|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
3D-HST:
A Spectroscopic Galaxy Evolution Survey with the Hubble Space Telescope
3D-HST is a near-infrared spectroscopic survey with the Hubble Space Telescope designed to study the physical processes that shape galaxies in the distant Universe (GO-12177 & GO-12328; PI: Pieter van Dokkum). This Treasury program was allocated 248 orbits of HST time during Cycles 18 and 19. 3D-HST is surveying ~600 square arcminutes of well-studied extragalactic survey fields (AEGIS, COSMOS, GOODS-S, UKIDSS-UDS) with two orbits of primary WFC3/G141 grism coverage and two to four orbits with ACS/G800L coverage. 3D-HST now provides the critical third dimension - redshift - for ~10,000 galaxies at z>1. This is the epoch when ~60% of the star formation in the Universe took place, the number density of quasars peaked, the first galaxies stopped forming stars and the structural regularity that we see in galaxies today emerged. The 3D-HST project details can be found in "3D-HST: A Wide-Field Grism Spectroscopic Survey with the Hubble Space Telescope", Brammer et al., 2012, ApJ, 758L.
The survey is optimally designed for the study of galaxy evolution over 1 < z < 3.5. The science objectives include: disentangling the processes that regulate star-formation in massive galaxies, evaluating the role of environment and mergers in shaping the galaxy population, and resolving the growth of disks and bulges, spatially and spectrally.
The observations for 3D-HST are completed and high level science products are available below. For further information about the survey and a mirror of all data products, please visit the 3D-HST home page.
Observations
The 248 3D-HST orbits are divided among 124 individual pointings, each observed for two orbits (figure and table below). In order to schedule 3D-HST concurrently with CANDELS observations of the same fields over Cycles 18 and 19, the orientations of the fields were determined only after the observations were scheduled. The positions of the individual pointings were optimized to provide contiguous mosaics and maximum overlap between the primary WFC3 G141 and parallel ACS G800L observations. Owing to this optimization, fully 90% of the G141 mosaic will be covered by between two and four orbits of the ACS grism. Within the GOODS-South mosaic, four of the two-orbit visits are centered on the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (HUDF) at the same orientation. The GOODS-South pointings outside of the area with CANDELS coverage provide WFC3 grism spectroscopy of the HUDF09 and WFC3-ERS fields.

Layout of the 124 3D-HST pointings. Primary WFC3 F140W+G141 pointings are shown in blue with the pointing ID numbers as defined in the HST Phase II file. The locations of the parallel ACS F814W+G800L observations are shown in light green. Also indicated is the distribution of the 28 pointings covering the GOODS-North field from program GO-11600 that are incorporated into 3D-HST. The light gray polygons indicate the footprint of the CANDELS WFC3 imaging, including both the “wide” and “deep” components of that survey. Note that the relative sizes of the separate fields are not shown exactly to scale. (Figure from Brammer et al. 2012).
| Field | Program ID | RA | Dec | N Pointings | Image | Region Files |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEGIS | 12177 | 14:19:31 | +52:51:00 | 30 | image | WFC3 / ACS |
| COSMOS | 12328 | 10:00:29 | +02:20:36 | 28 | image | WFC3 / ACS |
| GOODS-S | 12177 | 03:32:31 | -27:48:54 | 34 | image | WFC3 / ACS |
| HUDF | 12177 | 03:32:39 | -27:47:01 | 4 | image | WFC3 |
| UDS | 12328 | 02:17:26 | -05:12:13 | 28 | image | WFC3 / ACS |
The 28-pointing G141 grism coverage of most of the GOODS-N field from program GO-11600 (PI: B. Weiner) is incorporated into 3D-HST, as the observational strategy of these observations are nearly identical to that of 3D-HST. There are GOODS-N mosaics and weight images (image | regions) in the F125W, F140W and F160W WFC3 bands. These mosaics are available as part of the 3D-HST V3.0 data release. The F125W and F160W observations were taken as part of the CANDELS survey. Parallel ACS grism observations are available from GO-13420 (PI: Barro).
Data
The final release of the 3D-HST dataset was made available in October 2015 on the 3D-HST website. This v4.1.5 release as well as the 2014 v4.1 photometric release are mirrored and archived here. It covers all five 3D-HST/CANDELS fields: AEGIS, COSMOS, GOODS-N, GOODS-S and UDS. See Momcheva et al. (2015) and Skelton et al. (2014) for full descriptions of the data and methods. The v4.1.5 release includes:
-
Extracted WFC3 2D and 1D spectra for ~250,000 objects
-
Redshifts based on joint fits to the grism spectra and photometry for ~100,000 objects down to JH=26
-
Emission line fits for to all major emission lines down to JH=26
-
Best redshift catalog combining the spectroscopic, grism and photometric redshifts in the five fields
-
Stellar masses, UV+IR star formation rates, rest-frame colors in 22 bands for the grism redshift and best redshift catalogs
-
Extracted ACS 2D and 1D spectra for ~25,000 objects
Credit: When using the grism data products and derived parameters provided here, please cite Momcheva et al. (2015), Brammer et al. (2012) and include the following text: "This work is based on observations taken by the 3D-HST Treasury Program (GO 12177 and 12328) with the NASA/ESA HST, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS5-26555."
Full documentation is available HERE. Regions files of the pointing layouts are available under Observations.
NOTE: Some of the downloads in this realease are very large, occasionally exceeding 50 GB! If your internet connection is consistently excellent (~100 Mbpc), this download will take > 1 hour. We do realize that this is not the optimal way of distributing the dataset and are working on a database with an API interface. We hope to make it available soon.
We are grateful to the many colleagues who have provided public data and catalogs in the five deep 3D-HST fields; high redshift galaxy science has thrived owing to this gracious mindset and the TACs and Observatory Directors who have encouraged this.
This work is based on observations made with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, obtained from the MAST Data Archive at the Space Telescope Science Institute, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS 5-26555. Observations associated with the following GO and GTO programs were used: 12063, 12440, 12442, 12443, 12444, 12445, 12060, 12061, 12062, 12064 (PI: Faber); 12177 and 12328 (PI: van Dokkum); 12461 and 12099 (PI: Riess); 11600 (PI: Weiner); 9425 and 9583 (PI: Giavalisco); 12190 (PI: Koekemoer); 11359 and 11360 (PI: O’Connell); 11563 (PI: Illingworth); 13420 (PI: Barro).
The work, presented here, is based, in part, on data obtained at the W. M. Keck Observatory, which is operated as a scientific partnership among the California Institute of Technology, the University of California, and NASA and was made possible by the generous financial support of the W. M. Keck Foundation. This work makes use of data obtained as part of the ESO/GOODS survey. Observations have been carried out using the Very Large Telescope at the ESO Paranal Observatory under Programme ID 168.A-0485. Based on observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla or Paranal Observatories under programme number 168.A-0485. Based on data products from observations made with ESO Telescopes at the La Silla Paranal Observatory under ESO programme ID 179.A-2005 and on data products produced by TERAPIX and the Cambridge Astronomy Survey Unit on behalf of the UltraVISTA consortium. Based on observations obtained with MegaPrime/MegaCam, a joint project of CFHT and CEA/IRFU, at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) which is operated by the National Research Council (NRC) of Canada, the Institut National des Science de l’Univers of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) of France, and the University of Hawaii. This work is based in part on data products produced at Terapix available at the Canadian Astronomy Data Centre as part of the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey, a collaborative project of NRC and CNRS. This work makes use of data products produced at TERAPIX, the WIRDS consortium, and the Canadian Astronomy Data Centre. We thank H. Hildebrandt for providing the CARS-reduced CFHTLS images. This research has made use of the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive, which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. This study makes use of data from COSMOS, a multiwavelength sky survey conducted with the Chandra, GALEX, Hubble, Keck, CFHT, MMT, Subaru, Palomar, Spitzer, VLA, and other telescopes and supported in part by the NSF, NASA, and the STFC. This study makes use of data from the NEWFIRM Medium-Band Survey, a multi-wavelength survey conducted with the NEWFIRM instrument at the KPNO, supported in part by the NSF and NASA. This paper uses data products produced by the OIR Telescope Data Center, supported by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. This work is based on observations made with the Spitzer Space Telescope, which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology under contract with NASA. Based in part on data from the UKIDSS Ultra Deep Survey (UDS) and the Spitzer Public Legacy Survey of the UKIDSS Ultra Deep Survey (SpUDS), a Cycle 4 Spitzer Legacy program.
Credit: When using the catalogs, derived parameters, and rest-frame colors provided here, please cite Skelton et al. (2014), Brammer et al. (2012) and include the following text: “This work is based on observations taken by the 3D-HST Treasury Program (GO 12177 and 12328) with the NASA/ESA HST, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS5-26555.”
An up-to-date list of known issues is available HERE (also included in the full documentation).
| FIELD | DOWNLOAD TAR | Read me |
|---|---|---|
| AEGIS | AEGIS_TAR (120MB) |
READ-ME |
| COSMOS | COSMOS_TAR (132MB) |
READ-ME |
| GOODS-N | GOODS-N_TAR (190MB) |
READ-ME |
| GOODS-S | GOODS-S_TAR (263MB) |
READ-ME |
| UDS | UDS_TAR (224MB) |
READ-ME |
| ALL FIELDS | ALL_TAR (200MB) (contains selected entries; see readme for details) STAR-FORMATION RATES (8.7MB) (see Whitaker et al., 2014 for details) |
READ-ME |
All ground-based and HST images used in the creating of the 3D-HST photometric catalogs are available for download.
Credit: When using the F140W mosaics provided here, please cite Skelton et al. (2014). When using the F125W and F160W mosaics, please cite Skelton et al. (2014), Grogin et al. (2011) and Koekemoer et al. (2011).
When using images from other surveys, please cite the provided references.
An up-to-date list of known issues is available HERE (also included in the full documentation).
-
AEGIS HST IMAGES
MOSAICS PSFS README WFC3
ImagesAEGIS_F125W_TAR
(4.1GB)
AEGIS_F140W_TAR
(3.3GB)
AEGIS_F160W_TAR
(2.6GB)
AEGIS_WFC3_PSFs
(183KB)READ-ME WFC3
DetectionF140W+F125W+F160
(732MB)
SEGMENTATION
(4.5MB)
USE_MASK
(3.0MB)ACS
ImagesAEGIS_F606W_TAR
(4.4GB)
AEGIS_F814W_TAR
(4.4GB)
AEGIS_ACS_PSFs
(140KB)READ-ME ANCILLARY IMAGES
WARNING: The images in this section are based on publicly-available dataset. They are registered to the WFC3 mosaics above based on their header WCS and re-binned to a 0.06”/pix scale. Astrometric offsets and distortions exist between these ancillary images and the WFC3 images! Such offsets are accounted for in our photometric catalog, but the images are not corrected.
Bands Data Telescope Survey Reference u,g,r,i,z
DOWNLOADS
(2.6GB each)CFHT CFHTLS Erben et al. (2009); Hildebrandt et al. (2009) J1, J2, J3
H1, H2, K
DOWNLOADS
(1.1GB to 4GB each)KPNO/NEWFIRM NMBS Whitaker et al. (2011) J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(1.5GB to 3GB each)CFHT/WIRCam WIRDS Bielby et al. (2012) 3.6, 4.5 um
DOWNLOADS
(3.1GB each)Spitzer/IRAC SEDS Ashby et al. (2013) 5.8, 8.0 um
DOWNLOADS
(3.1GB each)Spitzer/IRAC EGS Barmby et al. (2008) -
COSMOS HST IMAGES
MOSAICS PSFS README WFC3
ImagesCOSMOS_F125W_TAR
(3.3GB)
COSMOS_WFC3_PSFs
(183KB)READ-ME WFC3
DetectionF140W+F125W+F160
(732MB)
SEGMENTATION
(4.5MB)
USE MASK
(3.0MB)ACS
ImagesCOSMOS_F606W_TAR
(3.5GB)
COSMOS_F814W_TAR
(3.5GB)
COSMOS_ACS_PSFs
(140KB)READ-ME ANCILLARY IMAGES
WARNING: The images in this section are based on publicly-available dataset. They are registered to the WFC3 mosaics above based on their header WCS and re-binned to a 0.06”/pix scale. Astrometric offsets and distortions exist between these ancillary images and the WFC3 images! Such offsets are accounted for in our photometric catalog, but the images are not corrected.
Bands Data Telescope Survey Reference u,g,r,i,z
DOWNLOADS
(1.5GB each)CFHT CFHTLS Erben et al. (2009)
Hildebrandt et al. (2009)BJ, VJ, r+, i+, z+
12 medium-bands
DOWNLOADS
(850MB each)Subaru
Suprime-CamTaniguchi et al. (2007)
Capak et al. (2007)J1, J2, J3
H1, H2, K
DOWNLOADS
(1.6GB each)KPNO/NEWFIRM NMBS Whitaker et al. (2011) J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(1.5GB each)CFHT/WIRCam WIRDS Bielby et al. (2012) Y, J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(1.5GB each)Vista UltraVista McCracken et al. (2012) 3.6, 4.5 um
DOWNLOADS
(3.3GB each)SEDSSpitzer/IRAC SEDS Ashby et al. (2013) 5.8, 8.0 um
DOWNLOADS
(1.6GB each)S-COSMOSSpitzer/IRAC S-COSMOS Sanders et al. (2007) -
GOODS-N HST IMAGES
MOSAICS PSFS README WFC3
ImagesGOODS-N_F125W_TAR
(2.3GB)
GOODS-N_F140W_TAR
(1.6GB)
GOODS-N_F160W_TAR
(1.7GB)
GOODS-N_WFC3_PSFs
(183KB)READ-ME WFC3
DetectionF140W+F125W+F160
(614MB)
SEGMENTATION
(4.0MB)
USE_MASK
(3.0MB)ACS
ImagesGOODS-N_F435W_TAR
(2.4GB)
GOODS-N_F606W_TAR
(2.6GB)
GOODS-N_F775W_TAR
(4.6GB)
GOODS-N_F850LP_TAR
(4.6GB)
GOODS-N_ACS_PSFs
(140KB)READ-ME ANCILLARY IMAGES
WARNING: The images in this section are based on publicly-available dataset. They are registered to the WFC3 mosaics above based on their header WCS and re-binned to a 0.06”/pix scale. Astrometric offsets and distortions exist between these ancillary images and the WFC3 images! Such offsets are accounted for in our photometric catalog, but the images are not corrected.
Bands Data Telescope Survey Reference U
DOWNLOADS
(1.5GB)HDFN-UKPNO 4m
MOSAICHawaii
HDFNCapak et al. (2004) G,Rs
DOWNLOADS
(580MB each)Keck/LRIS Steidel et al. (2003) B,V,R,i,z
DOWNLOADS
(~2.5GB each)Subaru
Suprime-CamHawaii
HDFNCapak et al. (2004) J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(~800MB each)MODSSubaru
MOIRCSMODS Kajisawa et al. (2011) 3.6, 4.5 um
DOWNLOADS
(2.8GB each)SEDSSpitzer/IRAC SEDS Ashby et al. (2013) 5.8, 8.0 um
DOWNLOADS
(~2.2GB each)GOODSSpitzer/IRAC GOODS Dickinson et al. (2003) -
GOODS-S HST IMAGES
MOSAICS PSFS README WFC3
ImagesGOODS-S_F125W_TAR
(2.5GB)
GOODS-S_F140W_TAR
(2.1GB)
GOODS-S_F160W_TAR
(1.8GB)
GOODS-S_WFC3_PSFs
(140KB)READ-ME WFC3
DetectionF140W+F125W+F160
(653MB)
SEGMENTATION
(5.0MB)
USE_MASK
(3.0MB)ACS
ImagesGOODS-S_F435W_TAR
(2.2GB)
GOODS-S_F606W_TAR
(2.4GB)
GOODS-S_F775W_TAR
(2.3GB)
GOODS-S_F850LP_TAR
(2.4GB)
GOODS-S_F606W_CAND_TAR
(700MB)
GOODS-S_F814W_CAND_TAR
(3.2GB)
GOODS-S_F850LP_CAND_TAR
(2.5GB)
GOODS-S_ACS_PSFs
(324KB)READ-ME ANCILLARY IMAGES
WARNING: The images in this section are based on publicly-available dataset. They are registered to the WFC3 mosaics above based on their header WCS and re-binned to a 0.06”/pix scale. Astrometric offsets and distortions exist between these ancillary images and the WFC3 images! Such offsets are accounted for in our photometric catalog, but the images are not corrected.
Bands Data Telescope Survey Reference U,R
DOWNLOADS
(2.2GB)VLT/VIMOS ESO GOODS Nonino et al. (2009) U38,B,V,Rc,I
DOWNLOADS
(2.2GB)ESO 2.2m GaBoDs Hildebrandt et al. (2006); Erben et al. (2005) 14 medium bands
DOWNLOADS
(1.2GB)Subaru
Suprime-CamMUSYC Cardamone et al. (2010) J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(~1.0GB)FIREWORKSVLT/ISAAC ESO GOODS Retzlaff et al. (2010)
Wuyts et al. (2008)J,Ks
DOWNLOADS
(2.2GB)TENISCFHT
WIRCamTENIS Hsieh et al. (2012) 3.6, 4.5 um
DOWNLOADS
(~2.2GB)SEDSSpitzer/IRAC SEDS Ashby et al. (2013) 5.8, 8.0 um
DOWNLOADS
(~2.3GB)GOODSSpitzer/IRAC GOODS Dickinson et al. (2003) -
UDS HST IMAGES
MOSAICS PSFS README WFC3
ImagesUDS_F125W_TAR
(2.7GB)
UDS_F140W_TAR
(1.6GB)
UDS_F160W_TAR
(2.0GB)
UDS_WFC3_PSFs
(140KB)READ-ME WFC3
DetectionF140W+F125W+F160
(724MB)
SEGMENTATION
(4.3MB)
USE MASK
(3.0MB)ACS
ImagesUDS_F606W_TAR
(3.0GB)
UDS_F814W_TAR
(3.0GB)
UDS_ACS_PSFs
(94KB)READ-ME ANCILLARY IMAGES
WARNING: The images in this section are based on publicly-available dataset. They are registered to the WFC3 mosaics above based on their header WCS and re-binned to a 0.06”/pix scale. Astrometric offsets and distortions exist between these ancillary images and the WFC3 images! Such offsets are accounted for in our photometric catalog, but the images are not corrected.
Bands Data Telescope Survey Reference U
DOWNLOADS
(2.5GB)MegacamCFHT
MegacamAlmaini/Foucaud
(in prep.)B,V,R,i,z
DOWNLOADS
(1.4GB)Subaru
Suprime-CamSXDS Furusawa et al. (2008) J, H, Ks
DOWNLOADS
(2.5GB)UKIRT
WFCAMUKIDSS
DR8Almani et al. (in prep.) 3.6, 4.5 um
DOWNLOADS
(2.6GB)Spitzer/IRAC SEDS Ashby et al. (2013) 5.8, 8.0 um
DOWNLOADS
(2.6GB)SpUDSSpitzer/IRAC SpUDS Dunlop et al. (in prep.)
Previous Data Releases
The v3.0 release described in van Dokkum et al (2013), including deep HUDF spectra, can be found here.
The preliminary data release v0.5 accompanying the survey paper Brammer et al. (2012) can be found here.
Acknowledgements
When using data from the 3D-HST survey, please include the following acknowledgement:
"This work is based on observations taken by the 3D-HST Treasury Program (GO 12177 and
12328) with the NASA/ESA HST, which is operated by the Association of Universities for
Research in Astronomy, Inc., under NASA contract NAS5-26555."
When using the grism data products and derived parameters provided here, please cite Momcheva et al. (2015) and Brammer et al. (2012).
When using the photometric catalogs, derived parameters, and rest-frame colors provided here, please cite Skelton et al. (2014) and Brammer et al. (2012).
When using the F140W mosaics provided here, please cite Skelton et al. (2014). When using the F125W and F160W mosaics, please cite Skelton et al. (2014), Grogin et al. (2011) and Koekemoer et al. (2011). When using images from other surveys, please cite the provided references.


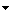

 Follow Us
Follow Us