Paper:
Development of Sensory Feedback Device for Myoelectric Prosthetic Hand to Provide Hardness of Objects to Users
Takakuni Morita*, Takeshi Kikuchi*, and Chiharu Ishii**
*Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Hosei University
3-7-2 Kajino-cho, Koganei-shi, Tokyo 184-8584, Japan
**Department of Mechanical Engineering, Hosei University
3-7-2 Kajino-cho, Koganei-shi, Tokyo 184-8584, Japan
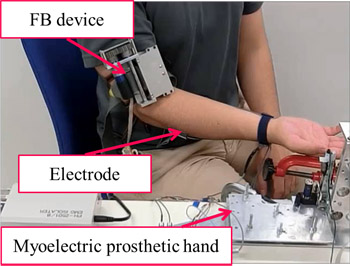
Sensory feedback device for myoelectric hand
- [1] K. Sato and S. Tachi, “Transmission System of Spatially Distributed Tactile Information using Finger-shaped GelForce and Electrotactile Display,” The Trans. of Human Interface Society, Vol.12, No.2, pp. 55-62, 2010 (in Japanese).
- [2] T. Kurogi, M. Nakayama, K. Sato, S. Kamuro, C. L. Fernando, M. Furukawa, K. Minamizawa, and S. Tachi, “Haptic Transmission System to Recognize Differences in Surface Textures of Objects for Telexistence,” Proc. of IEEE Virtual Reality 2013, pp. 137-138, 2013.
- [3] J. Kawamura, “Gisi no kankaku fiidbakku souti (Sensory Feedback Device of Artificial Limb),” J. of the Society of Biomechanisms Japan, Vol.8, No.2, pp. 56-60, 1984 (in Japanese).
- [4] N. Akimichi, K. Eguchi, and K. Suzuki, “Myoelectric Controlled Prosthetic Hand with Continuous Force-Feedback Mechanism,” Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pp. 3354-3359, 2013.
- [5] K. Yada et al., “A study of sensory feedback system for two kinds of information transmission of EMG prosthetic hand,” IEICE technical report. ME and bio cybernetics, Vol.104, No.401, pp. 11-14, 2004 (in Japanese).
- [6] N. H. H. Mohamad Hanif, P. H. Chappell, A. Cranny, and N. M. White, “Vibratory Feedback for Artificial Hands,” Proc. of Int. Conf. on Electronics Computer and Computation, pp. 247-250, 2013.
- [7] M. D’Alonzo, S. Dosen, C. Cipriani, and D. Farina, “HyVE: Hybrid Vibro-Electrotactile Stimulation for Sensory Feedback and Substitution in Rehabilitation,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol.22, No.2, pp. 290-301, 2014.
- [8] J. Wheeler, K. Bark, J. Savall, and M. Cutkosky, “Investigation of Rotational Skin Stretch for Proprioceptive Feedback With Application to Myoelectric Systems,” IEEE Trans. on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Vol.18, No.1, pp. 58-66, 2010.
- [9] A. Akhtar, M. Nguyen, L. Wan, B. Boyce, P. Slade, and T. Bretl, “Passive Mechanical Skin Stretch for Multiple Degree-of-Freedom Proprioception in a Hand Prosthesis,” Haptics: Neuroscience, Devices, Modeling, and Applications, pp. 120-128, 2014.
- [10] F. Kimura et al., “A Sensory Feedback System for EMG-Controlled Prosthetic Hands,” Proc. of the 48th JSME Hokkaido Branch conference, pp. 73-74, 2009 (in Japanese).
- [11] T. Yamamoto, S. Omatu, and H. Ishihara, “A Construction of Self-Tuning PID Control System,” Trans. of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, Vol.25, No.10, pp. 1069-1075, 1989 (in Japanese).
- [12] A. Harada, T. Nakakuki, M. Hikita, and C. Ishii, “Robot Finger Design for Myoelectric Prosthetic Hand and Recognition of Finger Motions via Surface EMG,” Proc. of the 2010 IEEE Int. Conf. on Automation and Logistics, pp. 273-278, 2010.
- [13] T. Kikuchi and C. Ishii, “Identification of Finger Operation using Support Vector Machine and Control of Myoelectric Prosthetic Hand based on Integrated Electromyogram,” Proc. of the 2014 IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Biomimetics, pp. 1272-1277, 2014.
- [14] J. Kawamura, N. Fukui, M. Nakagawa, T. Fujishita, T. Aoyama, and H. Furukawa, “The Upper-limb Amputees: A Survey and Trends in Kinki Area of Japan,” The Japanese J. of Rehabilitation Medicine, Vol.36, No.6, pp. 384-389, 1999.
- [15] Y. Tanaka, “Sinrigakuteki sokuteihou dai 2han (Psychological measurement method Second edition),” University of Tokyo Press, 1977 (in Japanese).
- [16] Y. Wada et al., “Kankaku, chikaku sinrigaku hando bukku (Handbook of sense and perceptual psychology),” Seishin Shobo, 1985 (in Japanese).
 This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.
This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 Internationa License.