Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule
- 150mg
- 300mg
injectable powder
- 600mg
Tuberculosis
10 mg/kg/day PO or 10 mg/kg PO twice weekly (directly observed therapy [DOT]); not to exceed 600 mg/day
Dosing considerations
- May be given in conjunction with isoniazid or with isoniazid and pyrazinamide
- Rifampin dosage not to exceed 600 mg/day
Neisseria Meningitidis Carrier
Indicated for treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis to eliminate meningococci from the nasopharynx
600 mg q12hr for 2 days
Haemophilus Influenzae Type B Infection (Off-label)
Prophylaxis of contacts of patients with Haemophilus influenzae type B infection
600 mg/day PO/IV for 4 days
Leprosy (Off-Label)
U.S. Health Resources & Services Administration (HRSA) and World Health Organization (WHO) treatment guidelines are presented below
HRSA guidelines
-
Treatment regimen for multibacillary (MB) leprosy
- Rifampin 600 mg PO qDay, plus
- Clofazimine 50 mg PO qDay, plus
- Dapsone 100 mg PO qDay
- Duration: 24 months
-
Treatment regimen for paucibacillary (PB) leprosy
- Rifampin 600 mg PO qDay, plus
- Dapsone 100 mg PO qDay
- Duration: 12 months
WHO guidelines
- Rifampin 600 mg PO once a month, plus
- Clofazimine 300 mg PO once a month, and 50 mg qDay, plus
- Dapsone 100 mg PO qDay
- Duration: 12 months (MB) or 6 months (PB)
Dosing Considerations
Leprosy
- National Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy) Program (NHDP) recommendations are for daily rifampin, and for longer duration of treatment than the WHO recommendations, largely due to WHO’s cost considerations for developing countries; treatment that is more intensive and of longer duration is medically preferable
- In resource-limited settings, the WHO allows for shorter durations of monthly dosing for 6 months (paucibacillary) or 12 months (multibacillary)
- Rifampin is administered once monthly if coadministered with prednisone or for resource-limited settings
-
Clofazimine
- Clofazimine, used for decades to treat leprosy, is no longer available on open market
- No longer distributed commercially
- Only way to obtain clofazimine in the U.S. is to treat it as an investigational new drug (IND)
- NHDP holds this IND for its use in treating leprosy in the U.S.
- Physicians may obtain clofazimine by registering as an investigator under the NHDP IND
Dosage Forms & Strengths
capsule
- 150mg
- 300mg
injectable powder
- 600mg
Tuberculosis
10-20 mg/kg/day IV/PO or 10-20 mg/kg PO twice weekly (DOT); not to exceed 600 mg/day
Neisseria Meningitidis Infection
Indicated for treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis to eliminate meningococci from the nasopharyn
≤1 month: 10 mg/kg/day PO divided q12hr for 2 days
>1 month: 20 mg/kg/day PO divided q12hr for 2 days; not to exceed 600 mg/day
Haemophilus Influenzae Type B Infection (Off-label)
Prophylaxis of contacts of patients with Haemophilus influenzae type B infection
≤1 month: 10 mg/kg/day PO for 4 days
>1 month: 20 mg/kg/day PO for 4 days; not to exceed 600 mg/day
Leprosy (Off-Label)
U.S. Health Resources & Services Administration (HRSA) and World Health Organization (WHO) treatment guidelines are presented below
HRSA guidelines
-
Treatment regimen for multibacillary (MB) leprosy
- Rifampin 10-20 mg/kg (not to exceed 600 mg/day) PO qDay, plus
- Clofazimine 1 mg/kg PO qDay, plus
- Dapsone 1 mg/kg PO qDay
- Duration: 24 months
-
Treatment regimen for paucibacillary (PB) leprosy
- Rifampin 10-20 mg/kg (not to exceed 600 mg/day) PO qDay, plus
- Dapsone 1 mg/kg PO qDay
- Duration: 12 months
WHO guidelines
-
<10 years or <40 kg
- Rifampin 10 mg/kg PO once a month, plus
- Clofazimine 100 mg PO once a month, and 50 mg twice weekly, plus
- Dapsone 2 mg/kg PO qDay
- Duration: 12 months (MB) or 6 months (PB)
-
10-14 years
- Rifampin 450 mg PO once a month, plus
- Clofazimine 150 mg PO once a month, and 50 mg on alternate days, plus
- Dapsone 50 mg PO qDay
- Duration: 12 months (MB) or 6 months (PB)
Dosing Considerations
Leprosy
- National Hansen’s Disease (Leprosy) Program (NHDP) recommendations are for daily rifampin, and for longer duration of treatment than the WHO recommendations, largely due to WHO’s cost considerations for developing countries; treatment that is more intensive and of longer duration is medically preferable
- In resource-limited settings, the WHO allows for shorter durations of monthly dosing for 6 months (paucibacillary) or 12 months (multibacillary)
- Rifampin is administered once monthly if coadministered with prednisone or for resource-limited settings
-
Clofazimine
- Clofazimine, used for decades to treat leprosy, is no longer available on open market
- No longer distributed commercially
- Only way to obtain clofazimine in the U.S. is to treat it as an investigational new drug (IND)
- NHDP holds this IND for its use in treating leprosy in the U.S.
- Physicians may obtain clofazimine by registering as an investigator under the NHDP IND
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results
Contraindicated
Serious
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor
Contraindicated (41)
- artemether/lumefantrine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of artemether/lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers can result in decreased serum concentrations and loss of antimalarial efficacy
- atazanavir
rifampin decreases levels of atazanavir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. May result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
- bictegravir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bictegravir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of strong CYP3A and UGT1A1 inducers can substantially decrease bictegravir plasma concentrations. This may result in the loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to bictegravir. Coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated.
- cabotegravir
rifampin will increase the level or effect of cabotegravir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Cabotegravir is metabolized by UGT1A1 and UGT1A9. Strong UGT1A1 or UGT1A9 inducers decrease cabotegravir systemic exposure, thereby increasing potential for loss of virologic response.
- cariprazine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cariprazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation and elimination of cariprazine's active metabolites. The effect of CYP3A4 inducers on cariprazine exposure has not been evaluated and the net effect is unclear.
- cobicistat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cobicistat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated due to potential for loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance.
- cobimetinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cobimetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid coadministration. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers may decrease cobimetinib systemic exposure by >80% and reduce its efficacy.
- darunavir
rifampin decreases levels of darunavir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. May result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
- doravirine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of doravirine with a strong CYP3A inducer may decrease doravirine plasma concentrations and/or effects. Potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to doravirine.
- elbasvir/grazoprevir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of elbasvir/grazoprevir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. The therapeutic effect of elbasvir/grazoprevir may be reduced if coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers and is therefore contraindicated.
- elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF
rifampin decreases levels of elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir DF by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. May lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance.
- etravirine
rifampin decreases levels of etravirine by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated.
- fosamprenavir
rifampin decreases levels of fosamprenavir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. May result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
- fostemsavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fostemsavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of fostemsavir (prodrug) with strong CYP3A4 inducers significantly decreases temsavir (active moiety) plasma concentrations, which may lead to loss of virologic response and resistance.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of rifampin (a strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inducer) with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir significantly decreased glecaprevir/pibrentasvir plasma concentrations and AUC. Potential for loss of therapeutic effect.
- irinotecan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- irinotecan liposomal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- isavuconazonium sulfate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of isavuconazonium sulfate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- ledipasvir/sofosbuvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Contraindicated. P-gp inducers decrease sofosbuvir levels, and therefore decrease conversion to sofosbuvir's active metabolite (GS-331007) responsible for 90% of pharmacologic effect
- lenacapavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lenacapavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lenacapavir with strong CYP3A inducers is contraindicated.
- lonafarnib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lonafarnib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Lonafarnib is a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is contraindicated.
- lorlatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lorlatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lorlatinib with strong CYP3A inducers is contraindicated. Discontinue the strong CYP3A inducer for 3 plasma half-lives before initiating lorlatinib.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lumacaftor/ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A inducers have minimal effect on lumacaftor exposure, but decreased ivacaftor exposure (AUC) by 57%. This may reduce the effectiveness of lumacaftor/ivacaftor. Therefore, coadministration is not recommended.
- lumefantrine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lumefantrine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers can result in decreased serum concentrations and loss of antimalarial efficacy
- lurasidone
rifampin decreases levels of lurasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration of lurasidone with strong CYP3A4 inducers is contraindicated.
- mavacamten
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Contraindicated.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mavacamten by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. - naloxegol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of naloxegol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of naloxegol with strong CYP3A4 inducers is not recommended
- nelfinavir
rifampin decreases levels of nelfinavir by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Decreased nelfinavir plasma concentrations may lead to loss of therapeutic effect and possible development of resistance to nelfinavir or other coadministered antiretroviral agents.
- nirmatrelvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nirmatrelvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Nirmatrelvir, a CYP3A4 substrate, is contraindicated with strong CYP3A4 inducers. Significantly reduced nirmatrelvir plasma concentrations may be associated with potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Do not initiate nirmatrelvir/ritonavir immediately after discontinuing a strong 3A4 inducer owing to time needed for systemic clearance of the inducer.
- nirmatrelvir/ritonavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Nirmatrelvir, a CYP3A4 substrate, is contraindicated with strong CYP3A4 inducers. Significantly reduced nirmatrelvir plasma concentrations may be associated with potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance. Do not initiate nirmatrelvir/ritonavir immediately after discontinuing a strong 3A4 inducer owing to time needed for systemic clearance of the inducer.
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC)
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP2C8 inducers may reduce dasabuvir levels, and therefore decreased efficacy of Viekira Pak
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir & dasabuvir (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may reduce partiaprevir and ritonavir levels, and therefore decreased efficacy of Viekira Pak - panobinostat
rifampin decreases levels of panobinostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers can reduce panobinostat levels by ~70% and lead to treatment failure.
- pirfenidone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pirfenidone by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Use of strong CYP1A2 inducers should be discontinued before initiating pirfenidone and avoided during treatment
- praziquantel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of praziquantel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- regorafenib
rifampin, regorafenib. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decrease regorafenib levels and increase exposure of the active metabolite M-5.
- rilpivirine
rifampin decreases levels of rilpivirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. Rilpivirine should not be co-administered with strong CYP 3A4 inducers. Potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to rilpivirine or to the NNRTI class.
- roflumilast
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of roflumilast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration not recommended; strong cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers decrease systemic exposure to roflumilast and may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of roflumilast by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated. Coadministration not recommended; strong cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers decrease systemic exposure to roflumilast and may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness - tipranavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tipranavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Contraindicated. May result in loss of antiviral efficacy and/or development of viral resistance.
- vandetanib
rifampin decreases levels of vandetanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid coadministration with potent CYP3A4 inducers; these drugs reduce exposure to vandetanib by up to 40%.
- velpatasvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of velpatasvir by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- voriconazole
rifampin decreases levels of voriconazole by increasing metabolism. Contraindicated.
Serious (247)
- abemaciclib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of abemaciclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of abemaciclib with strong CYP3A4 inducers reduces plasma concentration of abemaciclib and its metabolites.
- abrocitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of abrocitinib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Abrocitinib is a CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 substrate. Drugs that are strong inducers of CYP2C19 or CYP2C9 decreases the combined exposure of abrocitinib and its active metabolites, resulting in loss of or reduced clinical response.
- acalabrutinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of acalabrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of acalabrutinib with strong CYP3A inducers. If a strong CYP3A inducer must be used, increase acalabrutinib dose to 200 mg twice daily.
- adagrasib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of adagrasib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- afatinib
rifampin decreases levels of afatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increase afatinib daily dose by 10 mg as tolerated if chronic therapy with P-gp inducer required; resume previous afatinib dose 2-3 days after P-gp inducer discontinued.
- almotriptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of almotriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- alpelisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alpelisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of alpelisib (CYP3A4 substrate) with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- alprazolam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alprazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- amiodarone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amiodarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- apixaban
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of apixaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Rifampin, a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducer, may decrease exposure to apixaban.
- apremilast
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of apremilast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP inducers results in a significant decrease of systemic exposure of apremilast, which may result in loss of efficacy
- aprepitant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of aprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- aripiprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of aripiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- atazanavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of atazanavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- atorvastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of atorvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin increases toxicity of atorvastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy. - avapritinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of avapritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- axitinib
rifampin decreases levels of axitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Selection of concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4 induction potential is recommended.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin decreases levels of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. A reduction in bazedoxifene exposure may be associated with an increase risk of endometrial hyperplasia. - BCG vaccine live
rifampin decreases levels of BCG vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated.
- bedaquiline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bedaquiline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of bedaquiline with strong CYP3A4 inducers due to potential for decreased therapeutic effect
- bosutinib
rifampin decreases levels of bosutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased bosutinib plasma concentration by ~85%.
- brigatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of brigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease brigatinib efficacy.
- budesonide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of budesonide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- buspirone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buspirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cabozantinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cabozantinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of cabozantinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer is required, increase cabozantinib dose by 40 mg/day (Cometriq) or by 20 mg/day (Cabometyx). Resume previous dose 2-3 days after strong CYP3A4 inducer discontinued.
- capivasertib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of capivasertib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers decrease capivasertib exposure, which may reduce efficacy.
- capmatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of capmatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- carbamazepine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of carbamazepine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ceftobiprole medocaril sodium
ceftobiprole medocaril sodium will increase the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Ceftobiprole (an OATP1B1/1B3 inhibitor) may increase plasma concentrations of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrates.
- ceritinib
rifampin decreases levels of ceritinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cilostazol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cilostazol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- cinacalcet
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cinacalcet by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- clopidogrel
rifampin will increase the level or effect of clopidogrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite. Monitor patients for potential increase in antiplatelet effects when CYP3A4 inducers are used in combination with clopidogrel
- clozapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- colchicine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of colchicine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conivaptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of conivaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conjugated estrogens
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens, vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- copanlisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of copanlisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of copanlisib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- cortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dabigatran
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dabigatran by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration. P-gp inducers reduce systemic exposure of dabigatran
- dabrafenib
rifampin decreases levels of dabrafenib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP2C8 inducers may decrease dabrafenib levels.
rifampin decreases levels of dabrafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - daridorexant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of daridorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- darifenacin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of darifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- darolutamide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of darolutamide by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Darolutamide is a P-gp and CYP3A4 substrate. Avoid coadminstration of darolutamide with combined P-gp and strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- darunavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of darunavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- dasatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dasatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- deflazacort
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of deflazacort by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of deflazacort with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- deuruxolitinib
rifampin decreases levels of deuruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of deuruxolitinib with drugs that are both strong CYP3A4 inducers and moderate or strong CYP2C9 inducers.
rifampin decreases levels of deuruxolitinib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of deuruxolitinib with strong or moderate CYP2C9 inducers. - dexamethasone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dexamethasone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- diazepam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dihydroergotamine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dihydroergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- dihydroergotamine intranasal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dihydroergotamine intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- diltiazem
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diltiazem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with diltiazem and strong CYP3A4 inducers However, if concomitant use is necessary, consider dosage adjustment and close monitoring of pharmacologic effects (eg, blood pressure) whenever a strong CYP3A4 inducer is added to or discontinued from therapy.
- dronedarone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dronedarone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- duloxetine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of duloxetine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- duvelisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of duvelisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases duvelisib area under the curve (AUC), which may reduce duvelisib efficacy.
- edoxaban
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of edoxaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of edoxaban with potent P-gp inducers
- elacestrant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of elacestrant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eletriptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eletriptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- eliglustat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eliglustat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers significantly decreases eliglustat exposure; coadministration not recommended
- eluxadoline
rifampin increases levels of eluxadoline by decreasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Decrease eluxadoline dose to 75 mg PO BID if coadministered with OATP1B1 inhibitors. .
- elvitegravir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of elvitegravir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid; coadministration with CYP3A inducers may result in decreased plasma concentrations of elvitegravir and/or a concomitantly administered protease inhibitor and lead to loss of therapeutic effect and to possible resistance
- enasidenib
enasidenib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of enasidenib with sensitive OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or BCRP substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If unavoidable, decrease the substrate(s) dosage in accordance with their Prescribing Information.
- encorafenib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of encorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- entrectinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of entrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- enzalutamide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of enzalutamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Consider using an alternant that has no or minimal CYP3A4 induction potential when possible. If unavoidable, increase enzalutamide dose from 160 mg qDay to 240 mg qDay. If a strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, return enzalutamide dose to dose used before initiating the strong CY
- erdafitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erdafitinib by altering metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of strong CYP2C9 or CYP3A4 inducers with erdafitinib.
erdafitinib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration unavoidable, separate administration by at least 6 hr before or after administration of P-gp substrates with narrow therapeutic index. - ergotamine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ergotamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erlotinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erlotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin base
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin base by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin ethylsuccinate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin ethylsuccinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin lactobionate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin lactobionate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- erythromycin stearate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erythromycin stearate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estradiol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- estropipate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estropipate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ethinylestradiol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ethinylestradiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. The efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Use of a nonhormonal contraceptive is recommended.
- etonogestrel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etonogestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- etrasimod
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etrasimod by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Rifampin is a combined CYP3A4 (strong), CYP2C8 (moderate) and CYP2C9 (moderate) inducer. Rifampin decreases systemic exposure of etrasimod, which is a substrate of CYP3A4, CYP2C8, and CYP2C9.
- etravirine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- everolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of everolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of everolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Contraindicated. - fedratinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fedratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Effect of coadministering a strong CYP3A4 inducer with fedratinib has not been studied.
- felbamate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of felbamate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- felodipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of felodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fesoterodine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fesoterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fexinidazole
rifampin will increase the level or effect of fexinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP450 inducers may significantly increase plasma concentrations of fexinidazole?s active metabolites: fexinidazole sulfoxide (M1) and fexinidazole sulfone (M2). M2 plasma concentrations associated with increased QT prolongation risks.
fexinidazole will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration may decrease plasma concentrations of CYP2B6 substrates owing to fexinidazole inducing CYP2B6. - finerenone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of finerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fludrocortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fludrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fosamprenavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fosamprenavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- fosaprepitant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fosaprepitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fostamatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fostamatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- fruquintinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fruquintinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- futibatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of futibatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of futibatinib with drugs that are dual P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers may decrease futibatinib efficacy.
- ganaxolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ganaxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ganaxolone with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers. If coadministration unavoidable, consider increasing ganaxolone dose; however, do not exceed maximum daily dose for weight.
- gepirone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of gepirone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- gilteritinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of gilteritinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Gilteritinib is a P-gp and CYP3A4 substrates. Coadministration of gilteritinib with a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer decreases gilteritinib exposure and efficacy.
- glasdegib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of glasdegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of glasdegib with strong CYP3A inducers.
- glecaprevir/pibrentasvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- hydrocortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of hydrocortisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC)
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ibrutinib
rifampin decreases levels of ibrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers decrease ibrutinib plasma concentrations by ~10-fold.
- idelalisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of idelalisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration; strong CYP3A4 inducers significantly decrease idelalisib systemic exposure
- iloperidone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of iloperidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- infigratinib (DSC)
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of infigratinib (DSC) by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- irinotecan liposomal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- isoniazid
rifampin increases toxicity of isoniazid by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Rifampin enhances the metabolism of isoniazid to hepatotoxic metabolites.
- istradefylline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of istradefylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of istradefylline with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- ivabradine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ivabradine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ivabradine with moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- ivacaftor
rifampin decreases levels of ivacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers; systemic exposure of ivacaftor substantially reduced (ie, ~9-fold).
- ivosidenib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ivosidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ivosidenib with strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased ivosidenib plasma concentrations.
- ixabepilone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ixabepilone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ixazomib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ixazomib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of ixazomib with strong CYP3A inducers. Strong inducers have been shown to decrease ixazomib Cmax by 54% and AUC by 74%.
- lansoprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lapatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lapatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- larotrectinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of larotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration of larotrectinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers is unavoidable, double larotrectinib dose. Resume prior larotrectinib dose once CYP3A4 inducer discontinued for 3-5 half-lives
- lasmiditan
lasmiditan increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lefamulin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lefamulin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of lefamulin with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers unless the benefit outweighs risks. Monitor for reduced efficacy.
- lemborexant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lemborexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- leniolisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of leniolisib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- letermovir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of letermovir by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of letermovir with UCT1A1/3 inducers is not recommended.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of letermovir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of letermovir with P-gp inducers is not recommended. - lomitapide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lomitapide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lopinavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lopinavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- loratadine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of loratadine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lovastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lovastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lumateperone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lumateperone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- lurbinectedin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lurbinectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- macimorelin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of macimorelin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Potential for false positive test results if macimorelin and strong CYP3A4 inducers are coadministered. Discontinue strong CYP3A4 inducer, allowing for sufficient washout time, before testing.
- macitentan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of macitentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministering macitentan with strong CYP3A4 inducers
- maraviroc
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of maraviroc by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mavorixafor
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mavorixafor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- mestranol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mestranol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin decreases levels of mestranol by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. May result in contraceptive failure. - methadone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of methadone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- methylprednisolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of methylprednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- midazolam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of midazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- midostaurin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of midostaurin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease midostaurin concentrations resulting in reduced efficacy.
- naldemedine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of naldemedine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- neratinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of neratinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of neratinib with strong/moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- netupitant/palonosetron
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of netupitant/palonosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Netupitant is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4; avoid use in patients who are chronically using a strong CYP3A4 inducer
- nevirapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nevirapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- nicardipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nicardipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nilotinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nilotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nintedanib
rifampin decreases levels of nintedanib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration, particularly for P-gp inducers that are also CYP3A4 inducers; nintedanib is a substrate of P-gp and to a less extent CYP3A4.
- nirogacestat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nirogacestat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- nisoldipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nisoldipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- norethindrone
rifampin decreases levels of norethindrone by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of norethindrone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use of nonhormonal contraceptives advised - norethindrone acetate
rifampin decreases levels of norethindrone acetate by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
- norethindrone transdermal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of norethindrone transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration unless benefit outweighs risk. When coadministered, hormonal contraceptives are not a reliable method of effective birth control. Concomitant use may increase incidence of menstruation associated adverse effects (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia).
- norgestrel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of norgestrel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Contraceptive failure is possible owing to decreased serum concentration of norgestrel. Advise patients to use an alternative method of contraception or a back-up method during coadministration, and to continue back-up contraception for 28 days after discontinuing the strong CYP3A4 inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability
- olanzapine/samidorphan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of olanzapine/samidorphan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decrease levels of olanzapine and samidorphan by~50% and ~75% respectively.
- olaparib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of olaparib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of olaparib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- olutasidenib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of olutasidenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong or moderate CYP3A inducers decrease olutasidenib (a CYP3A4 substrate) plasma concentrations and efficacy.
- omaveloxolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of omaveloxolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- omeprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of omeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- osimertinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of osimertinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid concomitant use of osimertinib with strong CYP3A inducers.
- ozanimod
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ozanimod by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ozanimod (a CYP2C8 substrate) with strong CYP2C8 inducers decreases the exposure of the active metabolites (CC112273 and CC1084037) of ozanimod, which may decrease the effiicacy of ozanimod. Therefore, coadministration of ozanimod with strong CYP2C8 inducers is not recommended.
- palbociclib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of palbociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Strong CYP3A inducers decrease palbociclib plasma exposure by ~85%.
- palovarotene
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of palovarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pazopanib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pazopanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pemigatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pemigatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- perampanel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of perampanel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Increased perampanel dose may be needed when coadministered
- pexidartinib
rifampin will increase the level or effect of pexidartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If coadministration with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce pexidartinib dose (refer to drug monograph dosage modifications). After discontinuing the CYP3A4 inhibitor for 3 elimination half-lives, may resume previous pexidartinib dose.
rifampin and pexidartinib both increase inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Pexidartinib can cause hepatotoxicity. Avoid coadministration of pexidartinib with other products know to cause hepatoxicity. - pirtobrutinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pirtobrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pitavastatin
rifampin increases toxicity of pitavastatin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- pomalidomide
rifampin decreases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin decreases levels of pomalidomide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin decreases levels of pomalidomide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - ponatinib
rifampin decreases levels of ponatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid unless the coadministration outweighs the possible risk of ponatinib underexposure; monitor for signs of reduced efficacy.
- ponesimod
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ponesimod by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Not recommended. Based on limited data, coadministration of strong CYP3A4 and UGT1A1 inducers (eg, rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine) may decrease systemic exposure of ponesimod. The clinical relevance is unclear.
- pralsetinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pralsetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid, double current pralsetinib dose starting on Day 7 of coadministration with strong CYP3A inducer. After inducer has been discontinued for at least 14 days, resume previous pralsetinib dose.
- prednisolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of prednisolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- prednisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of prednisone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pretomanid
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pretomanid by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. CYP3A4 substrate. Avoid coadministration of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
rifampin, pretomanid. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: Pretomanid regimen associated with hepatotoxicity. Avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic agents, including herbal supplements and drugs other than bedaquiline and linezolid. - primaquine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of primaquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- progesterone intravaginal gel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of progesterone intravaginal gel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use of nonhormonal contraceptives advised
- progesterone micronized
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of progesterone micronized by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use of nonhormonal contraceptives advised
- progesterone, natural
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of progesterone, natural by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Use of nonhormonal contraceptives advised
- propofol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of propofol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- pyrazinamide
rifampin, pyrazinamide. Either increases toxicity of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Additive hepatotoxicity.
- quazepam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of quazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quetiapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of quetiapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quinidine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of quinidine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- quizartinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of quizartinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ranolazine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ranolazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repaglinide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of repaglinide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- repotrectinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of repotrectinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- resmetirom
rifampin will increase the level or effect of resmetirom by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of resmetirom (an OATP1B1/3 substrate) with OATP1B1/3 inhibitors.
- revefenacin
rifampin increases levels of revefenacin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Comment: OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 transport inhibitors may increase systemic exposure of revefenacin's active metabolite. Coadministration not recommended.
- ribociclib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ribociclib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of ribociclib with strong CYP3A inducers should be avoided.
- rifabutin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rifabutin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rimegepant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rimegepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ripretinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ripretinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with a strong CYP3A inhibitor will decrease systemic exposure to ripretinib and its active metabolite (DP-5439), which may decrease risk of adverse reactions.
- ritlecitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ritlecitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong CYP3A inducers may decrease ritlecitinib AUC and peak plasma concentration, which may result in loss of or reduced efficacy.
- ritonavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ritonavir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- rolapitant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rolapitant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Long-term coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers with rolapitant may significantly decrease rolapitant efficacy.
- romidepsin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of romidepsin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration with strong 3A4 inducers should be avoided if possible.
- selpercatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of selpercatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- selumetinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of selumetinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- silodosin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of silodosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- simvastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of simvastatin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- siponimod
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of siponimod by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of siponimod with a drug that causes moderate CYP2C9 plus a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducer is not recommended. Coadministration with moderate or strong CYP3A4 inducers alone is not recommended for patients with CYP2C9*1/*3 and*2/*3 genotype.
- sirolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sofosbuvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. P-gp inducers decrease sofosbuvir levels, and therefore decrease conversion to sofosbuvir's active metabolite (GS-331007) responsible for 90% of pharmacologic effect
- sofosbuvir/velpatasvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Sofosbuvir and velpatasvir are substrates of the drug transporter P-gp. Potent P-gp inducers may significantly decrease sofosbuvir and velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Velpatasvir is a substrate of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4. Drugs that are moderate-to-potent inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 may significantly decrease velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Velpatasvir is a substrate of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4. Drugs that are moderate-to-potent inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 may significantly decrease velpatasvir plasma concentrations, leading to potentially reduced therapeutic effect. - solifenacin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of solifenacin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- sonidegib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sonidegib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of sonidegib with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
- sorafenib
rifampin decreases levels of sorafenib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sorafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. - sotagliflozin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sotagliflozin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Glucuronidation by UGT1A9, to form the 3-O-glucuronide, was identified as a major metabolic pathway for sotagliflozin. Coadministration of UGT1A9 inducers may decrease exposure to sotagliflozin, which may decrease efficacy.
- sotorasib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sotorasib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
sotorasib will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If use is unavoidable, refer to the prescribing information of the P-gp substrate for dosage modifications. - sparsentan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sparsentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- stiripentol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of stiripentol with strong CYP3A4 inducers, increase stiripentol dose.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of stiripentol with strong CYP1A2 inducers, increase stiripentol dose.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of stiripentol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If unable to avoid coadministration of stiripentol with strong CYP1A2 inducers, increase stiripentol dose. - sulbactam/durlobactam
rifampin will increase the level or effect of sulbactam/durlobactam by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Sulbactam is predicted to have active secretion by OATP1 as a significant portion of total clearance; therefore, inhibition of OAT1 may increase sulbactam plasma concentrations
- sunitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sunitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tacrolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tamsulosin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tamsulosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tazemetostat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tazemetostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- temsirolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of temsirolimus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tepotinib
tepotinib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. If concomitant use unavoidable, reduce the P-gp substrate dosage if recommended in its approved product labeling.
- tezacaftor
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tezacaftor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- theophylline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tivozanib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tivozanib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tizanidine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tizanidine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- tolterodine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tolterodine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tolvaptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tolvaptan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- tovorafenib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tovorafenib by increasing metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of tovorafenib (a CYP2C8 substrate) with strong or moderate CYP2C8 inducers.
- trabectedin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of trabectedin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trazodone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of trazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- triazolam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of triazolam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- trofinetide
trofinetide will increase the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Trofinetide (an OATP131 and OATP13B inhibitor) may increase plasma levels of OATP131 or OATP13B substrates. Avoid coadministration with sensitive substrates.
- tucatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tucatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tucatinib by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Coadministration of tucatinib (a CYP2C8 substrate) with a strong or moderate CYP2C8 inducer decreases tucatinib plasma concentrations. - typhoid vaccine live
rifampin decreases levels of typhoid vaccine live by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Contraindicated.
- ubrogepant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ubrogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- ulipristal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ulipristal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- upadacitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of upadacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid upadacitinib coadministration with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- valbenazine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of valbenazine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Concomitant use not recommended.
- vardenafil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vardenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- velpatasvir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of velpatasvir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vemurafenib
rifampin decreases levels of vemurafenib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- venetoclax
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of venetoclax by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of venetoclax with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers. Consider alternative treatment with agents that have less CYP3A induction.
- verapamil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of verapamil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vonoprazan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vonoprazan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- vorapaxar
rifampin decreases levels of vorapaxar by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
- voriconazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of voriconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated.
- voxilaprevir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of voxilaprevir by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Contraindicated. Avoid use of voxilaprevir and rifampin. Rifampin is listed as contraindicated when coadministered with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir in the prescribing information.
- zanubrutinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of zanubrutinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. Avoid coadministration of zanubutinib with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
- zavegepant intranasal
rifampin will increase the level or effect of zavegepant intranasal by Other (see comment). Avoid or Use Alternate Drug. OATP1B3 inhibitors may result in a significant increase in systemic exposure of zavegepant (an OATP1B3 substrate).
- zuranolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of zuranolone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Avoid or Use Alternate Drug.
Monitor Closely (297)
- abiraterone
rifampin decreases levels of abiraterone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid coadministration of abiraterone with strong CYP3A4 inducers; if a strong CYP3A4 inducer must be used, increase abiraterone dosage frequency from once daily to twice daily.
- alfentanil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alfentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alfuzosin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alfuzosin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- alosetron
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - aluminum hydroxide
aluminum hydroxide will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium carbonate
aluminum hydroxide/magnesium carbonate will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium trisilicate
aluminum hydroxide/magnesium trisilicate will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- ambrisentan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ambrisentan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ambrisentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration was associated with a transient 2-fold increase in ambrisentan AUC; however, by day 7, rifampin had no clinically important effect on ambrisentan. Use with caution. - amikacin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amikacin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amitriptyline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amitriptyline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amitriptyline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amitriptyline by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - amlodipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of amlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amobarbital
rifampin decreases levels of amobarbital by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- antipyrine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of antipyrine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- apalutamide
apalutamide will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by increasing elimination. Use Caution/Monitor. Apalutamide weakly induces OATP1B1 and may decrease systemic exposure of drugs that are OATP1B1 substrates.
- armodafinil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of armodafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of armodafinil by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - artesunate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of artesunate by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration may decrease AUC and peak plasma concentration of active artesunate metabolite (DHA) by inducing UGT. Monitor for decreased efficacy.
- asenapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of asenapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atogepant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of atogepant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Recommended atogepant dosage with concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is 30 mg or 60 mg qDay.
rifampin will increase the level or effect of atogepant by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Recommended dosage of atogepant (an OATP1B1 substrate) with concomitant use of OATP inhibitors is 10 mg or 30 mg qDay. - atorvastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of atorvastatin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- atovaquone
rifampin decreases levels of atovaquone by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- avanafil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of avanafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. For patients with ED, monitor response carefully because of potential for decreased effectiveness.
- avatrombopag
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of avatrombopag by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. When treating ITP, coadministration of avatrombopag with a moderate or strong dual CYP2C9/3A4 inducer requires an increased avatrombopag starting dose. Refer to drug monograph for specific recommendations.
- azithromycin
azithromycin will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- belumosudil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of belumosudil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase belumosudil dosage to 200 mg PO BID when coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers.
- bendamustine
rifampin decreases levels of bendamustine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concentrations of active metabolites may be increased.
- benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of benzhydrocodone/acetaminophen by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution when discontinuing CYP3A4 inducers that are coadministered with benzhydrocodone (prodrug of hydrocodone); plasma concentrations of hydrocodone may increase and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression.
- berotralstat
rifampin decreases levels of berotralstat by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
berotralstat will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor or titrate P-gp substrate dose if coadministered. - bexagliflozin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bexagliflozin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Bexagliflozin is a major substrate of UGT1A9. If coadministered with a UGT1A9 inducer, consider adding another antihyperglycemic agent in patients requiring additional glycemic control.
- bexarotene
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bexarotene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bortezomib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bortezomib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- bosentan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bosentan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - bosutinib
bosutinib increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brentuximab vedotin
rifampin decreases levels of brentuximab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- brexpiprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of brexpiprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Double brexpiprazole dose over 1-2 weeks if administered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer.
- brivaracetam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of brivaracetam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The dose of brivaracetam should be increased up to 100% (ie, double the dosage) in patients while receiving concomitant treatment with rifampin.
- bromocriptine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bromocriptine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- budesonide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of budesonide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine buccal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine buccal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- buprenorphine subdermal implant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine subdermal implant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor patients already on buprenorphine subdermal implant who require newly-initiated treatment with CYP3A4 inducer for signs and symptoms of withdrawal. If the dose of the concomitant CYP3A4 inducer cannot be reduced or discontinued, implant removal may be necessary and the patient should then be treated with a buprenorphine dosage form that permits dose adjustments. If a CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued in a patient who has been stabilized on buprenorphine, monitor the patient for overmedication.
- buprenorphine transdermal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. If coadministration is necessary, consider increasing buprenorphine transdermal dosage until stable. Monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, consider reducing the buprenorphine dosage and monitor for signs of respiratory depression.
- buprenorphine, long-acting injection
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of buprenorphine, long-acting injection by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Patients who transfer to buprenorphine long-acting injection from transmucosal buprenorphine coadministered with CYP3A4 inducers should be monitored to ensure buprenorphine plasma levels are adequate. If the buprenorphine dose is inadequate and the CYP3A4 inducer cannot be reduced or discontinued, transition the patient back to a buprenorphine formulation that permits dose adjustments.
- bupropion
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of bupropion by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butabarbital
rifampin decreases levels of butabarbital by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- butalbital
rifampin decreases levels of butalbital by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cabazitaxel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cabazitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease cabazitaxel concentrations. Avoid coadministration.
- calcifediol
rifampin, calcifediol. affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Drugs that stimulate microsomal hydroxylation reduce the half-life of calcifediol.
- calcitriol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of calcitriol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- calcium/vitamin D
calcium/vitamin D will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- canagliflozin
rifampin decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- cannabidiol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cannabidiol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider an increase in cannabidiol dosage (based on clinical response and tolerability) when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer.
cannabidiol, rifampin. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Owing to the potential for both CYP2B6 induction and inhibition with the coadministration of CYP2B6 substrates and cannabidiol, consider reducing dosage adjustment of CYP2B6 substrates as clinically appropriate. - carvedilol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of carvedilol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of carvedilol by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - caspofungin
rifampin decreases levels of caspofungin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cenobamate
cenobamate will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase dose of CYP2B6 substrate, as needed, when coadministered with cenobamate.
- cevimeline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cevimeline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chlordiazepoxide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of chlordiazepoxide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- chloroquine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of chloroquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cholic acid
rifampin increases toxicity of cholic acid by decreasing elimination. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Avoid concomitant use of inhibitors of the bile salt efflux pump (BSEP). May exacerbate accumulation of conjugated bile salts in the liver and result in clinical symptoms. If concomitant use is necessary, monitor serum transaminases and bilirubin.
- citalopram
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of citalopram by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of citalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - clarithromycin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clarithromycin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clomipramine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clomipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - clonazepam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clonazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clorazepate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clorazepate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- clotrimazole
clotrimazole will increase the level or effect of rifampin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use with cotrimoxazole increase concentration of rifampin which may increase risk of toxicity; monitor for adverse reactions during coadministration
- clozapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of clozapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- conjugated estrogens, vaginal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of conjugated estrogens, vaginal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- cortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- crizotinib
rifampin decreases levels of crizotinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers should be avoided. .
crizotinib increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - cyclophosphamide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cyclophosphamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cyclophosphamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - cyclosporine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cyclosporine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cyclosporine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. - danicopan
danicopan will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Danicopan increases plasma concentrations of P-gp substrates; consider dose reduction of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
- dantrolene
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dantrolene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- daprodustat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of daprodustat by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. CYP2C8 inducers may decrease daprodustat exposure, which may result in loss of efficacy. Monitor hemoglobin and adjust daprodustat dose when initiating or stopping therapy with CYP2C8 inducers during treatment
- dapsone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dapsone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- daunorubicin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of daunorubicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- deferasirox
rifampin decreases levels of deferasirox by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Avoid concomitant use of potent UGT inducers with deferasirox. If co-administration is required then consider increasing initial dose of deferasirox to 30 mg/kg and monitor ferritin levels and clinical response.
- deflazacort
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of deflazacort by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexamethasone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dexamethasone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dexlansoprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dexlansoprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dexlansoprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - diazepam buccal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam buccal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP2C19 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam buccal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased. - diazepam intranasal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP2C19 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers may increase rate of diazepam elimination; therefore, efficacy of diazepam may be decreased. - digoxin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of digoxin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Reduced digoxin serum concentrations, possibly with a suboptimal therapeutic response, may be seen.
rifampin decreases levels of digoxin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - disopyramide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of disopyramide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- docetaxel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of docetaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of docetaxel by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - dolutegravir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dolutegravir by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase the dolutegravir dosage when coadministering with strong UGT1A/CYP3A4 inducers. Use an alternate to rifampin in patients with integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI)-associated resistance substitutions or clinically suspected INSTI resistance; concomitant use may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance of dolutegravir
- donepezil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of donepezil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxepin cream
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doxepin cream by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- doxorubicin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - doxorubicin liposomal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of doxorubicin liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - dronabinol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP2C9 substrate.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dronabinol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Dronabinol is a CYP3A4 substrate. - dutasteride
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of dutasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- duvelisib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of duvelisib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- efavirenz
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of efavirenz by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of efavirenz by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - elafibranor
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of elafibranor by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- elagolix
rifampin will increase the level or effect of elagolix by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Limit concomitant use of elagolix 150 mg qDay and rifampin to 6 months.
elagolix will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of elagolix by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Limit concomitant use of elagolix 150 mg qDay and rifampin to 6 months. - eliglustat
eliglustat increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor therapeutic drug concentrations, as indicated, or consider reducing the dosage of the P-gp substrate and titrate to clinical effect.
- eltrombopag
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eltrombopag by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eltrombopag by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
eltrombopag increases levels of rifampin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. OATP transporter protein inhibition. - encorafenib
encorafenib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Encorafenib (a OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 inhibitor) may increase the concentration and toxicities of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrates. Closely monitor for signs and symptoms of increased exposure and consider adjusting the dose of these substrates.
- enfortumab vedotin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of enfortumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eplerenone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eplerenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- erlotinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of erlotinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- escitalopram
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of escitalopram by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of escitalopram by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - esomeprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of esomeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of esomeprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - estradiol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estradiol by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estradiol vaginal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estradiol vaginal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens conjugated synthetic
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estrogens conjugated synthetic by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estrogens esterified
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estrogens esterified by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- estropipate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of estropipate by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eszopiclone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eszopiclone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. According to prescribing information, zopiclone AUC was decreased 80% by concomitant use of rifampin. A similar effect would be expected with eszopiclone (S-enantiomer of zopiclone).
- ethosuximide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ethosuximide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ethotoin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ethotoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- etoposide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etoposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etoposide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - etravirine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of etravirine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - eucalyptus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of eucalyptus by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- exemestane
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of exemestane by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. For patients receiving exemestane with a potent CYP3A4 inducer the recommended dose of exemestane is 50 mg daily after a meal.
- fenfluramine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fenfluramine by Other (see comment). Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration with drugs that increase serotonin may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- fentanyl
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl intranasal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl intranasal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl transdermal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl transdermal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- fentanyl transmucosal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fentanyl transmucosal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of fentanyl with CYP3A4 inducers could lead to a decrease in fentanyl plasma concentrations, lack of efficacy or, possibly, development of a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who has developed physical dependence to fentanyl. After stopping a CYP3A4 inducer, as the effects of the inducer decline, the fentanyl plasma concentration will increase which could increase or prolong both the therapeutic and adverse effects.
- finasteride
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of finasteride by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flibanserin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of flibanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inducers substantially decrease flibanserin systemic exposure.
- fluconazole
rifampin decreases levels of fluconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fludrocortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fludrocortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- flurazepam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of flurazepam by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fluvastatin
rifampin increases toxicity of fluvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- fosphenytoin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fosphenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- fostamatinib
fostamatinib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use of fostamatinib may increase concentrations of P-gp substrates. Monitor for toxicities of the P-gp substrate drug that may require dosage reduction when given concurrently with fostamatinib.
- gefitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of gefitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Increase gefitinib to 500 mg daily if coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer. Resume gefitinib dose at 250 mg/day 7 days after discontinuing the strong inducer.
- gentamicin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of gentamicin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glimepiride
rifampin decreases levels of glimepiride by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glipizide
rifampin decreases levels of glipizide by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glyburide
rifampin decreases levels of glyburide by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of glyburide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP2C9 inducers may increase glyburide metabolism. - guanfacine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of guanfacine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers significantly reduce guanfacine plasma concentrations and elimination half-life. If coadministered, more frequent dosing of the IR product may be required to achieve or maintain the desired hypotensive response. For patients with ADHD, FDA-approved labeling for ER guanfacine recommends that, if coadministered, doubling the recommended dose of guanfacine should be considered.
- haloperidol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of haloperidol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- hydrocodone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of hydrocodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Caution when discontinuing CYP3A4 inducers that are coadministered with hydrocodone; plasma concentrations of hydrocodone may increase and can result in potentially fatal respiratory depression
- hydrocortisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of hydrocortisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ifosfamide
rifampin increases effects of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration of ifosfamide with CYP2B6 inducers may increase metabolism of ifosfamide to its metabolite. Monitor for increased effects/toxicities if combined with CYP2B6 inducers.
rifampin increases toxicity of ifosfamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the metabolism of ifosfamide to its active alkylating metabolites. CYP3A4 inducers may increase the formation of the neurotoxic/nephrotoxic ifosfamide metabolite, chloroacetaldehyde. Closely monitor patients taking ifosfamide with CYP3A4 inducers for toxicities and consider dose adjustment. - imatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of imatinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of imatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - imipramine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of imipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - iptacopan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of iptacopan by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP2C8 inducers may reduce efficacy of iptacopan (a CYP2C8 substrate).
- irinotecan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- irinotecan liposomal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of irinotecan liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- isradipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of isradipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- istradefylline
istradefylline will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Istradefylline 40 mg/day increased peak levels and AUC of P-gp substrates in clinical trials. Consider dose reduction of sensitive P-gp substrates.
- itraconazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of itraconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of itraconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - ivacaftor
ivacaftor increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Ivacaftor and its M1 metabolite has the potential to inhibit P-gp; may significantly increase systemic exposure to sensitive P-gp substrates with a narrow therapeutic index.
- ivermectin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ivermectin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ketamine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ketamine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ketamine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ketoconazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lamotrigine
rifampin decreases levels of lamotrigine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of lamotrigine by increasing hepatic clearance. Use Caution/Monitor. - lapatinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lapatinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lemborexant
lemborexant will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Monitor CYP2B6 substrate for adequate clinical response. Consider increasing the CYP2B6 substrate dose according to specific prescribing recommendations.
- lesinurad (DSC)
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lesinurad (DSC) by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- levamlodipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of levamlodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- levoketoconazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of levoketoconazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel intrauterine
rifampin decreases levels of levonorgestrel intrauterine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel oral
rifampin decreases levels of levonorgestrel oral by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of levonorgestrel oral/ethinylestradiol/ferrous bisglycinate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. The efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Use an alternative method of contraception or a backup method when enzyme inducers are used with combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs), and continue backup contraception for 28 days after discontinuing enzyme inducer to ensure contraceptive reliability.
- lidocaine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lidocaine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- linagliptin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of linagliptin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a CYP3A4 inducer.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of linagliptin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a P-gp inducer. - lofepramine
rifampin decreases levels of lofepramine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lomitapide
lomitapide increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing dose when used concomitantly with lomitapide.
- loperamide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of loperamide by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- losartan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of losartan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of losartan by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - lovastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lovastatin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lumacaftor/ivacaftor
lumacaftor/ivacaftor, rifampin. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. In vitro studies suggest that lumacaftor may induce and ivacaftor may inhibit CYP2B6 substrates. .
- maraviroc
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of maraviroc by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- marijuana
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of marijuana by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mavorixafor
mavorixafor will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Caution if mavorixafor (a P-gp inhibitor) is coadministered with a sensitive P-gp substrate where minimal substrate concentration changes may lead to serious adverse effects.
- medroxyprogesterone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of medroxyprogesterone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Contraceptirve failure possible
- mefloquine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mefloquine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- melatonin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of melatonin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mestranol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mestranol by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methadone
rifampin decreases levels of methadone by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- methylprednisolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of methylprednisolone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- metoprolol
rifampin decreases levels of metoprolol by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mexiletine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mexiletine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- miconazole vaginal
rifampin decreases levels of miconazole vaginal by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- mifepristone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mifepristone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inducers have not been studied, coadministration not recommended by manufacturer
- mipomersen
mipomersen, rifampin. Either increases toxicity of the other by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Both drugs have potential to increase hepatic enzymes; monitor LFTs.
- mirtazapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of mirtazapine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- momelotinib
rifampin increases toxicity of momelotinib by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1/B3 inhibitor increases momelotinib (OATP1B1/B3 subtrate) plasma concentrations, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions with momelotinib.
- montelukast
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of montelukast by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nafcillin
nafcillin decreases effects of rifampin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Use Caution/Monitor. Nafcillin may show antagonistic effects against S. aureus.
- nefazodone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nefazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- neomycin PO
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of neomycin PO by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nifedipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nifedipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- nilotinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nilotinib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nimodipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nimodipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nitrendipine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of nitrendipine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- olanzapine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of olanzapine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oliceridine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of oliceridine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. If coadministration with a CYP3A4 inducer is necessary, consider increasing oliceridine dose until stable drug effects are achieved; monitor for signs of opioid withdrawal. If inducer is discontinued, consider oliceridine dosage reduction and monitor for signs of respiratory depression.
- omeprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of omeprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ondansetron
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ondansetron by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- osilodrostat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of osilodrostat by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Osilodrostat is a CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 subtrate. Monitor cortisol concentration and patient?s signs and symptoms during coadministration and discontinuation with strong CYP3A4 and/or CYP2B6 inducers. Adjust dose of osilodrostat if necessary.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of osilodrostat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - ospemifene
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of ospemifene by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - oxybutynin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of oxybutynin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- oxycodone
rifampin decreases levels of oxycodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- paclitaxel
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Paclitaxel levels/efficacy may decrease when coadministered with CYP2C8 inducers - paclitaxel protein bound
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paclitaxel protein bound by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Paclitaxel levels/efficacy may decrease when coadministered with CYP2C8 inducers - paliperidone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paliperidone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Paliperidone dose may need to be increased when coadministered with strong inducers of both CYP3A4 and P-gp
- pantoprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pantoprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- parecoxib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of parecoxib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of parecoxib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - paromomycin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of paromomycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pentobarbital
rifampin decreases levels of pentobarbital by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
rifampin decreases levels of phenobarbital by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenytoin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of phenytoin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pimavanserin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pimavanserin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration if possible. Monitor for reduced pimavanserin efficacy. An increase in pimavanserin dosage may be needed.
- pimozide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pimozide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pioglitazone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pioglitazone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pitavastatin
rifampin increases levels of pitavastatin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Do not exceed 2 mg/d pitavastatin.
- pitolisant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of pitolisant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Pitolisant exposure is decreased by 50% if coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inducers. For patients stable on pitolisant 8.9 mg/day or 17.8 mg/day, double the pitolisant dose (ie, 17.8 mg or 35.6 mg, respectively) over 7 days. If the strong CYP3A4 inducer is discontinued, reduce pitolisant dosage by half.
- polatuzumab vedotin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of polatuzumab vedotin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Polatuzumab undergoes catabolism to small peptides, amino acids, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), and unconjugated MMAE-related catabolites. MMAE is a CYP3A4 substrate. Coadministration of polatuzumab vedotin with a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease unconjugated MMAE AUC.
- ponatinib
ponatinib increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- posaconazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of posaconazole by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of posaconazole by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - pravastatin
rifampin increases toxicity of pravastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- prednisolone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of prednisolone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- prednisone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of prednisone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pretomanid
pretomanid will increase the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Increase monitoring for drug-related adverse effects if pretomanid is coadministered with sensitive OATP1B3 substrates.
- primidone
rifampin decreases levels of primidone by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- probenecid
probenecid will increase the level or effect of rifampin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant use with probenecid increase concentration of rifampin which may increase risk of toxicity; monitor for adverse reactions during coadministration
- propafenone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of propafenone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of propafenone by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - propranolol
rifampin decreases levels of propranolol by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of quinine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rabeprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rabeprazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- raltegravir
rifampin decreases levels of raltegravir by increasing hepatic clearance. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ramelteon
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - rasagiline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rasagiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Rifampin is a relatively weak inducer of CYP1A2, caution is advised.
- riociguat
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of riociguat by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Data not available for dose adjustment
- risperidone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of risperidone by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ritonavir
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ritonavir by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rivaroxaban
rifampin decreases levels of rivaroxaban by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid concomitant use of rivaroxaban with drugs that are combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducers. Consider increasing the rivaroxaban dose if these drugs must be coadministered.
- romidepsin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of romidepsin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ropinirole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ropinirole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- rosuvastatin
rifampin increases toxicity of rosuvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy.
- ruxolitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ruxolitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ruxolitinib topical
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ruxolitinib topical by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sacubitril/valsartan
rifampin will increase the level or effect of sacubitril/valsartan by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1; coadministration with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase valsartan systemic exposure
- sarecycline
sarecycline will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor for toxicities of P-gp substrates that may require dosage reduction when coadministered with P-gp inhibitors.
- saxagliptin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of saxagliptin by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- seladelpar
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of seladelpar by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. onitor biochemical response (eg, ALP and bilirubin) when initiating rifampin during seladelpar treatment.
- selegiline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of selegiline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- selexipag
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of selexipag by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of selexipag with rifampin, an inducer of CYP2C8, UGT1A3, and 2B7 enzymes, decreased exposure to selexipag's active metabolite by 50%. Increase selexipag dose up to twice of the typical dose if coadministered with rifampin.
- sildenafil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sildenafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Potent CYP3A4 inducers are expected to cause substantial decreases in sildenafil plasma levels
- silodosin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of silodosin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- simvastatin
rifampin will increase the level or effect of simvastatin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase risk of myopathy
- sirolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sirolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sodium bicarbonate
sodium bicarbonate will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Concomitant antacid administration may reduce absorption of rifampin; daily doses of rifampin should be given at least 1 hr before ingestion of antacids
- sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid
rifampin decreases effects of sodium picosulfate/magnesium oxide/anhydrous citric acid by altering metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with antibiotics decreases efficacy by altering colonic bacterial flora needed to convert sodium picosulfate to active drug.
- sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride
sodium sulfate/?magnesium sulfate/potassium chloride increases toxicity of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration with medications that cause fluid and electrolyte abnormalities may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment.
- sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate
sodium sulfate/potassium sulfate/magnesium sulfate increases toxicity of rifampin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Coadministration with medications that cause fluid and electrolyte abnormalities may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment.
- sparsentan
sparsentan will decrease the level or effect of rifampin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Sparsentan (a CYP2B6 inducer) decreases exposure of CYP2B6 substrates and reduces efficacy related to these substrates.
- stiripentol
stiripentol, rifampin. affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2B6 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Stiripentol is a CYP2B6 inhibitor and inducer. Monitor CYP2B6 substrates coadministered with stiripentol for increased or decreased effects. CYP2B6 substrates may require dosage adjustment.
stiripentol will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider reducing the dose of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrates, if adverse reactions are experienced when administered concomitantly with stiripentol. - streptomycin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of streptomycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sufentanil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sufentanil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- sufentanil SL
rifampin decreases effects of sufentanil SL by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Coadministration of CYP3A4 inducers may decrease sufentanil levels and efficacy, possibly precipitating withdrawal syndrome in patients who have developed physical dependence to sufentanil. Discontinuation of concomitantly used CYP3A4 inducers may increase sufentanil plasma concentration.
- sulopenem etzadroxil/probenecid
sulopenem etzadroxil/probenecid increases levels of rifampin by decreasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Probenecid is an OAT1/3 inhibitor and may increase plasma concentrations of drugs that are dependent on OAT1/3 for elimination. Monitor more frequently for adverse reactions associated with rifampin.
- suvorexant
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of suvorexant by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease suvorexant efficacy; if increased suvorexant dose required, do not exceed 20 mg/day
- tacrolimus
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tacrolimus by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tadalafil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tadalafil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid combination in pulmonary HTN patients. For patients with ED, monitor response to tadalafil carefully because of potential for decreased effectiveness.
- tamoxifen
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tamoxifen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tamoxifen by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tasimelteon
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tasimelteon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid coadministration of tasimelteon with strong CYP3A4 inducers
- teniposide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of teniposide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- terbinafine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of terbinafine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. - tetracycline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tetracycline by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- theophylline
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of theophylline by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tiagabine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tiagabine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- ticagrelor
rifampin decreases levels of ticagrelor by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Avoid use of ticagrelor with potent CYP3A inducers.
- tinidazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tinidazole by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tobramycin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tobramycin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tofacitinib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tofacitinib by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Loss of, or decreased response to tofacitinib may occur when coadministered with potent CYP3A4 inducers
- tolvaptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tolvaptan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
- toremifene
rifampin decreases levels of toremifene by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. CYP3A4 inducers increase rate of toremifene metabolism, lowering the steady-state concentration in serum.
- tramadol
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of tramadol by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Decreased AUC of tramadol and the active metabolite (O-desmethyltramadol) when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers
- trimethoprim
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of trimethoprim by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trimipramine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of trimipramine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tucatinib
tucatinib will increase the level or effect of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates, where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities.
- vadadustat
rifampin will increase the level or effect of vadadustat by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. OAT1/OAT3 inhibitors may increase vadadustat AUC. Closely monitor for too large or too rapid an increase in hemoglobin response and for adverse reactions.
- valoctocogene roxaparvovec
rifampin and valoctocogene roxaparvovec both increase Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Medications that may cause hepatotoxicity when combined with valoctogene roxaparvovec may potentiate the risk of elevated liver enzymes. Closely monitor these medications and consider alternative medications in case of potential drug interactions.
- valsartan
rifampin will increase the level or effect of valsartan by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. The results from an in vitro study with human liver tissue indicate that valsartan is a substrate of the hepatic uptake transporter OATP1B1; coadministration with OATP1B1 inhibitors may increase valsartan systemic exposure
- vemurafenib
vemurafenib increases levels of rifampin by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin decreases levels of vemurafenib by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vilazodone
rifampin decreases levels of vilazodone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Consider increasing vilazodone dose up to 2-fold (not to exceed 80 mg/day) when coadministered with strong CYP3A4 inducers for >14 days.
- vinblastine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vinblastine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vinblastine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vincristine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vincristine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vincristine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vincristine liposomal
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vincristine liposomal by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vincristine liposomal by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. - vinorelbine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vinorelbine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- vortioxetine
rifampin decreases levels of vortioxetine by increasing metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider increasing the vortioxetine dose when coadministered with strong CYP inducers for >14 days; not to exceed 3 times original vortioxetine dose.
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of vortioxetine by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider increasing vortioxetine dose when coadministered with a strong CYP inducer for >14 days. Do not exceed 3x the original dose. Reduce vortioxetine dose to original level within 14 days, when inducer is discontinued. - warfarin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of warfarin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- zaleplon
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of zaleplon by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zidovudine
rifampin decreases levels of zidovudine by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ziprasidone
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ziprasidone by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zolpidem
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of zolpidem by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
- zonisamide
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of zonisamide by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (62)
- acetaminophen
rifampin decreases levels of acetaminophen by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- acetaminophen IV
rifampin decreases levels of acetaminophen IV by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- acetaminophen rectal
rifampin decreases levels of acetaminophen rectal by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Enhanced metabolism incr levels of hepatotoxic metabolites.
- aliskiren
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of aliskiren by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alosetron
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alosetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- alvimopan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of alvimopan by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ampicillin
rifampin decreases levels of ampicillin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bentonite
bentonite decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- bisoprolol
rifampin decreases levels of bisoprolol by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- caffeine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of caffeine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- celecoxib
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of celecoxib by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chloramphenicol
rifampin decreases levels of chloramphenicol by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- chlordiazepoxide
rifampin decreases levels of chlordiazepoxide by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- cimetidine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of cimetidine by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- clofazimine
clofazimine decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diazepam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diazepam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- diclofenac
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of diclofenac by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- enalapril
rifampin decreases levels of enalapril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ethanol
ethanol decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Interaction more likely with chronic EtOH use.
- fexofenadine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fexofenadine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluconazole
fluconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- flurbiprofen
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of flurbiprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- fluvastatin
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of fluvastatin by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
rifampin decreases levels of fluvastatin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. - fosinopril
rifampin decreases levels of fosinopril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- frovatriptan
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of frovatriptan by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ibuprofen by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ibuprofen IV
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ibuprofen IV by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- imidapril
rifampin decreases levels of imidapril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isosorbide dinitrate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of isosorbide dinitrate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- isosorbide mononitrate
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of isosorbide mononitrate by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ketoconazole
ketoconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- lansoprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of lansoprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- leflunomide
rifampin increases effects of leflunomide by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Leflunomide's effects due to its active metabolite.
- levoketoconazole
levoketoconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- levothyroxine
rifampin decreases levels of levothyroxine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- liothyronine
rifampin decreases levels of liothyronine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- lisinopril
rifampin decreases levels of lisinopril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- loratadine
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of loratadine by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- meloxicam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of meloxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
rifampin decreases levels of meloxicam by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. - miconazole vaginal
miconazole vaginal decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- modafinil
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of modafinil by affecting hepatic/intestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- moexipril
rifampin decreases levels of moexipril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- morphine
rifampin decreases levels of morphine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nevirapine
rifampin decreases levels of nevirapine by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- nortriptyline
rifampin decreases levels of nortriptyline by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ondansetron
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ondansetron by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- opium tincture
rifampin decreases levels of opium tincture by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- oxacillin
rifampin decreases levels of oxacillin by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- perindopril
rifampin decreases levels of perindopril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- pirmenol
rifampin decreases levels of pirmenol by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- piroxicam
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of piroxicam by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- posaconazole
posaconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
- quinapril
rifampin decreases levels of quinapril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- rabeprazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of rabeprazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C19 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ramelteon
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of ramelteon by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ramipril
rifampin decreases levels of ramipril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- riluzole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of riluzole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP1A2 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- sulfamethoxazole
rifampin will decrease the level or effect of sulfamethoxazole by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2C9/10 metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- thyroid desiccated
rifampin decreases levels of thyroid desiccated by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- tibolone
rifampin decreases levels of tibolone by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown. Theoretical interaction.
- trandolapril
rifampin decreases levels of trandolapril by increasing metabolism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- voriconazole
voriconazole decreases levels of rifampin by inhibition of GI absorption. Applies only to oral form of both agents. Minor/Significance Unknown. Only applies to oral preparations of both agents.
Adverse Effects
1-10%
Elevated liver function test (LFT) results (up to 14%)
Rash (1-5%)
Epigastric distress (1-2%)
Anorexia (1-2%)
Nausea (1-2%)
Vomiting (1-2%)
Diarrhea (1-2%)
Cramps (1-2%)
Pseudomembranous colitis (1-2%)
Pancreatitis (1-2%)
Frequency Not Defined
Muscular weakness
Edema
Flushing
Ataxia
Impaired concentration
Fever
Fatigue
Headache
Numbness
Behavioral changes
Dizziness
Postmarketing Reports
Hepatotoxicity including transient abnormalities in liver function tests (eg, elevations in serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, serum transaminases, gamma-glutamyl transferase)
Hepatitis, a shock-like syndrome with hepatic involvement and abnormal liver function tests, and cholestasis
Pulmonary toxicity (including, but not limited to, interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates, organizing pneumonia, respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Hematologic: Thrombotic microangiopathy, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome
Warnings
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to rifamycins or excipients
Coadministration with atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, ritonavir/saquinavir, sazuinavir, lurasidone, or tipranavir
Cautions
May decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptive pills (OCPs)
Do not administer parenteral preparation IM or SC
Patients on regimens of >600 mg once or twice weekly may experience adverse reactions, including flulike syndrome
History of diabetes mellitus (rifampin may make diabetes management more difficult)
Regimens of >600 mg once or twice weekly may cause leukemia, anemia, or thrombocytopenia
Discontinue therapy if patient develops any signs of hepatocellular damage, including hyperbilirubinemia
Prolonged use may result in bacterial or fungal superinfection
Use with caution in patients with liver impairment and porphyria
Not for use in meningococcal disease; may be suitable for short-term use in asymptomatic carriers
Mild to severe cholestasis reported; discontinue therapy if confirmed
Use with caution in patients with history of alcoholism and patients receiving additional medications that may cause hepatotoxicity; advise patients to abstain from alcohol, hepatotoxic medications or herbal products while taking drug
Rifampin is not recommended for intermittent therapy; caution patient against intentional or accidental interruption of daily dosage regimen; rare renal hypersensitivity reactions have been reported when therapy was resumed in such cases
Rifampin has enzyme-inducing properties that can enhance metabolism of endogenous substrates, including adrenal hormones, thyroid hormones, and vitamin D
Systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including fever, rash, urticaria, angioedema, hypotension, acute bronchospasm, conjunctivitis, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, elevated liver transaminases or flu-like syndrome (weakness, fatigue, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, chills, aches, itching, sweats, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, syncope, palpitations);. reactions may be severe and fatal; monitor for signs and/or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions; discontinue therapy and administer supportive measures if symptoms occur
Patient should be told that rifampin may produce a discoloration (yellow, orange, red, brown) of teeth, urine, sweat, sputum, and tears, and should be forewarned of this; soft contact lenses may be permanently stained
Heartburn, epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, flatulence, cramps, and diarrhea reported; although Clostridium difficile shown in vitro to be sensitive to rifampin, pseudomembranous colitis reported with use of rifampin (and other broad spectrum antibiotics); consider this diagnosis in patients who develop diarrhea in association with antibiotic use
Monitor for symptoms and clinical/laboratory signs of liver injury, especially if treatment is prolonged or given with other hepatotoxic drugs
Instruct patients to notify their physician immediately if they experience rash with fever or blisters, with or without peeling skin, itching, or swollen lymph nodes, loss of appetite, malaise, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, darkened urine, yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, myalgias, light-colored bowel movements, cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and pain or swelling of the joints
Emphasize compliance with full course of therapy, and importance of not missing any doses
Bleeding and vitamin K-dependent coagulation disorders reported; monitor coagulation tests in patients at risk of vitamin K deficiency resulting from prolonged use of antibacterial agents, poor nutritional status, chronic liver disease, or use of anticoagulants
Cases of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome reported; if symptoms or signs of severe cutaneous adverse reactions develop, discontinue therapy immediately and institute appropriate therapy
Pulmonary toxicity manifested as interstitial lung disease (including, but not limited to, pneumonitis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates, and organizing pneumonia) reported with treatment; pulmonary toxicity could be fatal; if symptoms or signs of severe pulmonary toxicity (including respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome) develop, discontinue treatment immediately and initiate appropriate treatment
Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremia syndrome, some fatal, reported; discontinue therapy if clinical symptoms and laboratory findings consistent with TMA occur; the findings of unexplained thrombocytopenia and anemia should prompt further evaluation and consideration of the diagnosis of TMA
Paradoxical drug reactions
- Postmarketing cases of paradoxical drug reaction (recurrence or appearance of new symptoms, physical and radiological signs in a patient who had previously shown improvement with appropriate antimycobacterial treatment, in the absence of disease relapse, poor treatment compliance, drug resistance, side effects of treatment, or secondary infection/diagnosis)
- Paradoxical drug reactions are often transient and should not be misinterpreted as failure to respond to treatment; if worsening of symptoms or signs occurs during antimycobacterial treatment, consider paradoxical drug reaction in the differential diagnosis, monitor, or treat accordingly
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
No adequate and well-controlled studies have been performed in pregnant women; has been shown to be teratogenic in rodents
Rifampin has been reported to cross the placental barrier and appear in cord blood
When administered during the last few weeks of pregnancy, rifampin can cause postnatal hemorrhages in the mother and infant for which treatment with vitamin K may be indicated
Use during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus
Animal studies
- Congenital malformations, primarily spina bifida, were increased in offspring of pregnant rats given rifampin during organogenesis at oral doses of 150-250 mg/kg/day (~1-2 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] based on body surface area comparisons)
- Cleft palate was increased in a dose-dependent fashion in fetuses of pregnant mice treated at oral doses of 50-200 mg/kg (~0.2-0.8 times MRHD)
- Imperfect osteogenesis and embryotoxicity were also reported in pregnant rabbits given rifampin at oral doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (~3 times MRHD)
Lactation
Because of potential for tumorigenicity shown for rifampin in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue drug, taking into account importance of drug to mother
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by binding to beta subunit, which in turn blocks RNA transcription; potent enzyme inducer
Absorption
PO well absorbed; food may delay or slightly reduce peak
Peak plasma time: PO, 2-4 hr
Distribution
Highly lipophilic; crosses blood-brain barrier well, and relative diffusion from blood into CSF is adequate, with or without inflammation (exceeds usual MICs)
Protein bound: 80%
Metabolism
Metabolized by liver; undergoes enterohepatic recirculation
Elimination
Half-life: 3-4 hr (prolonged in hepatic impairment); in end-stage renal disease, 1.8-11 hr
Excretion: Feces (60-65%) and urine (~30%) as unchanged drug
Administration
PO
Take on empty stomach
IV Compatibilities
Solution: D5W (at 1.2 g/L within 4 hours)
IV Incompatibilities
Solution: NS (may be used within 24 hours)
Additive: Minocycline
Y-Site: Diltiazem
IV Preparation
Add 10 mL of SWI to 600 mg of rifampin in vial
Before administration, solution may be added to 500 mL of D5W or 100 mL of D5W
IV Administration
Prepare and administer within 4 hours
In 500 mL of D5W: Infuse within 3 hours
In 100 mL of D5W: Infuse within 30 minutes
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| rifampin intravenous - | 600 mg vial |  | |
| rifampin intravenous - | 600 mg vial |  | |
| rifampin intravenous - | 600 mg vial |  | |
| rifampin intravenous - | 600 mg vial |  | |
| Rifadin intravenous - | 600 mg vial |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 300 mg capsule | 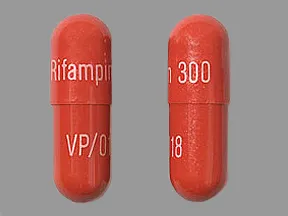 | |
| rifampin oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 150 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 300 mg capsule |  | |
| rifampin oral - | 300 mg capsule |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Patient Handout
rifampin intravenous
RIFAMPIN - INJECTION
(rif-AM-pin)
COMMON BRAND NAME(S): Rifadin
USES: This medication is used to prevent and treat tuberculosis and other bacterial infections. Rifampin belongs to a class of drugs known as rifamycin antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.This antibiotic treats only bacterial infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as common cold, flu). Using any antibiotic when it is not needed can cause it to not work for future infections.
HOW TO USE: This medication is given by injection into a vein as directed by your doctor, usually once or twice daily. It is injected slowly into a vein over 30 minutes.If you are using this medication at home, learn all preparation and usage instructions from your health care professional. Before using, check this product visually for particles or discoloration. If either is present, do not use the liquid. Learn how to store and discard medical supplies safely.The dosage and length of treatment are based on your medical condition, weight, and response to treatment.It is very important to keep using this medication (and other medications used to treat tuberculosis) exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not skip any doses.For the best effect, use this antibiotic at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, use this medication at the same time(s) every day.Continue to use this medication until the full prescribed amount is finished, even if symptoms disappear after a few days. Stopping the medication too early may result in a return of the infection.Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
SIDE EFFECTS: Upset stomach, heartburn, nausea, or headache may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.This medication may cause urine, sweat, saliva, or tears to change color (yellow, orange, red, or brown). This effect is harmless and will disappear when the medication is stopped. However, teeth and contact lens staining may be permanent.Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine), mental/mood changes (such as confusion, unusual behavior), unusual tiredness, easy bruising/bleeding, small red spots on the skin, joint pain/swelling, new or worsening shortness of breath.Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: chest pain.Rifampin may rarely cause serious (possibly fatal) liver disease. Get medical help right away if you have any symptoms of liver damage, such as: nausea/vomiting that doesn't stop, loss of appetite, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine.This medication may rarely cause a severe intestinal condition due to a bacteria called C. difficile. This condition may occur during treatment or weeks to months after treatment has stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn't stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.This medication may sometimes cause oral thrush or a new yeast infection. Contact your doctor if you notice white patches in your mouth, a change in vaginal discharge, or other new symptoms.A very serious allergic reaction to this drug is rare. However, get medical help right away if you notice any symptoms of a serious allergic reaction, including: fever that doesn't go away, new or worsening lymph node swelling, rash, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing.This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.In the US -Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
PRECAUTIONS: Before using rifampin, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or other rifamycins (such as rifabutin); or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: diabetes, liver problems (such as hepatitis), HIV infection, history of alcohol use/abuse.Alcohol may increase the risk of liver disease. Avoid alcoholic beverages while using this medication.Rifampin may cause live bacterial vaccines (such as typhoid vaccine) to not work well. Tell your health care professional that you are using rifampin before having any immunizations/vaccinations.Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).During pregnancy, this medication should be used only when clearly needed. When this drug is used during the last few weeks of pregnancy, the risk of bleeding in both mother and infant may be increased. Tell your doctor right away if you notice any bleeding in your newborn. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.Rifampin passes into breast milk but is unlikely to harm a nursing infant. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor's approval.Rifampin interacts with many medications. While you are using rifampin, it is very important to tell your doctor or pharmacist of any changes in medications that you are taking.Rifampin can speed up the removal of other medications from your body, which may affect how they work. Examples of affected drugs include atovaquone, certain anti-cancer drugs (such as irinotecan), certain azole antifungals (such as itraconazole), certain calcium channel blockers (such as nifedipine), certain products used to treat chronic hepatitis C (such as sofosbuvir), cobicistat, lurasidone, HIV NNRTIs (such as etravirine, nevirapine), praziquantel, HIV protease inhibitors (such as atazanavir, darunavir), among others.This medication may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control such as pills, patch, or ring. This could cause pregnancy. Discuss with your doctor or pharmacist if you should use reliable backup birth control methods while using this medication. Also tell your doctor if you have any new spotting or breakthrough bleeding, because these may be signs that your birth control is not working well.This medication may interfere with certain lab tests (such as urine screening for opiates, blood serum folate/vitamin B12), possibly causing false test results. Rifampin may also make it harder for your body to get rid of certain chemicals used in gallbladder tests. Make sure lab personnel and all your doctors know you use this drug.
OVERDOSE: If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call 1-844-764-7669.
NOTES: Do not share this medication with others.Lab and/or medical tests (such as liver/kidney function, bilirubin, complete blood count) may be done before you start using this medication and while you are using it. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later for another infection unless your doctor tells you to.
MISSED DOSE: It is important to get each dose of this medication as scheduled. If you miss a dose, ask your doctor or pharmacist right away for a new dosing schedule. Do not double the dose to catch up.
STORAGE: Consult the product instructions and your pharmacist for storage details. Keep all medications away from children and pets.Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Information last revised May 2024. Copyright(c) 2024 First Databank, Inc.
IMPORTANT: HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION: This is a summary and does NOT have all possible information about this product. This information does not assure that this product is safe, effective, or appropriate for you. This information is not individual medical advice and does not substitute for the advice of your health care professional. Always ask your health care professional for complete information about this product and your specific health needs.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.








