Y-27632
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||||||||
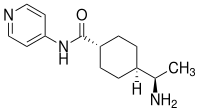
| Name | Y-27632 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
(1R,4r)-4-[(R)-1-Aminoethyl]-N-(pyridin-4-yl)cyclohexancarboxamid (IUPAC) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C14H21N3O | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
weißer Feststoff[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 247,34 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
löslich in Wasser[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Y-27632 ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der Cyclohexan-Carboxamide. Es ist ein Enzyminhibitor der Rho-Kinase (ROCK) und wird daher als ROCK-Inhibitor bezeichnet.
Eigenschaften
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Y-27632 wurde erstmals 1997 von Masayoshi Uehata und Kollegen beschrieben.[2][3] Es hemmt selektiv p160ROCK, wobei es in höheren Konzentrationen auch andere Proteinkinasen wie die PKC hemmt.[2] Y-27632 führt zu einer Umlagerung des Aktin-Zytoskeletts.[4] Zudem wirkt es anti-apoptotisch[5][6] und in Keratinozyten gegen die Zellseneszenz.[7]
Verwendung
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Y-27632 wird seit 2010 zur Erzeugung von konditional reprogrammierten Zellen (CR-Zellen) verwendet.[8] CR-Zellen bilden einen Grenzfall zwischen iPS, immortalisierten Zelllinien und normalen Zellen. Sie bestehen aus normalen Zellen, die sich unbegrenzt teilen können, solange zwei Faktoren hinzugegeben werden – Fütterzellen und der Inhibitor der Rho-Kinase Y-27632.[9][10]
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ a b c d e Datenblatt Y-27632 bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 1. Juni 2023 (PDF).
- ↑ a b M. Uehata, T. Ishizaki, H. Satoh, T. Ono, T. Kawahara, T. Morishita, H. Tamakawa, K. Yamagami, J. Inui, M. Maekawa, S. Narumiya: Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. In: Nature. Band 389, Nummer 6654, Oktober 1997, S. 990–994, doi:10.1038/40187, PMID 9353125.
- ↑ Masayoshi Uehata: Y-27632. Selective probe of ROCK/Rho-kinase (1999). In: Jikken Igaku. Band 17, Heft 7, S. 850–855.
- ↑ H. Gong, C. Y. Yang: Morphological and hydrodynamic correlations with increasing outflow facility by rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632. In: Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics : the official journal of the Association for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Band 30, Nummer 2–3, 2014, S. 143–153, doi:10.1089/jop.2013.0192, PMID 24460021, PMC 3991982 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ K. Kim, S. Min, D. Kim, H. Kim, S. Roh: A Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitor, Y-27632, Inhibits the Dissociation-Induced Cell Death of Salivary Gland Stem Cells. In: Molecules. Band 26, Nummer 9, Mai 2021, doi:10.3390/molecules26092658, PMID 34062818, PMC 8124333 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ Yaodong You, Kun Zhu, Jie Wang, Qi Liang, Wen Li, Lin Wang, Baojun Guo, Jing Zhou, Xuanlin Feng, Jianyou Shi: ROCK inhibitor: Focus on recent updates. In: Chinese Chemical Letters. 2023, S. 108336, doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108336.
- ↑ S. Niklander, D. Bandaru, D. W. Lambert, K. D. Hunter: ROCK inhibition modulates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in oral keratinocytes. In: FEBS open bio. Band 10, Nummer 12, Dezember 2020, S. 2740–2749, doi:10.1002/2211-5463.13012, PMID 33095981, PMC 7714064 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ S. Chapman, X. Liu, C. Meyers, R. Schlegel, A. A. McBride: Human keratinocytes are efficiently immortalized by a Rho kinase inhibitor. In: The Journal of clinical investigation. Band 120, Nummer 7, Juli 2010, S. 2619–2626, doi:10.1172/JCI42297, PMID 20516646, PMC 2898606 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ X. Wu, S. Wang, M. Li, J. Li, J. Shen, Y. Zhao, J. Pang, Q. Wen, M. Chen, B. Wei, P. J. Kaboli, F. Du, Q. Zhao, C. H. Cho, Y. Wang, Z. Xiao, X. Wu: Conditional reprogramming: next generation cell culture. In: Acta pharmaceutica Sinica. B. Band 10, Nummer 8, August 2020, S. 1360–1381, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.011, PMID 32963937, PMC 7488362 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ M. Zhong, L. Fu: Culture and application of conditionally reprogrammed primary tumor cells. In: Gastroenterology report. Band 8, Nummer 3, Juni 2020, S. 224–233, doi:10.1093/gastro/goaa023, PMID 32665854, PMC 7333928 (freier Volltext).