Aqaba Governorate
Aqaba Governorate
محافظة العقبة | |
|---|---|
 The city port of Aqaba | |
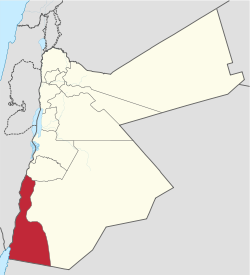 Location of Aqaba Governorate in Jordan | |
| Country | Jordan |
| Capital | Aqaba |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Fawaz Irshaidat |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,905 km2 (2,666 sq mi) |
| Population (2012) | |
| • Total | 139,200 |
| • Density | 20/km2 (52/sq mi) |
| Time zone | GMT +2 |
| • Summer (DST) | +3 |
| Area code | +(962)3 |
| Urban | 86% |
| Rural | 14% |
| HDI (2021) | 0.721[1] high · 3rd of 12 |
Aqaba (Arabic: العقبة al-ʻAqabah) is one of the governorates of Jordan, located south of Amman, capital of Jordan. Its capital is Aqaba. It is the fourth largest governorate in Jordan by area and is ranked 10th by population.
Aqaba, the port at the Red Sea, plays an important role in the economic life of Jordan. Two of Jordan's top three tourist destinations lie in Aqaba Governorate, Wadi Rum, and the port city of Aqaba. The port is Jordan's most important import/export hub. The industrial port lies about 15 km to the south from the beaches and the Aqaba city center.
Geography
[edit]Aqaba Governorate lies in the south western tip of Jordan, it borders Ma'an Governorate from the east, Tafilah Governorate from the north, Saudi Arabia from the south, Israel from the west, and the Gulf of Aqaba from the southwest. There are two international crossing points in Aqaba Governorate, the Durra Border Crossing and Wadi Araba crossing.
The Jordanian-Saudi border originally ran a few kilometers south of Aqaba. In 1965 the late King Hussein exchanged 12 km (7 mi) of the valuable coastal strip for areas in the desert.
History
[edit]
The city of Aqaba was inhabited since 4000 BC, it reached its peak during the Roman era, when the Romans constructed the Via Traiana Nova route that terminates in Aqaba. Aqaba (known then as Ayla) was also the garrison of the Roman 10th Legion of the Sea Strait (Legio X Fretensis).
Aqaba was also the site of some of the adventures of Sinbad the Sailor in the famous Arabian Nights.
In modern history, the city of Aqaba is known for Lawrence of Arabia and the Battle of Aqaba, one of the key battles in World War I in the Middle East.
The greatest archaeological treasure of the region is Petra. Petra lies on the eastern slope of Mount Hor in Wādī ʻAraba, a section of the Rift Valley that runs from the Gulf of Aqaba on the Red Sea to the Dead Sea.
The oldest script written in Arabic alphabets was found in Wadi Rum in Aqaba Governorate, and dates back to the 4th century.
Economy
[edit]The governorate's population depends heavily on tourism as a major source of income. The port of Aqaba is the only sea port for Jordan. Almost all of Jordan's foreign trade comes through Aqaba. During the Iraqi-Iranian War, Iraq used the port of Aqaba for its foreign trade.
Administrative divisions
[edit]
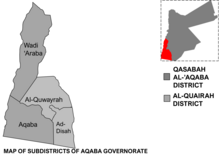
Aqaba Governorate is divided into three departments according to article 15 of the Administrative Divisions System of the year 2000 by the Ministry of Interior:
| Department | Arabic Name | Subdivisions | Administrative Center | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Capital Department (Al-Qasabah) | لواء قصبة العقبة | includes the city of Aqaba and three nearby villages | Aqaba |
| 2 | Wadi Araba Department | قضاء وادي عربة | includes nine villages | Al-Reeshah |
| 3 | Al-Quwairah Department | لواء القويرة | includes 15 villages | Al-Quwairah |
Demographics
[edit]The population of districts according to census results:[2]
| District | Population (Census 1994) |
Population (Census 2004) |
Population (Census 2015) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqaba Governorate | 79,839 | 102,097 | 188,160 |
| Al-Qūaīrah | 12,736 | 17,132 | 29,142 |
| Qaṣabah al-'Aqabah | 67,103 | 84,965 | 159,018 |
Gallery
[edit]-
The city of Aqaba is the capital of Aqaba Governorate
-
A train coming from the port of Aqaba
-
Aqaba Subdistrict Map
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- ^ "Jordan: Administrative Division, Governorates and Districts". citypopulation.de. Retrieved 25 December 2016.