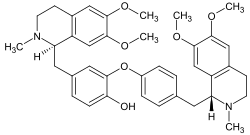
Dauricin
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Dauricin | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C38H44N2O6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 624,778 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
Dauricin ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der phenolischen Isochinolin-Alkaloide.[2]
Eigenschaften
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Dauricin ist ein sekundärer Pflanzenstoff der Pflanzen Menispermum dauricum und Menispermum canadense. Dauricin oder Wurzelpräparate von M. dauricum werden in China zur Behandlung der Ischämie, Angina, Arrhythmie und Entzündungskrankheiten verwendet.[3][4][5] Dauricin moduliert Ca2+- und manche Na+-Ionenkanäle.[5] Dauricin besitzt in Zellkulturen Anti-Tumor-Wirkung,[6][7][8] durch Induktion einer Autophagie.[9] Die Biotransformation von Dauricin führt zu einem Chinon-Methid, das zu Addukten von Proteinen führt und vermutlich toxisch ist.[10] Im Jahr 1964 wurde Dauricin erstmals von Tetsuji Kametani und Keiichiro Fukumoto über die Arndt-Eistert-Reaktion und die Bischler-Napieralski-Reaktion synthetisiert.[11] Dauricin kann per LC-MS im Urin nachgewiesen werden.[12]
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ a b Datenblatt Dauricine, phyproof bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 5. November 2019 (PDF).
- ↑ R. H. F. Manske: The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Physiology, Band 9. Academic Press, 1967. ISBN 9780080865331. S. 141.
- ↑ J. Q. Qian: Cardiovascular pharmacological effects of bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid derivatives. In: Acta pharmacologica Sinica. Band 23, Nummer 12, Dezember 2002, S. 1086–1092, PMID 12466045.
- ↑ K. Y. Feng, C. J. Hu, J. A. Zhou: [Clinical observations on sustained arrhythmias treated with dauricine]. In: Zhonghua xin xue guan bing za zhi. Band 12, Nummer 4, Dezember 1984, S. 265–7, 315, PMID 6544209.
- ↑ a b J. Zhao, Y. Lian, C. Lu, L. Jing, H. Yuan, S. Peng: Inhibitory effects of a bisbenzylisoquinline alkaloid dauricine on HERG potassium channels. In: Journal of ethnopharmacology. Band 141, Nummer 2, Juni 2012, S. 685–691, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.054, PMID 21920426.
- ↑ Z. Yang, C. Li, X. Wang, C. Zhai, Z. Yi, L. Wang, B. Liu, B. Du, H. Wu, X. Guo, M. Liu, D. Li, J. Luo: Dauricine induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and invasion through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. In: Journal of cellular physiology. Band 225, Nummer 1, Oktober 2010, S. 266–275, doi:10.1002/jcp.22261, PMID 20509140.
- ↑ H. Jin, J. Dai, X. Chen, J. Liu, D. Zhong, Y. Gu, J. Zheng: Pulmonary toxicity and metabolic activation of dauricine in CD-1 mice. In: The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. Band 332, Nummer 3, März 2010, S. 738–746, doi:10.1124/jpet.109.162297, PMID 20008063.
- ↑ X. D. Tang, X. Zhou, K. Y. Zhou: Dauricine inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-induced hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha protein accumulation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human breast cancer cells. In: Acta pharmacologica Sinica. Band 30, Nummer 5, Mai 2009, S. 605–616, doi:10.1038/aps.2009.8, PMID 19349962, PMC 4002832 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ S. Byun, E. Lee, K. W. Lee: Therapeutic Implications of Autophagy Inducers in Immunological Disorders, Infection, and Cancer. In: International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Band 18, Nummer 9, September 2017, S. , doi:10.3390/ijms18091959, PMID 28895911, PMC 5618608 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ H. Xie, Y. Liu, Y. Peng, D. Zhao, J. Zheng: Detection of protein adduction derived from dauricine by alkaline permethylation. In: Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry. Band 408, Nummer 15, Juni 2016, S. 4111–4119, doi:10.1007/s00216-016-9505-0, PMID 27071763.
- ↑ Tetsuji Kametani, Keiichiro Fukumoto: Total synthesis of (±)-dauricine. In: Tetrahedron Letters. Band 5, Nr. 38, 1964, S. 2771–2775, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)71728-X.
- ↑ F. M. Han, Z. H. Peng, W. Song, H. M. Zhang, M. M. Zhu, Y. Chen: Identification of dauricine and its metabolites in rat urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In: Journal of Chromatography B. Band 854, Nummer 1–2, Juli 2007, S. 1–7, doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.036, PMID 17448738.