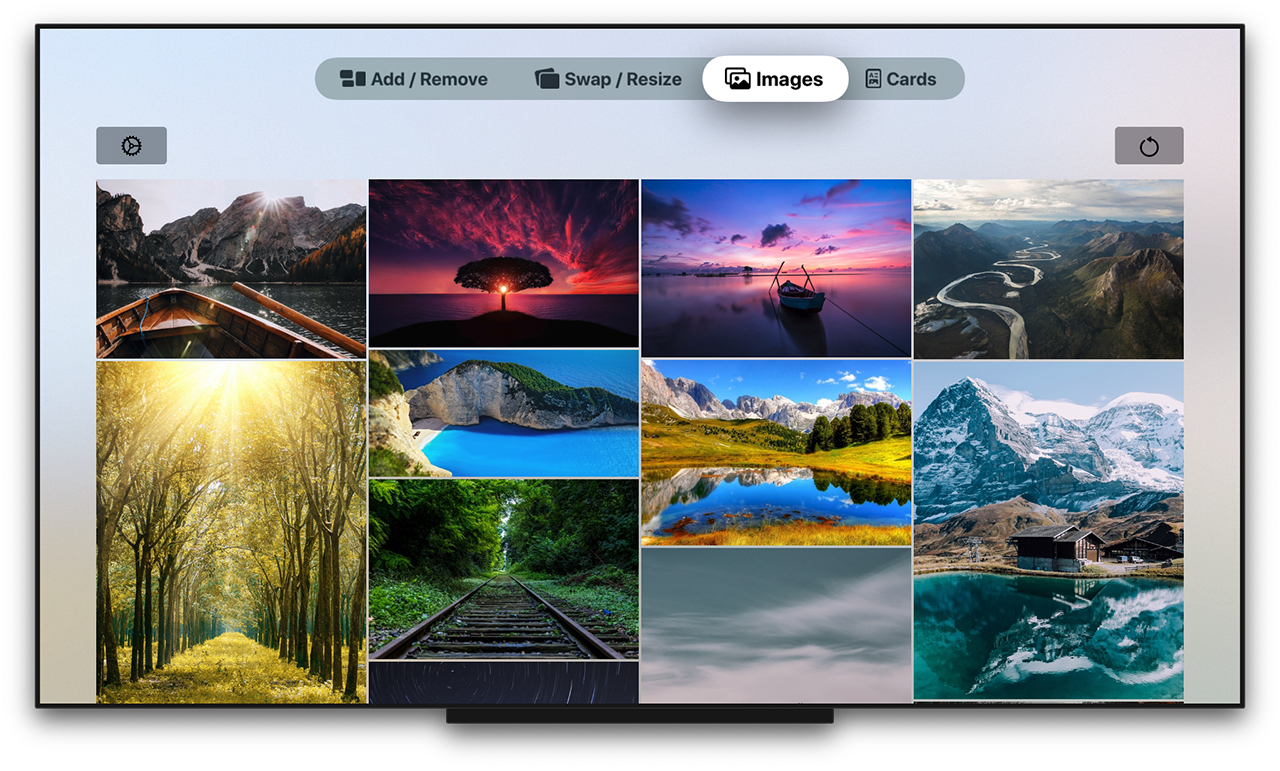
A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI.
- Irregular grid of content.
- Columns number different per device orientation.
- Spacing and grid padding customizable.
- Horizontal or vertical scroll direction.
- Items update can be animated.
You can create a grid that displays the elements of collection by passing your collection of data and a closure that provides a view for each element in the collection. The grid transforms each element in the collection into a child view by using the supplied closure.
WaterfallGrid works with identifiable data (like SwiftUI.List). You can make your data identifiable in one of two ways: by passing along with your data a key path to a property that uniquely identifies each element, or by making your data type conform to the Identifiable protocol.
Example 1
A grid of views of type Image from a collection of data identified by a key path.
WaterfallGrid((0..<10), id: \.self) { index in
Image("image\(index)")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
}Example 2
A grid of views of type RectangleView from a collection of Identifiable data.
WaterfallGrid(rectangles) { rectangle in
RectangleView(rectangle: rectangle)
}or, for simple cases like this, just:
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)To customise the appearance of the grid call the gridStyle function and pass the parameters you want to customise.
Columns
WaterfallGrid(cards) { card in
CardView(card: card)
}
.gridStyle(columns: 2)WaterfallGrid(cards, content: CardView.init)
.gridStyle(
columnsInPortrait: 2,
columnsInLandscape: 3
)Spacing and Padding
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.gridStyle(spacing: 8)
.padding(EdgeInsets(top: 16, leading: 8, bottom: 16, trailing: 8))Animation
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.gridStyle(animation: .easeInOut(duration: 0.5))Embed in ScrollView & Indicators option
ScrollView(showsIndicators: true) {
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
}Horizontal Scroll Direction
ScrollView(.horizontal) {
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.scrollOptions(direction: .horizontal)
}ScrollView(.horizontal, showsIndicators: false) {
WaterfallGrid(cards) { card in
CardView(card: card)
}
.gridStyle(
columnsInPortrait: 2,
columnsInLandscape: 3,
spacing: 8,
animation: .easeInOut(duration: 0.5)
)
.scrollOptions(direction: .horizontal)
.padding(EdgeInsets(top: 16, leading: 8, bottom: 16, trailing: 8))
}Explore the WaterfallGridSample app for some more detailed and interactive examples.
App dependency
select File > Swift Packages > Add Package Dependency and enter the repository URL (Adding Package Dependencies to Your App)
Package dependency
Add it as a dependency within your Package.swift manifest:
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid.git", from: "1.1.0")
]You can install WaterfallGrid via CocoaPods by adding the following line to your Podfile:
pod 'WaterfallGrid', '~> 1.1.0'Run the pod install command to download the library
and integrate it into your Xcode project.
For the versions available, see the releases on this repository.
Contributions are more than welcome. Please create a GitHub issue before submitting a pull request to plan and discuss implementation.
WaterfallGrid was inspired by the following projects:
- QGrid - https://github.com/Q-Mobile/QGrid
- Grid - https://github.com/SwiftUIExtensions/Grid
- The SwiftUI Lab - https://swiftui-lab.com
WaterfallGrid is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.