The Origin and Evolution of the Normal Type Ia SN 2018aoz with Infant-phase Reddening and Excess Emission
Abstract
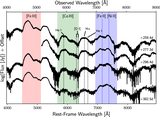
SN 2018aoz is a Type Ia SN with a B-band plateau and excess emission in infant-phase light curves ≲1 day after the first light, evidencing an over-density of surface iron-peak elements as shown in our previous study. Here, we advance the constraints on the nature and origin of SN 2018aoz based on its evolution until the nebular phase. Near-peak spectroscopic features show that the SN is intermediate between two subtypes of normal Type Ia: core normal and broad line. The excess emission may be attributable to the radioactive decay of surface iron-peak elements as well as the interaction of ejecta with either the binary companion or a small torus of circumstellar material. Nebular-phase limits on Hα and He I favor a white dwarf companion, consistent with the small companion size constrained by the low early SN luminosity, while the absence of [O I] and He I disfavors a violent merger of the progenitor. Of the two main explosion mechanisms proposed to explain the distribution of surface iron-peak elements in SN 2018aoz, the asymmetric Chandrasekhar-mass explosion is less consistent with the progenitor constraints and the observed blueshifts of nebular-phase [Fe II] and [Ni II]. The helium-shell double-detonation explosion is compatible with the observed lack of C spectral features, but current 1D models are incompatible with the infant-phase excess emission, ${B}_{\max }\mbox{--}{V}_{\max }$ color, and weak strength of nebular-phase [Ca II]. Although the explosion processes of SN 2018aoz still need to be more precisely understood, the same processes could produce a significant fraction of Type Ia SNe that appear to be normal after ~1 day.
- Publication:
-
The Astrophysical Journal
- Pub Date:
- March 2023
- DOI:
- 10.3847/1538-4357/aca9be
- arXiv:
- arXiv:2206.12437
- Bibcode:
- 2023ApJ...946....7N
- Keywords:
-
- Binary stars;
- Supernovae;
- Type Ia supernovae;
- White dwarf stars;
- Transient sources;
- Time domain astronomy;
- Astrophysics - Solar and Stellar Astrophysics;
- Astrophysics - High Energy Astrophysical Phenomena;
- High Energy Physics - Phenomenology
- E-Print:
- Submitted for publication in ApJ. 35 pages, 16 figures, 7 tables