1. 简介
Cloud Spanner 是一项可横向扩容的全球分布式全代管式关系型数据库服务,可提供 ACID 事务和 SQL 语义,同时不会影响性能和高可用性。
这些功能使 Spanner 非常适合希望支持全球玩家群体或注重数据一致性的游戏架构。
在本实验中,您将创建两个 Go 服务,它们与区域级 Spanner 数据库进行交互,使玩家能够注册并开始玩游戏。
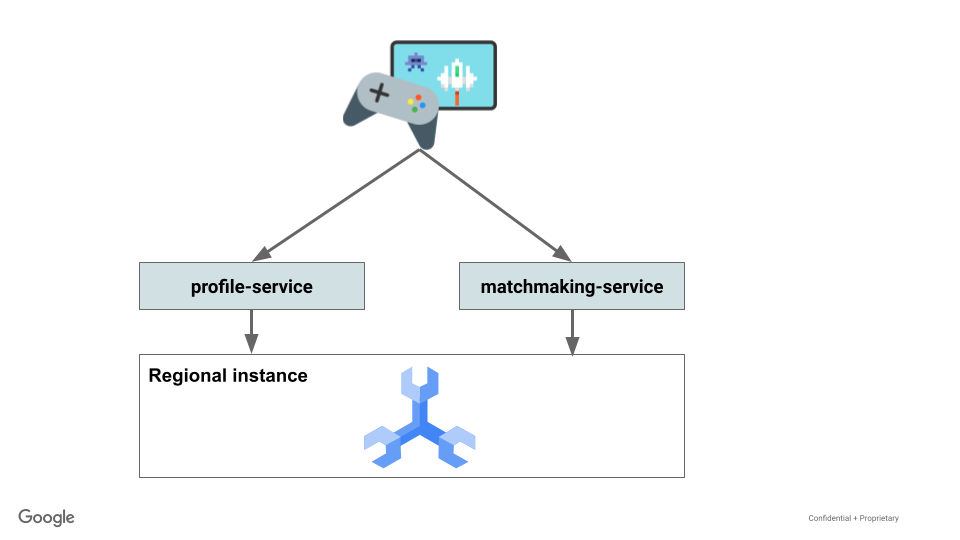
接下来,您将利用 Python 加载框架 Locust.io 生成数据,以模拟玩家注册和玩游戏的情况。然后,您将查询 Spanner 以确定正在玩游戏的人数以及有关玩家游戏进度的一些统计信息,获胜局数与所玩局数的对比。
最后,您将清理在本实验中创建的资源。
构建内容
在本实验中,您将:
- 创建 Spanner 实例
- 部署使用 Go 编写的配置文件服务来处理玩家注册
- 部署使用 Go 编写的配对服务,将玩家分配至游戏、确定获胜者并更新玩家游戏统计信息。
学习内容
- 如何设置 Cloud Spanner 实例
- 如何创建游戏数据库和架构
- 如何部署 Go 应用以使用 Cloud Spanner
- 如何使用 Locust 生成数据
- 如何在 Cloud Spanner 中查询数据以回答有关游戏和玩家的问题。
所需条件
2. 设置和要求
创建项目
如果您还没有 Google 账号(Gmail 或 Google Apps),则必须创建一个。登录 Google Cloud Platform 控制台 ( console.cloud.google.com) 并创建一个新项目。
如果您已经有一个项目,请点击控制台左上方的项目选择下拉菜单:
然后在出现的对话框中点击“新建项目”按钮以创建一个新项目:
如果您还没有项目,则应该看到一个类似这样的对话框来创建您的第一个项目:
随后的项目创建对话框可让您输入新项目的详细信息:
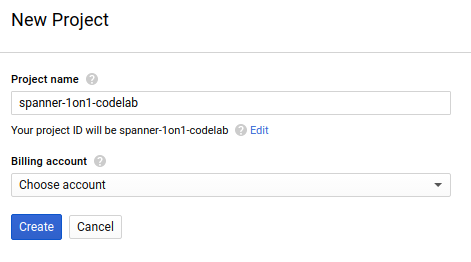
请记住项目 ID,它是所有 Google Cloud 项目中的唯一名称(很抱歉,上述名称已被占用,您无法使用!)。稍后,此 Codelab 将将其称为 PROJECT_ID。
接下来,如果尚未执行此操作,则需要在 Developers Console 中启用结算功能,以便使用 Google Cloud 资源并启用 Cloud Spanner API。

在此 Codelab 中运行不会花费您超过几美元,但是如果您决定使用更多的资源或让它们运行(请参阅本文档末尾的“清理”部分),则可能会花费更多。如需了解 Google Cloud Spanner 价格,请参阅此处。
Google Cloud Platform 的新用户均有资格获享 $300 赠金,免费试用此 Codelab。
Google Cloud Shell 设置
虽然 Google Cloud 和 Spanner 可以从笔记本电脑远程操作,但在此 Codelab 中,我们将使用 Google Cloud Shell,这是一个在云端运行的命令行环境。
基于 Debian 的这个虚拟机已加载了您需要的所有开发工具。它提供了一个持久的 5GB 主目录,并且在 Google Cloud 中运行,大大增强了网络性能和身份验证。这意味着在本 Codelab 中,您只需要一个浏览器(没错,它适用于 Chromebook)。
- 如需从 Cloud 控制台激活 Cloud Shell,只需点击“激活 Cloud Shell”图标
 即可(预配和连接到环境应该只需要片刻时间)。
即可(预配和连接到环境应该只需要片刻时间)。
在连接到 Cloud Shell 后,您应该会看到自己已通过身份验证,并且相关项目已设置为您的 PROJECT_ID。
gcloud auth list
命令输出
Credentialed accounts:
- <myaccount>@<mydomain>.com (active)
gcloud config list project
命令输出
[core]
project = <PROJECT_ID>
如果出于某种原因未设置项目,只需发出以下命令即可:
gcloud config set project <PROJECT_ID>
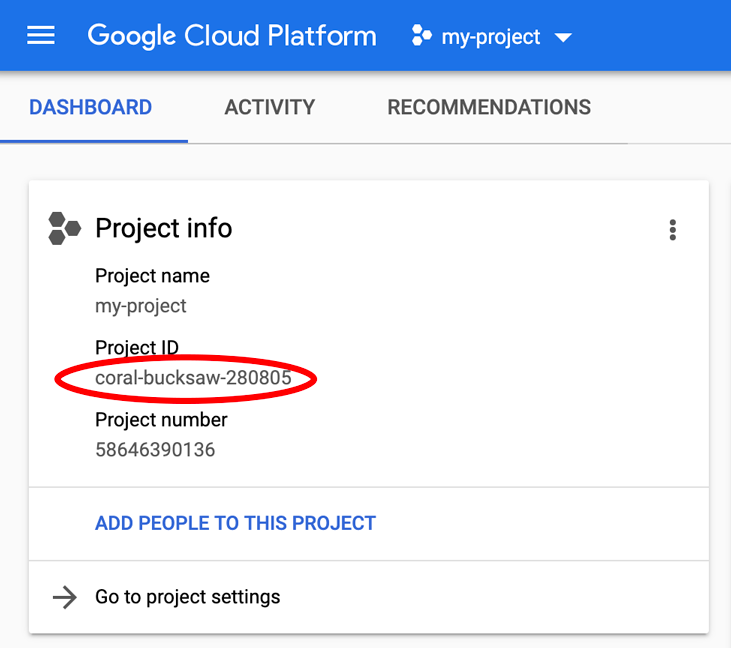
正在查找您的 PROJECT_ID?检查您在设置步骤中使用的 ID,或在 Cloud Console 信息中心查找该 ID:
默认情况下,Cloud Shell 还会设置一些环境变量,这对您日后运行命令可能会很有用。
echo $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
命令输出
<PROJECT_ID>
下载代码
您可以在 Cloud Shell 中下载本实验的代码。此版本基于 v0.1.0 版本,因此请检查该代码:
git clone https://github.com/cloudspannerecosystem/spanner-gaming-sample.git
cd spanner-gaming-sample/
# Check out v0.1.0 release
git checkout tags/v0.1.0 -b v0.1.0-branch
命令输出
Cloning into 'spanner-gaming-sample'...
*snip*
Switched to a new branch 'v0.1.0-branch'
设置 Locust 负载生成器
Locust 是一个 Python 负载测试框架,可用于测试 REST API 端点。在此 Codelab 中,“generators”中有 2 种不同的负载测试目录:
- authentication_server.py:包含用于创建玩家和获取随机玩家以模拟单点查询的任务。
- match_server.py:包含创建游戏和关闭游戏的任务。创建游戏后,系统会随机分配 100 个当前未玩游戏的玩家。关闭游戏后,系统会更新 games_played 和 games_won 统计信息,并允许将这些玩家分配至未来的游戏。
如需在 Cloud Shell 中运行 Locust,您需要 Python 3.7 或更高版本。Cloud Shell 自带 Python 3.9,因此您只需验证版本即可:
python -V
命令输出
Python 3.9.12
现在,您可以安装 Locust 的相关要求。
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
命令输出
Collecting locust==2.11.1
*snip*
Successfully installed ConfigArgParse-1.5.3 Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0 Flask-Cors-3.0.10 brotli-1.0.9 gevent-21.12.0 geventhttpclient-2.0.2 greenlet-1.1.3 locust-2.11.1 msgpack-1.0.4 psutil-5.9.2 pyzmq-22.3.0 roundrobin-0.0.4 zope.event-4.5.0 zope.interface-5.4.0
现在,更新 PATH,以便能够找到新安装的 locust 二进制文件:
PATH=~/.local/bin":$PATH"
which locust
命令输出
/home/<user>/.local/bin/locust
摘要
在此步骤中,您已经设置了项目(如果您还没有项目)、激活 Cloud Shell 并下载本实验的代码。
最后,您将在本实验的后面部分设置 Locust 以生成负载。
后续步骤
接下来,您将设置 Cloud Spanner 实例和数据库。
3. 创建 Spanner 实例和数据库
创建 Spanner 实例
在此步骤中,我们将为 Codelab 设置 Spanner 实例。搜索左上角汉堡式菜单中的  Spanner 条目
Spanner 条目  ,也可以按“/”并输入“Spanner”以搜索 Spanner。
,也可以按“/”并输入“Spanner”以搜索 Spanner。
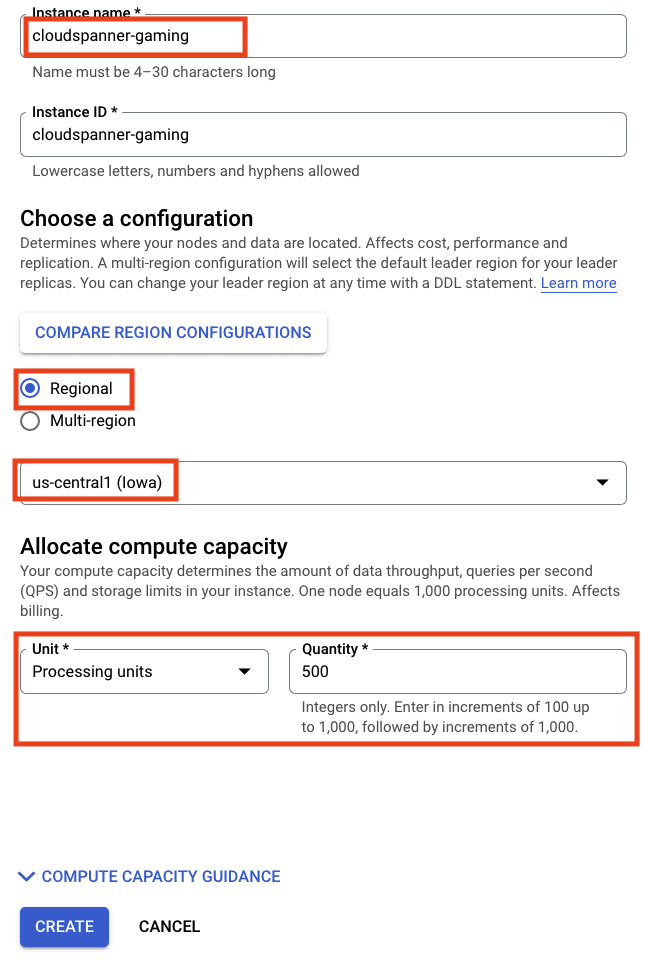
接下来,点击  并填写表单,具体做法是为您的实例输入实例名称
并填写表单,具体做法是为您的实例输入实例名称 cloudspanner-gaming,选择配置(选择 us-central1 等区域级实例),并设置节点数。在此 Codelab 中,我们只需要 500 processing units。
最后但并非最不重要的一点是,点击“创建”,然后在几秒钟内就可以使用 Cloud Spanner 实例。
创建数据库和架构
实例运行后,您就可以创建数据库了。Spanner 允许在单个实例上使用多个数据库。
数据库是您定义架构的地方。您还可以控制谁有权访问数据库、设置自定义加密、配置优化工具以及设置保留期限。
在多区域实例上,您还可以配置默认主要副本。详细了解 Spanner 上的数据库。
在本 Codelab 中,您将使用默认选项创建数据库,并在创建时提供架构。
本实验将创建两个表:players(玩家)和 games(游戏)。

玩家在一段时间内可以参与多款游戏,但一次只能玩一款游戏。玩家还可以使用 JSON 数据类型形式的统计信息,以跟踪有趣的统计信息,例如 games_played 和 games_won。由于后续可能会添加其他统计信息,因此对玩家而言,这实际上是一个无架构列。
Games 会使用 Spanner 的 ARRAY 数据类型跟踪参与游戏的玩家。在游戏结束之前,系统不会填充游戏的胜出者和已完成的属性。
有一个外键可确保玩家的 current_game 是有效的游戏。
现在,点击“Create Database”以创建数据库在实例概览中执行以下操作:
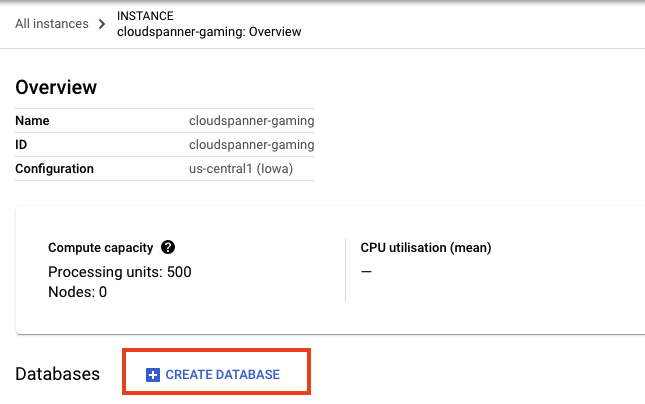
然后填写详细信息。重要的选项包括数据库名称和方言。在本例中,我们将数据库命名为 sample-game,并选择 Google 标准 SQL 方言。
对于架构,请复制此 DDL 并将其粘贴到框中:
CREATE TABLE games (
gameUUID STRING(36) NOT NULL,
players ARRAY<STRING(36)> NOT NULL,
winner STRING(36),
created TIMESTAMP,
finished TIMESTAMP,
) PRIMARY KEY(gameUUID);
CREATE TABLE players (
playerUUID STRING(36) NOT NULL,
player_name STRING(64) NOT NULL,
email STRING(MAX) NOT NULL,
password_hash BYTES(60) NOT NULL,
created TIMESTAMP,
updated TIMESTAMP,
stats JSON,
account_balance NUMERIC NOT NULL DEFAULT (0.00),
is_logged_in BOOL,
last_login TIMESTAMP,
valid_email BOOL,
current_game STRING(36),
FOREIGN KEY (current_game) REFERENCES games (gameUUID),
) PRIMARY KEY(playerUUID);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX PlayerAuthentication ON players(email) STORING (password_hash);
CREATE INDEX PlayerGame ON players(current_game);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX PlayerName ON players(player_name);
然后,点击“创建”按钮并等待几秒钟,以便您的数据库创建完成。
创建数据库页面应如下所示:
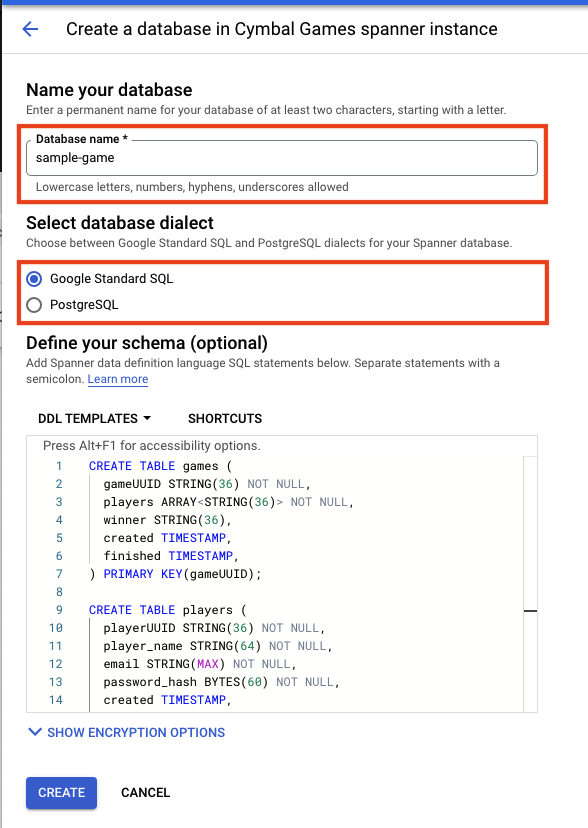
现在,您需要在 Cloud Shell 中设置一些环境变量,以便稍后在 Codelab 中使用。因此,请记下 instance-id,并在 Cloud Shell 中设置 INSTANCE_ID 和 DATABASE_ID
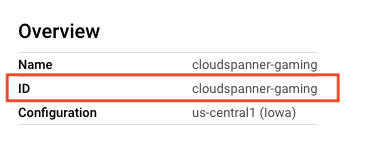
export SPANNER_PROJECT_ID=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
export SPANNER_INSTANCE_ID=cloudspanner-gaming
export SPANNER_DATABASE_ID=sample-game
摘要
在此步骤中,您创建了一个 Spanner 实例和 sample-game 数据库。您还定义了此示例游戏使用的架构。
后续步骤
接下来,您将部署玩家资料服务,以允许玩家注册玩游戏!
4. 部署配置文件服务
服务概览
配置文件服务是使用 Go 编写的 REST API,利用了 gin 框架。
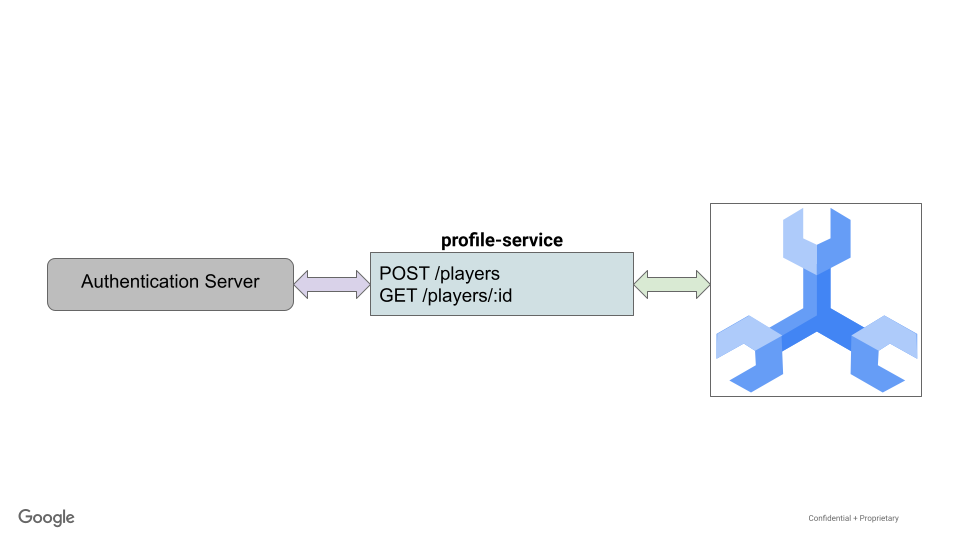
在此 API 中,玩家可以注册玩游戏。这是通过简单的 POST 命令创建,该命令接受玩家名称、电子邮件地址和密码。密码使用 bcrypt 加密,且哈希值存储在数据库中。
Email 被视为唯一标识符,而 player_name 则用于显示游戏。
此 API 目前不处理登录,但实现此 API 可以作为附加练习。
配置文件服务的 ./src/golang/profile-service/main.go 文件公开了两个主要端点,如下所示:
func main() {
configuration, _ := config.NewConfig()
router := gin.Default()
router.SetTrustedProxies(nil)
router.Use(setSpannerConnection(configuration))
router.POST("/players", createPlayer)
router.GET("/players", getPlayerUUIDs)
router.GET("/players/:id", getPlayerByID)
router.Run(configuration.Server.URL())
}
这些端点的代码将路由到 player 模型。
func getPlayerByID(c *gin.Context) {
var playerUUID = c.Param("id")
ctx, client := getSpannerConnection(c)
player, err := models.GetPlayerByUUID(ctx, client, playerUUID)
if err != nil {
c.IndentedJSON(http.StatusNotFound, gin.H{"message": "player not found"})
return
}
c.IndentedJSON(http.StatusOK, player)
}
func createPlayer(c *gin.Context) {
var player models.Player
if err := c.BindJSON(&player); err != nil {
c.AbortWithError(http.StatusBadRequest, err)
return
}
ctx, client := getSpannerConnection(c)
err := player.AddPlayer(ctx, client)
if err != nil {
c.AbortWithError(http.StatusBadRequest, err)
return
}
c.IndentedJSON(http.StatusCreated, player.PlayerUUID)
}
该服务首先会设置 Spanner 连接。这在服务级别实现,以便为服务创建会话池。
func setSpannerConnection() gin.HandlerFunc {
ctx := context.Background()
client, err := spanner.NewClient(ctx, configuration.Spanner.URL())
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return func(c *gin.Context) {
c.Set("spanner_client", *client)
c.Set("spanner_context", ctx)
c.Next()
}
}
Player 和 PlayerStats 是按如下方式定义的结构体:
type Player struct {
PlayerUUID string `json:"playerUUID" validate:"omitempty,uuid4"`
Player_name string `json:"player_name" validate:"required_with=Password Email"`
Email string `json:"email" validate:"required_with=Player_name Password,email"`
// not stored in DB
Password string `json:"password" validate:"required_with=Player_name Email"`
// stored in DB
Password_hash []byte `json:"password_hash"`
created time.Time
updated time.Time
Stats spanner.NullJSON `json:"stats"`
Account_balance big.Rat `json:"account_balance"`
last_login time.Time
is_logged_in bool
valid_email bool
Current_game string `json:"current_game" validate:"omitempty,uuid4"`
}
type PlayerStats struct {
Games_played spanner.NullInt64 `json:"games_played"`
Games_won spanner.NullInt64 `json:"games_won"`
}
添加玩家的函数利用 ReadWrite 事务内的 DML 插入,因为添加玩家是单个语句,而不是批量插入。该函数如下所示:
func (p *Player) AddPlayer(ctx context.Context, client spanner.Client) error {
// Validate based on struct validation rules
err := p.Validate()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// take supplied password+salt, hash. Store in user_password
passHash, err := hashPassword(p.Password)
if err != nil {
return errors.New("Unable to hash password")
}
p.Password_hash = passHash
// Generate UUIDv4
p.PlayerUUID = generateUUID()
// Initialize player stats
emptyStats := spanner.NullJSON{Value: PlayerStats{
Games_played: spanner.NullInt64{Int64: 0, Valid: true},
Games_won: spanner.NullInt64{Int64: 0, Valid: true},
}, Valid: true}
// insert into spanner
_, err = client.ReadWriteTransaction(ctx, func(ctx context.Context, txn *spanner.ReadWriteTransaction) error {
stmt := spanner.Statement{
SQL: `INSERT players (playerUUID, player_name, email, password_hash, created, stats) VALUES
(@playerUUID, @playerName, @email, @passwordHash, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), @pStats)
`,
Params: map[string]interface{}{
"playerUUID": p.PlayerUUID,
"playerName": p.Player_name,
"email": p.Email,
"passwordHash": p.Password_hash,
"pStats": emptyStats,
},
}
_, err := txn.Update(ctx, stmt)
return err
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
// return empty error on success
return nil
}
如需根据玩家的 UUID 检索玩家,可执行简单的读取操作。这将检索玩家 playerUUID、player_name、email 和 stats。
func GetPlayerByUUID(ctx context.Context, client spanner.Client, uuid string) (Player, error) {
row, err := client.Single().ReadRow(ctx, "players",
spanner.Key{uuid}, []string{"playerUUID", "player_name", "email", "stats"})
if err != nil {
return Player{}, err
}
player := Player{}
err = row.ToStruct(&player)
if err != nil {
return Player{}, err
}
return player, nil
}
默认情况下,服务是使用环境变量进行配置的。请参阅 ./src/golang/profile-service/config/config.go 文件的相关部分。
func NewConfig() (Config, error) {
*snip*
// Server defaults
viper.SetDefault("server.host", "localhost")
viper.SetDefault("server.port", 8080)
// Bind environment variable override
viper.BindEnv("server.host", "SERVICE_HOST")
viper.BindEnv("server.port", "SERVICE_PORT")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.project_id", "SPANNER_PROJECT_ID")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.instance_id", "SPANNER_INSTANCE_ID")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.database_id", "SPANNER_DATABASE_ID")
*snip*
return c, nil
}
您可以看到,默认行为是在 localhost:8080 上运行服务。
有了这些信息,您就可以运行服务了。
运行配置文件服务
使用 go 命令运行该服务。这将下载依赖项,并建立在端口 8080 上运行的服务:
cd ~/spanner-gaming-sample/src/golang/profile-service
go run . &
命令输出:
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] POST /players --> main.createPlayer (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /players --> main.getPlayerUUIDs (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /players/:id --> main.getPlayerByID (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /players/:id/stats --> main.getPlayerStats (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on localhost:8080
通过发出 curl 命令来测试服务:
curl http://localhost:8080/players \
--include \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request "POST" \
--data '{"email": "test@gmail.com","password": "s3cur3P@ss","player_name": "Test Player"}'
命令输出:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: <date> 18:55:08 GMT
Content-Length: 38
"506a1ab6-ee5b-4882-9bb1-ef9159a72989"
摘要
在此步骤中,您部署了个人资料服务,允许玩家注册以玩游戏,并通过发出 POST API 调用来创建新玩家来测试该服务。
后续步骤
在下一步中,您将部署配对服务。
5. 部署配对服务
服务概览
配对服务是使用 Go 编写的 REST API,利用了 gin 框架。
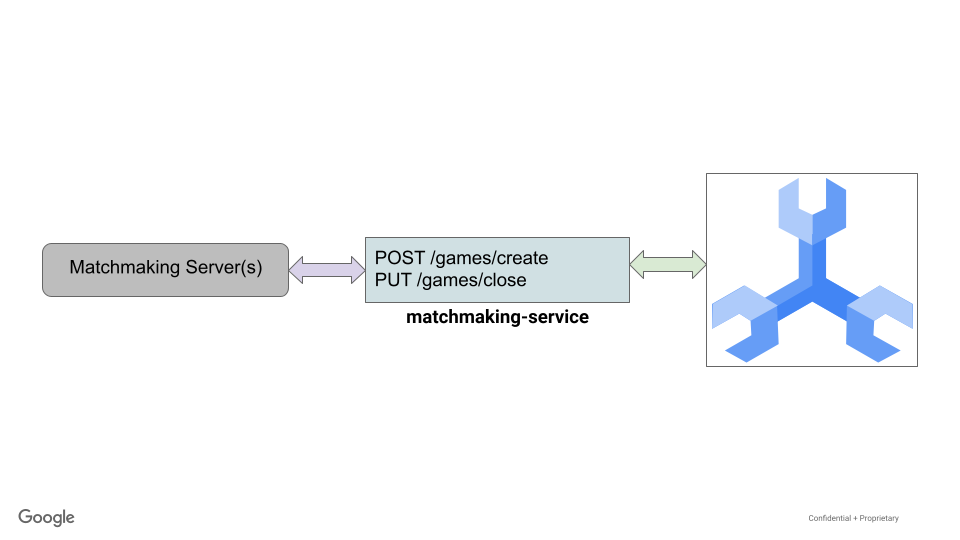
在此 API 中,游戏是创建和关闭的。创建游戏后,系统会向该游戏分配 10 位当前未玩游戏的玩家。
在比赛结束时,系统会随机选出一名获胜者,调整 games_played 和 games_won 的统计数据。此外,每个玩家都会进行更新,以表明他们已不再玩,因此可以继续玩以后的游戏。
配对服务的 ./src/golang/matchmaking-service/main.go 文件采用了与 profile 服务类似的设置和代码,因此,此处不再重复。此服务公开了两个主要端点,如下所示:
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.SetTrustedProxies(nil)
router.Use(setSpannerConnection())
router.POST("/games/create", createGame)
router.PUT("/games/close", closeGame)
router.Run(configuration.Server.URL())
}
此服务提供了一个 Game 结构体,以及进行了精简的 Player 和 PlayerStats 结构体:
type Game struct {
GameUUID string `json:"gameUUID"`
Players []string `json:"players"`
Winner string `json:"winner"`
Created time.Time `json:"created"`
Finished spanner.NullTime `json:"finished"`
}
type Player struct {
PlayerUUID string `json:"playerUUID"`
Stats spanner.NullJSON `json:"stats"`
Current_game string `json:"current_game"`
}
type PlayerStats struct {
Games_played int `json:"games_played"`
Games_won int `json:"games_won"`
}
为了创建游戏,配对服务会从 100 名当前未在玩游戏的玩家中随机选择多个选项。
系统会选择 Spanner 变更来创建游戏并为其分配玩家,因为对于大型变更,变更比 DML 的性能更高。
// Create a new game and assign players
// Players that are not currently playing a game are eligble to be selected for the new game
// Current implementation allows for less than numPlayers to be placed in a game
func (g *Game) CreateGame(ctx context.Context, client spanner.Client) error {
// Initialize game values
g.GameUUID = generateUUID()
numPlayers := 10
// Create and assign
_, err := client.ReadWriteTransaction(ctx, func(ctx context.Context, txn *spanner.ReadWriteTransaction) error {
var m []*spanner.Mutation
// get players
query := fmt.Sprintf("SELECT playerUUID FROM (SELECT playerUUID FROM players WHERE current_game IS NULL LIMIT 10000) TABLESAMPLE RESERVOIR (%d ROWS)", numPlayers)
stmt := spanner.Statement{SQL: query}
iter := txn.Query(ctx, stmt)
playerRows, err := readRows(iter)
if err != nil {
return err
}
var playerUUIDs []string
for _, row := range playerRows {
var pUUID string
if err := row.Columns(&pUUID); err != nil {
return err
}
playerUUIDs = append(playerUUIDs, pUUID)
}
// Create the game
gCols := []string{"gameUUID", "players", "created"}
m = append(m, spanner.Insert("games", gCols, []interface{}{g.GameUUID, playerUUIDs, time.Now()}))
// Update players to lock into this game
for _, p := range playerUUIDs {
pCols := []string{"playerUUID", "current_game"}
m = append(m, spanner.Update("players", pCols, []interface{}{p, g.GameUUID}))
}
txn.BufferWrite(m)
return nil
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
玩家的随机选择是通过使用 GoogleSQL 的 TABLESPACE RESERVOIR 功能通过 SQL 完成的。
关闭游戏稍微复杂一些。它涉及从游戏玩家中选择随机获胜者、标记游戏完成时间,并更新每个玩家的games_played 和 games_won 的统计数据。
由于这种复杂性和大量更改,系统会再次选择变更以结束游戏。
func determineWinner(playerUUIDs []string) string {
if len(playerUUIDs) == 0 {
return ""
}
var winnerUUID string
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
offset := rand.Intn(len(playerUUIDs))
winnerUUID = playerUUIDs[offset]
return winnerUUID
}
// Given a list of players and a winner's UUID, update players of a game
// Updating players involves closing out the game (current_game = NULL) and
// updating their game stats. Specifically, we are incrementing games_played.
// If the player is the determined winner, then their games_won stat is incremented.
func (g Game) updateGamePlayers(ctx context.Context, players []Player, txn *spanner.ReadWriteTransaction) error {
for _, p := range players {
// Modify stats
var pStats PlayerStats
json.Unmarshal([]byte(p.Stats.String()), &pStats)
pStats.Games_played = pStats.Games_played + 1
if p.PlayerUUID == g.Winner {
pStats.Games_won = pStats.Games_won + 1
}
updatedStats, _ := json.Marshal(pStats)
p.Stats.UnmarshalJSON(updatedStats)
// Update player
// If player's current game isn't the same as this game, that's an error
if p.Current_game != g.GameUUID {
errorMsg := fmt.Sprintf("Player '%s' doesn't belong to game '%s'.", p.PlayerUUID, g.GameUUID)
return errors.New(errorMsg)
}
cols := []string{"playerUUID", "current_game", "stats"}
newGame := spanner.NullString{
StringVal: "",
Valid: false,
}
txn.BufferWrite([]*spanner.Mutation{
spanner.Update("players", cols, []interface{}{p.PlayerUUID, newGame, p.Stats}),
})
}
return nil
}
// Closing game. When provided a Game, choose a random winner and close out the game.
// A game is closed by setting the winner and finished time.
// Additionally all players' game stats are updated, and the current_game is set to null to allow
// them to be chosen for a new game.
func (g *Game) CloseGame(ctx context.Context, client spanner.Client) error {
// Close game
_, err := client.ReadWriteTransaction(ctx,
func(ctx context.Context, txn *spanner.ReadWriteTransaction) error {
// Get game players
playerUUIDs, players, err := g.getGamePlayers(ctx, txn)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Might be an issue if there are no players!
if len(playerUUIDs) == 0 {
errorMsg := fmt.Sprintf("No players found for game '%s'", g.GameUUID)
return errors.New(errorMsg)
}
// Get random winner
g.Winner = determineWinner(playerUUIDs)
// Validate game finished time is null
row, err := txn.ReadRow(ctx, "games", spanner.Key{g.GameUUID}, []string{"finished"})
if err != nil {
return err
}
if err := row.Column(0, &g.Finished); err != nil {
return err
}
// If time is not null, then the game is already marked as finished.
// That's an error.
if !g.Finished.IsNull() {
errorMsg := fmt.Sprintf("Game '%s' is already finished.", g.GameUUID)
return errors.New(errorMsg)
}
cols := []string{"gameUUID", "finished", "winner"}
txn.BufferWrite([]*spanner.Mutation{
spanner.Update("games", cols, []interface{}{g.GameUUID, time.Now(), g.Winner}),
})
// Update each player to increment stats.games_played
// (and stats.games_won if winner), and set current_game
// to null so they can be chosen for a new game
playerErr := g.updateGamePlayers(ctx, players, txn)
if playerErr != nil {
return playerErr
}
return nil
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
配置同样是通过环境变量处理的,如相应服务的 ./src/golang/matchmaking-service/config/config.go 中所述。
// Server defaults
viper.SetDefault("server.host", "localhost")
viper.SetDefault("server.port", 8081)
// Bind environment variable override
viper.BindEnv("server.host", "SERVICE_HOST")
viper.BindEnv("server.port", "SERVICE_PORT")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.project_id", "SPANNER_PROJECT_ID")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.instance_id", "SPANNER_INSTANCE_ID")
viper.BindEnv("spanner.database_id", "SPANNER_DATABASE_ID")
为避免与 profile-service 发生冲突,此服务默认在 localhost:8081 上运行。
有了这些信息,现在就可以运行配对服务了。
运行配对服务
使用 go 命令运行该服务。这将建立在端口 8082 上运行的服务。此服务的许多依赖项与 profile-service 相同,因此系统不会下载新的依赖项。
cd ~/spanner-gaming-sample/src/golang/matchmaking-service
go run . &
命令输出:
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] POST /games/create --> main.createGame (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] PUT /games/close --> main.closeGame (4 handlers)
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on localhost:8081
创建游戏
测试服务以创建游戏。首先,在 Cloud Shell 中打开一个新终端:
然后,发出以下 curl 命令:
curl http://localhost:8081/games/create \
--include \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--request "POST"
命令输出:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: <date> 19:38:45 GMT
Content-Length: 38
"f45b0f7f-405b-4e67-a3b8-a624e990285d"
关闭游戏
curl http://localhost:8081/games/close \
--include \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"gameUUID": "f45b0f7f-405b-4e67-a3b8-a624e990285d"}' \
--request "PUT"
命令输出:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: <date> 19:43:58 GMT
Content-Length: 38
"506a1ab6-ee5b-4882-9bb1-ef9159a72989"
摘要
在此步骤中,您部署了配对服务,用于处理游戏创建以及为该游戏分配玩家。此服务还可处理结束游戏的操作,即选择随机获胜者并更新所有游戏玩家的games_played 和 games_won 的统计数据。
后续步骤
现在您的服务已正常运行,是时候让玩家注册并玩游戏了!
6. 开始播放
鉴于配置文件和配对服务正在运行,您可以使用提供的 locust 生成器生成负载。
Locust 提供了一个用于运行生成器的网页界面,但在本实验中,您将使用命令行(–headless 选项)。
为玩家注册账号
首先,您需要吸引玩家。
在 ./generators/authentication_server.py 文件中创建播放器的 Python 代码如下所示:
class PlayerLoad(HttpUser):
def on_start(self):
global pUUIDs
pUUIDs = []
def generatePlayerName(self):
return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits, k=32))
def generatePassword(self):
return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits, k=32))
def generateEmail(self):
return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits, k=32) + ['@'] +
random.choices(['gmail', 'yahoo', 'microsoft']) + ['.com'])
@task
def createPlayer(self):
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
data = {"player_name": self.generatePlayerName(), "email": self.generateEmail(), "password": self.generatePassword()}
with self.client.post("/players", data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers, catch_response=True) as response:
try:
pUUIDs.append(response.json())
except json.JSONDecodeError:
response.failure("Response could not be decoded as JSON")
except KeyError:
response.failure("Response did not contain expected key 'gameUUID'")
玩家名称、电子邮件地址和密码是随机生成的。
成功注册的玩家将由第二个任务检索,以生成读取负载。
@task(5)
def getPlayer(self):
# No player UUIDs are in memory, reschedule task to run again later.
if len(pUUIDs) == 0:
raise RescheduleTask()
# Get first player in our list, removing it to avoid contention from concurrent requests
pUUID = pUUIDs[0]
del pUUIDs[0]
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
self.client.get(f"/players/{pUUID}", headers=headers, name="/players/[playerUUID]")
以下命令会调用 ./generators/authentication_server.py 文件,该文件将生成 30 秒 (t=30s) 的新播放器,同时并发设置两个线程 (u=2):
cd ~/spanner-gaming-sample
locust -H http://127.0.0.1:8080 -f ./generators/authentication_server.py --headless -u=2 -r=2 -t=30s
玩家加入游戏
既然您已有玩家注册,他们就想开始玩游戏了!
在 ./generators/match_server.py 文件中创建和关闭游戏的 Python 代码如下所示:
from locust import HttpUser, task
from locust.exception import RescheduleTask
import json
class GameMatch(HttpUser):
def on_start(self):
global openGames
openGames = []
@task(2)
def createGame(self):
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
# Create the game, then store the response in memory of list of open games.
with self.client.post("/games/create", headers=headers, catch_response=True) as response:
try:
openGames.append({"gameUUID": response.json()})
except json.JSONDecodeError:
response.failure("Response could not be decoded as JSON")
except KeyError:
response.failure("Response did not contain expected key 'gameUUID'")
@task
def closeGame(self):
# No open games are in memory, reschedule task to run again later.
if len(openGames) == 0:
raise RescheduleTask()
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
# Close the first open game in our list, removing it to avoid
# contention from concurrent requests
game = openGames[0]
del openGames[0]
data = {"gameUUID": game["gameUUID"]}
self.client.put("/games/close", data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)
此生成器在运行时会以 2:1(打开:关闭)的比例打开和关闭游戏。以下命令将运行生成器 10 秒 (-t=10s):
locust -H http://127.0.0.1:8081 -f ./generators/match_server.py --headless -u=1 -r=1 -t=10s
摘要
在此步骤中,您使用配对服务模拟玩家注册玩游戏,然后运行模拟让玩家玩游戏。这些模拟利用 Locust Python 框架向 Google 服务REST API。
您可以随意修改创建玩家和玩游戏所用的时间,以及并发用户数量 (-u)。
后续步骤
模拟结束后,您需要通过查询 Spanner 来查看各种统计信息。
7. 检索游戏统计信息
现在,我们已经模拟了玩家可以注册并玩游戏的情况,接下来您应该查看统计信息。
为此,请使用 Cloud 控制台向 Spanner 发出查询请求。

检查开放式游戏和封闭式比赛
关闭的游戏是填充了“finished”时间戳的游戏,而打开的游戏的“finished”时间戳是 NULL。此值在游戏关闭时设置。
因此,您可以在以下查询中查看有多少游戏开玩,又有多少游戏关掉:
SELECT Type, NumGames FROM
(SELECT "Open Games" as Type, count(*) as NumGames FROM games WHERE finished IS NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT "Closed Games" as Type, count(*) as NumGames FROM games WHERE finished IS NOT NULL
)
结果:
|
|
|
|
|
|
查看玩游戏和未玩游戏的玩家数量
如果设置了 current_game 列,表示玩家正在玩游戏。否则,表示他们目前没有玩游戏。
因此,如需比较当前正在玩和未玩的玩家数量,请使用以下查询:
SELECT Type, NumPlayers FROM
(SELECT "Playing" as Type, count(*) as NumPlayers FROM players WHERE current_game IS NOT NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT "Not Playing" as Type, count(*) as NumPlayers FROM players WHERE current_game IS NULL
)
结果:
|
|
|
|
|
|
确定最佳胜出组合
游戏结束时,系统会随机选出一名玩家成为获胜者。该玩家的 games_won 统计信息会在关闭游戏时递增。
SELECT playerUUID, stats
FROM players
WHERE CAST(JSON_VALUE(stats, "$.games_won") AS INT64)>0
LIMIT 10;
结果:
playerUUID | stats |
07e247c5-f88e-4bca-a7bc-12d2485f2f2b | {"games_played":49,"games_won":1} |
09b72595-40af-4406-a000-2fb56c58fe92 | {"games_played":56,"games_won":1} |
1002385b-02a0-462b-a8e7-05c9b27223aa | {"games_played":66,"games_won":1} |
13ec3770-7ae3-495f-9b53-6322d8e8d6c3 | {"games_played":44,"games_won":1} |
15513852-3f2a-494f-b437-fe7125d15f1b | {"games_played":49,"games_won":1} |
17faec64-4f77-475c-8df8-6ab026cf6698 | {"games_played":50,"games_won":1} |
1abfcb27-037d-446d-bb7a-b5cd17b5733d | {"games_played":63,"games_won":1} |
2109a33e-88bd-4e74-a35c-a7914d9e3bde | {"games_played":56,"games_won":2} |
222e37d9-06b0-4674-865d-a0e5fb80121e | {"games_played":60,"games_won":1} |
22ced15c-0da6-4fd9-8cb2-1ffd233b3c56 | {"games_played":50,"games_won":1} |
摘要
在此步骤中,您使用 Cloud 控制台查询 Spanner,查看了玩家和游戏的各种统计信息。
后续步骤
接下来该清理了!
8. 清理(可选)
如需进行清理,只需进入 Cloud 控制台的 Cloud Spanner 部分,然后删除我们在 Codelab 步骤中名为“设置 Cloud Spanner 实例”时创建的“cloudspanner-gaming”实例。
9. 恭喜!
恭喜,您已成功在 Spanner 上部署示例游戏
后续操作
在本实验中,我们向您介绍了关于使用 golang 驱动程序使用 Spanner 的各种主题。它应该能够帮助您为理解重要概念打下坚实的基础,例如:
- 架构设计
- DML 与变更
- 使用 Golang
请务必查看 Cloud Spanner Game Trading Post Codelab,了解将 Spanner 用作游戏后端的另一个示例!