Science and Technology Development at the National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory (NVFEL)
The National Vehicle and Fuel Emissions Laboratory (NVFEL) leads in the development of scientific laboratory-based testing methods to assess advanced vehicle technology in support of EPA’s compliance and regulation activities in the transportation sector. This state-of-the-art test facility provides a wide array of dynamometer and analytical testing and engineering services supporting the Office of Transportation and Air Quality’s technology assessment and test method development programs for light-duty cars and trucks, heavy-duty engines, and small non-road engines.
NVFEL, which is an ISO 17025:2017 accredited and ISO 14001:2015 certified laboratory, has a long history of conducting research, development, demonstration and commercialization programs associated with advanced automotive engines, drivetrains, testing equipment and test methods. The laboratory has been issued over 90 U.S. patents on advanced technology developed at the lab and continues to be a leading innovator in finding novel ways to assess and reduce the environmental impact of vehicles, engines and fuels.
Low Emission Light-Duty Vehicle Technology
The Advanced Technology Assessment Branch (ATAB), formerly known as the National Center for Advanced Technology (NCAT), located at NVFEL develops technical methods to assess the effectiveness of advanced emission and fuel consumption technologies for a broad range of key light-duty applications. These activities fall broadly into the following categories:

- Benchmarking the Technology:
The ATAB team characterizes advanced technology vehicles, engines and transmissions using scientific laboratory testing and analysis methods to benchmark emissions and fuel consumption performance.
For more information on benchmarking, see: - Combining Data into Complete Engine and eMotor Maps:

Sample Complete Engine Map for Fuel Consumption (BSFC) To robustly characterize vehicle operation for a variety of analytical and modeling purposes, a complete engine map for fuel consumption (BSFC) is required for each engine modeled in a simulation project. These maps identify an engine’s fuel consumption across the entire operating boundaries of the engine, including idle, wide-open-throttle, minimum motoring torque and maximum operating speed.
ATAB has also developed a consistent process to create complete electric motor efficiency maps utilizing benchmarking test data and other published technical materials.
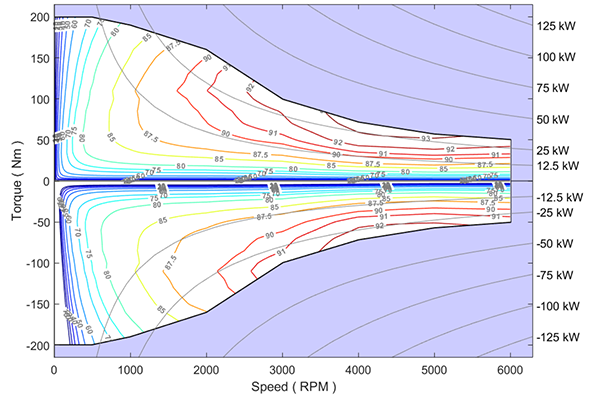
Sample Complete Emotor Map These complete engine and electric motor maps are used both for vehicle simulations (described see below) and for engineering analyses in technical papers. For more information on EPA’s complete engine and electric motor maps, see:
- Simulating the Operation of Future Vehicle Technology Packages:

Example Drive Schedules Used in Benchmark Testing EPA’s Advanced Light-Duty Powertrain and Hybrid Analysis (ALPHA) tool uses complete engine maps (described above) and other technical component data to perform full vehicle simulations for many different vehicle technology configurations. ALPHA is a physics-based full vehicle simulation tool which estimates fuel consumption and emission results from vehicles configured with various combinations of advanced technologies as driven over various types of driving schedules used in laboratory benchmark testing (illustrated by the examples in the image on the right).
The ALPHA model supports various EPA emission control programs. ALPHA simulation results have been used in technical engineering analyses of CO2 emissions from advanced automotive technologies which could be used to meet light-duty vehicle standards, as well as in numerous technical papers, see:
For more information on ALPHA simulation, see:
Low Emission Heavy-Duty Technology
The Engine Testing Branch (ETB) tests heavy-duty engine technologies and the Advanced Testing Branch (ATB) performs heavy-duty chassis testing. Both support EPA’s heavy- and medium-duty truck criteria pollutant emission and fuel consumption standards. These testing teams support programs that demonstrate new technology and develop new test methods for heavy-duty on-road and non-road engines, powertrains, and chassis. ETB measures the criteria emissions and fuel consumption of heavy-duty engines at various operating conditions. The fuel consumption measurements were used to validate OTAQ’s Greenhouse Gas Emissions Model (GEM). ATB measures the criteria emissions and fuel consumption of the entire heavy-duty truck chassis.