Converting binary floating-point to decimal floating-point numbers.
Contains an implementation of the Grisu2 and Grisu3 algorithms as described in
The Grisu3 implementation uses the Dragon4 algorithm as a fallback.
- Steele, White, How to Print FloatingPoint Numbers Accurately,
- Burger, Dybvig, Printing Floating-Point Numbers Quickly and Accurately,
Contains an implementation of the Ryu algorithm as described in
The implemenation also contains a (fast!) strtod implementation, which can be
used to convert decimal numbers with at most 17 significant decimal digits back
into binary floating-point numbers. (Note that none of the algorithms here will
ever produce more than 17 significant digits.)
Contains an implementation of the Schubfach algorithm as described in
- Giulietti, The Schubfach way to render doubles
The name of this algorithm "deliberately departs from a long lineage of fabulous drakes".
Contains a slightly modified version the reference implementation of Junekey Jeon's Dragonbox algorithm.
Grisu3, Ryu, Schubfach, and Dragonbox are optimal, i.e. the output string
- rounds back to the input number when read in,
- is as short as possible,
- is as close to the input number as possible.
These algorithms (currently) assume that the input rounding algorithm uses round-to-nearest-even to break ties. Grisu2 only is optimal for ~99% of all floating point numbers, though it guarantees the first property for all of its inputs, regardless of how the input rounding mode breaks ties.
Benchmarks were run on an Intel Core i7-9750H, using Visual Studio 2019 16.7.7, Clang 10.0, 64-bit.
Timings are in ns.
For this benchmark uniformly distributed random doubles in the
range [1,2] have been generated. These numbers were then rounded to N
significant digits and converted to decimal using the given algorithm.
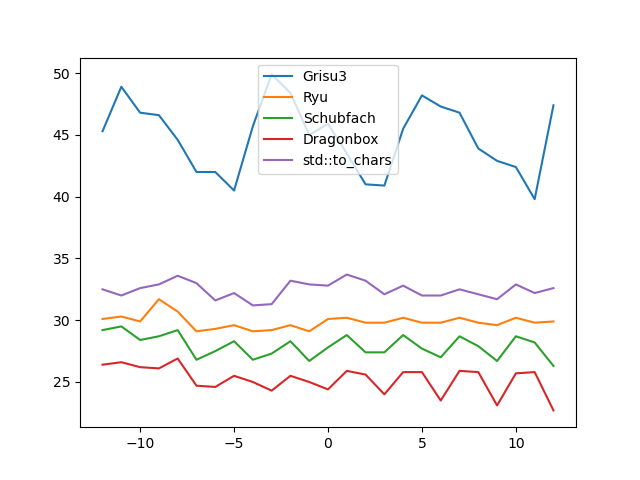
Uniformly distributed random numbers in the range [10^i, 10^(i+1)] for
i=-12,...,12.
Uniformly distributed random numbers in the range [0, 10^10]. Each benchmark
is run 10 times (using different numbers each run).
Random bit patterns. Each benchmark is run 10 times (using different numbers each run).