English | 简体中文
dt-sql-parser is a SQL Parser project built with ANTLR4, and it's mainly for the BigData field. The ANTLR4 generated the basic Parser, Visitor, and Listener, so it's easy to complete the Lexer, Parser, traverse the AST, and so on features.
Additionally, it provides advanced features such as SQL Validation, Code Completion and Collecting Table and Columns in SQL.
Supported SQL:
- MySQL
- Flink
- Spark
- Hive
- PostgreSQL
- Trino
- Impala
Tip
This project is the default for Typescript target, also you can try to compile it to other languages if you need.
We also have provided monaco-sql-languages to easily to integrate dt-sql-parser with monaco-editor.
# use npm
npm i dt-sql-parser --save
# use yarn
yarn add dt-sql-parserWe recommend learning the fundamentals usage before continuing. The dt-sql-parser library provides SQL classes for different types of SQL.
import { MySQL, FlinkSQL, SparkSQL, HiveSQL, PostgreSQL, TrinoSQL, ImpalaSQL } from 'dt-sql-parser';Before using syntax validation, code completion, and other features, it is necessary to instantiate the Parser of the relevant SQL type.
For instance, one can consider using MySQL as an example:
const mysql = new MySQL();The following usage examples will utilize the MySQL, and the Parser for other SQL types will be used in a similar manner as MySQL.
First instanced a Parser object, then call the validate method on the SQL instance to validate the sql content, if failed returns an array includes error message.
import { MySQL } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const mysql = new MySQL();
const incorrectSql = 'selec id,name from user1;';
const errors = mysql.validate(incorrectSql);
console.log(errors); output:
/*
[
{
endCol: 5,
endLine: 1,
startCol: 0,
startLine: 1,
message: "..."
}
]
*/Call the getAllTokens method on the SQL instance:
import { MySQL } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const mysql = new MySQL()
const sql = 'select id,name,sex from user1;'
const tokens = mysql.getAllTokens(sql)
console.log(tokens)output:
/*
[
{
channel: 0
column: 0
line: 1
source: [SqlLexer, InputStream]
start: 0
stop: 5
tokenIndex: -1
type: 137
_text: null
},
...
]
*/Traverse the tree node by the Visitor:
import { MySQL, MySqlParserVisitor } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const mysql = new MySQL();
const sql = `select id, name from user1;`;
const parseTree = mysql.parse(sql);
class MyVisitor extends MySqlParserVisitor<string> {
defaultResult(): string {
return '';
}
aggregateResult(aggregate: string, nextResult: string): string {
return aggregate + nextResult;
}
visitProgram = (ctx) => {
return this.visitChildren(ctx);
};
visitTableName = (ctx) => {
return ctx.getText();
};
}
const visitor = new MyVisitor();
const result = visitor.visit(parseTree);
console.log(result);output:
/*
user1
*/Access the specified node in the AST by the Listener
import { MySQL, MySqlParserListener } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const mysql = new MySQL();
const sql = 'select id, name from user1;';
const parseTree = mysql.parse(sql);
class MyListener extends MySqlParserListener {
result = '';
enterTableName = (ctx): void => {
this.result = ctx.getText();
};
}
const listener = new MyListener();
mysql.listen(listener, parseTree);
console.log(listener.result)output:
/*
user1
*/Take FlinkSQL as an example, call the splitSQLByStatement method on the SQL instance:
import { FlinkSQL } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const flink = new FlinkSQL();
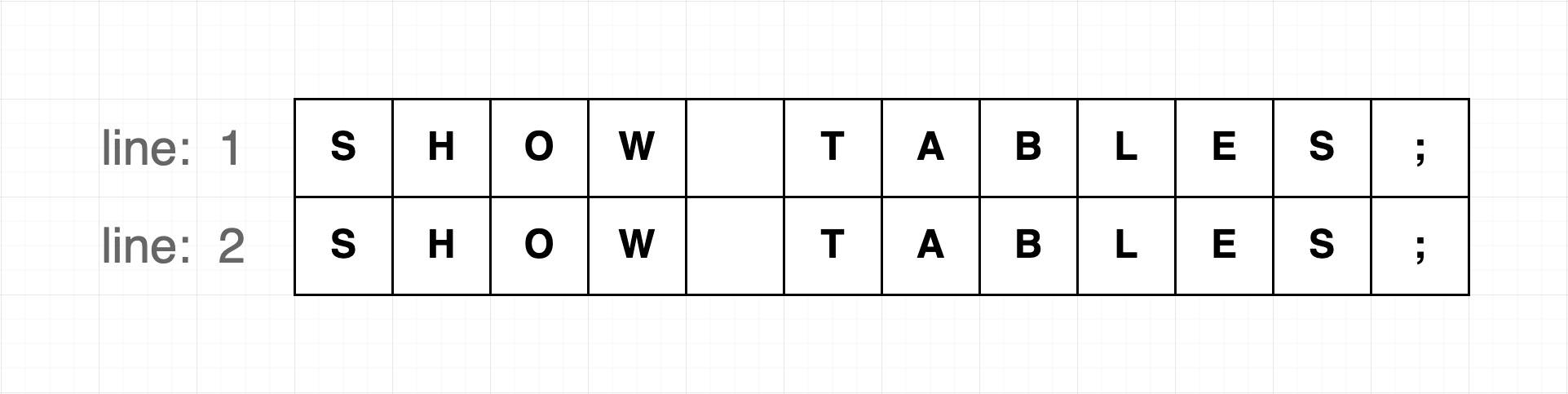
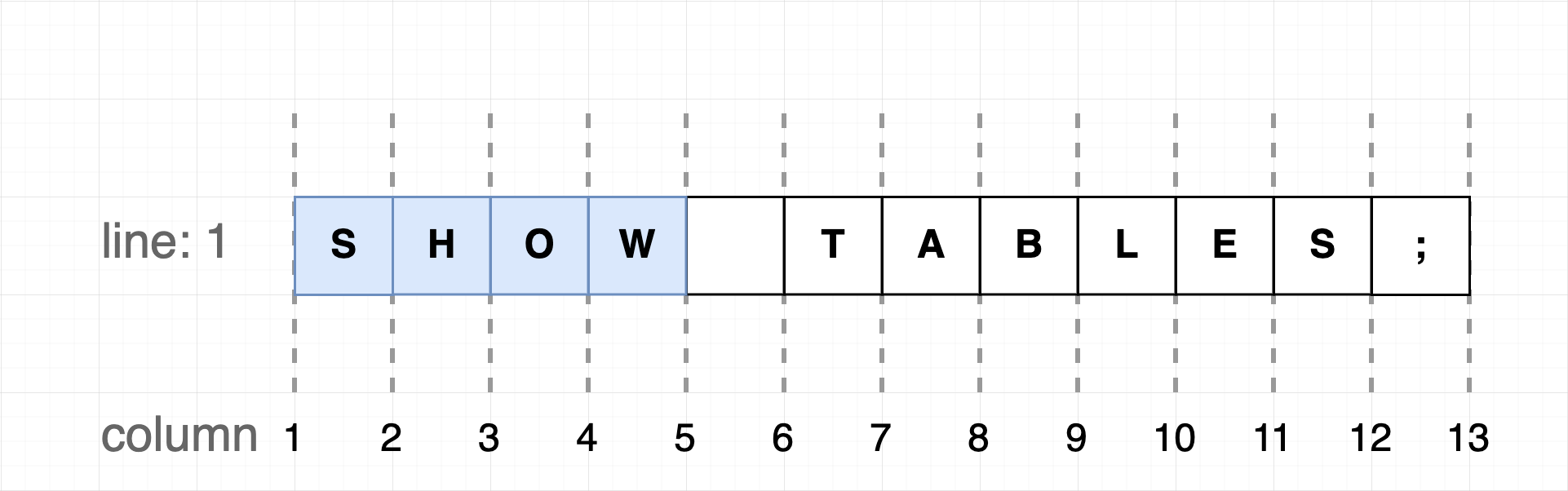
const sql = 'SHOW TABLES;\nSELECT * FROM tb;';
const sqlSlices = flink.splitSQLByStatement(sql);
console.log(sqlSlices)output:
/*
[
{
startIndex: 0,
endIndex: 11,
startLine: 1,
endLine: 1,
startColumn: 1,
endColumn: 12,
text: 'SHOW TABLES;'
},
{
startIndex: 13,
endIndex: 29,
startLine: 2,
endLine: 2,
startColumn: 1,
endColumn: 17,
text: 'SELECT * FROM tb;'
}
]
*/Obtaining code completion information at a specified position in SQL.
Call the getAllEntities method on the SQL instance, pass the SQL content and the row and column numbers indicating the position where code completion is desired. The following are some additional explanations about CaretPosition.
-
keyword candidates list
import { FlinkSQL } from 'dt-sql-parser'; const flink = new FlinkSQL(); const sql = 'CREATE '; const pos = { lineNumber: 1, column: 16 }; // the end position const keywords = flink.getSuggestionAtCaretPosition(sql, pos)?.keywords; console.log(keywords);
output:
/* [ 'CATALOG', 'FUNCTION', 'TEMPORARY', 'VIEW', 'DATABASE', 'TABLE' ] */
-
Obtaining information related to grammar completion
import { FlinkSQL } from 'dt-sql-parser'; const flink = new FlinkSQL(); const sql = 'SELECT * FROM tb'; const pos = { lineNumber: 1, column: 16 }; // after 'tb' const syntaxSuggestions = flink.getSuggestionAtCaretPosition(sql, pos)?.syntax; console.log(syntaxSuggestions);
output:
/* [ { syntaxContextType: 'table', wordRanges: [ { text: 'tb', startIndex: 14, stopIndex: 15, line: 1, startColumn: 15, stopColumn: 16 } ] }, { syntaxContextType: 'view', wordRanges: [ { text: 'tb', startIndex: 14, stopIndex: 15, line: 1, startColumn: 15, stopColumn: 16 } ] } ] */
The grammar-related code completion information returns an array, where each item represents what grammar can be filled in at that position. For example, the output in the above example represents that the position can be filled with either a table name or a view name. In this case, syntaxContextType represents the type of grammar that can be completed, and wordRanges represents the content that has already been filled.
Call the getAllEntities method on the SQL instance, and pass in the sql text and the row and column numbers at the specified location to easily get them.
import { FlinkSQL } from 'dt-sql-parser';
const flink = new FlinkSQL();
const sql = 'SELECT * FROM tb;';
const pos = { lineNumber: 1, column: 16 }; // tb 的后面
const entities = flink.getAllEntities(sql, pos);
console.log(entities);output
/*
[
{
entityContextType: 'table',
text: 'tb',
position: {
line: 1,
startIndex: 14,
endIndex: 15,
startColumn: 15,
endColumn: 17
},
belongStmt: {
stmtContextType: 'selectStmt',
position: [Object],
rootStmt: [Object],
parentStmt: [Object],
isContainCaret: true
},
relatedEntities: null,
columns: null,
isAlias: false,
origin: null,
alias: null
}
]
*/