Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Dr Amanda Oakley Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Reviewed by Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer, February 2014.
Oil folliculitis is inflammation of hair follicles due to exposure to various oils in the workplace. Excessive oil on the skin can result in small pustules with a red halo in affected areas. Commonly, the lesions are seen on the forearms and thighs. The follicles may be obviously plugged with oil. The pustules may be sterile or contain the harmless skin bacteria, Staphylococcus epidermidis. They may be painless or painful.
Occupational or therapeutic contact with mineral oils or tar can result in comedones and inflamed hair follicles (folliculitis). Occupations at risk of oil folliculitis include:
In some cases, topical creams or ointments containing coal tar can also cause oil folliculitis. These are used for the treatment of eczema and psoriasis.

Folliculitis
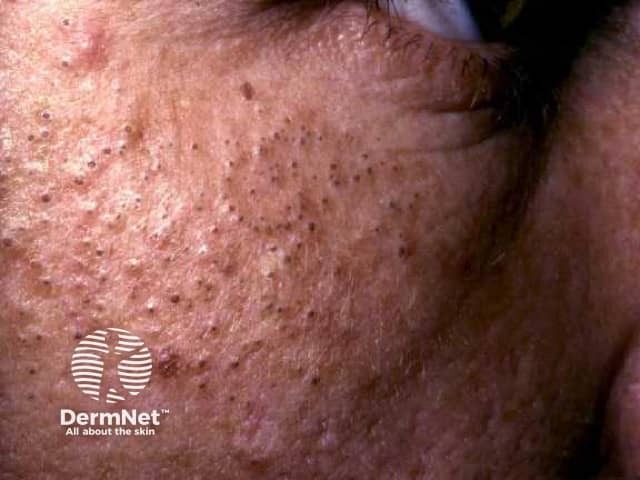
Folliculitis
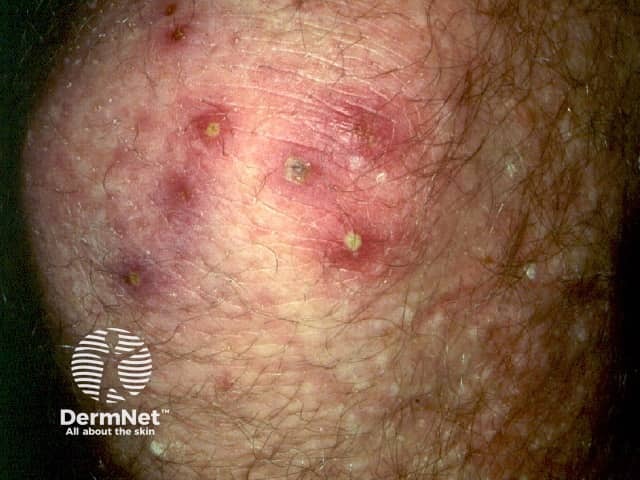
Folliculitis
Skin affected by oil folliculitis should be carefully protected from contact with the responsible material and washed twice daily with a mild soap and water. Change overalls every day.
If the folliculitis doesn't settle by itself, standard treatments for moderate acne usually prove effective.