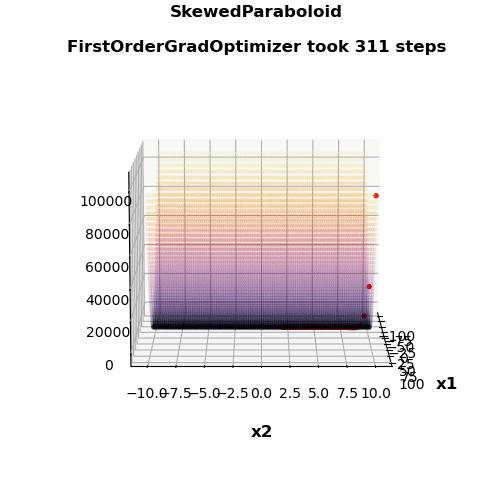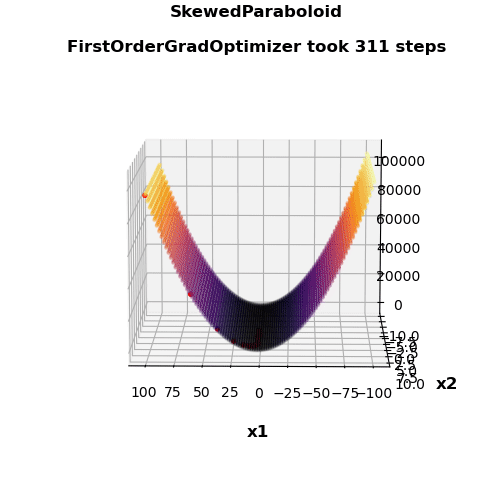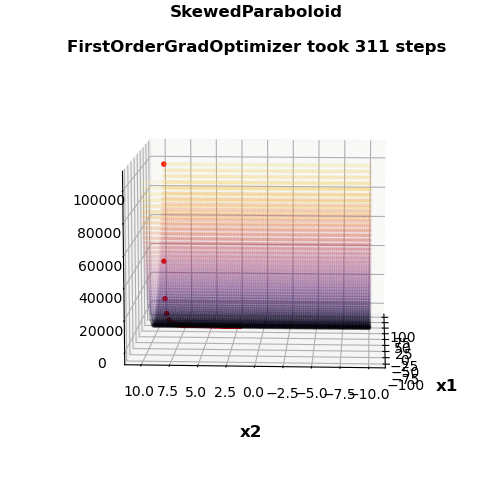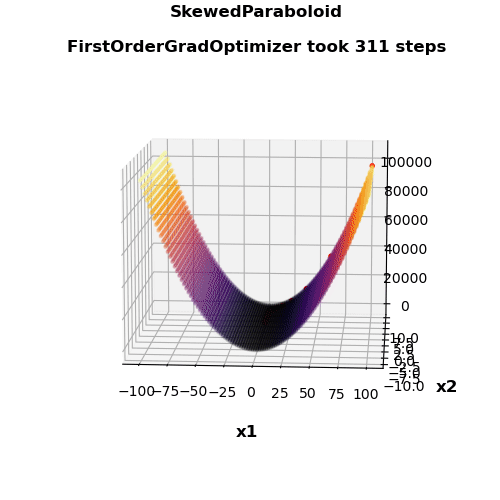
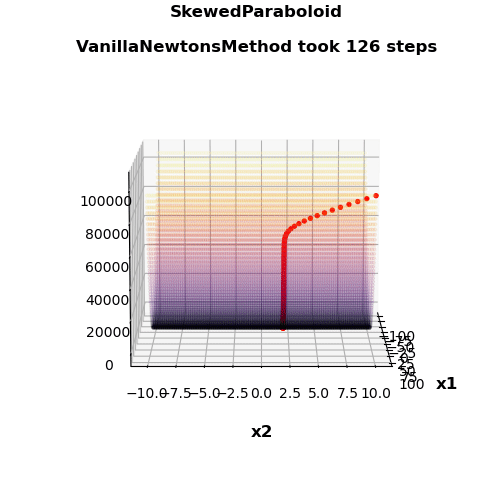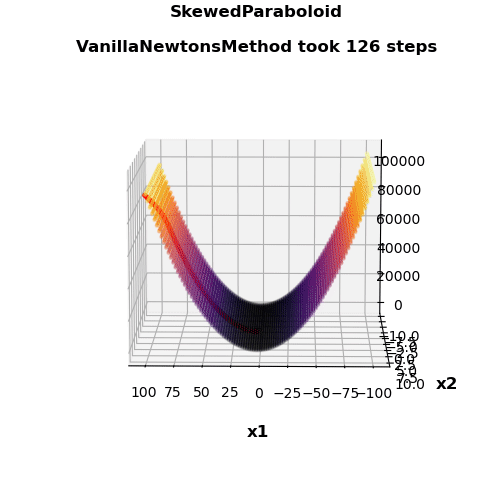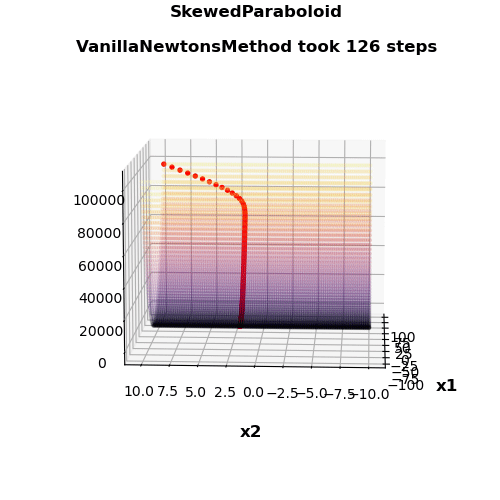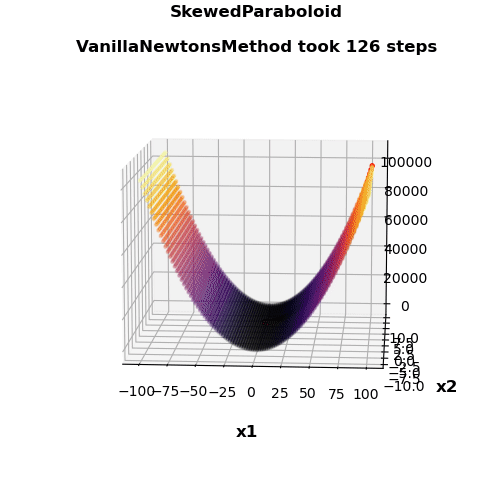
This project was carried out as a part of a coursework term project [CSED490Y]: Optimization for Machine Learning @ POSTECH.
- Implemented from scratch with minimal dependency (e.g. numpy, matplotlib)
- Four Newton’s method supported
- Two-variate convex functions supported
- Nice visualization
optim: choice of optimizer among{firstorder, newton, davidon, dfp, bfgs}.func: choice of two-variate function. The example functions are{paraboloid, skewedparaboloid, steepsidedvalley}.maxiter: int: number of max iteration.stepsize: float: step size (or learning rate)init: two-dimensional coordinate.viz: flag to visualize the landscape.
python main.py --optim dfp \
--func skewedparaboloid \
--stepsize 0.002 \
--init 100 10 \
--viz| total steps until convg. | computation time per iterations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| method | s. paraboloid | steep valley | s. paraboloid | steep valley |
| First-order gradient method | 311 | 4431 | 0.231 | 0.267 |
| Vanilla Newton’s method | 126 | 5 | 0.582 | 0.549 |
| Davidon’s method | 292 | 4 | 0.489 | 0.538 |
| Davidon-Fletcher-Powell method | 134 | 4 | 0.537 | 0.747 |
| Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shanno | 77 | 4 | 0.564 | 0.556 |