22-Sep-19
ETE 305
DPCM, DM & ADM
Avijit Hira
Lecturer, ETE; CUET
Department of ETE
Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET)
Differential Pulse code modulation
Definition: One way to minimize redundant transmission and reduce the BW is
to transmit PCM signals corresponding to the difference in adjacent sample
values. This scheme is known as Differential Pulse code modulation (DPCM).
Consider, instead of transmitting the sample value, we transmit the difference
between the successive sample values.
If, m[k] = the kth sample of transmitting signal.
We transmit the difference
At the receiver, knowing d[k] and the previous sample value
m[k-1], we can reconstruct m[k] .
1
� 22-Sep-19
DPCM (2)
DPCM (5)
Analysis:
2
� 22-Sep-19
DPCM (3)
DPCM (4)
3
� 22-Sep-19
DPCM (7)
DPCM (6)
Analysis:
mˆ [ k ] predicted value
m q [ k 1], m q [ k 2 ],....... Quantized version of m[ k 1], m[ k 2 ],.......
mˆ q [ k ] Estimate of quantized sample
Now,
4
� 22-Sep-19
DPCM (8)
SNR Improvement: Let,
mp= Peak amplitude of m(t)
dp = Peak amplitude of d(t)
Using same value of L in both case, the quantization step Δv is reduced by dp / dm .
Quantization noise power
v 2
12
2
mp
Quantization noise reduces by
d
p
P
SNR improvement is, Gp m
Pd
P
10Log10 m dB
Pd
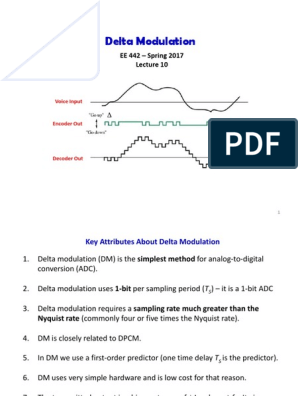
Delta Modulation
Delta modulation (DM) is a special case of DPCM where there are 2 quantizing levels.
5
� 22-Sep-19
DM (2)
DM (3)
The integrator output at a time, t=nTs
n
1
zn
Vc
y
i0
i
where ,
y i y ( iT )
6
� 22-Sep-19
DM (4)
The quantizing noise error signal may be classified into 2 types of noise
1) Slop overload noise
2) Granular noise.
Slop overload noise: Slop overload noise occurs when the step size δ is too small
for the accumulator output to follow quick changes in the input waveform.
Granular noise: Similar to the Granular noise of a PCM system
DM (5)
δ should have an optimum
value, because if δ is increased,
the granular noise will increase
but the slop overload noise will
decrease.
7
� 22-Sep-19
DM (6)
Example 3-5: Design of a DM system.
Find the step size δ required to prevent slope overload noise for the case when the input
signal is a sine wave.
Soln: The maximum slope from accumulator output
For no slope overload noise,
δ should not be too much larger
DM (7)
SNR: Spectrum of granular noise is uniformly distributed over the frequency band ІfІ ≦
fs. 2
Total granular noise =
3
PSD is
The granular noise power,
Using,
8
� 22-Sep-19
DM (8)
Where,
fs = DM sampling frequency
fa = Sinusoidal input frequency
B = Bandwidth of receiving system.
For voice frequency audio signal,
Adaptive Delta modulation
Definition: Adaptive Delta modulation (ADM) is used to minimize the slope
overload noise at a reasonable value.
the step size is varied as a function of time as the input waveform changes.
The step size is kept small to minimize the granular noise until the slope
overload noise begins to dominate .
The step size is increased to reduce the slope overload noise .
The step size may be adapted.
9
� 22-Sep-19
Step size changes with discrete variation
ADM (3)
10
� 22-Sep-19
ADM (4)
Another variation of ADM is Continuously Variable Slope Delta Modulation (CVSDM).
Here, the step size is made continuously variable instead of stepped in discrete increment.
Speech coder: Digital speech coder can be classified into 2 categories –
1. Waveform coder.
2. Vocoder.
1. Waveform coder: Waveform coder use algorithms to encode and decode so that the
system output is an approximation to the input waveform.
2. Vocoder: Vocoder encodes the speech by extracting a set of parameter.
Comparison between DM and PCM
• DM PCM
SNR varies as a power of BT/B, being SNR varies exponentially with BT/B
proportional to (BT/B)3 for single
integration and(BT/B)5 for double
integration .
DM has all advantages of a digital PCM has not.
system
In case of detection error, DM is more Error probability can cause serious
immune than PCM. error leading to threshold in PCM.
For multiplexing several channel, each For multiplexing several channel, 1 own
channel requires its own coder and coder and 1 decoder are shared by all
decoder. channels.
11
� 22-Sep-19
Comparison(2)
•
12