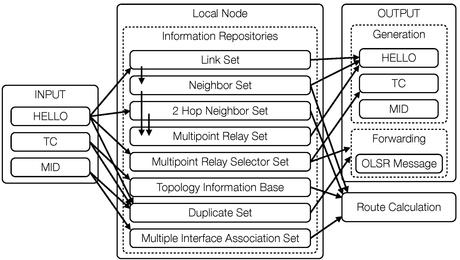
The Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR)[1] is an IP routing protocol optimized for mobile ad hoc networks, which can also be used on other wireless ad hoc networks. OLSR is a proactive link-state routing protocol, which uses hello and topology control (TC) messages to discover and then disseminate link state information throughout the mobile ad hoc network. Individual nodes use this topology information to compute next hop destinations for all nodes in the network using shortest hop forwarding paths.
Features specific to OLSR
editLink-state routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) elect a designated router on every link to perform flooding of topology information. In wireless ad hoc networks, there is different notion of a link, packets can and do go out the same interface; hence, a different approach is needed in order to optimize the flooding process. Using Hello messages the OLSR protocol at each node discovers 2-hop neighbor information and performs a distributed election of a set of multipoint relays (MPRs). Nodes select MPRs such that there exists a path to each of its 2-hop neighbors via a node selected as an MPR. These MPR nodes then source and forward TC messages that contain the MPR selectors. This functioning of MPRs makes OLSR unique from other link state routing protocols in a few different ways: The forwarding path for TC messages is not shared among all nodes but varies depending on the source, only a subset of nodes source link state information, not all links of a node are advertised but only those that represent MPR selections.
Since link-state routing requires the topology database to be synchronized across the network, OSPF and IS-IS perform topology flooding using a reliable algorithm. Such an algorithm is very difficult to design for ad hoc wireless networks, so OLSR doesn't bother with reliability; it simply floods topology data often enough to make sure that the database does not remain unsynchronized for extended periods of time.
Multipoint relays
editMultipoint relays (MPRs) relay messages between nodes. They also have the main role in routing and selecting the proper route from any source to any desired destination node.
MPRs advertise link-state information for their MPR selectors (a node selected as a MPR) periodically in their control messages. MPRs are also used to form a route from a given node to any destination in route calculation. Each node periodically broadcasts a Hello message for the link sensing, neighbor detection and MPR selection processes.[2]
Benefits
editBeing a proactive protocol, routes to all destinations within the network are known and maintained before use. Having the routes available within the standard routing table can be useful for some systems and network applications as there is no route discovery delay associated with finding a new route.
The routing overhead generated, while generally greater than that of a reactive protocol, does not increase with the number of routes being created.
Default and network routes can be injected into the system by Host and Network Association (HNA) messages allowing for connection to the internet or other networks within the OLSR MANET cloud. Network routes are something reactive protocols do not currently execute well.
Timeout values and validity information is contained within the messages conveying information allowing for differing timer values to be used at differing nodes.
Criticisms
editThe original definition of OLSR does not include any provisions for sensing of link quality; it simply assumes that a link is up if a number of hello packets have been received recently. This assumes that links are bi-modal (either working or failed), which is not necessarily the case on wireless networks, where links often exhibit intermediate rates of packet loss. Implementations such as the open source OLSRd (commonly used on Linux-based mesh routers) have been extended (as of v. 0.4.8) with link quality sensing.
Being a proactive protocol, OLSR uses power and network resources in order to propagate data about possibly unused routes. While this is not a problem for wired access points, and laptops, it makes OLSR unsuitable for sensor networks that try to sleep most of the time. For small scale wired access points with low CPU power, the open source OLSRd project showed that large scale mesh networks can run with OLSRd on thousands of nodes with very little CPU power on 200 MHz embedded devices. [citation needed]
Being a link-state protocol, OLSR requires a reasonably large amount of bandwidth and CPU power to compute optimal paths in the network. In the typical networks where OLSR is used (which rarely exceed a few hundreds of nodes), this does not appear to be a problem.
By only using MPRs to flood topology information, OLSR removes some of the redundancy of the flooding process, which may be a problem in networks with moderate to large packet loss rates[3] – however the MPR mechanism is self-pruning (which means that in case of packet losses, some nodes that would not have retransmitted a packet, may do so).
Messages
editOLSR makes use of "Hello" messages to find its one hop neighbors and its two hop neighbors through their responses. The sender can then select its multipoint relays (MPR) based on the one hop node that offers the best routes to the two hop nodes. Each node has also an MPR selector set, which enumerates nodes that have selected it as an MPR node. OLSR uses topology control (TC) messages along with MPR forwarding to disseminate neighbor information throughout the network. Host and network association (HNA) messages are used by OLSR to disseminate network route advertisements in the same way TC messages advertise host routes.
Hello
editTopology control (TC)
editOther approaches
editThe problem of routing in ad hoc wireless networks is actively being researched, and OLSR is but one of several proposed solutions. To many, it is not clear whether a whole new protocol is needed, or whether OSPF could be extended with support for wireless interfaces.[4][5]
In bandwidth- and power-starved environments, it is interesting to keep the network silent when there is no traffic to be routed. Reactive routing protocols do not maintain routes, but build them on demand. As link-state protocols require database synchronisation, such protocols typically use the distance vector approach, as in AODV and DSDV, or more ad hoc approaches that do not necessarily build optimal paths, such as Dynamic Source Routing.
For more information see the list of ad hoc routing protocols.
OLSR version 2
editOLSRv2 was published by the IETF in April 2014 as a standards-track protocol.[6] It maintains many of the key features of the original including MPR selection and dissemination. Key differences are the flexibility and modular design using shared components: packet format packetbb, and neighborhood discovery protocol NHDP. These components are being designed to be common among next generation IETF MANET protocols. Differences in the handling of multiple address and interface enabled nodes is also present between OLSR and OLSRv2.
Implementations
edit- OLSR.ORG – Downloadable code for OLSR on Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, NetBSD and OpenBSD systems. Features a great deal of documentation, including an informative survey of related work.
- NRL-OLSR – Open source code of NRL-OLSR. Works on Windows, MacOS, Linux, and various embedded PDA systems such as Arm/Zaurus and PocketPC as well as simulation environments ns2 and OPNET., http://cs.itd.nrl.navy.mil/focus/
- SOURCEFORGE.NET-OLSR – Created by MOVIQUITY and based on studies within the project Workpad, it offers a code in C# to deploy a MANET (Ad Hoc, Meshnet) with protocol OLSR. Developed for WM 6, Win XP and can be adapted to other platforms using .Net Framework and Compact. http://sourceforge.net/projects/wmolsr/
See also
edit- B.A.T.M.A.N., Better Approach To Mobile Adhoc Networking
- IEEE 802.1aq
- TRILL, Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links
References
edit- ^ Thomas Heide Clausen; Philippe Jacquet (October 2003). Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC3626. RFC 3626. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ Performance Comparison of Wireless Mobile AdHoc Network Routing - Arun Kumar, Lokanatha C. Reddy, Prakash S. Hiremath [clarification needed]
- ^ M. Abolhasan; B. Hagelstein; J. C.-P. Wang (2009). Real-world performance of current proactive multi-hop mesh protocols. 15th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications.
- ^ Madhavi Chandra; Abhay Roy (March 2010). Extensions to OSPF to Support Mobile Ad Hoc Networking. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC5820. RFC 5820. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ Richard Ogier; Phil Spagnolo (August 2009). Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) Extension of OSPF Using Connected Dominating Set (CDS) Flooding. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC5614. RFC 5614. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
- ^ Thomas Heide Clausen; Christopher Dearlove; Philippe Jacquet; Ulrich Herberg (April 2014). The Optimized Link State Routing Protocol Version 2. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC7181. RFC 7181. Retrieved 22 October 2024.
External links
edit- IETF Home Page The Internet Engineering Task Force standards body
- olsr.funkfeuer.at currently advancing the olsr.org implementation to improve scalability
- Optimized Link State Routing, which includes this Flash Demo.
- Pyramid Linux – an embedded distro for embedded x86 boards with OLSR, web interface, etc. Primarily used in Community Networks.
- NRL's Networks and Communication Systems Branch – includes project information and open source networking tools and software developed by the U.S. Naval Research Lab.