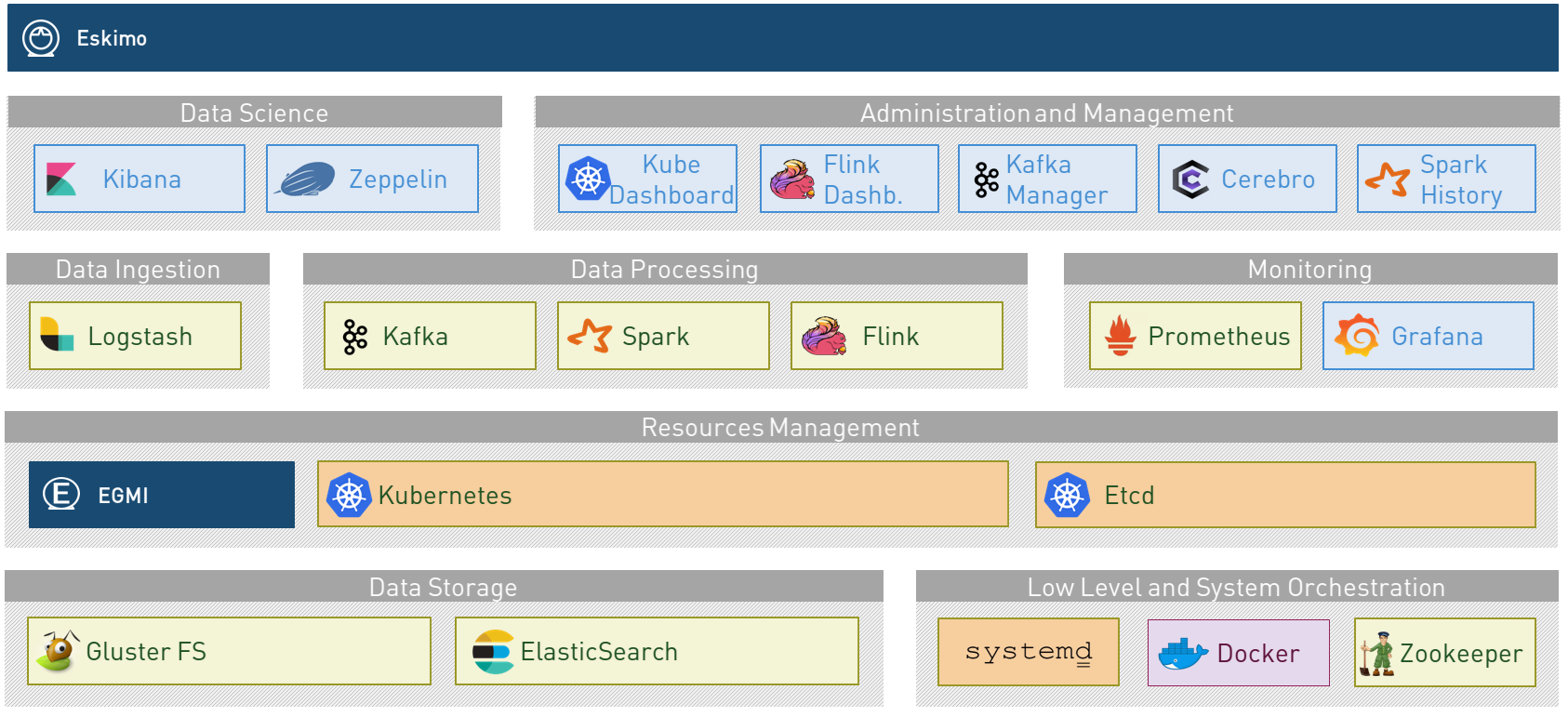
A state of the art Big Data Infrastructure and Management Platform to build, manage and operate Big Data 2.0 Analytics clusters on Kubernetes.
Eskimo is in a certain way the Operating System of your Big Data Cluster:
-
A plug and play, working out of the Box, Big Data Analytics platform fulfilling enterprise environment requirements.
-
A state of the art Big Data 2.0 platform
-
based on Kubernetes (and heavily relying on Docker and SystemD as well)
-
packaging Gluster, Spark, Kafka, Flink, ElasticSearch
-
with all the administration and management consoles such as Cerebro, Kibana, Zeppelin, Kafka-Manager, Grafana, Prometheus and of course the Kubernetes Dashboard.
-
everything all 100% pre-configured and setup to work perfectly together.
-
-
An Administration Application aimed at drastically simplifying the deployment, administration and operation of your Big Data Cluster
-
A Data Science Laboratory and Production environment where Data Analytics is both
-
developed and
-
operated in production
-
Eskimo is as well:
-
a collection of ready to use docker containers packaging fine-tuned and highly customized plug and play services with all the nuts and bolts required to make them work well together.
-
a framework for developing, building and deploying Big Data and NoSQL services based on Kubernetes, Docker and SystemD.
Eskimo Packages all the components above and takes care of all the configuration and tuning required to make them work together smoothly and without the user or administrator needing to take care of anything, Big Data the Plug & Play way.
Reach http://www.eskimo.sh for more information on Eskimo or look at the documentation in the folder doc.
Eskimo uses plain old Apache Maven for building (https://maven.apache.org/) as well as JDK 11+ (https://openjdk.java.net/) for both building and execution.
Minimum requirements are as follows:
-
JDK 11 or greater
-
Apache maven 3.5 or greater.
Every other dependency will be downloaded during the maven build process (except trilead-ssh2, see Install maven dependency trilead-ssh2
below).
Theoretically, Eskimo can be built on any Operating System providing a command line and supporting Java 11+ (Note : previous versions of JDK down to 8 may be supported without any guarantee) and Maven 3+.
However, the eskimo source tree makes an extensive use of symbolic links which - unfortunately - are only supported on Microsoft Windows 10 and 11 through "Developer Mode".
In order to checkout and develop Eskimo on Windows, some precautions need to be taken:
-
First, Developer Mode should be enabled on Windows to support symbolic links.
See https://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/windows-dev-docs/blob/docs/hub/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging.md -
Second, The
git clonecommand should explicitly enable symbolic link support. That would mean using following command for instance to checkout Eskimo master branch:
git clone -c core.symlinks=true https://github.com/eskimo-sh/eskimo.git
If these two precautions are well taken, one should be able to develop Eskimo on Windows.
A significant portion of the unit tests will however be skipped when executed on Windows since they require a Unix
Operating System to work properly.
In order to build eskimo, simply run the following command in this very folder (the one containing this readme.adoc
file):
mvn clean install
As a result of the build process, Eskimo is available as an extractable archive in eskimo-version-bin.zip or
eskimo-version-bin.tar.gz in the folder target.
You might want to read carefully the following additional information related to building eskimo.
Of course, for the above command to work, you need to have java and mvn in your path.
Use for instance the following commands on Linux:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/lib/jdk-11 ## (or wherever it's installed) export MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/lib/apache-maven-3.5.3 ## (same) export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$MAVEN_HOME/bin:$PATH
(You might want to put above commands in your /etc/profile or /etc/bash.bashrc)
And for instance the following commands on Windows
set JAVA_HOME=C:\programs\jdk-11 :: (or wherever it's installed) set MAVEN_HOME=C:\programs\apache-maven-3.6.1 :: (same) set PATH=%MAVEN_HOME%\bin;%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%PATH%
Eskimo used the library trilead-ssh2 version build-217-jenkins-27 which is not available in standard maven
repositories.
This library is bundled with the eskimo sources in the folder lib.
One can install it in his own local maven repository using the following command:
cd libs bash install_libs.sh
The build results at the end of the maven build process is located in the folder `target.
The results are two archive files:
-
A zip archive :
eskimo-version-bin.zip -
A tarball archive :
eskimo-version-bin.tar.gz
You can find pre-built packages of Eskimo on https://www.eskimo.sh.
The archive contains the full software packages with all dependencies and command line executables required to start it as well as the full documentation, etc.
This section gives instructions about running eskimo.
Eskimo itself can run on any Operating System supporting a JVM (Linux, Windows, Mac OSX) but cluster nodes are only supported running Linux.
In order to run eskimo, one needs to have
-
At least 20Gb of disk storage space on the machine running Eskimo
-
At least one linux machine available on the network (can be the same machine than the one running Eskimo) with either a debian-based (Ubuntu, Debian, etc.), red-hat-based (CentOS, RHEL, etc.) or OpenSUSE Operating System.
(See The Eskimo User Guide for more information on Eskimo cluster requirements.)
Eskimo is reached using a web browser (see startup logs). Supported web browsers are:
-
Microsoft Edge 14 or greater
-
Mozilla FireFox 54 or greater
-
Google Chrome 58 or greater
Note: there may be other browsers / versions supported (Safari, Opera but they are not certified to work with Eskimo)
In order to run eskimo, one needs to have java in the path.
Use for instance the following commands on Linux:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/lib/jdk-11 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
(You might want to put above commands in your /etc/profile or /etc/bash.bashrc)
And for instance the following commands on Windows
set JAVA_HOME=C:\programs\jdk-11 set PATH=%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%PATH%
After building eskimo using maven, the zip and tarball archives are located in the folder target.
One of these archives needs to be extracted on the local filesystem.
Then in the folder bin under the newly extracted eskimo binary distribution folder, one can find two scripts:
-
a script
eskimo.batto execute eskimo on Windows -
a script
eskimo.shto execute eskimo on Linux.
With eskimo properly started using the above scripts, one can reach eskimo using http://machine_ip:9191.
The default port number is 9191. This can be changed in configuration file eskimo.properties.
The default login / password credentials are admin / password.
Several issues can happen upon first eskimo startup.
This section describes common issues and ways to resolved them.
If you meet an error as the following on startup:
Caused by: ch.niceideas.common.utils.FileException: ./eskimo-users.json (Unauthorized access)
at ch.niceideas.common.utils.FileUtils.writeFile(FileUtils.java:154)
at ch.niceideas.eskimo.security.JSONBackedUserDetailsManager.<init>(JSONBackedUserDetailsManager.java:81)
at ch.niceideas.eskimo.configurations.WebSecurityConfiguration.userDetailsService(WebSecurityConfiguration.java:127)
... 50 more
Caused by: java.io.FileNotFoundException: ./eskimo-users.json (Unauthorized access)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.open0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.open(FileOutputStream.java:276)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.<init>(FileOutputStream.java:220)
at java.base/java.io.FileOutputStream.<init>(FileOutputStream.java:170)
at java.base/java.io.FileWriter.<init>(FileWriter.java:90)
at ch.niceideas.common.utils.FileUtils.writeFile(FileUtils.java:149)
... 52 more
Eskimo uses a local file to define users and access credentials. Upon first startup, if that file doesn’t exist already,
it is created by eskimo (with the default credentials above) at the path pointed to by the property
security.userJsonFile in eskimo.properties.
If you experience the error above or something alike, change that propery to point to a location where the first version of the file can successfully be created.
With released versions of Eskimo, operators / administrators have the choice to either build packages / docker images
locally - which boils down to creating container images where the target software (e.g. spark, flink, gluster, etc.) is
downloaded from internet and installed - or download pre-built images from www.eskimo.sh.
Whereas on development - SNAPSHOT - versions of Eskimo downloading pre-built images is not possible, only the
possibility to build images locally is available.
Whenever building images locally, the majority of the failures from from references versions of software components not
avaiilable anymore. For instance, when the Apache flink team releases a new minor version, they most of the time remove
the previous minor from the download site.
When such think happen the building of the corresponding local image will fail in Eskimo.
The only solution to this is to update the target version in the file packages_dev/common/common.sh.
The directory structure of the eskimo source distribution is as follows:
-
doccontains the source documentation in asciidoc format -
libscontains dependencies not available in standard maven repositories -
packages_devcontains the docker images development framework and packages -
packages_distribis the destination folder in which downloaded or built images are placed -
services_setupcontains the services installation framework and packages -
srccontains the source files to build eskimo -
test_labcontains various tools to build VMs aimed at testing eskimo
The folder test_lab folder in the Eskimo CE project root folder contains a Vagrant framework used to create virtual
machines to test Eskimo.
The supported virtual machines are declared in the file VagrantFile in the variable nodes:
# Define cluster nodes
nodes = [
{ :hostname => 'deb-node1', :box => 'debian/buster64',
:ip => '192.168.10.11', :ram => 8000 },
{ :hostname => 'deb-node2', :box => 'ubuntu/xenial64',
:ip => '192.168.10.12', :ram => 6000 },
{ :hostname => 'cent-node1', :box => 'centos/7',
:ip => '192.168.10.13', :ram => 6000},
{ :hostname => 'cent-node2', :box => 'fedora/29-cloud-base',
:ip => '192.168.10.14', :ram => 6000 }
]
The defined VMs use different Operating Systems to test Eskimo’s installation on different OSes.
One can edit this variable to declare one’s own VM’s as required.
An individual VM is then started with vargrant using VirtualBox as follows:
$ cd ./test_lab/vagrant/ $ vagrant up deb-node1
Vagrant can also start VM’s using libvirt / QEMU / kvm if the required libraries and provider are properly installed:
$ cd ./test_lab/vagrant/ $ vagrant up deb-node1 --provider=libvirt
A script integration-test.sh is provided in test_lab/integration_test that is instrumental in building and testing
eskimo in depth.
It enables to test rebuilding a full fledged Eskimo environment from scratch on a test platform of one single of
multiple node(s) (VMs) and test all its features (run all the zeppelin sample notebooks, ensure proper deployment of
all services, etc.).
A specific command line flag in this script even enables to build a full Demo VM from scratch (See user guide on Demo
VM).
It’s usage is at follows:
eskimo@notebook:/work/eskimo/test_lab/integration_test$ ./integration-test.sh -h
Usage: integration-test.sh [Options] [Target Box IP]
where [Target Box IP] is optional IP address of box to target tests at
where [Options] in
-h Display this help message.
-p Rebuild eskimo service packages
-n Skip packages rebuild (useful when used with -a)
-r Rebuild eskimo (otherwise take latest build)
-f Fast repackage
-b Recreate box(es)
-e (Re-)install Eskimo on box
-s Setup Eskimo
-l Run Data load
-z Run Zeppelin notebooks test
-i Run CLI tests
-t Run other tests
-c Run cleanup
-o Take screenshots
-a RUN ALL OF THE ABOVE
-w Use screenshots to overwrite git tree images
-d Prepare the VM for DemoVM
-m Test on multiple nodes
For instance, the DemoVM is built using the following call:
eskimo@notebook:/work/eskimo/test_lab/integration_test$ ./integration-test.sh -ad
Multiple dependencies are required on the machine where this `integration-test.sh `script is intended to run:
-
Vagrant 2.2+
-
VirtualBox 6+
-
Apache Maven 3+
-
Java 11+
-
Docker 20+
-
OpenSSH and sshpass
All of these needs to be available in the PATH. (Lower versions of these software components might work as well but without any guarantee).
Look at the following files for more information
-
readme.adocin the folderpackages_devfor information about the components docker images building framework -
readme.adocin the folderservices_setupfor information about the services installation and operation framework.
Eskimo is Copyright 2019 - 2023 eskimo.sh - All rights reserved.
Author : http://www.eskimo.sh
Eskimo is available under a dual licensing model : commercial and GNU AGPL.
If you did not acquire a commercial licence for Eskimo, you can still use it and consider it free software under the
terms of the GNU Affero Public License. You can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Affero
Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
any later version.
Compliance to each and every aspect of the GNU Affero Public License is mandatory for users who did no acquire a
commercial license.
Eskimo is distributed as a free software under GNU AGPL in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Affero Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero Public License along with Eskimo. If not, see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/ or write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA, 02110-1301 USA.
You can be released from the requirements of the license by purchasing a commercial license. Buying such a commercial license is mandatory as soon as :
-
you develop activities involving Eskimo without disclosing the source code of your own product, software, platform, use cases or scripts.
-
you deploy eskimo as part of a commercial product, platform or software.
For more information, please contact eskimo.sh at https://www.eskimo.sh
The above copyright notice and this licensing notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.