The AODN open geospatial portal is a Grails application for discovering, subsetting, and downloading geospatial data.
The application is a stateless front end to other servers:
- GeoNetwork metadata catalog
- GeoServer data server (WMS and WFS and our WPS subsetting and aggregation services
- THREDDS Gridded (ncWMS files) data server with embedded ncWMS (http://www.resc.rdg.ac.uk/trac/ncWMS/) web map server
You can view the portal in action at AODN Portal, which always runs the latest version of the code.
info@aodn.org.au or see https://help.aodn.org.au/ .
- Easy 1-2-3 workflow (1.Search, 2.Subset, 3.Download)
- Faceted search for easy discovery of data collections
- Visualise subsetting results before download via WMS
- Download data from a variety of web services (eg. WFS)
- Configurable themes and splash page
This project is licensed under the terms of the GNU GPLv3 license.
If you want to build from source you will need to have Grails 2.4.4 and JDK 1.8 installed on your
build machine. The JDK needs to be Oracle, version 1.8.0_31 to use run-app. Download
Java SE Development Kit 8u31 from https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase/javase8-archive-downloads.html.
The recommended way of installing grails is by using SdkMan:
$ curl -s http://get.sdkman.io | bash
$ source $HOME/.sdkman/bin/sdkman-init.sh
$ sdk install grails 2.4.4
$ sdk use grails 2.4.4
Alternatively an archive of Grails 2.4.4 can be obtained from s3://imos-binary/static/grails/
Once you have the source it should be as simple as $ grails war in the root folder where you have checked out portal
then deploy the war to your application server.
Yes, you can download it from our public binaries repo.
The AODN Portal has been tested with Tomcat. All you need to do is deploy the WAR and add a configuration file that tells the portal:
- Where to find GeoNetwork
- Your CSS for branding and styling
- Trusted servers
Define the location of the configuration file by setting an environment context variable named aodn.configuration
One way to do this is by adding a file called <context>.xml in the $CATALINA_BASE/conf/[enginename]/[hostname]/ directory. Where <context> matches the context of the deployed WAR (eg. "aodn-portal-3.42.1-production.xml"). Set the variable by adding the following line to the file:
<Environment name="aodn.configuration" value="<path to file>/Portal.groovy" type="java.lang.String" override="true"/>
Then add the file called Portal.groovy
You can clone an example here and modify as required.
Although other versions may work the following assumes you have:
- Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS or 18.04.6 LTS
- Latest IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate (2021.3.2 was used at time of writing). The Ultimate edition is required for Grails support.
- Java OpenJDK 1.8
The Java JDK should normally be installed using a package manager suitable to your environment from OpenJDK. Alternatively an archive can be downloaded from s3://imos-binary/static/java
Requirements:
- Grails 2.4.4 (see Building From Source)
Configure IntelliJ:
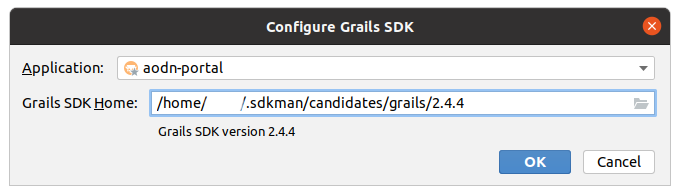
Access Tools --> Grails --> Configure Grails SDK and set the project name and location to the Grails 2.4.4 SDK.
Make sure the correct JDK (Oracle OpenJDK 1.8.0_31) is selected in the Project Structure.
Debugging:
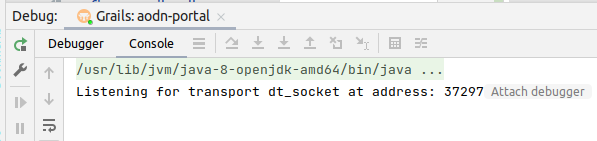
The project includes a run configuration suitable for debugging (Grails_aodn-portal.run.xml). Select this from the run configurations list and click the debug button. This will run the application using the development configuration found in Config.groovy. A JDWP transport mechanism is accessible via dt_socket.
Go to the IntelliJ debug panel and click on the Console tab. This will show the command line used to run the application along with the address to which a debugger can be attached. To use the IntelliJ debugger, click the "Attach debugger" link.
To view the full command line used to run the application click on the ellipsis. The command line will be something like the following which is provided to aid troubleshooting. In particular note the paths to plugins and dependencies which are provided by IntelliJ.
/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/bin/java
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,address=40253,suspend=y,server=y
-Dmaven.multiModuleProjectDirectory=/home/user/git/scratch/aodn-portal
-Dgrails.env=development
-Xmx1G -Xms512m
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=8008 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -XX:+UnlockCommercialFeatures -XX:+FlightRecorder
-Dmaven.home=/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/maven/lib/maven3
-Dclassworlds.conf=/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/maven/lib/maven3/bin/m2.conf
-Dmaven.ext.class.path=/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/maven/lib/maven-event-listener.jar
-Dgrails.full.stacktrace=true
-javaagent:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/Groovy/lib/agent/gragent.jar
-javaagent:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/Grails/lib/grails-rt.jar
-DforkDebug=true
-javaagent:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/Groovy/lib/agent/gragent.jar
-javaagent:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/java/lib/rt/debugger-agent.jar
-Didea.grails.kind.file=/tmp/grailsStartFlag637409810572985153
-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8
-classpath /home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/maven/lib/maven3/boot/plexus-classworlds-2.6.0.jar:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/plugins/maven/lib/maven3/boot/plexus-classworlds.license:/home/user/.local/share/JetBrains/Toolbox/apps/IDEA-U/ch-0/213.6777.52/lib/idea_rt.jar
org.codehaus.classworlds.Launcher -Didea.version=2021.3.2
grails:run-app
After a brief pause the Portal UI will run in your default browser at http://localhost:8080. Two processes will be listed in the IntelliJ "Stop Process" menu. Now you can set breakpoints and use other IntelliJ debug functions.
The provided run configuration also includes Java JVM options which enable monitoring via JConsole on port 8008.
Before you can properly run the application in a docker container you will need to add trusted certificates to the JVM running
in the Docker container. These are used to access the configured Geonetwork and Geoserver instances. This is no different
to running in a local environment so all you will need to do is to make sure that there is a copy of your trusted certificates
store in a file called cacerts located in the aodn-portal directory. The dockerfile will take care of copying this to
the correct location on the container.
Locate your cacerts file in the jre/lib/security directory of your JDK and copy it to your aodn-portal root directory.
For more information on adding required certificates to this file see stack overflow.
The docker-compose.yml file includes a service 'debug'. This will run the app in a Docker container with the JDWP
transport mechanism watching on port 5005:
$ docker-compose up debug
Alternatively use the Remote debug run configuration.run/docker-compose.yml.debug_ Compose Deployment.run.xml in
IntelliJ.
Attaching your debugger to the JDWP transport port will depend on your IDE. In IntelliJ you can use the provided Remote debug run
configuration by selecting it in the dropdown and clicking the debug button.
Docker development assumes the localhost ports 8080 and 5005 are available.
Grails does not complete launching the application until after you have connected your debugger to the JDWP port. Once it is launched the application will be available on http://localhost:8080.
If you have difficulties building and running make sure you are using the correct JDK and version of Grails. Then run
grails clean and try again.
Read the Getting Started guide on the wiki
We welcome contributions so please feel free to fork the project, address any issues or add features and submit a pull request.