Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
oral solution
- 20mg/mL (Ziagen)
tablet
- 300mg (generic)
HIV Infection
Indicated for treatment of HIV infection in combination with other antiretroviral agents
300 mg PO q12hr, OR
600 mg PO qDay
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment required
Hepatic impairment
- Mild (Child-Pugh A); adults and adolescents aged ≥16 years: Reduce dose to 200 mg q12hr (use oral solution)
- Moderate-to severe (Child-Pugh B or C): Contraindicated
Dosage Forms & Strengths
oral solution
- 20mg/mL (Ziagen)
tablet
- 300mg (generic)
HIV Infection
Indicated for treatment of HIV infection in combination with other antiretroviral agents
Neonates/infants <3 months: Safety and efficacy not established
Oral solution
Tablet
- Available as a scored tablet; if unable to reliably swallow tablets, prescribe the oral solution
- ≥14 kg to <20 kg: 150 mg PO q12hr, OR 300 mg qDay
- ≥20 to <25 kg: 150 mg AM and 300 mg PM, OR 450 mg qDay
- ≥25 kg: 300 mg PO q12hr, OR 600 mg PO qDay in combination with other antiretroviral agents
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment: No dosage adjustment required
Hepatic impairment
- Mild (Child-Pugh A); adults and adolescents aged ≥16 years: Reduce dose to 200 mg q12hr (use oral solution)
- Moderate-to severe (Child-Pugh B or C): Contraindicated
Dosing Considerations
Once daily dosing: NIH pediatric HIV guidelines (March, 2016) recommend initiation of therapy with once-daily dosing in children who can be treated with the tablet formulation
Twice daily dosing: Use twice daily dosing in infants and young children initiating therapy with liquid formulations; consider switching to once-daily dosing after 6 months when viral load is undetectable and CD4 cell count is stable
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results
Contraindicated
Serious
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor
Contraindicated (1)
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
abacavir, elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF. Other (see comment). Contraindicated. Comment: Elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir is a complete regimen for HIV and should not be administered with other antiretrovirals.
Serious (7)
- atidarsagene autotemcel
abacavir, atidarsagene autotemcel. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Antiretroviral (ART) medications may interfere with the manufacturing of atidarsagene autotemcel. Do not take ARTs for at least 1 month before cell mobilization or the expected duration for elimination of the medications.
- betibeglogene autotemcel
abacavir, betibeglogene autotemcel. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Do not take antiretroviral medications for at least 1 month before mobilization or expected duration for elimination of the medications, and until all cycles of apheresis are completed. Antiretroviral medications may interfere with manufacturing of apheresed cells.
- elivaldogene autotemcel
elivaldogene autotemcel, abacavir. Either decreases effects of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Patients should not take antiretroviral medications for at least 1 month before initiating medications for stem cell mobilization, for the duration of the medications? elimination, and until all cycles of apheresis are completed.
- ganciclovir
ganciclovir, abacavir. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Increased risk of hematologic toxicity.
- lovotibeglogene autotemcel
abacavir, lovotibeglogene autotemcel. Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Discontinue antiretrovirals (ARTs) at least 1 month before mobilization and until all apheresis cycles are completed. Some long-acting ARTs may require a longer duration of discontinuation for elimination. ARTs may interfere with lovotibeglogene autotemcel manufacturing.
- ribavirin
ribavirin increases toxicity of abacavir by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Increased risk of lactic acidosis and hepatic decompensation.
- valganciclovir
valganciclovir, abacavir. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Increased risk of hematologic toxicity.
Monitor Closely (18)
- atazanavir
atazanavir and abacavir both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cabozantinib
abacavir will increase the level or effect of cabozantinib by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. MRP2 inhibitors increase cabozantinib toxicity
- didanosine
abacavir and didanosine both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- efavirenz
abacavir and efavirenz both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- emtricitabine
abacavir and emtricitabine both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- enfuvirtide
abacavir and enfuvirtide both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fosamprenavir
fosamprenavir and abacavir both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lamivudine
abacavir and lamivudine both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methadone
abacavir will decrease the level or effect of methadone by unknown mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for opioid withdrawal symptoms.
- nelfinavir
nelfinavir and abacavir both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nevirapine
abacavir and nevirapine both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- orlistat
orlistat will decrease the level or effect of abacavir by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Use Caution/Monitor. Loss of virological control reported in HIV-infected patients taking orlistat concomitantly. Exact mechanism is unclear, but may include a drug-drug interaction that inhibits systemic absorption of the antiretroviral drug. Monitor HIV RNA levels frequently and if increased HIV viral load confirmed, discontinue orlistat.
- riociguat
abacavir will increase the level or effect of riociguat by unknown mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Riociguat dose reduction may be necessary
- ritonavir
ritonavir and abacavir both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tenofovir DF
abacavir and tenofovir DF both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tipranavir
tipranavir and abacavir both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
tipranavir decreases levels of abacavir by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ublituximab
ublituximab decreases effects of abacavir by immunosuppressive effects; risk of infection. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- zidovudine
abacavir and zidovudine both increase risk of immune reconstitution syndrome. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (1)
- ethanol
ethanol increases levels of abacavir by decreasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Interaction usually not clinically significant.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Nausea (17-19%)
Headache (9-13%)
Malaise/fatigue (12%)
Nausea & vomiting (10%)
1-10%
Hypersensitivity reaction (2-8%)
Diarrhea (5-7%)
Musculoskeletal pain (5-7%)
Hypertriglyceridemia (6%)
Hepatic: AST increased (6%)
Depression (4-6%)
Fever/chills (3-6%)
Viral respiratory infections (5%)
Ear/nose/throat infections (4-5%)
Rash (4-5%)
Anxiety (3-5%)
Thrombocytopenia (1%)
<1%
Anaphylactoid reaction
Pulmonary hypertension
Erythema multiforme
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Pancreatitis
GGT increased
Hepatic steatosis
Heptaomegaly
Hepatotoxicity
Lactic acidosis
MI
Warnings
Black Box Warnings
Hypersensitivity reactions
- Severe and sometimes fatal hypersensitivity reaction, with multiple organ involvement, have occurred
- Patients who carry the HLA-B*5701 allele are at a higher risk of a hypersensitivity reaction; although, hypersensitivity reactions have occurred in patients who do not carry the HLA-B*5701 allele
- Contraindicated with history of prior hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir and in patients who are HLA-B*5701-positive
- All patients should be screened for the HLA-B*5701 allele before initiating or reinitiating abacavir, unless patients have a previously documented HLA-B*5701 allele assessment
- If hypersensitivity is suspected, discontinue abacavir immediately, regardless of HLA-B*5701 status and even when other diagnoses are possible
- Following a hypersensitivity reaction, never restart therapy or any other abacavir-containing product because more severe symptoms, including death can occur within hours; similar severe reactions have also occurred rarely following the reintroduction of abacavir-containing products in patients who have no history of abacavir hypersensitivity
Contraindications
Prior hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir
Presence of HLA-B*5701 allele
Moderate or severe hepatic impairment
Cautions
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, reported with nucleoside analogs, including abacavir; a majority of these cases have been in women; female gender and obesity may be risk factors; suspend dosing in those who develop clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity, which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations
Immune reconstitution syndrome reported with combination ART; during the initial treatment phase, patients whose immune systems respond may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (eg, Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis); autoimmune disorders (eg, Graves disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported
Use has been associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction in observational studies, but not in a meta-analysis of 26 randomized trials; caution with risks for coronary heart disease and minimizing modifiable risk factors, including smoking, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, prior to use
Hypersensitivity
- Before starting therapy, review medical history for prior exposure to any abacavir containing product
- Increased risk of serious or fatal hypersensitivity reactions; patients with human leukocyte antigen allele, HLA-B*5701 are at a higher risk; do not restart abacavir following hypersensitive reaction; may cause hypotension, multiorgan failure, and/or death (see Contraindications and Black Box Warnings)
- If a hypersensitivity reaction is ruled out, patients may restart therapy; rarely, patients who have stopped abacavir for reasons other than symptoms of hypersensitivity have also experienced life-threatening reactions within hours of reinitiating abacavir therapy; reintroduction to drug or any other abacavir-containing product recommended only if medical care can be readily accessed
- A Medication Guide and Warning Card that provide information about recognition of hypersensitivity reactions should be dispensed with each new prescription and refill
Drug interaction overview
-
Methadone
- In a trial of 11 HIV-1-infected subjects receiving methadone-maintenance therapy with abacavir 600 mg BID (twice the currently recommended dose), PO methadone clearance increased
- This alteration will not result in a methadone dose modification in the majority of patients; however, an increased methadone dose may be required in a small number of patients
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) at 1-800-258-4263
Available data from the APR show no difference in the overall risk of birth defects for abacavir compared with the background rate for birth defects of 2.7% in the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP) reference population
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of abacavir to pregnant rats during organogenesis resulted in fetal malformations and other embryonic and fetal toxicities at exposures 35 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended clinical daily dose; however, no adverse developmental effects were observed following oral administration of abacavir to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis, at exposures approximately 9 times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended clinical dose
Lactation
Abacavir is present in human milk; there is no information on effects of abacavir on breastfed infant or effects of drug on milk production; because of potential for (1) HIV-1 transmission (in HIV-negative infants), (2) developing viral resistance (in HIV- positive infants), and (3) serious adverse reactions in breastfed infant, instruct mothers not to breastfeed if they are receiving abacavir
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Guanosine analog that inhibits HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by competing with dGTP as substrate, which in turn inhibits viral replication
Absorption
Rapid and extensive PO absorption
Bioavailability: 83%
Peak plasma concentration: 3 mcg/mL (300 mg); 4.26 mcg/mL (600 mg)
AUC: 6.02 mcg·h/mL (300 mg); 11.95 mcg·h/mL (600 mg)
Distribution
Vd: 0.86 L/kg
Protein bound: 50%
Metabolism
Hepatic via alcohol dehydrogenase and glucuronyl transferase to inactive carboxylate and glucuronide metabolites
Elimination
Half-life: 1.5 hr
Peak plasma time: 0.7-1.7 hr
Excretion: Urine (80%); feces (16%)
Pharmacogenomics
Patients who carry the HLA-B*5701 allele are at high risk for experiencing a hypersensitivity reaction
Prior to initiating therapy with abacavir, screening for the HLA-B*5701 allele is recommended
For HLA-B*5701-positive patients, treatment with an abacavir-containing regimen is not recommended
Genetic testing laboratories
- The following companies provide genetic testing for HLA variants
- Kashi Clinical Laboratories (www.kashilab.com)
- LabCorp (https://www.labcorp.com)
- Specialty Laboratories (https://www.specialtylabs.com)
- Quest (https://www.questdialgnotics.com)
Administration
Oral Administration
May take with or without food
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| abacavir oral - | 300 mg tablet | 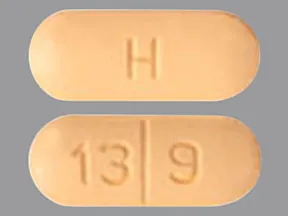 | |
| abacavir oral - | 300 mg tablet |  | |
| abacavir oral - | 300 mg tablet |  | |
| abacavir oral - | 300 mg tablet |  | |
| abacavir oral - | 20 mg/mL solution |  | |
| abacavir oral - | 300 mg tablet |  | |
| Ziagen oral - | 300 mg tablet | 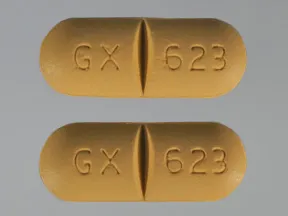 | |
| Ziagen oral - | 20 mg/mL solution |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
abacavir oral
ABACAVIR - ORAL
(a-BAK-a-vir)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Ziagen
WARNING: In some patients, abacavir has caused a serious (sometimes fatal) allergic reaction. Your doctor should order a blood test to measure your risk before you start this medication or take it again. If the blood test shows you are at greater risk, you should not take this medication and your doctor should discuss other treatment choices with you. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include any of the following: rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing, fever, extreme tiredness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, muscle aches, sore throat, or cough. Get medical help right away if you experience any of these symptoms. If you have stopped taking abacavir because of an allergic reaction, you must never take any form of abacavir again, or death could result. Tell all of your doctors and pharmacists if you have stopped taking abacavir due to an allergic reaction. Also, properly throw away any unused abacavir. Read the warning card provided with this medication for more details.
USES: This drug is used with other HIV medications to help control HIV infection. It helps to decrease the amount of HIV in your body so your immune system can work better. This lowers your chance of getting HIV complications (such as new infections, cancer) and improves your quality of life. Abacavir belongs to a class of drugs known as nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors-NRTI.Abacavir is not a cure for HIV infection. To decrease your risk of spreading HIV disease to others, continue to take all HIV medications exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Use an effective barrier method (latex or polyurethane condoms/dental dams) during sexual activity as directed by your doctor. Do not share personal items (such as needles/syringes, toothbrushes, and razors) that may have contacted blood or other body fluids. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more details.
HOW TO USE: Read the Medication Guide and Warning Card provided by your pharmacist before you start taking abacavir and each time you get a refill. Carry the Warning Card with you at all times. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor, usually 1 or 2 times daily. If you are using the liquid form of this medication, carefully measure the dose using a special measuring device/spoon. Do not use a household spoon because you may not get the correct dose.The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Children's dosage is also based on weight.If you stop using abacavir even for a short time and then restart the drug, you have an increased chance of developing a very serious (possibly fatal) allergic reaction. Refill your medication before you run out. Do not stop treatment unless directed by your doctor. Before restarting abacavir, consult your doctor or pharmacist, and be sure you have easy access to medical care.It is very important to keep taking this medication (and other HIV medications) exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not skip any doses. Do not increase your dose, take this drug more often than prescribed, or stop taking it (or other HIV medicines) even for a short time unless directed to do so by your doctor. Skipping or changing your dose without approval from your doctor may cause the amount of virus to increase, make the infection more difficult to treat (resistant), or worsen side effects.For the best effect, take this medication at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time(s) every day.
SIDE EFFECTS: See also Warning and How to Use sections.Trouble sleeping or loss of appetite may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.As your immune system gets stronger, it can begin to fight off infections you already had, possibly causing disease symptoms to come back. You could also have symptoms if your immune system becomes overactive. This reaction may happen at any time (soon after starting HIV treatment or many months later). Get medical help right away if you have any serious symptoms, including: unexplained weight loss, severe tiredness, muscle aches/weakness that doesn't go away, headaches that are severe or don't go away, joint pain, numbness/tingling of the hands/feet/arms/legs, vision changes, signs of infection (such as fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes, trouble breathing, cough, non-healing skin sores), signs of an overactive thyroid (such as irritability, nervousness, heat intolerance, fast/pounding/irregular heartbeat, bulging eyes, unusual growth in the neck/thyroid known as a goiter), signs of a certain nerve problem known as Guillain-Barre syndrome (such as unsteadiness, loss of coordination, trouble swallowing/speaking/chewing, trouble moving your eyes).Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: mental/mood changes (depression, anxiety).Rarely, this medication has caused severe (sometimes fatal) liver problems and a buildup of lactic acid in the blood (lactic acidosis). These serious side effects may occur more often in women and obese patients. Get medical help right away if you have any of the following serious symptoms, including: symptoms of liver problems (such as nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine), symptoms of lactic acidosis (such as deep/rapid breathing, drowsiness, nausea/vomiting).This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: See also Warning and How to Use sections.Before taking abacavir, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: liver problems (such as hepatitis B or C, or cirrhosis), kidney problems, alcohol use.Abacavir may increase your risk of a heart attack. Discuss the risks and benefits of treatment with your doctor and ways to lower your risk of heart disease. Tell your doctor if you have heart problems, if you smoke, or if you have other conditions that increase your risk of heart disease such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol levels.Before having surgery, tell your doctors or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).Tell your doctor if you are pregnant before using this medication. Treatment can lower the risk of passing HIV infection to your baby. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.This medication passes into breast milk. Because breast milk may transmit HIV, consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Some products that may interact with this drug include: alcohol, methadone, orlistat.This medication must not be taken with other medications that contain abacavir. Check the labels on all your other prescription medications to make sure they do not contain abacavir. If you have any questions, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as liver function, viral load, T-cell counts) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
MISSED DOSE: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Store abacavir solution or tablets at room temperature away from light and moisture. Abacavir solution may also be stored in the refrigerator. Do not freeze. The solution may turn from a clear or yellow color to a brown color over time. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised August 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.




