Savoy
Savoy | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Le Chant des Allobroges The Song of the Allobroges | |
 | |
| Capital | Chambéry |
| Largest city | Annecy |
| Common languages | |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Legislature | Sovereign Senate of Savoy (dissolved in 1860) |
| Establishment | |
• Foundation of County | 1003 |
• Promotion to Duchy by Emperor Sigismund | February 19, 1416 |
• Annexation by France | June 14, 1860 |
| Area | |
• Total | 10,416 km2 (4,022 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 1,274,956 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | 33 |
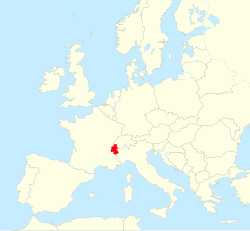
Savoy (/səˈvɔɪ/;[2] French: Savoie [savwa] ) [n 1] is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Valley in the east.
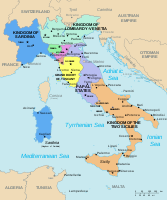
Savoy emerged as the feudal County of Savoy ruled by the House of Savoy during the 11th to 14th centuries.[3] The original territory, also known as "ducal Savoy" or "Savoy proper", is largely co-terminous with the modern French Savoie and Haute-Savoie départements, but the historical expansion of Savoyard territories, as the Duchy of Savoy (1416–1860) included parts of what is now western Italy and southwestern Switzerland. The current border between France and Italy is due to the Plombières Agreement of 1858, which in preparation for the unification of Italy ceded western Savoy to France, while the eastern territories in Piedmont and Liguria were retained by the House of Savoy, which was to become the ruling dynasty of Italy.
Geography
[edit]
In modern France, Savoy is part of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region. Following its annexation to France in 1860, the territory of Savoy was divided administratively into two separate departments, Savoie and Haute-Savoie.
The traditional capital remains Chambéry (in Italian: Ciamberì from the Latin: Camberia), on the rivers Leysse and Albane, hosting the castle of the House of Savoy and the Savoyard senate. The state included six districts:
- Savoie Propre, sometimes known as Ducal Savoy (capital Chambéry)
- Chablais (capital Thonon-les-Bains)
- Faucigny (capital Bonneville)
- Tarentaise (capital Moûtiers)
- Maurienne (capital Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne)
- Genevois (capital Annecy)
The County and Duchy of Savoy incorporated Turin and other territories in Piedmont, a region in northwestern Italy that borders Savoy, which were also possessions of the House of Savoy. The capital of the Duchy remained at the traditional Savoyard capital of Chambéry until 1563, when it was moved to Turin.
History
[edit]Early history
[edit]
The region was occupied by the Allobroges, a Gallic people[4] that the Roman Republic subdued in 121 BC. The name Savoy stems from the Late Latin Sapaudia[n 2], referring to a fir, or upland, forest.[n 3] The word is likely ultimately from Gaulish – sapin itself is a blend of Gaulish sappos (fir tree) and Latin pinus (pine tree). It is first recorded in Ammianus Marcellinus (354), to describe the southern part of Maxima Sequanorum. According to the Chronica Gallica of 452, the Burgundians were settled in the territory of Sapaudia in 443, after the Burgundian defeat by Flavius Aetius.[n 4]
Early and High Middle Ages
[edit]
By the 8th century, the territory that would later become known as Savoy was part of Francia, and at the division of Francia at the Treaty of Verdun in 843, it became part of the short-lived kingdom of Middle Francia. After only 12 years, at the death of Lothair I in 855, Middle Francia was divided into Lotharingia north of the Alps, Italy south of the Alps, and the parts of Burgundy in the Western Alps, inherited by Charles of Provence. This latter territory comprised what would become known as Savoy and Provence. For a short time, this province fell to the Arabs.
From the 10th to 14th century, parts of what would ultimately become Savoy remained within the Kingdom of Burgundy-Arles. Beginning in the 11th century, the gradual rise to power of the House of Savoy is reflected in the increasing territory of their County of Savoy between 1003 and 1416.
The County of Savoy was detached de jure from the Kingdom of Arles by Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor in 1361. It acquired the County of Nice in 1388, and in 1401 added the County of Geneva, the area of Geneva except for the city proper, which was ruled by its prince-bishop, nominally under the duke's rule: the bishops of Geneva, by unspoken agreement, came from the House of Savoy until 1533.[n 5]
Duchy of Savoy
[edit]
On 19 February 1416 Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, made the County of Savoy an independent duchy, with Amadeus VIII as the first duke. Straddling the Alps, Savoy lay within two competing spheres of influence, a French sphere and a North Italian one. At the time of the Renaissance, Savoy showed only modest development.[7] Its towns were few and small.[7] Savoy derived its subsistence from agriculture.[7] The geographic location of Savoy was also of military importance.[7] During the interminable wars between France and Spain over the control of northern Italy, Savoy was important to France because it provided access to Italy.[7] Savoy was important to Spain because it served as a buffer between France and the Spanish held lands in Italy.[7] In 1563 Emmanuel Philibert moved the capital from Chambéry to Turin, which was less vulnerable to French interference.[8]
Vaud was annexed by Bern in 1536, and Savoy officially ceded Vaud to Bern in the Treaty of Lausanne of 30 October 1564.
In 1714, as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession, Savoy was technically subsumed into the Kingdom of Sicily, then (after that island was traded to Austria for Sardinia) the Kingdom of Sardinia from 1720. While the heads of the House of Savoy were known as the Kings of Sardinia, Turin remained their capital.
French Revolutionary Wars
[edit]
Savoy was occupied by French revolutionary forces between 1792 and 1815. The entire region was first created to form the département of Mont-Blanc. In 1798, it was then divided between the departments of Mont-Blanc and Léman (French name of Lake Geneva).[9] In 1801, Savoy officially left the Holy Roman Empire.[10] On 13 September 1793 the combined forces of Savoy, Piedmont and Aosta Valley fought against and lost to the occupying French forces at the Battle of Méribel (Sallanches).
Two-thirds of Savoy was restored to the Kingdom of Sardinia in the First Restoration of 1814 following Napoleon's abdication; approximately one-third of Savoy, including the two most important cities of Chambéry and Annecy, remained in France. Following Napoleon's brief return to power during the Hundred Days and subsequent defeat at Waterloo, the remaining one-third of Savoy was restored to the Kingdom of Sardinia at the Congress of Vienna to strengthen Sardinia as a buffer state on France's southeastern border.
Modern history
[edit]Annexation to France
[edit]The French Second Republic first attempted to annex Savoy in 1848. A corps of 1,500 was dispatched from Lyon and invaded Savoy on 3 April, occupying Chambéry (capital city) and proclaiming the annexation to France. On learning about the invasion countrymen rushed to Chambéry. The corps were chased away by the local population. Five Frenchmen were killed and 800 captured.[11]
On 21 July 1858 in Plombières-les-Bains, Vosges, the prime minister of the Kingdom of Sardinia, Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour, met in secret with Napoleon III to secure French military support against the Austrian Empire during the conflicts associated with the Italian unification. During the discussion, Cavour promised that Sardinia would cede the County of Nice and Duchy of Savoy to the Second French Empire. Though this was a secret arrangement, it quickly became widely known.[12]
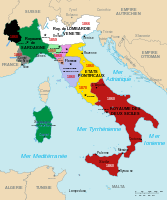
The treaty annexing Nice and Savoy to France was signed in Turin on 24 March 1860 (Treaty of Turin).[13] In the northern provinces of the Chablais and Faucigny, there was some support for annexation to neighboring Switzerland, with which the northern provinces had longstanding economic ties. To help reduce the attractiveness of Switzerland, the French government conceded a Free-Trade Zone that maintained the longstanding duty-free relationship of northern Savoyard communes to Geneva. After the treaty was already signed, a plebiscite was held on 22–23 April. Employing universal male suffrage, voters in the ceded provinces were offered the option of voting "Yes" to approve the treaty and join France or voting "No" and rejecting the treaty. Voters were not permitted the options of either joining Switzerland, remaining with Italy, or regaining its independence, were the source of some opposition. With a 99.8% vote in favour of joining France, there were allegations of vote-rigging, notably by the British government, which opposed continental expansion by its traditional French enemy. The correspondent of The Times in Savoy who was in Bonneville on 22 April called the vote "the lowest and most immoral farce(s) which was ever played in the history of nations".[14] He finished his letter with those words:
I leave you to draw your own conclusions from this trip, which will show clearly what the vote was in this part of Savoy. The vote was the bitterest irony ever made on popular suffrage. The ballot-box in the hands of those very authorities who issued the proclamations; no control possible; even travellers suspected and dogged lest they should pry into the matter; all opposition put down by intimidation, and all liberty of action completely taken away. One can really scarcely reproach the Opposition with having given up the game; there was too great force used against them. As for the result of the vote, therefore, no one need trouble himself about it; it will be just as brilliant as that in Nice. The only danger is lest the Savoy authorities in their zeal should fare as some of the French did in the vote of 1852, finding to their surprise rather more votes than voters inscribed on the list.
In his letter to the ambassador of Vienna Lord Augustus Loftus, the then–Foreign Secretary, Lord John Russell, said, "Voting in Savoy and Nice a farce ... we are neither entertained or edified".[15]
The annexation was promulgated on 14 June 1860. On 23 August 1860 and 7 March 1861, two agreements were signed between the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Sardinia to settle the remaining issues concerning the annexation.[16][17]
This was part of a secret agreement (the Plombières Agreement) brokered between the French emperor Napoleon III and the Count Camillo of Cavour (Prime Minister of Sardinia at that time) that allowed the final steps in the process of unification of Italy. Victor Emmanuel's dynasty, the House of Savoy, retained its Italian lands of Piedmont and Liguria and became the ruling dynasty of Italy.
-
People of Chambéry with French flags celebrating the annexation in 1860.
-
Map of Savoy in the 19th century and other Italian states in 1843.
-
French annexation in 1860 (black) after the signing of the Treaty of Turin and a regional referendum in favor of the attachment to France (French)
-
The Château de Chambéry, seat of government, was given a grand new façade following annexation
20th century
[edit]In 1919, contrary to the annexation treaty, France officially ended the military neutrality of the parts of the country of Savoy that had originally been agreed to at the Congress of Vienna, and also eliminated the free trade zone – both treaty articles having been broken unofficially in World War I. France was condemned in 1932 by the international court for noncompliance with the measures of the Treaty of Turin regarding the provinces of Savoy and Nice.[18]
In 1960, the term annexation having acquired negative connotations in France, particularly after Germany's 1871 annexation of Alsace-Lorraine, the annexation was renamed Rattachement de la Savoie à la France (Incorporation of Savoy to France).[n 6] It was the latter term which was used by the French authorities during the festivities celebrating the 100th anniversary of the annexation.[19] Daniel Rops of the French Academy justified the new title with these words:
Savoy has begun to solemnize the feasts in 1960, commemorating the centenary of its incorporation (rattachement) to France. It is on purpose that the word incorporation (rattachement) is highlighted here: the Savoyards attach great value to it, and it is the only one they have resolved to use in the official terminology of the Centenary. In that, they are infinitely right. Yesterday another term that was used: annexation. Looking at it more closely it was wrong! Can we say annexation when we talk about a decision which was approved by 130,889 voters over 135,449? [...]. Savoy was not annexed [...] but actually incorporated freely and by the will of its inhabitants.
A former French deputy, P. Taponnier, spoke of the annexation:[citation needed]
In late March 1860, the betrothal ceremony of Savoy to France took place in Tuileries Palace [...], a ceremony which was a pact of love and fidelity [...] it is with free consent that she [Savoy] gave itself to France by a solemn plebiscite of which our leaders can ignore neither the terms nor the commitments. [...] May the bells of our cities [...] in Savoy vibrate in unison to glorify, in this magnificent Centenary, the indefectible commitment of Savoy to France. The Savoyards did not feel Italian. Besides, they spoke French. This explains why in 1858–1859 when rumours ran of the Plombières secret agreement, where Napoleon III and Cavour decided of the fate of Savoy, the Savoyards themselves took the initiative to ask for the incorporation (rattachement). [...] Incorporation, not annexation [...] The incorporation was an act of free will, in the logical order of geography and history [...].
Politics
[edit]Modern regionalist politics
[edit]Since the mid-20th century, regionalist movements have appeared in Savoy much as in other historic provinces of France. The Mouvement Région Savoie (Savoy Regional Movement) was founded in December 1971 as a 'movement' (rather than a traditional political party) in favour of regional autonomy. Unlike other historic provinces, including Normandy and Brittany, Savoy does not currently have its own region within France and is part of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region. In the 1996 local elections, the Savoy Regional Movement received 19,434 votes; it received 4,849 in the 1998 regional elections. A new non-party organisation, La Région Savoie, j’y crois ! (I believe in the Savoy Region!), was founded in 1998. The organisation campaigns for the replacement of the Savoie and Haute-Savoie departments with a regional government, separate from the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, with greater devolved powers.
A very marginal separatist movement has also appeared in Savoy within the past twenty years, most prominently represented by the Ligue Savoisienne, founded in 1994. In the March 1998 regional elections, 1 seat (out of 23) was won by Patrice Abeille, leader of the Ligue, which won a total of 17,865 votes across the two departments. In 2004, Waiting for Freedom in Savoy[20] was founded to promote the peaceful separatist cause to young people.
According to surveys conducted in 2000, between 41% and 55% of the population were in favour of the proposal for a separate Savoy region. Towards the end of 2005, Hervé Gaymard called for Savoie to be given special status, similar to a French region, under his proposed "Conseil des Pays de Savoie".[21]
Modern historiographical debates
[edit]In recent years,[when?] sparked by the tiny Savoyard separatist movement, much attention has been focused on questioning the validity of the 1860 annexation. The Ligue Savoisienne, for example, rejects the Treaty of Turin and subsequent plebiscite as null and void, arguing that the plebiscite did not meet the standards of a free and fair vote. Today, historians generally acknowledge that the plebiscite of 1860 did feature irregularities, but they also affirm that the annexation instrument was the Treaty of Turin and not the plebiscite, whose main purpose was to demonstrate favorable public opinion in Savoy for the annexation after the signature of the treaty.[22] In an interview for the newspaper Le Dauphiné Libéré, Sylvain Milbach, a historian at the University of Savoy, qualifies the vote as Napoleonic, but also argues that a completely free and fair vote would not have dramatically changed the outcome, as the majority of Savoyards wished to become French.[23] This is today the official stance of the General Council of Savoie.
See also
[edit]- House of Savoy
- Italian Savoyards
- List of active separatist movements in Europe § France
- Savoy States
- Maurice-Mollard Plaza
- Tourism in Savoie
Notes
[edit]- ^ Arpitan: Savouè [saˈvwɛ]; Italian: Savoia [saˈvɔ.ja]
- ^ The territory, which has no modern counterpart, was perhaps bounded by the rivers Ain and Rhône, Lake Geneva, the Jura and the Aar, though historians differ, and there seems to be insufficient evidence.[5]
- ^ Modern French sapin; sapinière signifies "fir forest".
- ^ Sapaudia Burgundionum reliquiis datur cum indigenis dividenda.[6]
- ^ See the career of the last prince-bishop Pierre de La Baume.
- ^ The word rattachement (incorporation) was preferred to réunion which could be reminiscent of the Anschluss.
References
[edit]- ^ Jack D. Street. "The Independence of Savoy and the Autonomy of the Valle d'Aosta", The French Review, Vol 71, No 3, Feb. 1998, pp 396–404 JSTOR 398970 accessed 4 Oct 2008.
- ^ "Savoy on www.oxforddictionaries.com". Archived from the original on 2018-12-25. Retrieved 2014-02-16.
- ^ The Romance of the House of Savoy (Vol.1). Weil, Alethea. Putnam, New York (1898), Intro. p.1
- ^ Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Norman H. Baynes, reviewing A. Coville, Recherches sur l'Histoire de Lyon du Ve au IXe Siècle (450–800) in The English Historical Review 45 No. 179 (July 1930:470 474) p 471.
- ^ T. Mommsen, Chronica Minora II:660, 128.
- ^ a b c d e f Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation (Harper & Bros. Publishers: New York, 1960) p. 42.
- ^ Robert Katz, The Fall of the House of Savoy (The MacMillan Company: New York, 1971) p. 18.
- ^ "Le nom des départements". Le Monde. 11 December 1999. Archived from the original on 2020-07-30. Retrieved 2018-12-26.
- ^ Heiliges Römisches Reich
- ^ Mike Rapport, 1848: Year of Revolution (Basic Books, 2010), 115–16.
- ^ John Russell, 1st Earl Russell, address to the House of Common, July 5, 1861,HC Deb 05 July 1861 vol 164 cc436-61 Archived 13 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Traité de Turin, Signé à Turin le 24 mars 1860 entre la France et la Sardaigne". mjp.univ-perp.fr. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ The Times Archived 2008-10-06 at the Wayback Machine, April 28, 1860, Universal Suffrage In Savoy Archived 2010-09-20 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ PRO 30/22/98 Austria. Vol 1. Legation (from Nov. 1860) embassy in Vienna. Private correspondence (drafts). Lord John (earl from 1861) Russell, foreign secretary to Hon. Julian Fane, legation later embassy secretary; Lord Augustus Loftus, envoy; Lord Bloomfield, ambassador. Document conserved at The National Archives Archived 2010-10-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Convention entre la France et la Sardaigne destinée à régler diverses questions auxquelles a donné lieu la réunion de la Savoie et de l'arrondissement de Nice à la France; signée a Paris le 23 août 1860. G.Fr.de Martens, Nouveau Recueil Général de Traités et autre actes relatifs aux rapports de droit international, t. XVII, p.460 (pdf). Oxford University. 1843. Archived from the original on 2021-05-29. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ Convention de délimitation entre la France et la Sardaigne, conclue a Turin le 7 mars 1861. G.Fr.de Martens, Nouveau Recueil Général de Traités et autre actes relatifs aux rapports de droit international, t. XVII, p.406 (pdf). Oxford University. 1843. Archived from the original on 2021-05-07. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ La vérité sur la zone franche de la Haute-Savoie, F.Murullaz. Bulletin de l'académie chablaisienne 1915–1916 Séance du 8 Novembre 1915. Oxford University. 1815. Archived from the original on 2021-05-07. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ La Savoie au miroir du Centenaire de son Rattachement à la France Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine, Lacharme Amandine
- ^ "Waiting for Freedom in Savoy". Archived from the original on 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
- ^ Région Savoie Archived 2007-03-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ 1860, La Savoie de l'Annexion Archived 2016-03-03 at the Wayback Machine, Archives Départementales de la Savoie
- ^ Savoie Française: Sylvain Milbach: "Le 'oui' était acquis" Archived 2009-04-24 at the Wayback Machine
External links
[edit]- Universal Suffrage under Napoleon III by Adams, Charles Kendall
- Savoy Region Movement (in French)
- Ligue Savoisienne (in English)
- Francia Media: a territorial and genealogical disambiguation of Lorraine and Burgundy, with a section on Savoy
- The History of the Annexation of Savoy and Nice to France according to the United Kingdom, Switzerland and the others